The Culture of Architecture Needs an Overhaul, Part II: Historical Background, Today’s Context and Future Steps
Evelyn Lee is the Head of Workplace Strategy and Innovation at Slack Technologies, founder of Practice of Architecture, and co-host of the podcast, Practice Disrupted. She takes inspiration from her experience in tech and outside of the profession to reimagine practice operations for firms.
The great resignation, the shesession, labor shortages, burnout and a reprioritization of life priorities have made culture conversations much more topical, but they aren’t new. This article explores some new(er) and old(er) organizations that have been making strides to address culture change at all points within the profession, starting in school.
The following is Part II of the three-part series looking at the need to redesign the culture of architecture.
- Part I defined culture and explored recent events that bring to light the increasing need for cultural change at the industry level.
- Part II looks deeper at the history of organizations working to change the profession’s culture for over a decade.
- Part III looks at how to intentionally create a values-based teaching and learning culture.
Studio Culture in Architecture Schools
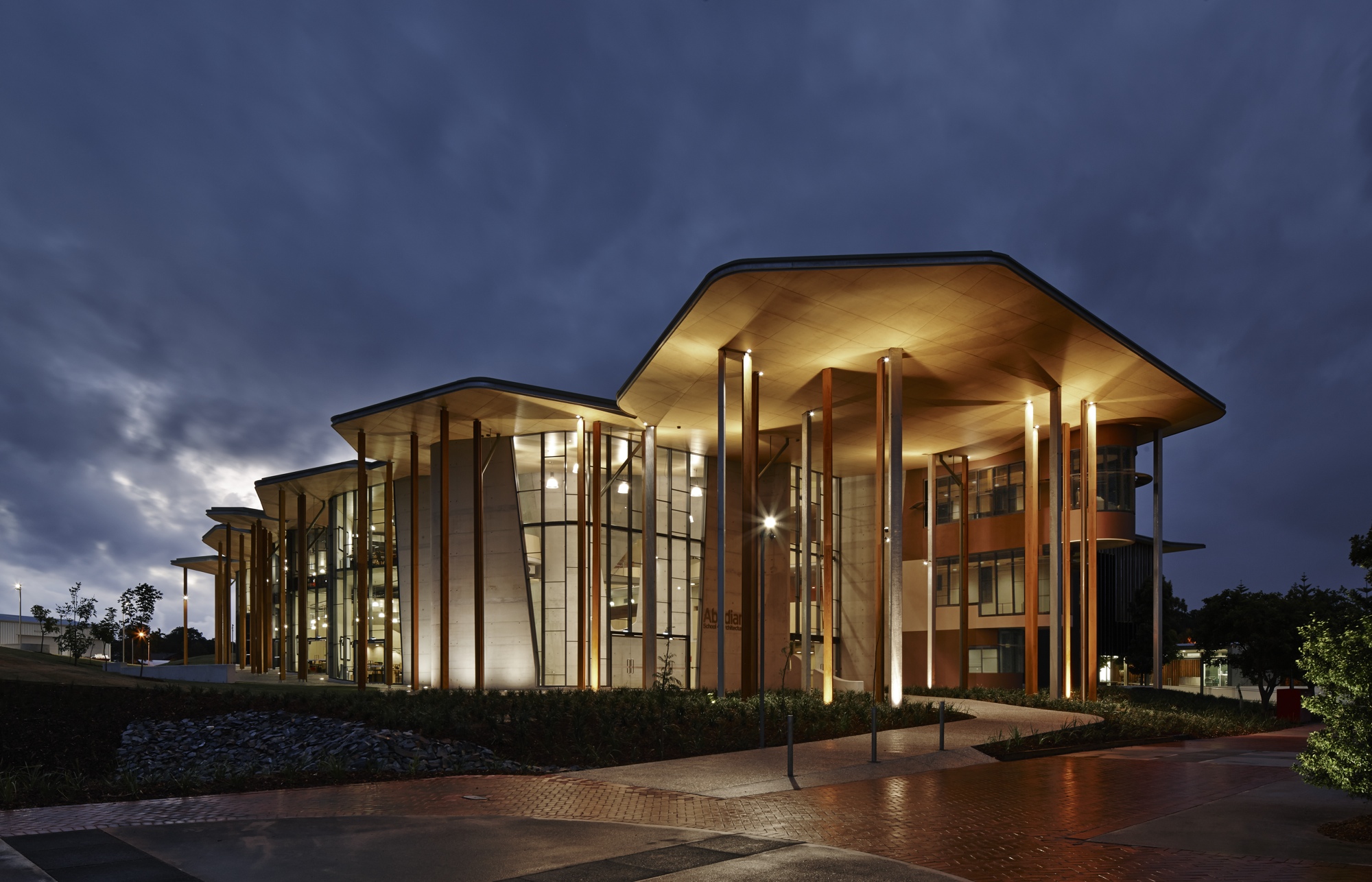

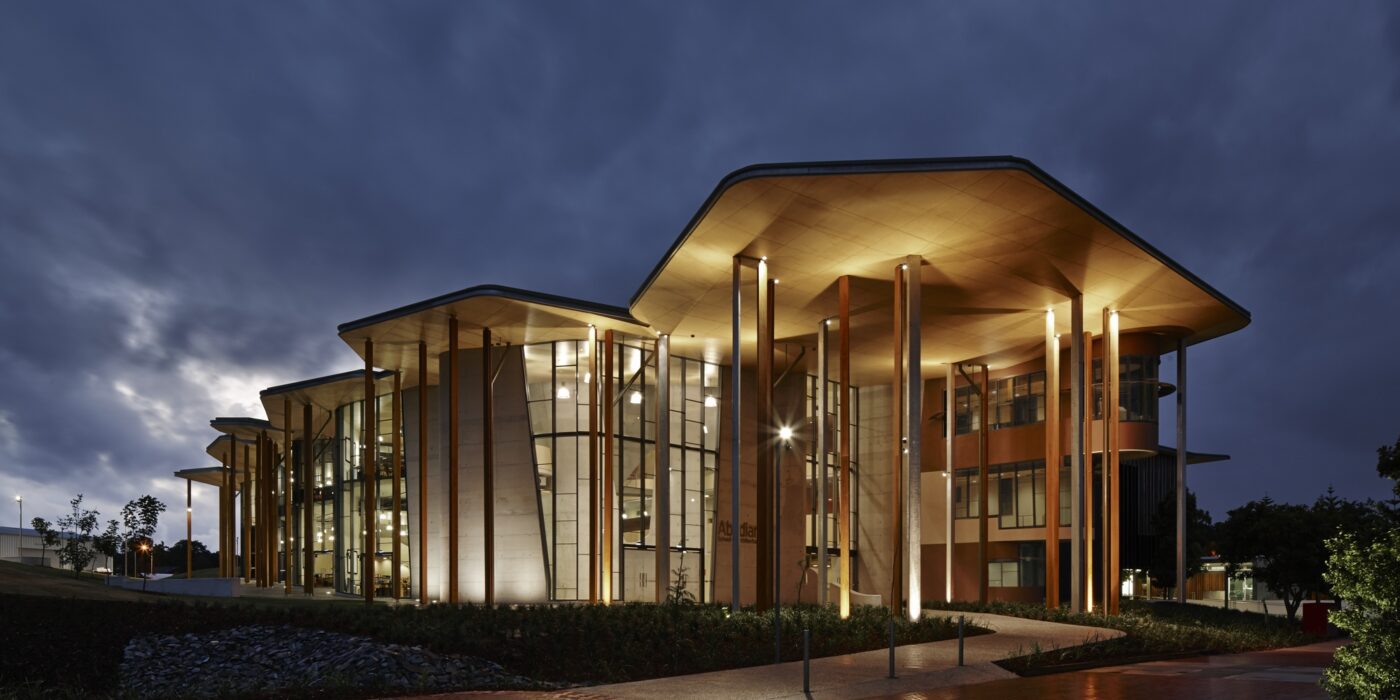
In their design for the Abedian School of Architecture in QLD, Australia, Crab Studio sought to rethink the traditional bounds of architecture’s pedagogical spaces.
