How can architecture be a force for good in our ever-changing world? During Future Fest, we’ll pose this question to some of the world’s best architects. Launching in September, our three-week-long virtual event will be 100% free to attend. Register here!
Concrete is one of the most widely used substances on Earth, it has been around for centuries and makes up most of our modern-day and past world. It is used to build our roads, our buildings and the many historic monuments we cherish today. Humankind relies on concrete for everything: to build our hospitals, transportation systems and schools. We have greatly benefitted from this material and it is thanks to its relatively straightforward manufacturing process that makes it easy to use on a global scale.
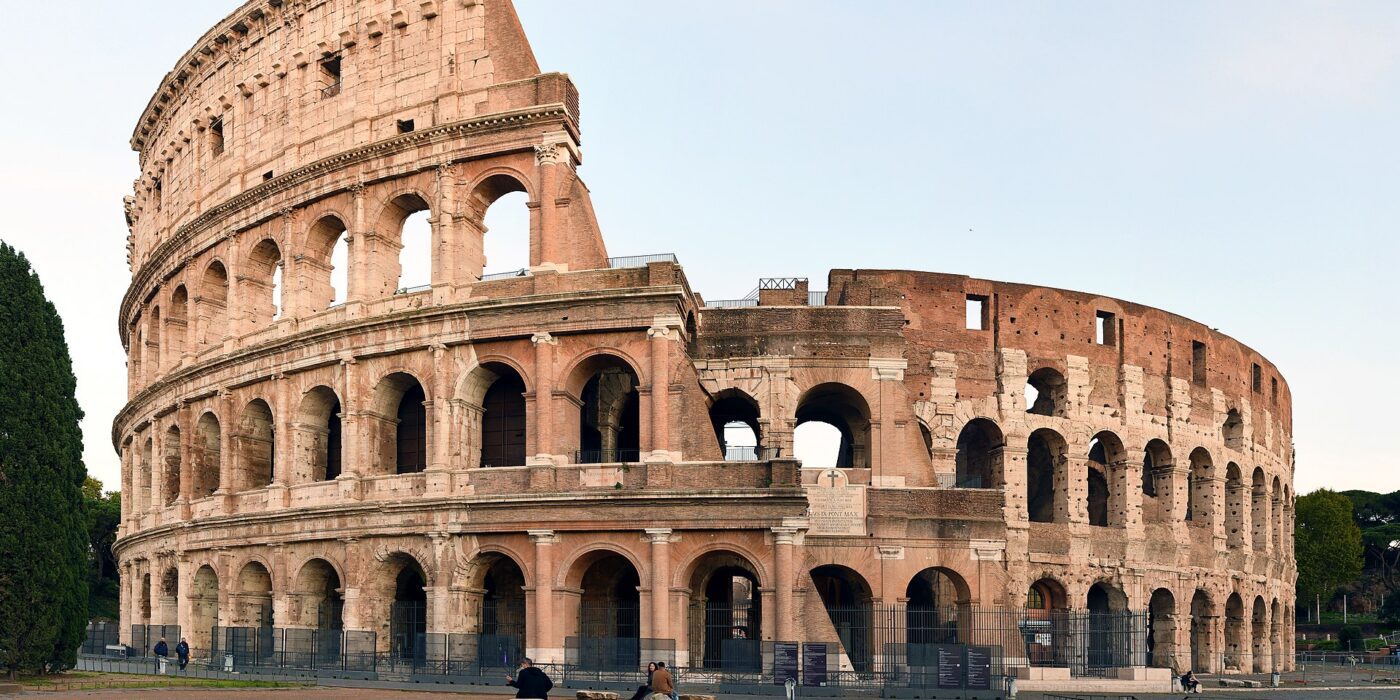
When we think back, some of the most important historic monuments still stand thanks to concrete. Take the Colosseum for example, or Le Corbusier’s Unité d’Habitation, such architectural wonders are owing to concrete.
