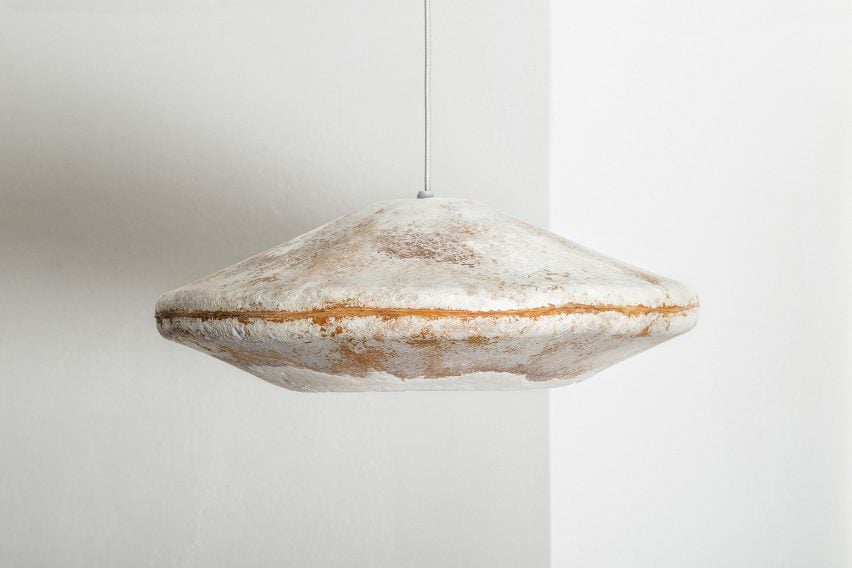
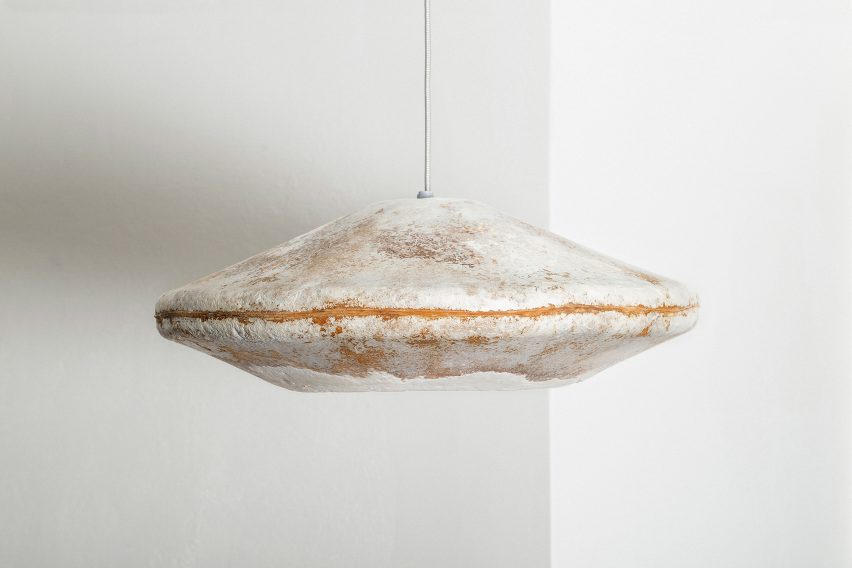
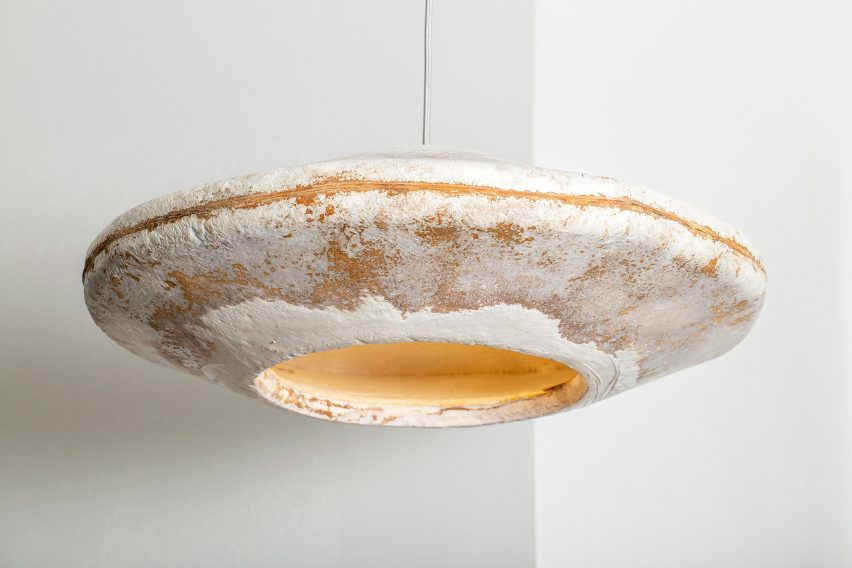
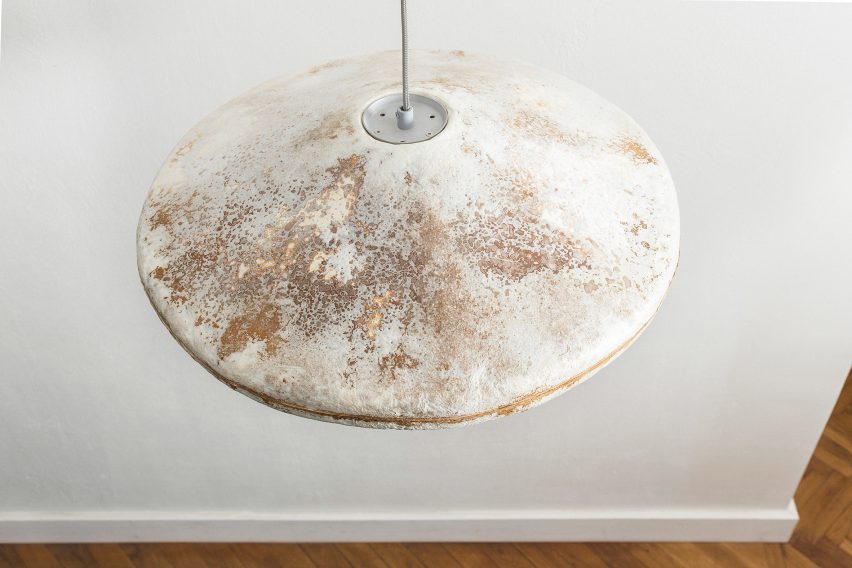
7 Simple Steps to Decarbonize Your Home
By Peter Dull
With carbon emissions reaching an all-time high, it is important to discuss how we, as a global community, can minimize the carbon load of our buildings. As of March 29th of 2019, we surpassed over 410 ppm (parts per million) of carbon dioxide (CO2) in our atmosphere. To put this into perspective, our sea levels have risen between 0.1 to 0.13 inches per year; and our global temperature rises 2 to 3 degrees Celsius yearly because of carbon emissions. These astronomical figures are the necessary wake-up calls we need in order to help meet the goals of the Paris Agreement*.
*The Paris Agreement is a worldwide initiative that calls for action on the threat of climate change. The agreement consists of two parts: decrease the global temperature by 1.5 degrees Celsius yearly and increase access for countries that require resources (i.e. technology and finance).
What is Decarbonization?
Decarbonizing our homes is one of many ways we can be more conscious of our current lifestyles. Decarbonization refers to the removal of carbon from the environment. In the case of housing, homeowners can reduce energy use and reliance on fossil fuels (i.e. gas furnaces), and choose building materials that require either low amounts of carbon emissions to manufacture and transport, or actively sequestrate carbon by storing carbon that is drawn from the atmosphere. We will address why you should consider your energy and material uses, and how you can develop a carbon-neutral home.
How Can You Decarbonize Your Home?
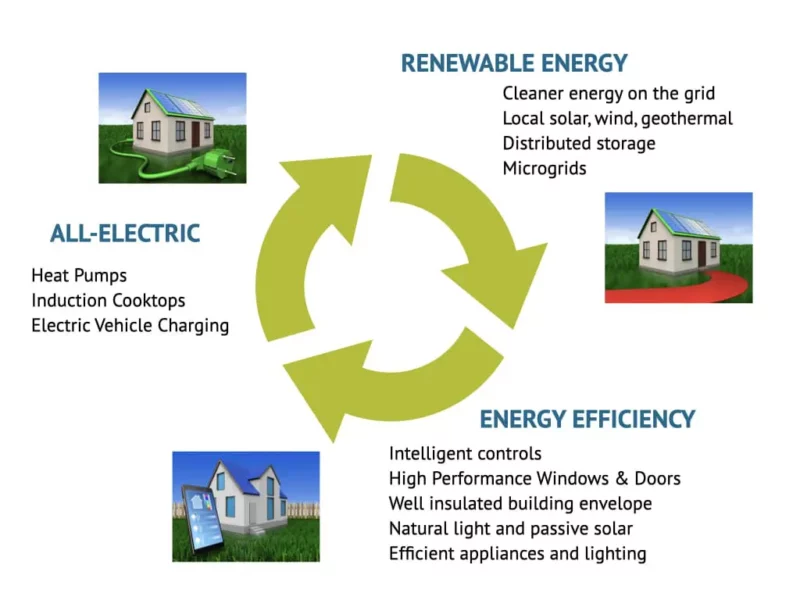
Energy Efficiency
When considering how to decarbonize your living space, first think of this in terms of the amount of energy (and carbon) being used. You can reduce your carbon load by losing less energy to leakage, making use of passive heating and cooling, and upgrading the efficiency of your appliances.
Insulate and Eliminate Air Leaks
As Katrin Klingenberg, Co-Founder and Executive Director of Passive House Institute US, says “The greenest energy is the energy we don’t use at all.” A well insulated house which is extremely airtight has an oversized impact on the heating and cooling needs and therefore reduces carbon emissions. If you go for a Passive House standard, you can see overall energy savings as much as 90% on space heating. Innovative new products such as Havelock wool insulation and Aerobarrier have envelope sealing technology that make this easier and more cost effective than ever before.
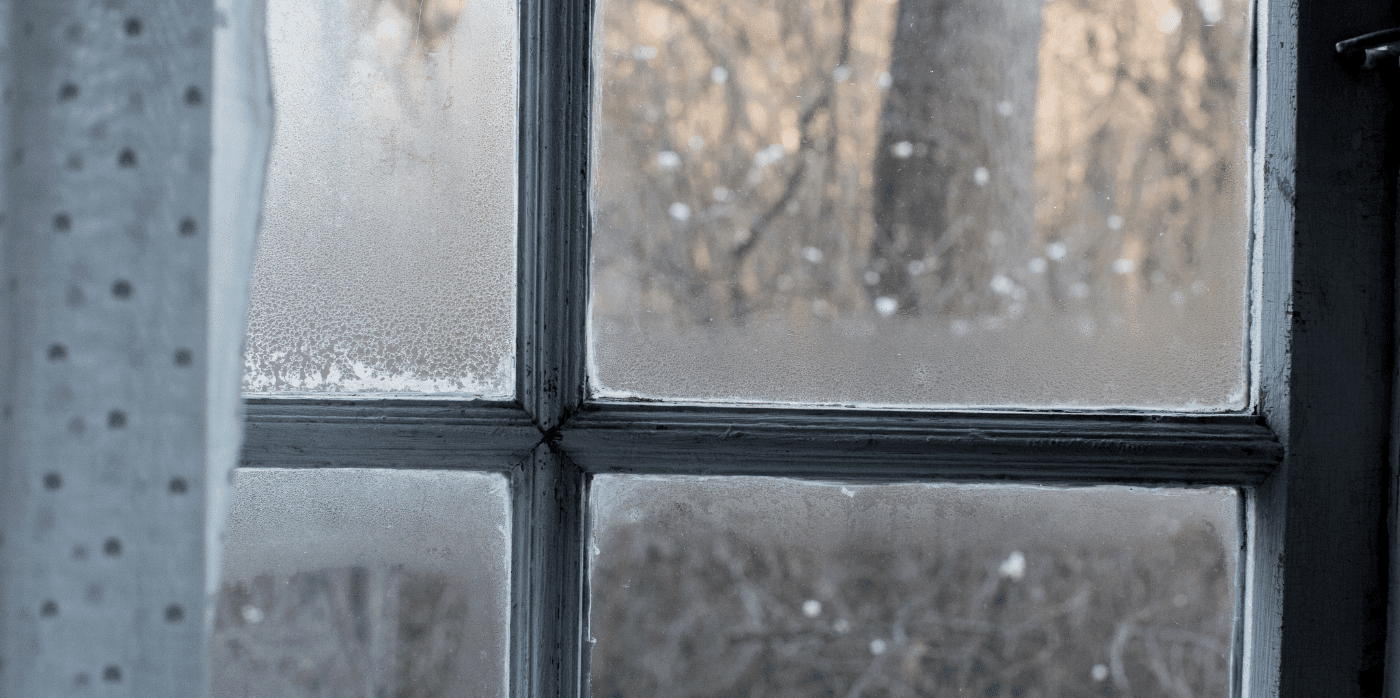
High-Performance Windows & Doors
You may ask yourself “aren’t all windows and doors created the same?” While this may sound realistic, there are advantages when you invest time researching these products. Not only can you allow natural ventilation in your home, you also can have a virtually airtight seal when closed.
Natural Lighting and Passive Solar
Using skylights and repositioning your windows at home are some savvy ways to change-up your home. Skylights and windows reduce the need for artificial lighting and rely on more beneficial, natural lighting to lighten up the aesthetics in your home. By repositioning your windows to face southward, your home can be protected with overhangs to protect against the high summer sun and be aligned with the recently-trending design of Passive solar. If you are looking to buy supplies that reduce your sunlight intake, buy some awnings and window shutters to make that possible.
Efficient Lighting and Appliances
Your electric load can be greatly reduced by using LED lighting in your home.
Always look for Energy Star appliances that are certified to use less energy to get the job done.
Intelligence Controlled
As a quick reminder, always remember that when you are not using something, turn it off or close it off! As simple as it sounds, many homeowners seem to forget, resulting in a utility bill higher than their expected value.
Now that we are immersed in the “digital age,” it is easier than ever to control your home through your smartphone and/or virtual home assistants. This type of intelligence can save you money as you can monitor and control your usage from virtually anywhere to reduce energy use. Some innovative products include airtouch and switchmate.
Renewable Energy
Currently, the average American household produces 7.5 tons of carbon dioxide per year. By switching to renewable power sources, homeowners not only save money on their utility bills, but can reduce their carbon footprint. Keeping additional carbon out of the atmosphere takes us closer to meeting goals that correlate to sustainable living.
What does it mean to have “cleaner energy” on the grid?
Expanding your grid is like adding colors to a painter’s palette. As you discover new ways to diversify your power sources, you have more options to work with and it can be easier to construct a house through a variety of styles and sources. By incorporating appliances and innovations that rely on and produce renewable energy, you decrease your carbon output and help reduce the amount of “bad energy” that’s being utilized. In addition, you can install battery storage that helps bridge the gap between times of excess energy generation during the day and times of lower renewable production.
Solar
The most well-known renewable energy solution homeowners are investing in is solar energy. Solar panels, either placed on their roofs and/or walls, are helpful for homeowners in locations where the sun is apparent throughout the year. Solar photovoltaics (or PV for short) increase your grid security and are a very economical source of energy.
The SunPower Equinox system, for example, offers innovation at every level, from its Maxeon solar cell technology to each panel’s individual microinverter to the SunPower SunVault battery. The latter allows the solar panels to remain powered for longer even in times of power outages and shade.
Wind
As much as the term “wind turbine” sounds daunting, there is nothing to be scared of! If you have a large plot of unused land, consider installing a small turbine. These windmill-like structures generate energy through the rotation of their propellers and then transfer that energy to an electricity grid for use. With an average payback of fewer than 13 years (machines last 20+ years), this is a smart investment in the long-run.
Geothermal
Geothermal energy can be an option to provide heating, cooling, and hot water for the home. Although there might not be any volcanoes near your home, modern heat pump technology becomes handy when warming your living space. These systems take advantage of the relatively constant temperatures below ground to transfer heat and apply cooling properties where they are needed. Even though this system may be costly up front, they are a great carbon-neutral option for your home’s operation – even Alphabet is getting in on the action with their spin out Dandelion.