Cultural change became a focus of the American Institute of Architecture Students (AIAS) in the late 1990s. It was made official by forming the first AIAS Studio Culture Task Force in 2000. The task force was created in response to unhealthy culture within architecture schools and a particular event where a student lost their life in a vehicular accident after leaving the studio with little sleep. Findings from the first task force were published in the 2002 report, The Redesign of Studio Culture.
That report opened conversations between the AIAS and the National Architecture Accreditation Board (NAAB) to add a Studio Culture Policy as one of their conditions for accreditation in 2004. However, a subsequent report in 2008 found that many things have stayed the same within studio culture with their publication, Toward an Evolution of Studio Culture.
I had the opportunity to sit down with 2007-2008, AIAS President and Vice Presidents on Season One of my podcast, Practice Disrupted, to talk with Andrew Caruso and Anthony Vankey, respectively, on their perspective of how Studio Culture translates into practice. Unsurprisingly some of the areas of concern that they address remain unchanged.
The subsequent report by the AIAS Advocacy Advisory Group, Studio Culture: Stories and Interpretations, published in 2016, raised questions about the lack of enforcement of school culture policies. Most students were unaware that a Studio Culture document/policy existed at their school, and the same individuals surveyed expressed a desire to have greater collaboration between students and faculty on conversations around studio culture.
In 2020 the AIAS redefined Studio Culture as a Learning & Teaching Culture to expand the conversation of culture to that of the students, teachers, and administrators. The subsequent AIAS Model Learning & Teaching Culture Policy is top of mind of the current 22-23 AIAS President, Cooper Moore, who notes that “The future of Learning and Teaching Culture needs to be student-led since students are the ones living it, although no culture can be truly healthy without input from all parties involved. The AIAS is committed to leading an inclusive and collaborative effort among allied organizations in the coming year to address the current environment and build a healthier and more positive culture for future architects and faculty alike.”
Separately, in a grassroots initiative. Alvin Zhu, a current M Arch student at UNSW Sydney, launched a docu-series called “Critiquing Architecture School” to bring to light the student perspective in University and bring about positive change on a broader scale.
Studio Culture in Practice

Alexander House (AH) is the home of Alexander &CO., (where their 24-person team actually works!). The purpose-built live/work set up aiming to challenge preconceptions of home, land, family and work. Conceived as a design laboratory, the space rethinks studio culture by supporting a diversity of uses including working environments for both collaboration, meeting and solo time.
The architectural labor movement, particularly unionization, is relatively new. However, there have been two previously successful union attempts in the US. The first was in 1933 with the Federation of Architects, Engineers, Chemists and Technicians (FAECT), and the second was in 1934 with the formation of the Architectural Guild of America. By the 1950s, FAECT was defunct, and the Architectural Guild of America evolved to support engineers and construction workers, though, despite the name, architects were not included. Later, In the 1970s there was a failed bid by SOM’s San Francisco office to unionize.
Then, in 2013 the Architecture Lobby was launched to demystify architecture’s labor conditions, especially illegal and humane practices, and value its workers as much more than starving artists. Most recently, coming out of the SHOP Architects’ bid for a union, Architectural Workers United (AWU) was launched.
AWU is today affiliated with the International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers (IAMAW) union. It is “a collaborative project with the goal of building on the tremendous inherent value the profession offers the industry, but is not recognized nor rewarded for.” The AWU has a full-time employee working on their behalf and coordinating several efforts.
I had the opportunity to sit down with AWU’s Andrew Daley and assistant professor at Rhode Island School of Design, Jess Meyers, to have an open conversation about the Architecture Labor Movement last year, including questions about misconceptions and benefits from unionization within the profession.
Late last year, efforts from AWU resulted in Bernheimer Architecture creating the Industry’s only Private-Sector Union, hoping “to prompt changes to industry-wide problems like long hours and low pay.”
Outside of the Union conversations, there’s been an uptick in the industry’s interest in mental health and burnout. In 2021 Monograph launched its State of Burnout in Architecture survey, stating that the Coronavirus pandemic didn’t cause burnout for architects but made it worse for 90% of its 225 respondents. In 2022, following their article “We Need a Safe Place to Address Our Mental Health,” the authors are working together to coordinate an effort similar to LAP, or the Lawyer’s Assistance Program, in an attempt to help those within the industry who struggle with anything from anxiety, burnout, depression, to substance abuse.
