“We can’t plead ignorance” on sustainability says panel of design experts
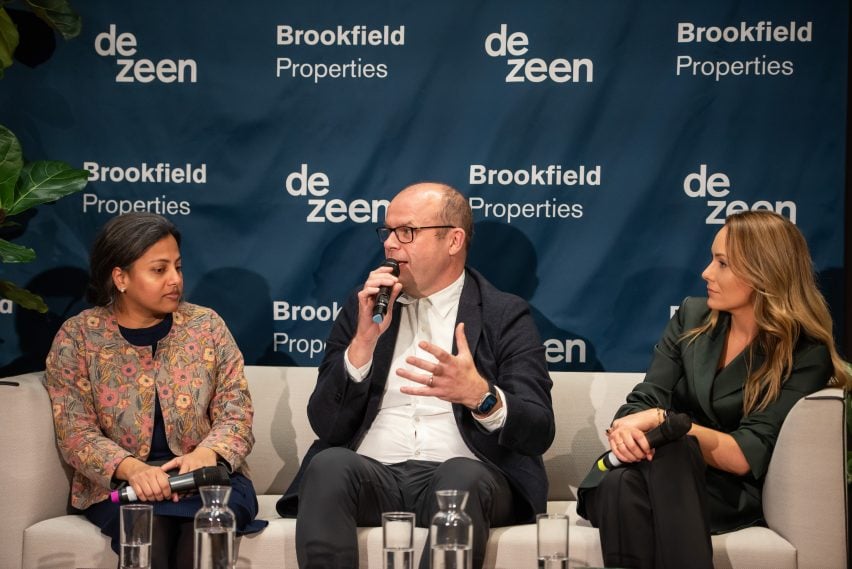
Architects need to listen to younger generations and take a collaborative approach to sustainability, according to a panel of design experts in this filmed talk hosted by Dezeen for developer Brookfield Properties.
The panel included Brookfield Properties director of design Pragya Adukia, architecture studio Foster + Partners senior partner Dan Sibert and architecture studio BVN strategy director Esme Banks Marr. The talk was moderated by Dezeen co-CEO Ben Hobson.
The discussion followed the publication of a report commissioned by Brookfield Properties and Foster + Partners, which surveyed workers’ thoughts on the importance of sustainability in the workplace.
The panelists discussed how younger generations are increasingly more invested in furthering sustainable practices in their workplaces, with the report finding that 93 per cent of people working in an “environmentally friendly office” felt happier in their job.
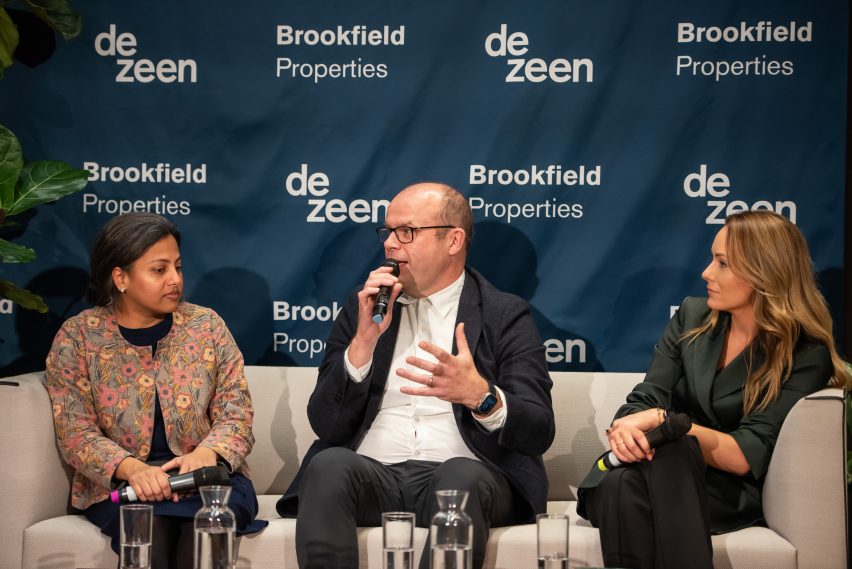

“We want to make sure that we’re hearing what people say, which is why we co-commissioned this report with Foster + Partners – to listen to what the younger generation at work was saying, to give them a voice around their own sustainability, ideas and goals,” Adukia explained.
“The idea of sustainability is really a community-based thing,” added Sibert. “[There’s] a generational shift. People are no longer interested in just sitting and letting it happen to them, they actually want to be involved in it.”
“Our approach has always been ‘this is what can be realistically achieved’, it’s not just a fancy hashtag or a strapline,” continued Adukia.
“Let’s look at the data points, that’s very strong evidence, and then talk about what can be achieved, how we can future proof it.”