Going All-Electric
As your home’s grid takes in more renewable sources, it makes sense for homeowners to switch to all-electric appliances and systems. Modern high-efficiency electric systems such as heat pump water heaters and induction cooktops are more effective and efficient than their gas counterparts – it is all win and no loss. Now that you can cook with an upgraded system, your stoves reduce the output of CO2 to zero and you and your family can keep warm without the worries of fossil fuel. As a bonus, you can also invest in transportation that is dependent on electricity, like hybrid cars and your local train system.
Materials
So far, we have been discussion “operational carbon”. The carbon emissions that are generated in order to run your home.
You should also consider “embodied carbon”. This is the carbon that was used to create, extract, fabricate, and transport the materials to your site.
When selecting materials for your build or renovation, you can ask yourself some basic questions:
- Is this manufactured and transported in a low carbon manner?
- Does this store (sequester) carbon in my home by using materials which pulled carbon out of the air?
If any of your answers are yes, then congrats – you are on your way to decarbonizing your home. When you consult with a local construction firm, keep in mind not only the structure of your ideal home, but how different sustainable materials can save you energy and money. You can explore certifications such as the LEED or the Living Building Challenge. You can find information on your product choices through online resources such as the Carbon Smart Materials Palette.
Low-Embodied Carbon Materials
CO2 emissions, which are used to manufacture and transport a material, are referred to as the ’embodied carbon’ of that product. Between 2020 and 2050, it is expected that embodied carbon will be responsible for almost half of total new construction emissions. So how can we work as homeowners to reduce carbon in our materials? Just keep on scrolling down!
Renovate and Reuse
When undertaking a new project, it is almost always more carbon efficient to renovate instead of demolishing and building anew. If you are taking out an existing structure, look for opportunities to donate and reuse building materials instead of sending them to a landfill. By using reclaimed materials for your project, this will result in a net-zero carbon product and will take less labor to start something new.
Avoid Carbon Intensive Materials
With the continued push towards transparency, it is becoming easier to understand the carbon footprint of materials. Databases such as the Inventory of Carbon and Energy provide critical insights that allow homeowners to better comprehend what they are installing for their home. Some carbon-intensive materials (i.e. concrete) can be produced using materials which are waste (such as fly-ash) and other materials (i.e. cork) that are naturally low-carbon or even no-net-carbon.
