How can architecture be a force for good in our ever-changing world? During Future Fest, we’ll pose this question to some of the world’s best architects. Launching in September, our three-week-long virtual event will be 100% free to attend. Register here!
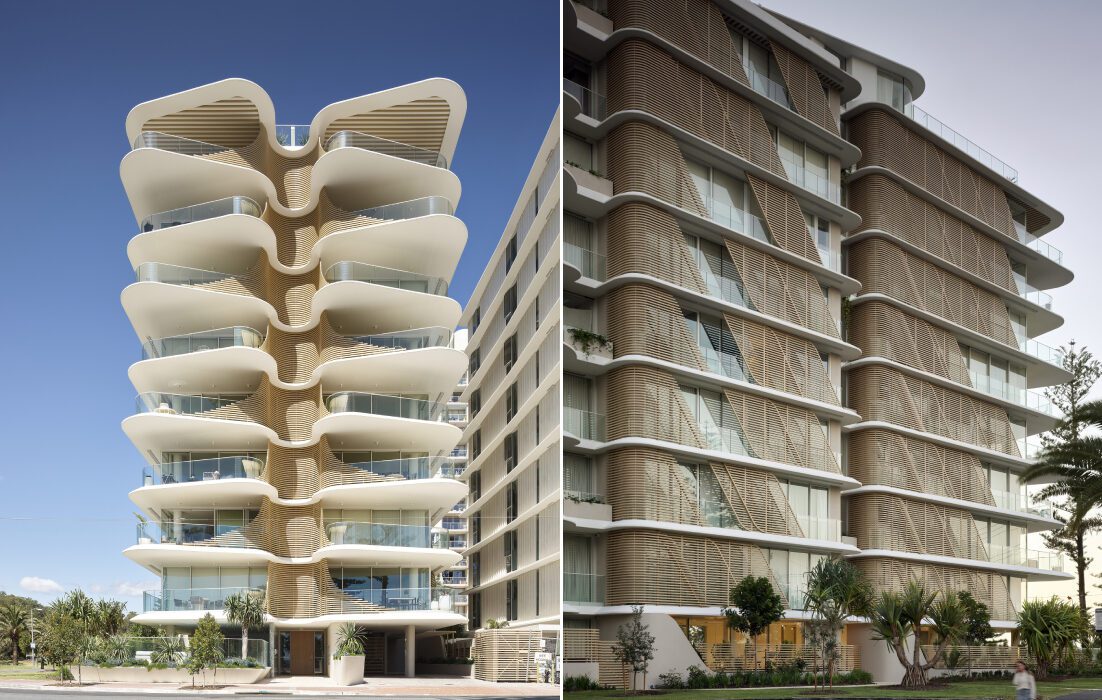
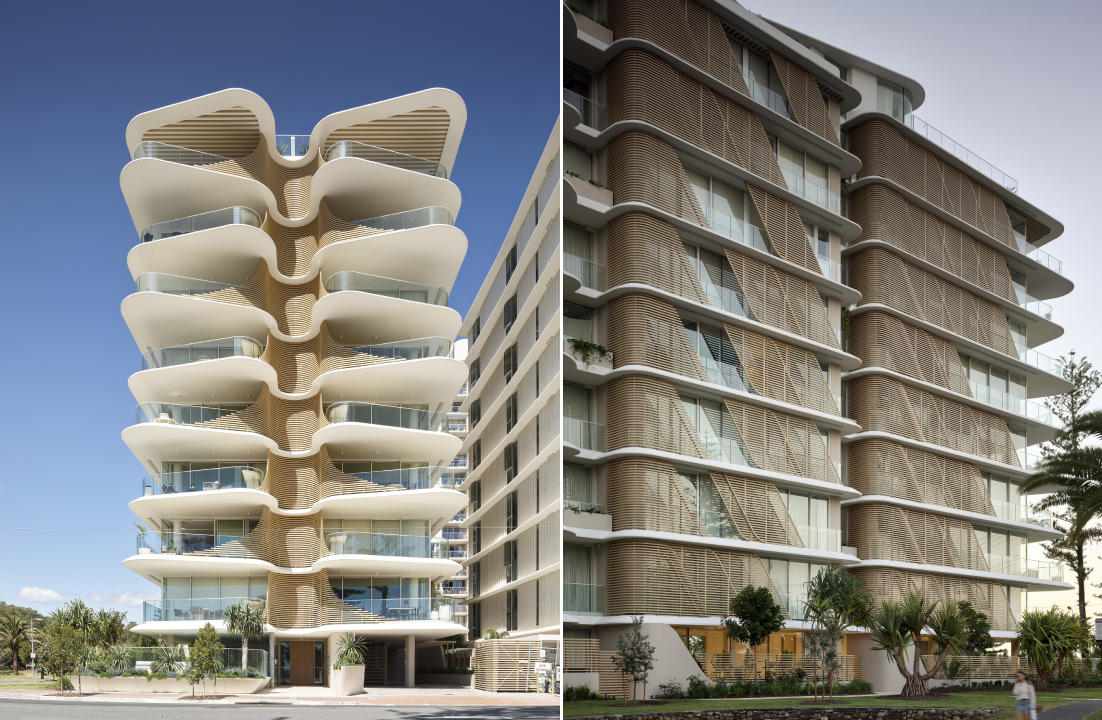
Nestled between beloved Surfers Paradise and chill Coolangatta, Burleigh Heads is a small suburb on Australia’s famed Golden Coast, known for its crowd-drawing surf breaks and iconic towering pine trees. In recent years, a hip dining scene has emerged, reflecting how the area’s popularity has grown. Now, there is a need for more multi-residential developments has increased to help house the growing influx of locals and visitors alike. For the first time in the area in three decades, a multi-residential development has gone up, taking the name of Norfolk, Burleigh Heads.
