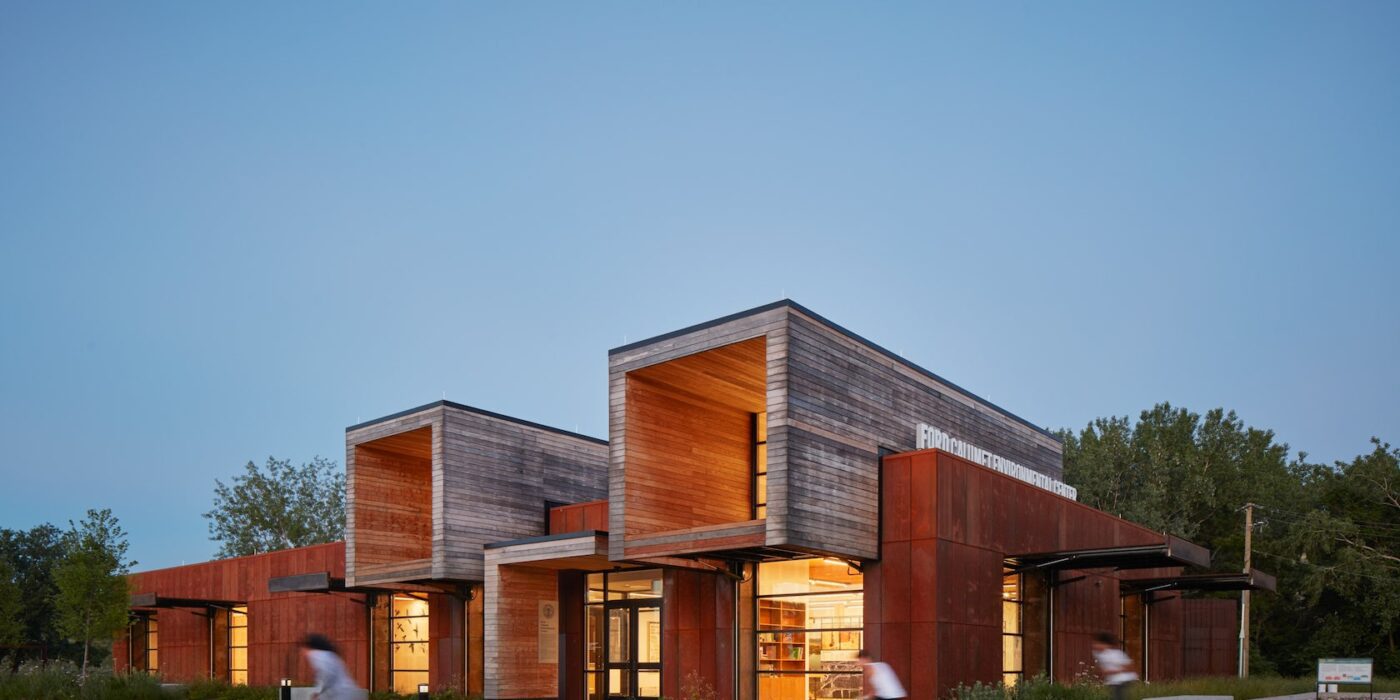
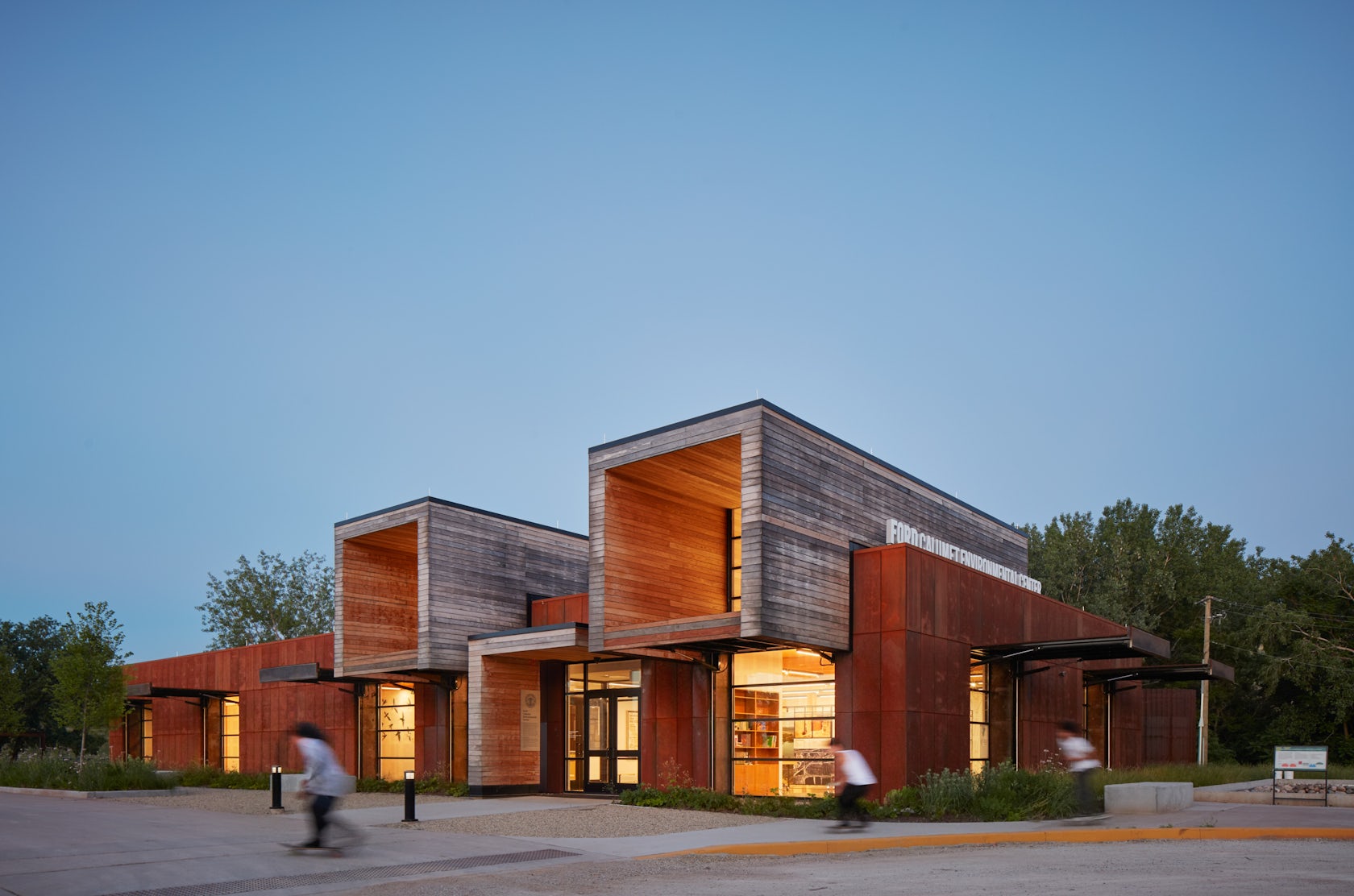
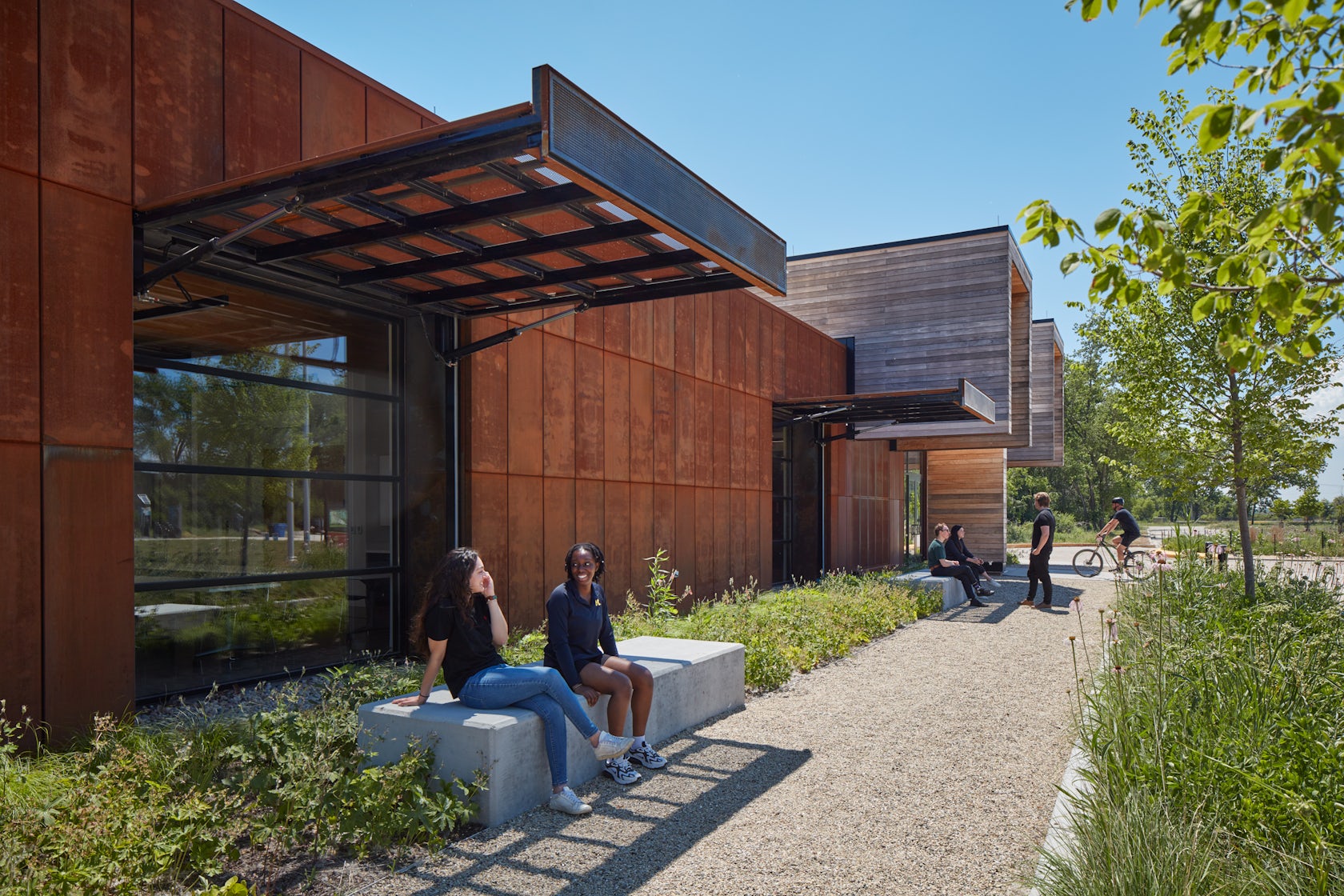
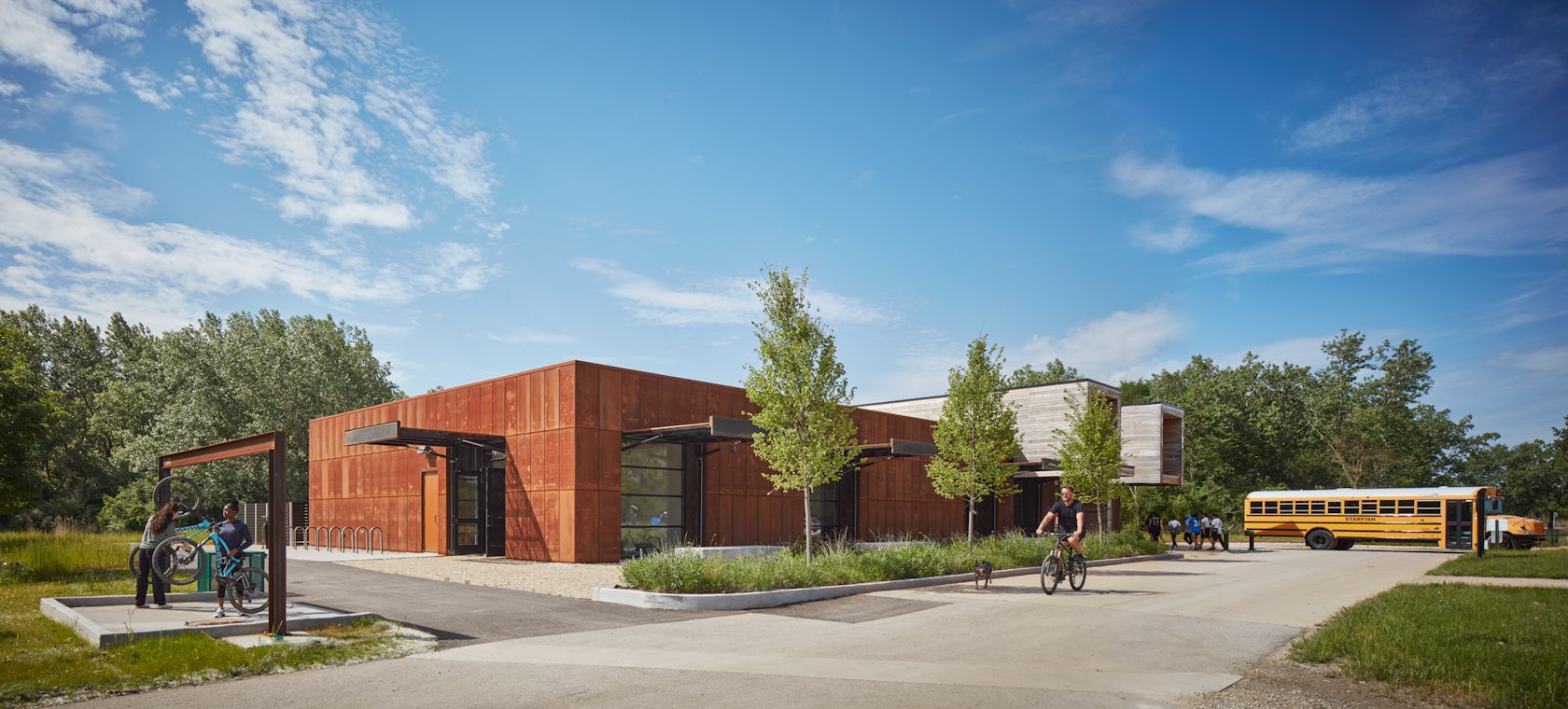
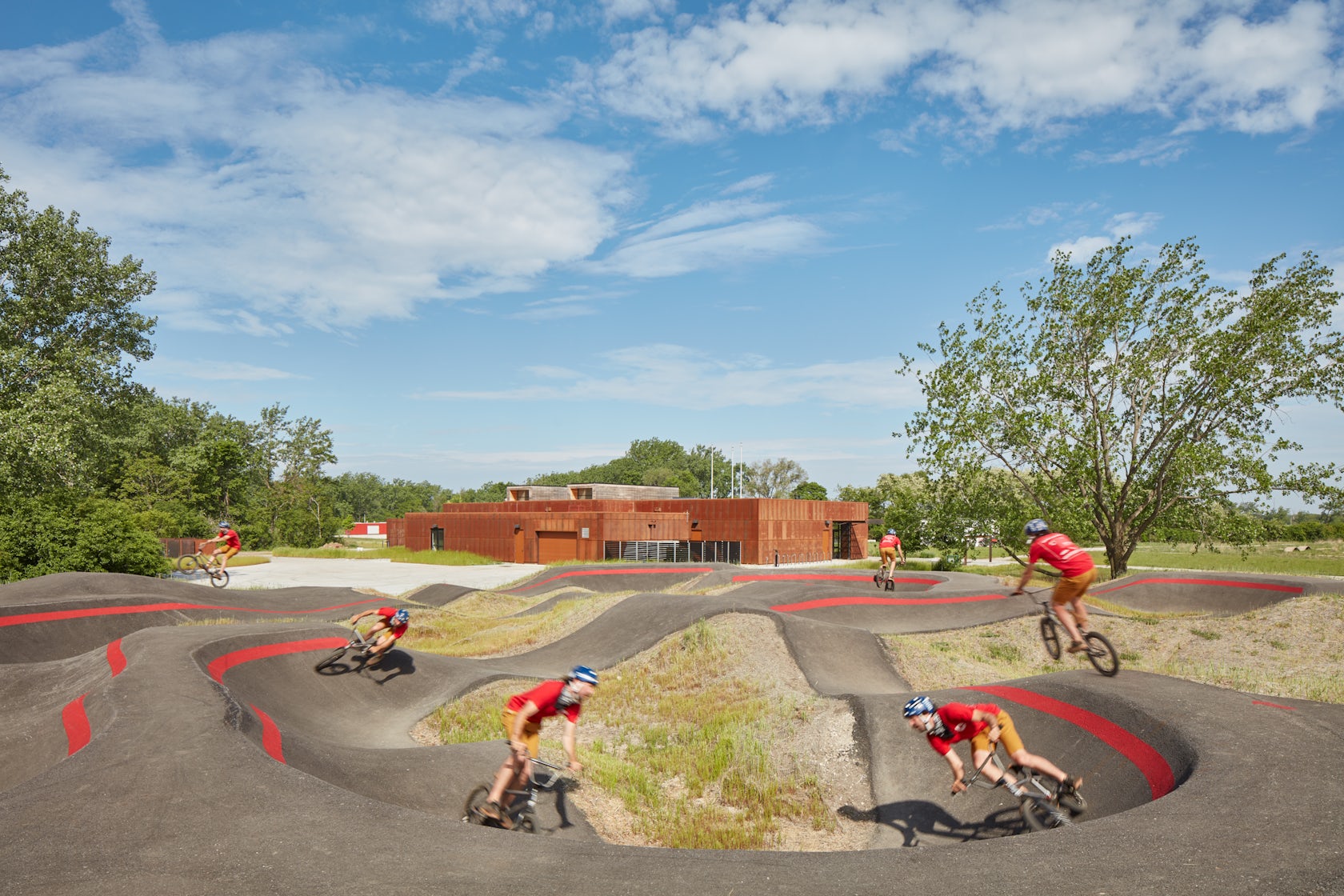
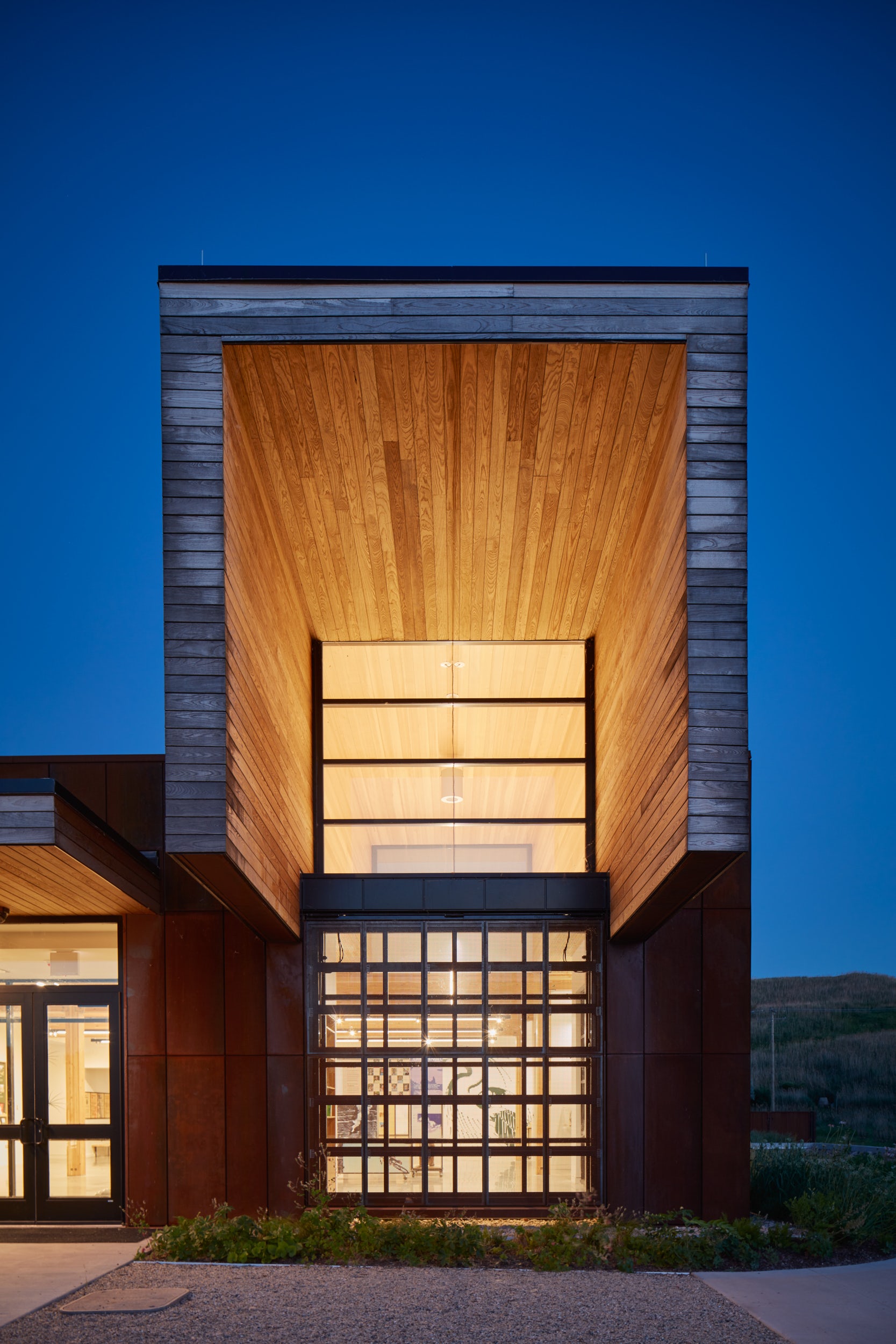
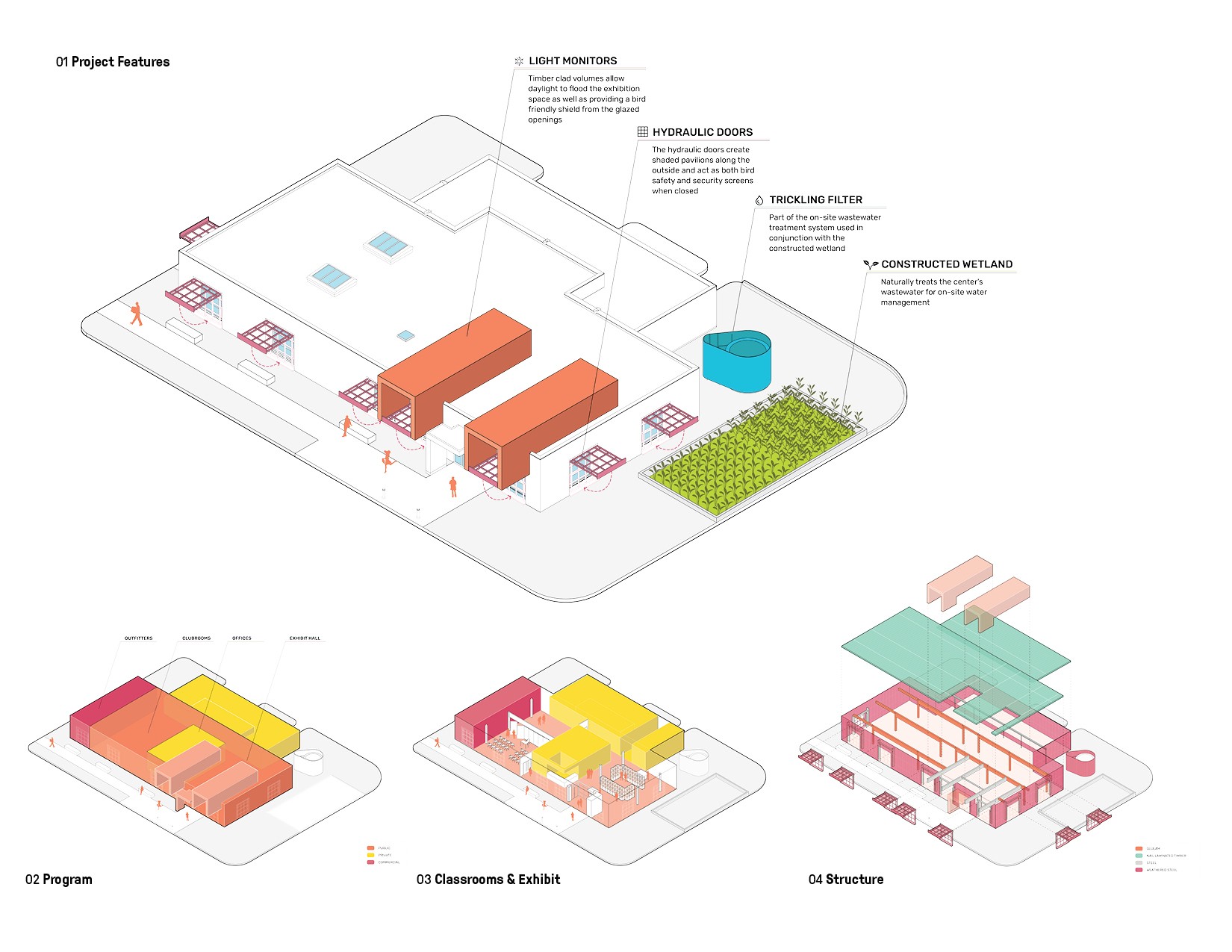
Ford Calumet Environmental Center – Once a dumping ground from nearby steel mills, Big Marsh park opened in 2016 on the southeast side of Chicago. The Chicago Park District asked Valerio Dewalt Train to design an environmental center that serves as an education hub and a gateway to eco-recreation opportunities throughout the region. The design responded to the