Consider Materials that Sequester Carbon
If your project uses materials that pull carbon out of the air, aka materials that are natural and undergo photosynthesis, then those materials can be said to sequester carbon in your home. When constructing your home, it is important to consider the longevity of your building and how carbon can be drawn from the air and be safely stored in your home. By supporting sustainable forestry practices in your choices, you will contribute to carbon drawdown and the overall green movement.
New products such as cross-laminated timber (CLT) allow wood to replace steel and concrete for many structural applications.
For your consideration
Thanks to programs such as the Technology and Equipment for Clean Heating (TECH) and Building Initiative for Low Emissions Development (BUILD), which are both found in California, sustainable living can be a reality for homeowners. These complementary, statewide initiatives facilitate easier access to water and heating equipment at a lower cost and require residential and commercial buildings to cut their carbon emissions by 2040.
Search online to see if your state has tax incentives and rebates to make your greener housing dreams possible.
See how easy this was? Watch as your home becomes more energy efficient by incorporating practices of renewable energy from your own system or the grid. Just as a reminder, you should select products and materials that were created via efficient use of carbon and consider opportunities that store atmospheric carbon with materials within your home. Good luck and happy building!
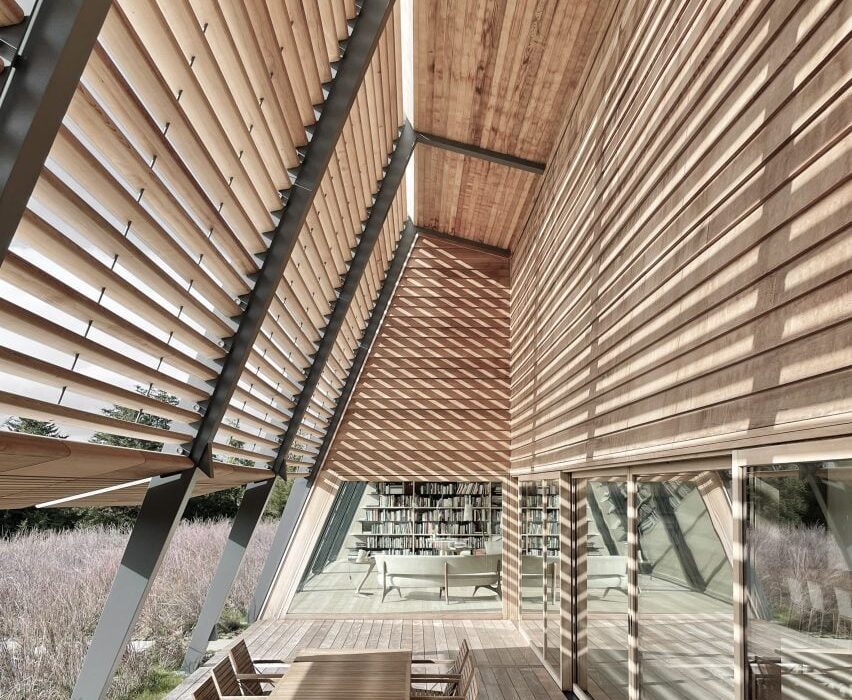
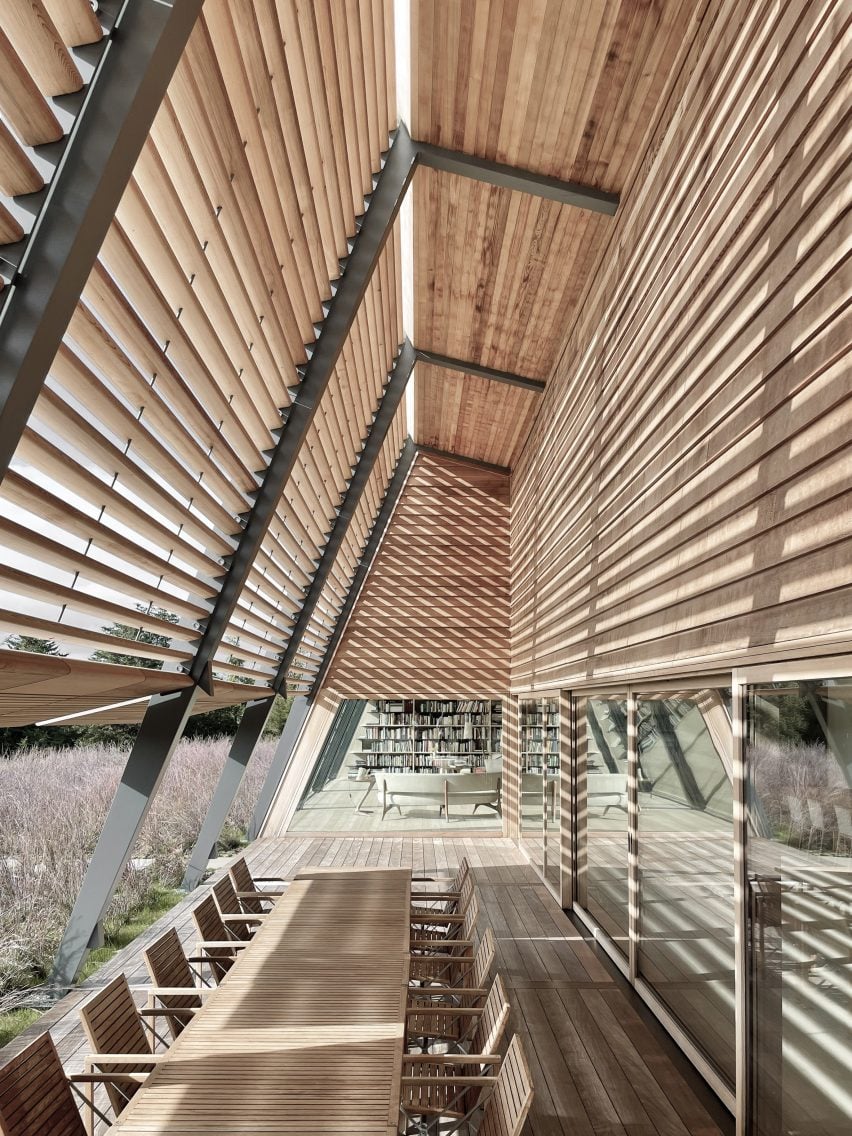
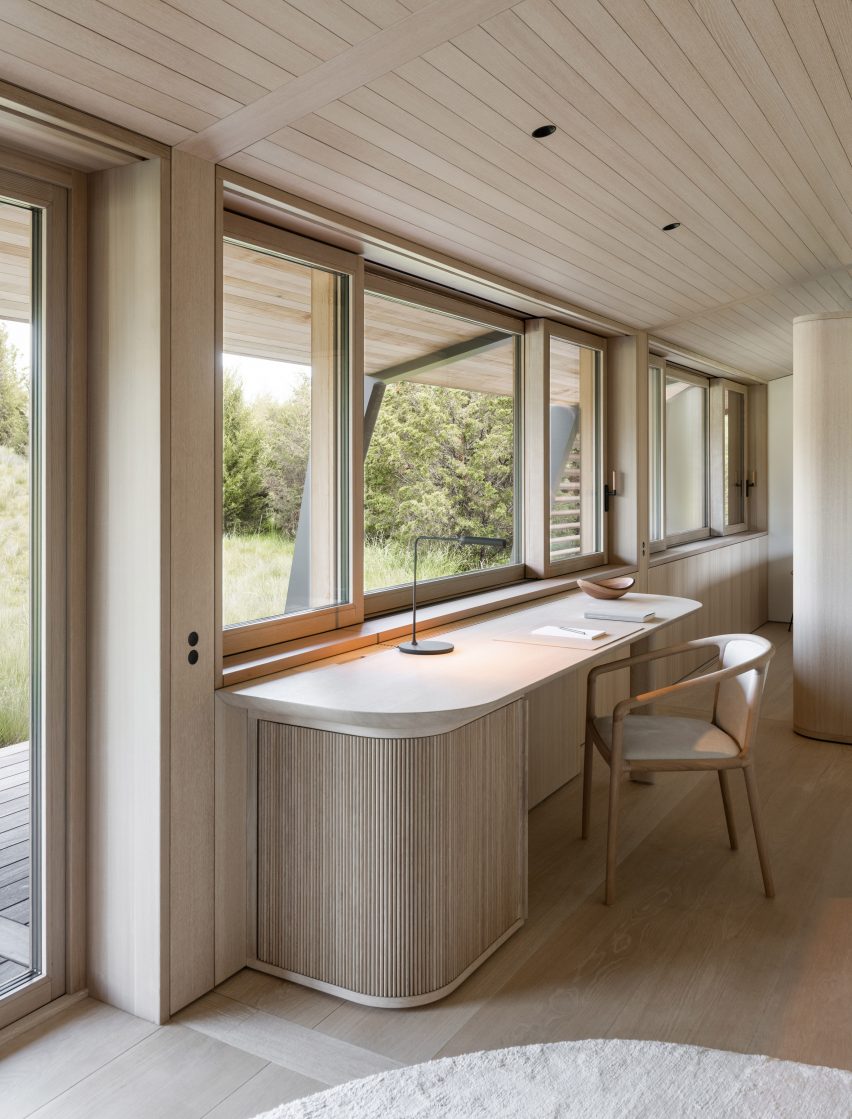
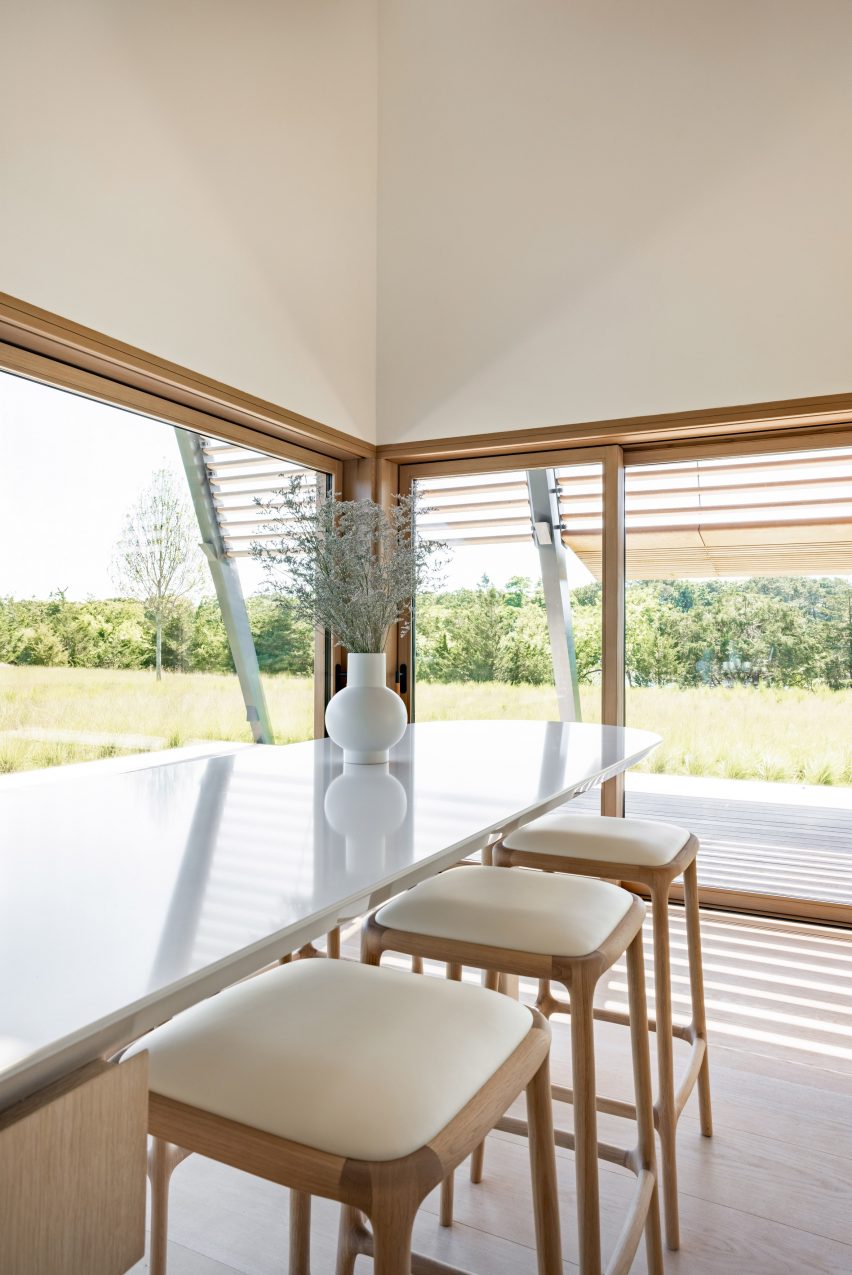
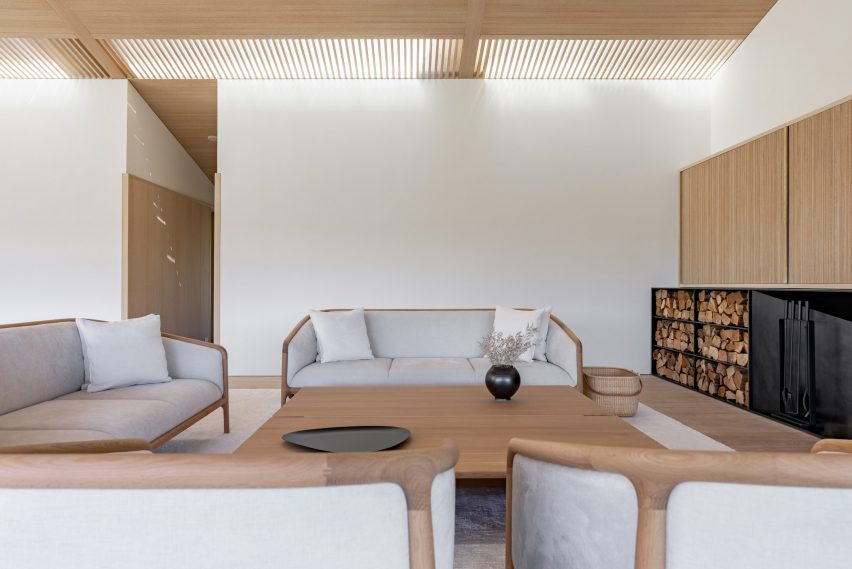
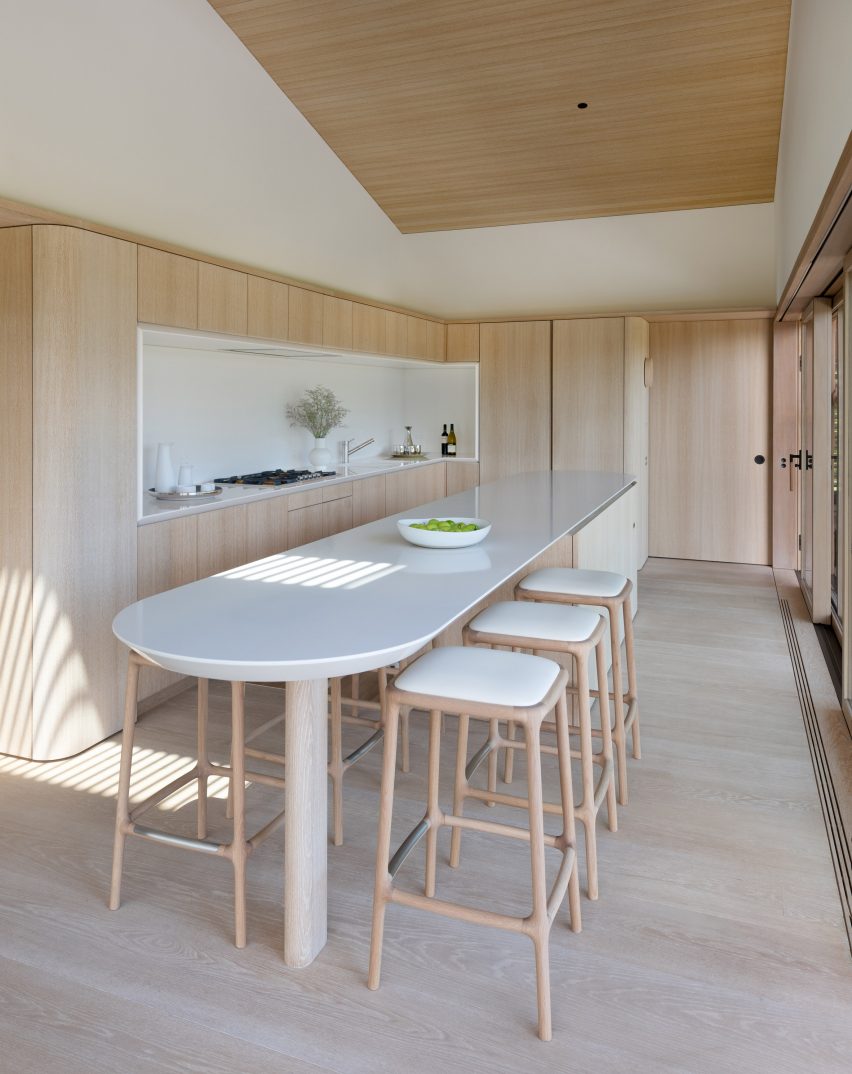
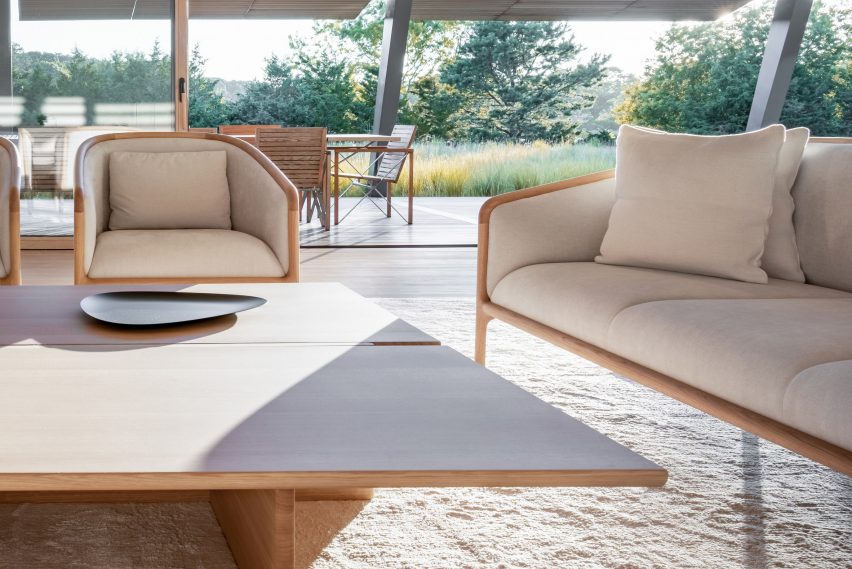
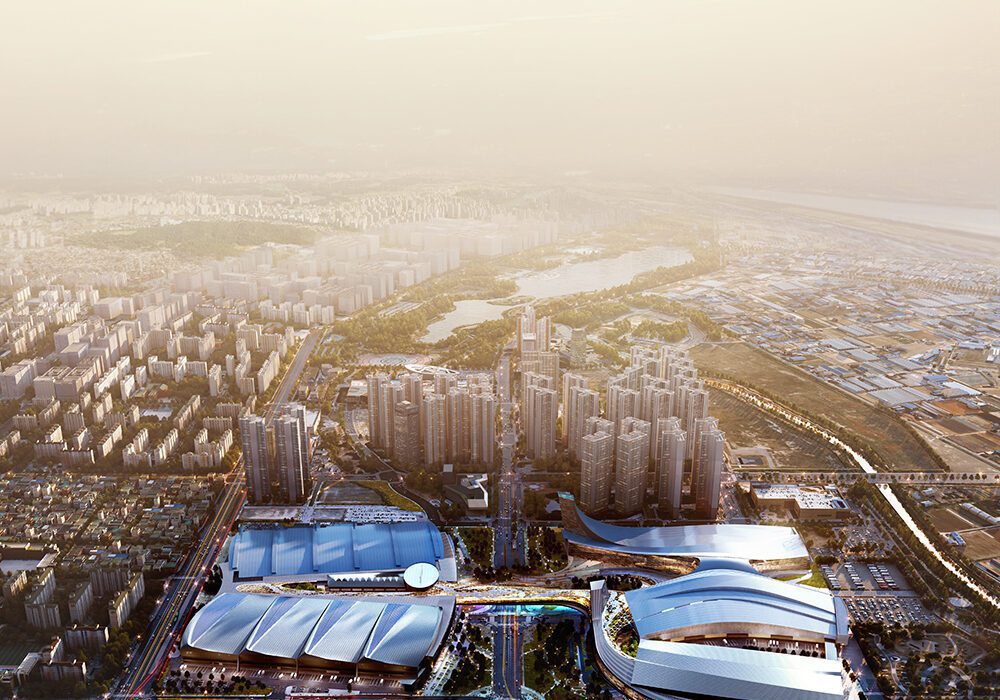
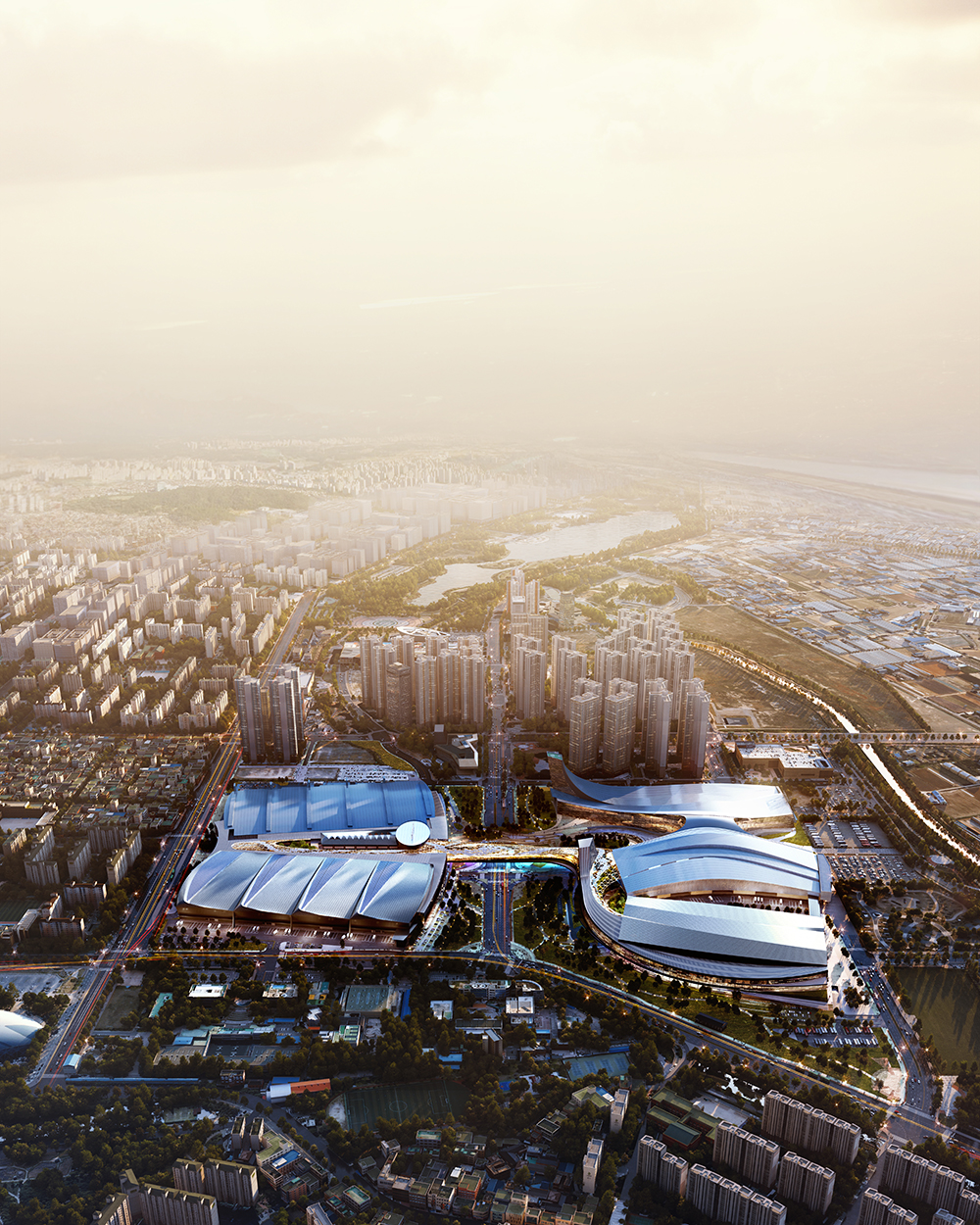
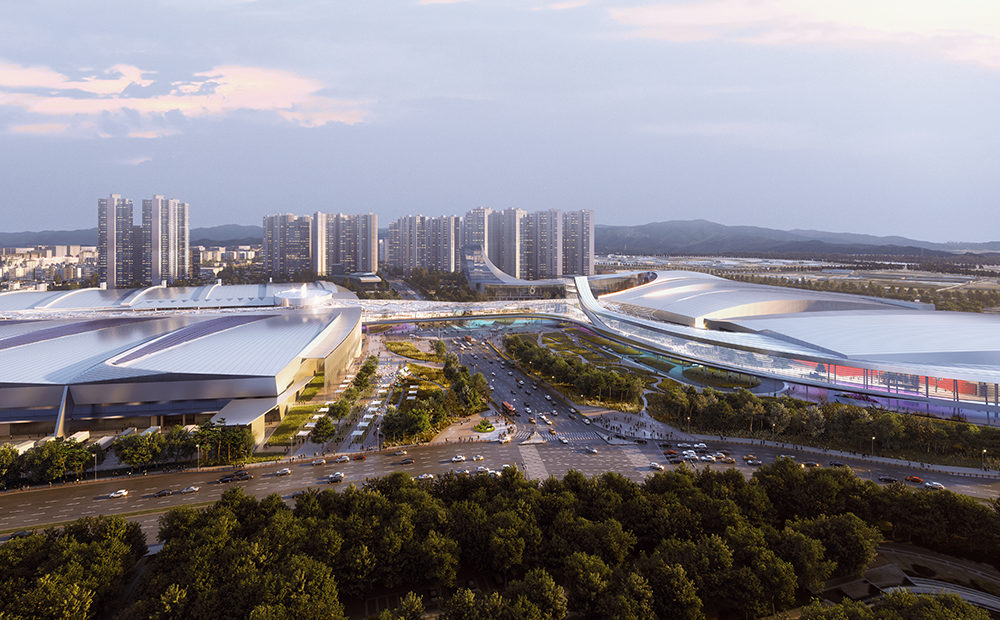























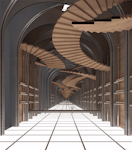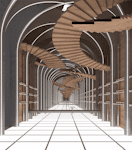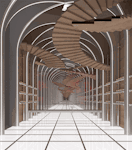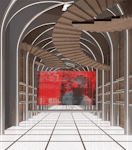


 With two preexisting exhibition halls on the site, the architects were tasked with creating a harmonious third that would expand the existing buildings’ functions while adding an integrated path to connect all three. An urban concourse is an open concourse in Goyang City while weaving the entire exhibition hall, and it is connected to an outside walking square to become a communication space between the city and citizens. While the architectural precedents exuded a somewhat soft image (the existing buildings were inspired by a flower and a butterfly), overall the complex needed to project its identity as a global business platform.
