Growth Environment: Architect’s Role in Modernizing Farming Practices and Smart Agriculture
Architectural Transformations: RIO ECO2 Venture and Smart Agriculture

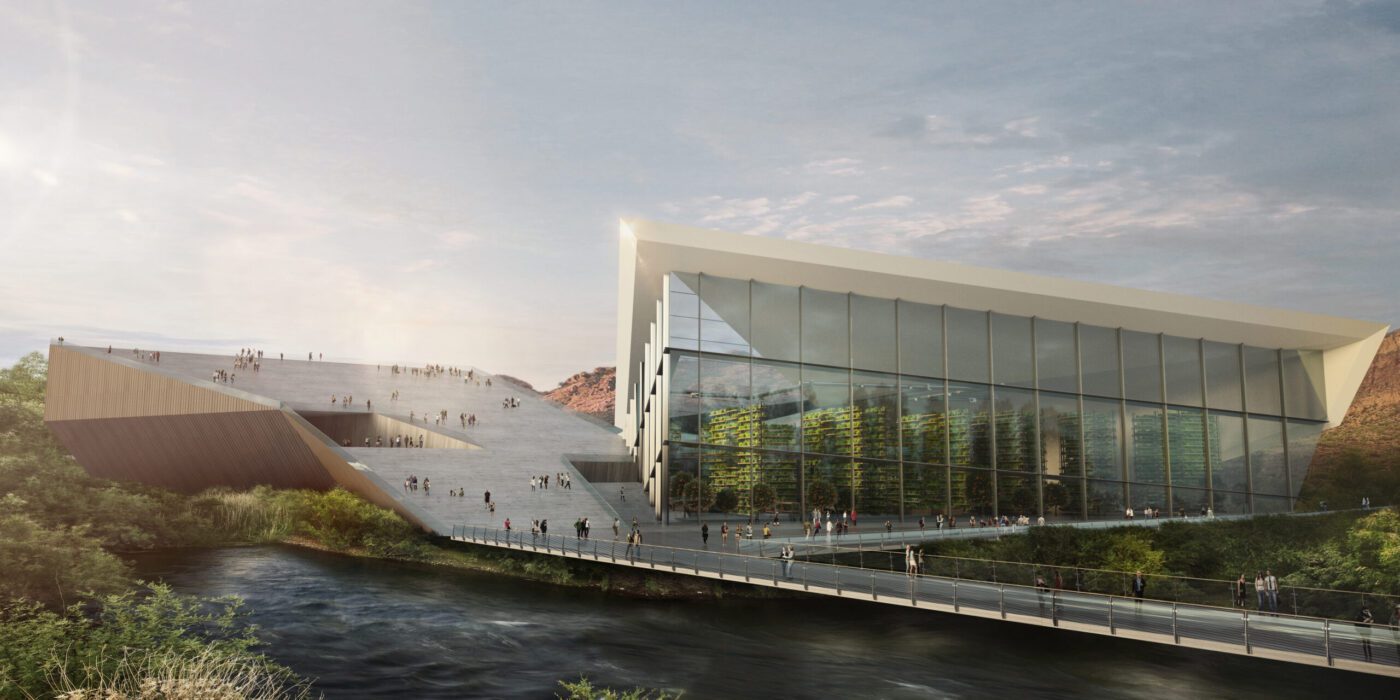
RIO ECO2 Venture by KRAUSE Architecture/Interior, Phoenix, Arizona | Concept.
Smart agriculture technology in architectural design undergoes a concrete manifestation in projects like the RIO ECO2 Venture. This transformative approach integrates advanced technologies into the landscape of agricultural spaces. Architects draw inspiration from such endeavors, conceptualizing structures that embrace precision farming, serving as living laboratories. By incorporating sensors and IoT devices, these structures facilitate data-driven decision-making concerning soil conditions, crop health and climate factors.
In the spirit of the RIO ECO2 Venture, vertical farming facilities emerge as intricately designed hubs with controlled environments, utilizing automation and robotics for tasks like planting and harvesting. The visionary designs prioritize energy-efficient greenhouses, integrating renewable energy sources and smart irrigation systems, exemplifying a commitment to optimizing resource usage.
