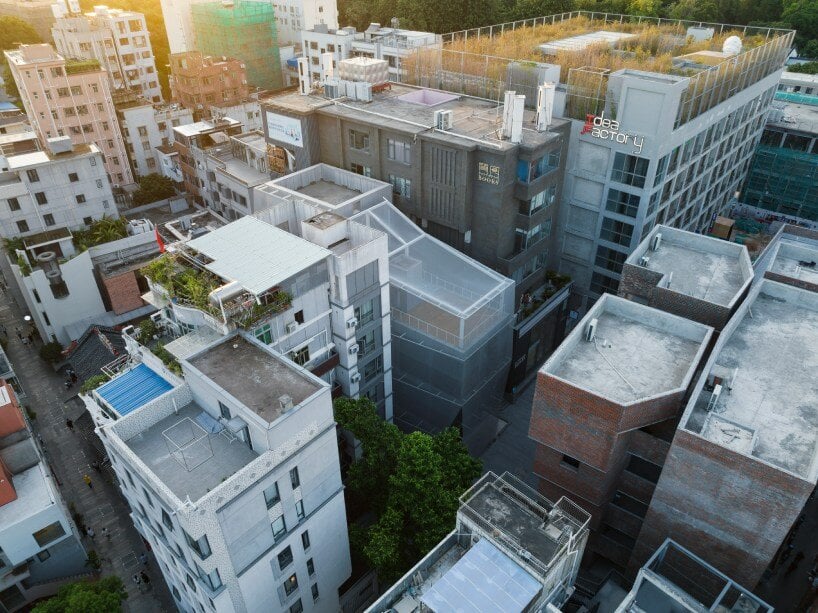
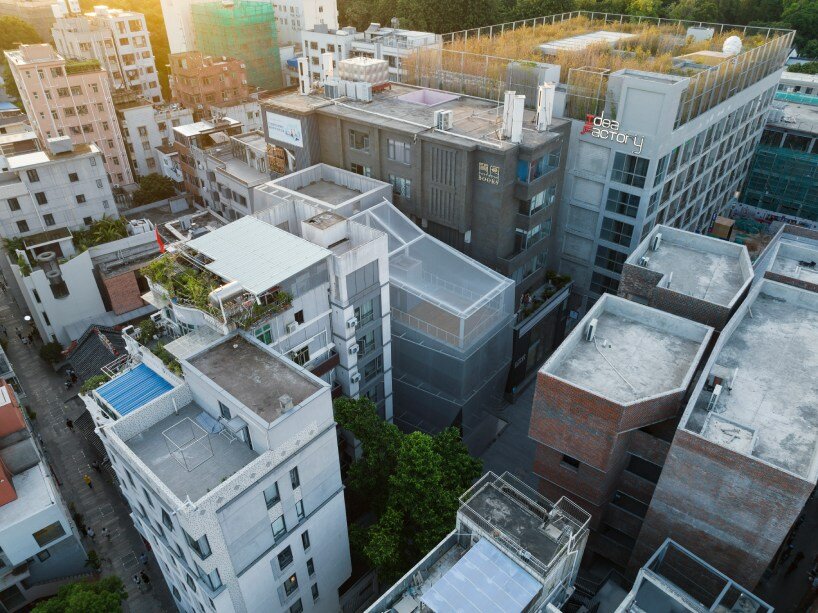
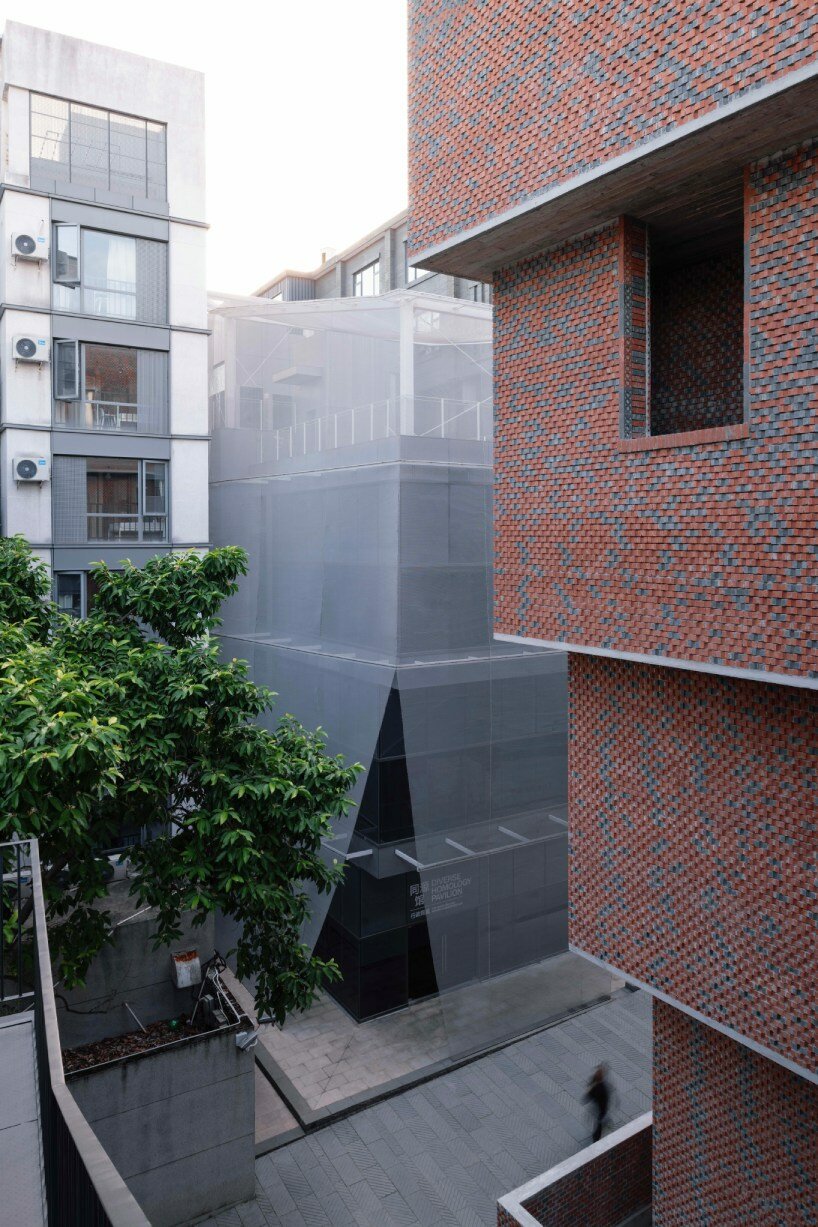
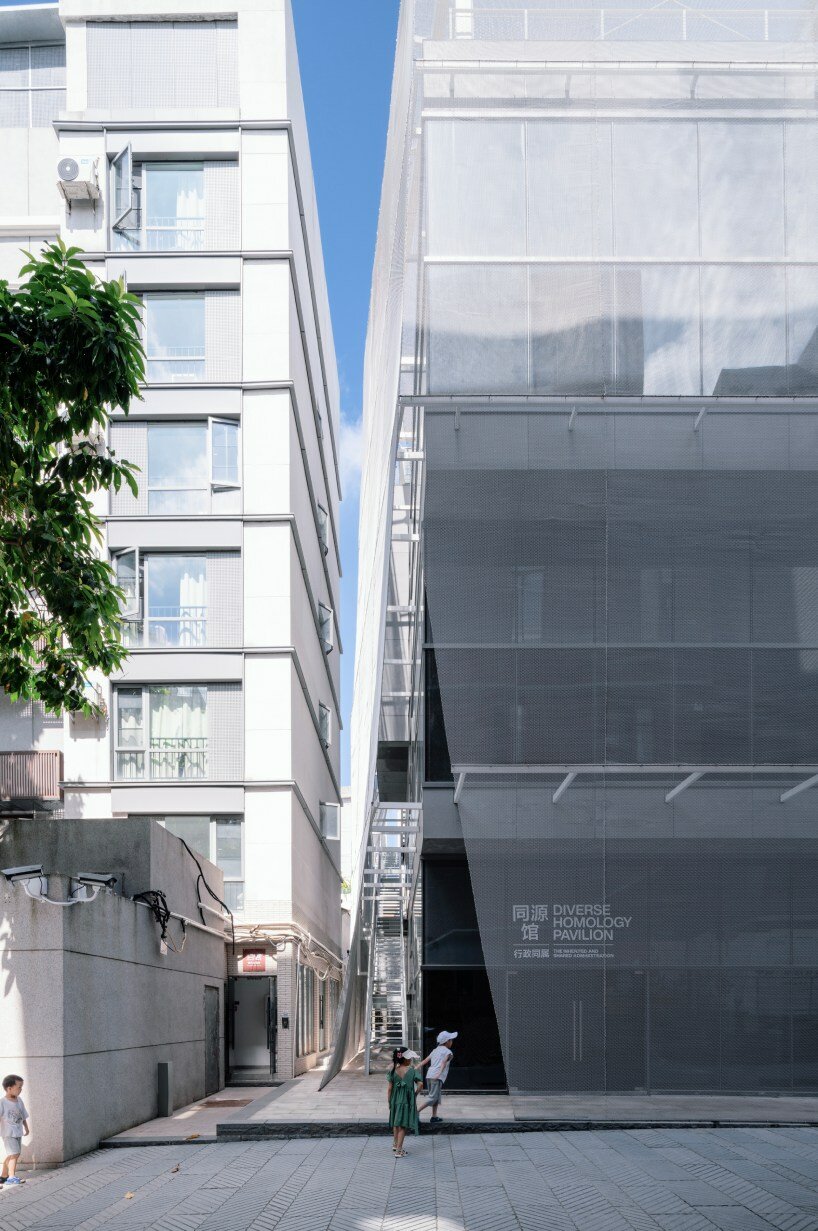
Architects: Want to have your project featured? Showcase your work through Architizer and sign up for our inspirational newsletters.
Housing is central to architecture and cities. Across generations and socio-economic backgrounds, a mix of housing options makes cities more lively, sustainable and human. Amidst global housing scarcity, the need to build more multifamily and affordable housing is widespread. Equitable housing begins with policy and planning, but it’s also tied to design. Architects worldwide are considering this idea and how to create more beautiful, integrated housing that reflects how we live today.
Multifamily housing is key to creating more equitable cities. In this type of housing, multiple separate units are contained within one or several buildings within one complex. A key benefit of multifamily in the current market is that it’s usually more affordable than single-family housing. With real estate today, it’s increasingly difficult for people to buy a home, especially for first-time buyers. In multifamily housing, less land is needed, and it helps to meet the growing demand for households of all ages and income levels. As architects consider the impact of housing, the following projects represent multifamily housing design across the world. Made for residents to either rent or own, they represent a cultural shift and underline the importance of housing in architecture today.
Timber House
MESH Architectures, Brooklyn, NY, United States
Jury Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Multi-Unit Residential Building
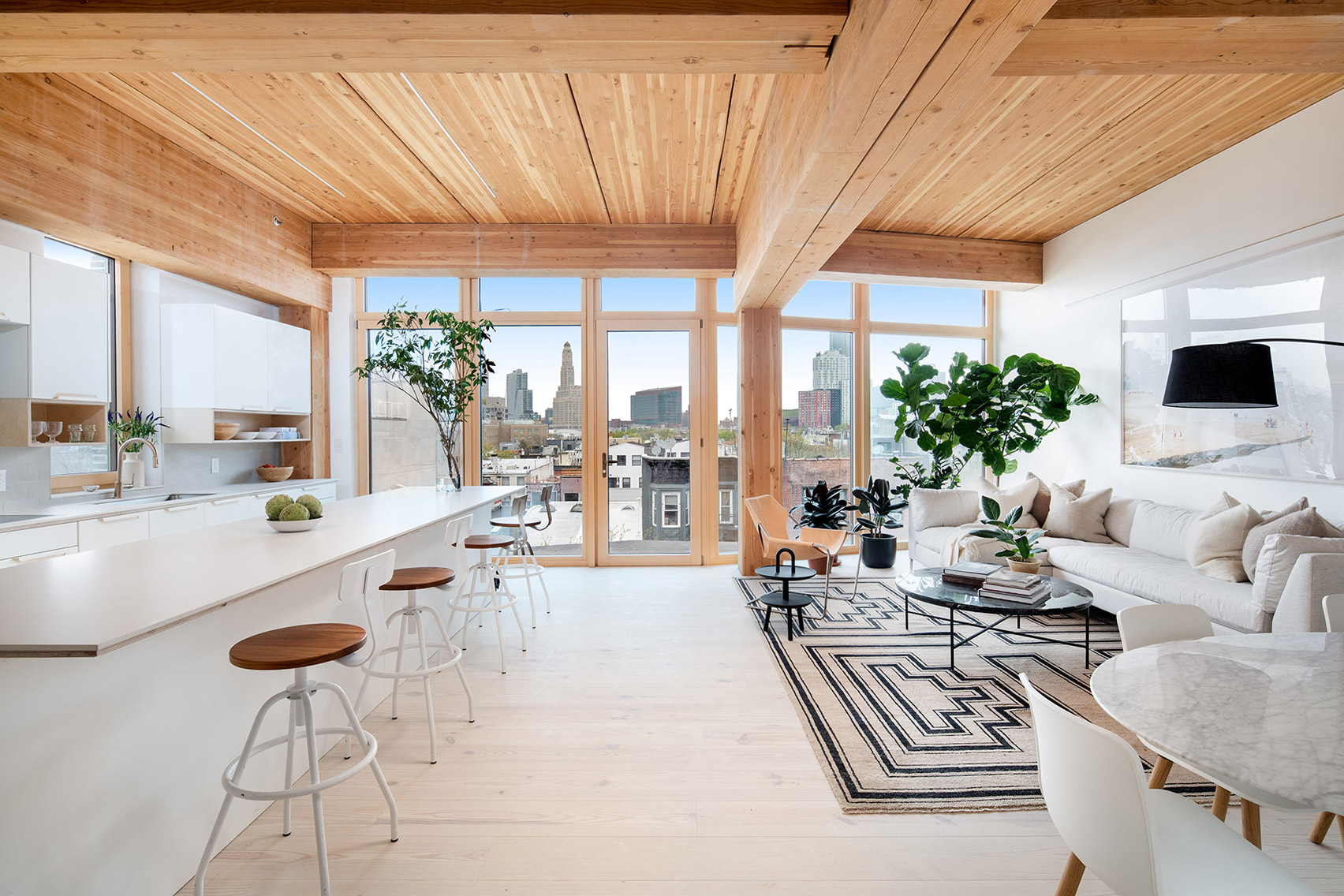
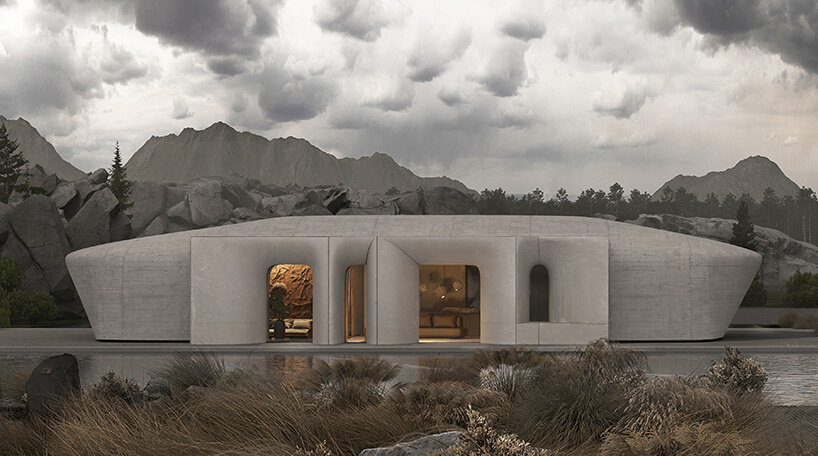
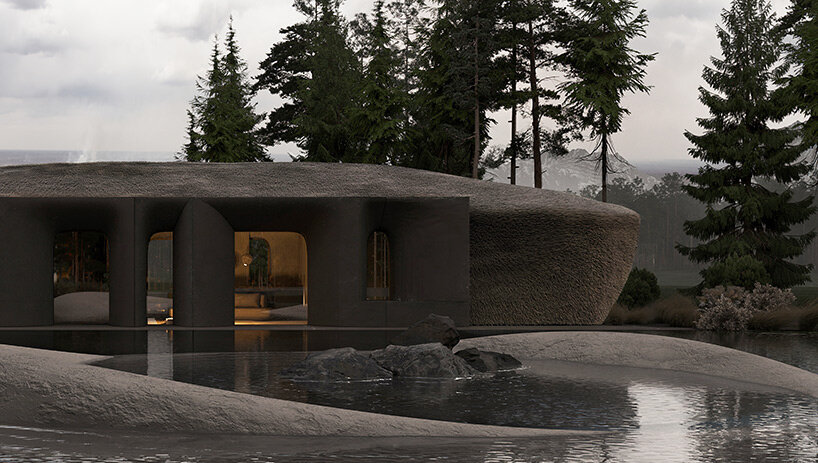
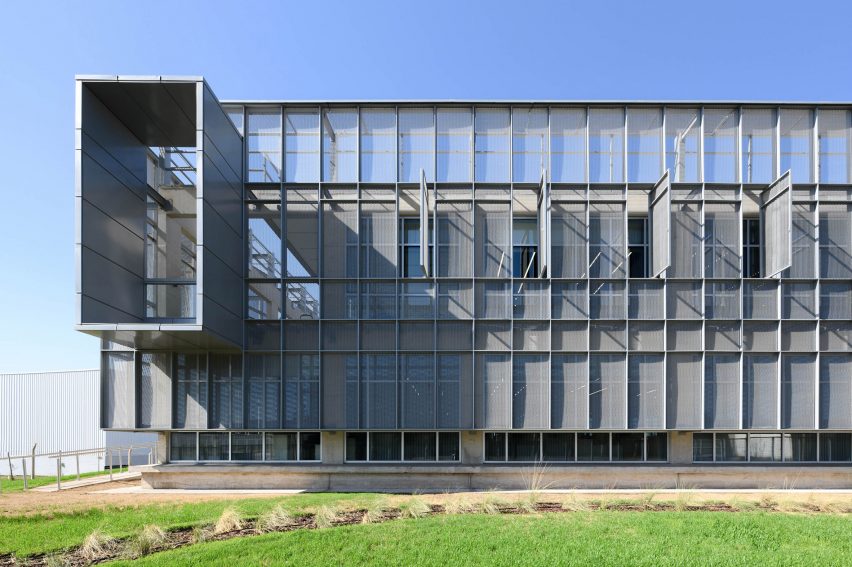
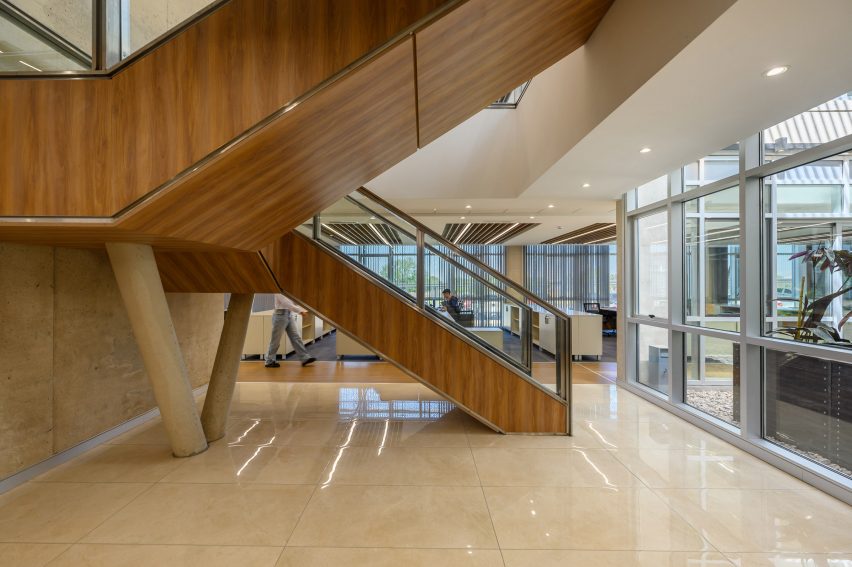
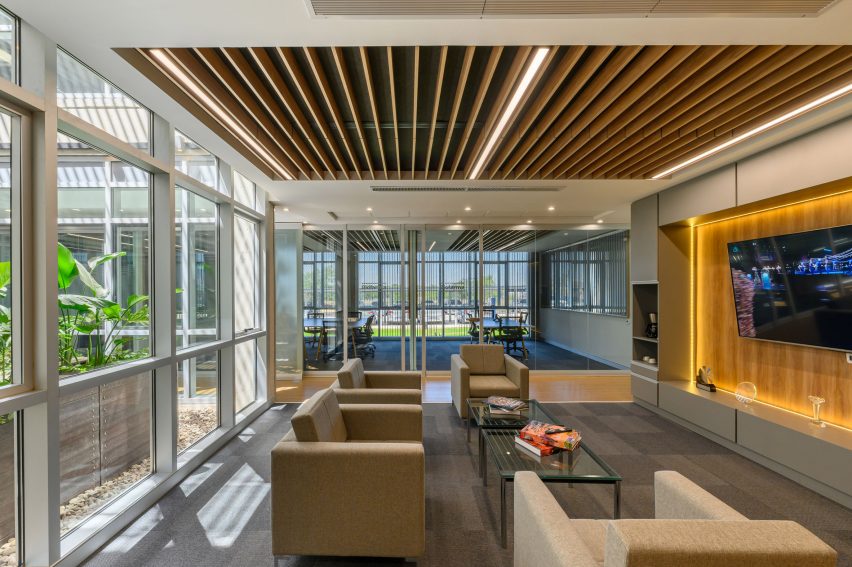
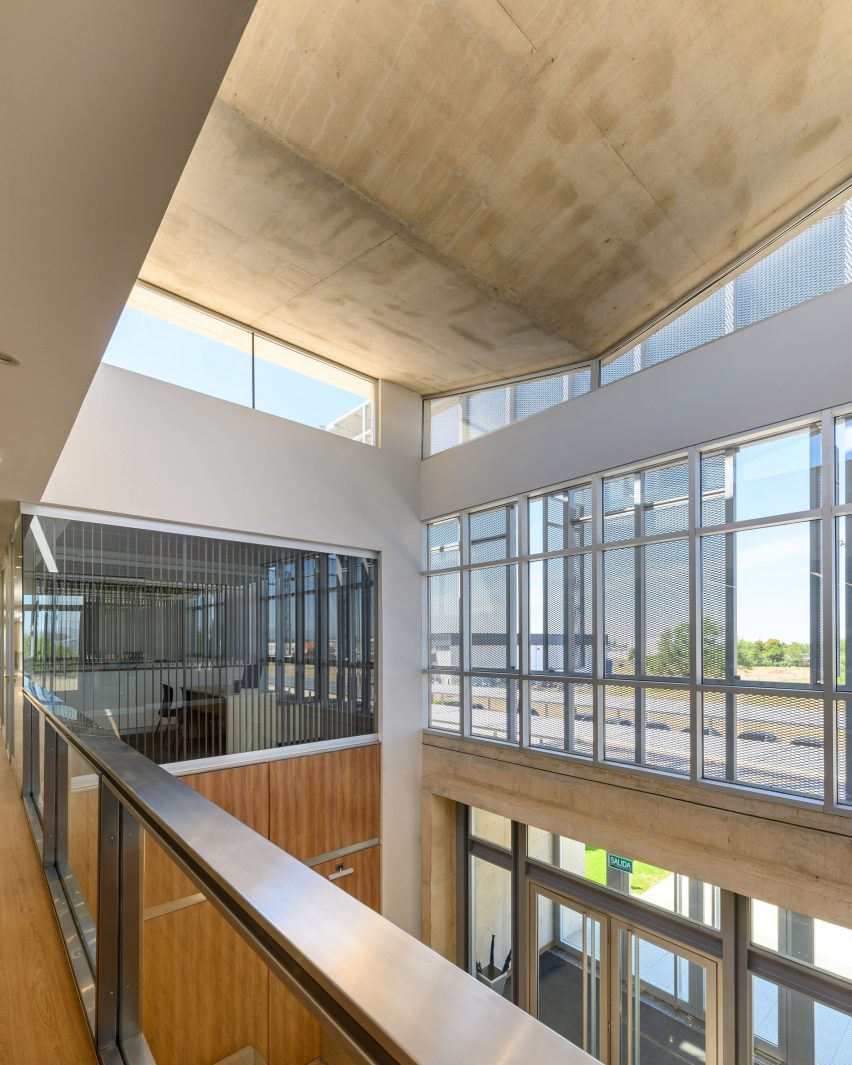
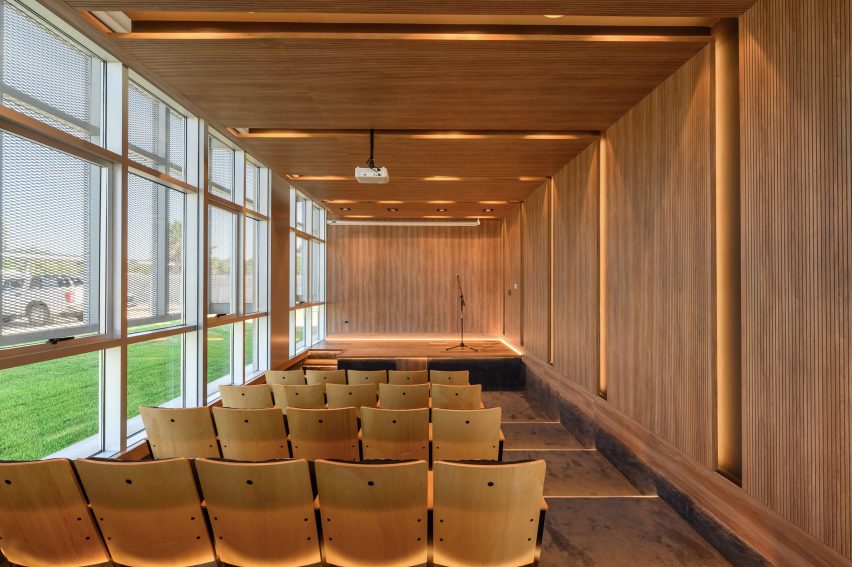
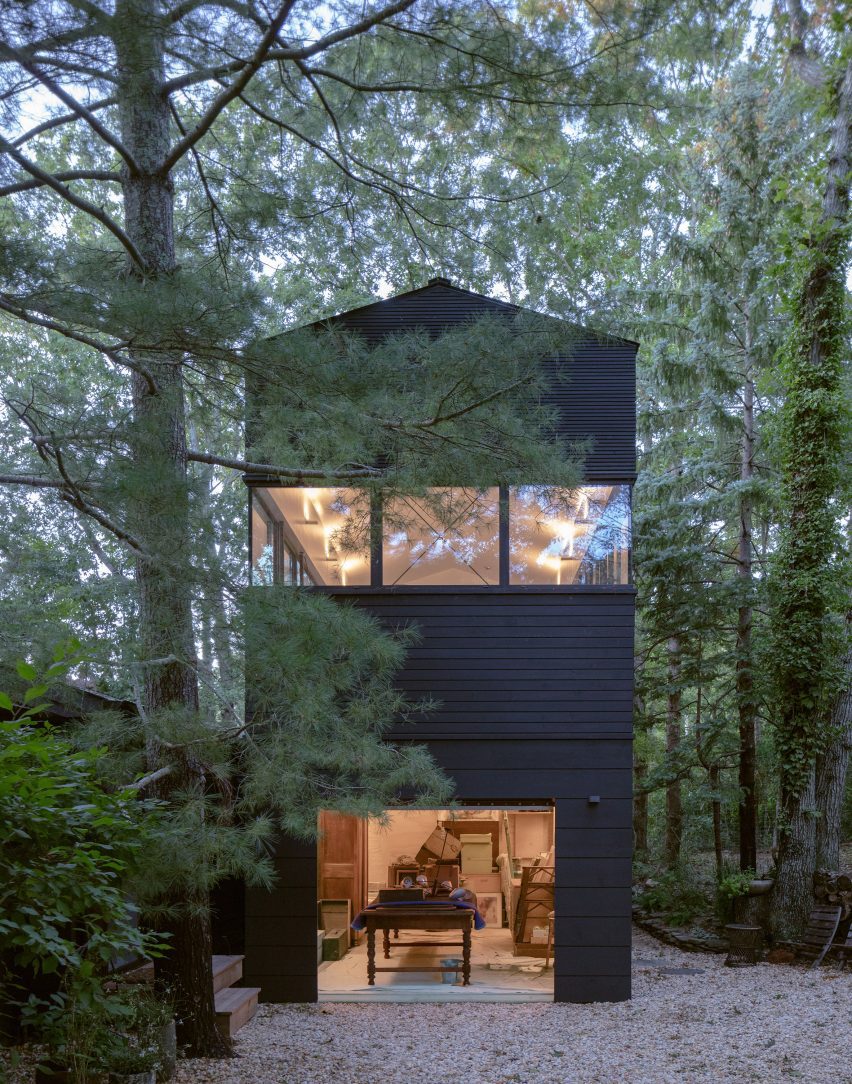
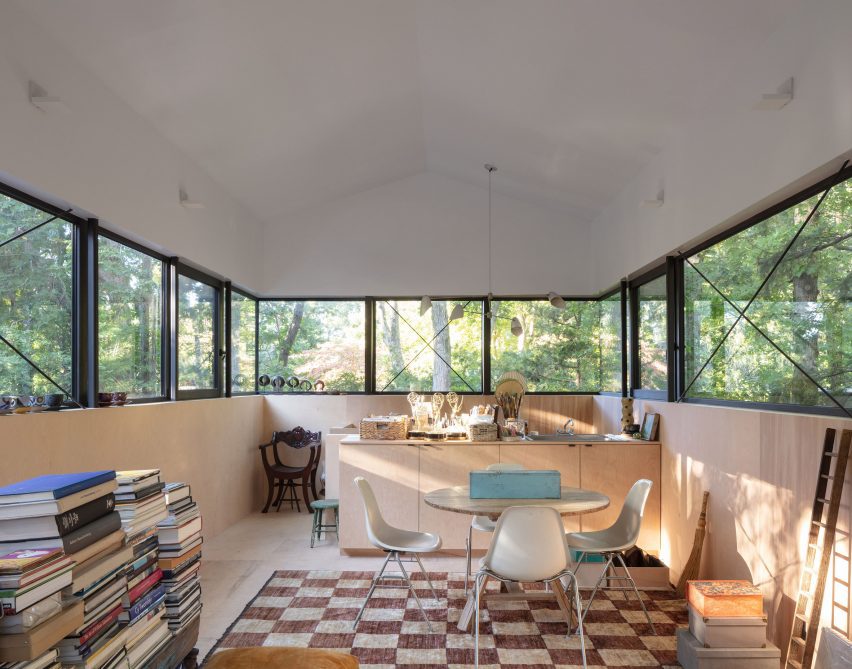
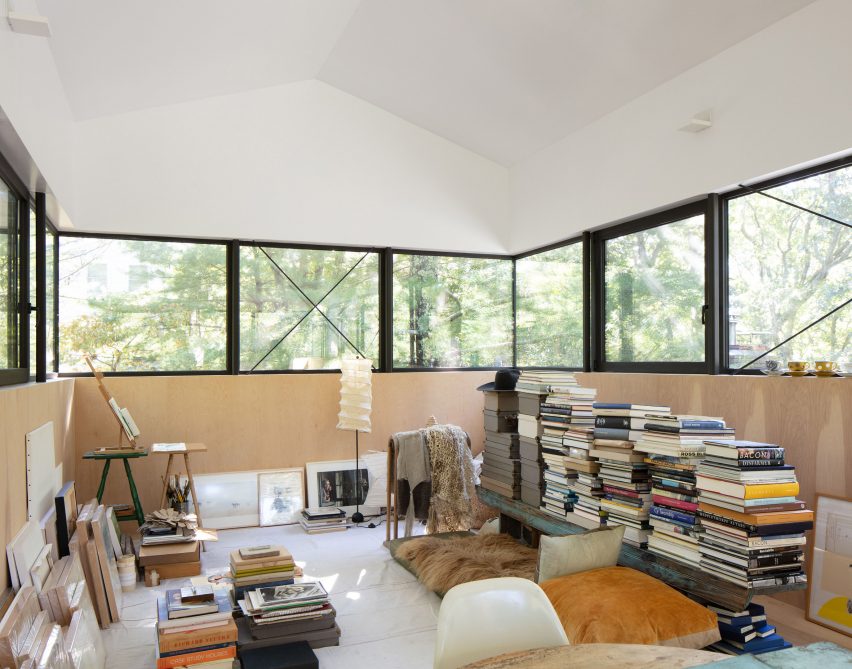
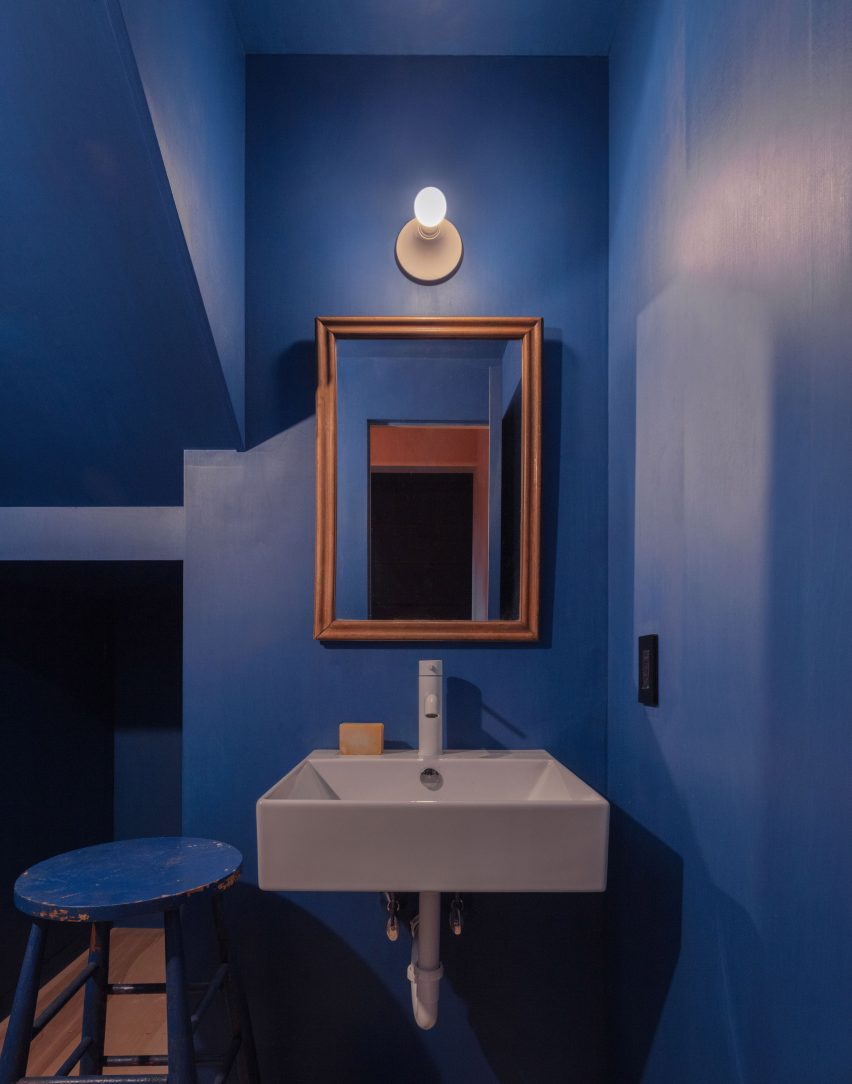
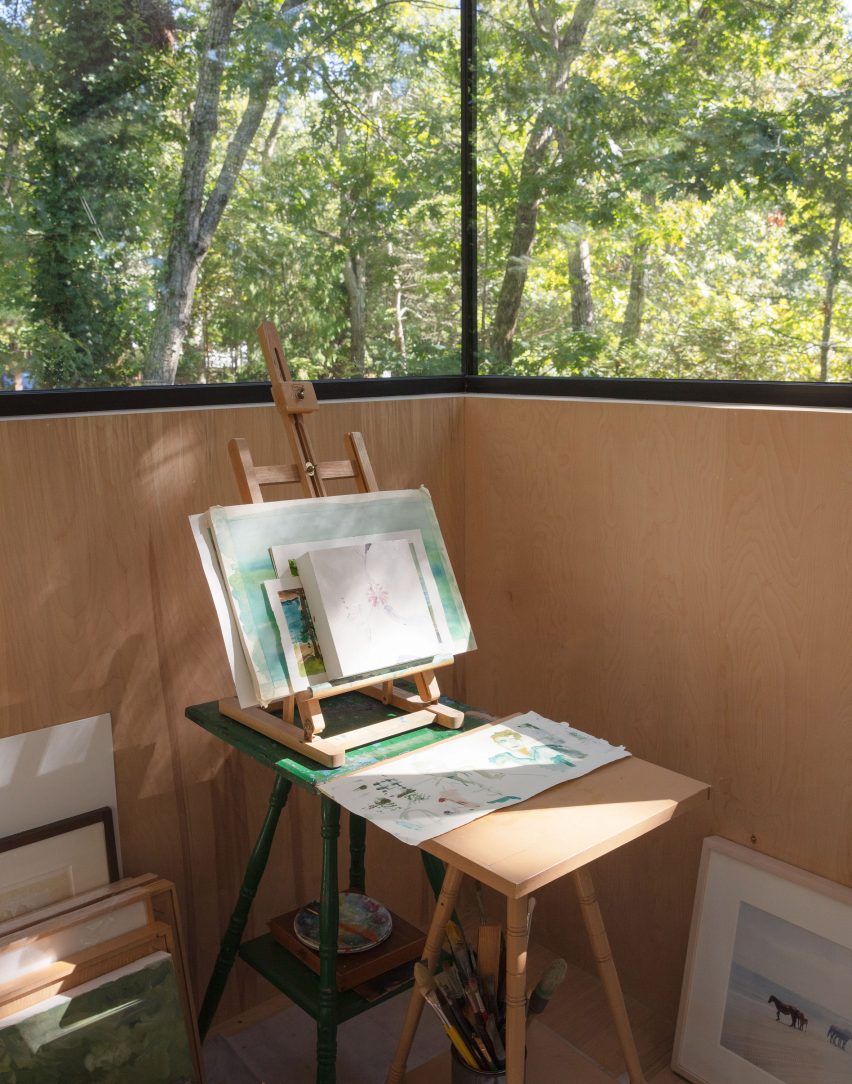