The iconic luxury apartment building gets both its name and from the heritage Norfolk pine trees found around the site, making a significant contribution to the unique features that set this area apart from the rest. “Just like their pinecones protect its seeds from bad weather and open when in ideal natural settings, Norfolk’s architecture can be adapted to protect residents from the elements or opened up to take in the 300 days of subtropical sunshine and stunning natural surroundings,” said the building’s visionary Koichi Takada Architects, a firm known for the diversity of their portfolio and imaginative willingness to push the bounds of architectural form.

Images by Scott Burrows
The 10-story building bagged both the Jury and Popular Choice A+Awards in the Multi-Unit Housing – Mid Rise category and for a good reason. It makes a statement, challenging how we imagine multi-residential towers, while staying true to the unique features that make the site special. Fanned balconies, a ribbed spine and endless views are just a few other elements that make it special. Its organic form allows it to be a spectacle from every angle and makes it seem like it will take flight. And while its geometry sets it apart, its neutral beige hue helps tie it to the beachy surroundings.
Large open balconies and maximized exterior surfaces allow more natural light to enter the building and increase the resident’s connection with the outdoors. Instead of being stacked uniformly on top of one another, the floating balcony slabs all vary in shape and are strategically overlapped to create additional shade and privacy for the homes below. Imitating the Norfolk pine, their sides are covered in slatted screening to create additional privacy. One can see that these floating slabs are also tapered at the edges and extend beyond the glass balustrade, making them seem even lighter and reflect natural light further into the homes.
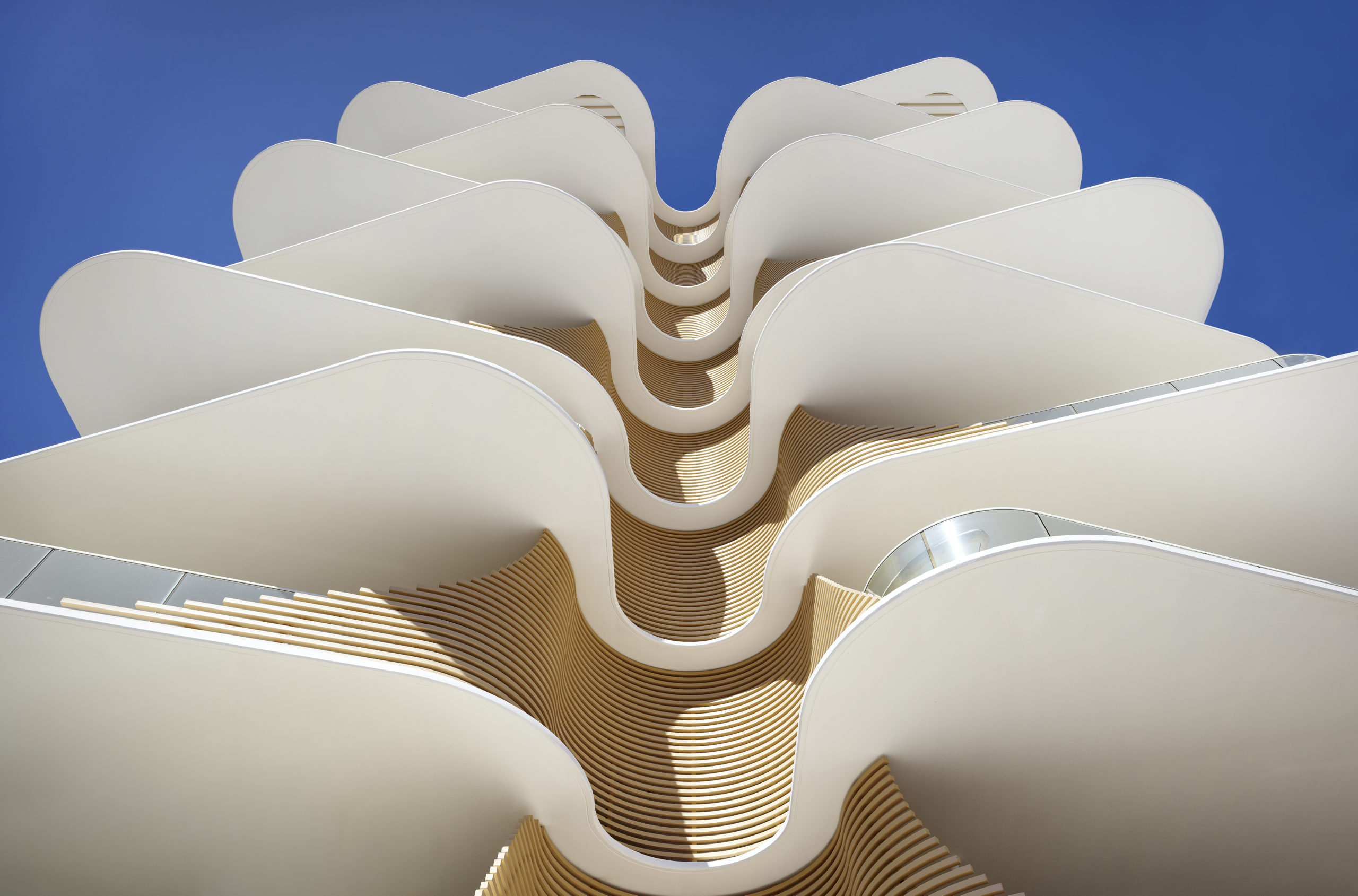

Image by Scott Burrows
Cementing the relationship with nature, the architects have also added a spine to the building that curves inwards and allows the blades of the balconies to connect together like ribs. This provision creates shade in the summer, enhancing privacy while also allowing those inside to get glimpses of the ocean. The sides of the building also have slatted screens arranged in a diagonal pattern across the balconies to break up vertical lines and add some dynamism. Since these diagonal panels are movable, the façade is constantly changing are creating new patterns, further reflecting the ever-changing qualities of nature.
