Making waves with floating offshore solar panels

Spotted: According to the International Energy Agency’s Renewables 2023 report, last year saw a ‘step change’ in renewable capacity additions, driven in large part by solar power, particularly in China. And, in the year ahead, it is expected that the world will pass an important milestone with the combination of solar and wind forecast to generate more renewable electricity than hydropower for the first time.
Despite this heartening progress, there is still scope for innovation in renewable generation, and not every problem is solved. For example, offshore wind had a difficult year in 2023, and Netherlands-based energy company SolarDuck believes that another offshore technology will become an important part of the energy mix.
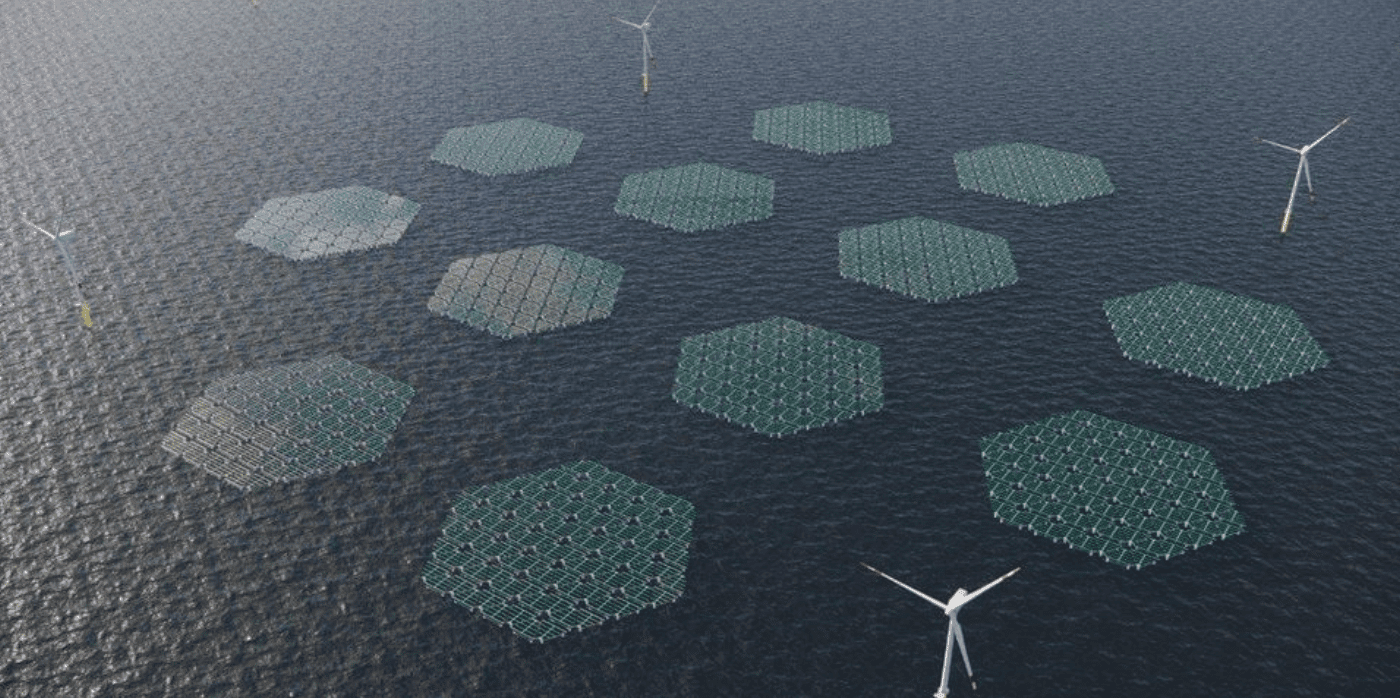
The startup believes that offshore solar power will be a key component in the push to meet net-zero emissions goals. The company’s founders all have experience in the energy and maritime sectors, expertise that lent itself to the creation of low-maintenance, offshore, floating solar panels designed specifically to withstand high-velocity winds and waves for up to 30 years.
The patented design includes built-in safety aspects, along with improved means of access for maintenance teams. The solar panels are arranged in a triangle shape with a 10-degree tilt to help maximise self-cleaning capabilities and are placed on a floating foundation several feet above the water. Being slightly raised helps minimise corrosion and marine growth, and each structure is designed to be easily connected to another for quick scalability of energy supply.
Sea water provides an important cooling factor that helps the panels maintain higher levels of conversion efficiency. SolarDuck plans to generate at least one gigawatt of energy from its solution annually by 2030.
From a solar-powered cooker to new means of rejuvenating aging PV panels, solar power is such as important source of renewable energy that Springwise’s library contains a range of examples of innovations working to reduce the world’s dependence on oil and gas.
Written By: Keely Khoury