frank gehry designs new center for young artists at LA’s colburn school
frank gehry-designed school: breaking ground ceremony
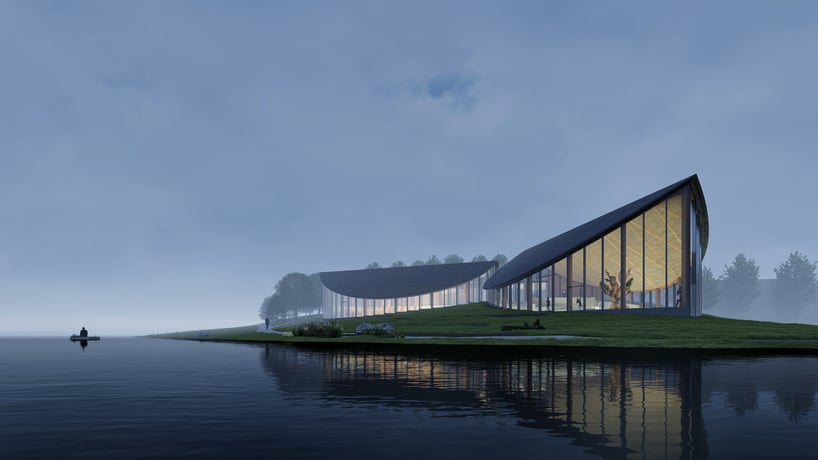
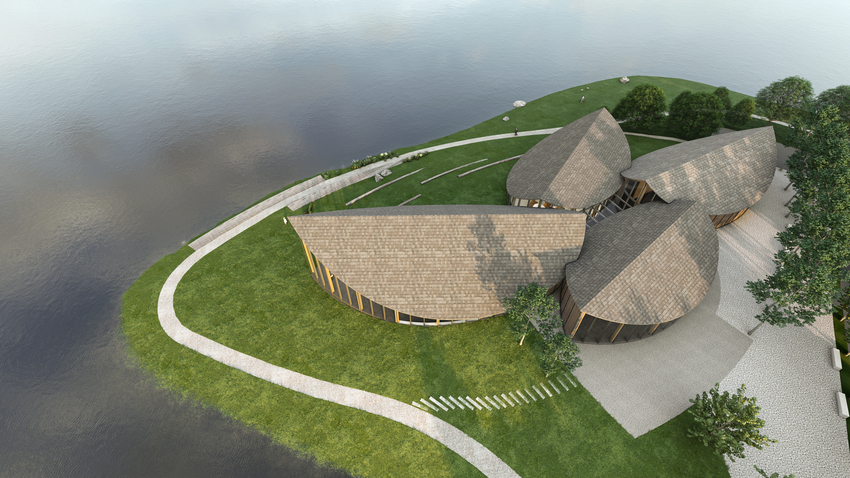
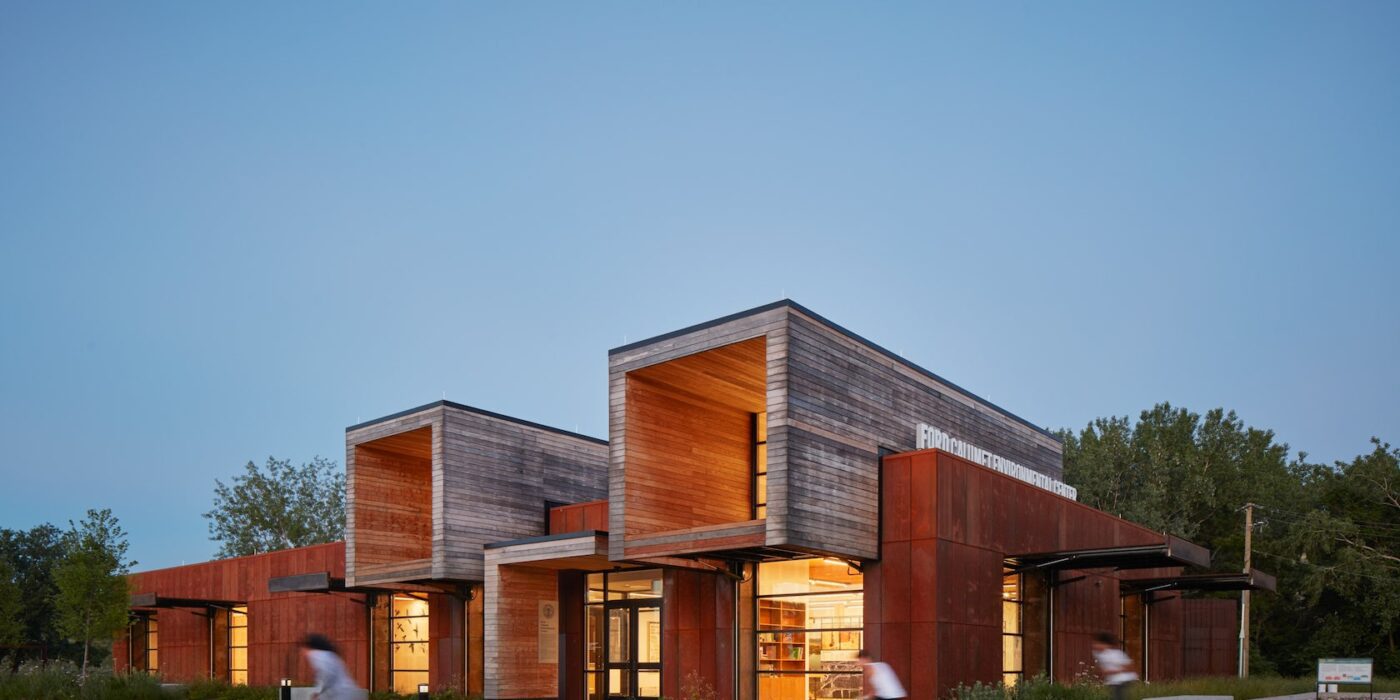
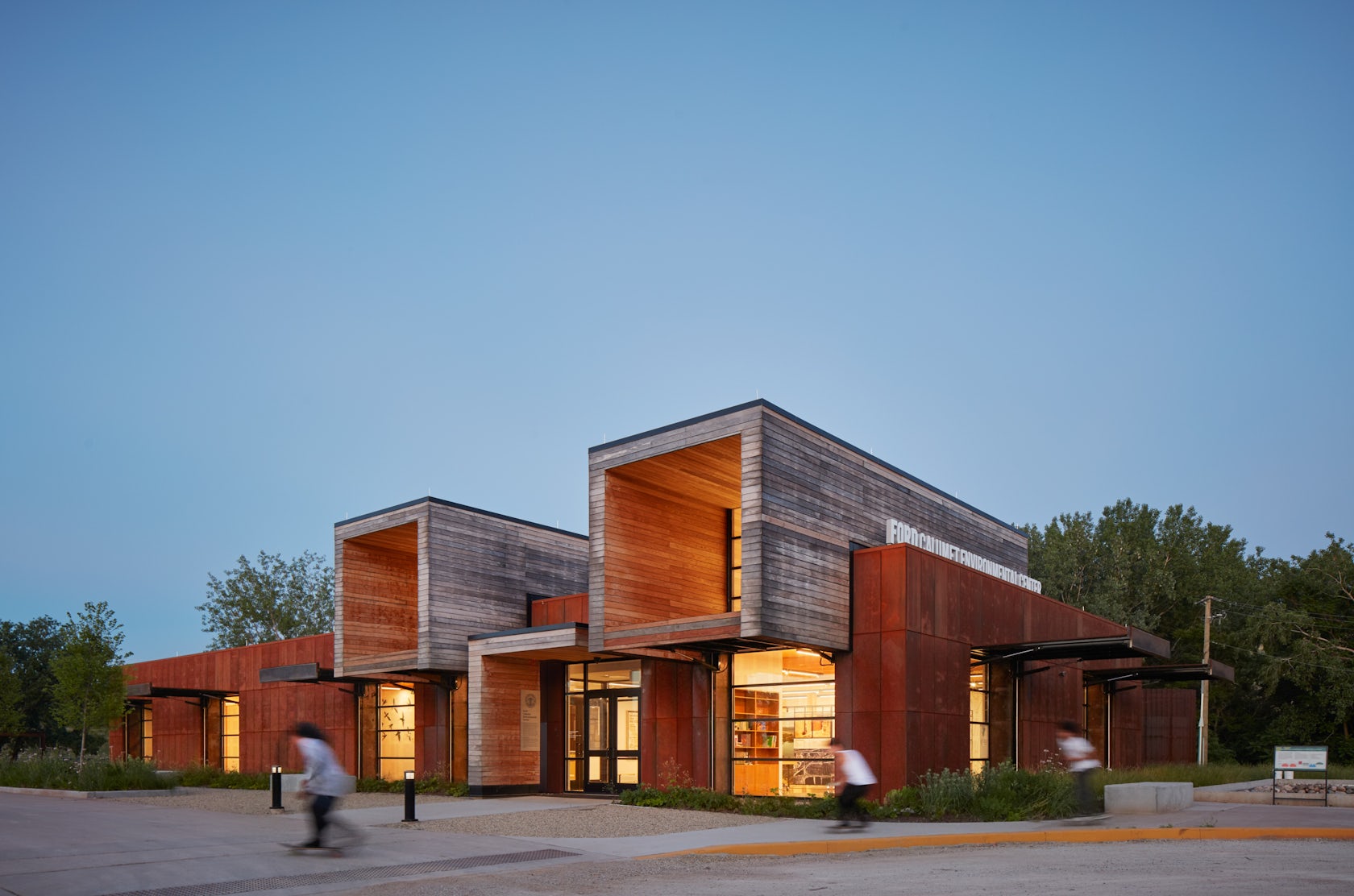
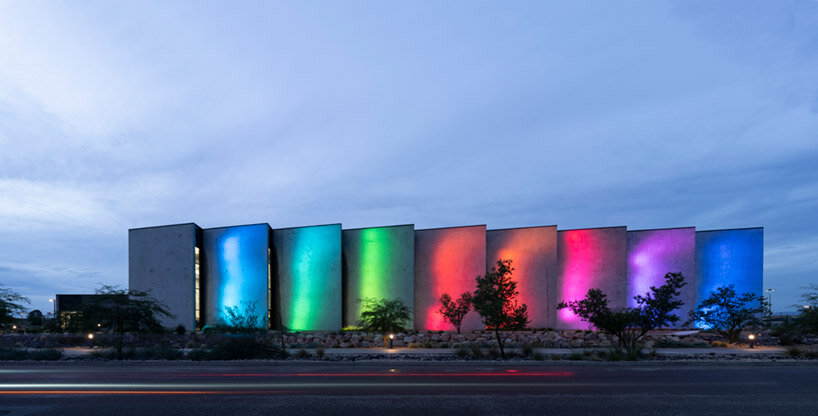
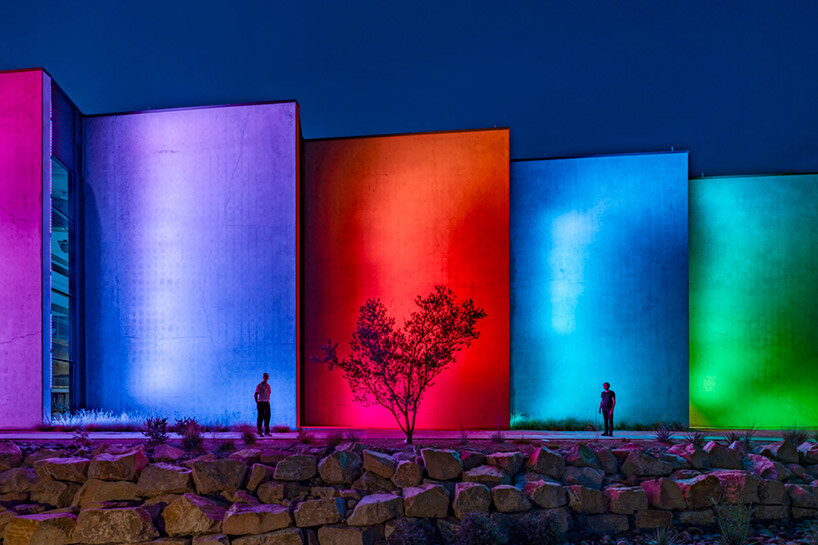
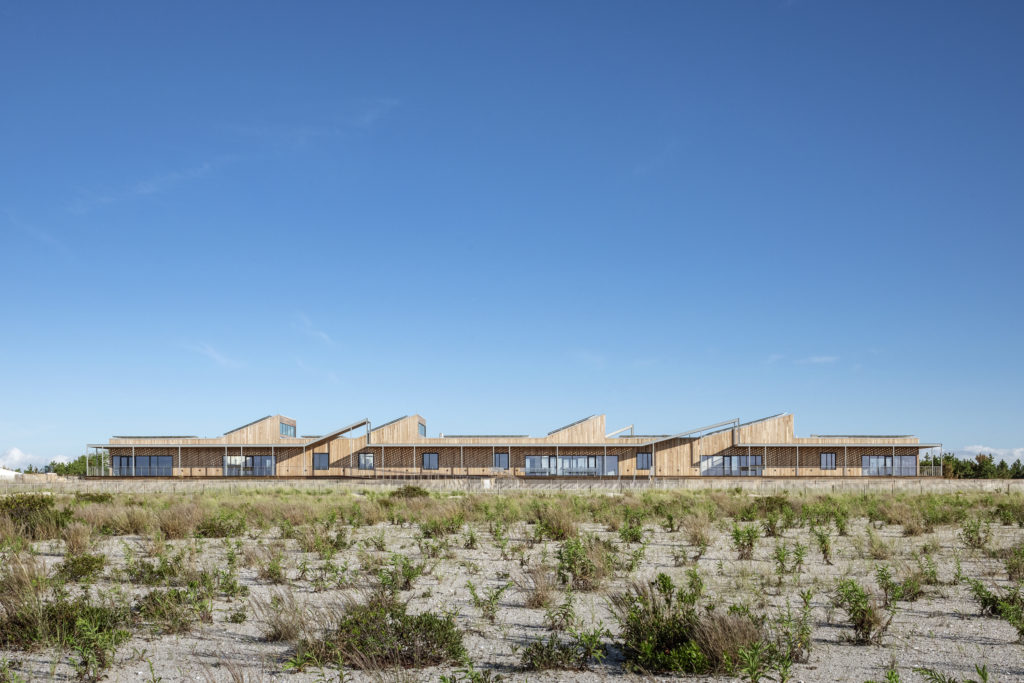
The Colburn School in Los Angeles, one of the world’s leading schools for music and dance, held a groundbreaking ceremony for its 100,000-square-foot expansion designed by Frank Gehry. The new Colburn Center will dramatically increase the school’s elite training and performance facilities and provide much-needed performance space, including a 1,000-seat, state-of-the-art concert hall, for young artists across LA. The groundbreaking