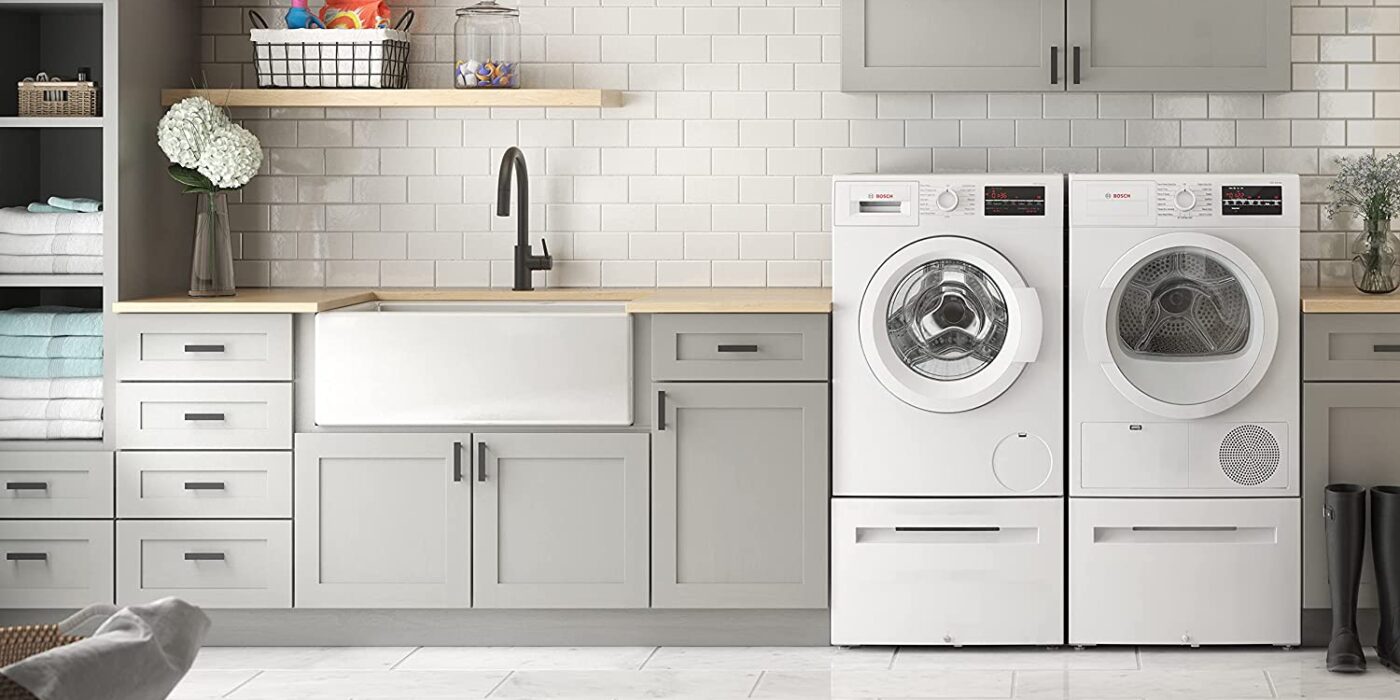
Heat Pump Clothes Dryers: Low-Impact Laundry
If you’re interested in shaving off perhaps 10% of your household energy use (and your electric bill) with a single purchase, it’s time to look into heat pump clothes dryers. “An electric dryer can use anywhere from 700 to 1000 kilowatt-hours of electricity each year. That’s about a tenth of the average American’s electricity usage,” said Joe Wachunas, electrification advocate for Electrify Now and Project Manager at New Buildings Institute. “You can cut that by 75% or more using heat pump dryers.”
With options on the market that use as little as 200 kWh of energy in a year, it’s not hard to see why their market share is increasing. “Heat pump technology is critical here in America, especially,” Wachunas says. “And heat pump dryers are an exciting, relatively new technology.”
Traditional vented dryers
Vented dryers can be either gas or electric, and they require venting to the outside of the home through ducts. A heating element heats the air in the drum, evaporating the moisture from clothes. Then as the dryer runs, the hot, moist air is vented outside and replaced with air pulled in from your laundry room, basement, or wherever it’s located. This influx of fresh air must be heated to continue drying the clothes.
Ga-Young Park, Residential Appliances Manager at ENERGY STAR, pointed out another inefficiency. “Because vented dryers pull in cooled or heated air from your home and vent it outdoors, your air conditioner or heater has to work even harder to maintain the indoor temperature.” Also, vented dryer drums get very hot during operation, which—aside from the fire risk—can overdry clothes and potentially damage fabrics.