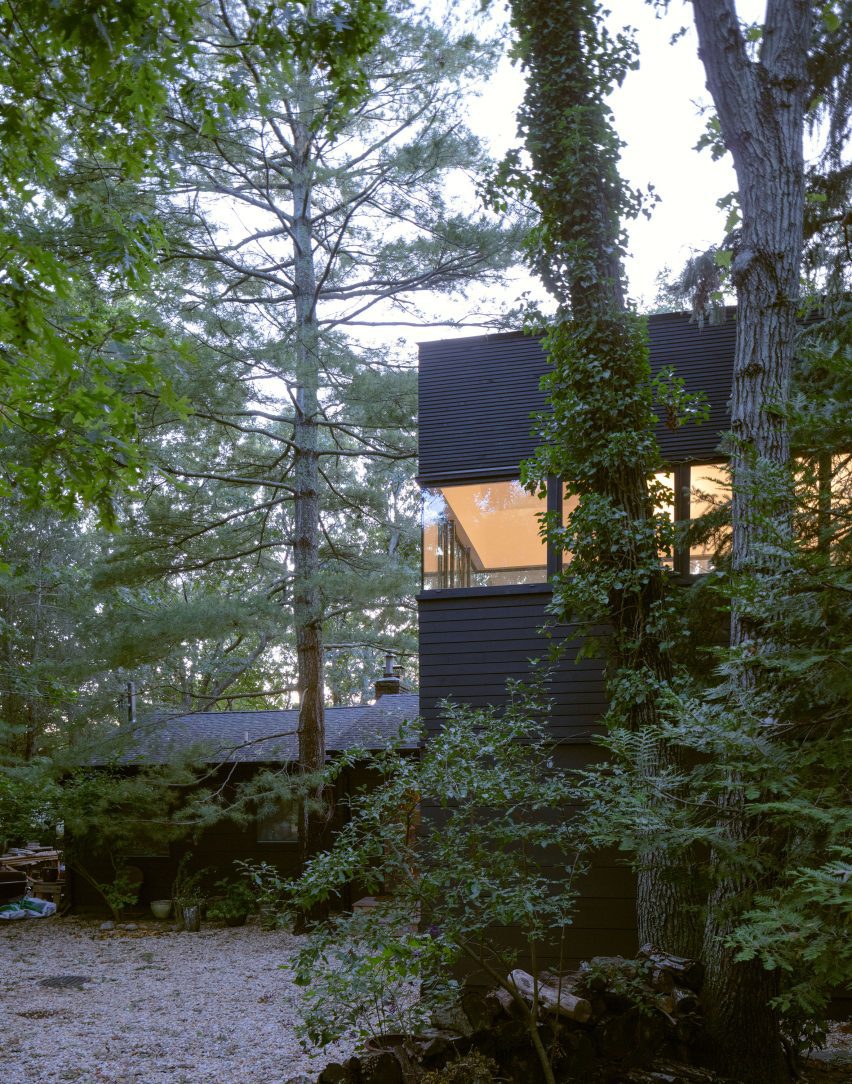
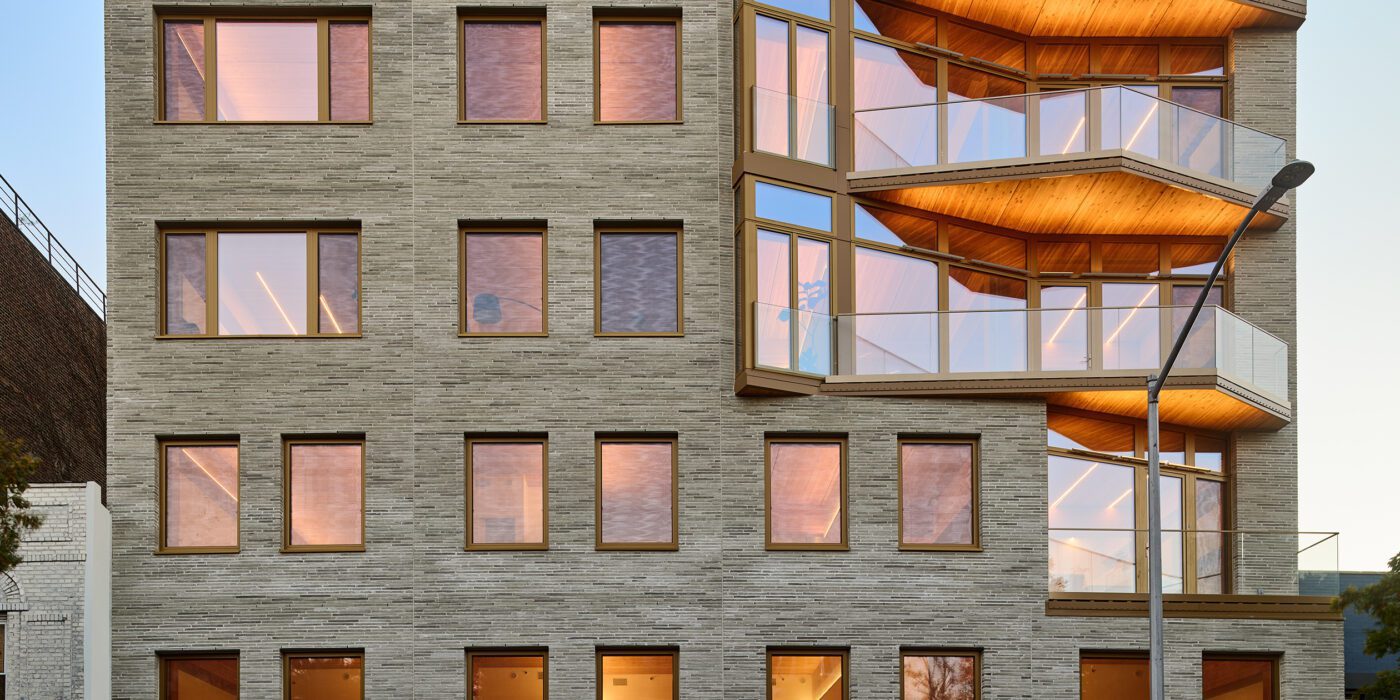
 New York is a city known for housing scarcity, and a place that’s defined by reinvention. For Timber House, MESH Architectures was inspired by natural finishes and “botanical architecture.” The idea was not only to foster well-being, but create a new model for timber construction in the city. The project is the first mass-timber condominium in New York, and the structure was built with glue-laminated timber columns, beams, and floor plates. The six-story, multifamily project is comprised of fourteen homes.
New York is a city known for housing scarcity, and a place that’s defined by reinvention. For Timber House, MESH Architectures was inspired by natural finishes and “botanical architecture.” The idea was not only to foster well-being, but create a new model for timber construction in the city. The project is the first mass-timber condominium in New York, and the structure was built with glue-laminated timber columns, beams, and floor plates. The six-story, multifamily project is comprised of fourteen homes.
Beyond the novel material approaches to construction in Timber House, it was also a test in learning from passive-house design. Those principles informed its high-performance envelope, with “intensive insulation, smart air sealing, and triple-glazed wood windows.” Less interior finishes were required thanks to leaving the wood structure exposed, while the team also prioritized low-carbon material choices. For Timber House, MESH wanted to demonstrate that sustainable multifamily buildings can balance well-being and comfort, as well as beauty.
Valley
MVRDV, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Jury Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Façades
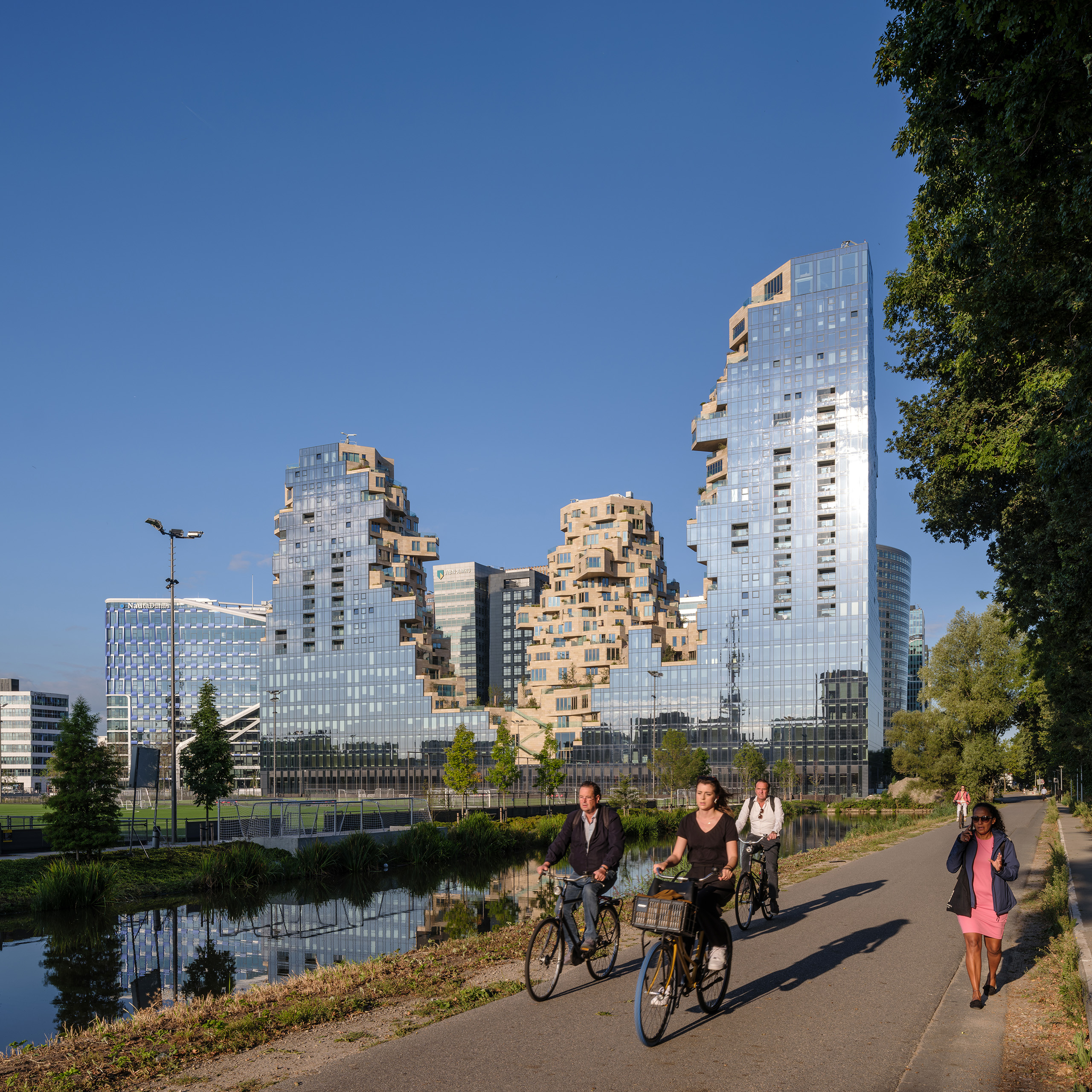
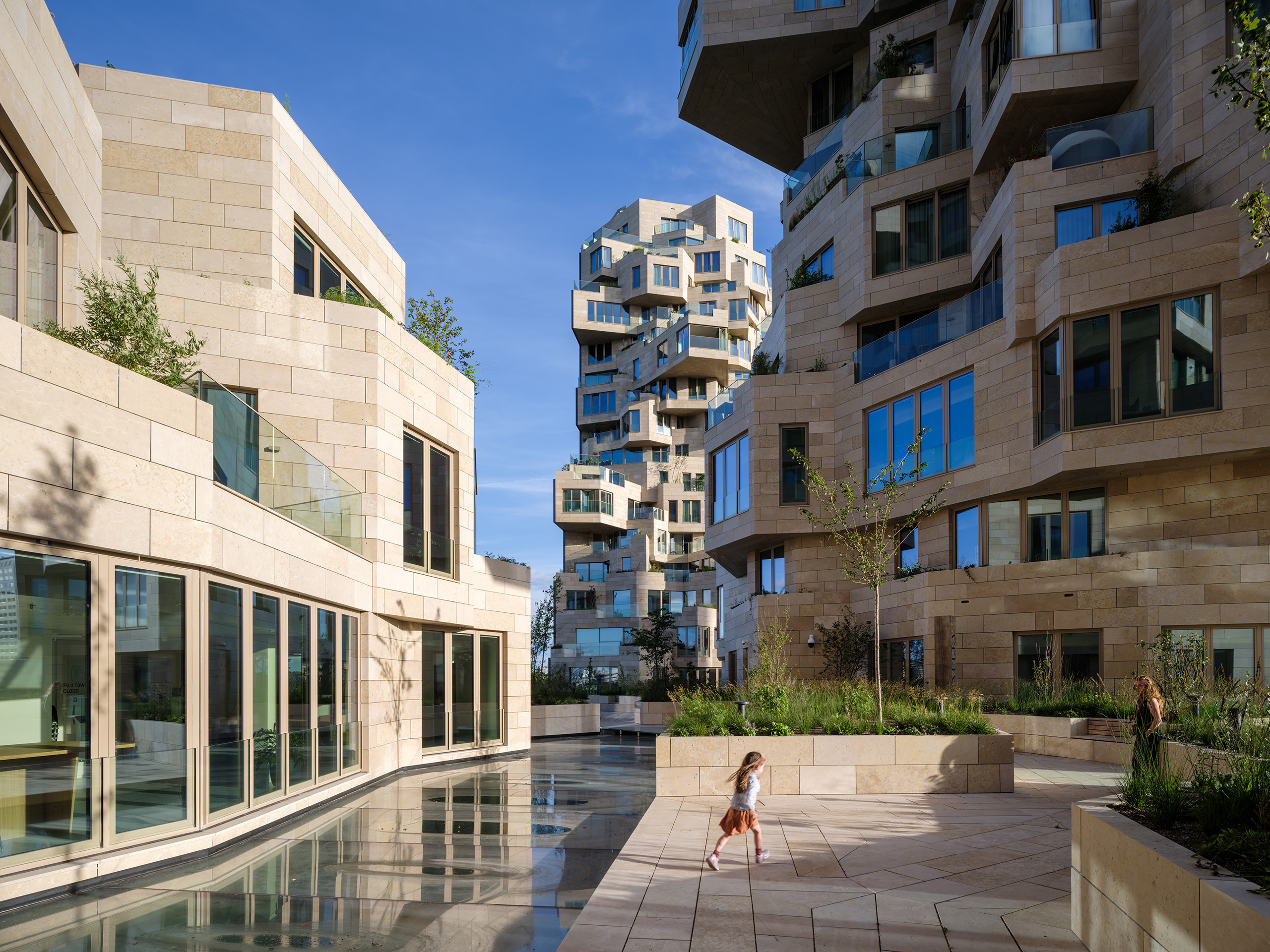
 MVRDV has earned a reputation for reinvention and creating new building forms. That same approach extends to housing, where the team designed Valley with a more “green and human” touch. Built for developer Edge, the project is located in Amsterdam Zuidas. Rising to three distinct towers, the façades shift across the complex. The outer edges are mirrored glass, while the inner façades are clad with stone and swaths of greenery.