With two preexisting exhibition halls on the site, the architects were tasked with creating a harmonious third that would expand the existing buildings’ functions while adding an integrated path to connect all three. An urban concourse is an open concourse in Goyang City while weaving the entire exhibition hall, and it is connected to an outside walking square to become a communication space between the city and citizens. While the architectural precedents exuded a somewhat soft image (the existing buildings were inspired by a flower and a butterfly), overall the complex needed to project its identity as a global business platform.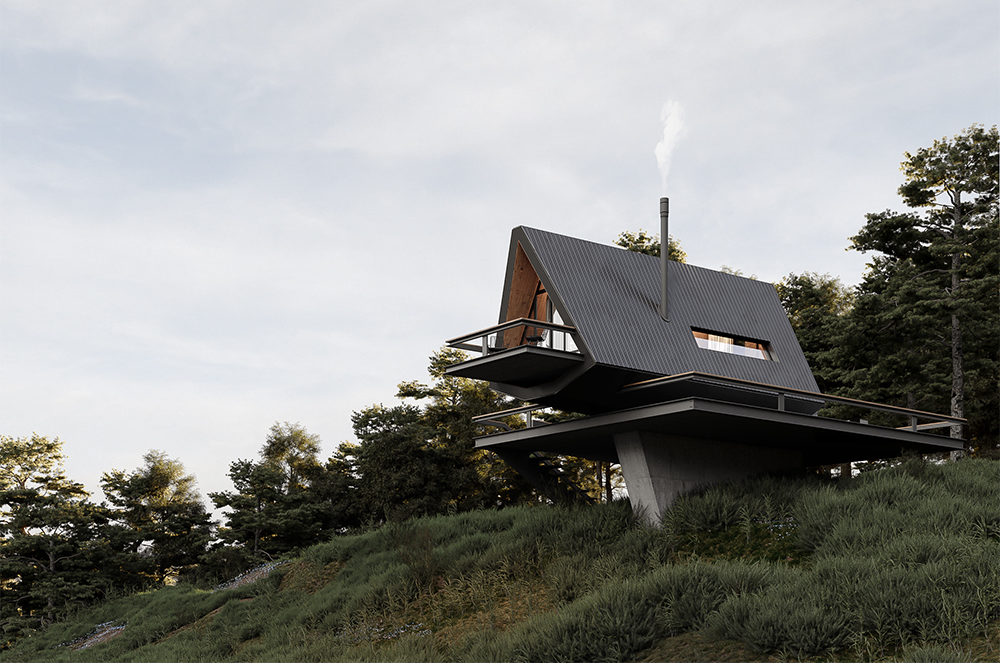
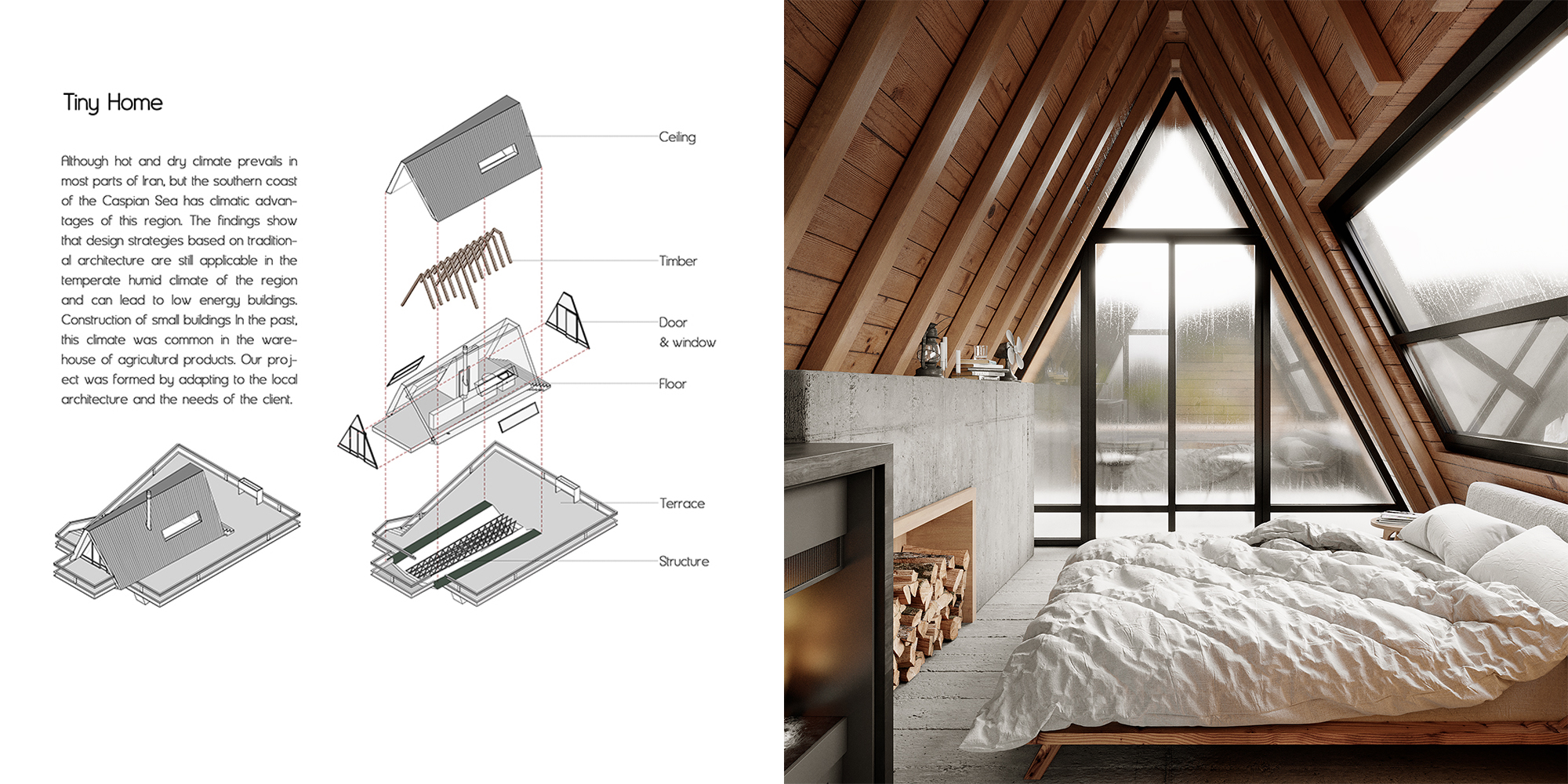 Architects everywhere are tasked with building high quality spaces at the lowest possible costs. This is no different for architects in Iran, where micro living spaces aren’t just space-saving solutions in dense cities; they’re increasingly seen as cost-saving measures on large lots. This particular tiny home falls into the latter category. Sited in a forested and mountainous area, the metal-framed villa is raised above the ground so that it stands amongst the surrounding trees. with their trunks and create a sense of suspension in it. So, one column, like the trunks of trees, separate the building from the ground and lift it up.
Architects everywhere are tasked with building high quality spaces at the lowest possible costs. This is no different for architects in Iran, where micro living spaces aren’t just space-saving solutions in dense cities; they’re increasingly seen as cost-saving measures on large lots. This particular tiny home falls into the latter category. Sited in a forested and mountainous area, the metal-framed villa is raised above the ground so that it stands amongst the surrounding trees. with their trunks and create a sense of suspension in it. So, one column, like the trunks of trees, separate the building from the ground and lift it up.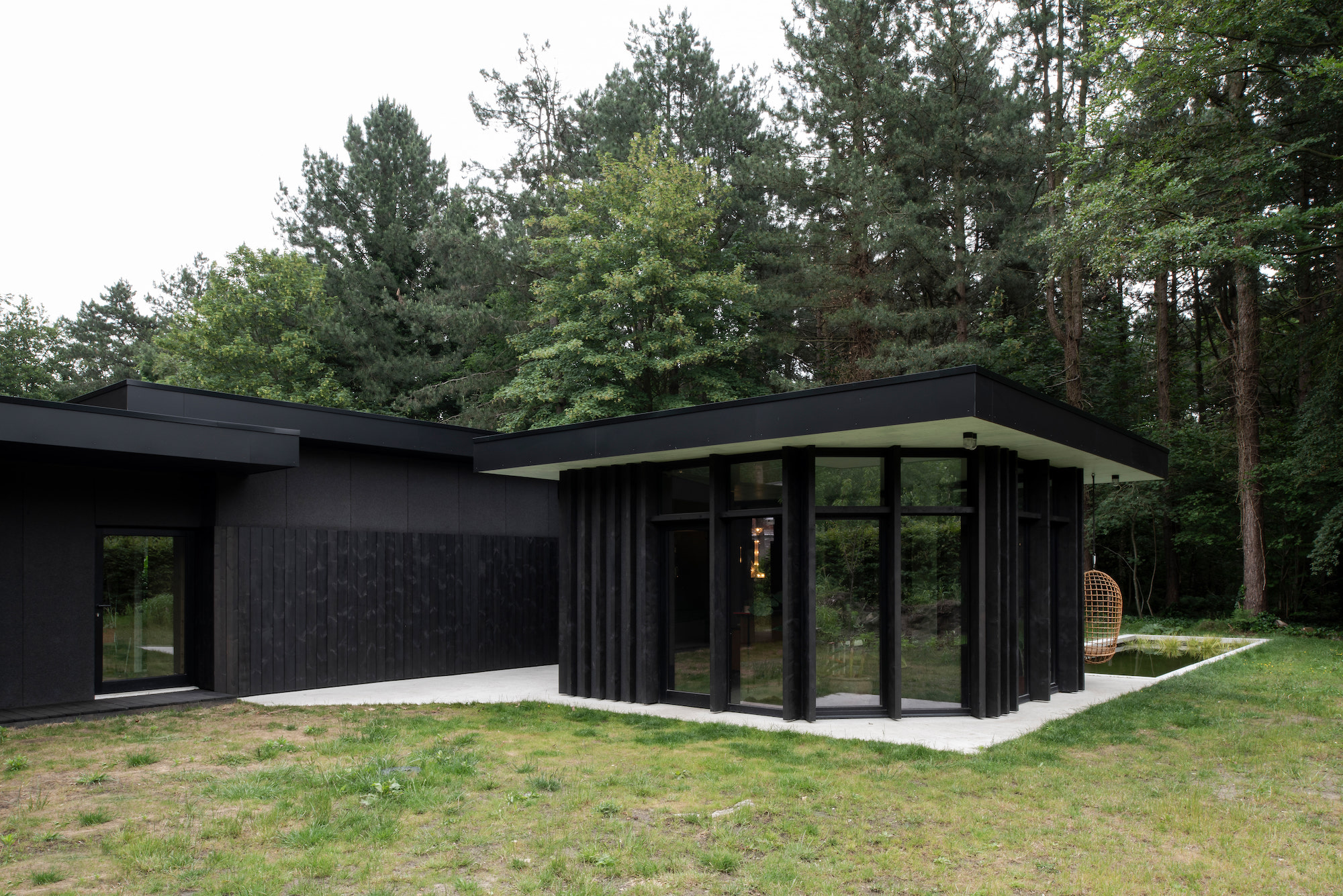
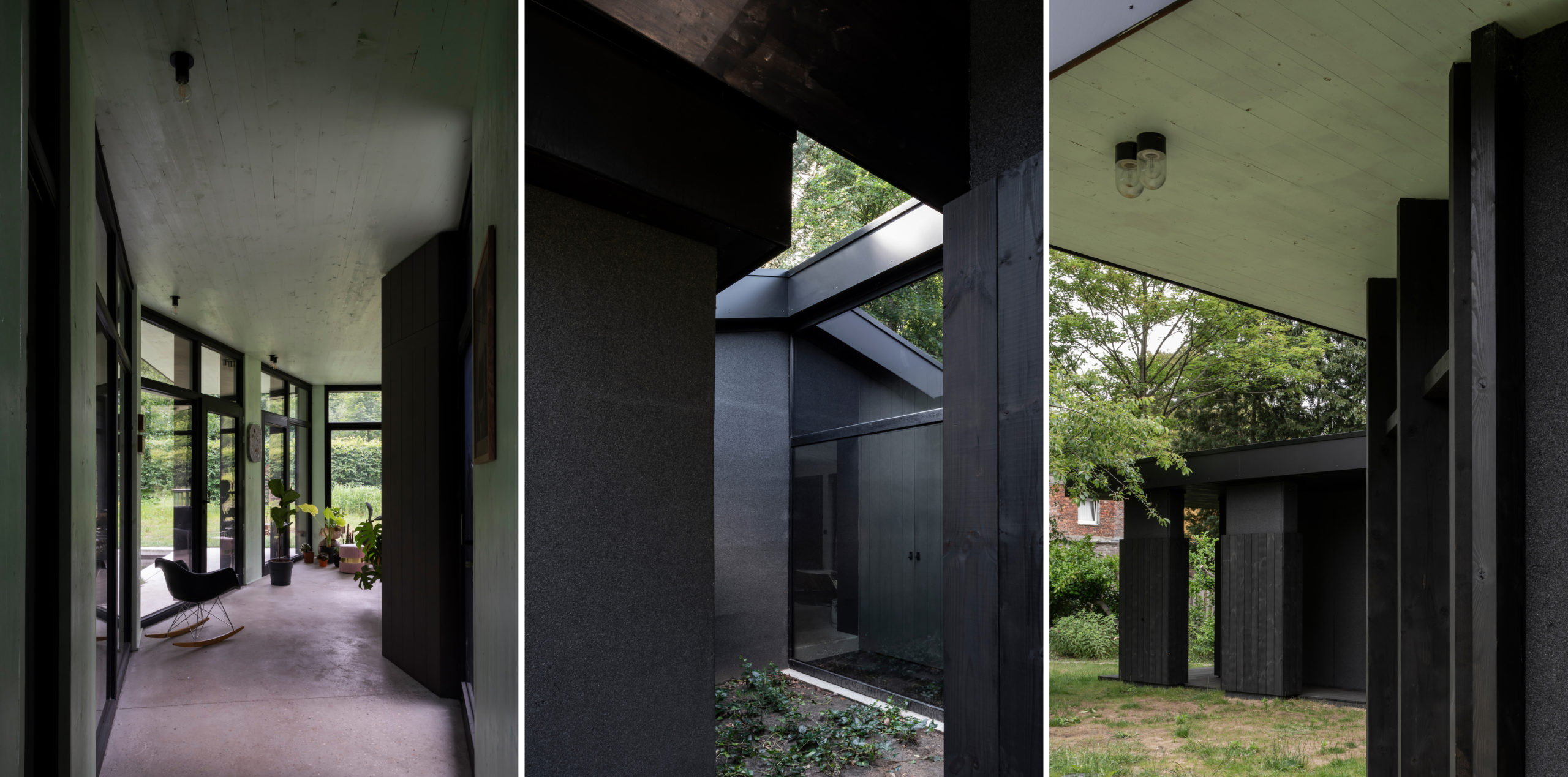 Inspired by the movie “A Single Man”, which features a Californian home built by the one and only Lautner, this residential project involved the renovation and extension of an existing house. The resulting design was based on the principle of the viewfinder of a camera — a reference to the professional activity of one of the residents — and in this vain, each room has just one window to look out, as if you were looking through the lens of your camera.
