Feeding fish with plastic-eating insects

Spotted: Seafood is one of the most highly traded commodities in the global food system, and in 2018, for the first time in history, global farmed fish production surpassed that of beef production. And experts expect demand for aquatic foods to double by 2050. How to sustainably farm fish to meet such high levels of global demand is a pressing concern for the aquaculture industry.
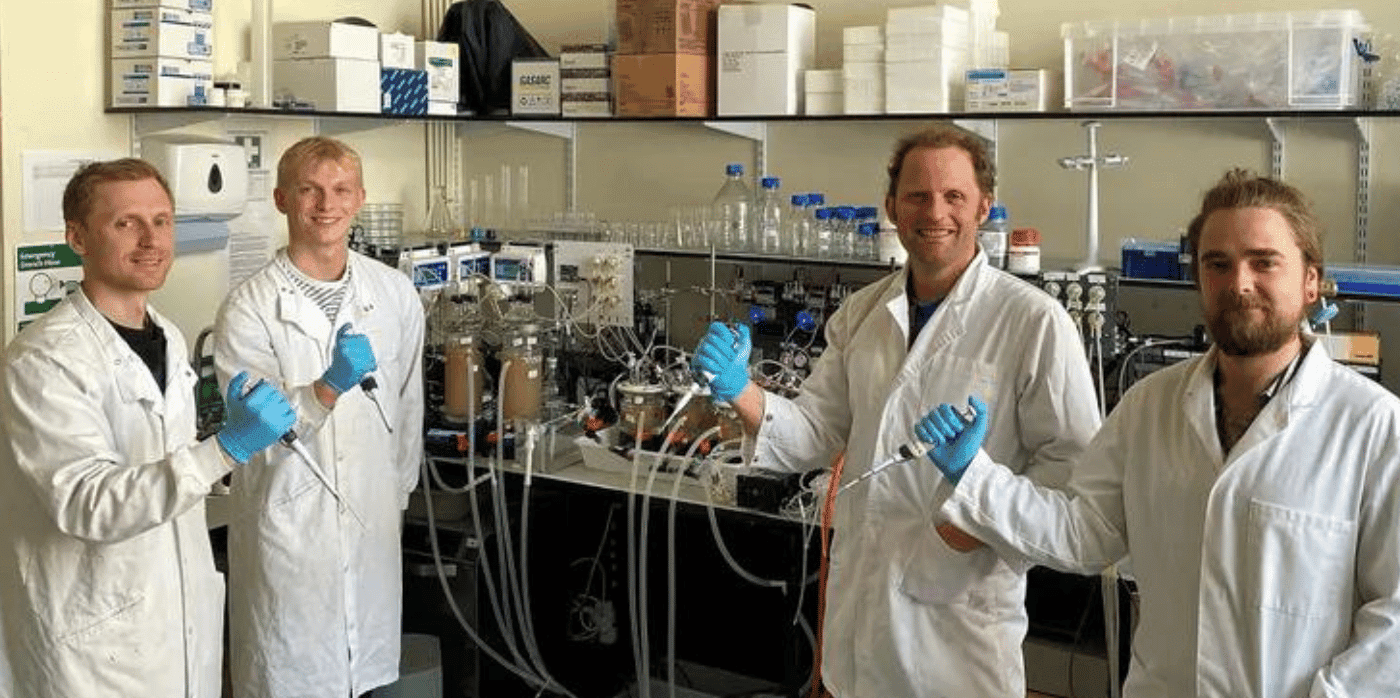
Part of that concern lies in finding the best solution to the challenge of what to feed farmed fish. Many growers seek circular solutions that minimise waste at all stages of the production process, including Glasgow-based researchers who recently discovered a surprising option for fishmeal. The team found that waxworms fed on plastic appeared more digestible to salmon than those fed on a regular diet.
Set up by Dr. Martin Llewellyn at the University of Glasgow, SalmoSim is an in-vitro Atlantic Salmon gut simulator that helps those in the aquaculture industry test out new medicines or feedstock for farmed fish. The team provides tailored experiments that analyse the absorption of sugars, volatile fatty acids, amino acids, and more throughout a salmon’s digestive process, and it was in one of these experiments that plastic-fed waxworms were found to be a highly digestible feed.
By reducing demand for marine-grown fish meal, plastic-fed waxworms could provide a dual purpose – reducing plastic waste while feeding the high volumes of fish demanded by a growing global market. The research team’s next steps include assessing the healthfulness of the salmon fed on the waxworms for human consumption.
Springwise has spotted other innovations improving the sustainability of the aquaculture industry, including tiles made from fish scales and a cellular growth technology used to make cultivated seafood.
Written By: Keely Khoury