MVRDV has earned a reputation for reinvention and creating new building forms. That same approach extends to housing, where the team designed Valley with a more “green and human” touch. Built for developer Edge, the project is located in Amsterdam Zuidas. Rising to three distinct towers, the façades shift across the complex. The outer edges are mirrored glass, while the inner façades are clad with stone and swaths of greenery.
Valley was built for a mix of residents, as well as workers and visitors. Not only for multifamily housing, the project also includes offices while much of the building is open to the public. For the materials, over 40,000 stone tiles of varying sizes were used throughout the building’s façades. “Each of the 198 apartments has a unique floorplan, made possible by the interior designs by Heyligers Architects.” Outside, the team worked with landscape architect Piet Oudolf on the placement and selection of trees, shrubs and approximately 13,500 smaller plants that are in within the natural stone planters.
One Hundred
Studio Gang, St. Louis, MO, United States
Jury Winner, 9th Annual A+Awards, Multi Unit Housing High Rise (16+ Floors)
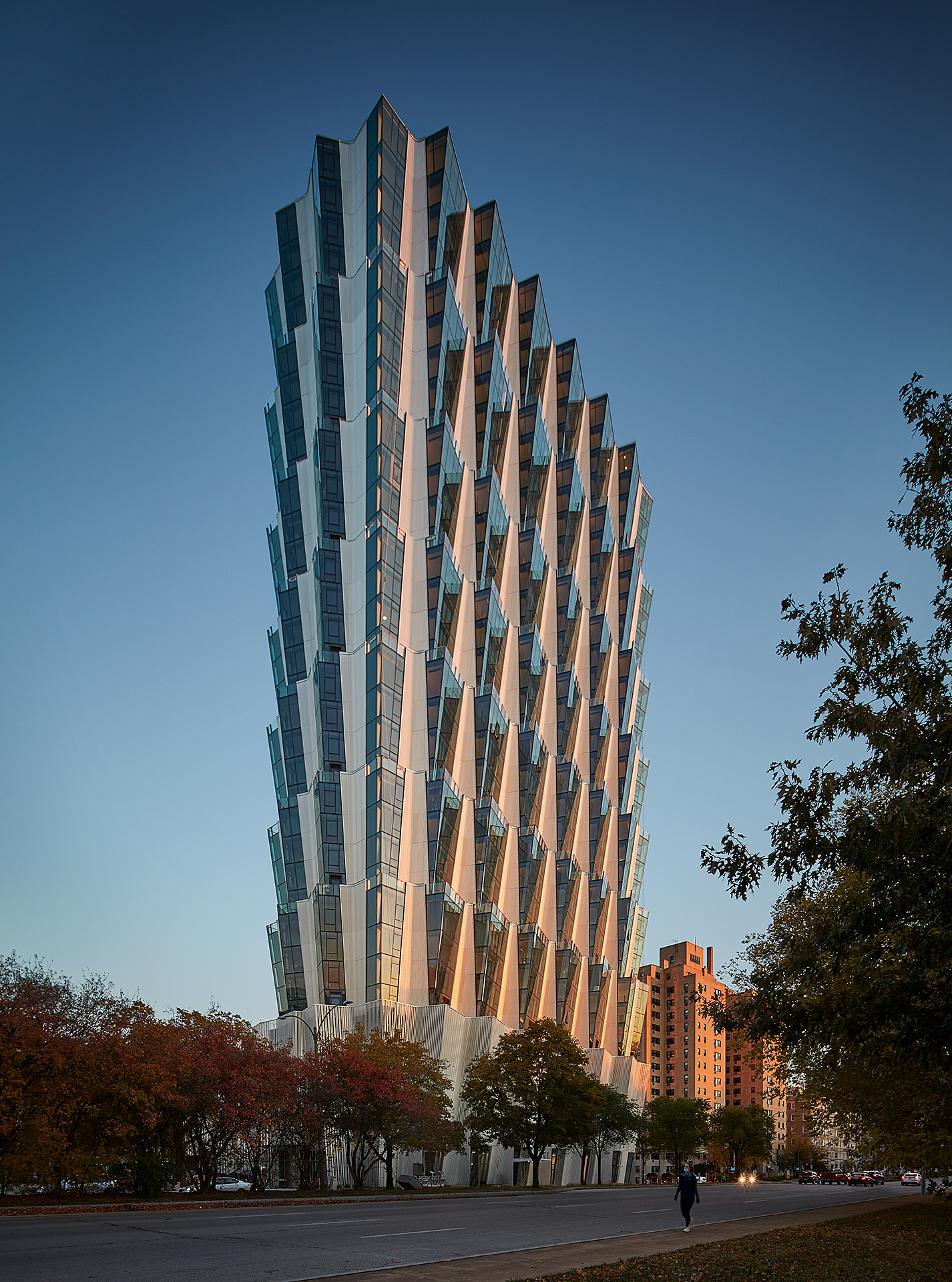
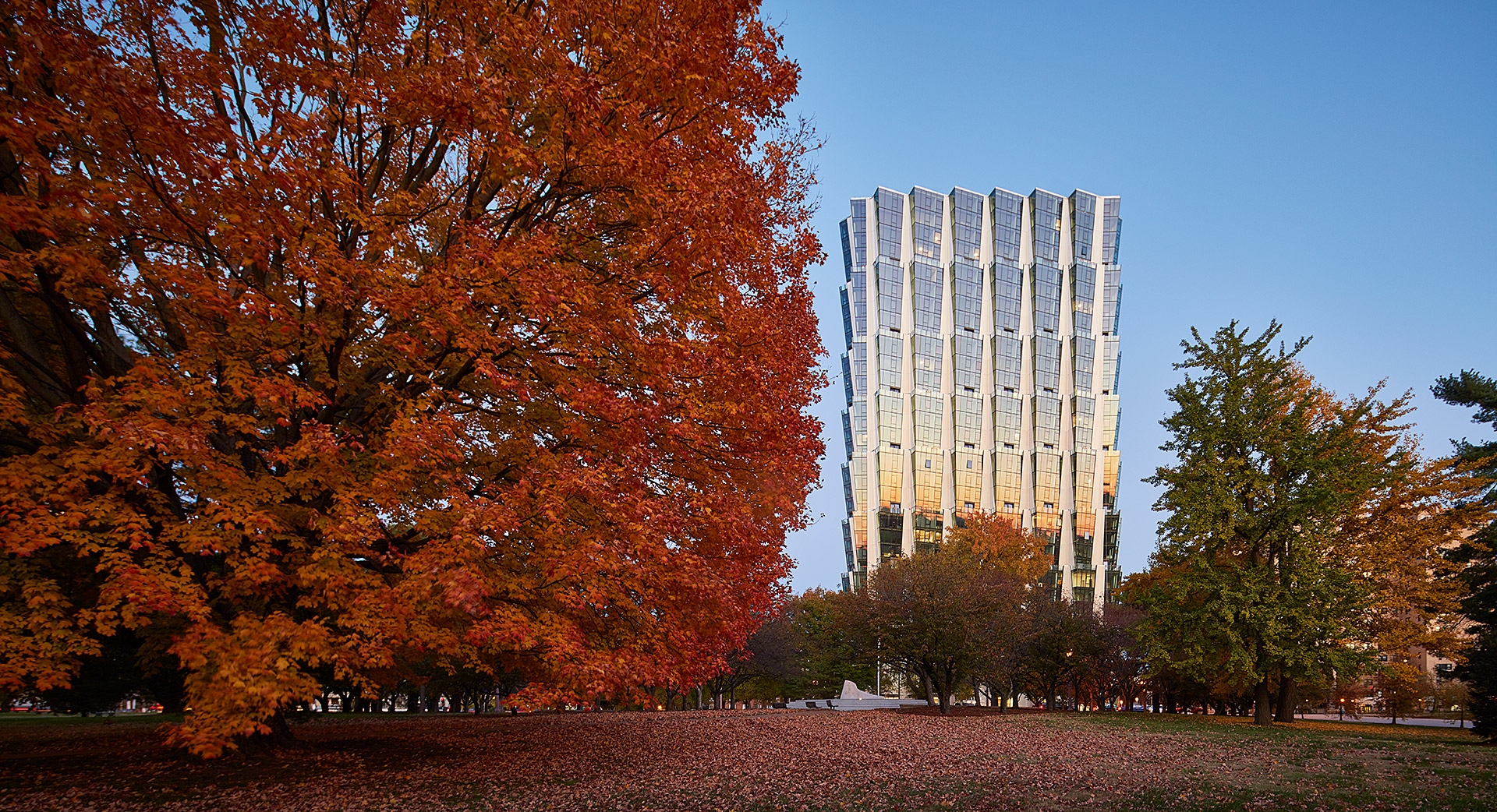
 Few locations are more prominent for multifamily housing in St. Louis than Forest Park. Designed by Studio Gang, One Hundred is a residential tower overlooking the park and the studio’s first project in the city. The tower includes a mix of housing, retail and amenities on four-story stacked tiers. The apartments were designed for views of Forest Park and east to the Gateway Arch.
Few locations are more prominent for multifamily housing in St. Louis than Forest Park. Designed by Studio Gang, One Hundred is a residential tower overlooking the park and the studio’s first project in the city. The tower includes a mix of housing, retail and amenities on four-story stacked tiers. The apartments were designed for views of Forest Park and east to the Gateway Arch.
From a formal approach, Studio Gang designed the tower with an angled façade that creates a series of large outdoor spaces atop each tier. This move also produces outdoor space for residents atop the green roof podium. The team notes that, “each apartment features its own corner living room with double exposures that, in addition to offering panoramic views, enhance the amount and quality of daylight within the units.” The tower includes public and retail spaces at ground level adjacent to the park, while establishing a new landmark for St. Louis.
Cirqua Apartments
BKK Architects, Melbourne, Australia
Jury & Popular Choice Winner, 2018 A+Awards, Multi Unit Housing Low Rise (1-4 Floors)
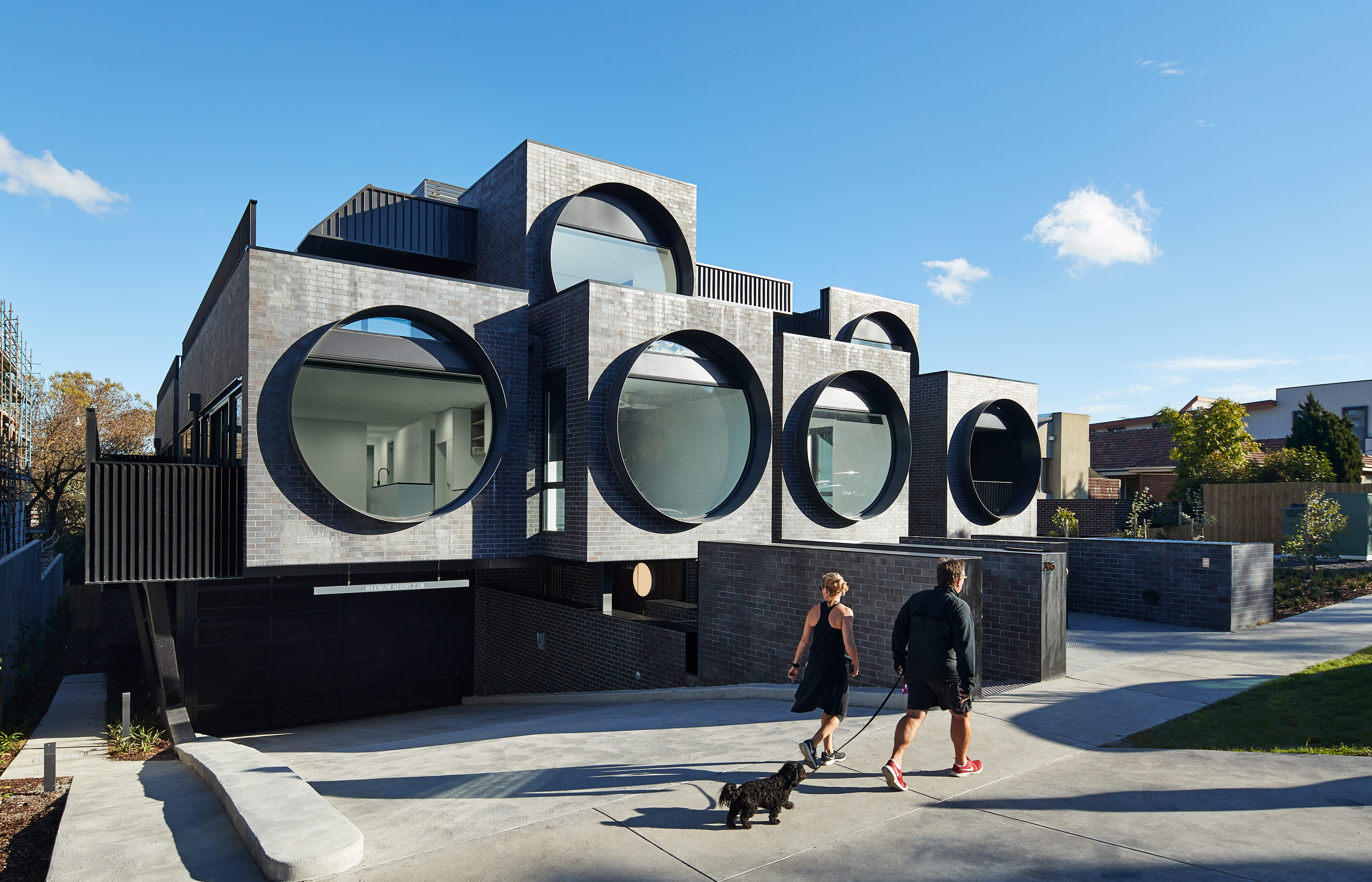
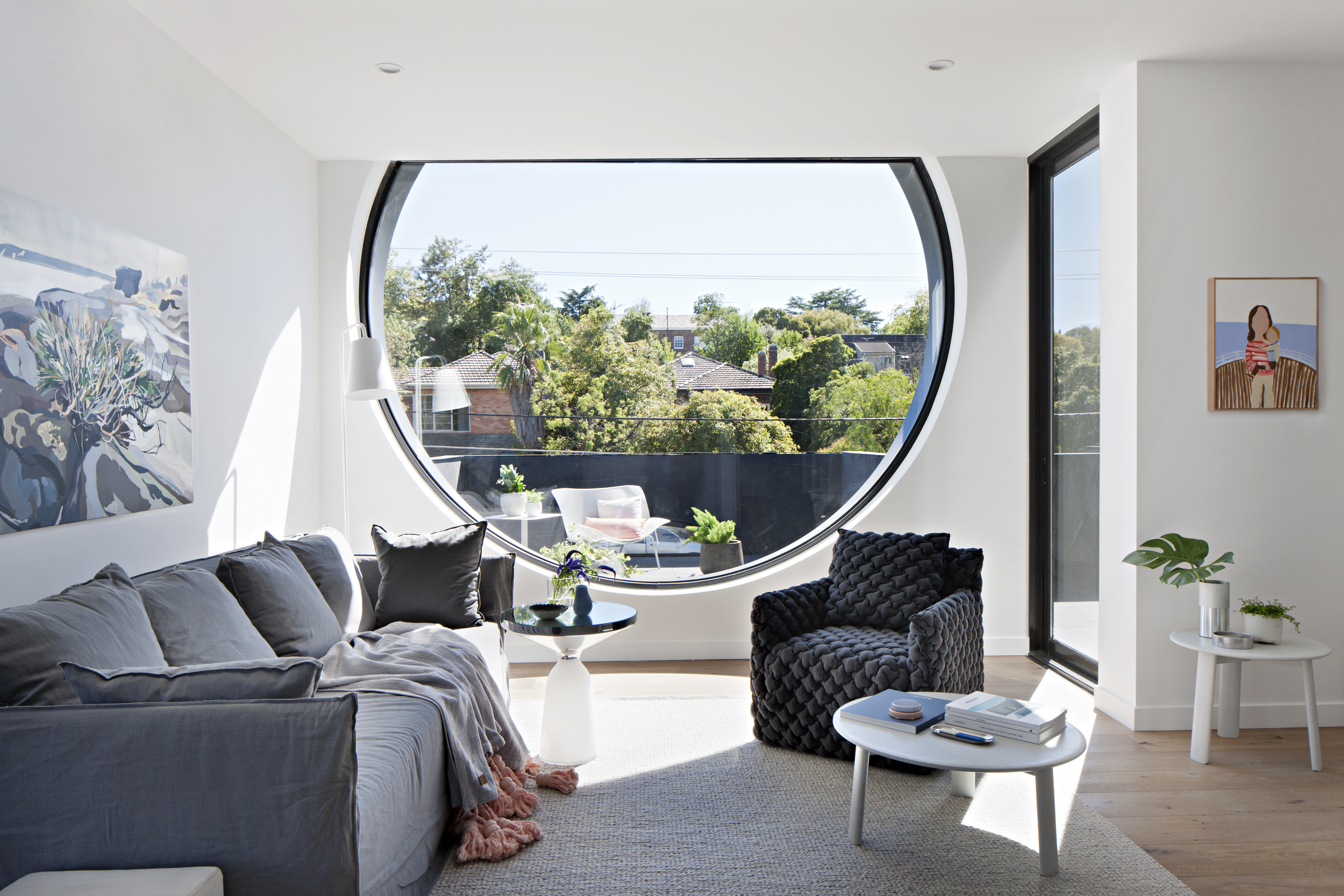
 The Cirqua project by BKK gained widespread recognition for creating beautiful, inventive multifamily architecture. The project includes 38 unique unit types out of the 42 total apartments made with spacious balconies and an integrated approach to landscaping. Combining two properties into a single block, the project was formed with careful attention paid to scale and the surrounding context. Cirqua not only showcases a smart, nuanced approach to multifamily housing, but also how to design for accessibility and passive performance.
The Cirqua project by BKK gained widespread recognition for creating beautiful, inventive multifamily architecture. The project includes 38 unique unit types out of the 42 total apartments made with spacious balconies and an integrated approach to landscaping. Combining two properties into a single block, the project was formed with careful attention paid to scale and the surrounding context. Cirqua not only showcases a smart, nuanced approach to multifamily housing, but also how to design for accessibility and passive performance.
As the team noted, prospective owners are increasingly buying into the apartment market (over detached housing) as owner-occupiers. A sense of place was a key driver of the design, establishing a neighborly feel. All living areas and bedrooms have direct access to ventilation, natural light and views, while maximizing glazing created connections to the surrounding garden. From the neighborhood scale, a study in massing led to reducing the overall building volume to make the development fit seamlessly into its site.
Caterpillar
Prince Concepts, Detroit, MI, United States
 Caterpillar approaches density through a novel construction and design in Core City, Detroit. It utilizes a Quonset Hut structure that holds eight units, all entirely prefabricated. The result is an 8,000 square foot (745 square meter) residential project that prioritizes indoor and outdoor space. Prince Concepts created the project with tall ceilings that rise to 23 feet (7 meters); the units were designed to capture morning light in the bedrooms and evening sunsets in the living room.
Caterpillar approaches density through a novel construction and design in Core City, Detroit. It utilizes a Quonset Hut structure that holds eight units, all entirely prefabricated. The result is an 8,000 square foot (745 square meter) residential project that prioritizes indoor and outdoor space. Prince Concepts created the project with tall ceilings that rise to 23 feet (7 meters); the units were designed to capture morning light in the bedrooms and evening sunsets in the living room.
Multifamily housing and density are charged subjects, but they also hold the potential to reimagine everyday life in cities. For Caterpillar, the team wanted to rethink the standard ratios of a multifamily project. To do so, instead of “150 apartments surrounded by eight trees with just one window per room, Caterpillar provides eight apartments surrounded by 150 trees and 12-18 windows per room.” The multifamily project built on the success of True North, completed in 2017. That Prince Concepts development was made with eight Quonset huts and ten leasable units.