“People are more vocal about their beliefs and what they’d like to see, it’s a good idea to involve these people in bigger conversations, and then take on board what they want to see,” she added.
“We can’t plead ignorance, none of us can plead ignorance anymore” said Banks Marr, echoing the importance of listening to public opinion around sustainability.
“There are some baseline things that we need to fundamentally just get right in buildings, new and existing, first and foremost. Sounds quite simple, but a lot of people still fail to do it,” she concluded.
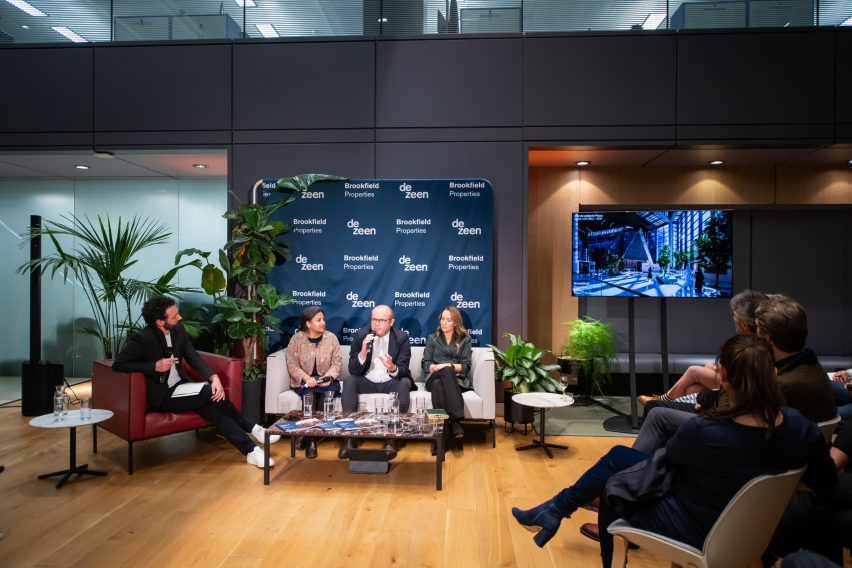

The panel also discussed how approaches such as biophilic design could help lead to more engagement with the environment and green policy-making.
Defining biophilic design, Banks Marr said “it’s not [just] putting plants into a space. Biophilic design is a term that’s been used for such a long time and in lots of different types of ways, when actually it means all of your senses, your experience with the space and your connection to nature.”
“It’s a stepping stone, or a starting point, to taking a really ecological world view of things,” she added.
“If I’m in these concrete jungle cities that do not have any connection to nature, and I don’t experience that on a daily basis, it doesn’t live in my psyche. So how am I expected to care about it and create real change?”
“There’s a desire across the board, not just in the city, to make sure we’ve got spaces to live and breathe in,” Adukia concluded.
Similarly, the panel noted the importance of creating long-lasting and future-proofed spaces.
“We need to get ourselves into that mindset where we actually think about things for a much longer term, and think and design them so they will change over time,” said Sibert. “So, can the building be designed for multiple lifespans rather than a single lifespan?”
“One has to take the overall sense of why you’re building in a city like this,” he added.
“Why do we build where, what does it mean for the overall picture of carbon and regeneration? What’s possible, but why would you make these choices as clients?”
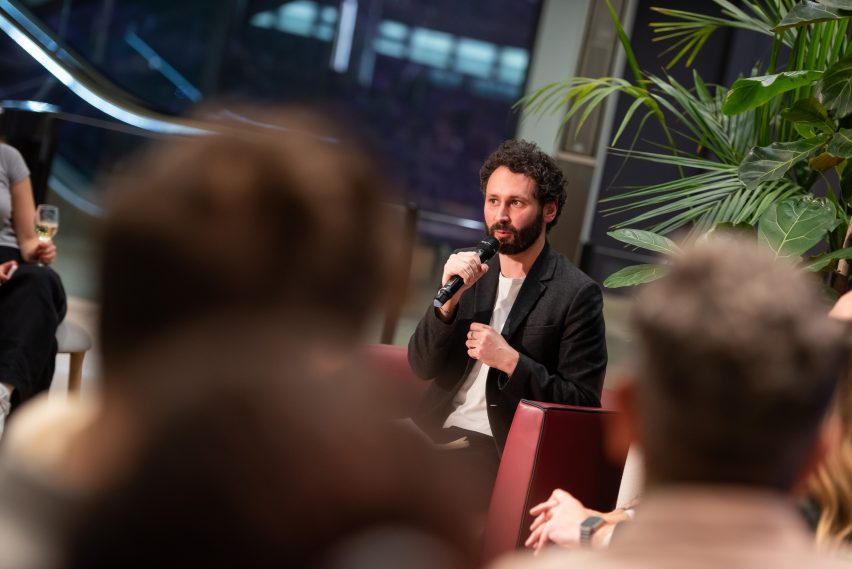

To conclude the talk, Hobson asked each of the speakers what they believed the key challenges the industry needed to overcome were.
“I think one thing we could definitely get better at, which we’re perhaps not currently doing enough, is knowing when to invite the real experts to the table. We don’t have to know everything,” answered Banks Marr.
“Data is absolutely key,” Sibert added. “If we could allow ourselves to find both the right dataset for the purposes of the buildings we have, and also then make the way we manufacture it be database based, I think that would be a massive step forward for us as an industry.”
“Our more successful projects have been where we’ve worked collaboratively and transparently. For any change to be implemented, I think it needs to be taken on board by all of its stakeholders. And that’s not just as landlords or developers – tenants, individuals, everyone has to be on board vocal about what they want out of it,” Adukia concluded.
The event was held at 30 Fenchurch Street, one of Brookfield Properties’ landmark office developments in the City of London.
Partnership content
This video was produced by Dezeen as part of a partnership with Brookfield Properties. Find out more about Dezeen partnership content here.