Redesigning Culture Going Forward
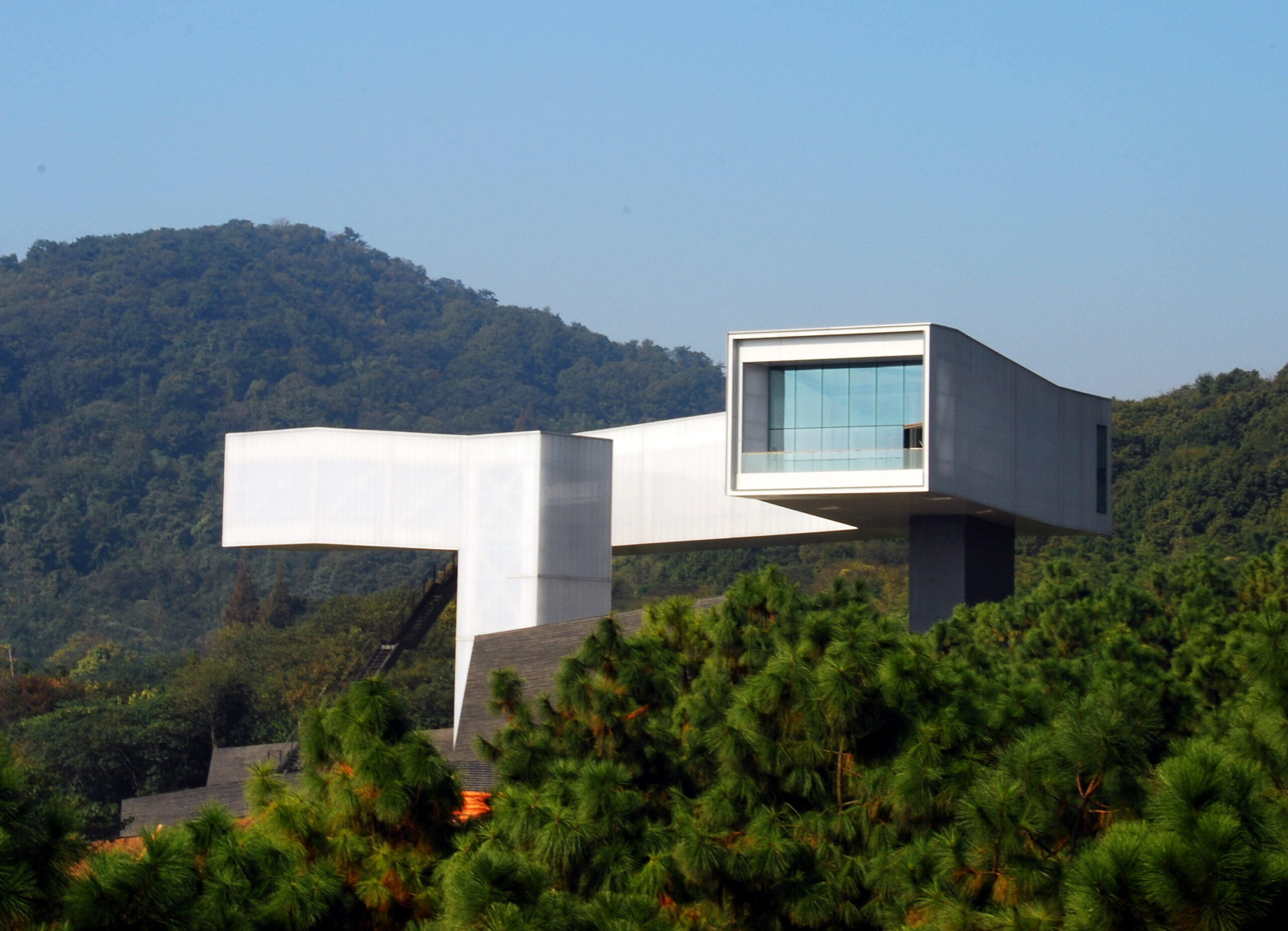

Steven Holl Architects‘ Nanjing Museum of Art and Architecture explores shifting viewpoints, an apt metaphor for the multi-perspectival type of rethinking the industry requires.