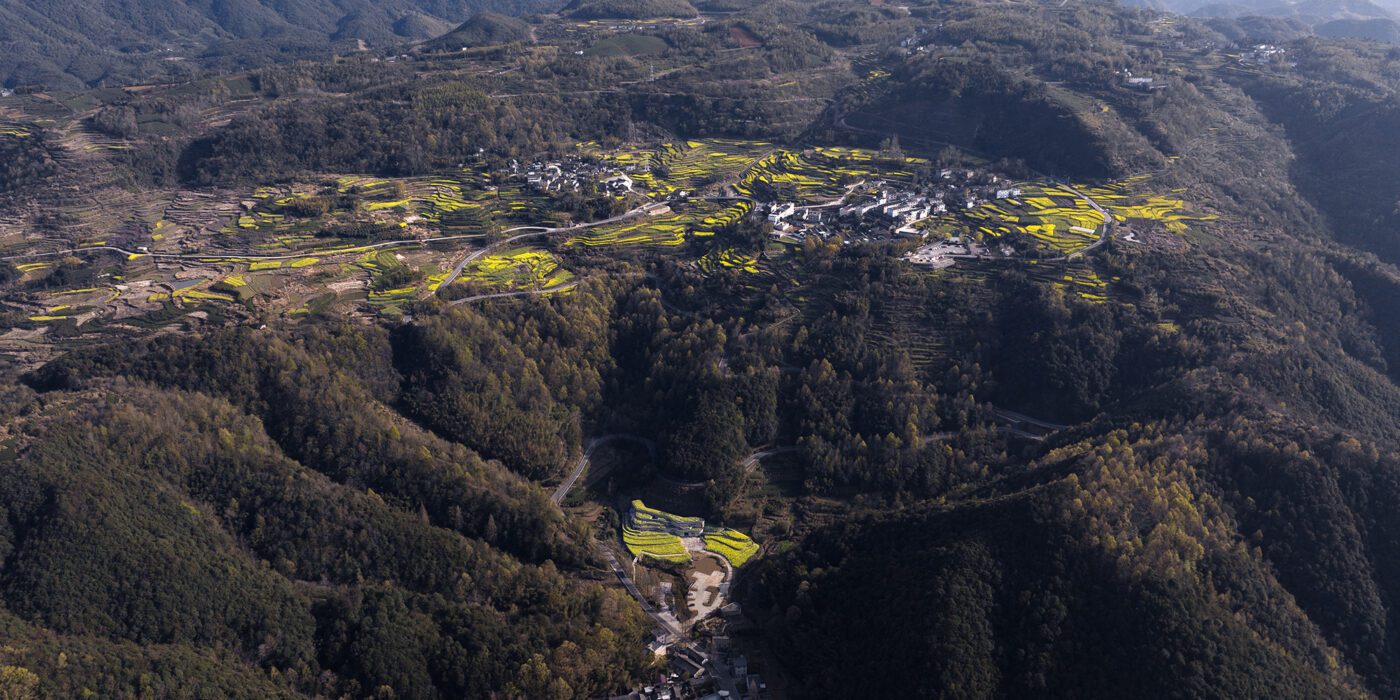
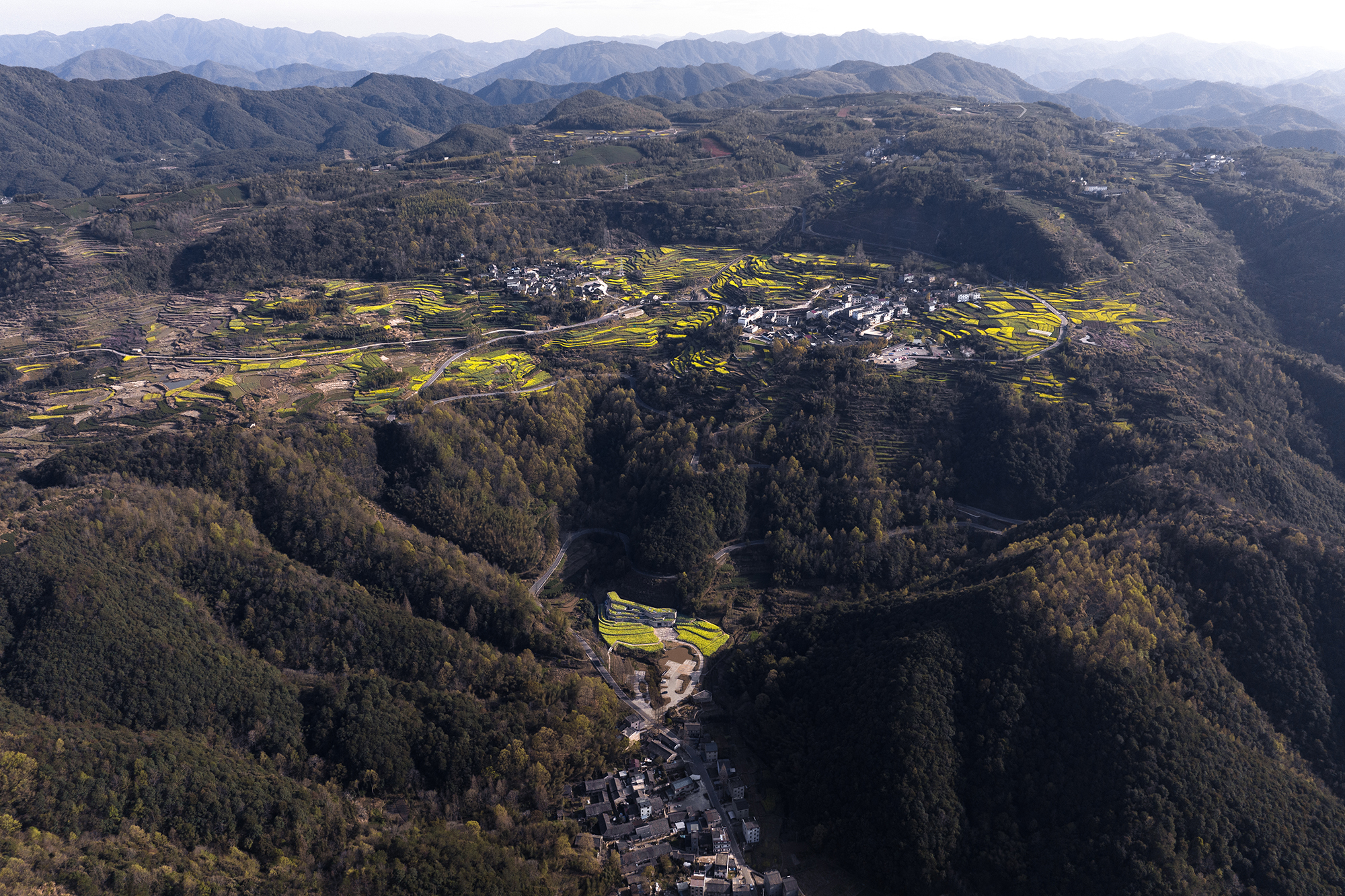
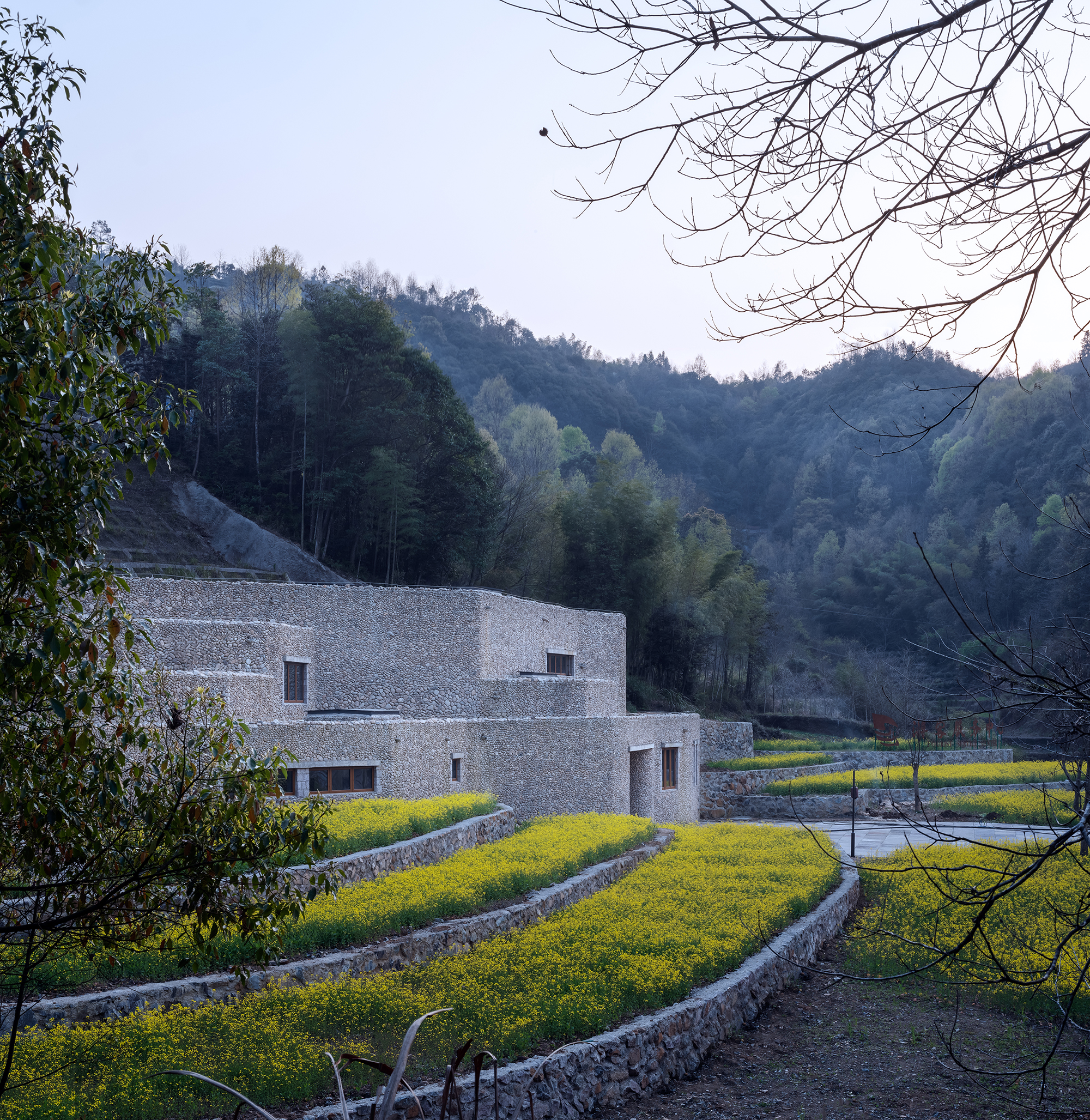
Casa Jardin Escandon
CPDA ARQUITECTOS, Mexico City, Mexico
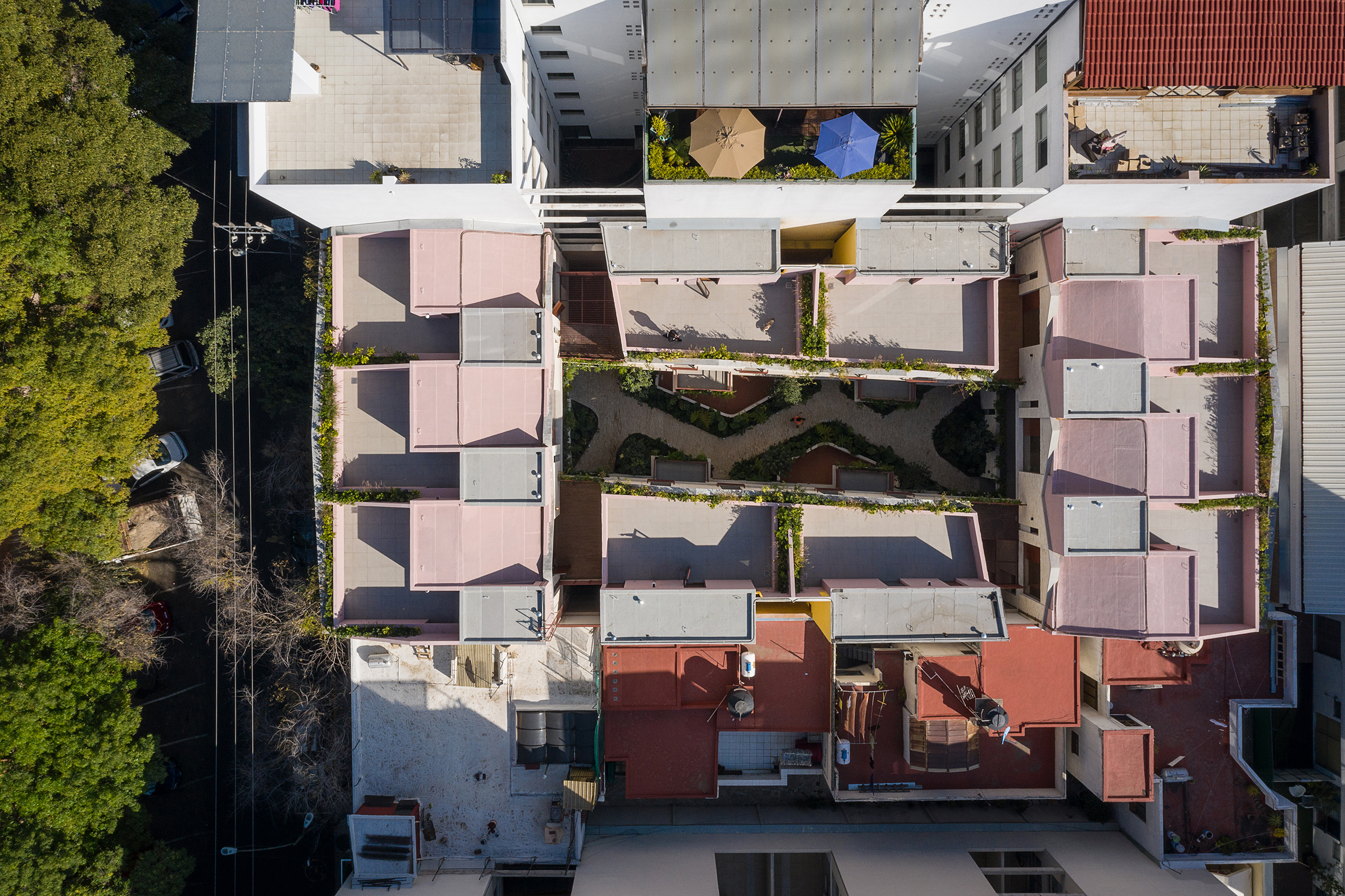
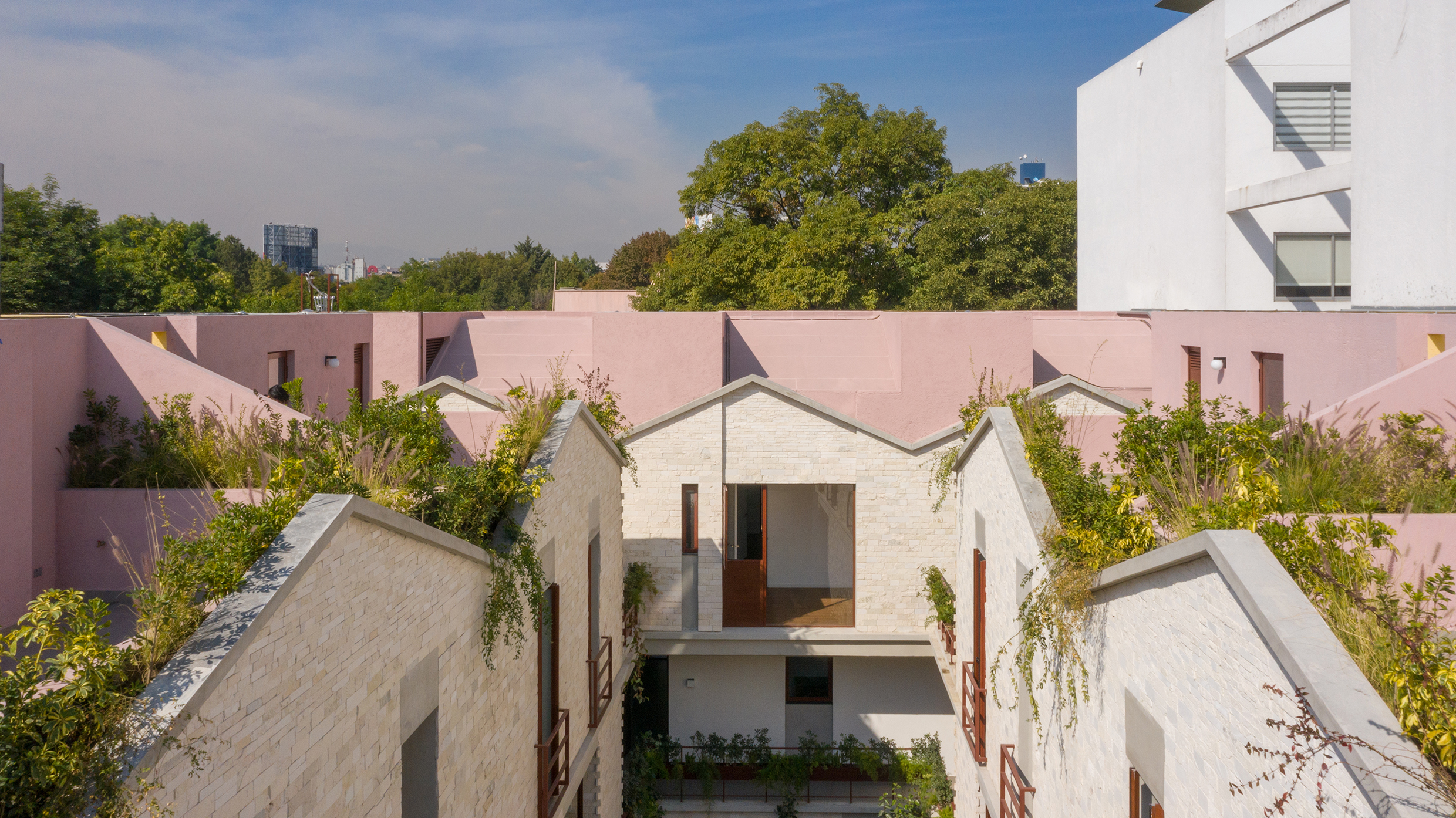
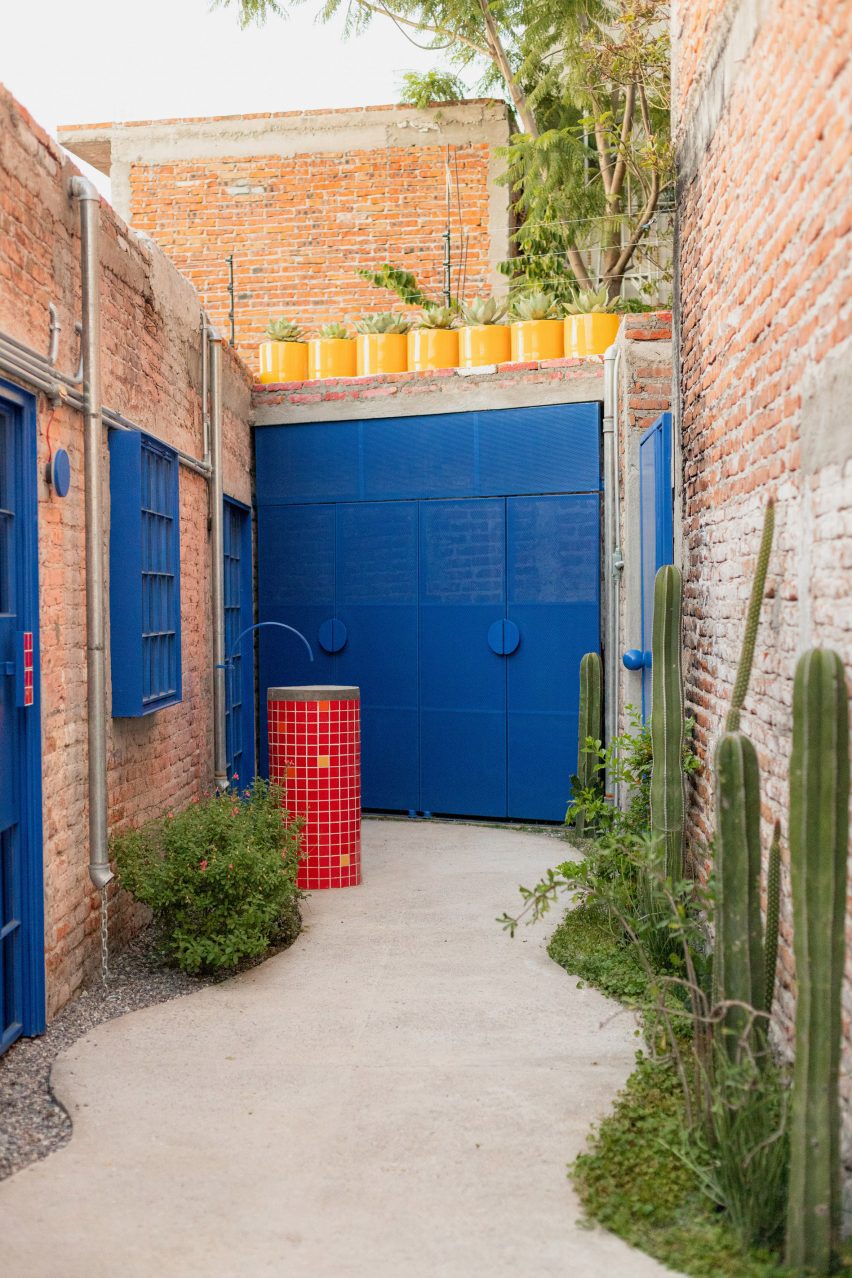
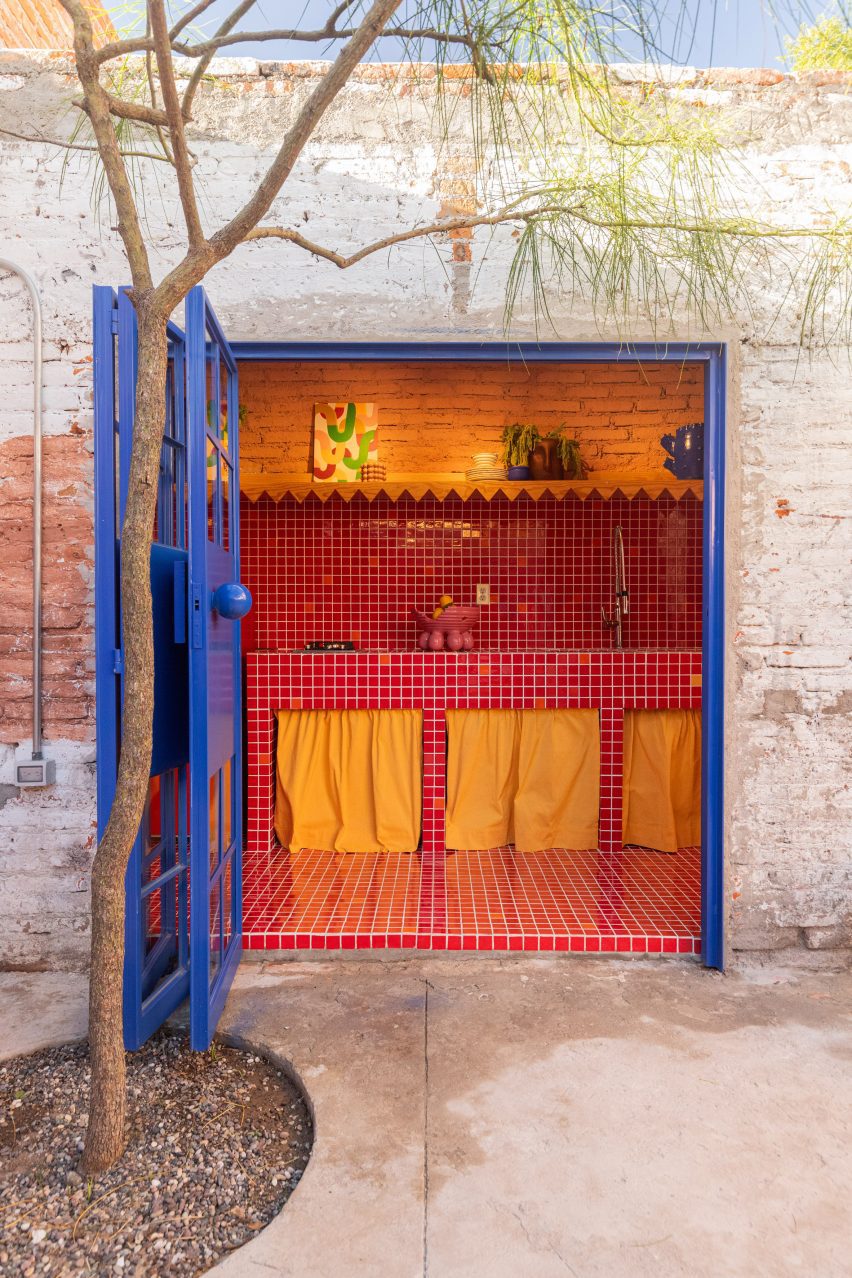
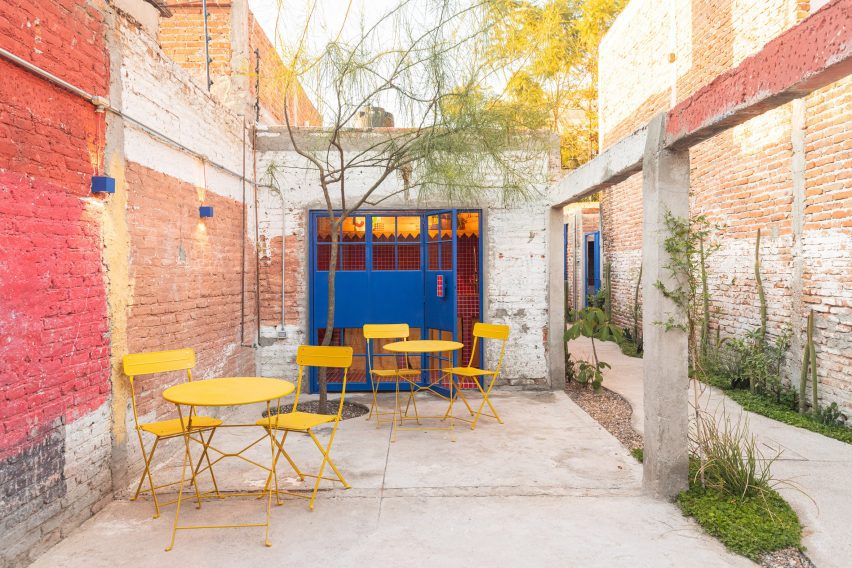
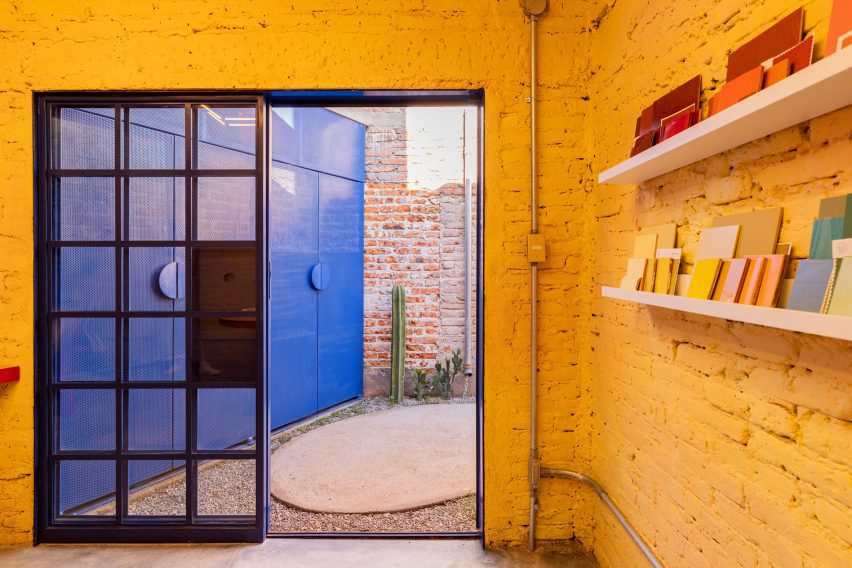
 CPDA Architects designed this garden house project as a multifamily development in Mexico City. Located in the Escandón neighborhood, the project includes fourteen residential units. At its heart, a central courtyard is the connective element that defines the housing project, opening up access to natural light and cross ventilation. Ten townhouse units are set up the four ground-floor units below, all of which share a similar material relationship.
CPDA Architects designed this garden house project as a multifamily development in Mexico City. Located in the Escandón neighborhood, the project includes fourteen residential units. At its heart, a central courtyard is the connective element that defines the housing project, opening up access to natural light and cross ventilation. Ten townhouse units are set up the four ground-floor units below, all of which share a similar material relationship.
As the Escandón neighborhood has seen rapid growth, new populations moved in across age and income levels. The project provides a mix of unit types, as well as changing faces along its façade. The exterior showcases the concrete slabs that stand out and the gabled façade, while the interior has simple, seamless and integrated forms that define the inside complex. The idea was to create a “secret garden” that residents can enjoy within the city.
The SIX Veterans Housing
Brooks + Scarpa Architects, Los Angeles, CA, United States
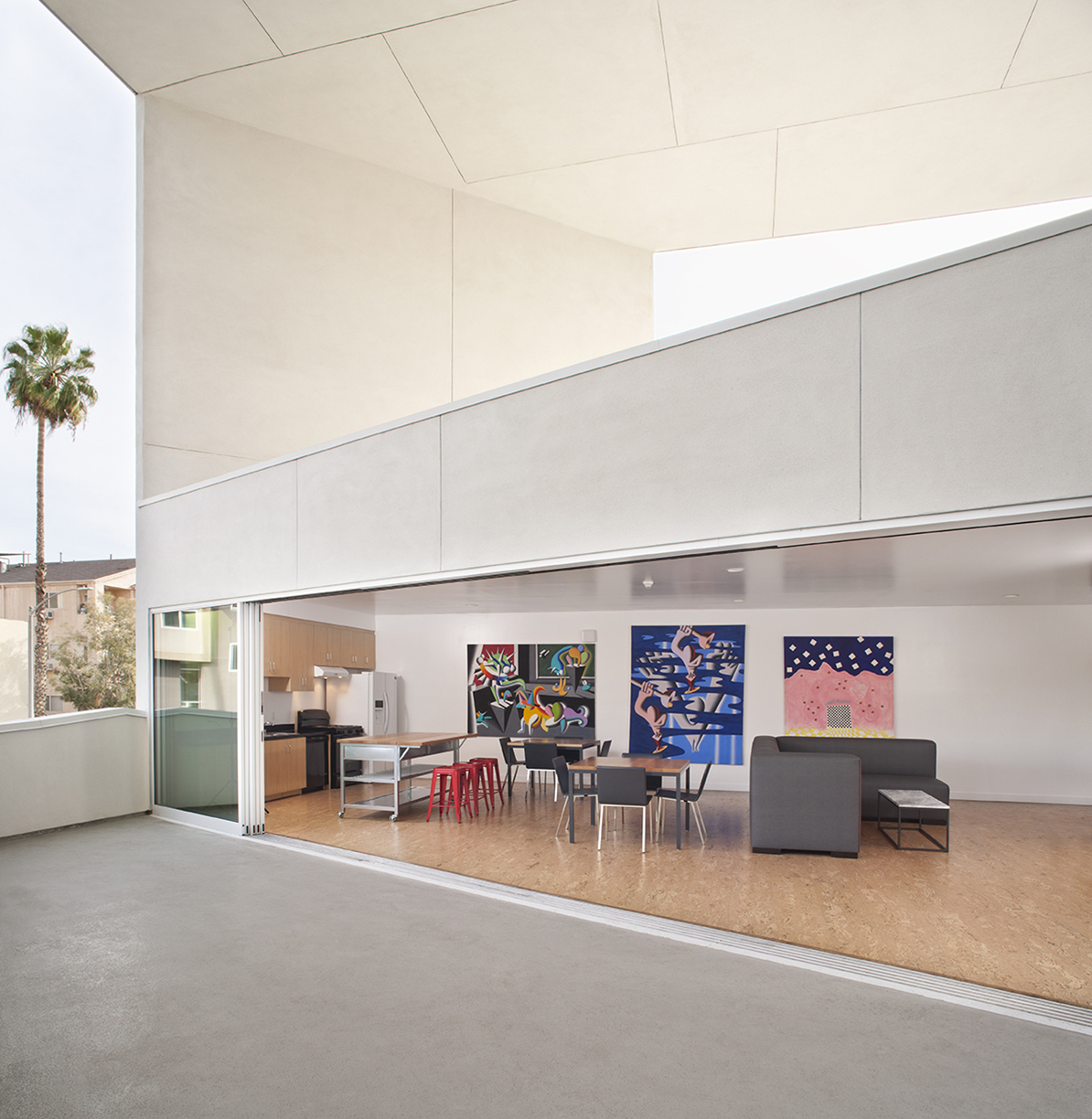
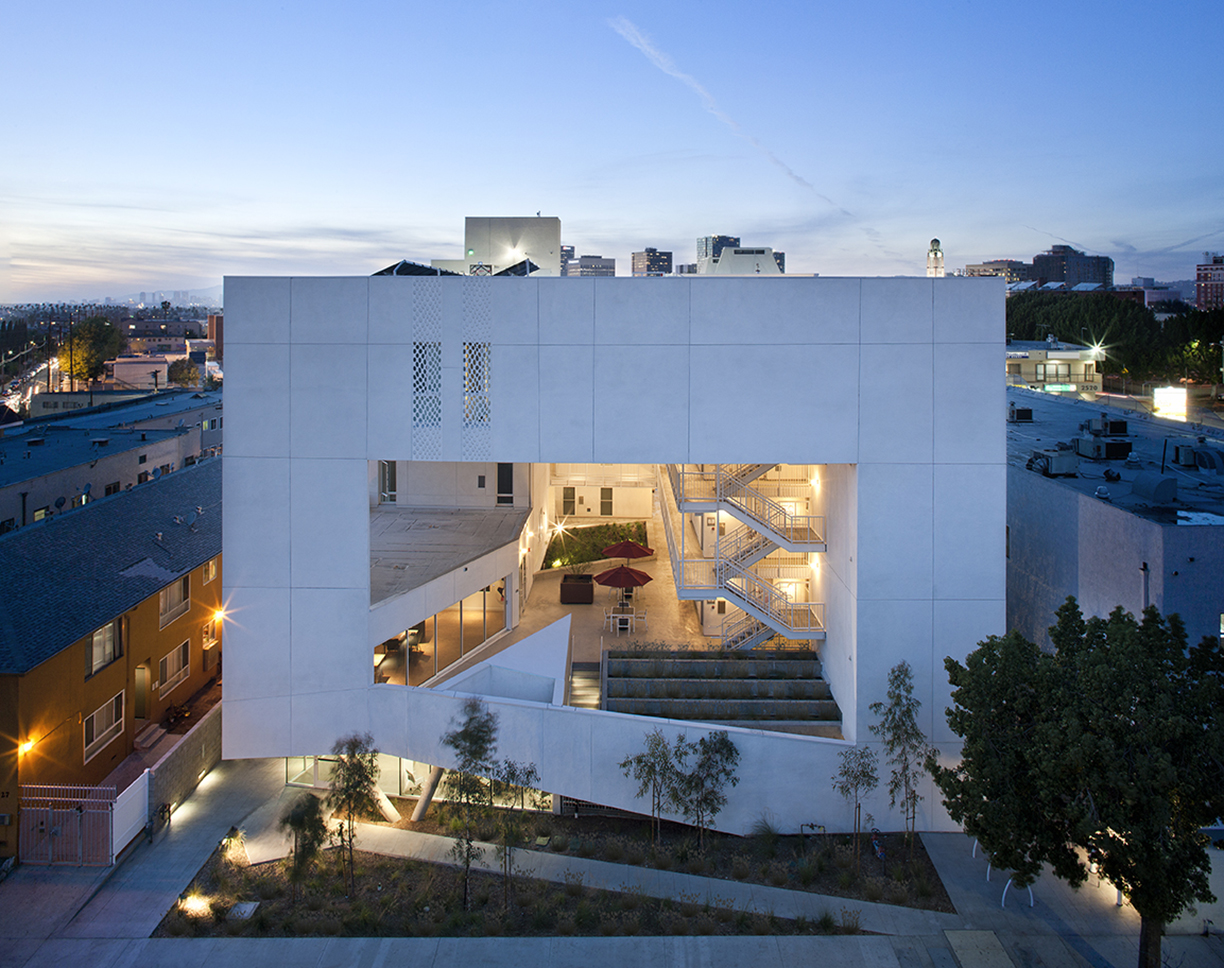
 Few cities in the world are grappling with homelessness and a severe lack of housing affordability like Los Angeles. Brooks+Scarpa has built a practice addressing issues in the city and across the nation. For this multifamily residential, The SIX was designed as a 52-unit affordable housing project that “provides a home, support services and rehabilitation for previously homeless and/or disabled veterans.”