park’s past by marrying the industrial with the natural. The exterior is clad in a rain screen of weathered steel that recalls the site’s steel mill history, with an exposed mass timber interior. Two large rooftop light monitors, clad in exposed Nail-Laminated-Timber, flood a double-height exhibition area with daylight.
Architizer chatted with Tom Daly, Project Manager and Joe Valerio, Design Principal at Valerio Dewalt Train, to learn more about this project.

© Tom Harris Photography

© Tom Harris Photography
Architizer: What inspired the initial concept for your design?
Tom Daly: Historically, Chicago’s Southeast Side has been burdened with the effects of industrialization and left with remnants of steel production in the region of the city. The building’s materiality serves as a metaphor to the site’s industrial past and forward-thinking future: the corten steel that wraps around the building is an acknowledgement of that past, while the two wooden forms cantilever dramatically to both mark the entry and frame a view of the interior, while from the inside they focus your attention on small but significant vignettes of the restored natural landscape. They deliver a message about an environmentally responsive and conscious future.

© Tom Harris Photography
This project won in the 10th Annual A+Awards! What do you believe are the standout components that made your project win?
The design serves as an example for a progressive future of building in the City of Chicago, a city known for design innovation. The center was the first wastewater wetland system in the city, and the first mass timber building for the Chicago Park District. The building also actively improves living conditions for its surrounding inhabitants. Its highly bird-safe design rates a 4 out of a 100 level scale, with 0 being the highest, and provides a resource for the surrounding communities who have suffered from a lack of investment and park services for decades. It’s sculptural form and rich materiality serve as a gateway to the park at large.