ceremony took place adjacent to the construction site at 130 Olive Street, located within Downtown Los Angeles’s Bunker Hill area diagonally across the street from Colburn’s existing campus on Grand Avenue. The expansion will stand as an important addition to the cultural corridor which includes Gehry Partners’ Walt Disney Concert Hall, the Music Center, the Museum of Contemporary Art, and the Diller Scofidio + Renfro-designed broad. Anticipated completion is expected for the first quarter of 2027.

left to right: Sel Kardan, Carol Colburn Grigor, Andrew Millstein, Jerry Kohl, Terri Kohl, Maeesha Merchant, Toby Mayman, Merle Mullin, and Terry Greene at Colburn Center groundbreaking ceremony, April 5, 2024 | image © Loreen Sarkis
a hall for all
Designed by Frank Gehry (see more), the Colburn Center at the Colburn School (see more) will be a ‘hall for all,’ giving artists and students a place to shine. the center will stand at the crossroads of culture, education, and landmark architecture — marking frank gehry’s third project within three blocks to become the world’s greatest concentration of his architecture. The colburn school welcomes over 2,000 students from across los angeles and around the world, with ages ranging from seven months to adult. the new center will make the colburn campus an even livelier hub of artistic activity and enable the school to expand its mission of presenting programs for the public, which include performance and educational collaborations with acclaimed local and touring artists and ensembles. it will also provide much needed performance space in a mid-sized hall for the region’s established and emerging performing arts organizations.