Inspired by the movie “A Single Man”, which features a Californian home built by the one and only Lautner, this residential project involved the renovation and extension of an existing house. The resulting design was based on the principle of the viewfinder of a camera — a reference to the professional activity of one of the residents — and in this vain, each room has just one window to look out, as if you were looking through the lens of your camera.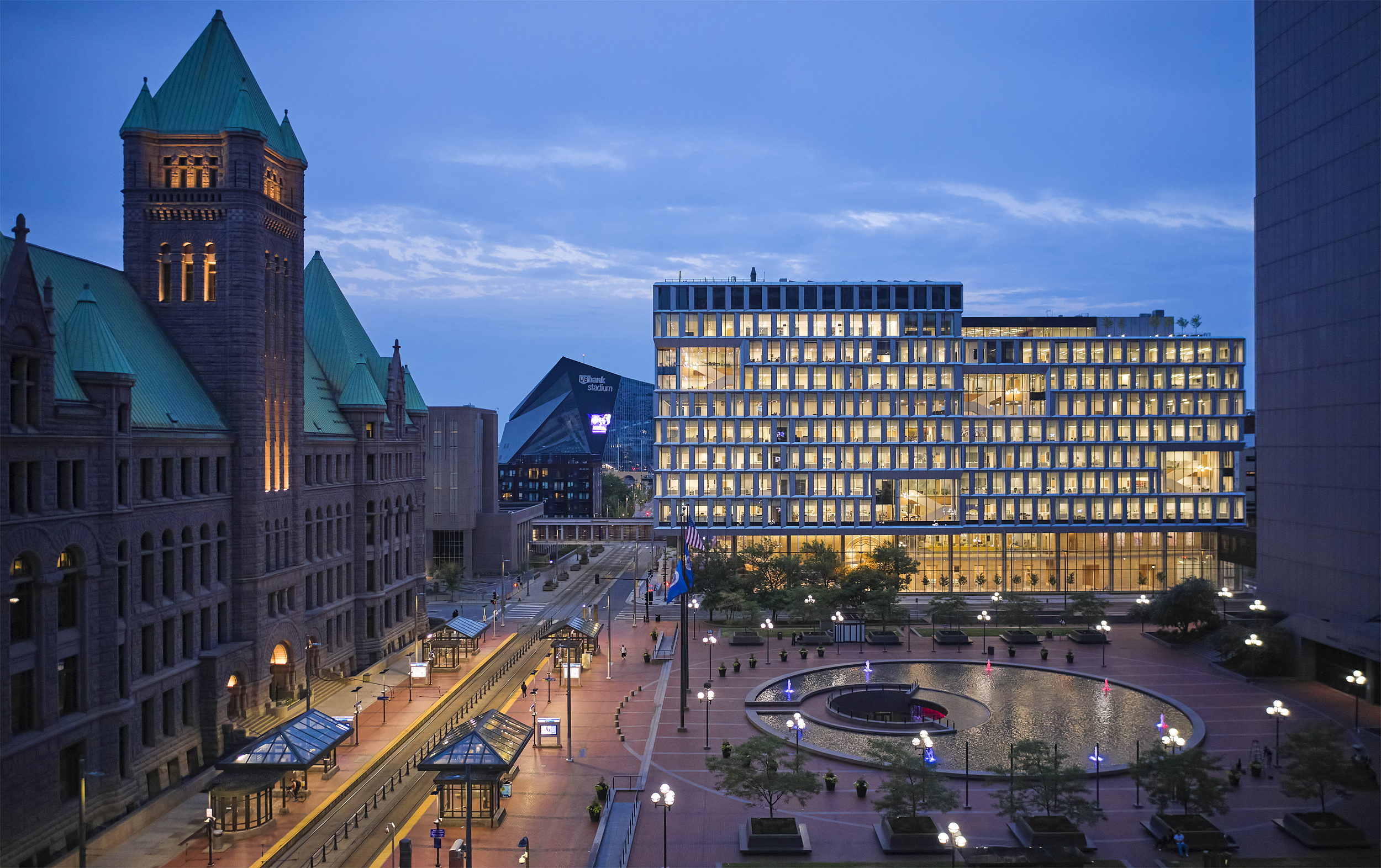
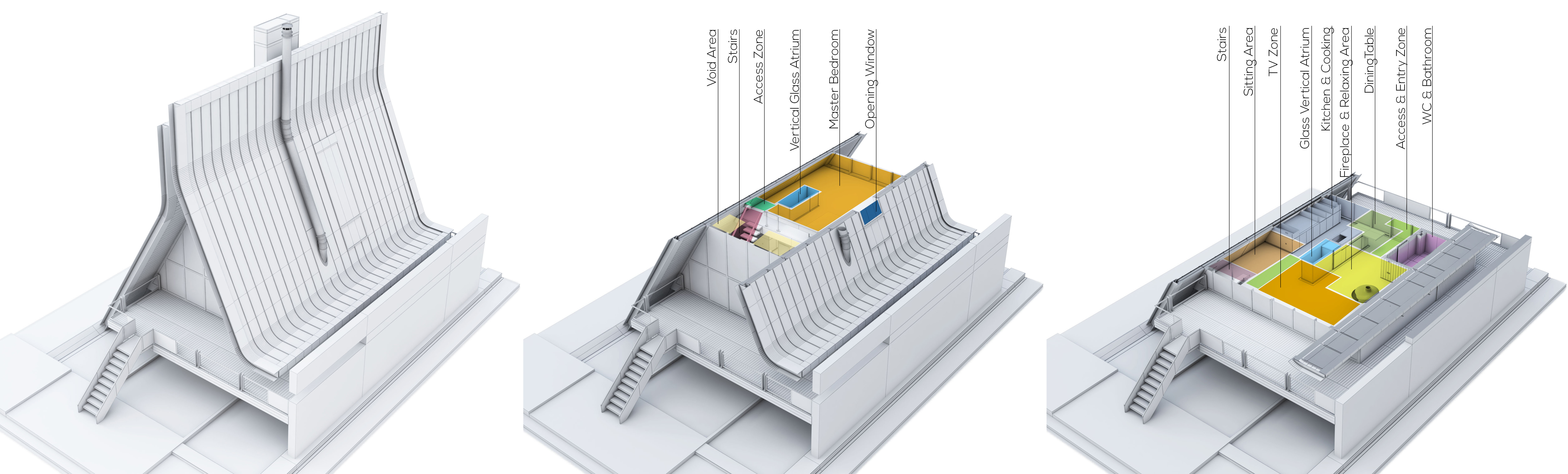
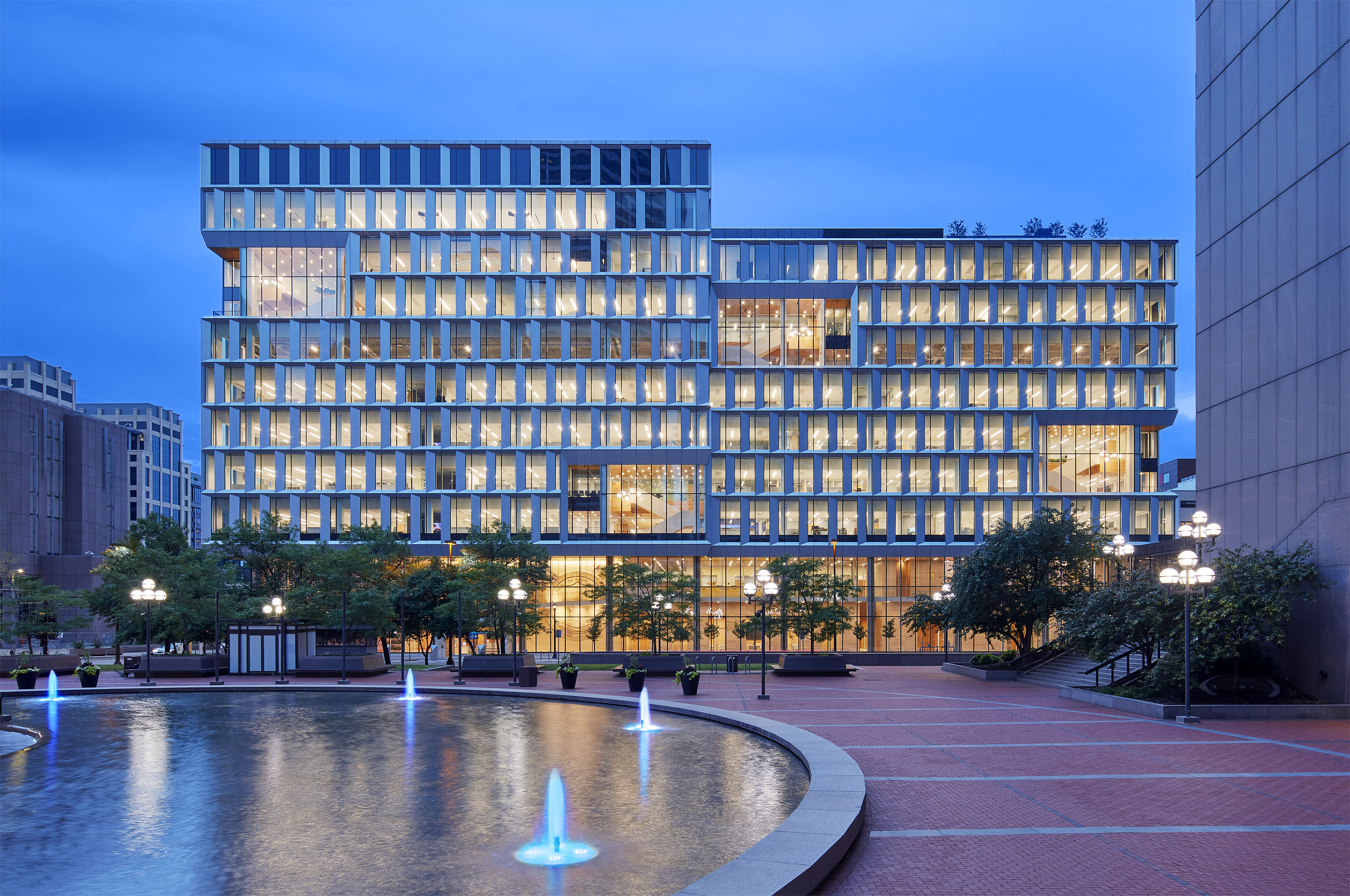 Minneapolis’s Government District makes a stately architectural statement of civic duty. Yet, the dominant materiality of the historical area is granite: a material that may be associated with strength, but does not exactly emit democratic values openness and unity. This new contemporary alternative asks: “How can our public spaces better reflect the communities they serve?” In response, the design’s soaring glass and aluminum façades and double height pockets break up its massing, announcing themes of transparency and connection that continue inside. In recent year as, public trust in government has slipped; civic buildings can stand as monuments of the ideals that democracies should strive towards: a collective, reflective and pluralistic future.
Minneapolis’s Government District makes a stately architectural statement of civic duty. Yet, the dominant materiality of the historical area is granite: a material that may be associated with strength, but does not exactly emit democratic values openness and unity. This new contemporary alternative asks: “How can our public spaces better reflect the communities they serve?” In response, the design’s soaring glass and aluminum façades and double height pockets break up its massing, announcing themes of transparency and connection that continue inside. In recent year as, public trust in government has slipped; civic buildings can stand as monuments of the ideals that democracies should strive towards: a collective, reflective and pluralistic future.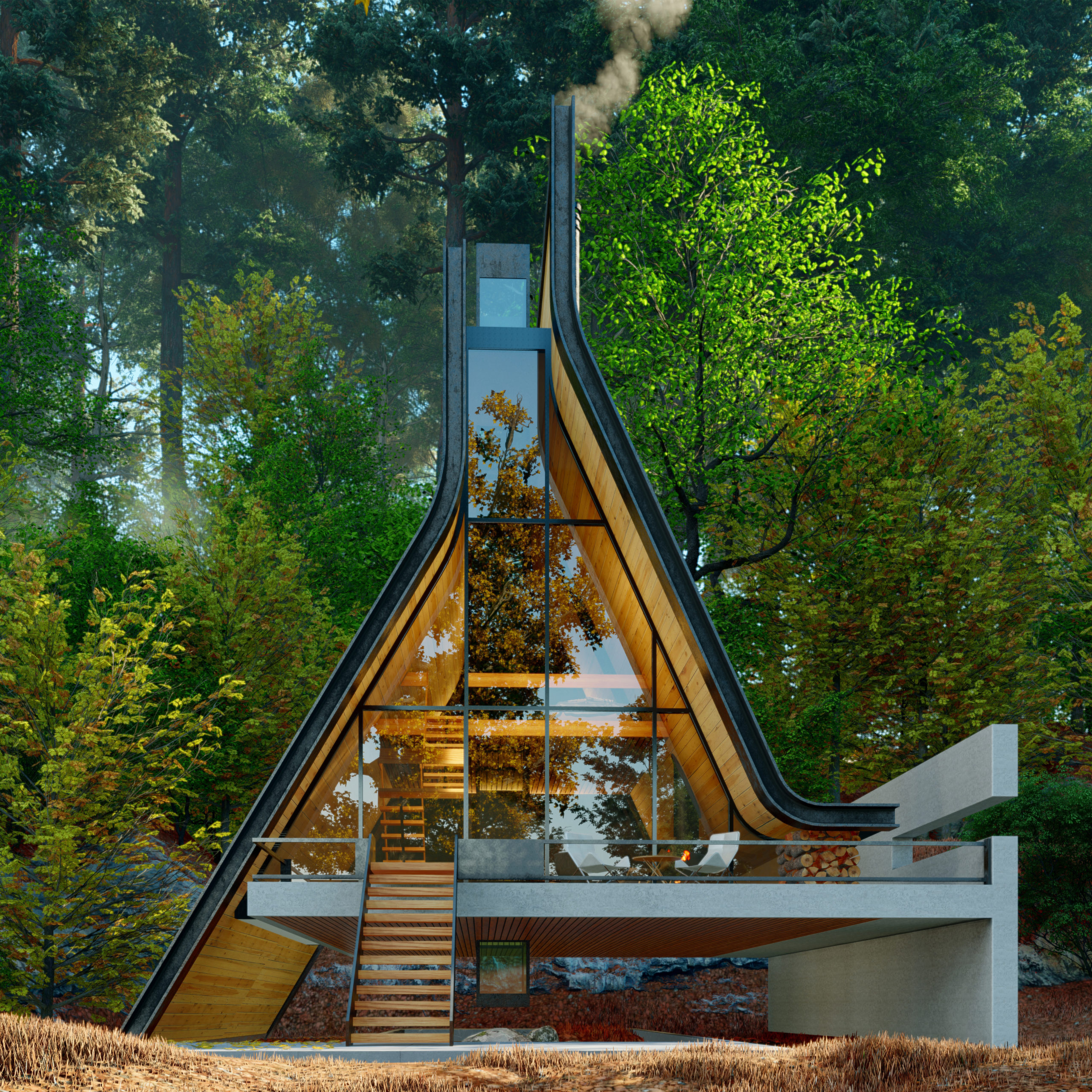
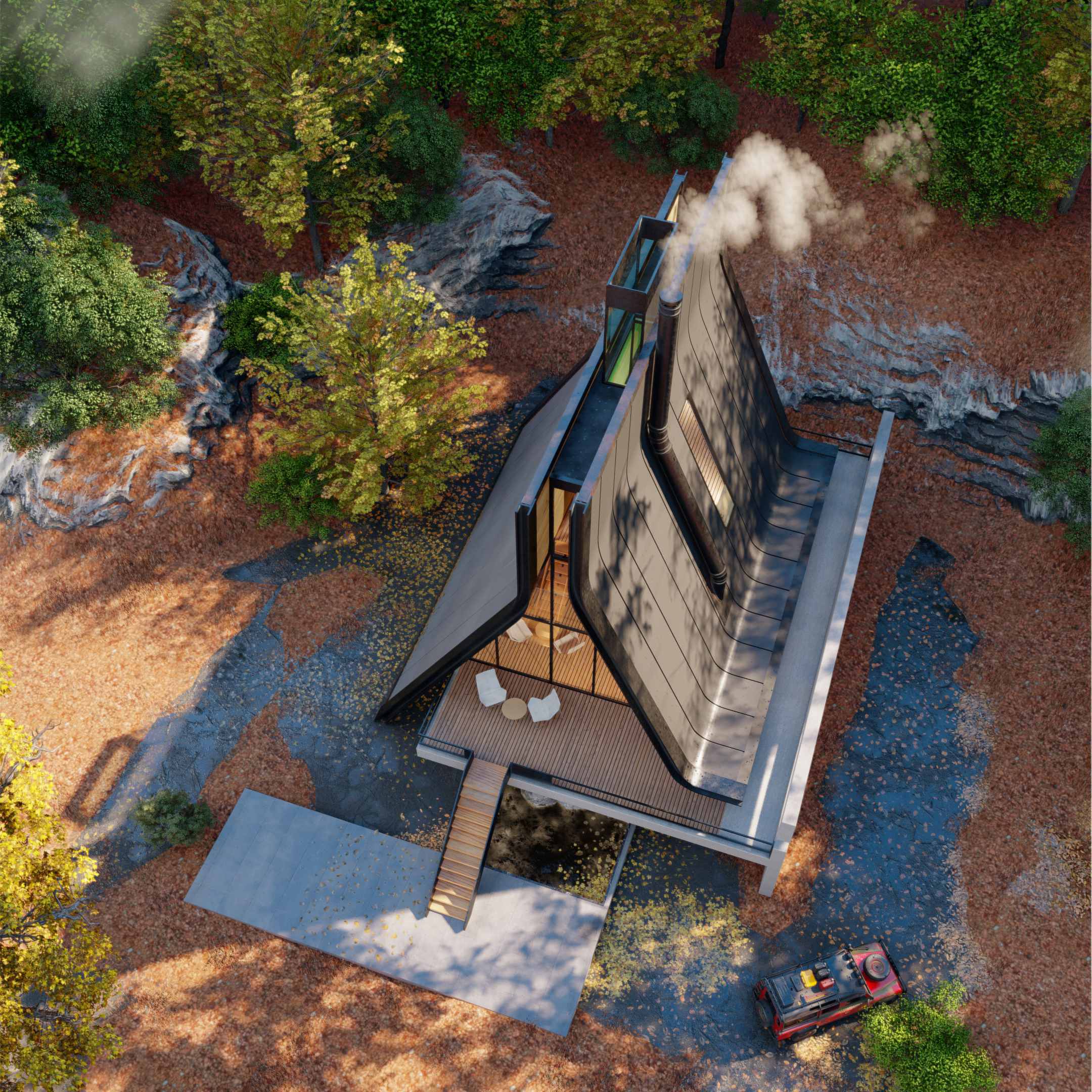
 Old becomes new in this distinctive update on this traditional A-frame cabin, located in the woods of northern Iran. One key aspect of this is the split that forms down the center of the the conventional sloping roof, which is filled with luminous glass window instead. Then, the usual sharp-angled corners of the A-frame are softened with curving lines, imbuing the structure with a sense of warmth and playfulness.