© Tom Harris Photography
What was the greatest design challenge you faced during the project, and how did you navigate it?
The overall project budget was $6.6M, and was made possible by a major contribution from the Ford Motor Company. The Design Team was immediately challenged when it was discovered that the nearest sanitary sewer line was 1.6 miles from the site. The cost of bringing a sanitary sewer to the site was $2.0M – threatening the viability of the entire development. Working with our civil and plumbing engineers, we developed a design for an on-site black water treatment system where the outflow was clean water. The Ford Calumet Environmental Center is the first time a wastewater wetland system has been permitted by the City of Chicago.

© Tom Harris Photography
How did the context of your project — environmental, social or cultural — influence your design?
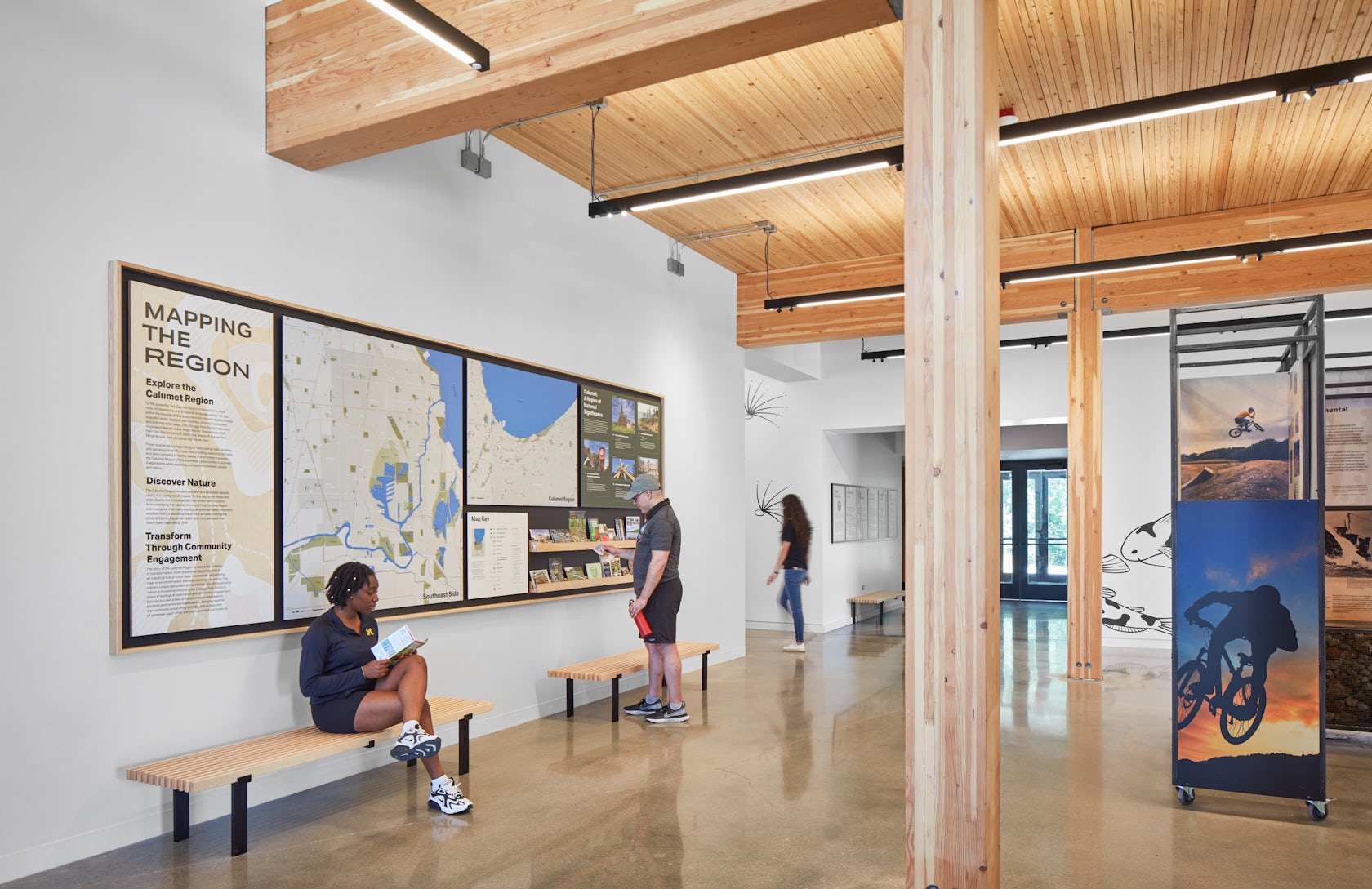
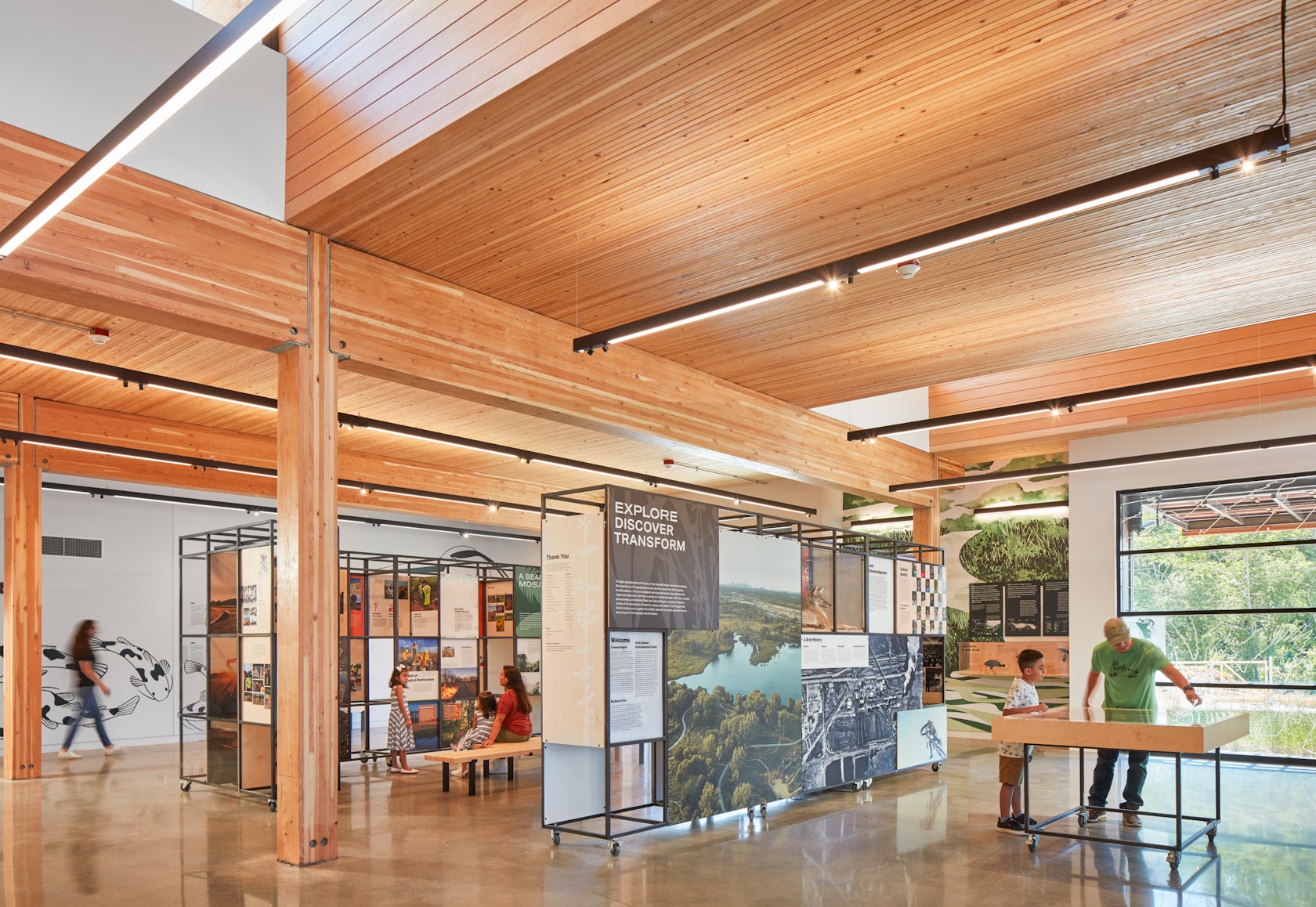
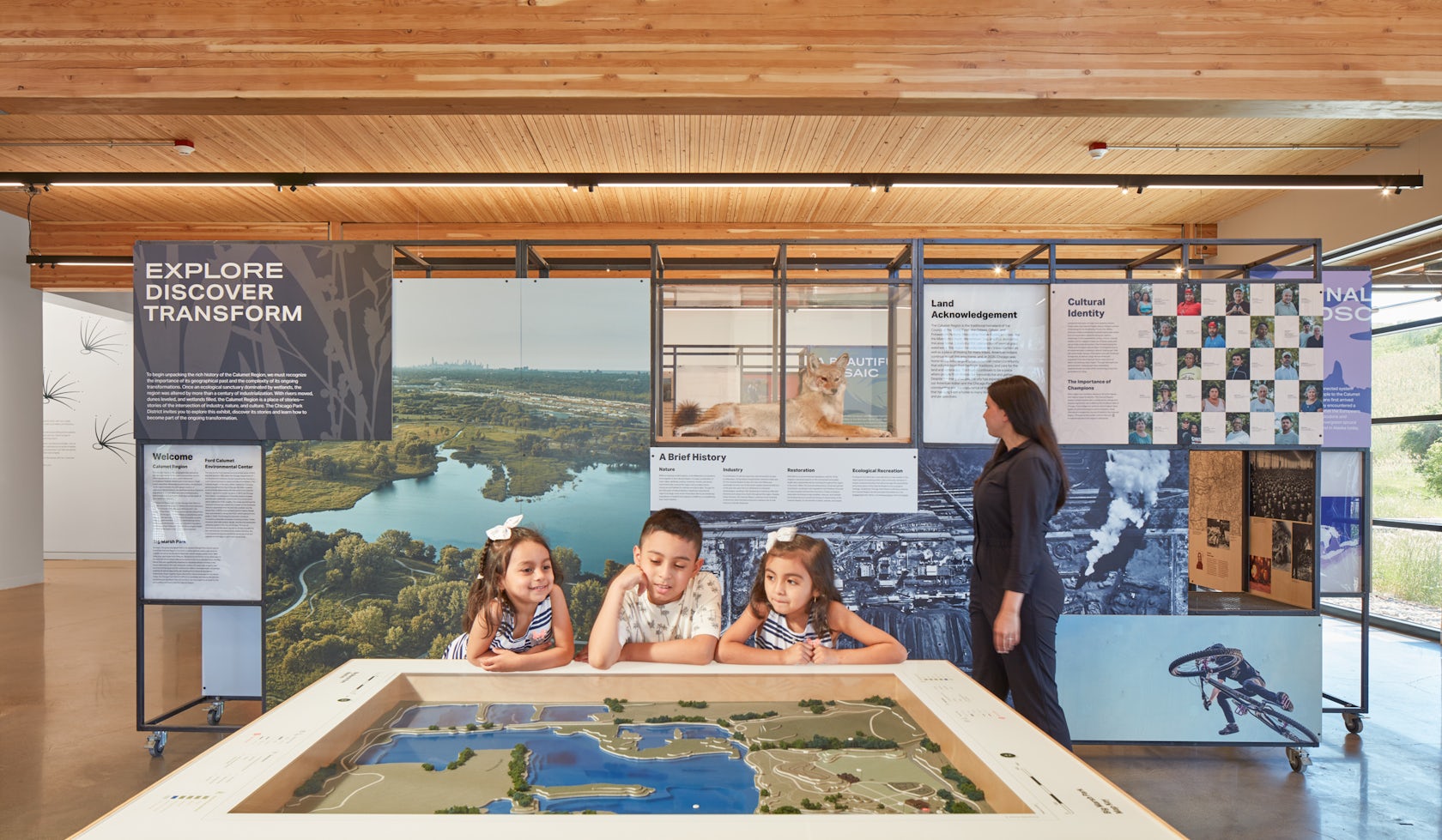
The project’s environmental, social and cultural context are intertwined. Historically, Chicago’s Southeast Side has been financially underserved and burdened with the effects of industrialization. The Ford Calumet Environmental Center is a bold statement of how we can re-inhabit landscapes destroyed by 20th Century technology. A major focus were local residents of the four surrounding neighborhoods including South Deering, Pullman, Trumbull Hill and Hegewisch. Our Media-Objectives Studio reached out to community leaders and developed an award winning exhibit which focuses on their past and optimistic future. Through environmental education and eco-recreation, the center serves as a community resource and cultivates advocacy for positive change across the Calumet Region.

© Tom Harris Photography
What drove the selection of materials used in the project?