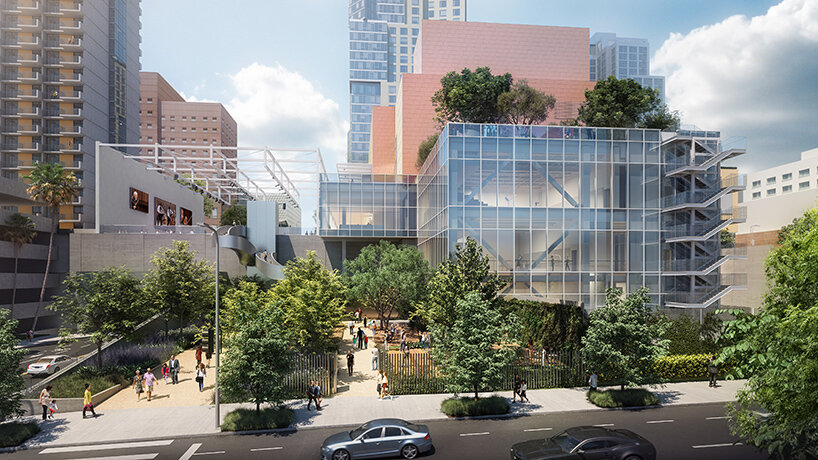

view from hill street west towards dance school entrance | image © Gehry Partners
the 1,000 seat theater, ‘terri and jerry kohl hall’
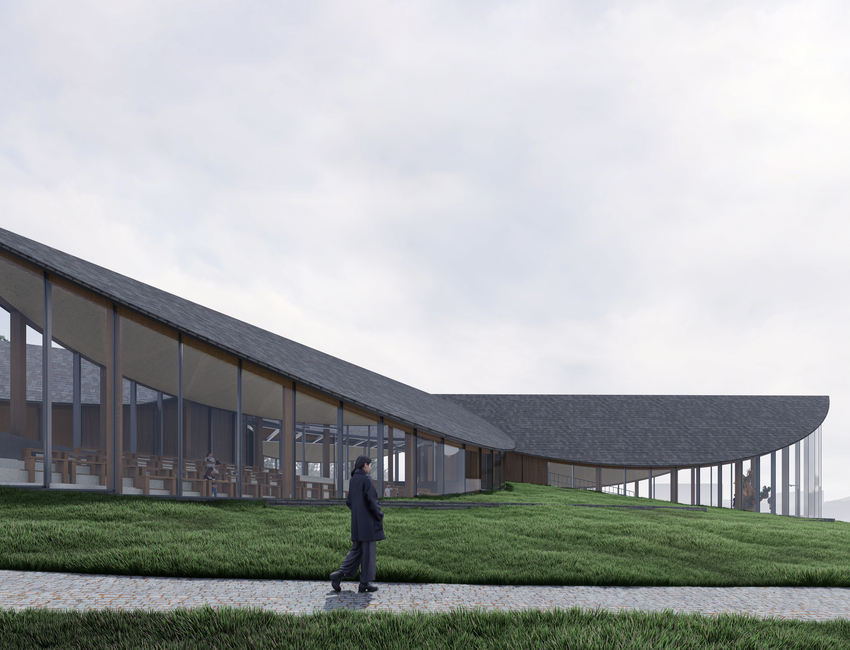
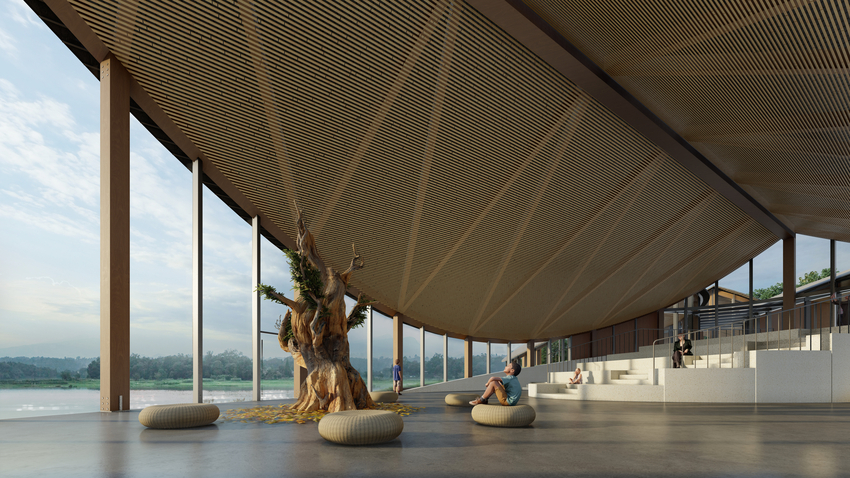
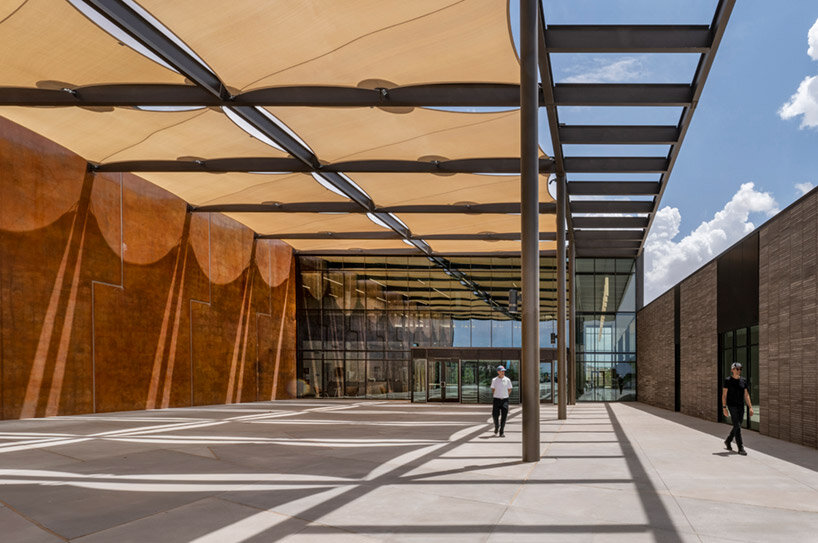
Frank Gehry’s Colburn Center will welcome students and audiences alike, with a dynamic composition of transparent and opaque interlocking blocks that step down into the natural contour of the site. A 1,000-seat concert hall uses an in-the-round design to create intimacy between the performers and the audience and removes the stage lip, putting front-row seats at eye-level with the performers. Orchestra, opera, dance, and musical theater will all be at home in the hall, which is equipped with an orchestra pit and a stage large enough to accommodate the grandest works and the largest orchestrations.