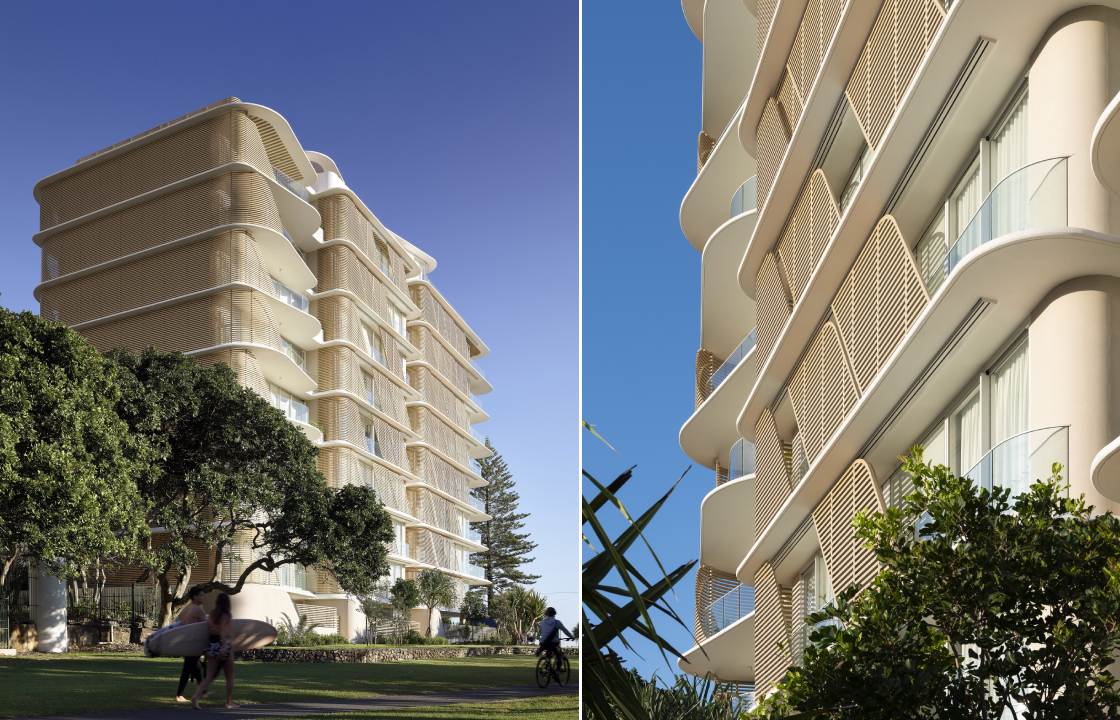


Images by Scott Burrows and Tom Ferguson
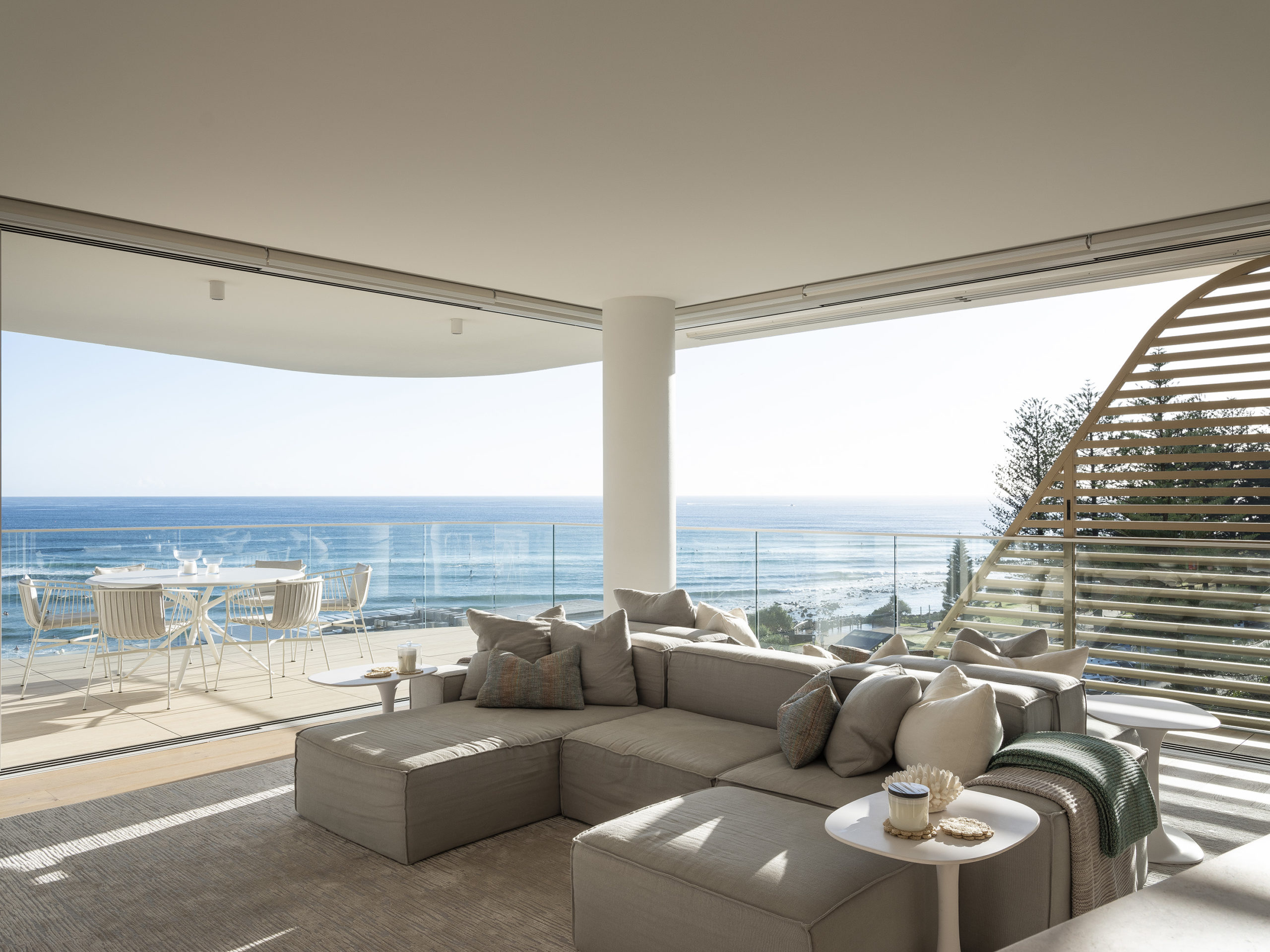
The structure holds fifteen apartments and a part of two-level penthouses with private rooftops. Making it even more enticing to residents is the inclusion of a gym, outdoor pool and sauna. While all the apartments have generous light and ventilation, the north-facing homes have an unhindered 180-degree view of the ocean. The living, dining and kitchen areas spill out into the large balconies. The southern end of the building holds the en-suite bedroom. There are two additional rooms in the center of the floor as well. Natural timber floors used within the home extend to the balconies as well and create a clear visual connection with the sandy shore beyond. The interior spaces of these homes, fashioned by Mim Design, build on the natural tones found on the exterior of the building to create a cozy coastal home.
How can architecture be a force for good in our ever-changing world? During Future Fest, we’ll pose this question to some of the world’s best architects. Launching in September, our three-week-long virtual event will be 100% free to attend. Register here!