Heat pump clothes dryers
Electric-powered heat pump dryers (aka ventless or condensation dryers) dry clothes without using a heating element or vent. Instead, heat pump technology pulls air into a condenser, heats it, and sends it into the drum, where it absorbs moisture from the wet clothes. Then, the air cycles to an evaporator, where it’s cooled. As the air gets colder, it loses moisture, which is either drained or collected in a removable tray.
That same air is then pulled from the evaporator into the condenser to be reheated while it’s still warm. In other words, heat pump dryers recycle warm air instead of venting it to the outdoors. Not having to heat fresh, cold air leads to big energy savings. Park added, “Heat pump models dry laundry at lower temperatures, which is much gentler on clothes. And unlike vented dryers, there’s basically no fire risk.”
Hybrid heat pump dryers
Hybrid heat pump dryers combine the heat pump cycle with the heating element of a vented dryer. This pairing helps the dryer drum get hotter, so clothes dry faster. Hybrid heat pump dryers are much more efficient than vented dryers, but because of the heating element, they’re less efficient than pure heat pump dryers.
Size, price, and dry time
“People often think heat pump dryers take way longer to dry clothes because they use lower temperatures,” said Park. In reality, heat pump models can have dry times comparable to many vented dryers on the market today. All models with the ENERGY STAR label meet an 80 minute maximum dry time for a “typical” cycle, and some newer models demonstrate dry times as low as 50 to 35 minutes.
Historically, heat pump dryers have been compact in size, smaller than typical US household dyers. Things are changing, though. Park reported only ten options for standard-size dryers with heat pump technology, but expects that more standard-size heat pump dryers will continue to come on the market, particularly as hybrid models become more available.
Heat pump dryers are definitely more expensive than traditional vented dryers, but more and more, utility-sponsored rebates are available to offset the cost differential. Owners may also save on installation. Heat pump dryers do not require venting ductwork, which makes them simpler and less expensive to install. Homeowners can install the dryers nearly anywhere, provided the condensed water is allowed to collect or drain along with the washer.
Of course, you’ll also see major savings on your monthly energy bill.
Finally, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) will provide additional rebates and tax credits for homeowners looking to make energy-efficient home upgrades. (This savings calculator can help you estimate how much money you can save on a heat pump dryer through the IRA.)
Note: European households use an average of 3,700 kWh of electricity each year, just a third of what Americans use. Not coincidentally, while most of the world saves big money and energy by hanging clothes outside to dry, the practice is restricted or completely banned by many communities across the United States!
ENERGY STAR’s 5 Most Efficient Dryers
ENERGY STAR, run by the US Environmental Protection Agency, has overseen testing and labeling of quality, energy-efficient products for more than 30 years. The blue ENERGY STAR label signifies brands and models that are leaders in energy efficiency.
ENERGY STAR ranks dryers based on their Combined Energy Factor (CEF), a measure of energy efficiency. The higher a dryer’s CEF, the more energy efficient it is.
ENERGY STAR’s five most energy-efficient clothes dryers (unpaired units) are all heat pump dryers (as of January 1, 2024).
Blomberg – DHP24404W
- Combined Energy Factor (CEF): 11.0
- Estimated Annual Energy Use: 217 kWh/yr
- Estimated Energy Test Cycle Time: 67 minutes
- Additional Features: Sanitization cycle, Filter cleaning indicator, Steam cycle, Drum light, Time remaining display
Beko – HPD24414W
- Combined Energy Factor (CEF): 11.0
- Estimated Annual Energy Use: 217 kWh/yr
- Estimated Energy Test Cycle Time: 67 minutes
- Additional Features: Sanitization cycle, Filter cleaning indicator, Steam cycle, Drum light, Time remaining display
Miele – PDR908 HP
- Combined Energy Factor (CEF): 9.75
- Estimated Annual Energy Use: 245 kWh/yr
- Estimated Energy Test Cycle Time: 53 minutes
- Additional features: Filter cleaning indicator, Drum light, Wrinkle prevention option, Time remaining display
Asko – T411HS.W.U
- Combined Energy Factor (CEF): 9.1
- Estimated Annual Energy Use: 263 kWh/yr
- Estimated Energy Test Cycle Time: 80 minutes
- Additional features: Filter cleaning indicator, Drum light, Wrinkle prevention option, Time remaining display
LG – DLHC5502*
- Combined Energy Factor (CEF): 9.0
- Estimated Annual Energy Use: 266 kWh/yr
- Estimated Energy Test Cycle Time: 68 minutes
- Additional features: Wrinkle prevention option, time remaining display, drum capacity 7.8 cu-ft
This article springs from Electrify Now’s webinar on Heat Pump Dryers. Their followup, Heat Pump Dryers – Update on Brands and Options, compares units from Bosch, Miele, GE, and LG:
The author:
Catherine Poslusny is a freelance writer and content marketing specialist based out of Norman, OK. You can find her at catherinerosewrites.com.