Few cities in the world are grappling with homelessness and a severe lack of housing affordability like Los Angeles. Brooks+Scarpa has built a practice addressing issues in the city and across the nation. For this multifamily residential, The SIX was designed as a 52-unit affordable housing project that “provides a home, support services and rehabilitation for previously homeless and/or disabled veterans.”
Located in the MacArthur Park area of Los Angeles, The SIX was made to break the mold of multifamily housing by creating public and private “zones” in which private space was deemphasized to create large public areas. At ground level, the program includes support spaces for veterans, as well as bike storage, parking and offices. The second level is the core of the project, with a large, public courtyard. The idea was to create a community-oriented, interactive space that opens to its surroundings.
Jinshan 9
Steffian Bradley Architects, Shenzhen, China
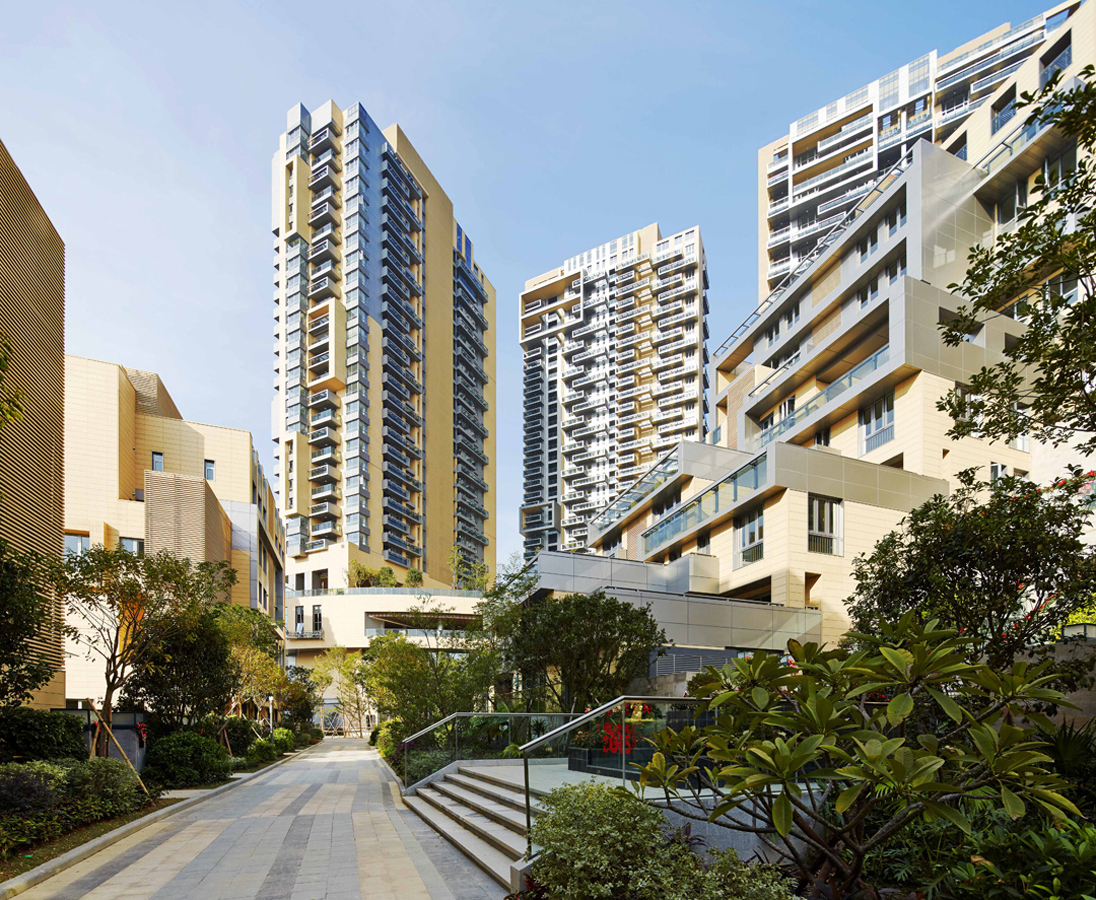
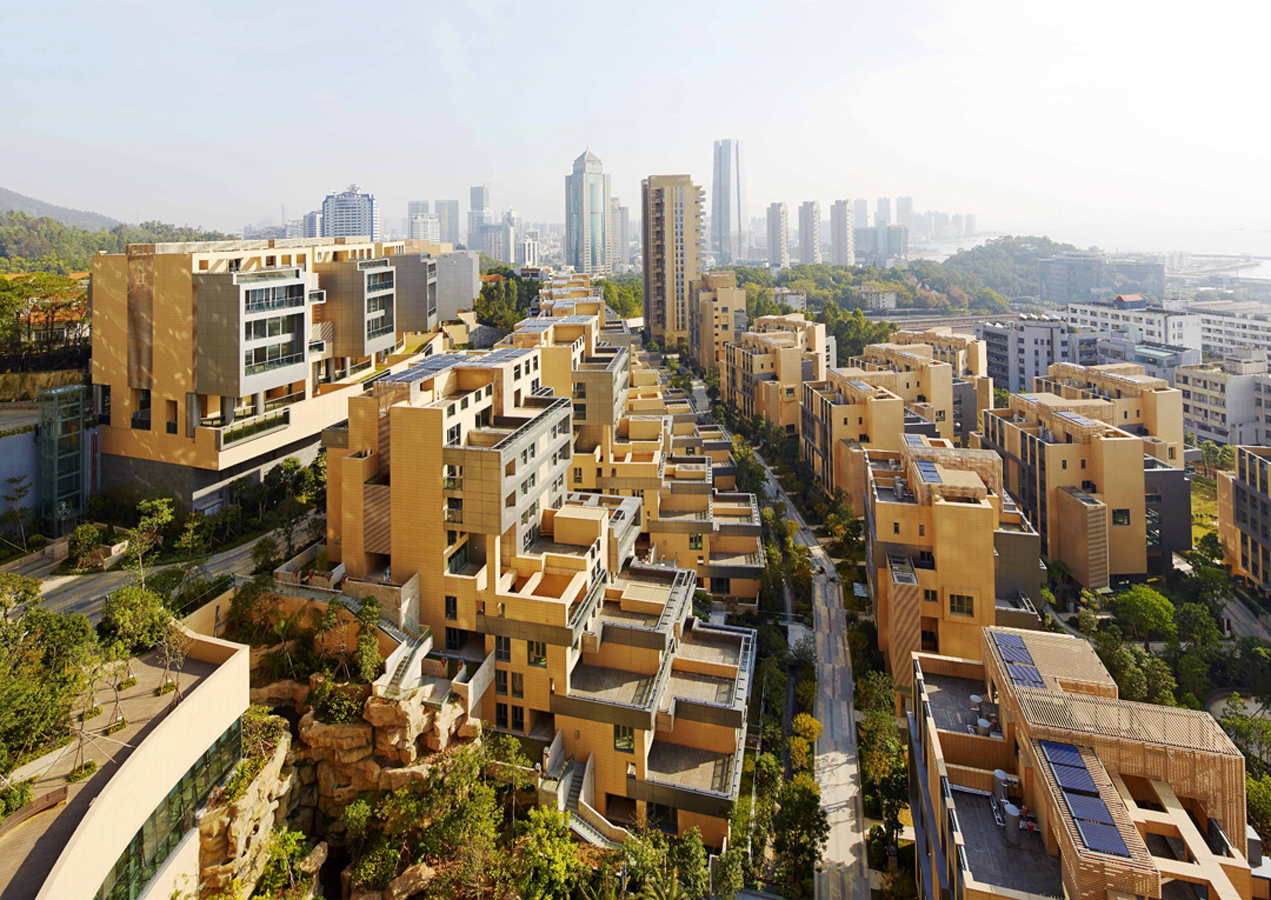
 Over the last two decades, development in China has been defined by a dizzying pace and new architecture produce in-mass. For Jinshan 9, this force behind new buildings was directed into a multifamily living community. Located in China’s Shekou mixed-use district, the project looks out west to wild, forested mountains and east to Shenzhen Bay Bridge. With a range of both low-rise and high-rise structures, the development was made for diverse lifestyles and populations.
Over the last two decades, development in China has been defined by a dizzying pace and new architecture produce in-mass. For Jinshan 9, this force behind new buildings was directed into a multifamily living community. Located in China’s Shekou mixed-use district, the project looks out west to wild, forested mountains and east to Shenzhen Bay Bridge. With a range of both low-rise and high-rise structures, the development was made for diverse lifestyles and populations.
With 210 townhouse units, the project also has four residential towers rising 32 floors in height. Between integrated pedestrian paths and trails, the development comprises a network of gardens and interconnected terraces. From its material palette, Jinshan 9 includes natural-colored terracotta panels with aluminum trim on the exterior. This combines with marine-inspired imagery and forms, like balcony details echoing sailboat decks.
Architects: Want to have your project featured? Showcase your work through Architizer and sign up for our inspirational newsletters.
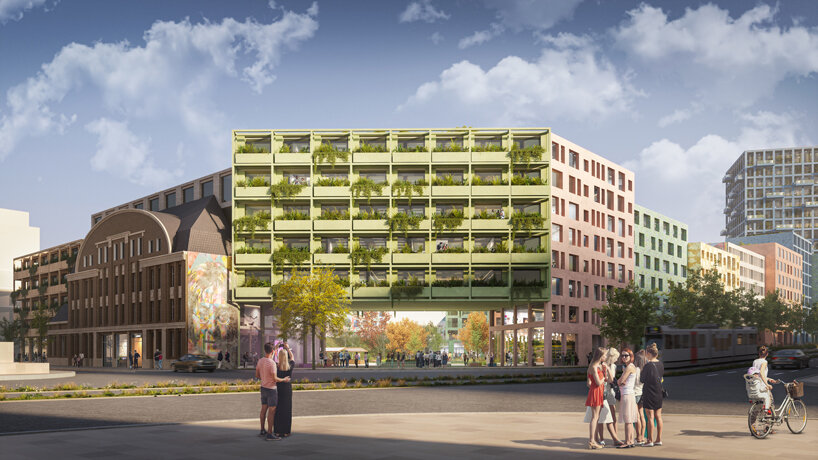
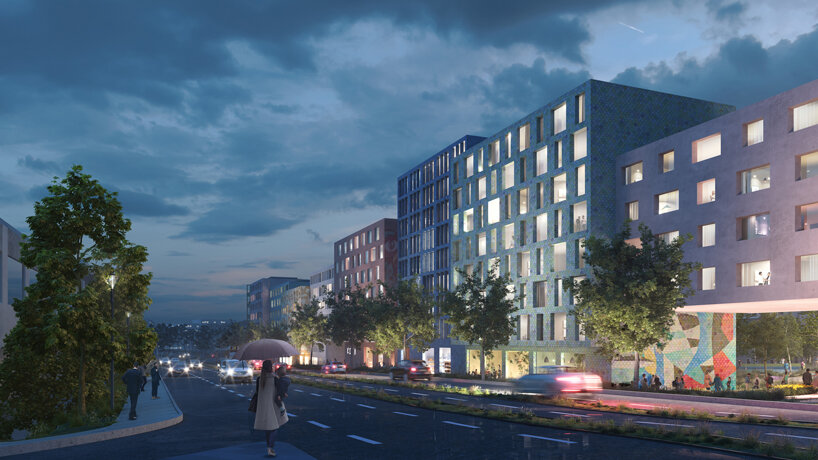
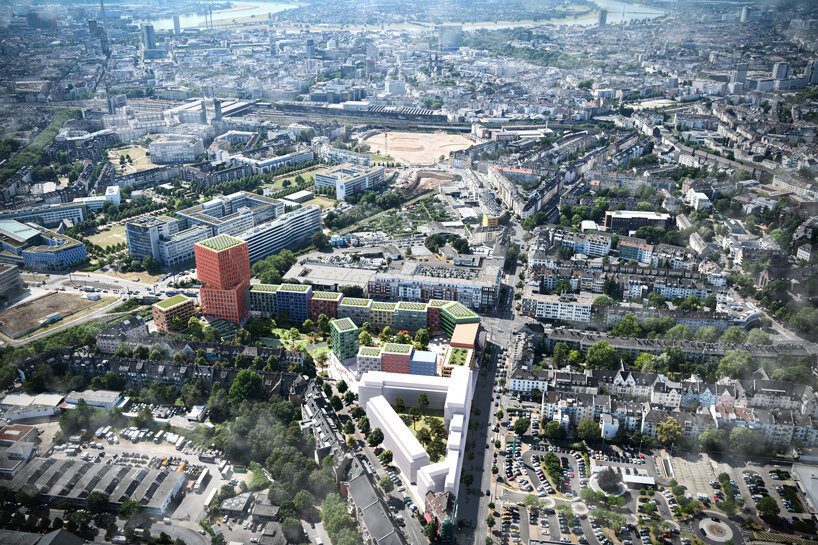
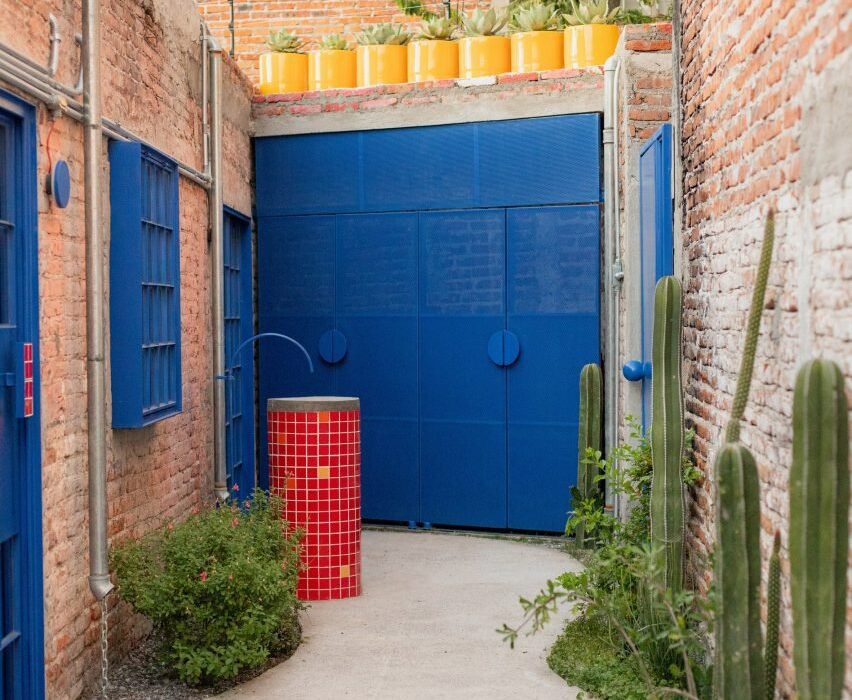
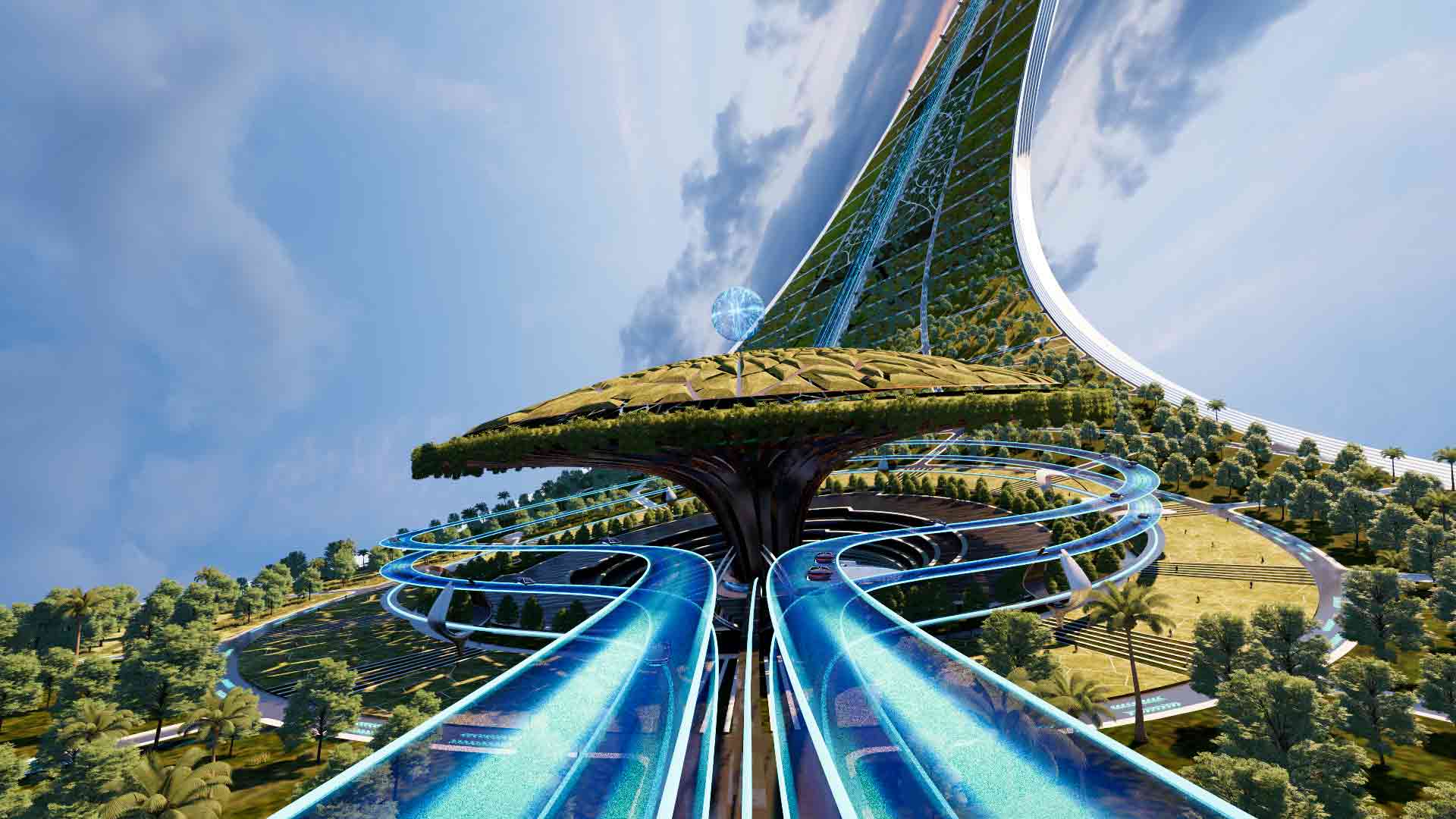














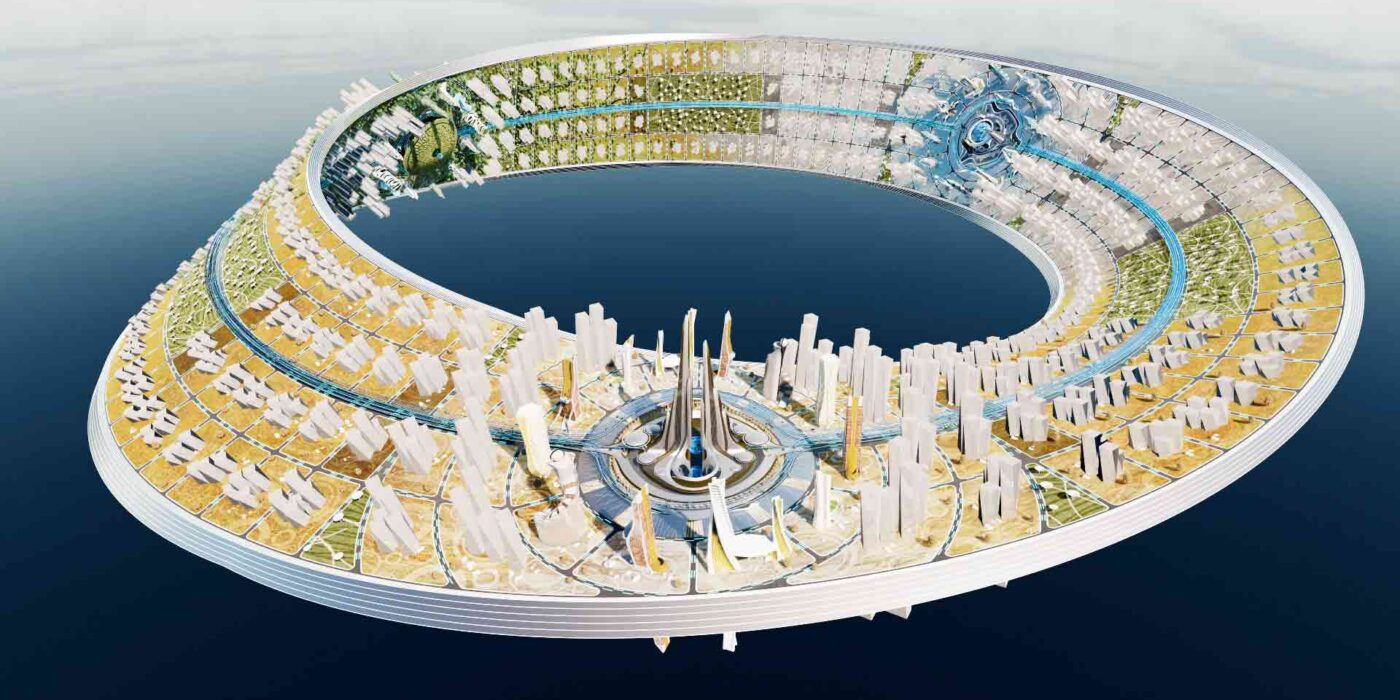
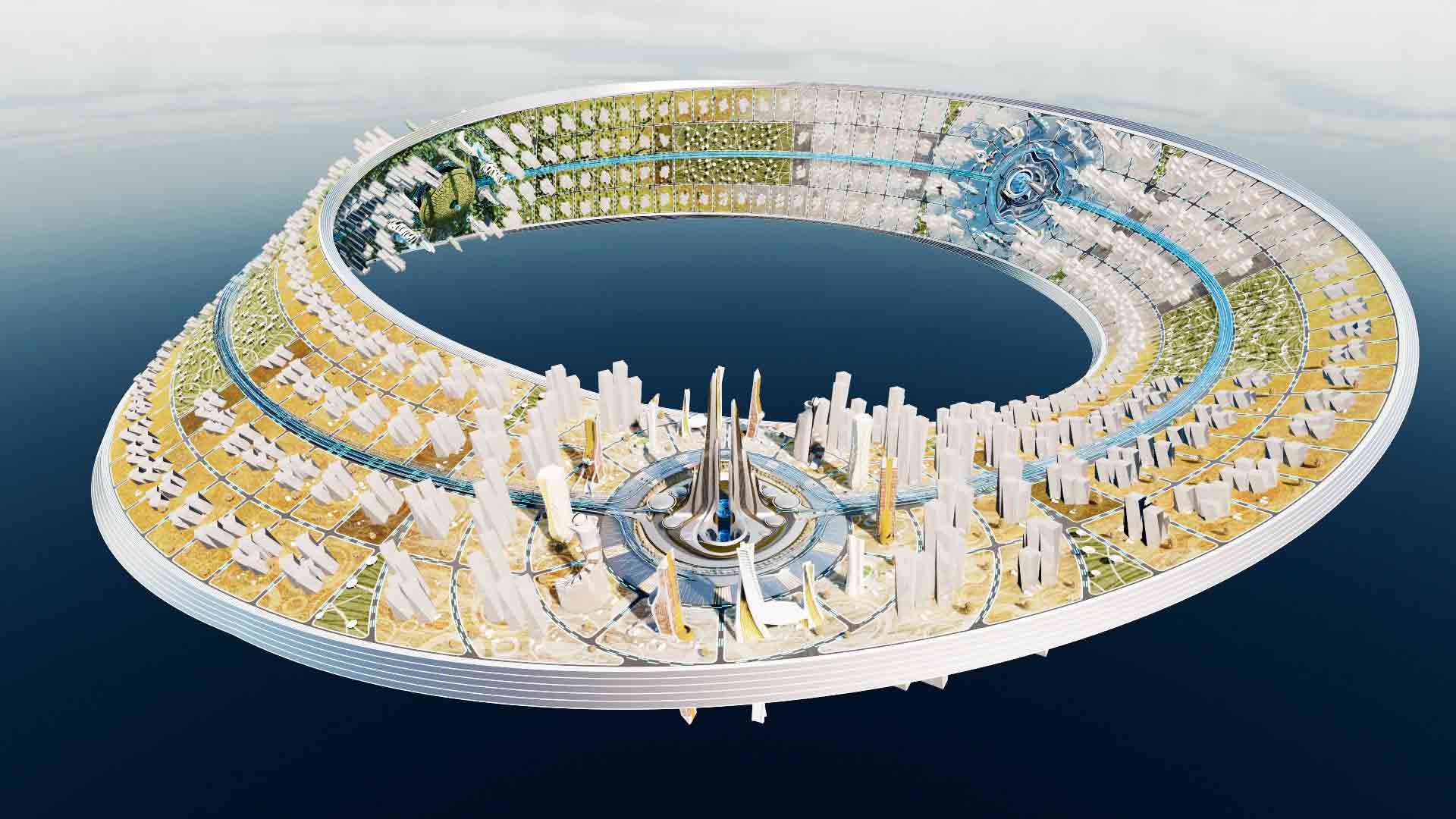
 This metaverse masterplan is designed for a futuristic, dystopian world in which global warming has flooded the Earth, rendering it uninhabitable. The Metacity will consist of five cities, the first of which will take the form of a Möbius strip, hovering above the ocean. The city will function as a self-contained eco-system, featuring a gravity-coated surface that generates perpendicular gravity.