Firms are currently operating in an employee marketplace. 86% of respondents in the February 2023 AIA Architecture Billings Index (ABI) reported that recruiting architecture staff continues to be an issue at their firm, with 62% saying it is a significant issue.
This has led many individuals to discuss the need to fill the architecture pipeline, but ACSA’s most recent survey on Budget and Enrollment Survey Results shows a continuous growth in applications and corresponding faculty load. The greater question we need to ask is, are we truly experiencing a labor shortage, or do we find ourselves in a position where we are struggling to keep those who we already have in the pipeline?
The best way forward is to chart a new path and understand that organizational culture within a business is a strategic advantage to attracting and retaining talent. In Part III of the series on evolving culture, we look at the importance and history behind Petter Drucker’s famous saying, “Culture eats strategy for breakfast.” As well as some tactics that architecture firms can implement to have meaningful conversations with their employees on creating a culture that supports their individual needs and creates high-performing teams.
Browse the Architizer Jobs Board and apply for architecture and design positions at some of the world’s best firms. Click here to sign up for our Jobs Newsletter.
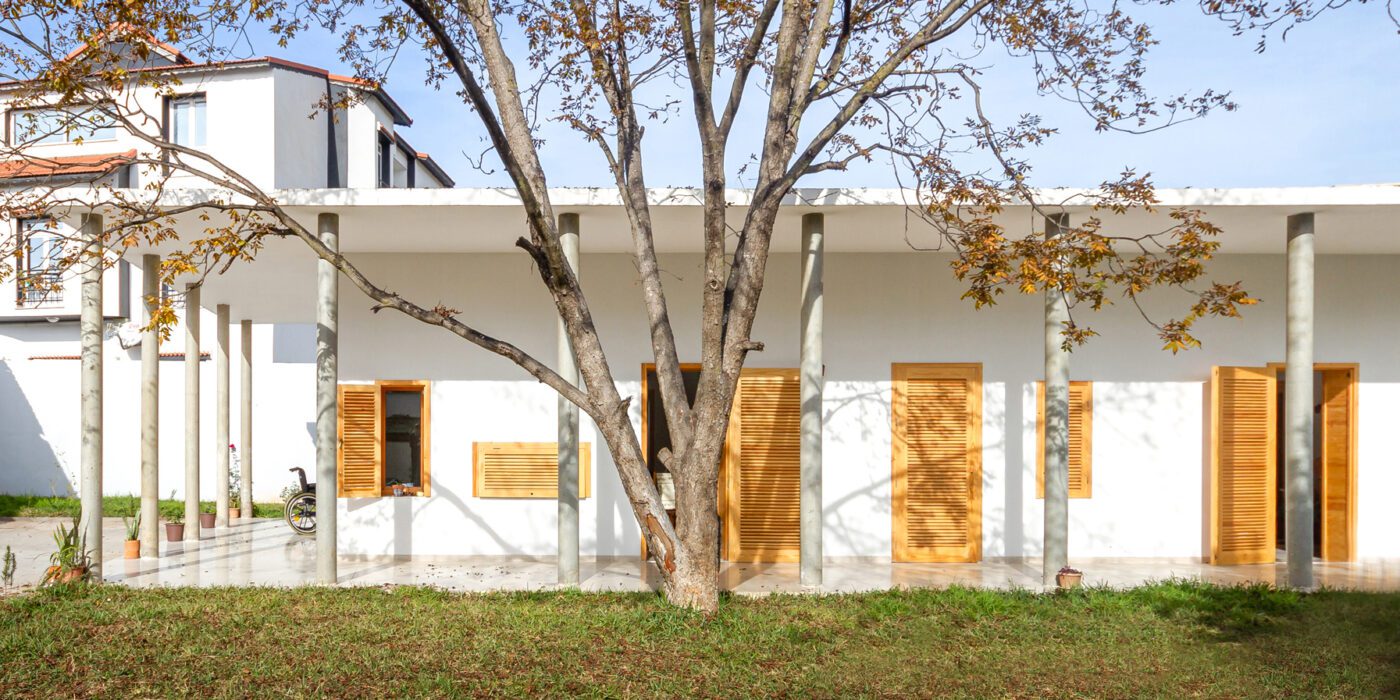
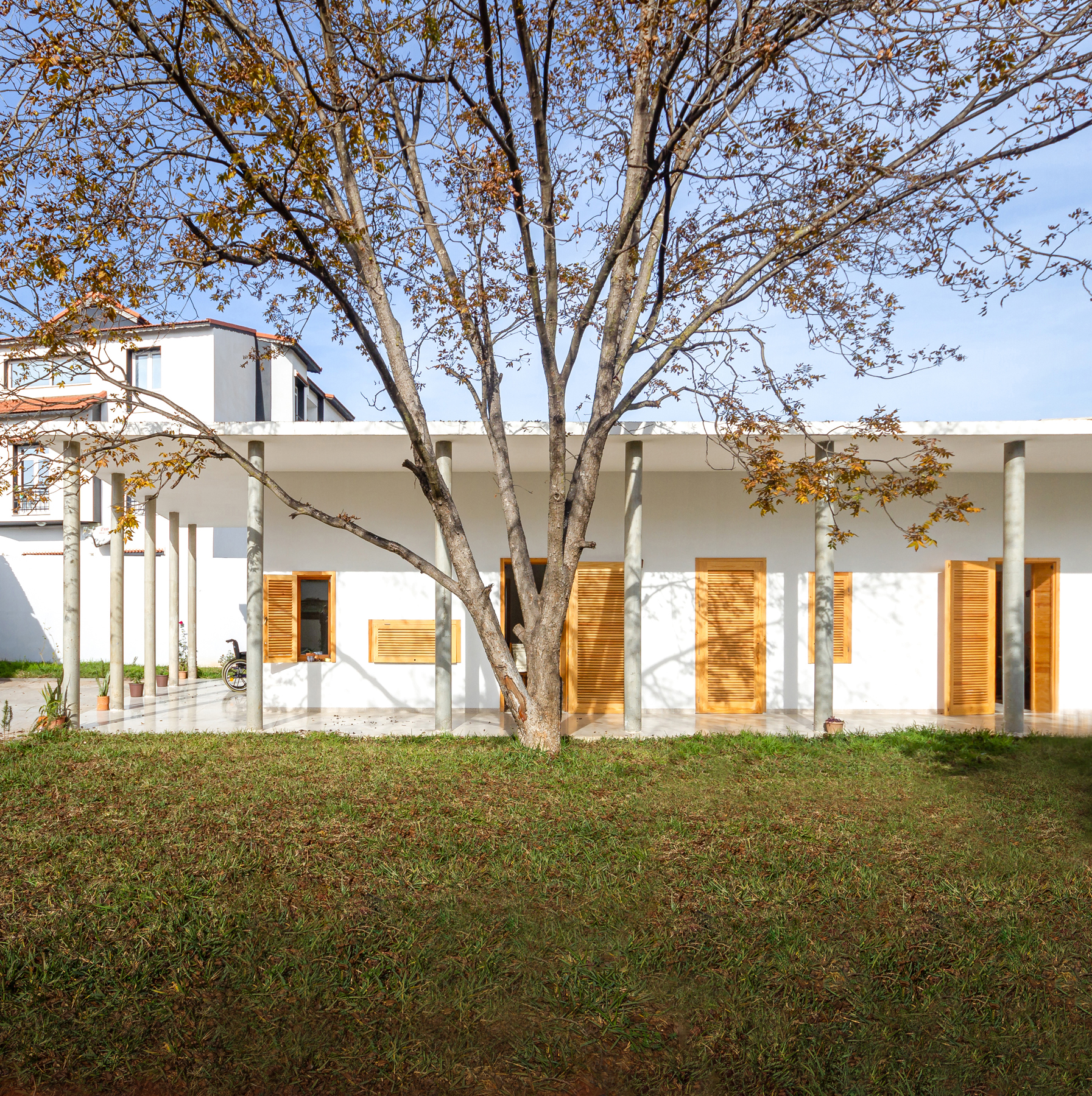




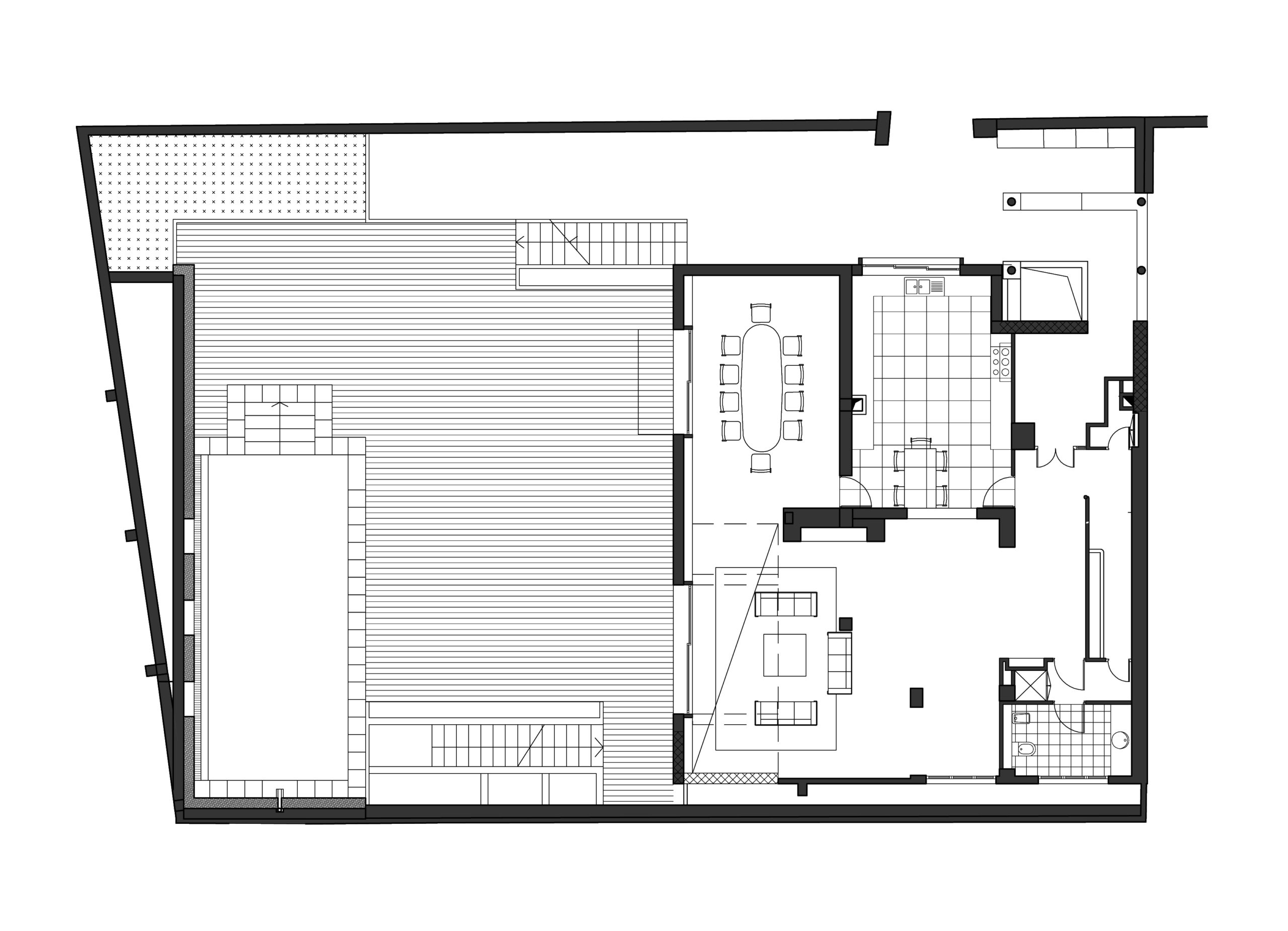
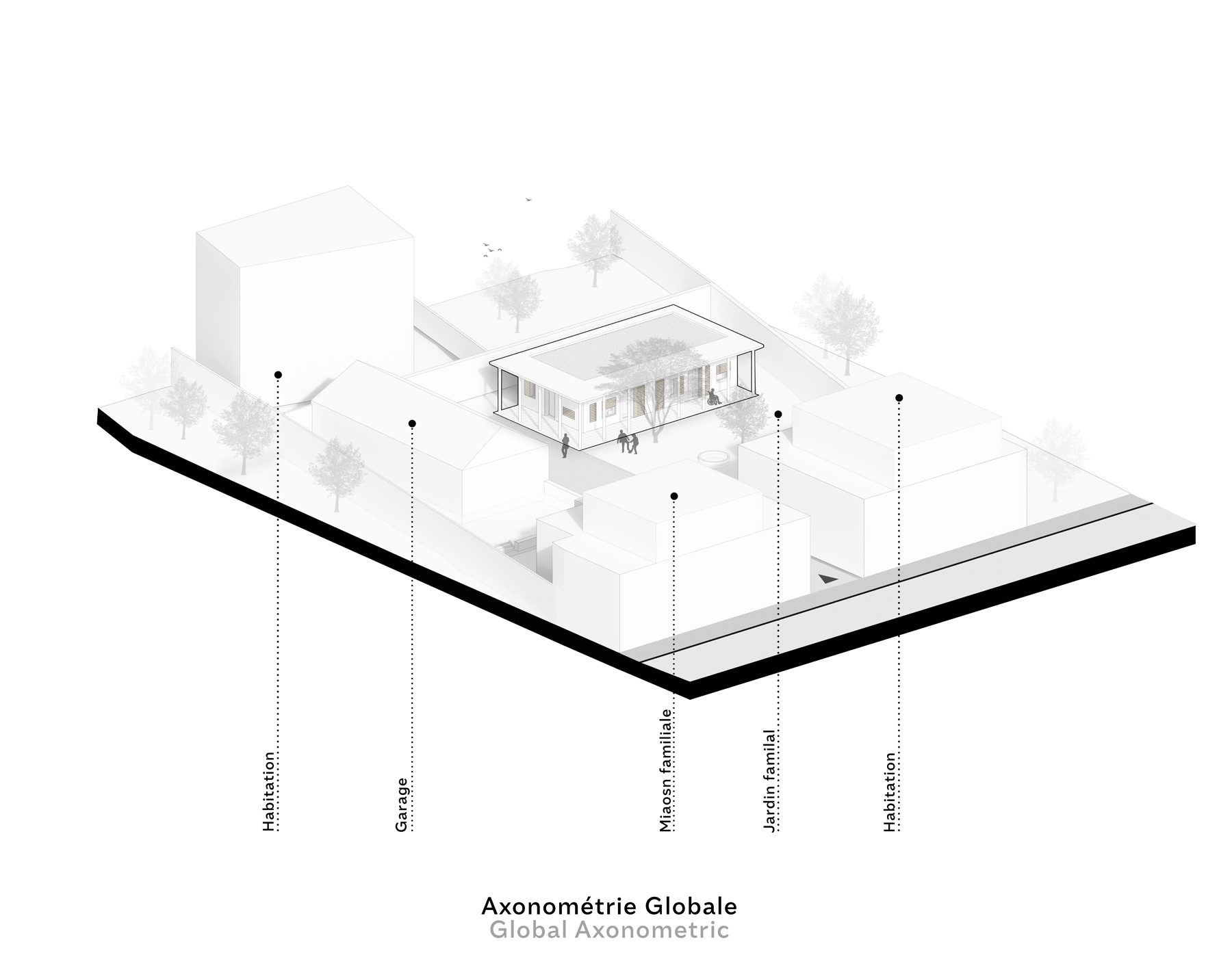 In this highly accessible house that was designed for two elderly parents in Tipaza, three factors guided the design process: privacy, weather conditions and activity, which reflected on the building envelope, building layout and building orientation. The design of the openings achieved the required level of privacy for Algerian culture, while opening up the house to the surrounding garden for natural ventilation, sunlight and views, taking in consideration the challenging weather conditions of the area.
In this highly accessible house that was designed for two elderly parents in Tipaza, three factors guided the design process: privacy, weather conditions and activity, which reflected on the building envelope, building layout and building orientation. The design of the openings achieved the required level of privacy for Algerian culture, while opening up the house to the surrounding garden for natural ventilation, sunlight and views, taking in consideration the challenging weather conditions of the area.