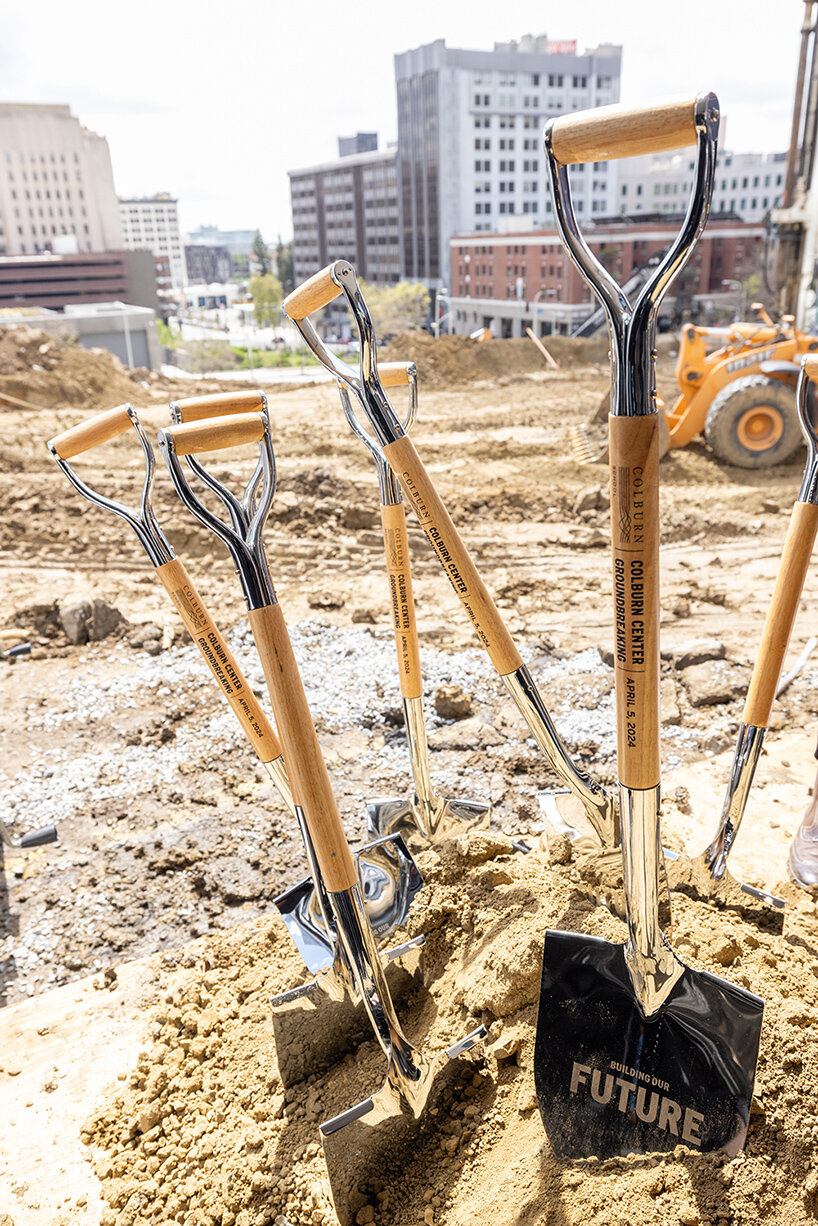

branded shovels used for groundbreaking ceremony | image © Loreen Sarkis
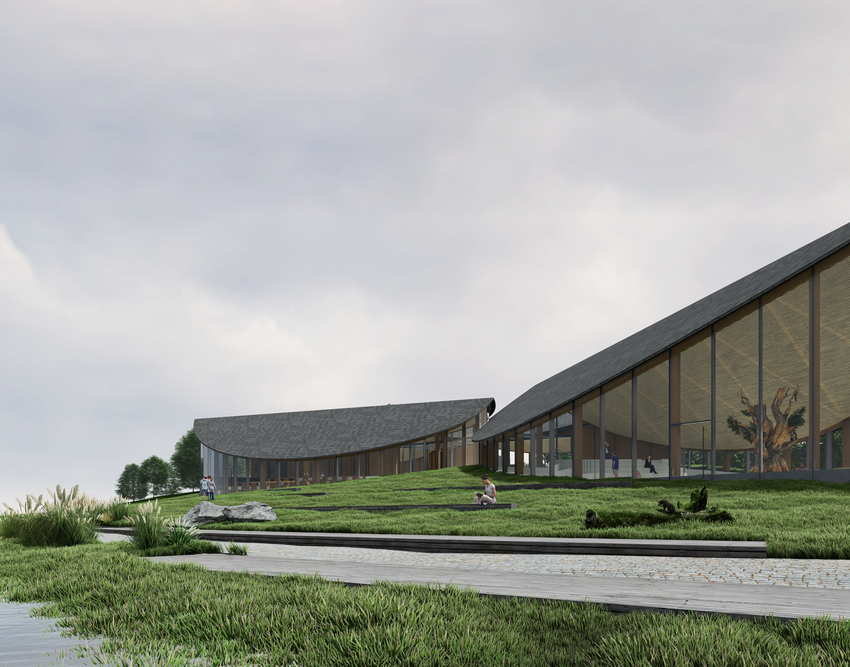
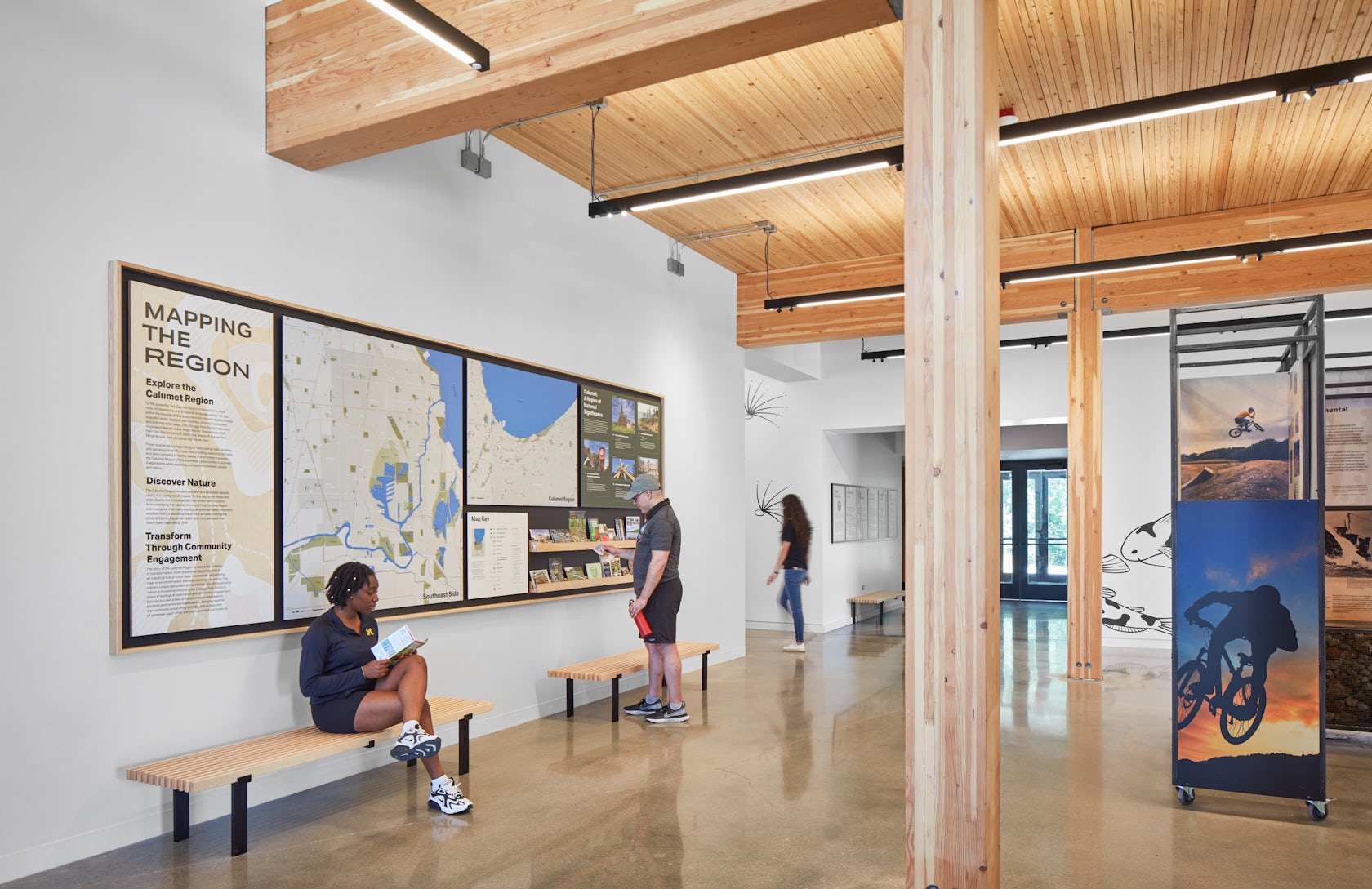
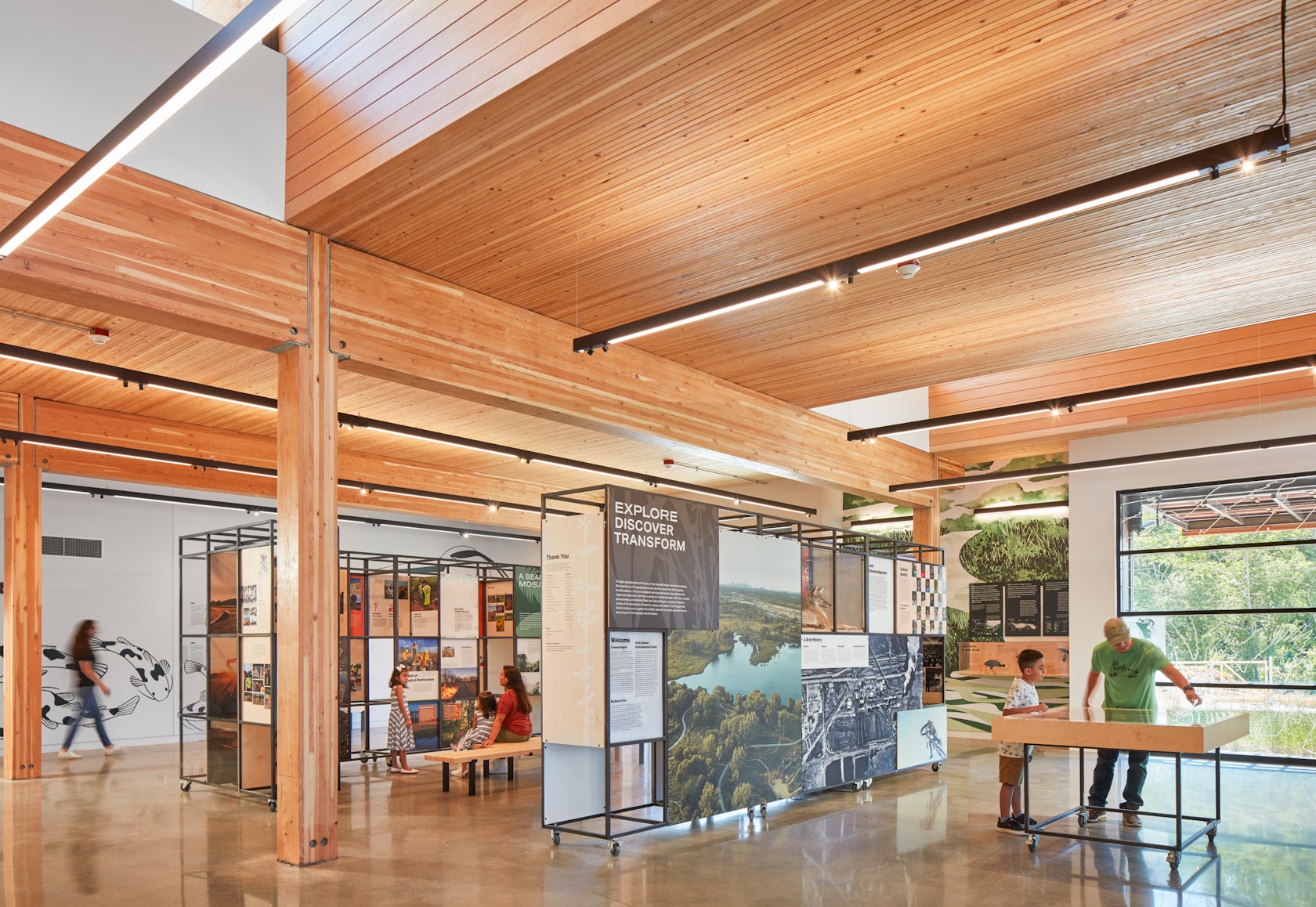
the theater and dance studios
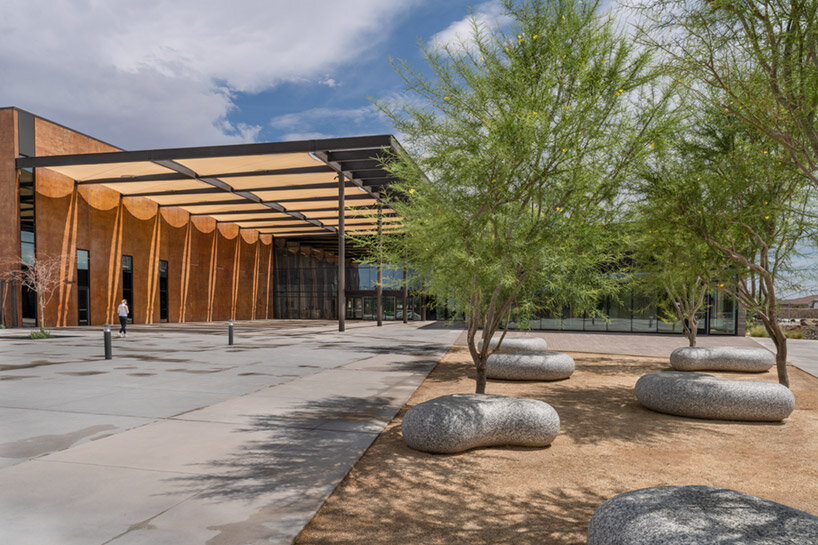
Four professional-sized dance studios and a 100-seat flexible studio theater are enveloped in glass and provide a literal window into the beauty and rigor of dance training and performance. Qith a separate entrance and distinct architectural character, the light-filled dance facilities will have their own identity while harmonizing with the larger project. The Colburn Center will be equipped to take a modern approach to multi-media technology and production. The facilities include commercial-quality recording and streaming capabilities, and performance spaces will be outfitted with state-of-the-art lighting. Public spaces include an outdoor plaza, giving visitors a front-row seat to the performing arts, and gardens which provide much-needed green space and pedestrian access to nearby public transit hubs.