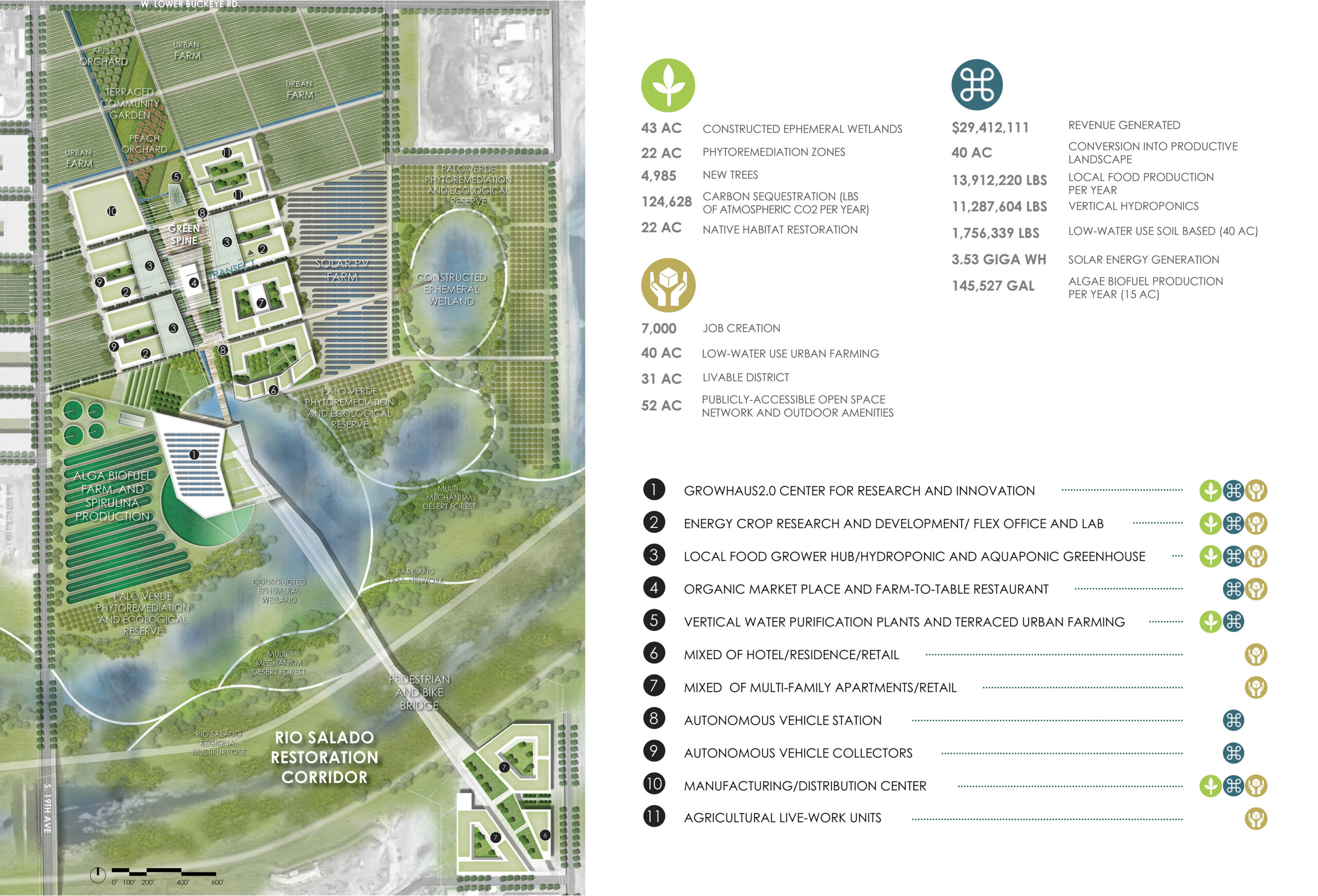
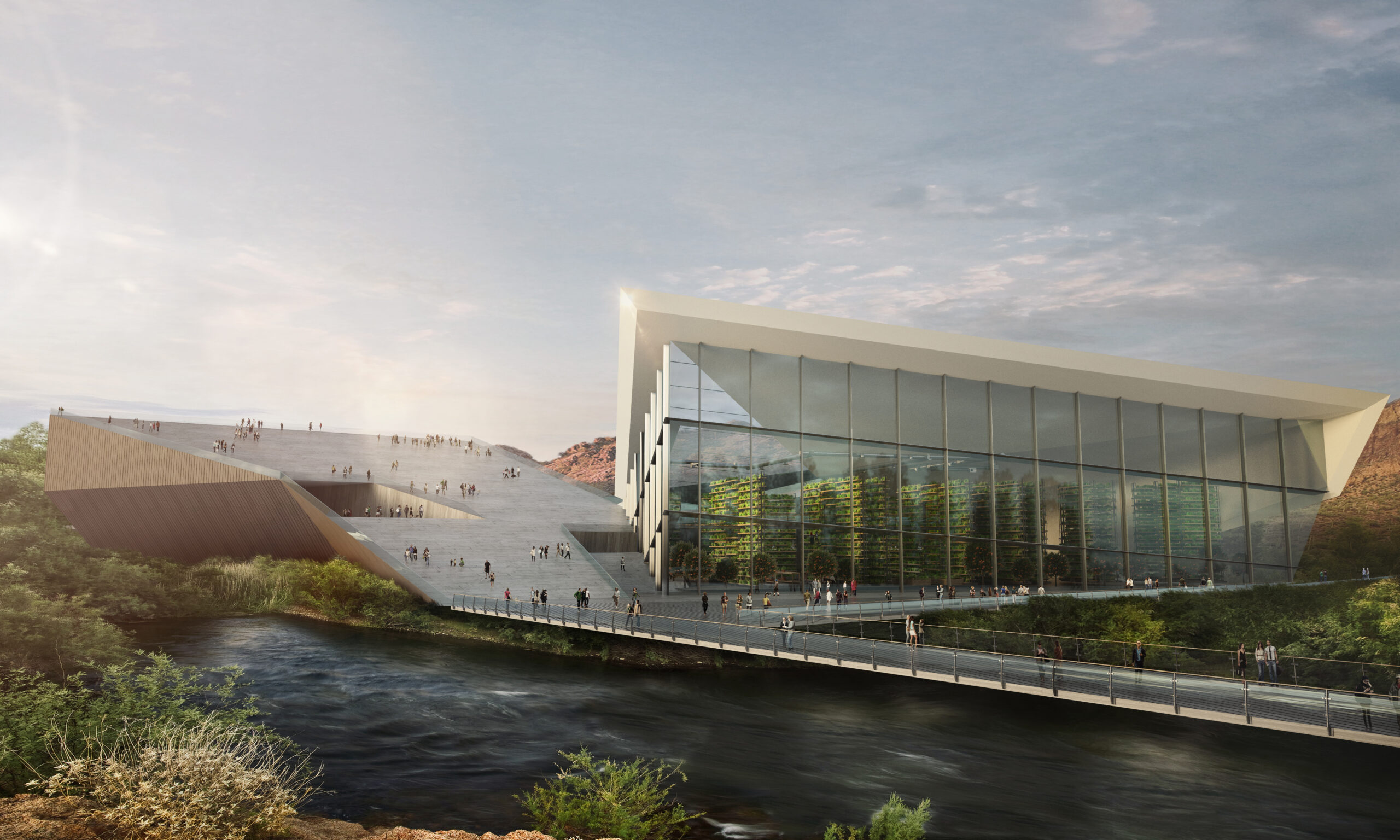
RIO ECO2 Venture by KRAUSE Architecture/Interior, Phoenix, Arizona | Concept
Architects extend their vision beyond physical infrastructure to create collaborative spaces that inspire research and education. This synthesis of architectural ingenuity and smart agriculture technologies, mirrored in projects like RIO ECO2 Venture, gives rise to environments that harmonize innovative farming practices with sustainable architectural design, fostering efficiency, productivity and environmental consciousness.
