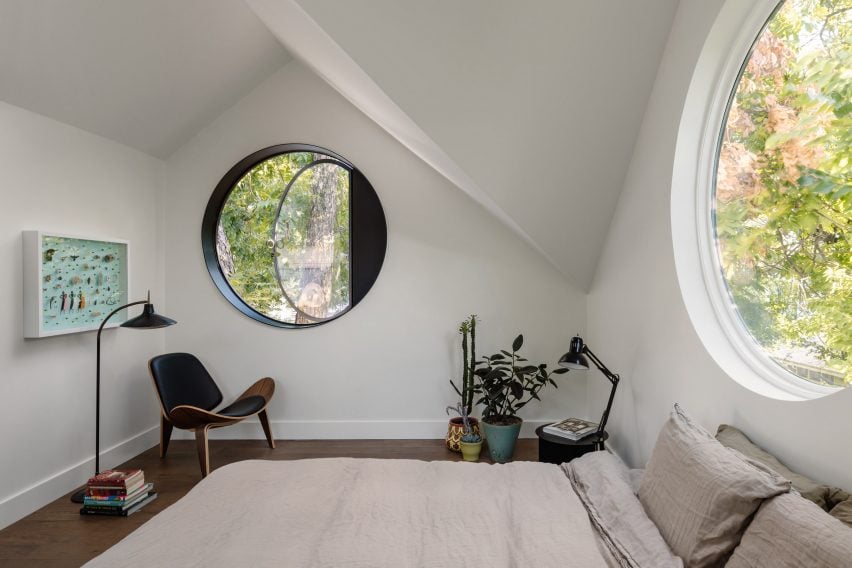
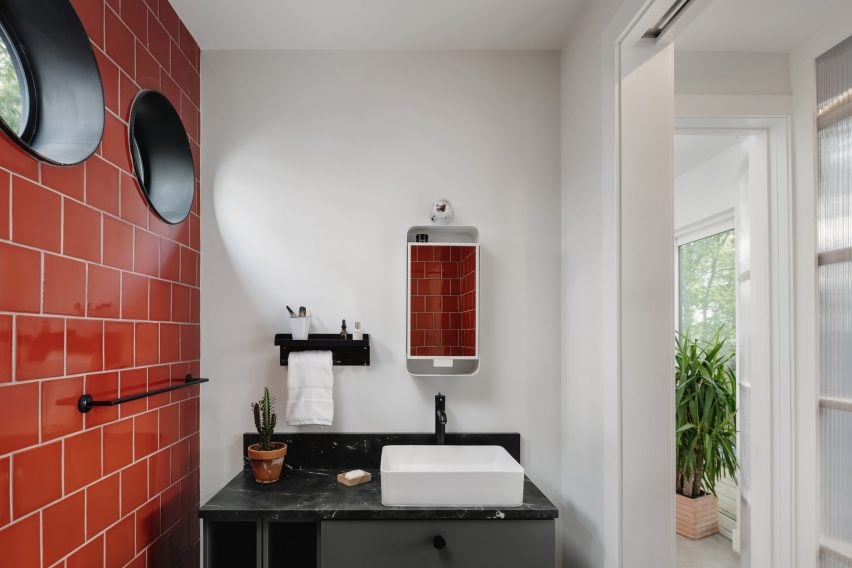
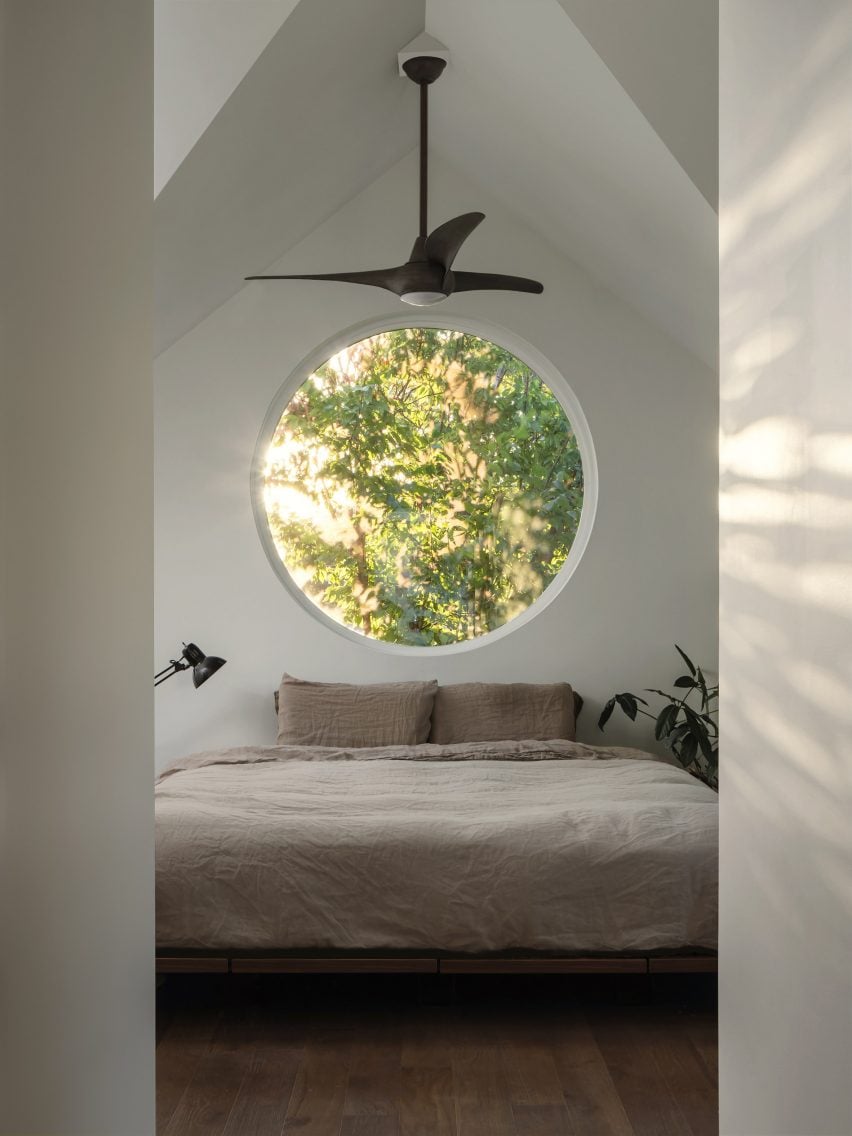
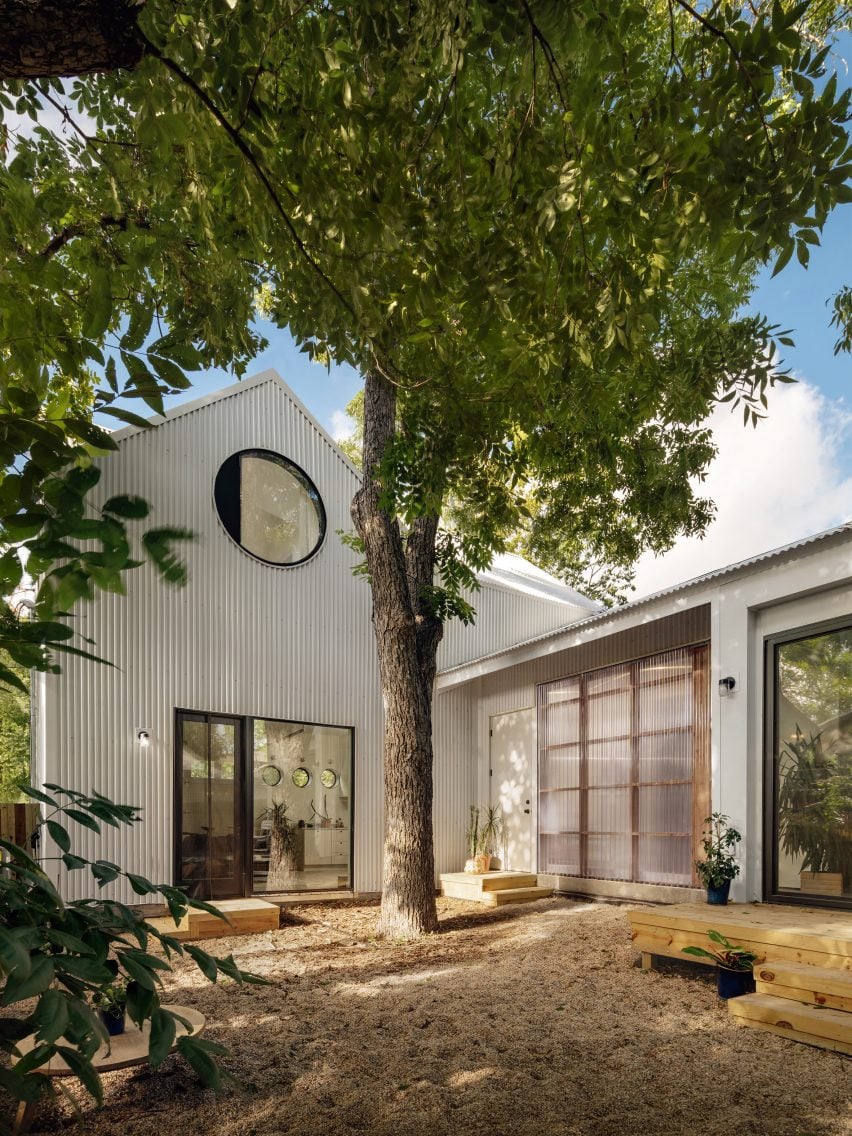
ADUs Bring Organic Growth to Suburbia, And We Desperately Need More Of It.
Browse the Architizer Jobs Board and apply for architecture and design positions at some of the world’s best firms. Click here to sign up for our Jobs Newsletter.