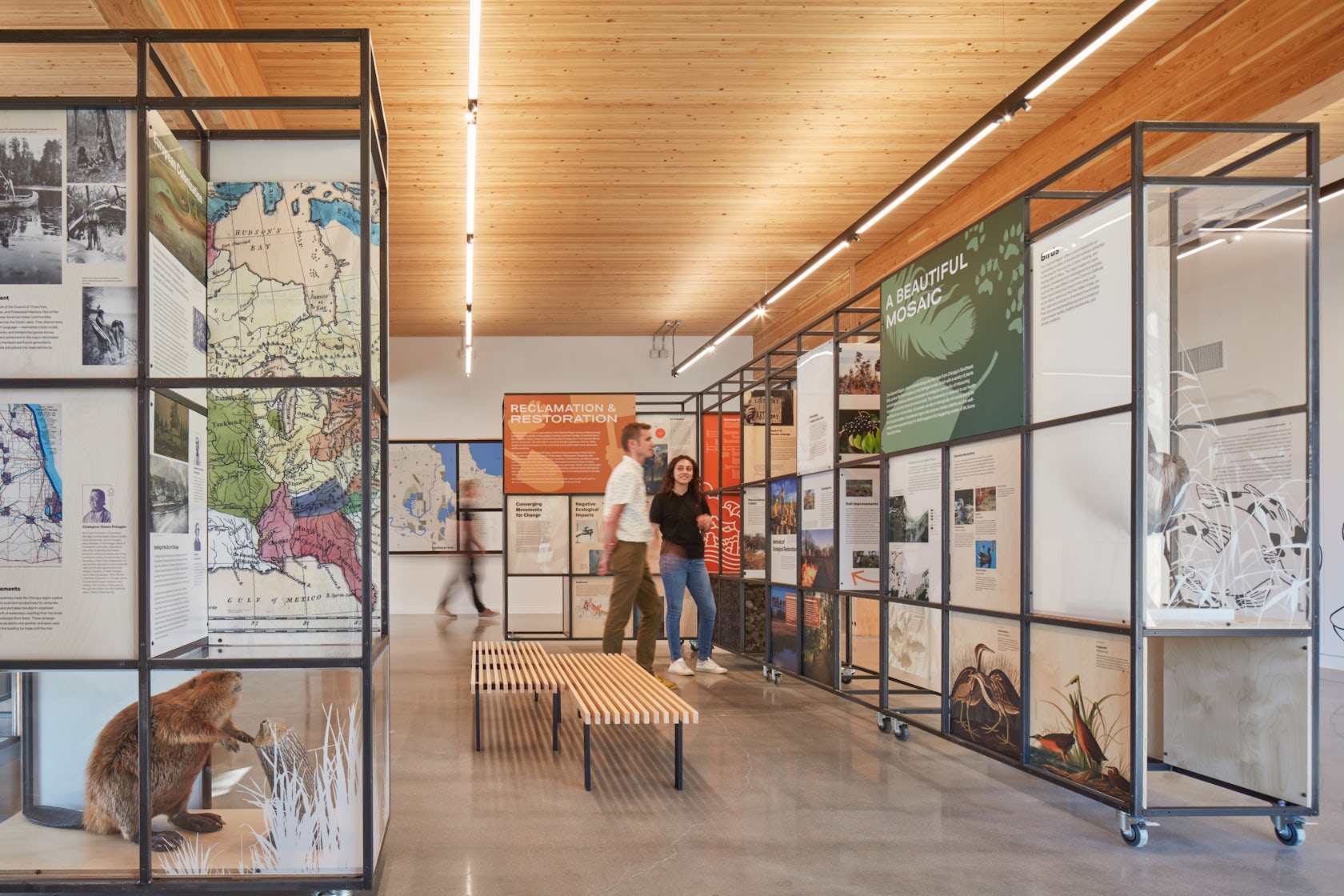
The building’s materials reinforce its mission. The 20th Century industries that so damaged this region were major sources of carbon released in the atmosphere. The weathered steel cladding is recycled – which has a low level of embodied carbon compared to other building materials. The decision with the most impact is the use of a mass timber structure. The embodied carbon is lower than almost any other material, in addition the timber sequesters carbon leading the way to an environmentally-responsive future.

© Tom Harris Photography
What is your favorite detail in the project and why?
Early in the design process our focus was on creating an open and welcoming architecture with a daylit interior. Big Marsh Park is also on one of the major migratory routes for birds, drawing attention from an important constituency for the Park – bird watchers.
The two wooden forms that cantilever over the corten facade, bring daylight from above into the exhibit space. The eight foot cantilever results in eliminating the reflection of the sky in the large clerestory windows, bird safe glass is also used for these window. There are six large windows around the perimeter that bring daylight into all the interior rooms. Each is equipped with large doors, covered in perforated corten steel. In the open position, the doors shade the glass reducing the reflection of the sky. During the migratory season, the doors are kept closed, with the perforated metal still providing adequate light

© Tom Harris Photography
How important was sustainability as a design criteria as you worked on this project?
Sustainability was a driving factor in the design and overall project mission. Sustainable features like the wastewater wetland system are put on display, demonstrating how it takes inspiration from the marshes’ natural processes to treat the building’s blackwater and release clean water back to the site via a leach field. Renewable resources in the project include Nail Laminated Timber, giving the building warmth and a lower carbon footprint. An eco-friendly alternative to aluminum, weathered steel has a lower carbon footprint as well, reducing the building’s overall embodied carbon while providing a durable layer of protection with a beautiful orange patina.

© Tom Harris Photography
In what ways did you collaborate with others, and were there any team members or skills that were essential in bringing this Award winning project to life?
Collaboration was critical to the success of the FCEC. It began with the Chicago Park District who were willing to explore new solutions to old problems. In addition, from the beginning one of the Districts goals was to engage the adjacent minority communities.
Designing and permitting the wasteland wastewater system involved many members of the design team, the Park District, and the Chicago Building Department.
Finally, our Media-Objectives Studio brought leaders and residents of the surrounding neighborhoods into the design of the exhibit which includes the history of these communities including photographs of some of the residents including their own words about the past and future of the region.

© Tom Harris Photography
Were any parts of the project dramatically altered from conception to construction, and if so, why?
There were a number of changes, but nothing that represented a dramatic change.
How have your clients responded to the finished project?
The FCEC is one of the most widely recognized buildings completed by the Chicago Park District. Among the awards and publications the most significant is first place in the yearly Driehaus Foundation Award for Architectural Excellence in Community Design was established to recognize the importance of great architecture and craftsmanship to city life.
How do you believe this project represents you or your firm as a whole?
Good design is always the answer.
Team Members
Steffan Schoenauer – Project Manager (Chicago Park District); Joe Valerio – Design Principal Mark Dewalt – Principal-in-Charge, Tom Daly, Alexander Raynor – Project Manager, Lauren Shelton, Matt Gamache, Michael Johnson, Susan Crockett, Nina Cackovic, Haydyn Jones, (Valerio Dewalt Train); Joe Lawton – Principal, Allison Rokusek, Jacob Goble, Rafael Barontoni, Stephen Killion – Graphic Designers (Media–Objectives)
Consultants
Chicago Commercial Construction – General Contractor; Primera – Civil Engineer; Jacobs Ryan Associates – Landscape Architecture; Matrix Engineering – Structural Engineering; dbHMS – MEP Engineering; Tom Harris – Photography; TetraTech – Environmental Consultants; BioHabitats – Green Infrastructure
Products and Materials
ReSawn Timber Co; Axis Lighting; Dri Design; Arborwood; Shaw; Crossville; Steelcase;
For more on Ford Calumet Environmental Center, please visit the in-depth project page on Architizer.
Ford Calumet Environmental Center Gallery