ECO2, a visionary 213-acre self-sustaining development, tackles the challenges of rising temperatures and water scarcity through sustainable food technology, serving as a beacon of innovation and underlining the critical importance of food and water security. Beyond its role as an educational center and community strengthener with a holistic Net Positive approach, ECO2 stands as a model for Arizona’s future, adeptly embracing technology, repurposing land for sustainability, and seamlessly integrating urbanity with agriculture.
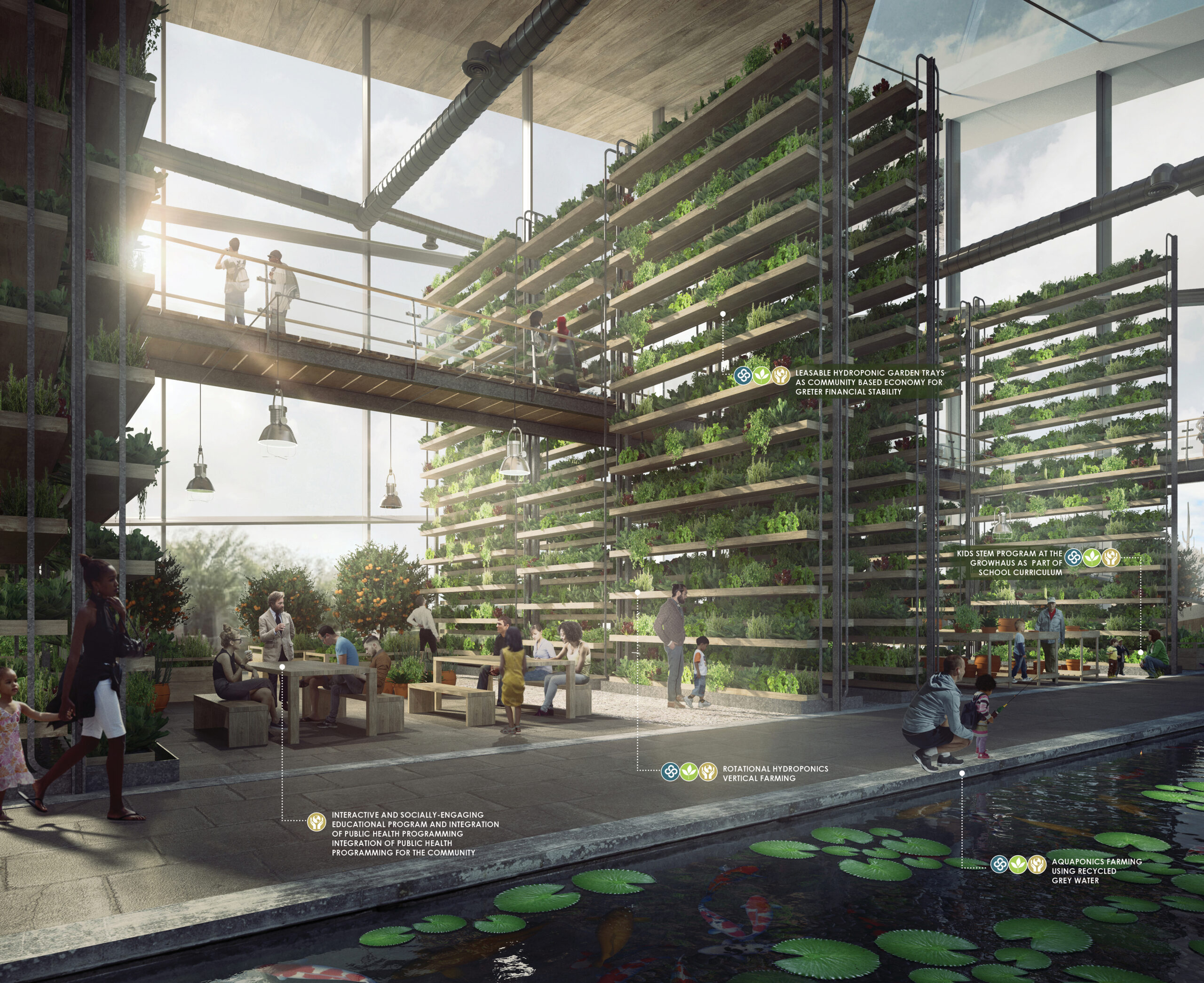

RIO ECO2 Venture by KRAUSE Architecture/Interior, Phoenix, Arizona | Concept
The community-driven GrowHaus 2.0 within ECO2 is a testament to this foresight, fostering distribution, production and education while addressing climate change and enhancing food access. As ECO2’s comprehensive plan champions the coexistence of agriculture and development, emphasizing sustainability, water reuse, and acknowledging the impact of increasing heat, it harmoniously integrates smart agriculture technologies. ECO2 stands at the forefront, symbolizing the convergence of innovation and circular food supply chains, pursuing a more resilient, sustainable and interconnected food system.