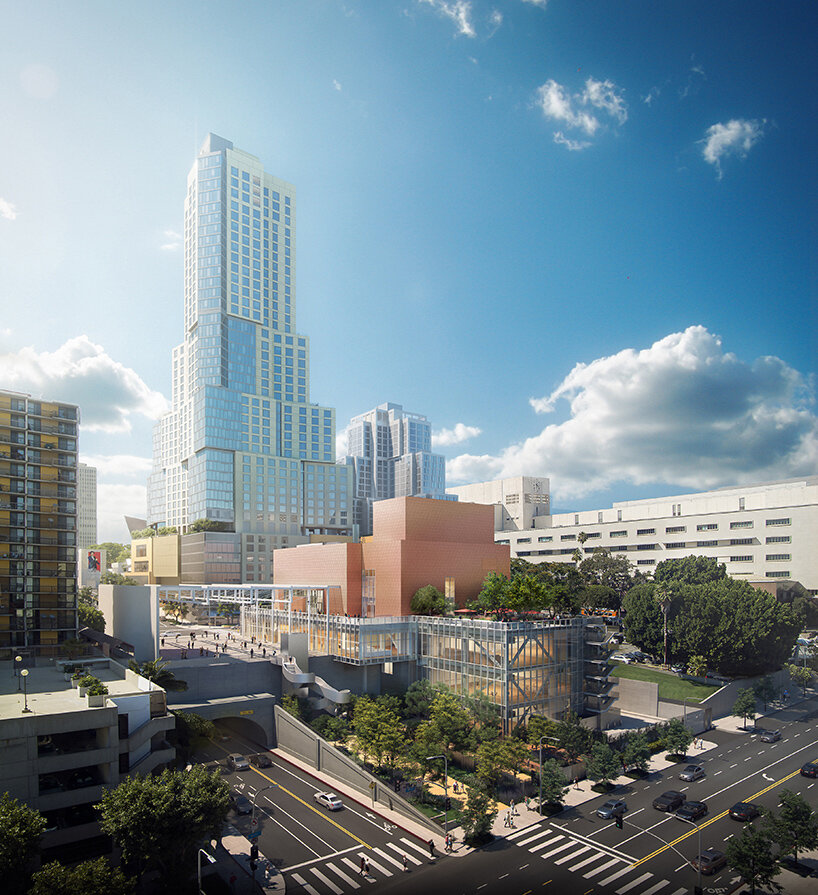

view from Hill Street and 2nd Street intersection
colburn president sel kardan comments: ‘With great joy and excitement, we share the design of Frank Gehry’s multi-dimensional project, which will welcome our students, performing artists, and audiences from across los angeles.The Colburn Center is a physical manifestation of the school’s founding principle of ‘access to excellence,’ allowing Colburn to continue and expand our educational and performance activities in a design which breaks down barriers between audience and performer and reveals the educational process. We look forward to collaborating with our artistic partners in Terri and Jerry Kohl hall, which complements the other stellar performance spaces in Downtown Los Angeles.’
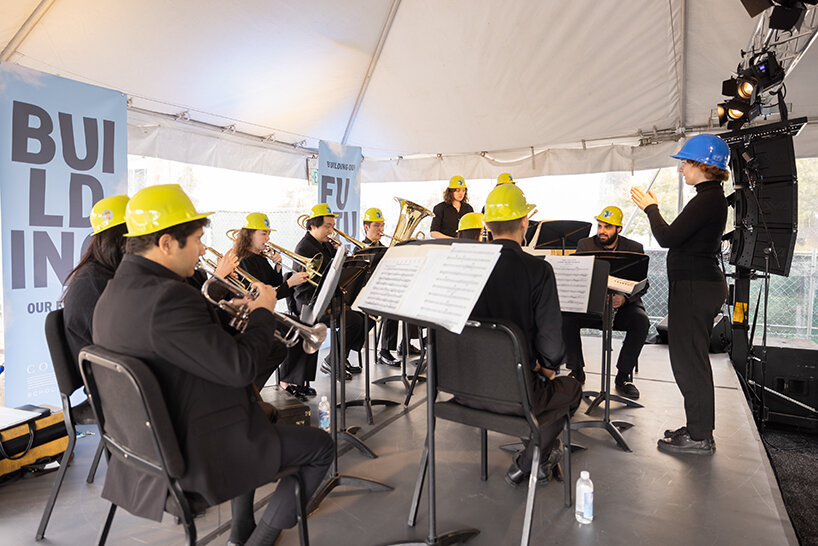

performance by the Colburn Conservatory’s Pep Band | image © Loreen Sarkis
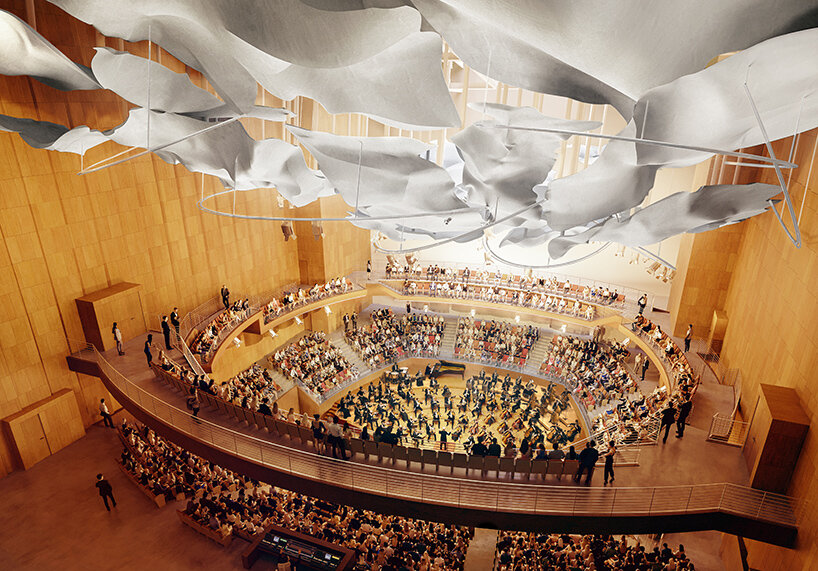 inside the 1,000-seat Terri and Jerry Kohl Hall | image © Gehry Partners
inside the 1,000-seat Terri and Jerry Kohl Hall | image © Gehry Partners