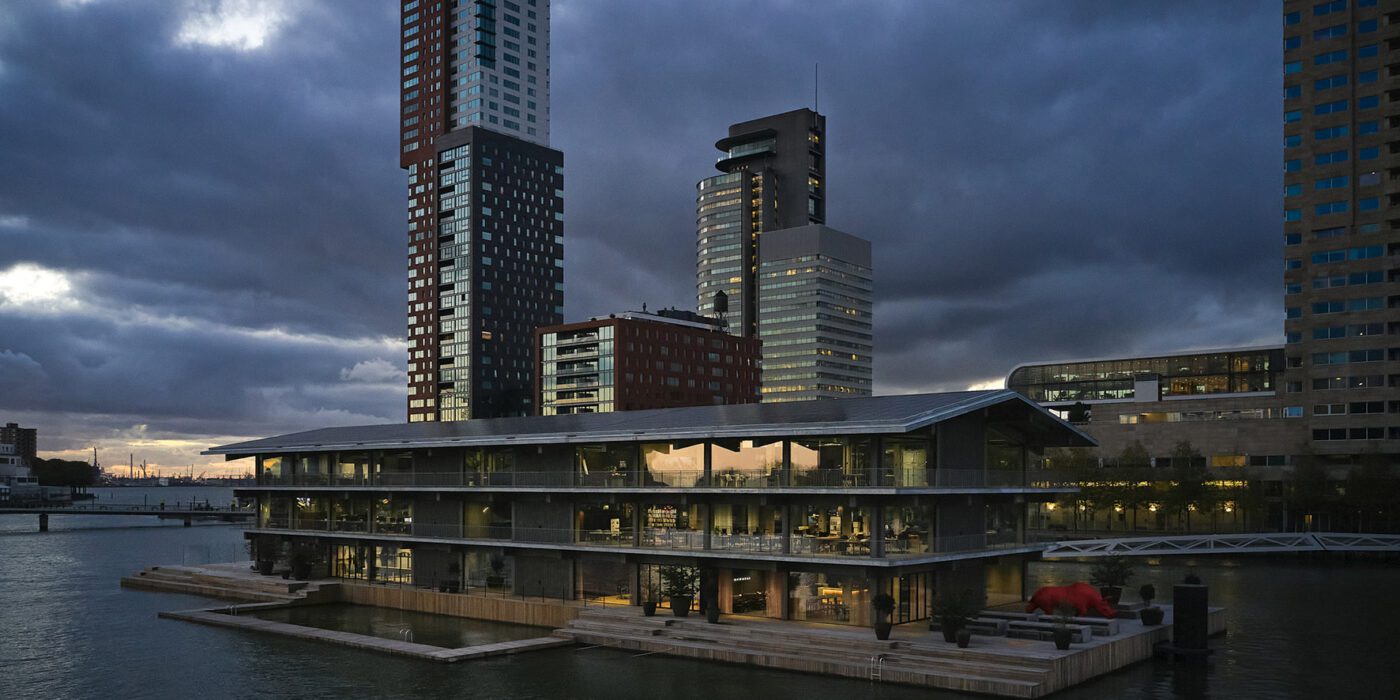
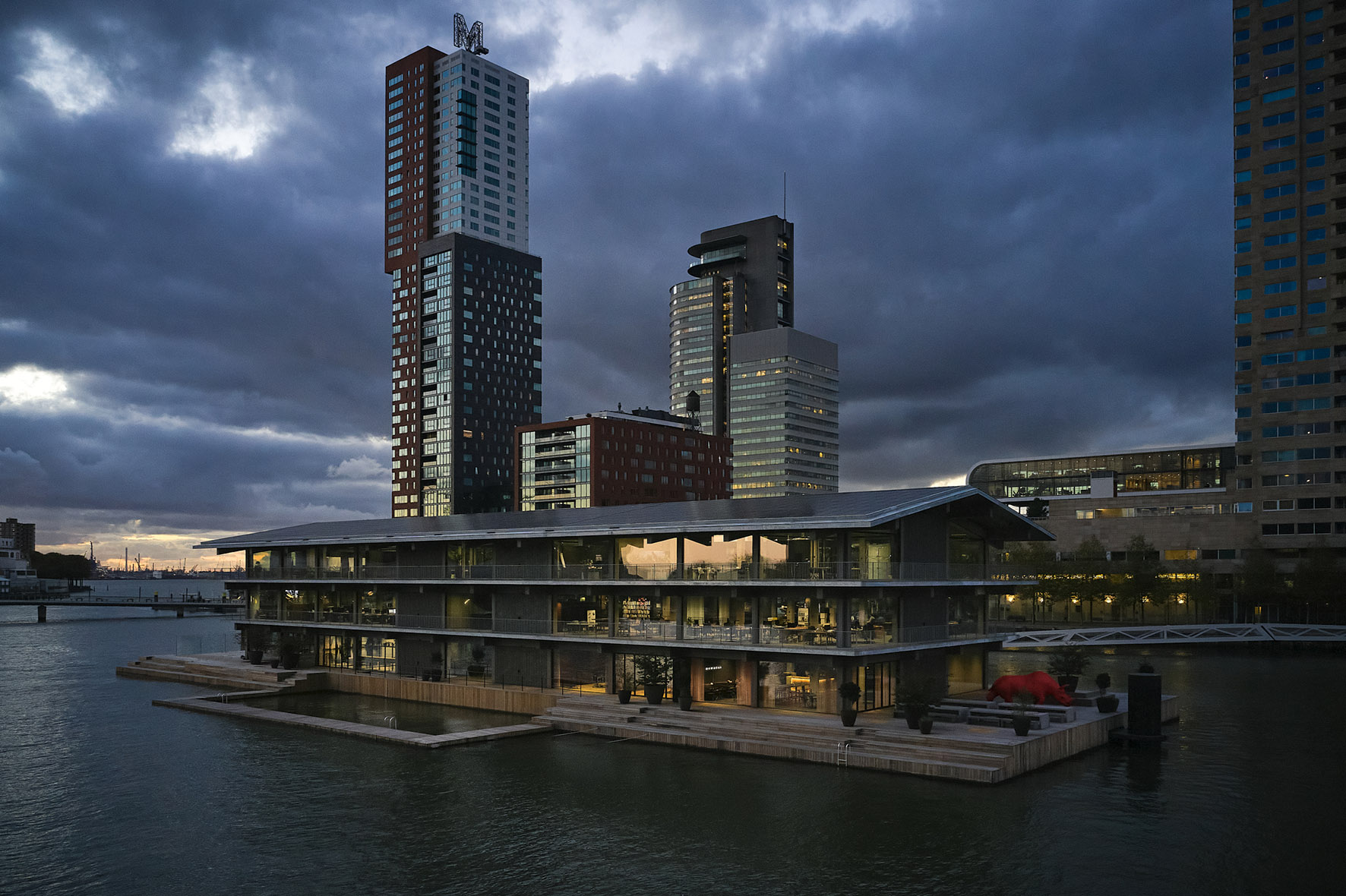
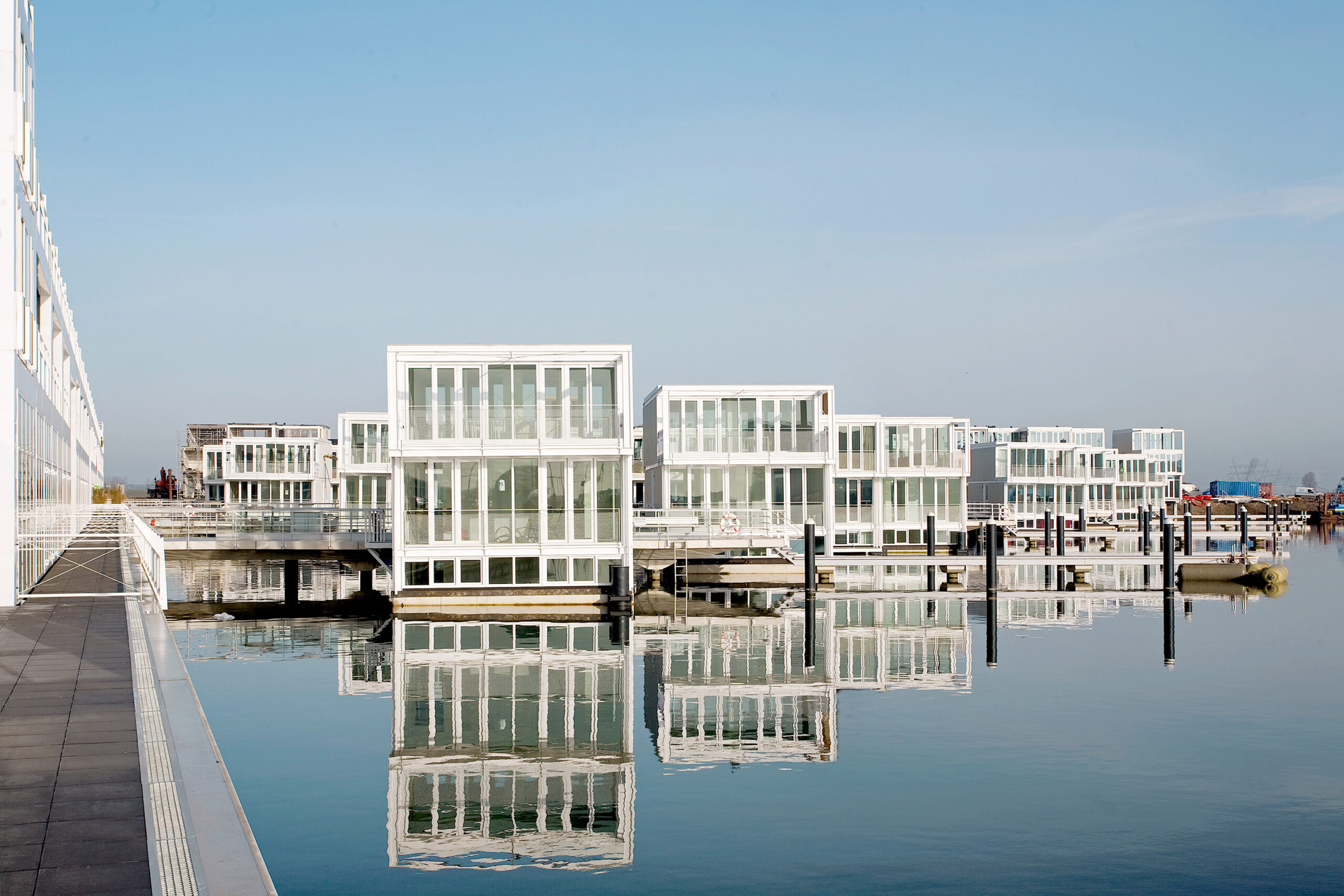
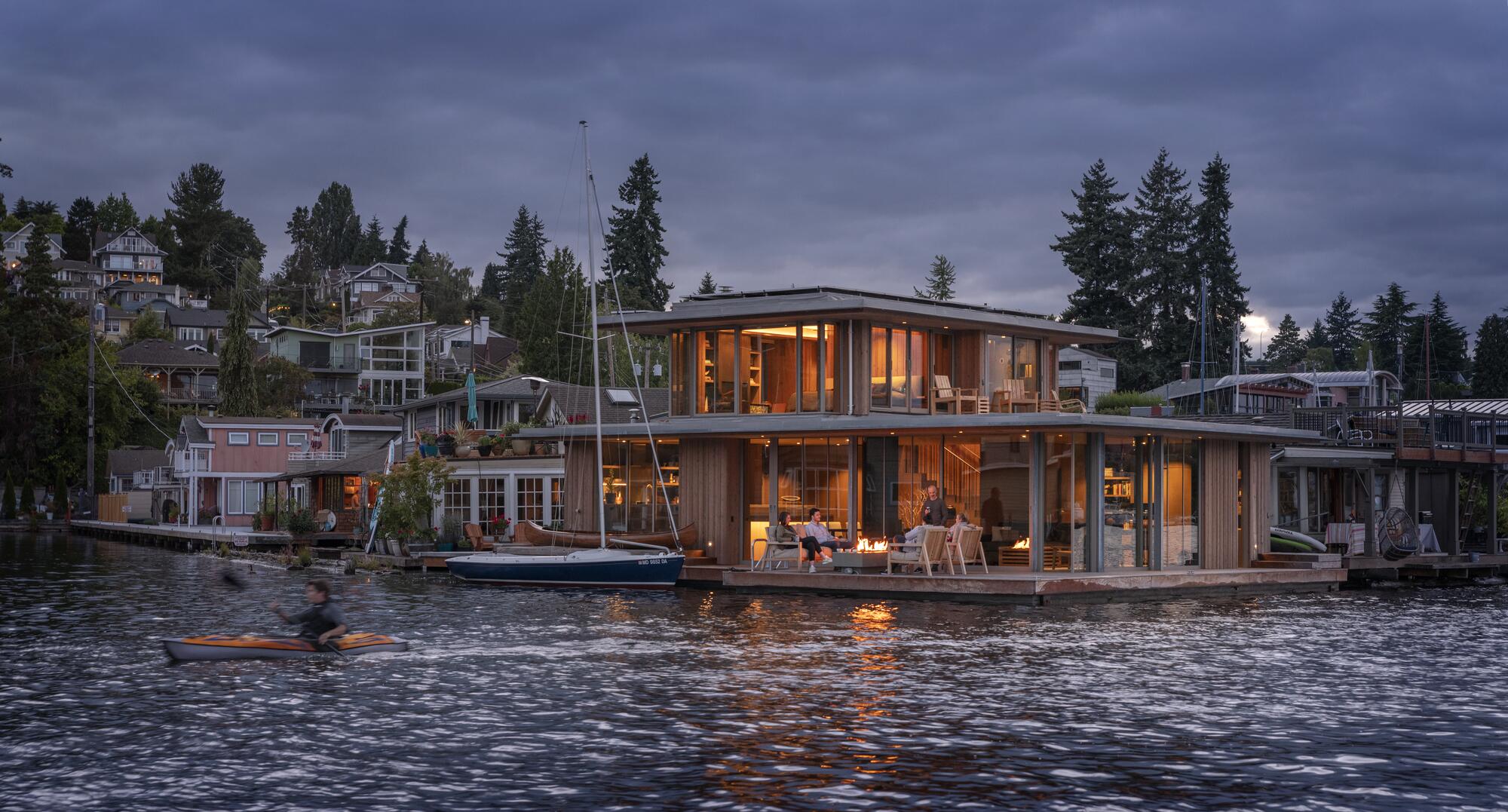
Browse the Architizer Jobs Board and apply for architecture and design positions at some of the world’s best firms. Click here to sign up for our Jobs Newsletter.
Questions abound when architecture firms choose to undertake a project intended for community use. How can a building fulfill multiple client purposes in ever-more diverse communities? How will architects respect and contribute to a sense of identity for the people intending to use the place? How will a building incorporate sustainable design and technology given budgetary limitations? These questions constantly challenge architects because they require a different answer for every new context. Moreover, such projects require teams of architects and designers who have a rigorous understanding of the multi-faceted needs of a community but who are still willing to make bold architectural statements.
KSS Architects is one of those firms that regularly handle a high level of coordination between design teams, client interests and the built environment. It’s why for this week’s jobs newsletter, we want to highlight KSS, the award-winning firm designing new and adaptive reuse community-oriented projects across the United States.