Agrotopia: Pioneering Circular Food Systems and Sustainable Architecture
Designing modern agricultural facilities with a focus on circular food supply chains is a visionary pursuit that harmonizes sustainable principles with innovative technologies. Architects and planners create closed-loop systems in these facilities, turning waste into valuable resources to prioritize resource efficiency. These designs prioritize community-supported agriculture and regional resilience, embracing local sourcing and distribution networks. The integration of precision agriculture technologies ensures optimal resource utilization, minimizing waste and environmental impact. In the quest for sustainability, the incorporation of urban farming and vertical agriculture maximizes land efficiency and shortens supply chains.
These facilities are conceived as modular, adaptable spaces constructed with sustainable materials and powered by renewable energy sources. Water recycling systems and efficient irrigation practices are seamlessly woven into the designs, while smart packaging solutions aim to reduce excess waste. Engaging communities through educational spaces within the facility fosters awareness and understanding of the circular food supply chain model.
As the principles of circularity and sustainability take root in the conceptualization of modern agricultural facilities, tangible exemplars like Agrotopia, Europe’s largest rooftop greenhouse, showcase the transformative marriage of visionary design and sustainable urban agriculture.
Agrotopia is a cutting-edge research center for urban food production, situated on the roof of the REO vegetable and fruit auction in Roeselare, Belgium. The innovative 102,257 square foot (9,500 square meters) building features striking faceted glass façades, a monumental entrance staircase and multifunctional spaces, exemplifying the future of sustainable urban agriculture.
With a focus on intensive space utilization, circular energy and water use, Agrotopia serves as a transparent sculpture of glass and steel, standing out against the city skyline. The building houses high-tech research facilities for cultivating fruits and vegetables, with an educational route for the public. The building’s unique design includes a double-height façade conservatory for innovative vertical cultivation, utilizing rainwater from the roof for irrigation.
Agrotopia embraces circular practices, utilizing rainwater for irrigation, cleaning and reusing residual water, and incorporating municipal residual heat from a nearby waste incinerator. The greenhouse is a model of circular symbiosis with the city, representing the forefront of sustainable urban food production and architecture.
Innovation in Design: Architectural Solutions for Smart Agriculture’s Impact on Food Production
The harmonious integration of smart agriculture into architectural design, exemplified by projects like RIO ECO2 Venture, is a testament to the synergy between technological advancement and environmental consciousness. Beyond physical structures, visionary designs such as RIO ECO2 Venture are catalysts for collaboration, research and education, engendering efficiency and heightened environmental awareness.
In the realm of circular food supply chains, exemplified by Agrotopia, the marriage of visionary design and sustainable urban agriculture takes center stage. Agrotopia’s circular practices and space efficiency position it as a leading model in sustainable urban food production.
This symphony of innovation and circularity concludes with a resonant echo, championing resilience, sustainability and interconnectedness. The aspiration is to achieve a harmonious equilibrium between food production and the environment, recognizing the crucial need to transform agriculture for sustained productivity and address issues of hunger and malnutrition. Investing in development and research plays a pivotal role in making new technologies accessible to farmers, contributing to a broader goal of educating the wider public and ensuring a more sustainable and equitable future.
The judging process for Architizer’s 12th Annual A+Awards is now away. Subscribe to our Awards Newsletter to receive updates about Public Voting, and stay tuned for winners announcements later this spring. Â Â