Old becomes new in this distinctive update on this traditional A-frame cabin, located in the woods of northern Iran. One key aspect of this is the split that forms down the center of the the conventional sloping roof, which is filled with luminous glass window instead. Then, the usual sharp-angled corners of the A-frame are softened with curving lines, imbuing the structure with a sense of warmth and playfulness.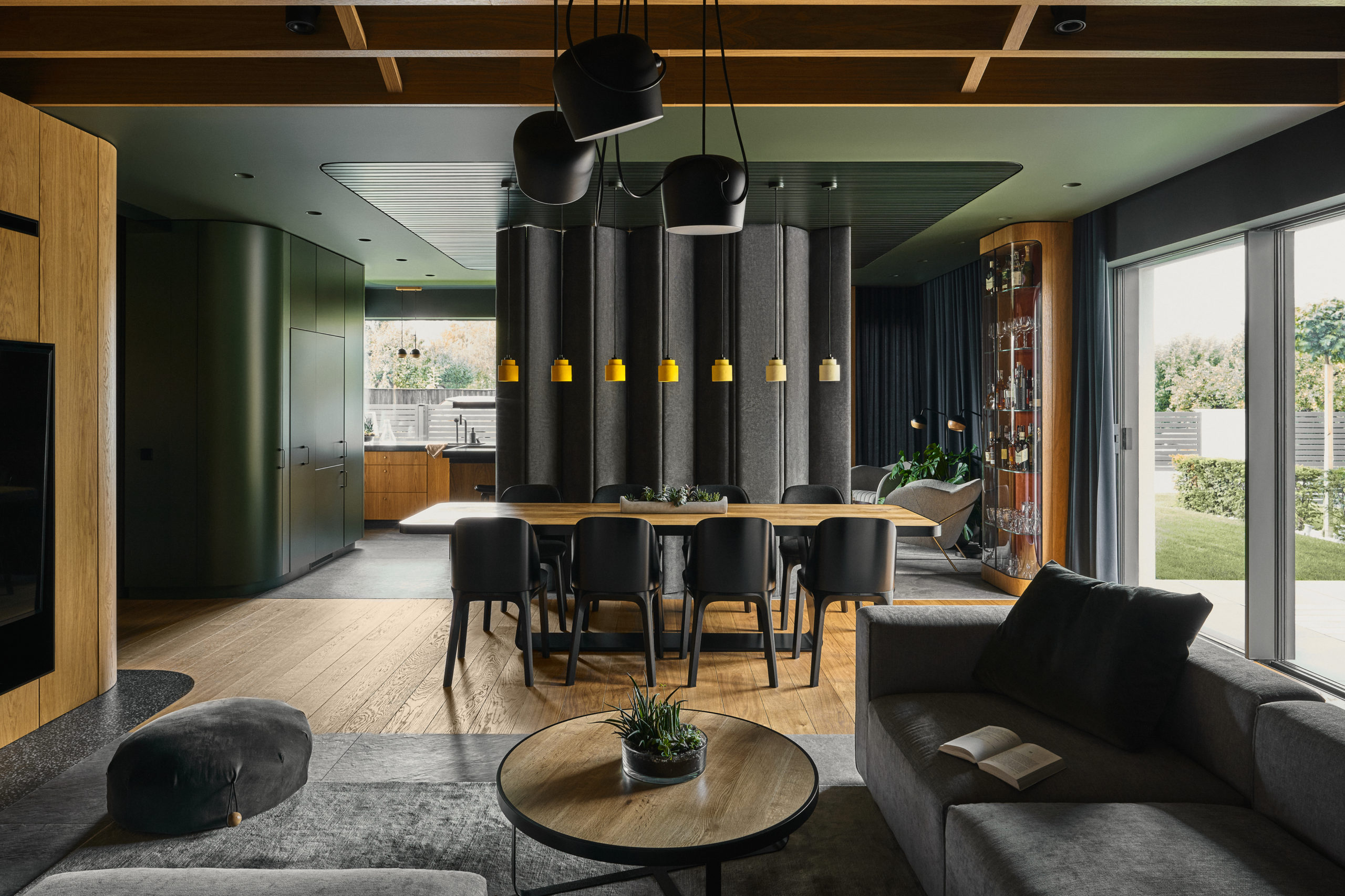
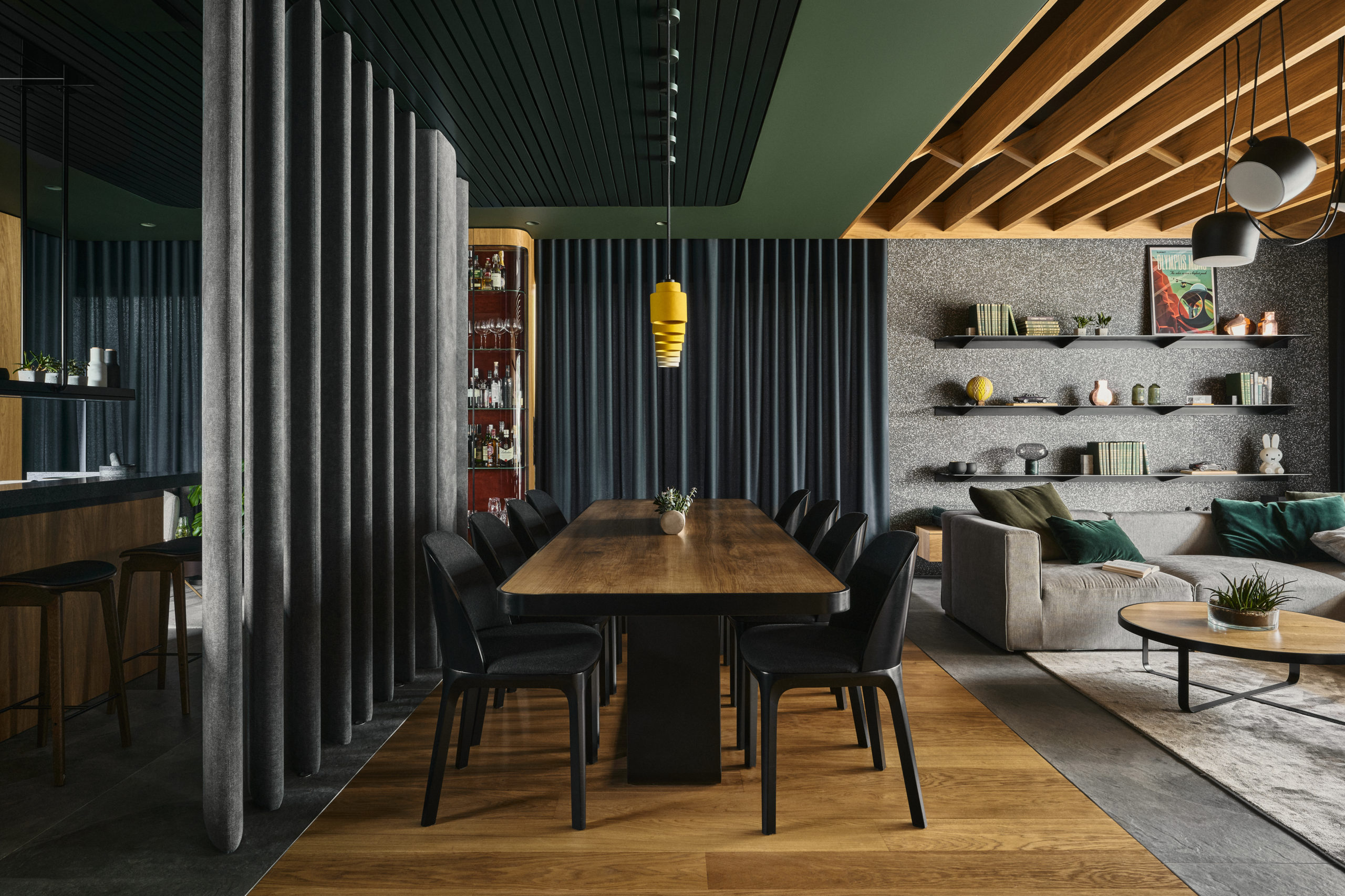 Earth colours, deep greens, deep reds with oak and stone, terrazzo finishes make up the warm and welcoming color palette for this three-person home which boldly blends forest cabin with luxury mid-century vibes. Embracing the family’s passion for pushing the design envelope, the interior is shaped by a composition of intersecting blocks, structures, textiles and colors. This compositional move at once separates the spaces while, at the same time uniting them under the umbrella of a consistent design. Unique spaces abound; one particularly delightful standout is a private tree house inside a child’s room.
Earth colours, deep greens, deep reds with oak and stone, terrazzo finishes make up the warm and welcoming color palette for this three-person home which boldly blends forest cabin with luxury mid-century vibes. Embracing the family’s passion for pushing the design envelope, the interior is shaped by a composition of intersecting blocks, structures, textiles and colors. This compositional move at once separates the spaces while, at the same time uniting them under the umbrella of a consistent design. Unique spaces abound; one particularly delightful standout is a private tree house inside a child’s room.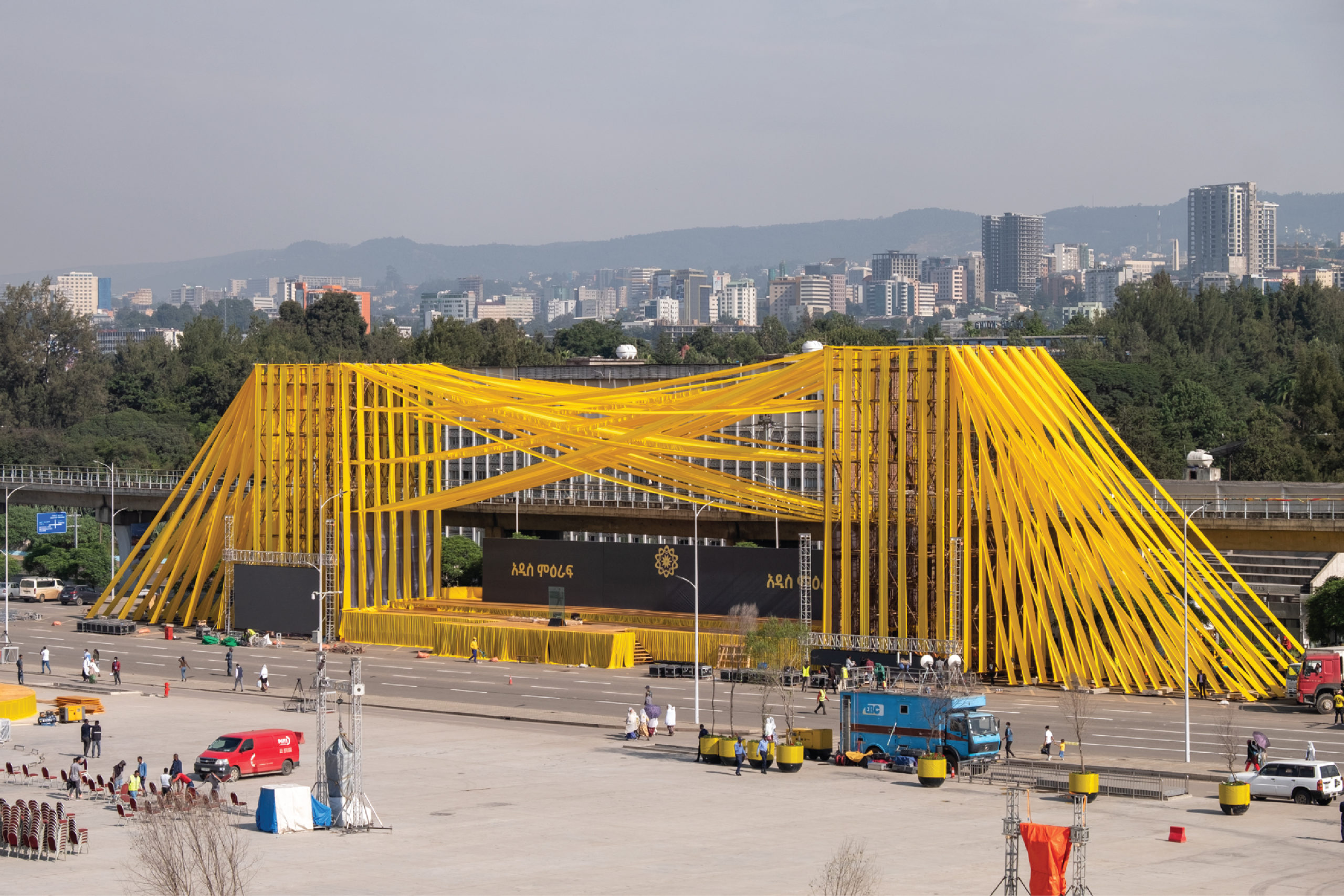
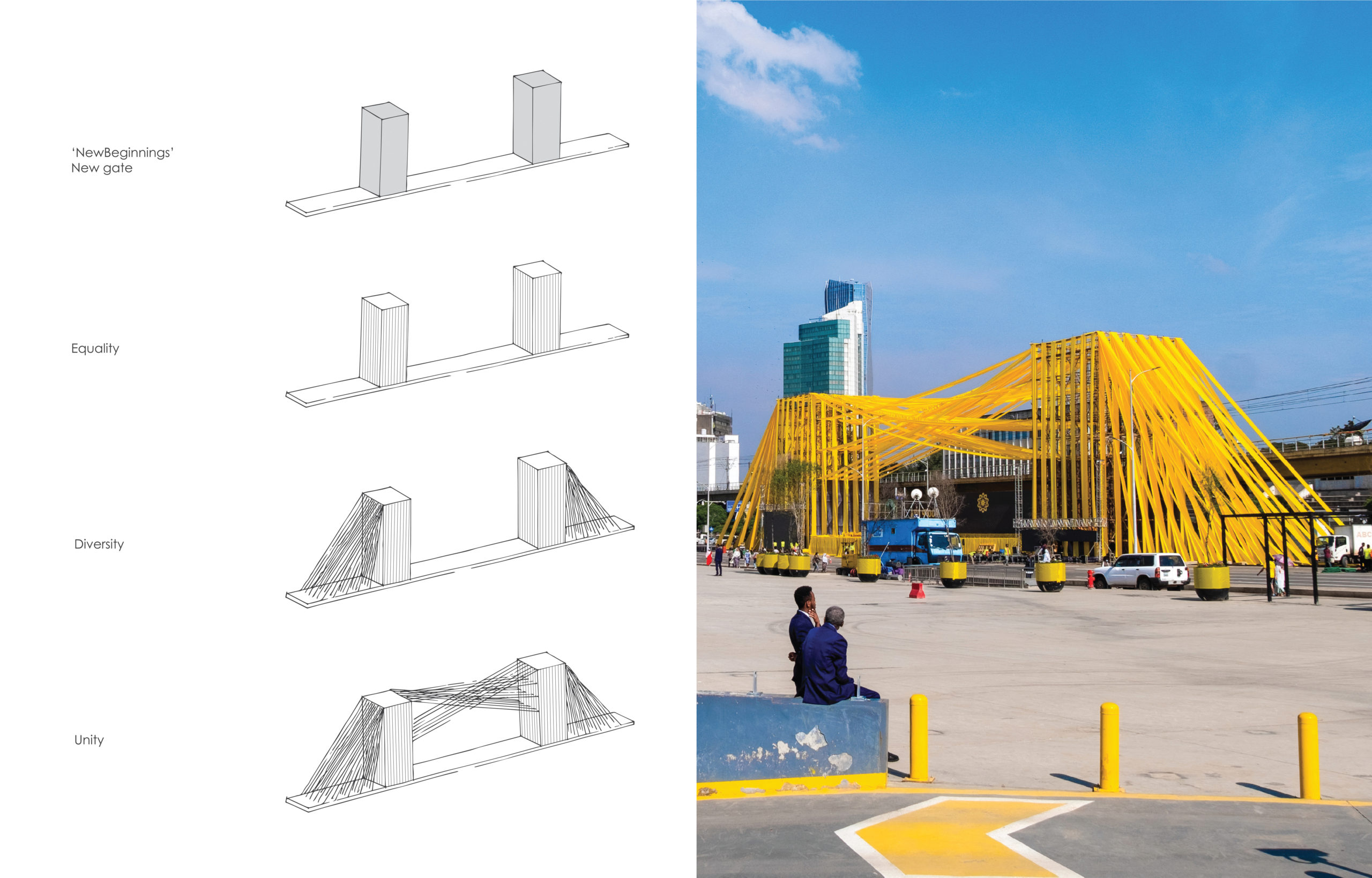 This bright, yellow temporary urban installation represented Ethiopian history and culture while reflecting the existing reality morphing into a joyous “New beginning’. Two grand colossal vertical tower components form both a portal and a performance stage on Meskel square. These towers are flanked by numerous diagonal satin strips, varying inclinations, sizes, locations, and linkages that depict diversity. In the face of myriad challenges — climatic, social and economic — Ethiopians’ resilience in tolerating pressure and moving spiritedly forward is reflected in the fabric’s flexibility.