The award-winning full-service architecture, planning, and interior design firm has offices in New York, Philadelphia, and Princeton. Founded in 1983, KSS has grown to a team of 80 design professionals, building a reputation for design projects that stimulate the intersections of learning, commerce, and community.

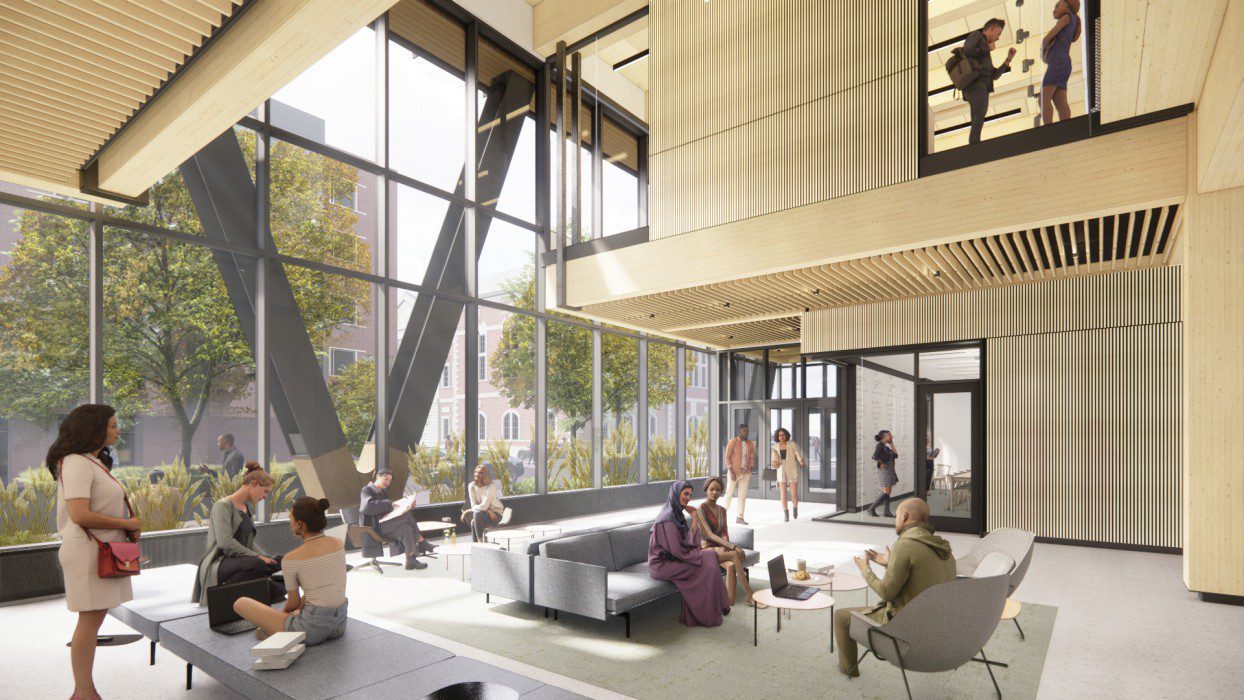
When completed, the Amy Gutmann Hall by KSS Architects will be Philadelphia’s tallest timber building; image by KSS Architects
KSS’s architects takes pride in the firm’s comprehensive design approach – a quality apparent in the dozens of projects the firm has developed over the past few years. Take for instance the Amy Gutmann Hall, the University of Pennsylvania’s future data science building. The university wanted a building that would bring the digital and natural worlds together but was unsure how this vision could materialize. After extensive consultation with the administration, members of faculty, students and other community groups, KSS developed a plan to achieve just that: their final design is not only the first mass timber project for UPenn, but also the first six-story mass timber building in the city of Philadelphia. The timber structure reduces the building’s carbon footprint by 52% relative to concrete and 41% relative to steel. The project, which is slated for completion in 2024, is bound to herald a new era for sustainable architecture at the university and beyond. It will also provide a new spacious, warm and tactile environment welcoming to students, instructors and visitors alike.