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) mandated by the State of California override local planning regulations to permit a second unit on almost any single-family zoned property. The law also allows any single-family zoned lot to be subdivided into two parcels. Additionally, it allows ADUs to be built with just a four-foot setback or no setback at the new interior property line of a subdivided parcel, in contrast with most towns, which have setbacks of more than 7 feet, up to 30 feet. It also mandates very relaxed parking requirements or no parking if the project is near public transit.
Is California paving the way for ADUs across the US?
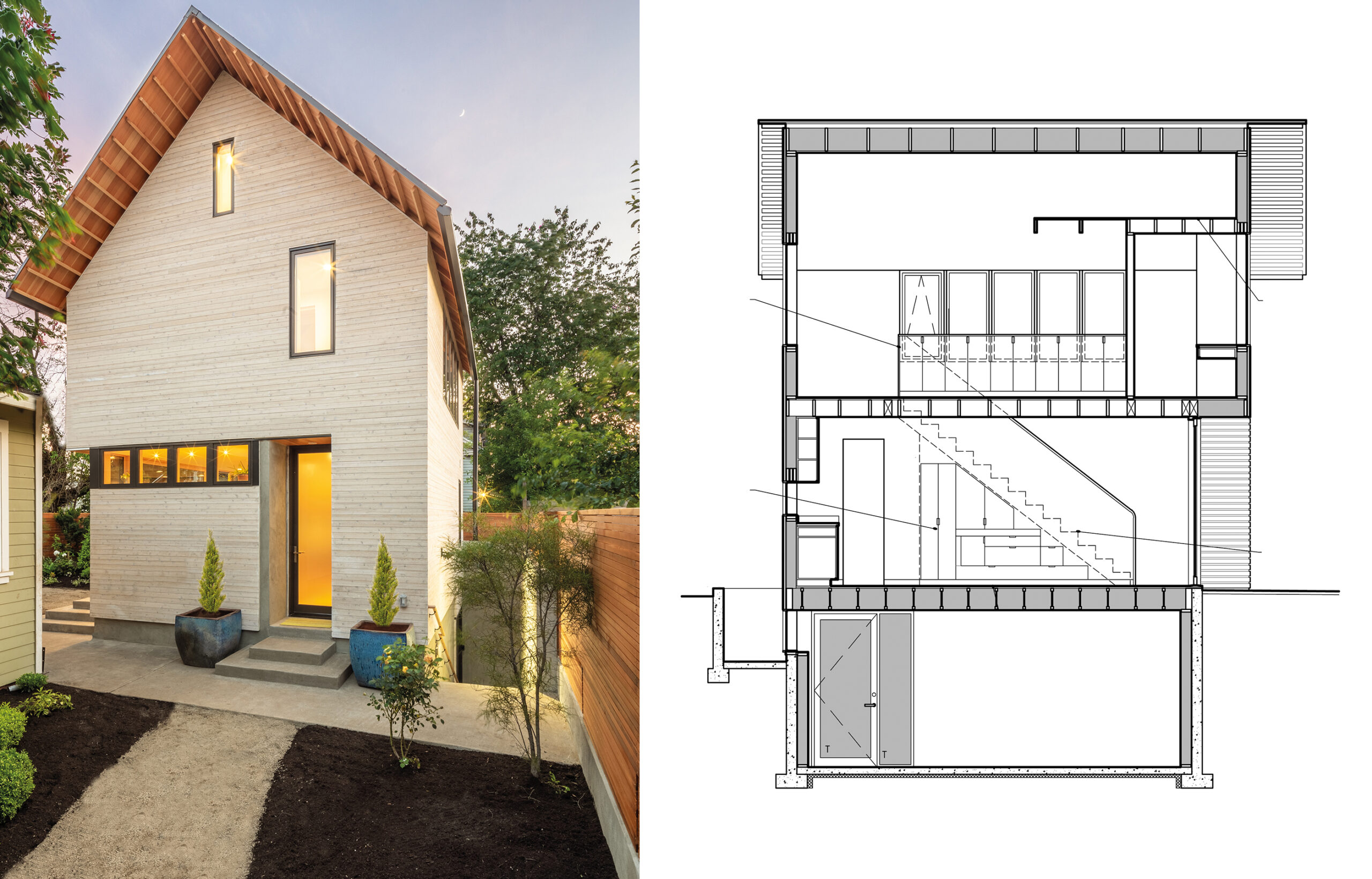
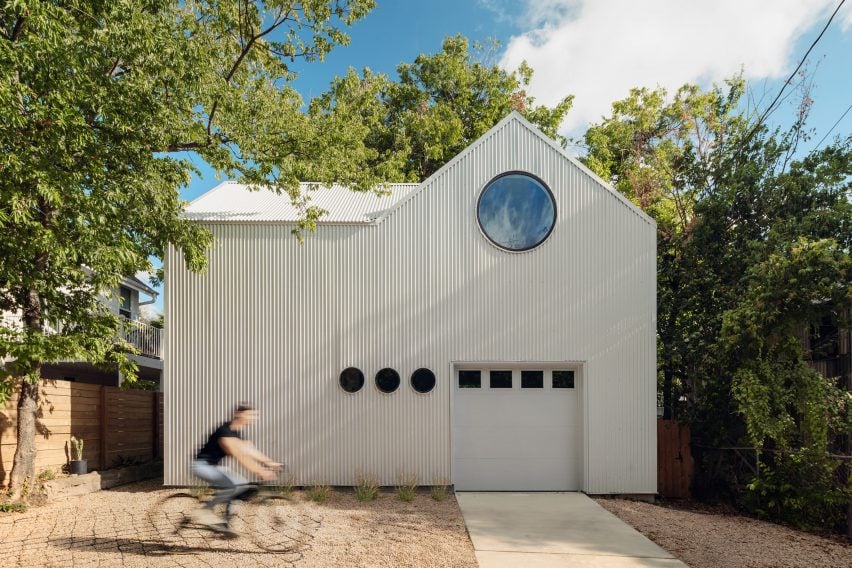
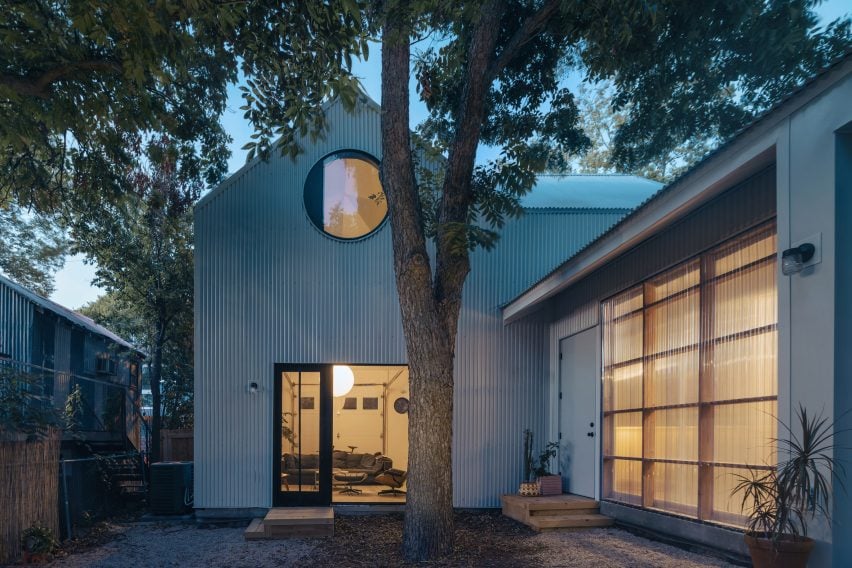
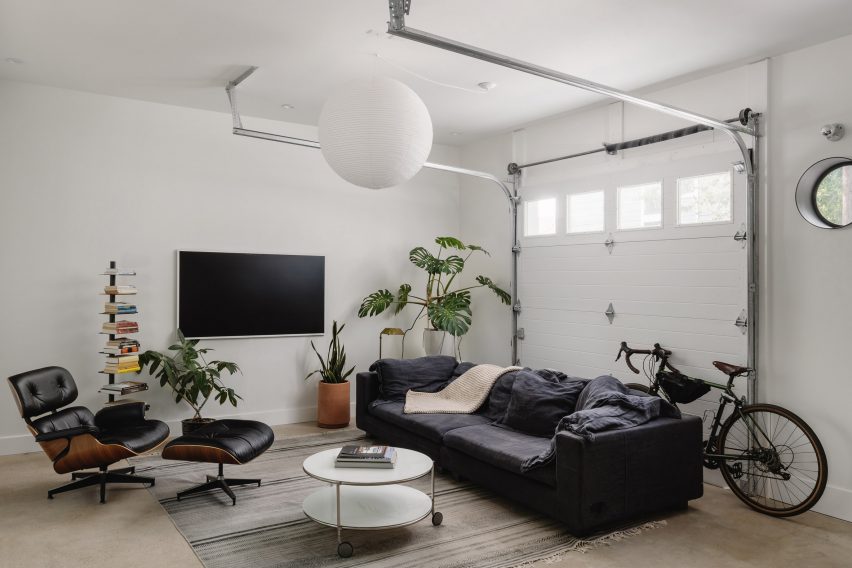
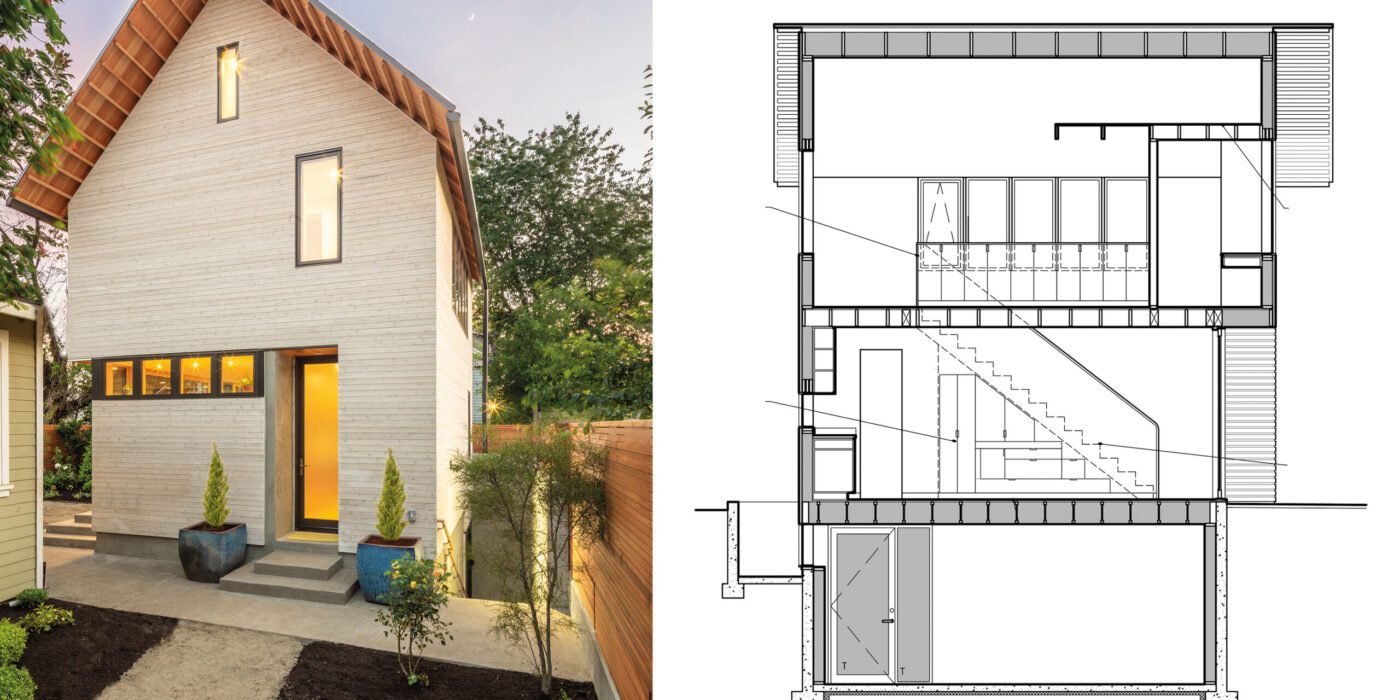
ADU Portland. Left: Exterior view; right: building section. Courtesy of Webster Wilson Architect. Image by Caitlin Murray.
ADUs: A Solution for Affordable Housing Shortage
California has long grappled with an acute housing shortage, especially affordable housing. Local governments, under the thrall of NIMBY residents trying to preserve the rural/suburban “character” of their communities, have not been very cooperative with state goals for new housing.
Local planning departments bristle at their authority being usurped by the state, but for growing numbers of people, these ADU rules offer welcome flexibility and opportunities for growth in a place that is building better, more stable communities, providing housing, and stemming sprawl.
ADUs for Families of all Sorts of Forms
The endless swaths of single-family houses spreading across the hills and valleys of suburbia are the physical manifestation of a culture that fetishized the nuclear family — and conspicuous consumption. But, a simple nuclear family unit has never been anywhere near the universal living arrangement and is becoming ever less universal. Homeowners are using the ADU rules to build houses for a kaleidoscopic variety of living arrangements and “families” of all shapes, types, and sizes.