This metaverse masterplan is designed for a futuristic, dystopian world in which global warming has flooded the Earth, rendering it uninhabitable. The Metacity will consist of five cities, the first of which will take the form of a Möbius strip, hovering above the ocean. The city will function as a self-contained eco-system, featuring a gravity-coated surface that generates perpendicular gravity.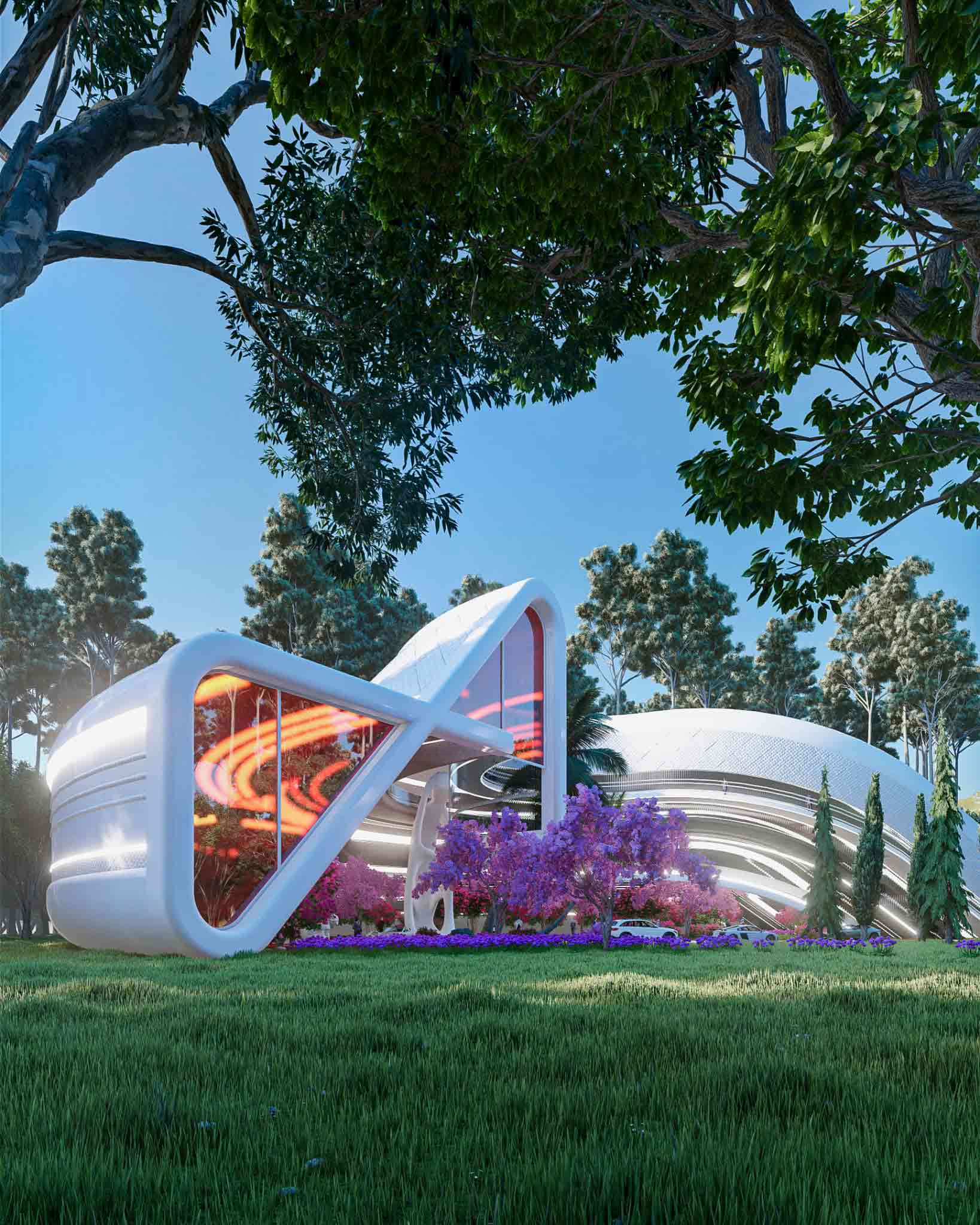
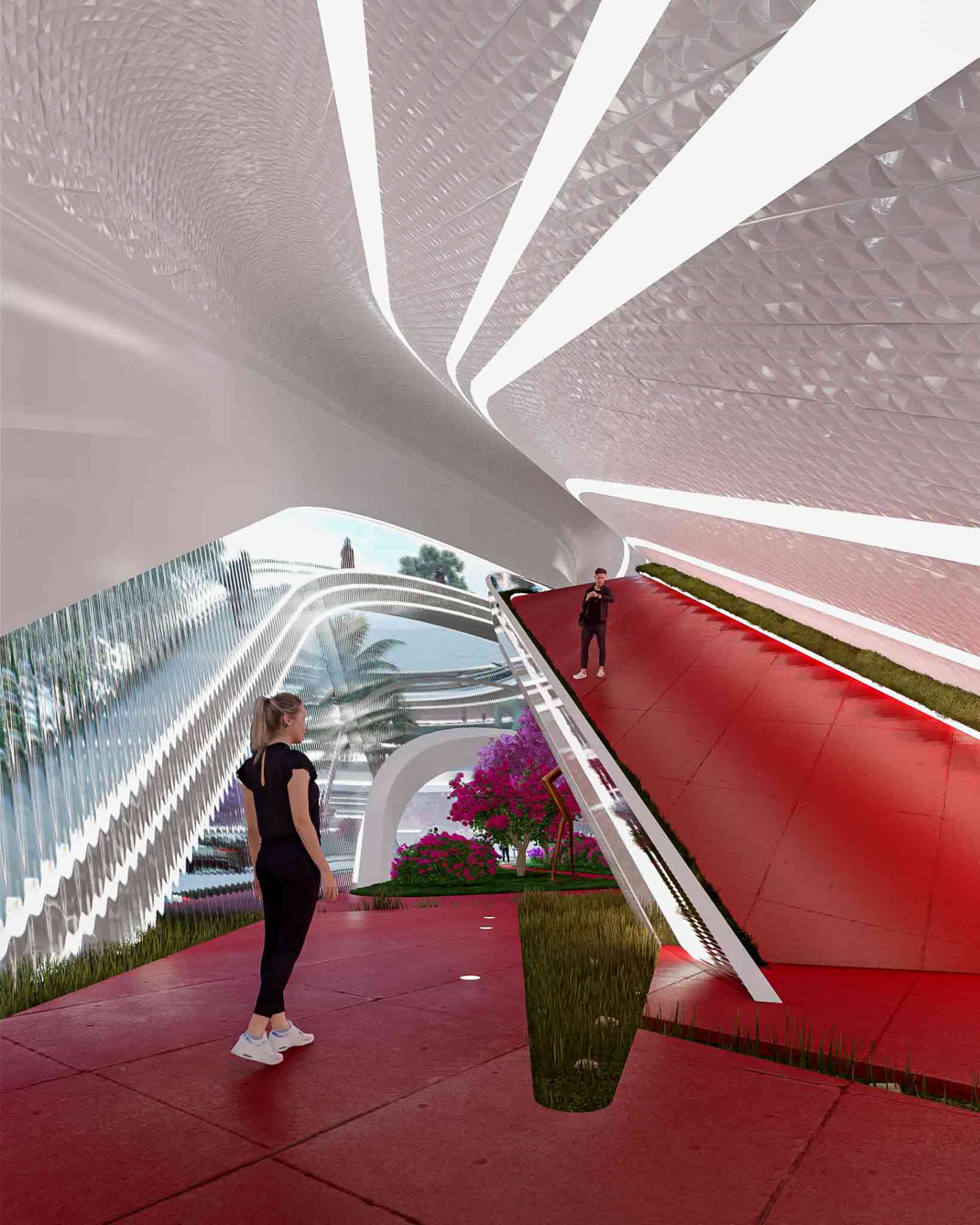 One of the unique draws of the metaverse is its ability to bridge the voids of geography. You can share the same virtual space as someone thousands of miles away — no arduous traveling required. It makes sense then to leverage this new realm as a business and networking tool.
One of the unique draws of the metaverse is its ability to bridge the voids of geography. You can share the same virtual space as someone thousands of miles away — no arduous traveling required. It makes sense then to leverage this new realm as a business and networking tool.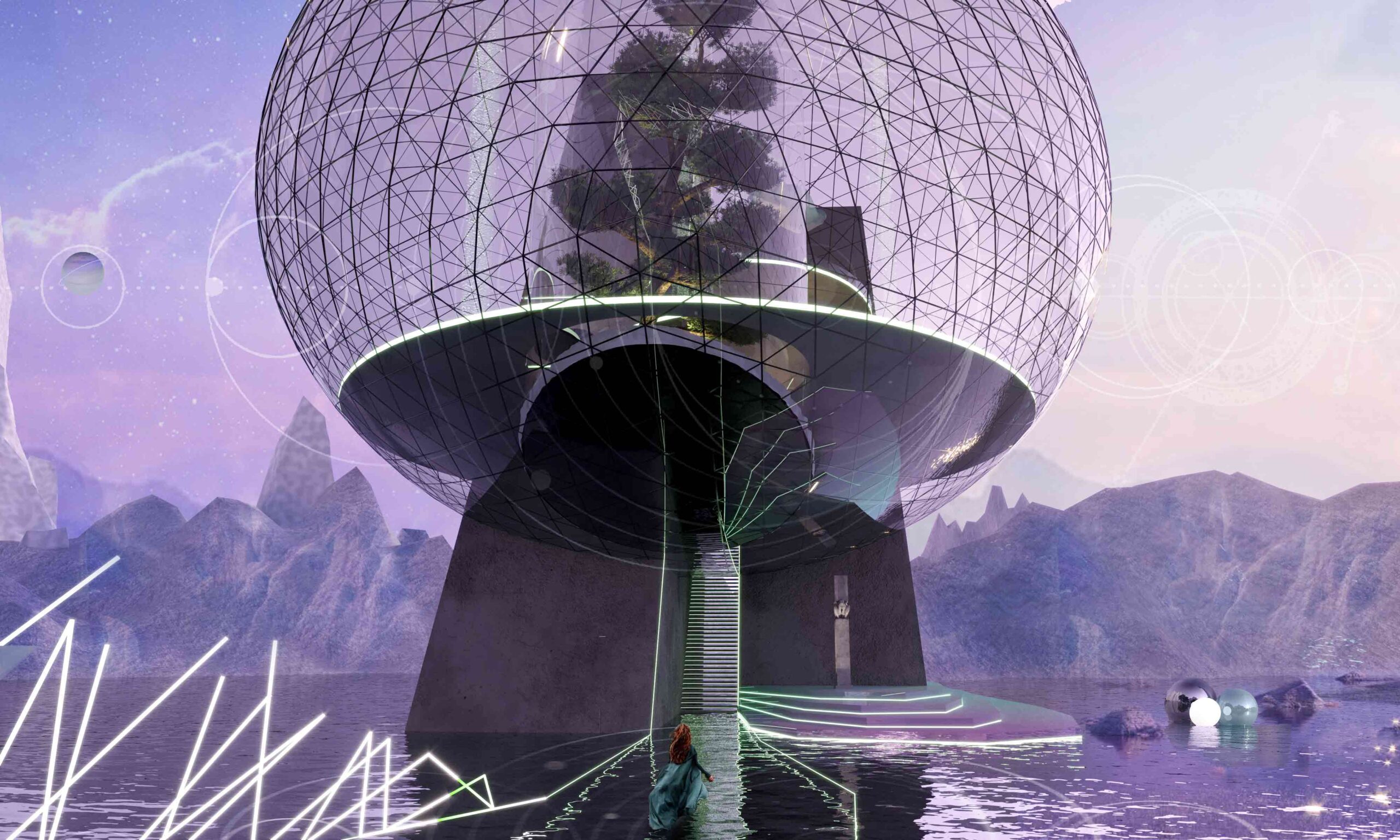
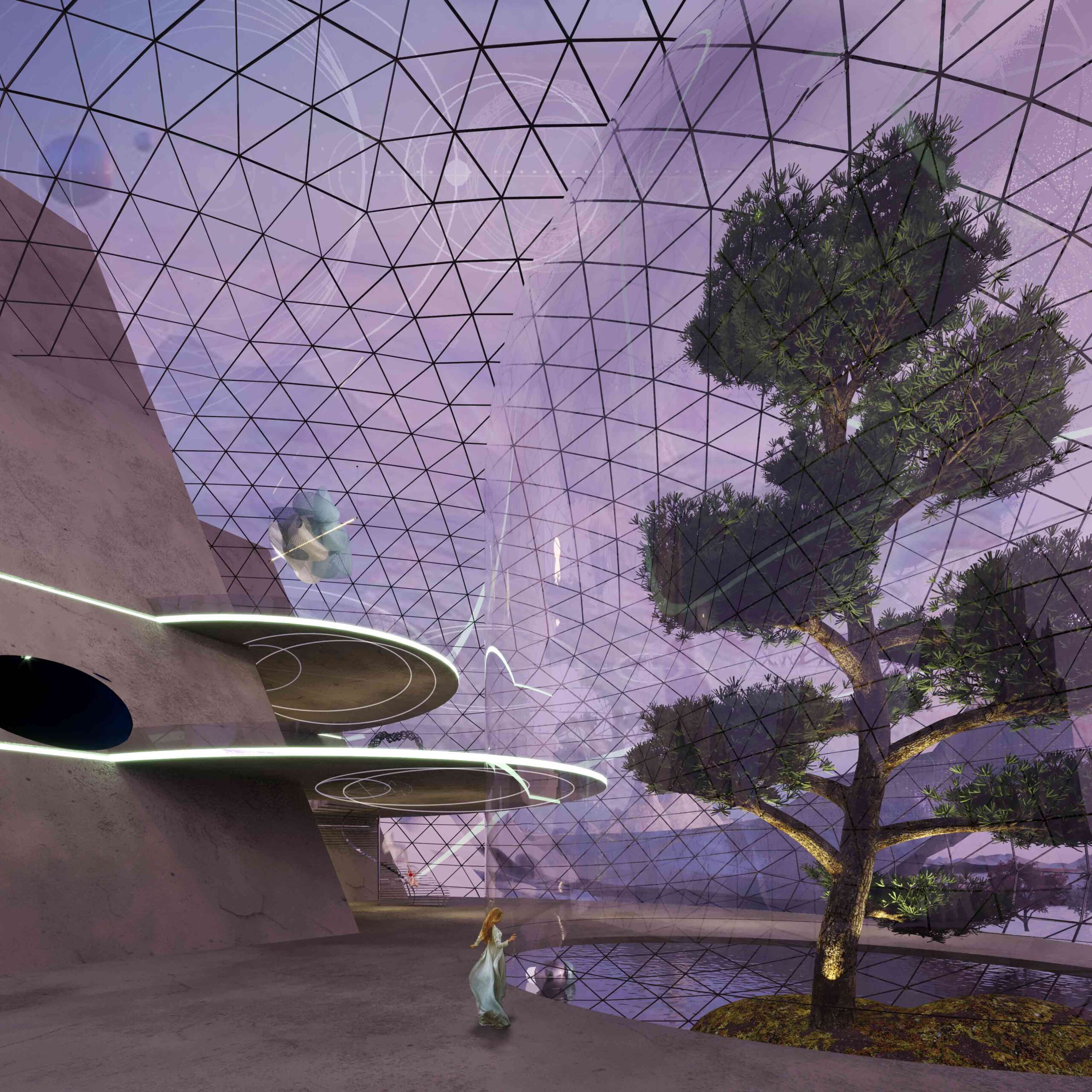 Defined by its amethyst hues and the glass globe at its heart, the Unusualverse is conceived as a plain of artistic community. A reaction to the The term ‘metaverse’ first appeared in the 1992 dystopian novel, but in more recent years, fiction has truly become (virtual) reality. of the physical world, this new virtual reality universe offers a space for creativity to flourish, at a distance from the pressures of society and day-to-day life.
Defined by its amethyst hues and the glass globe at its heart, the Unusualverse is conceived as a plain of artistic community. A reaction to the The term ‘metaverse’ first appeared in the 1992 dystopian novel, but in more recent years, fiction has truly become (virtual) reality. of the physical world, this new virtual reality universe offers a space for creativity to flourish, at a distance from the pressures of society and day-to-day life.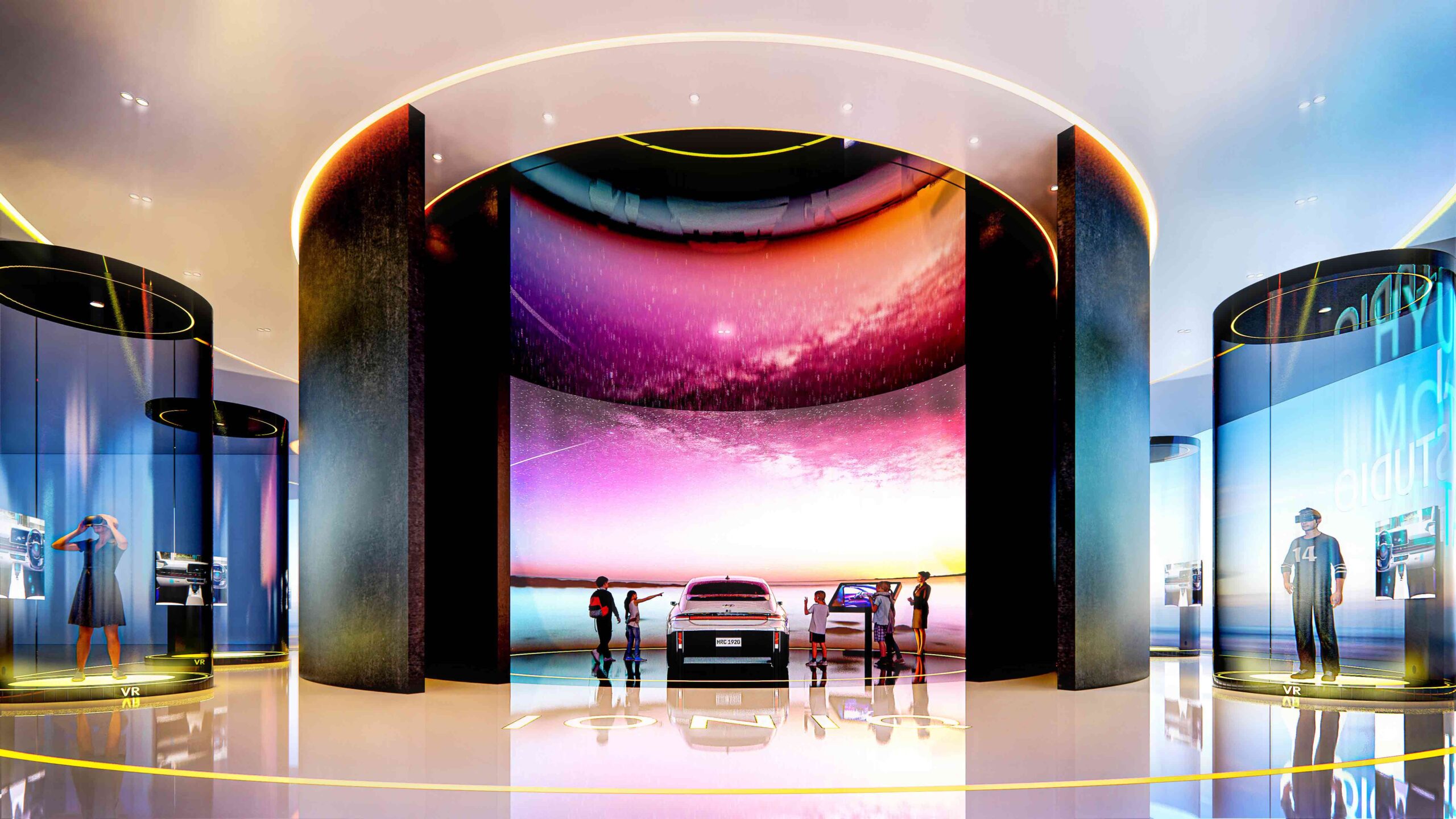
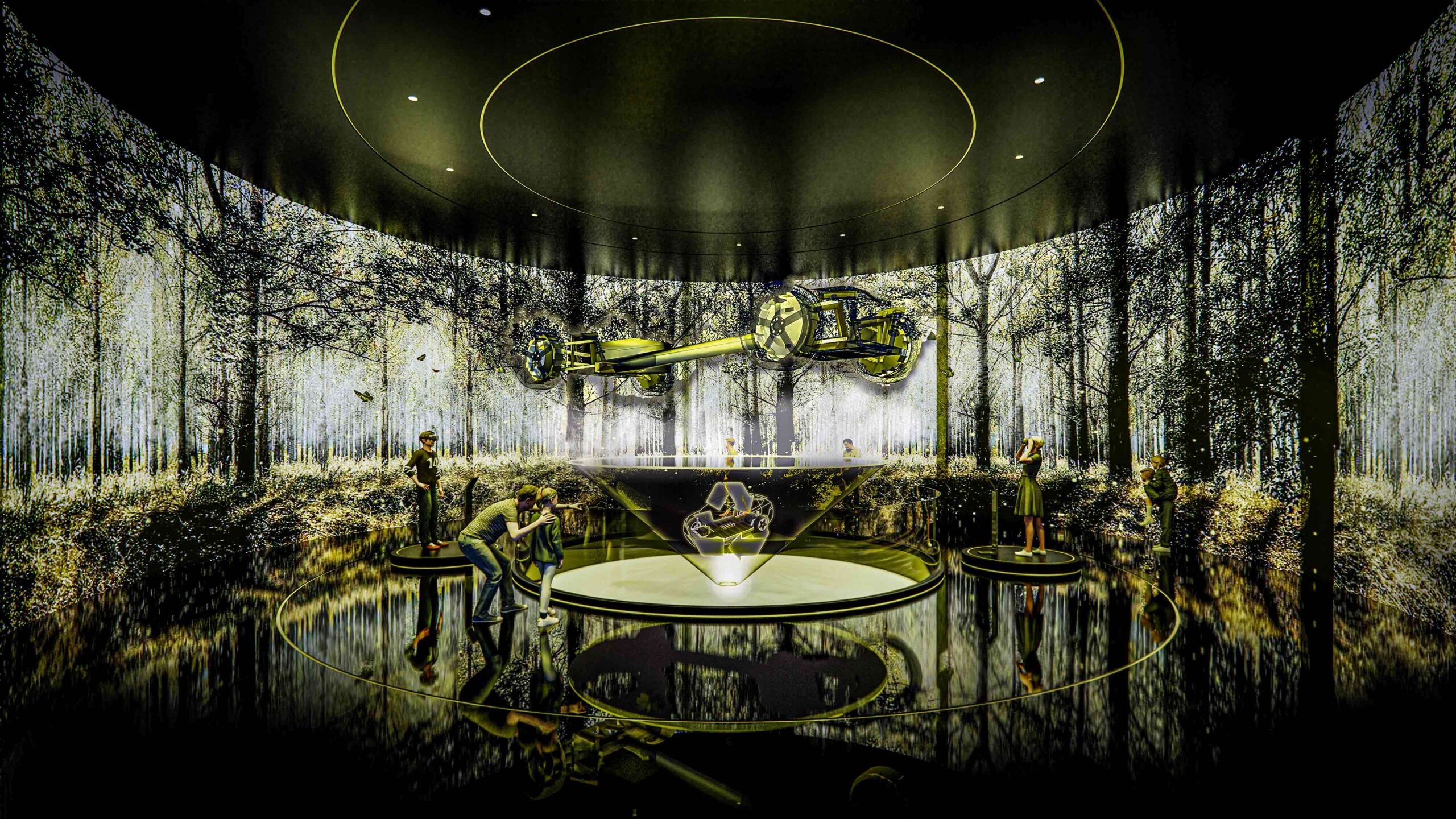 A car showroom with a difference, this innovative concept space deftly combines reality and virtual reality. In contrast to the other projects in this round-up, the exhibition hall was designed for a real-world location: Yongsan-gu, Seoul. Created to promote eco-friendly vehicles, the metaverse fuses with the material fabric of the space, conjuring up new horizons of exploration.