This bright, yellow temporary urban installation represented Ethiopian history and culture while reflecting the existing reality morphing into a joyous “New beginning’. Two grand colossal vertical tower components form both a portal and a performance stage on Meskel square. These towers are flanked by numerous diagonal satin strips, varying inclinations, sizes, locations, and linkages that depict diversity. In the face of myriad challenges — climatic, social and economic — Ethiopians’ resilience in tolerating pressure and moving spiritedly forward is reflected in the fabric’s flexibility.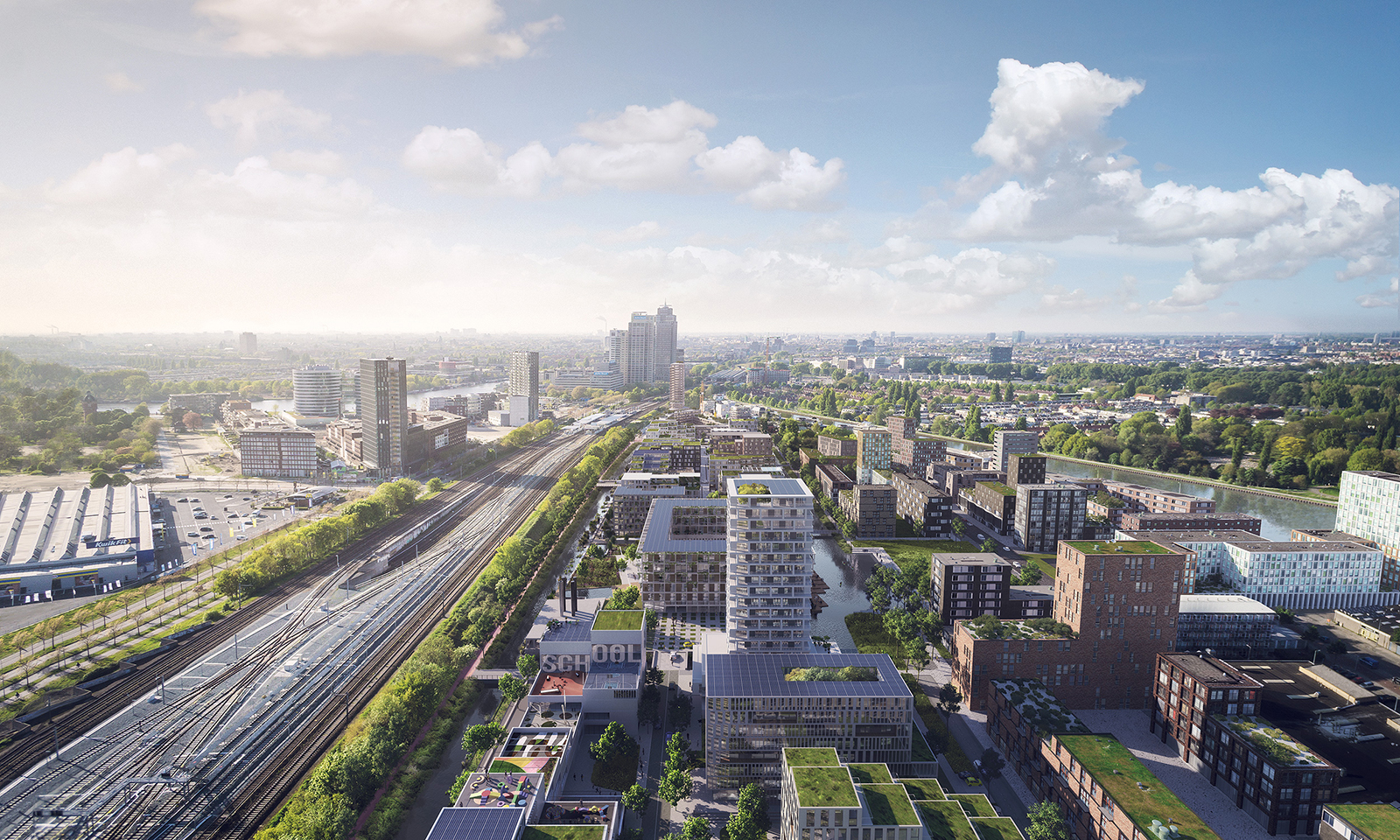 
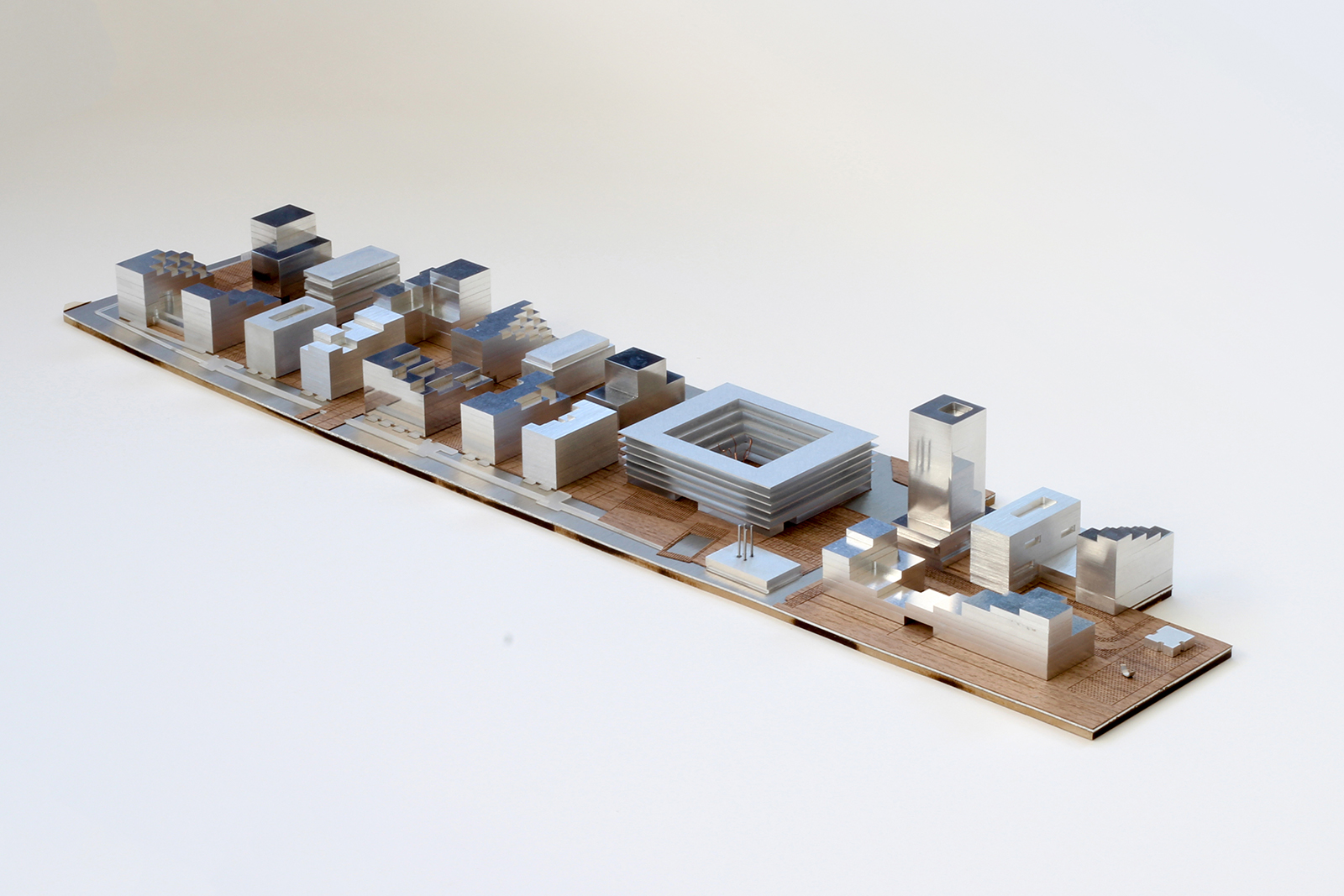
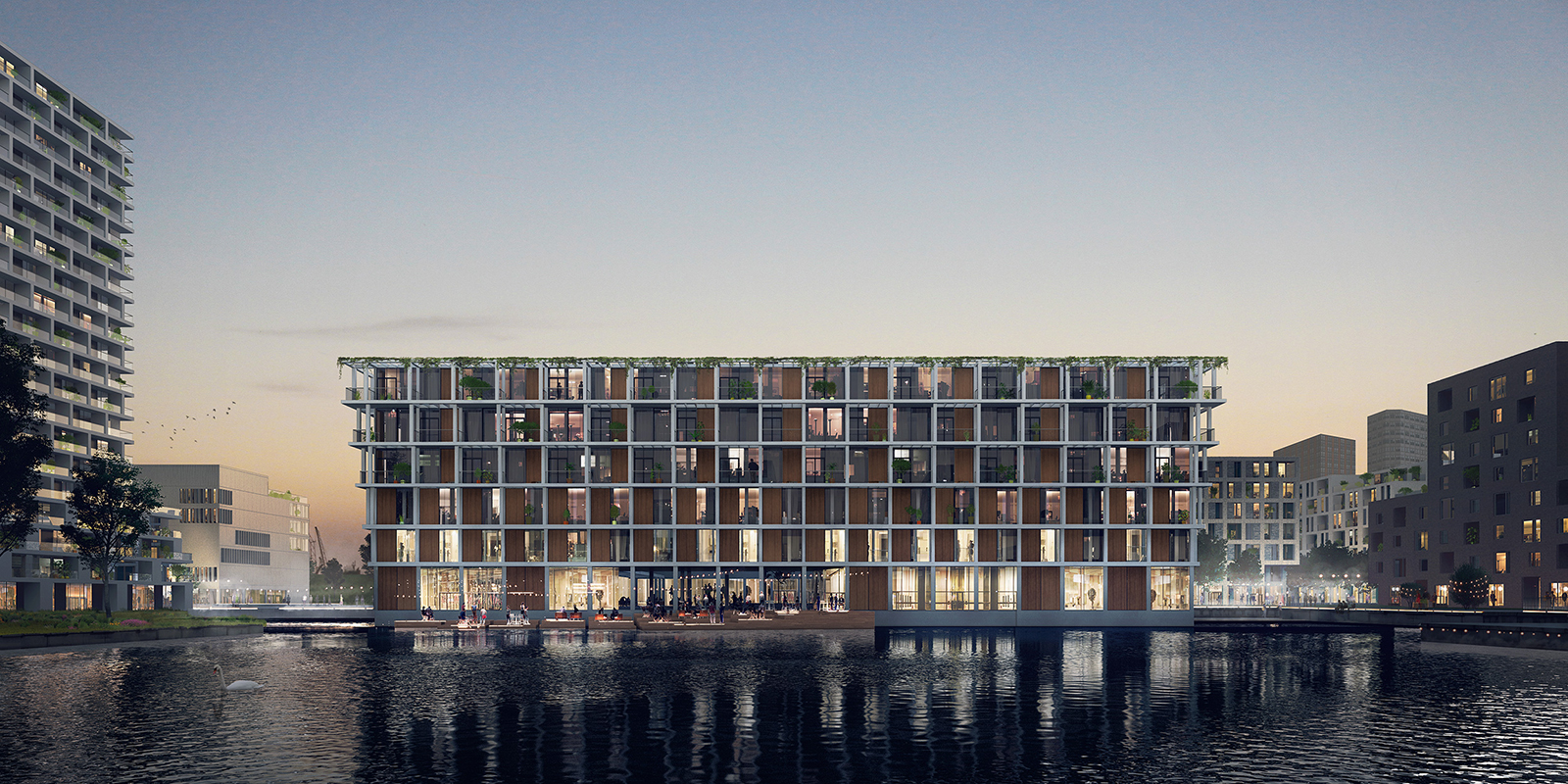
 Bijlmer Bajes was once an Amsterdam prison; now, it is a pleasant, safe and social urban neighbourhood. With a total program of 135.000m², the mixed-use masterplan was sprawling, but the former correctional facilities that stood on part of the site served a disproportionately large role in the overall design. Visually, three key elements — the canal, the main building and the wall — became motifs that guided the architects in designing a cohesive community space with a distinct urban feel.