The Amy Gutmann Hall project illustrates well the design approach and work culture undertaken at KSS. The firm pairs extensive community research with deft consensus-building in which every member of the team has a voice — and a stake — in the collective success of the project. Thanks to its collaborative and transparent design process, KSS builds strong relationships of trust with clients, allowing the firm to make boldly imaginative designs to address the unique goals of clients and the environmental challenges of today.

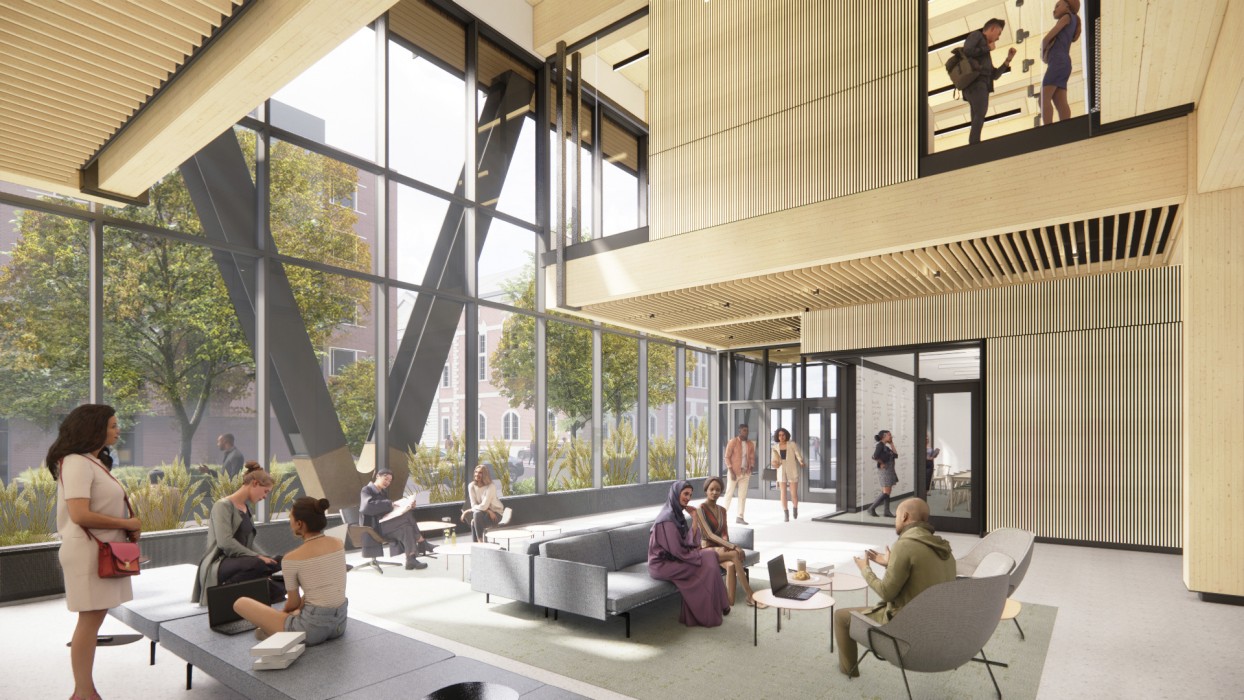
The Foundation Collegiate Academy in Newark, NJ, is one of many renovation projects KSS Architects has undertaken on charter schools in underserved communities; photo by KSS Architects
Interested in working for one of the most dynamic architectural firms in the United States focusing on community and sustainability? Consider applying to KSS Architects through Architizer’s jobs board.
The firm is currently for eight new positions for their Philadelphia offices: including Project Architects with levels of experience ranging from 3 to 10 years for QA/QC and Industrial Markets, as well as Architectural Designers with 3-5 years’ experience.
Browse the Architizer Jobs Board and apply for architecture and design positions at some of the world’s best firms. Click here to sign up for our Jobs Newsletter.