A car showroom with a difference, this innovative concept space deftly combines reality and virtual reality. In contrast to the other projects in this round-up, the exhibition hall was designed for a real-world location: Yongsan-gu, Seoul. Created to promote eco-friendly vehicles, the metaverse fuses with the material fabric of the space, conjuring up new horizons of exploration.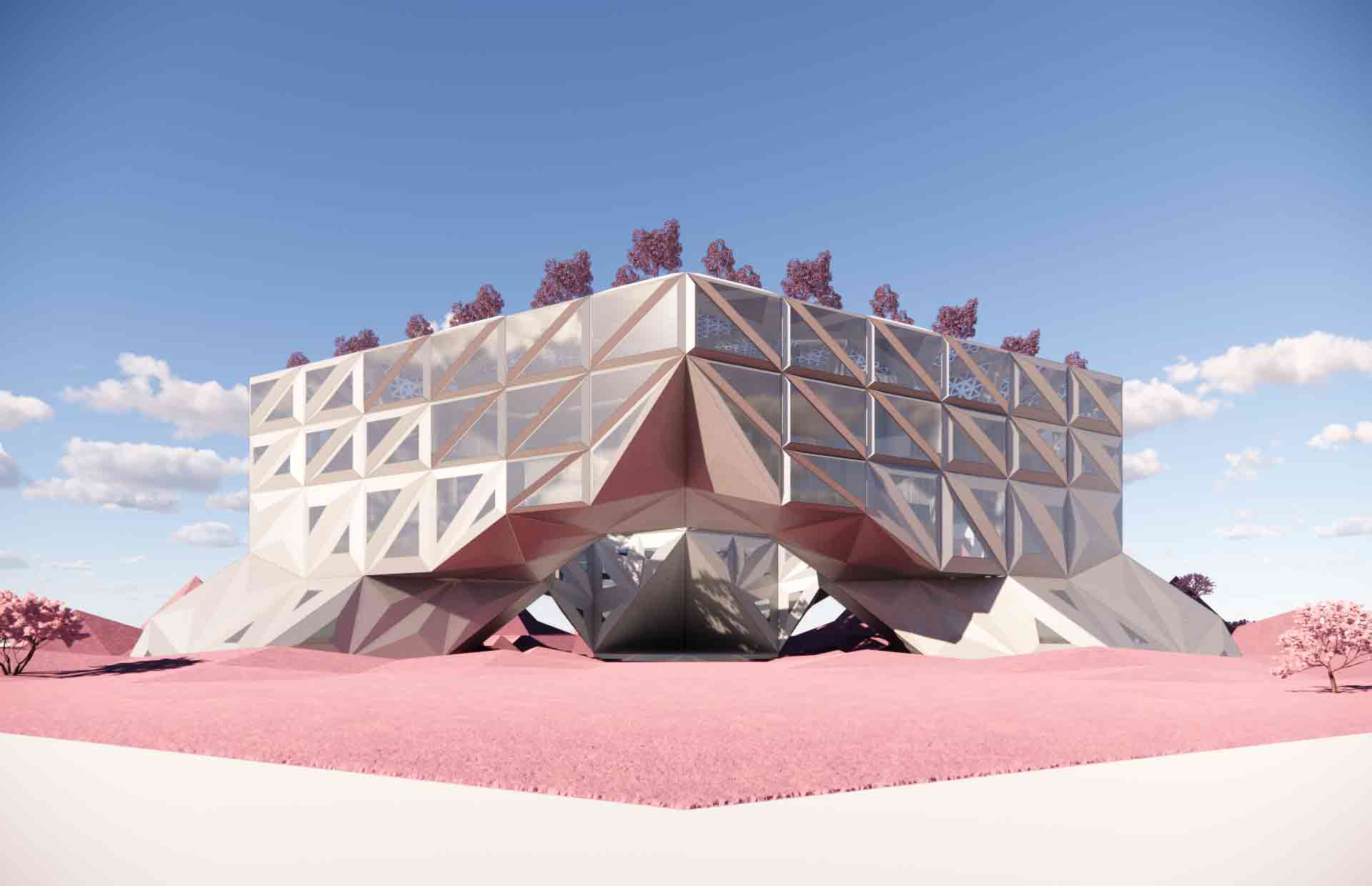
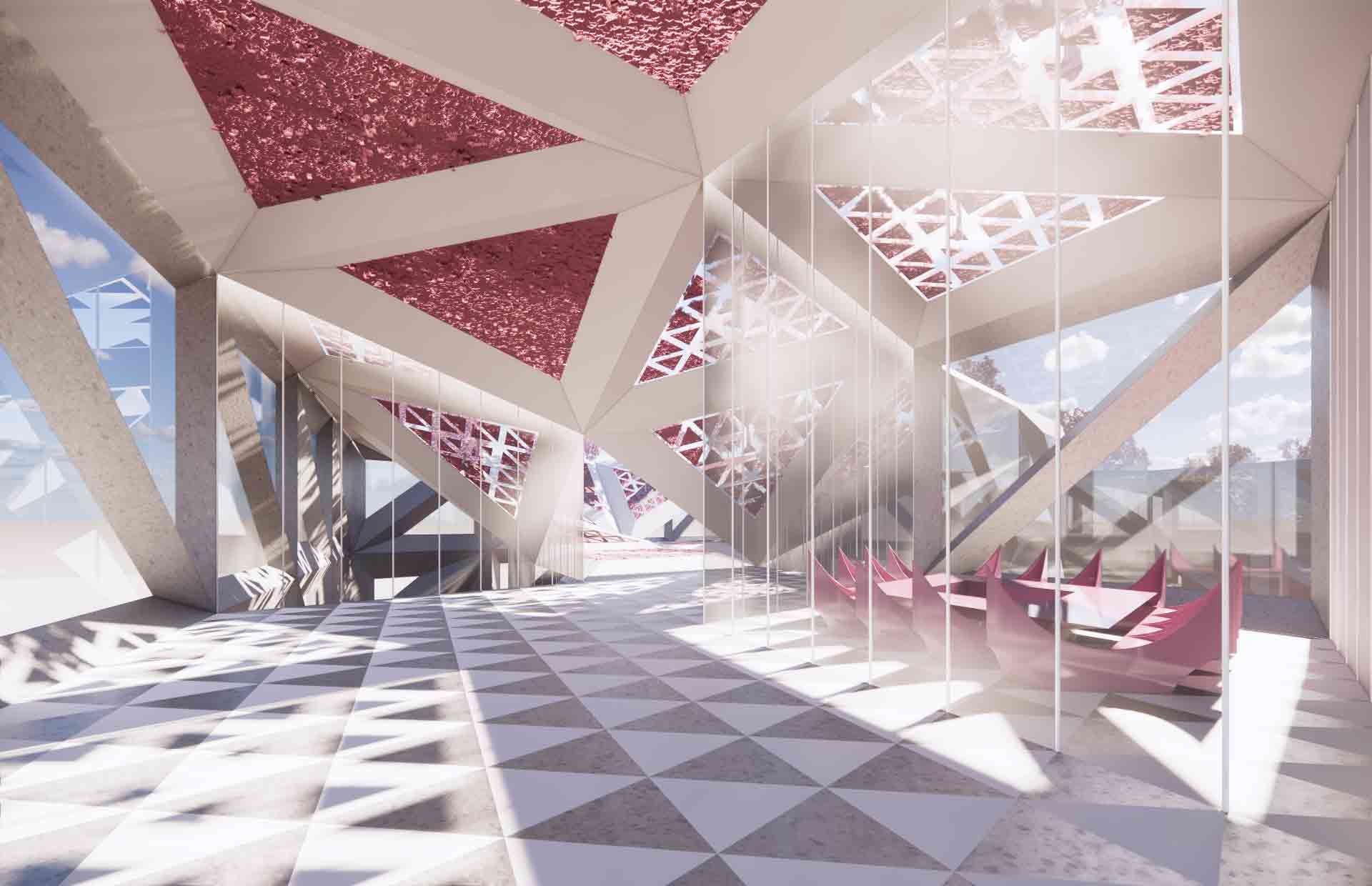 HWKN Architecture was chosen to design a virtual cultural hub by metaverse company Pax.World. Dubbed a metaserai, the concept was inspired by
HWKN Architecture was chosen to design a virtual cultural hub by metaverse company Pax.World. Dubbed a metaserai, the concept was inspired by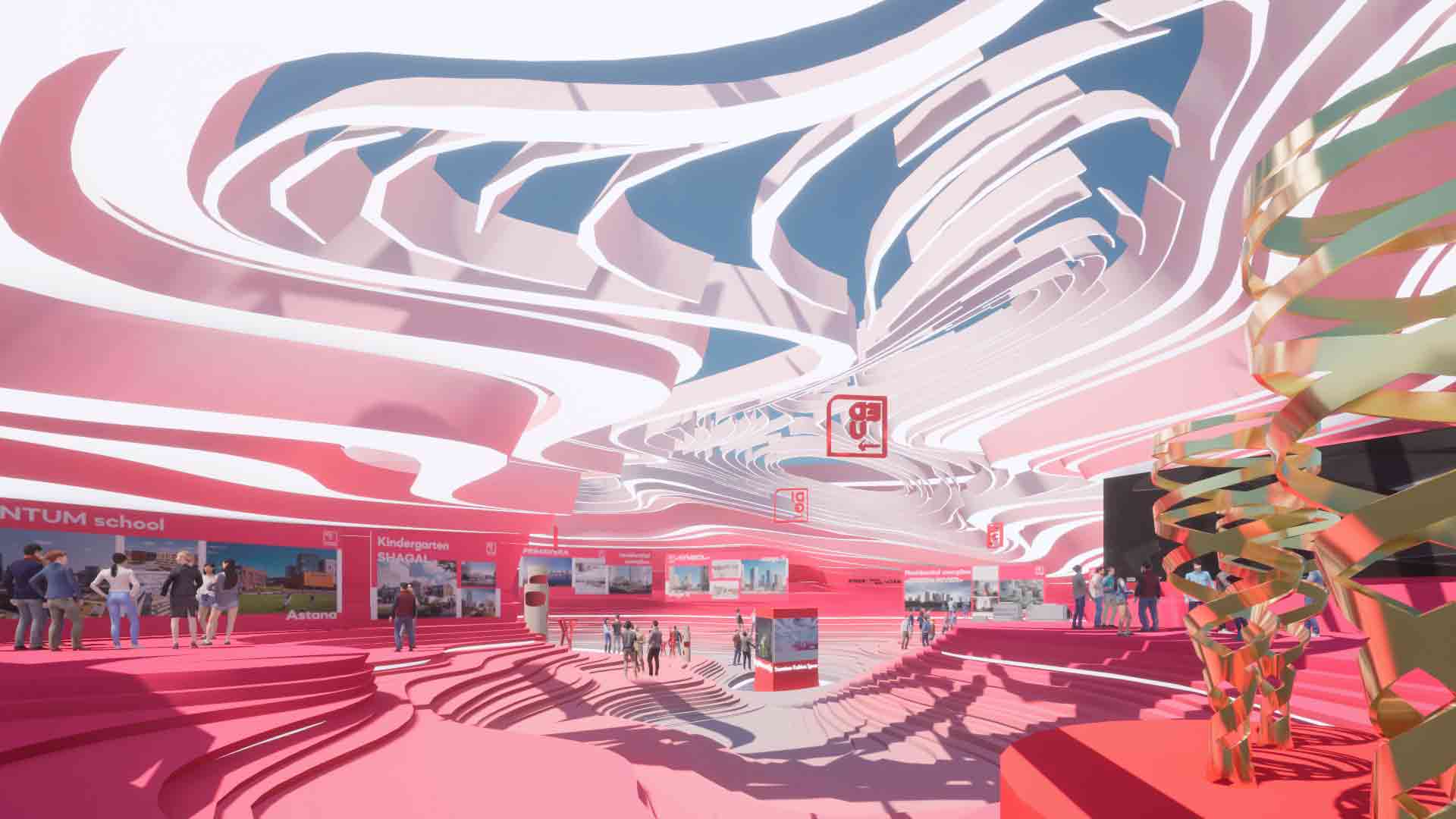 
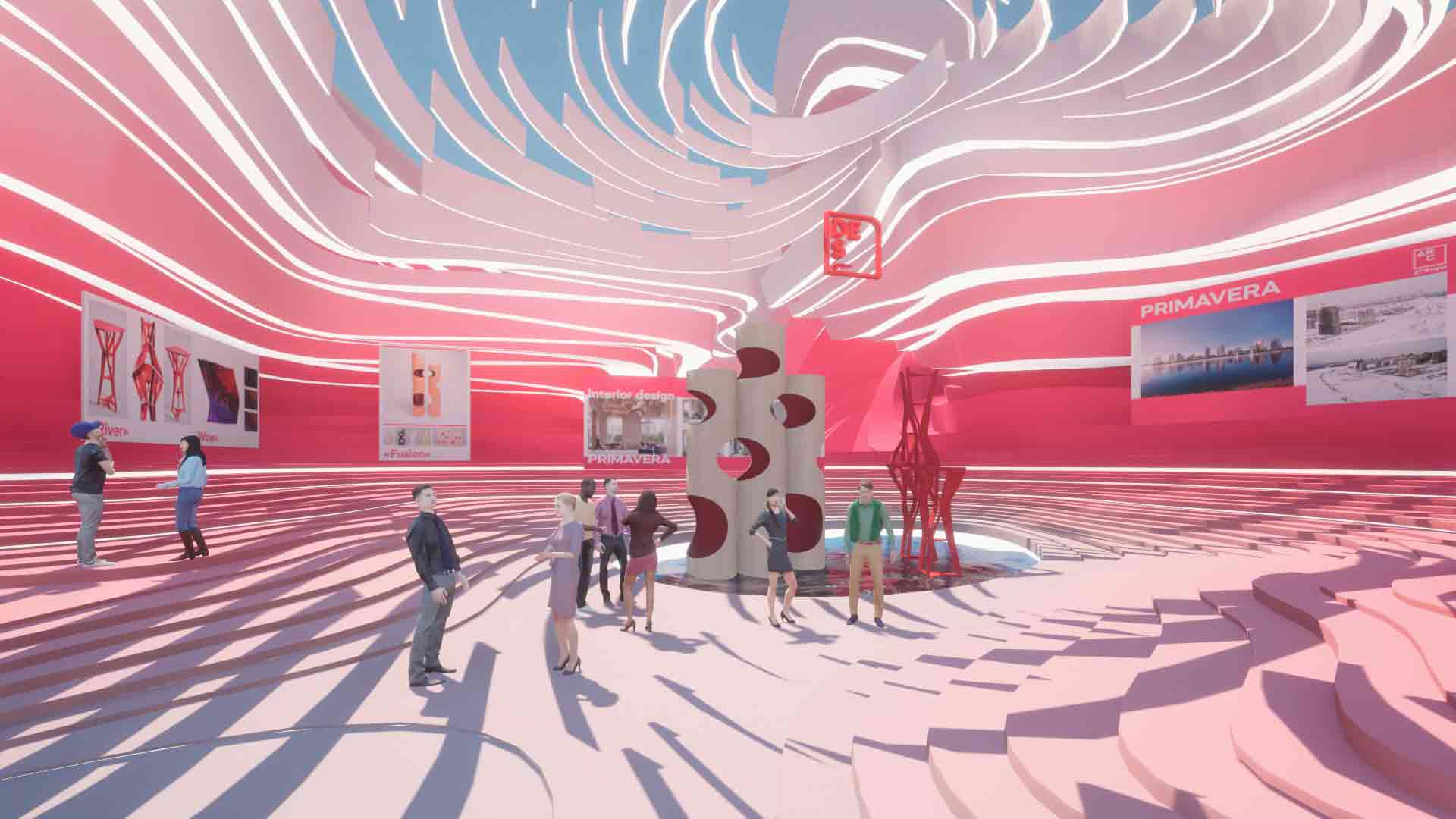 A virtual gallery showcasing the work of architecture firm ATRIUM, this dynamic, cave-like space envelops users with its curvilinear lines. Forming a rippling, multi-layered terrain, pale pink blurs into hot pink hues across the floor and walls, before cooling to white across the ceiling, where architectural elements hang in the air.
A virtual gallery showcasing the work of architecture firm ATRIUM, this dynamic, cave-like space envelops users with its curvilinear lines. Forming a rippling, multi-layered terrain, pale pink blurs into hot pink hues across the floor and walls, before cooling to white across the ceiling, where architectural elements hang in the air.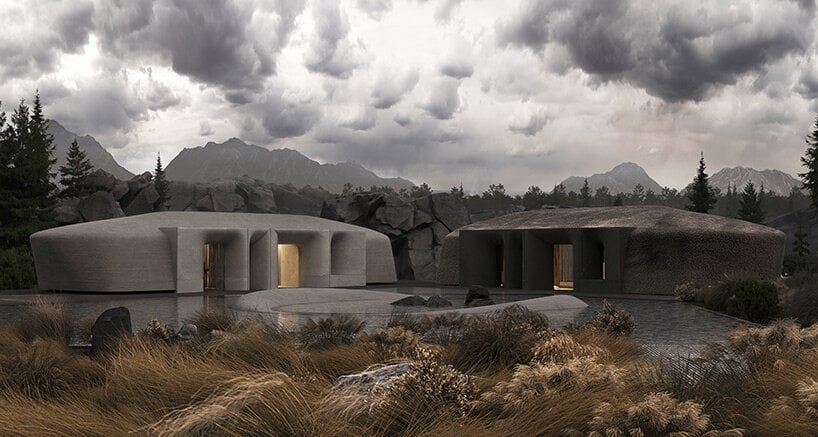
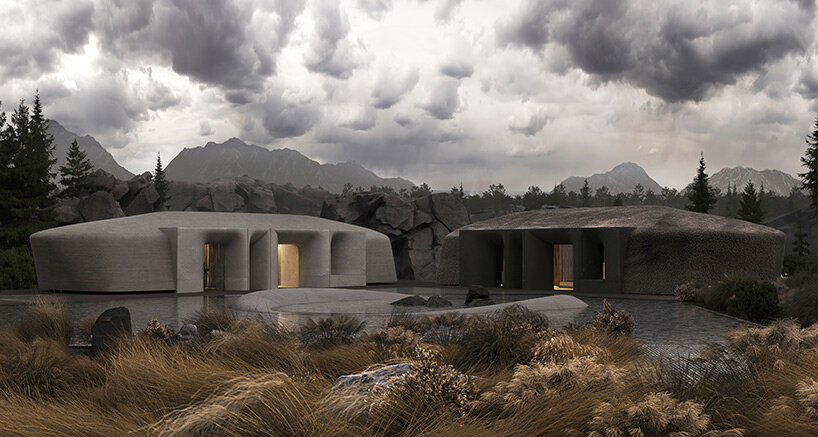 visualizations © MAKHNO Studio
visualizations © MAKHNO Studio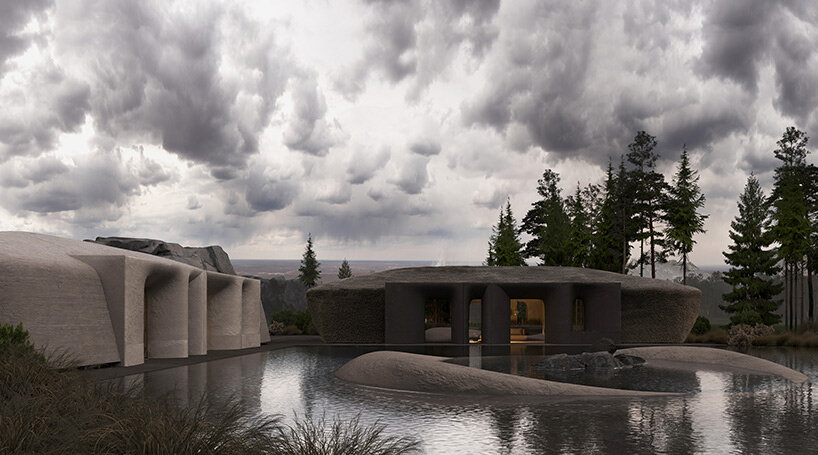
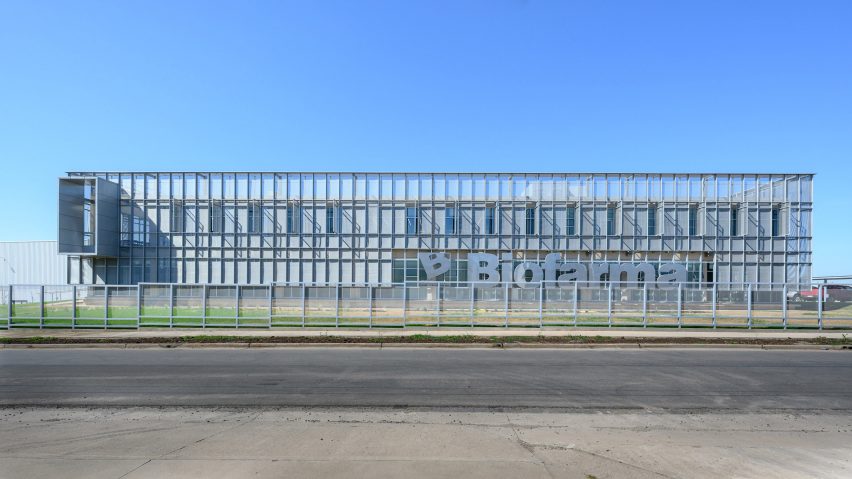
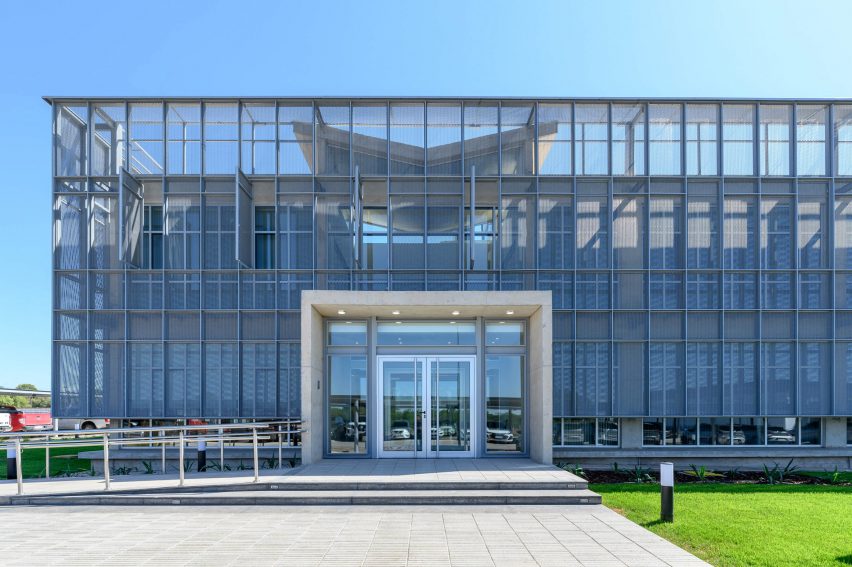
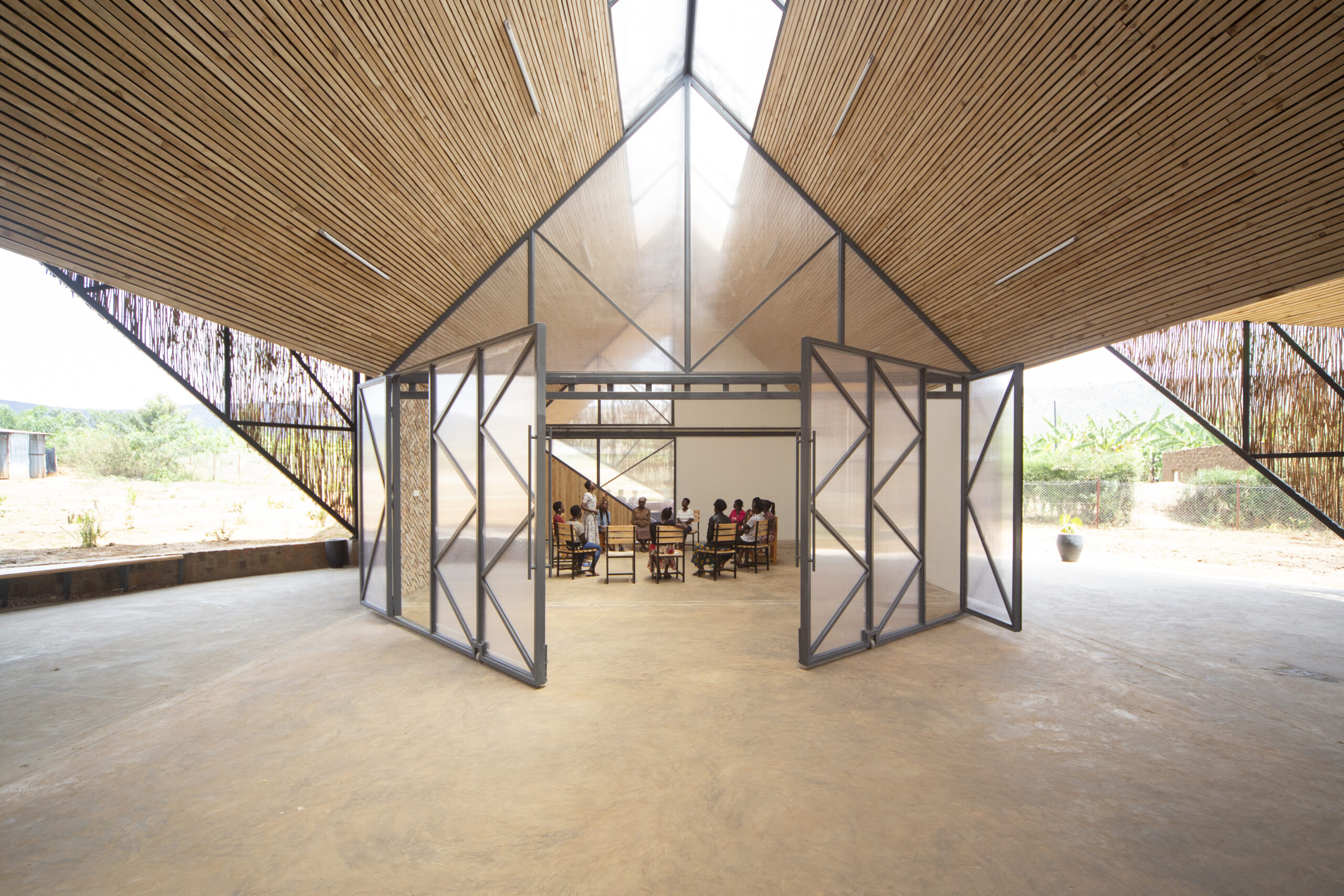
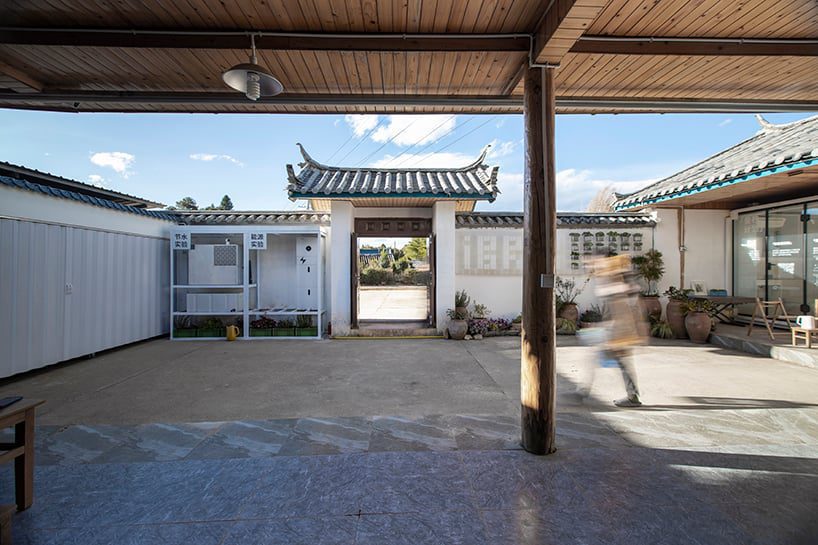
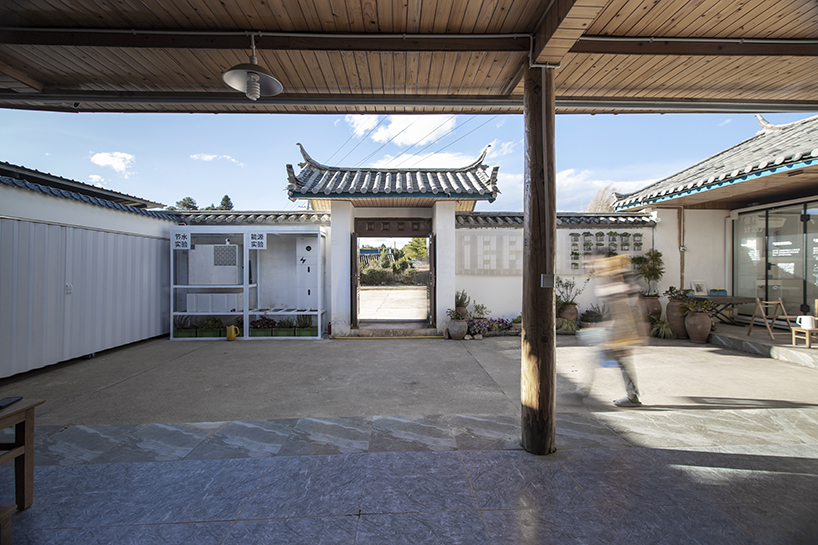
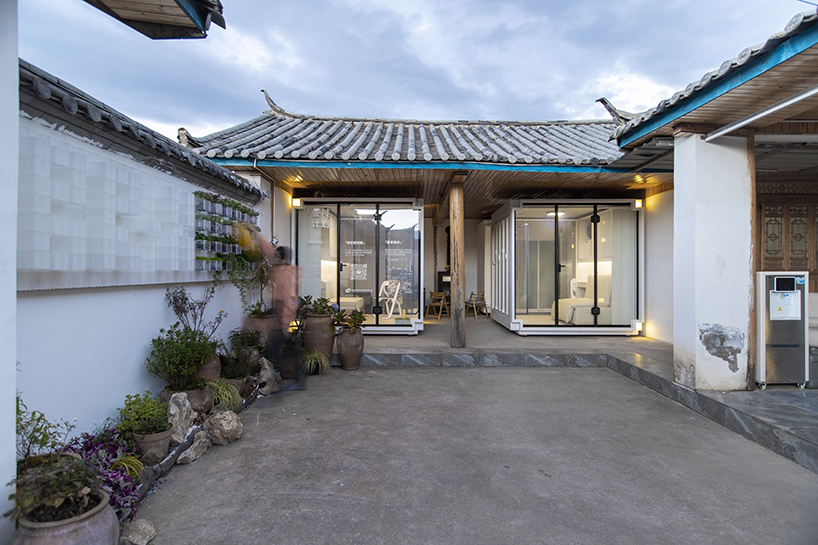
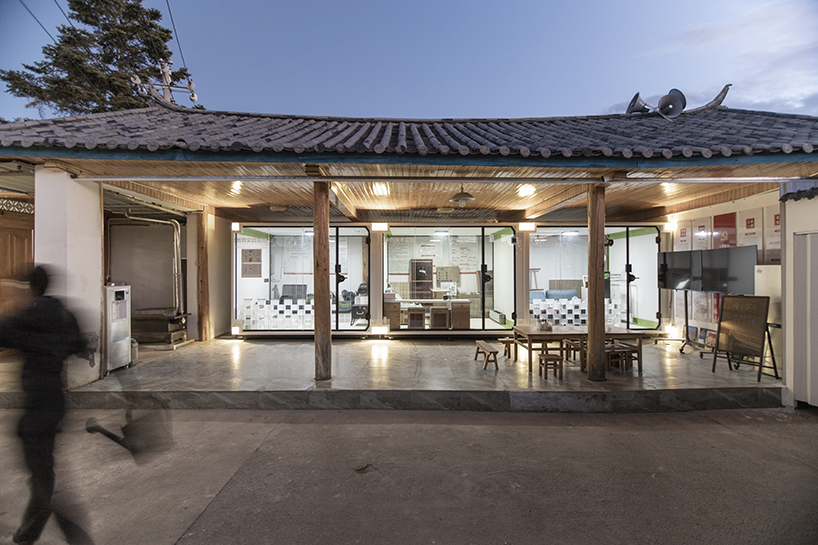
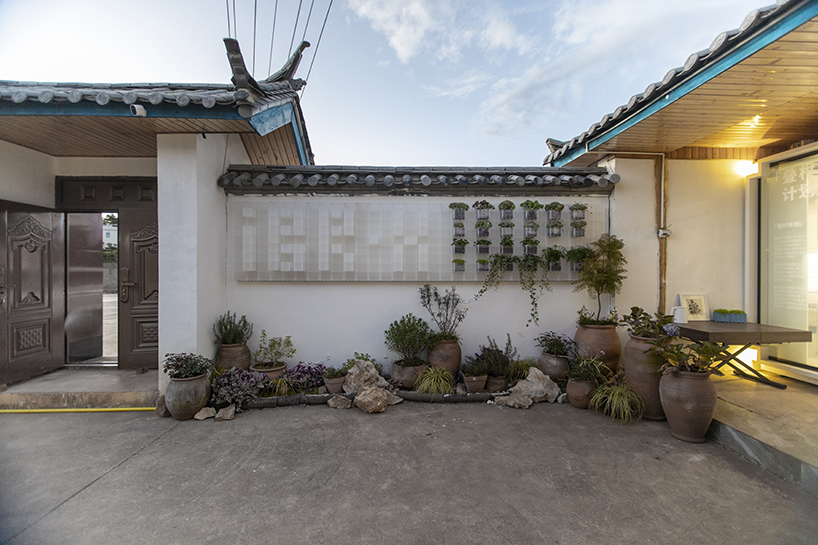
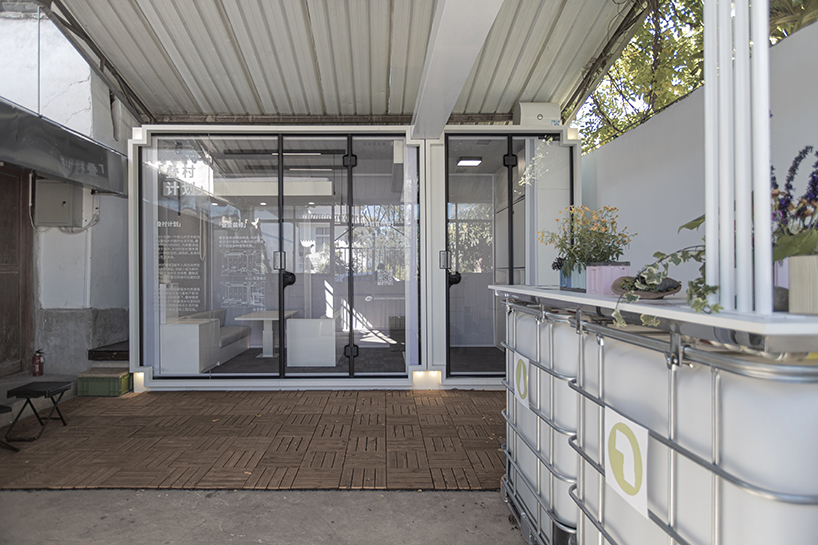
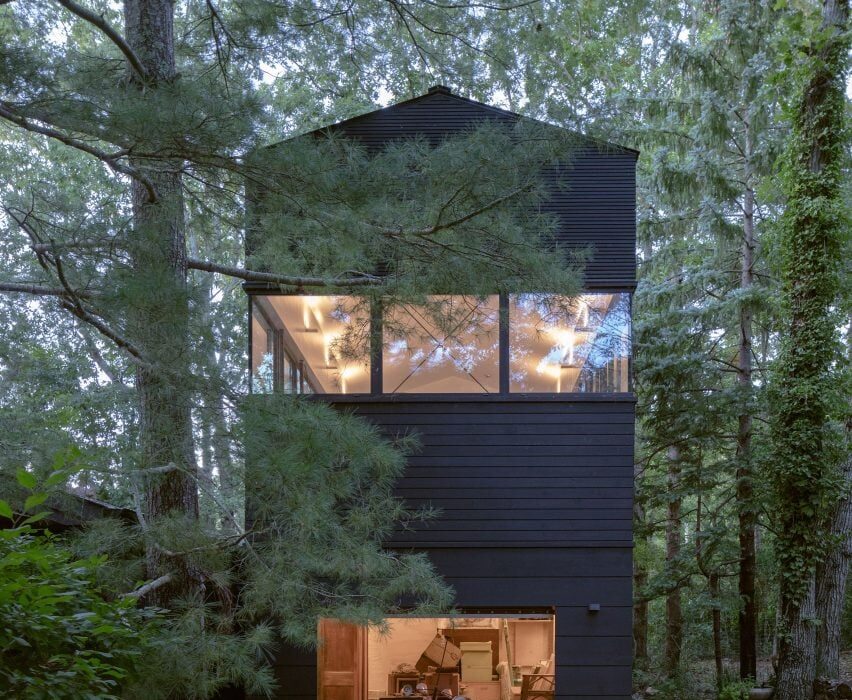































 New York is a city known for housing scarcity, and a place that’s defined by reinvention. For Timber House, MESH Architectures was inspired by natural finishes and “botanical architecture.” The idea was not only to foster well-being, but create a new model for timber construction in the city. The project is the first mass-timber condominium in New York, and the structure was built with glue-laminated timber columns, beams, and floor plates. The six-story, multifamily project is comprised of fourteen homes.
New York is a city known for housing scarcity, and a place that’s defined by reinvention. For Timber House, MESH Architectures was inspired by natural finishes and “botanical architecture.” The idea was not only to foster well-being, but create a new model for timber construction in the city. The project is the first mass-timber condominium in New York, and the structure was built with glue-laminated timber columns, beams, and floor plates. The six-story, multifamily project is comprised of fourteen homes.
 MVRDV has earned a reputation for reinvention and creating new building forms. That same approach extends to housing, where the team designed Valley with a more “green and human” touch. Built for developer Edge, the project is located in Amsterdam Zuidas. Rising to three distinct towers, the façades shift across the complex. The outer edges are mirrored glass, while the inner façades are clad with stone and swaths of greenery.
MVRDV has earned a reputation for reinvention and creating new building forms. That same approach extends to housing, where the team designed Valley with a more “green and human” touch. Built for developer Edge, the project is located in Amsterdam Zuidas. Rising to three distinct towers, the façades shift across the complex. The outer edges are mirrored glass, while the inner façades are clad with stone and swaths of greenery.
 Few locations are more prominent for multifamily housing in St. Louis than Forest Park. Designed by Studio Gang, One Hundred is a residential tower overlooking the park and the studio’s first project in the city. The tower includes a mix of housing, retail and amenities on four-story stacked tiers. The apartments were designed for views of Forest Park and east to the Gateway Arch.
Few locations are more prominent for multifamily housing in St. Louis than Forest Park. Designed by Studio Gang, One Hundred is a residential tower overlooking the park and the studio’s first project in the city. The tower includes a mix of housing, retail and amenities on four-story stacked tiers. The apartments were designed for views of Forest Park and east to the Gateway Arch.