Bijlmer Bajes was once an Amsterdam prison; now, it is a pleasant, safe and social urban neighbourhood. With a total program of 135.000m², the mixed-use masterplan was sprawling, but the former correctional facilities that stood on part of the site served a disproportionately large role in the overall design. Visually, three key elements — the canal, the main building and the wall — became motifs that guided the architects in designing a cohesive community space with a distinct urban feel.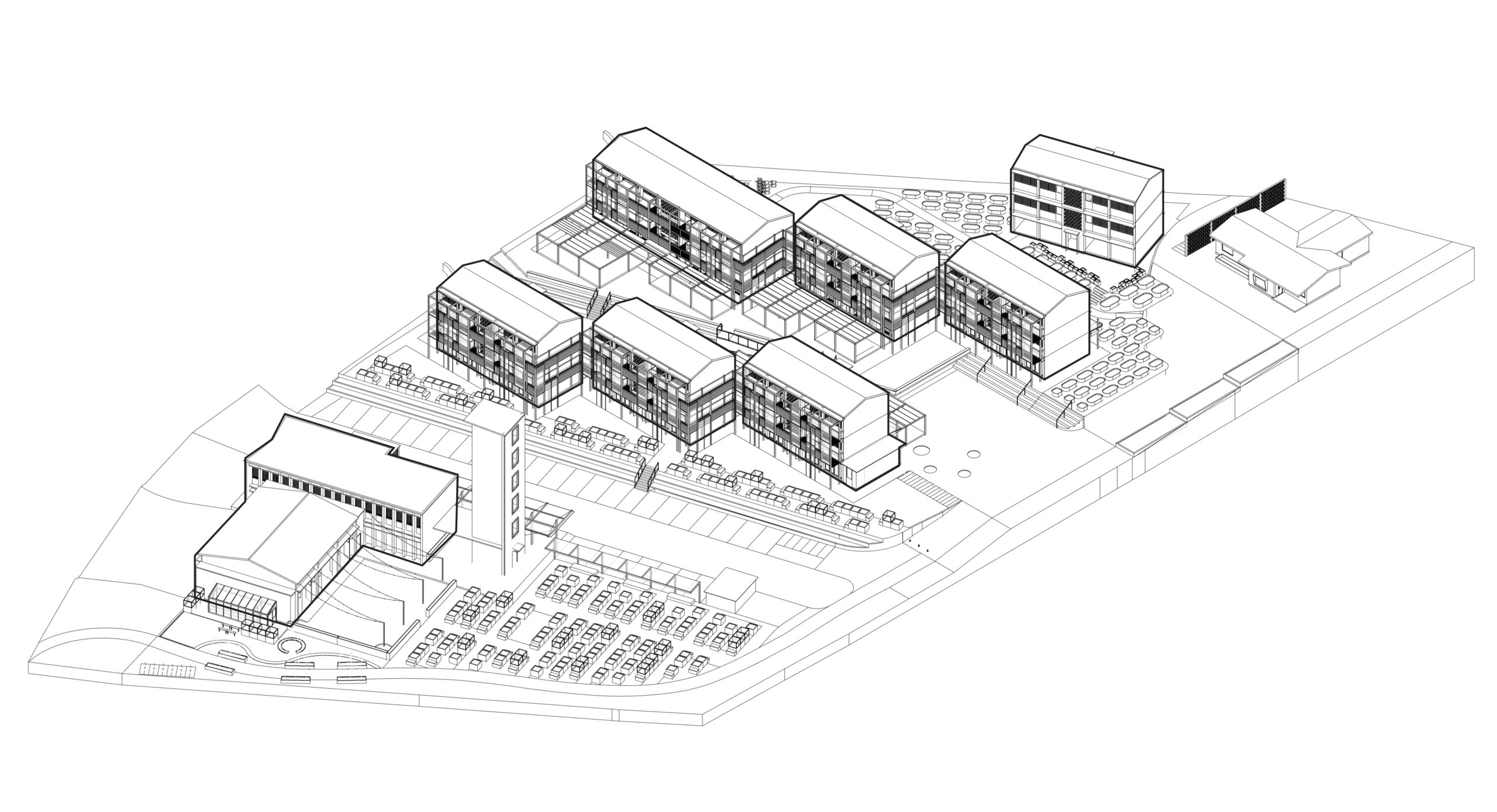
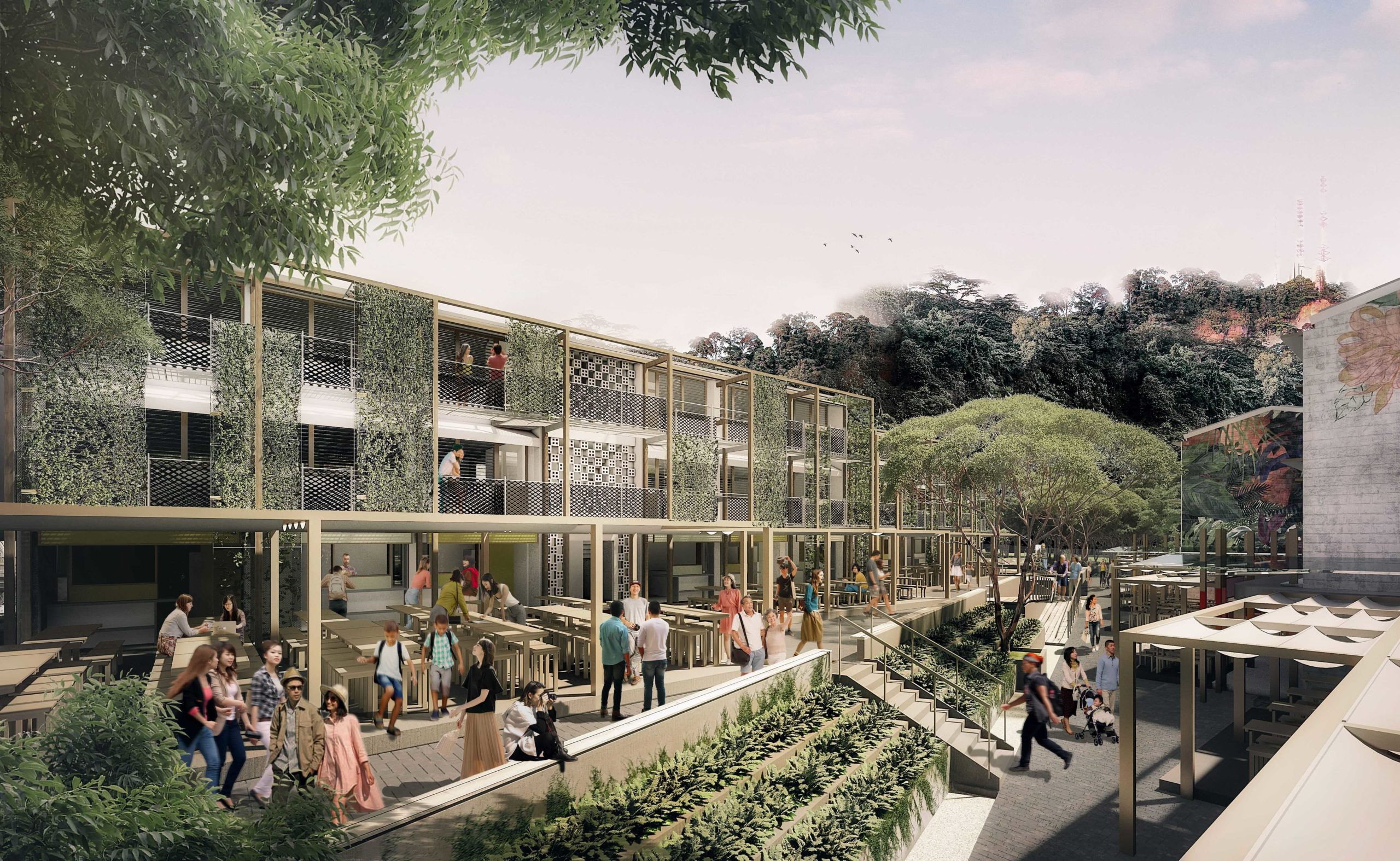
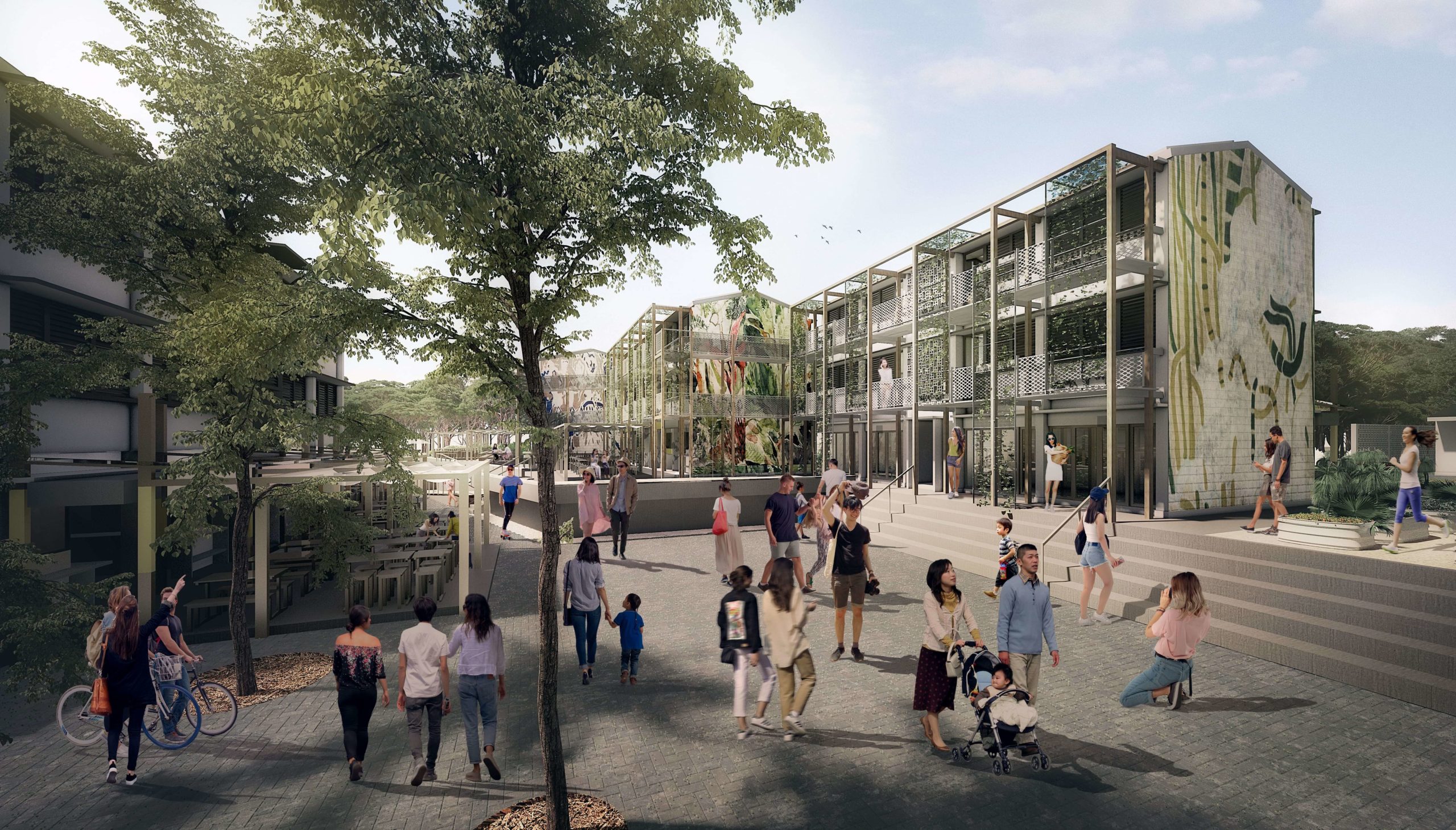
 Following the C40’s design priorities for the 10 climate challenges, this adaptive reuse project exemplifies a new architectural model of building for circularity and inclusivity. The master plan layers various programmes with the aim of inspiring habit changes in inhabitants, ultimately encouraging a carbon-neutral lifestyle. From urban farming to vertical timber greenery facades, the eco-conscious design provides practical functions, while harnessing construction techniques that won’t add unnecessary environmental stress.
Following the C40’s design priorities for the 10 climate challenges, this adaptive reuse project exemplifies a new architectural model of building for circularity and inclusivity. The master plan layers various programmes with the aim of inspiring habit changes in inhabitants, ultimately encouraging a carbon-neutral lifestyle. From urban farming to vertical timber greenery facades, the eco-conscious design provides practical functions, while harnessing construction techniques that won’t add unnecessary environmental stress.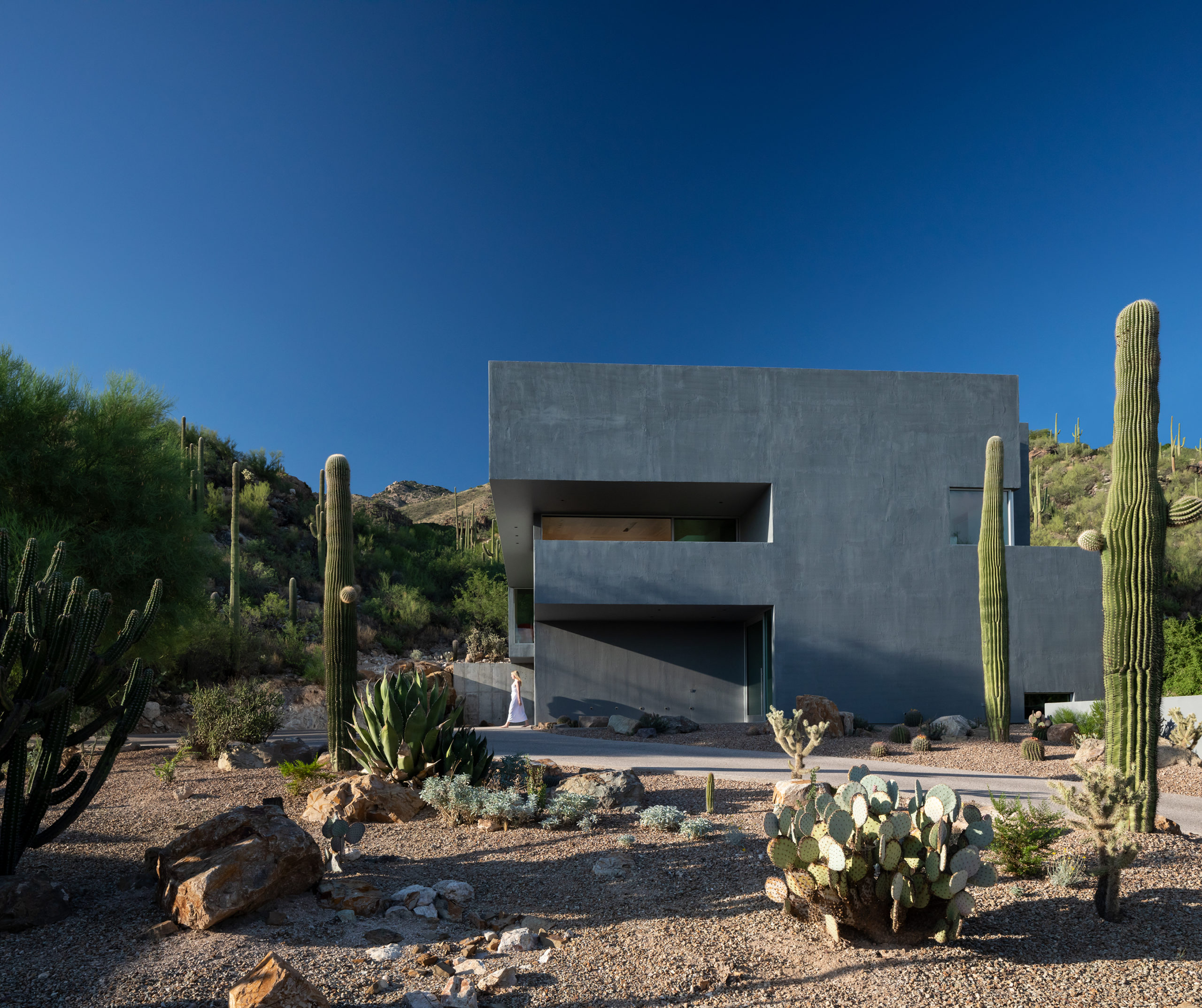
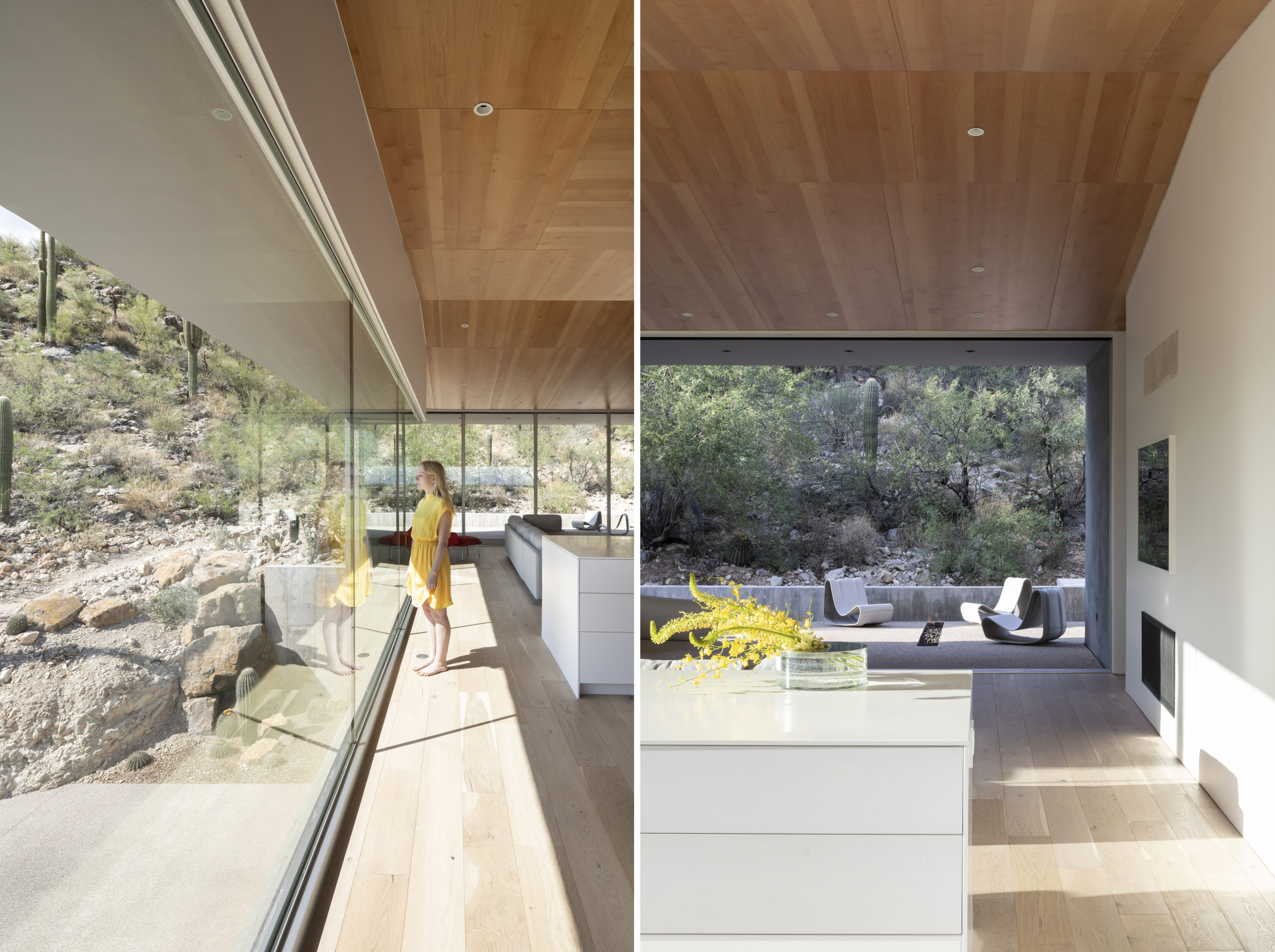 The expressive, geological form of this two-story private home couldn’t be more apt for its setting. Sitting proudly at the foot of the Catalina mountains, the Ventana House straddles a line between the sprawling desert and a protected mountain peak. Yet, the rock metaphor can be extended. As the architects explain, the building is “like a geode,” with a surprisingly elegant, inviting and light-filled interior, the spaces of which are sequenced to move visitors through space cinematically by reorienting them while simultaneously revealing both interior and exterior spaces through the gaping windows.
The expressive, geological form of this two-story private home couldn’t be more apt for its setting. Sitting proudly at the foot of the Catalina mountains, the Ventana House straddles a line between the sprawling desert and a protected mountain peak. Yet, the rock metaphor can be extended. As the architects explain, the building is “like a geode,” with a surprisingly elegant, inviting and light-filled interior, the spaces of which are sequenced to move visitors through space cinematically by reorienting them while simultaneously revealing both interior and exterior spaces through the gaping windows.
























