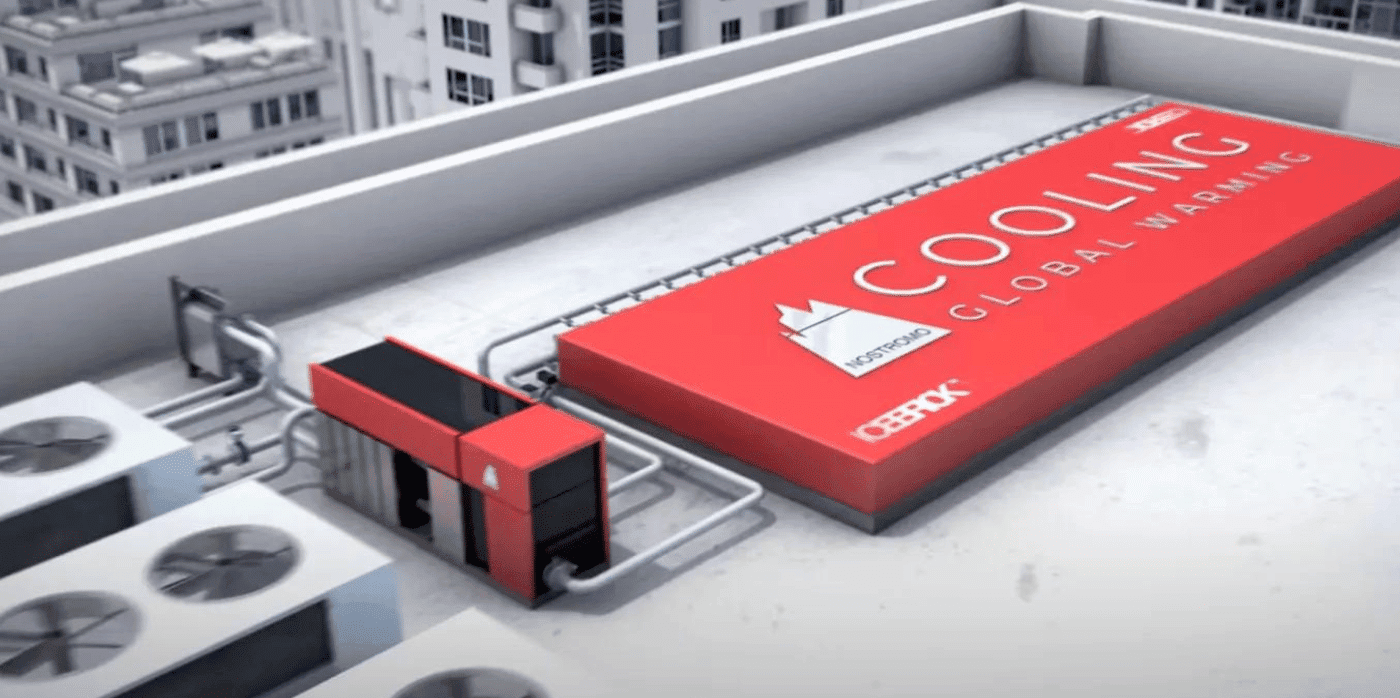
Spotted: In the US alone, around 74 per cent of all energy is used by buildings, and of that figure, 50 per cent of the peak hour consumption is used keeping buildings cool with air conditioning. This is where startup Nostromo Energy comes in, with its new methodology for energy storage that could relieve the power grid of some of the strain – and environmental cost – of cooling buildings. The company’s ‘IceBrick’ system utilises off-peak hours energy to freeze water in an ice brick array, which can then be used to chill water for cooling at a later point.
Today’s commercial-scale air conditioners are energy-intensive because they constantly run ‘chillers’ to cool water, which then circulates in a building, cooling the air. Nostromo’s system reduces the use of chillers by creating ice in an array of capsules at off-peak times – a process that ‘stores’ cooling energy. The building’s circulated water can then be passed through the array to be cooled at peak times, without the energy drain of constantly running the chillers. In fact, the chillers can be turned off when the IceBrick is in use, reducing electricity consumption at key moments.
The system is extremely modular and can be fitted to a building’s available rooftop and basement space. The technology also has good longevity as water can be frozen and unfrozen for many years with only minimal degradation.
A cloud-based management platform is used to control the system and make adjustments depending on the business’s particular goals. For example, the system can be optimised for financial gains or to reduce carbon emissions, maximise electric vehicle charging capacity, or provide enhanced backup. Nostromo works with a business’s engineers to install the IceBrick system on new builds or as a retrofit, with the company taking care of permitting and installation.
Springwise has also spotted other innovations using ice for cooling, such as fridges for areas without constant power. The Springwise library also contains other innovations reducing the impact of air conditioning, such as a system that uses salt water to remove moisture, and a 3D-printed air conditioning system.
Written by Archie Cox and Matthew Hempstead