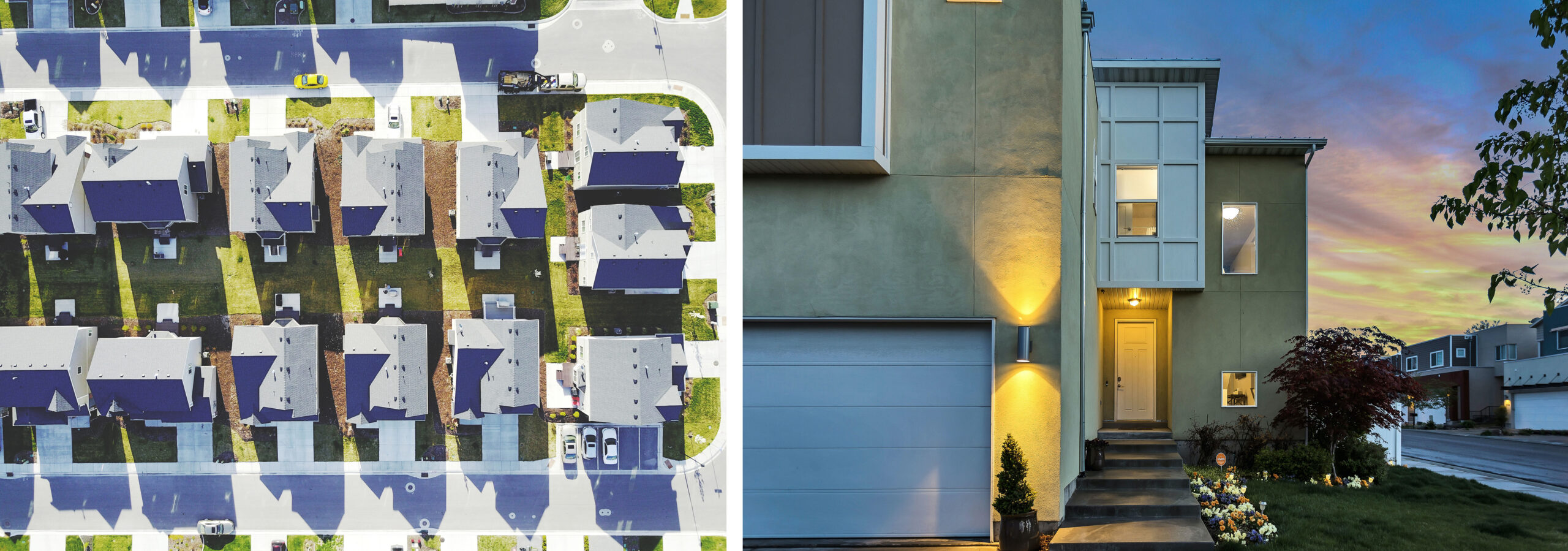

Left: Drone view of similar houses, driveways, and yards in the Utah suburbs. Original public domain image from Wikimedia Commons via rawpixel; right: Modern addition to an existing suburban house in the Salt Lake City area. Image by Brian Babb via Unsplash.
From Granny Flat to Rental Property
Having a place for “granny” is hardly the only use for these units. Homeowners may be looking for something affordable for grown children and their partners that doesn’t force them to move hours away. They’re also looking for flexibility and future-proofing. What is grandma’s house today can become an income rental property that allows a homeowner on a fixed income to afford to stay in place.
Building Stronger Communities
The law allows a single-family zoned parcel to be subdivided into two parcels, and each of these parcels to have two units, so up to four units can be made from a single-family house. This lets people do what traditionally has often been standard operating procedure: houses are extended to accommodate growing and branching families. It can help keep extended families together, which in turn, builds stronger communities.
Breaking the Monotony of Suburban Architecture
These new units are also changing the look and feel of suburbia for the better as well. Blank two-car garage doors are being replaced by lively facades of windows and openings. The tighter setbacks help give the remodeled houses a different rhythm and feel on the street, breaking the monotonous sameness of cookie-cutter ranchers.