 The Cirqua project by BKK gained widespread recognition for creating beautiful, inventive multifamily architecture. The project includes 38 unique unit types out of the 42 total apartments made with spacious balconies and an integrated approach to landscaping. Combining two properties into a single block, the project was formed with careful attention paid to scale and the surrounding context. Cirqua not only showcases a smart, nuanced approach to multifamily housing, but also how to design for accessibility and passive performance.
The Cirqua project by BKK gained widespread recognition for creating beautiful, inventive multifamily architecture. The project includes 38 unique unit types out of the 42 total apartments made with spacious balconies and an integrated approach to landscaping. Combining two properties into a single block, the project was formed with careful attention paid to scale and the surrounding context. Cirqua not only showcases a smart, nuanced approach to multifamily housing, but also how to design for accessibility and passive performance.
 Caterpillar approaches density through a novel construction and design in Core City, Detroit. It utilizes a Quonset Hut structure that holds eight units, all entirely prefabricated. The result is an 8,000 square foot (745 square meter) residential project that prioritizes indoor and outdoor space. Prince Concepts created the project with tall ceilings that rise to 23 feet (7 meters); the units were designed to capture morning light in the bedrooms and evening sunsets in the living room.
Caterpillar approaches density through a novel construction and design in Core City, Detroit. It utilizes a Quonset Hut structure that holds eight units, all entirely prefabricated. The result is an 8,000 square foot (745 square meter) residential project that prioritizes indoor and outdoor space. Prince Concepts created the project with tall ceilings that rise to 23 feet (7 meters); the units were designed to capture morning light in the bedrooms and evening sunsets in the living room.
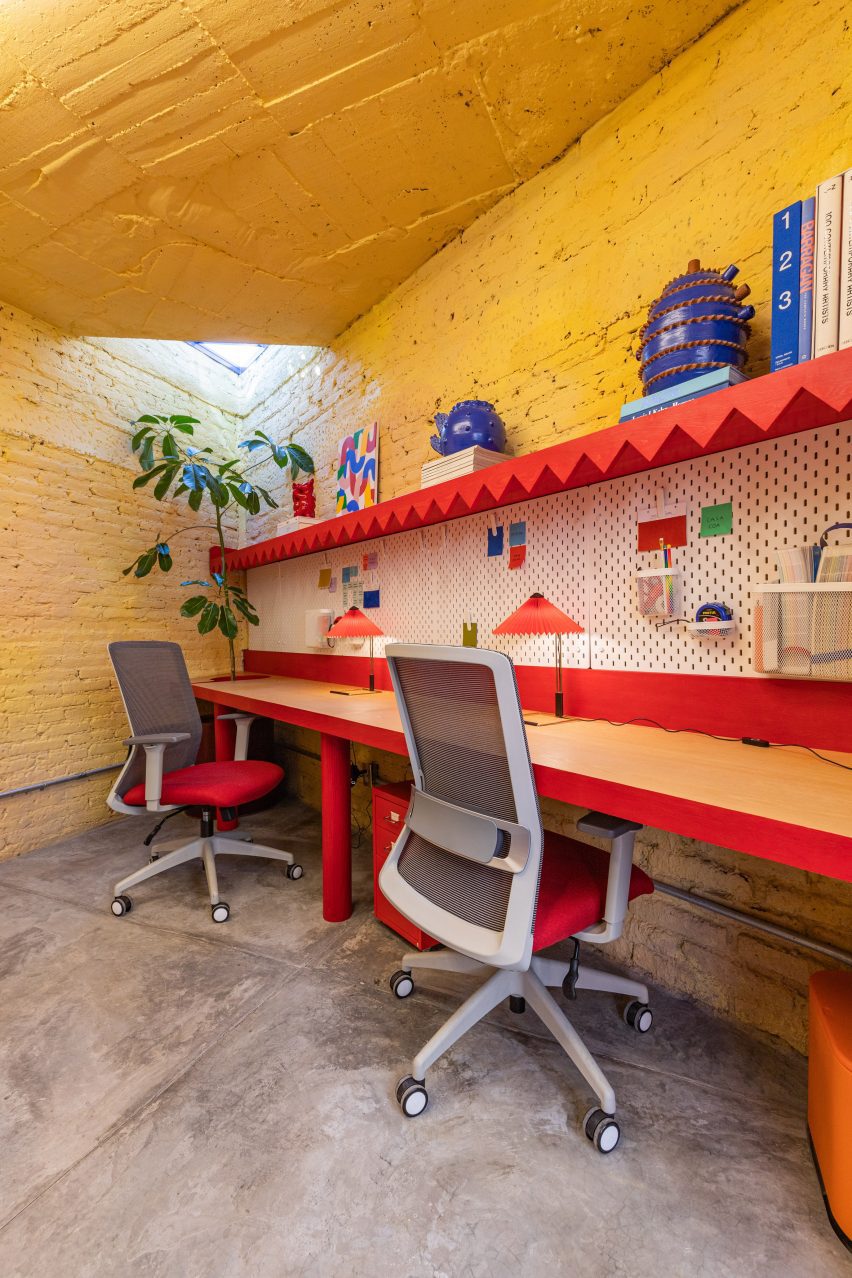
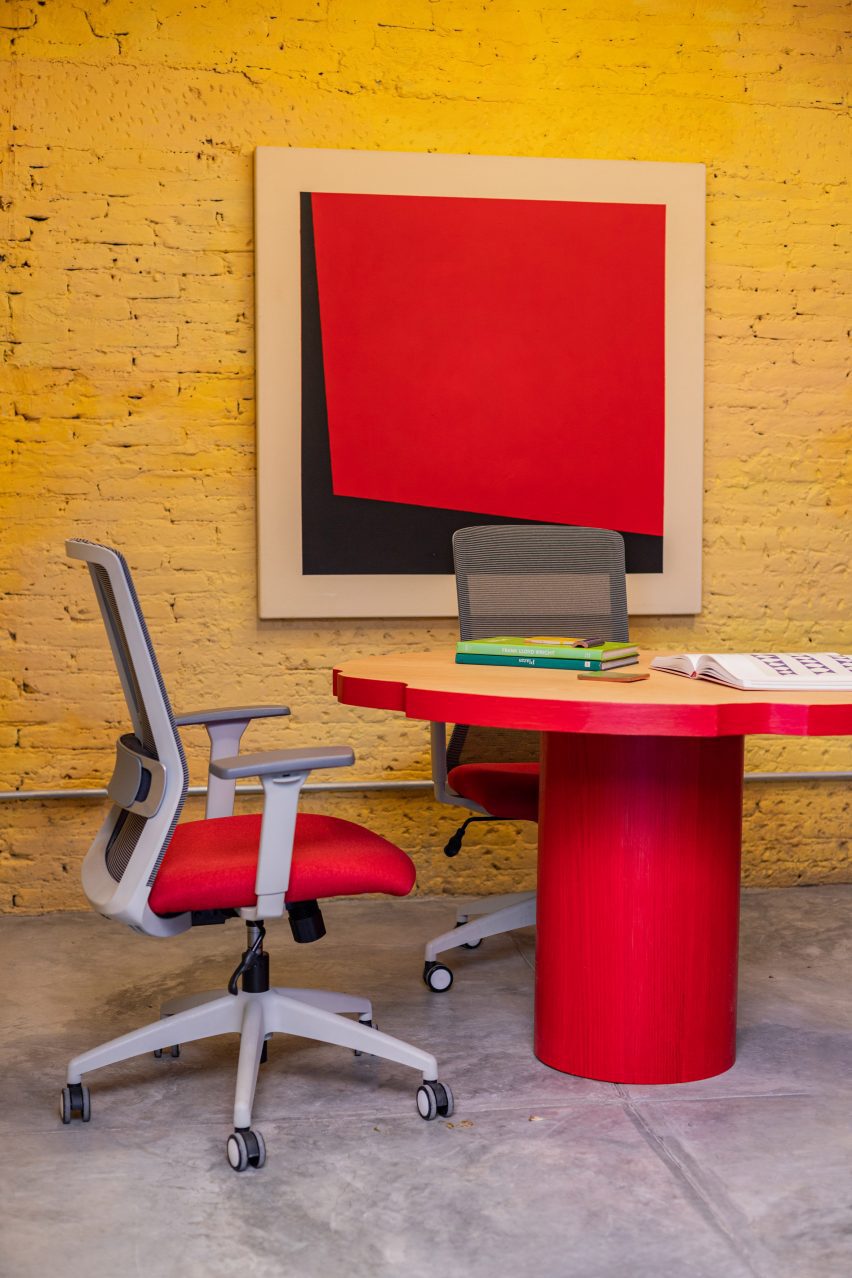
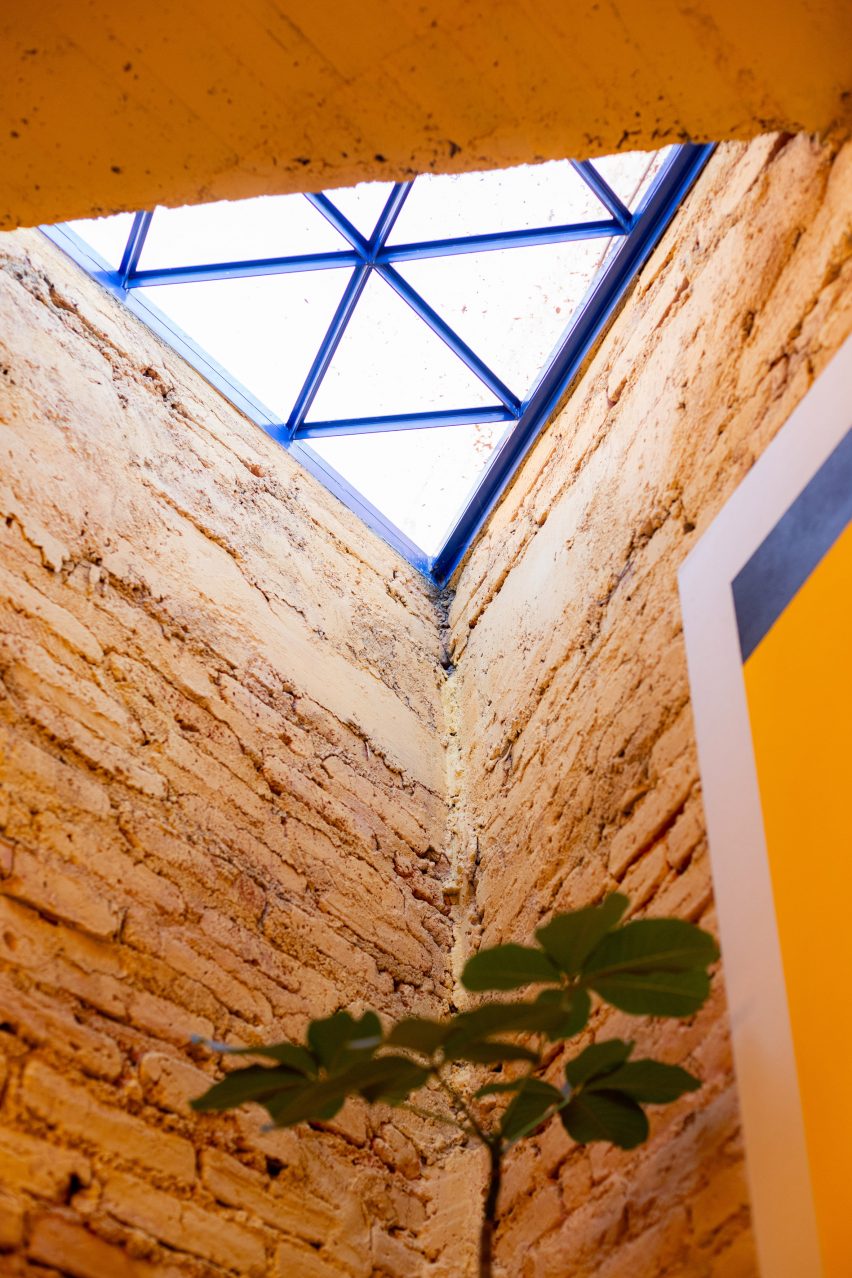
 CPDA Architects designed this garden house project as a multifamily development in Mexico City. Located in the Escandón neighborhood, the project includes fourteen residential units. At its heart, a central courtyard is the connective element that defines the housing project, opening up access to natural light and cross ventilation. Ten townhouse units are set up the four ground-floor units below, all of which share a similar material relationship.
CPDA Architects designed this garden house project as a multifamily development in Mexico City. Located in the Escandón neighborhood, the project includes fourteen residential units. At its heart, a central courtyard is the connective element that defines the housing project, opening up access to natural light and cross ventilation. Ten townhouse units are set up the four ground-floor units below, all of which share a similar material relationship.
 Few cities in the world are grappling with homelessness and a severe lack of housing affordability like Los Angeles. Brooks+Scarpa has built a practice addressing issues in the city and across the nation. For this multifamily residential, The SIX was designed as a 52-unit affordable housing project that “provides a home, support services and rehabilitation for previously homeless and/or disabled veterans.”
Few cities in the world are grappling with homelessness and a severe lack of housing affordability like Los Angeles. Brooks+Scarpa has built a practice addressing issues in the city and across the nation. For this multifamily residential, The SIX was designed as a 52-unit affordable housing project that “provides a home, support services and rehabilitation for previously homeless and/or disabled veterans.”
 Over the last two decades, development in China has been defined by a dizzying pace and new architecture produce in-mass. For Jinshan 9, this force behind new buildings was directed into a multifamily living community. Located in China’s Shekou mixed-use district, the project looks out west to wild, forested mountains and east to Shenzhen Bay Bridge. With a range of both low-rise and high-rise structures, the development was made for diverse lifestyles and populations.
Over the last two decades, development in China has been defined by a dizzying pace and new architecture produce in-mass. For Jinshan 9, this force behind new buildings was directed into a multifamily living community. Located in China’s Shekou mixed-use district, the project looks out west to wild, forested mountains and east to Shenzhen Bay Bridge. With a range of both low-rise and high-rise structures, the development was made for diverse lifestyles and populations.