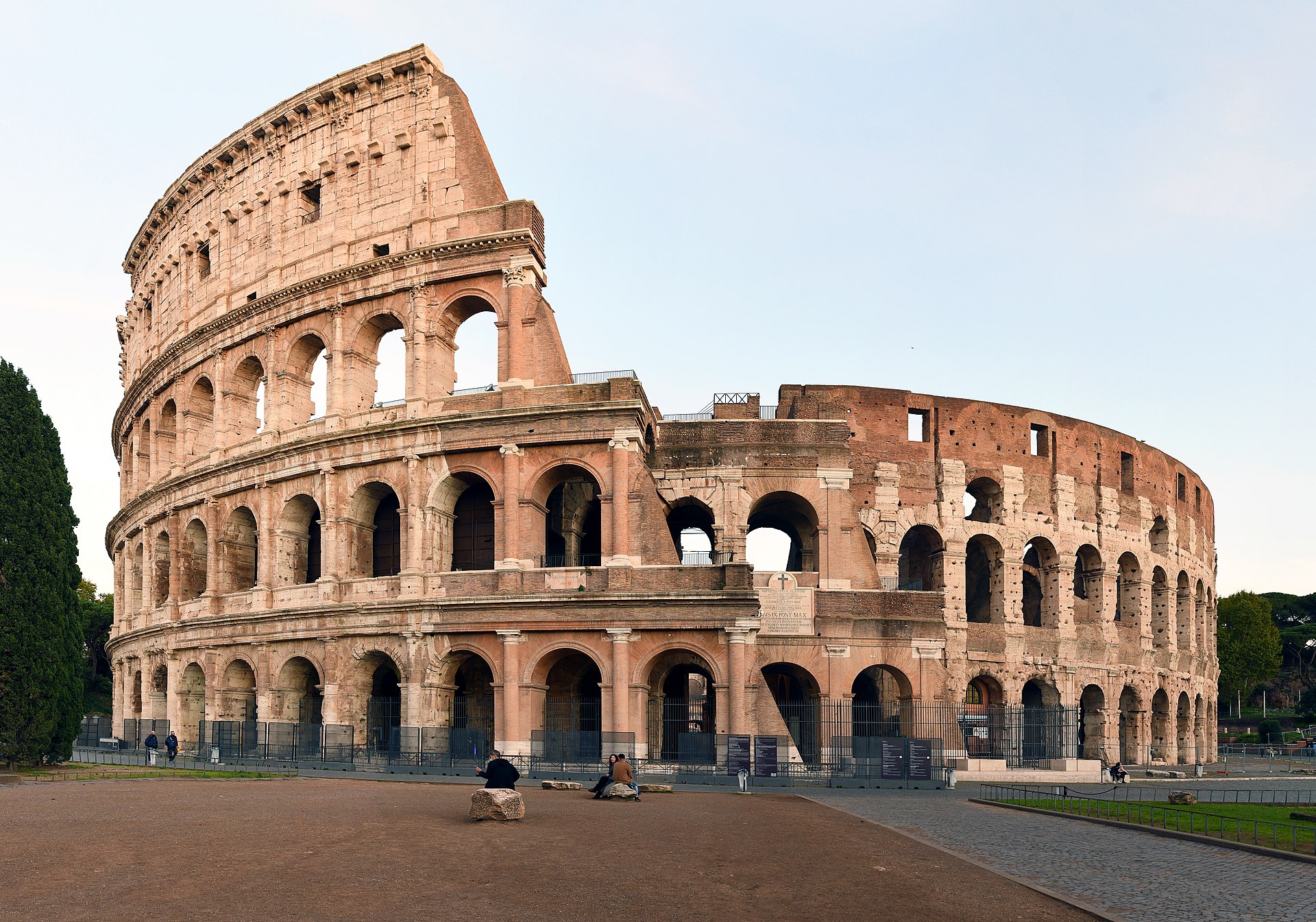

The Colosseum metro exit, Rome, Italy, Courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
Concrete has played a pronounced role in architectural movements like Brutalism and Futurism and its aesthetic properties have been contested and debated time and time again. When and where concrete was first used is often debated and it typically depends on how one defines the term “concrete.” Although its origins are contested, it is clear that ancient civilizations have combined limestone with water and sand for a very long time. This historic mixing of limestone, water and aggregates can be seen as a precursor to the modern-day cement-making practices we use today.
In 2022, we live in a world dominated by concrete.The Romans were known to use concrete similarly to the way we do today. This ancient civilization built everything with concrete – bathhouses, harbors and important religious structures like the Pantheon. What’s significant about these ancient Roman structures is their ability to have lasted centuries. The lifecycle of modern-day concrete is roughly 100 years, however, there was something about the Roman structures that stood the test of time. Many believe the longevity seen in the structures built by the Romans is thanks to the use of volcanic ash, otherwise known as pozzolana.
Today, concrete is made by blending Portland cement with water and then mixing the paste with aggregates — typically sand, gravel and crushed stone — which hardens and binds into an incredibly durable substance. Portland cement is a limestone powder developed in the late 19th century and is hugely popular in today’s cement-making industry. Concrete’s unyielding nature mixed with its relatively straightforward construction process has helped it land its name as the most used substance on Earth (after water, of course).