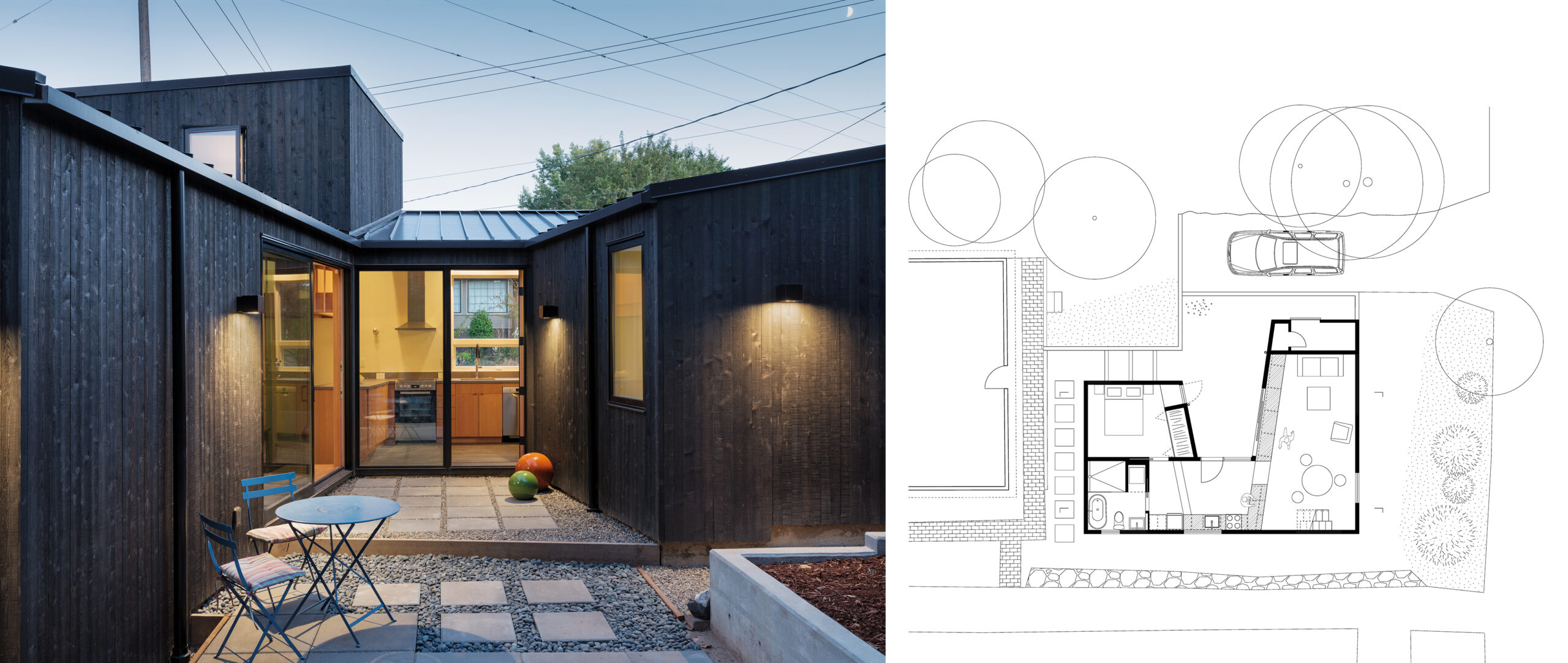
Courtyard DADU, Seattle, Washington. Left: View from the courtyard; right: floor plan. Courtesy of Robert Hutchison Architecture. Photo by Eirik Johnson.
YIMBY!
Until the advent of professional planners, towns and cities almost always grew and became more densely developed in small steps in exactly this way. This laisser-faire method of “planning” has produced most of the best, most treasured urban landscapes across the world. Our banal suburban sprawl may yet be redeemed through organic in-fill growth done by and for residents who are increasingly proclaiming YIMBY! (Yes, In My Back Yard).
This article was written in collaboration with Californian architect Ian Ayers.
Browse the Architizer Jobs Board and apply for architecture and design positions at some of the world’s best firms. Click here to sign up for our Jobs Newsletter.