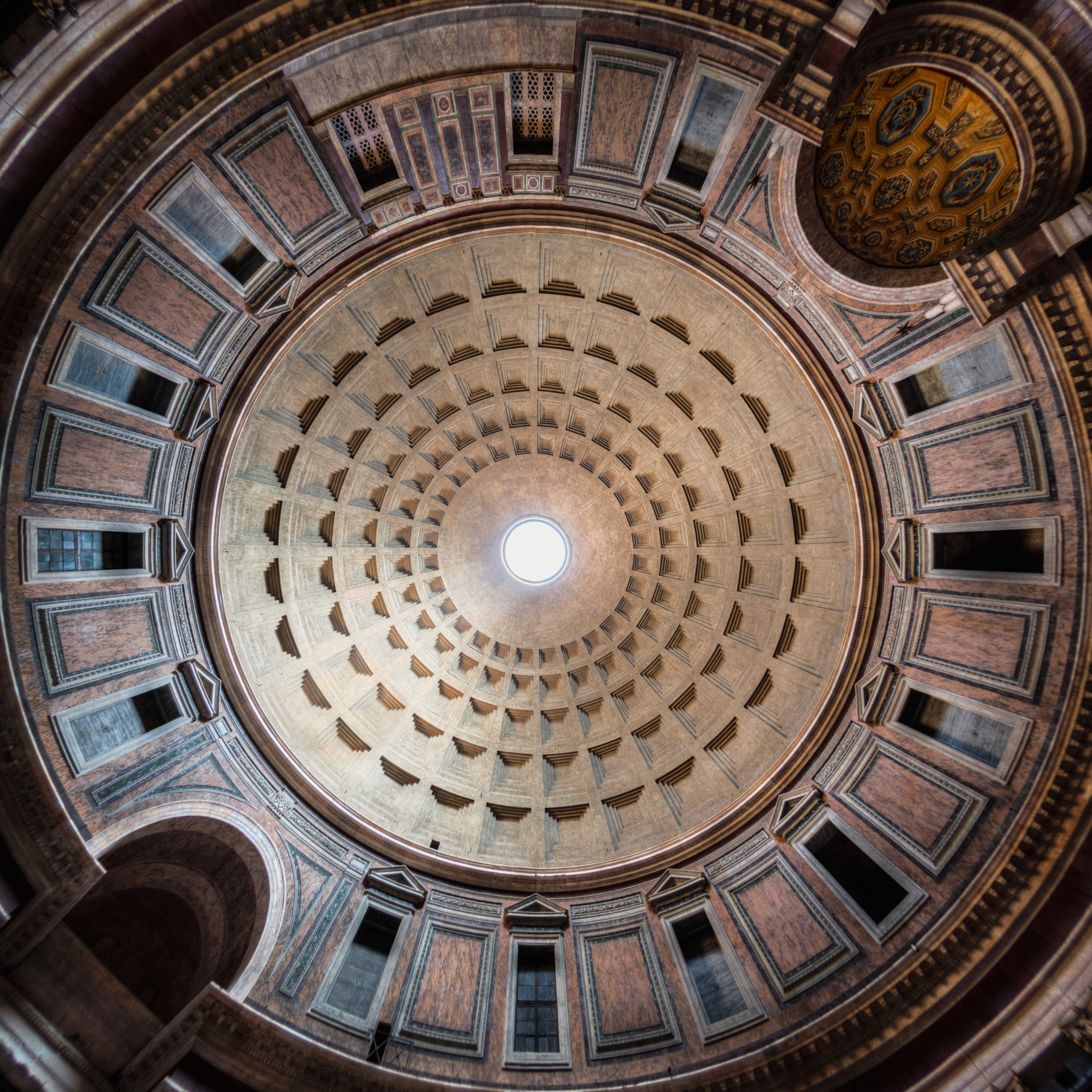

The Pantheon dome, Rome, Italy, Courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
We are living through the age of concrete, and the time has come for this epoch to draw to a close. The world’s most beloved material is, simply put, detrimental to our planet.
Concrete has kept us sheltered and secure for a long time. Safe from the elements, inside our concrete fortresses unaware of what’s happening outside. We have reached a time in history where concrete is competing — and winning — against the Earth’s fauna. Concrete accounts for around 4-8% of the world’s CO2 emissions and most of that is produced during the manufacturing stage. The concrete industry has tried to divert attention toward the material’s positive capability of capturing CO2, but studies have proven that concrete absorbs a mere 17% of emissions produced, and that’s over its lifecycle of 100 years.
However, it’s not just CO2 emissions that worry scientists: the cement-making process accounts for one 10th of the world’s industrial water consumption. An equally worrying issue is concrete’s impact on natural resources. The cement-making process is draining many natural infrastructures that humans rely upon. For example, the acquisition of sand to make concrete is destroying many of the world’s beaches. The glorified concrete jungle is covering the productive land we rely upon for our very existence.

Unité d’Habitation by Le Corbusier, Marseille, France, Courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
The craze for concrete, excess and grandeur is seen all over the world and is especially pronounced in China. Statistically speaking, China has poured more concrete into its land every three years than the United States has in the past hundred years. Not only is this significant in terms of environmental impact, but it is a costly endeavor for governments to replace and dispose of old concrete.
What can possibly be the solution to replacing the world’s most used substance? There is certainly no clear path to doing so, but there are ways to start. Architects, builders, manufacturers and consumers all carry a responsibility when it comes to making conscious choices that will impact our planet. Rethinking the production process, using alternative materials and conserving existing concrete structures are starting points. Finding alternative construction practices, such as timber-framed buildings, is important areas to explore. However, it is crucial not to replace one ecological issue with another.
The situation is complex, political and far from resolved. Demanding architects, who have been taught to rely upon concrete, to avoid the material altogether will take time. However, we need to start somewhere. We should be striving toward a mindset shift, one where humans understand their place on Earth and respect their ecosystems and natural terrains. We must shift our priority from grandeur and excess to preserving the Earth’s natural resources and ultimately, close the chapter on the concrete era.
How can architecture be a force for good in our ever-changing world? During Future Fest, we’ll pose this question to some of the world’s best architects. Launching in September, our three-week-long virtual event will be 100% free to attend. Register here!