World’s Best Design Details: Bendheim’s Bespoke Glass Façades
Architizer’s A+Awards Best Firm categories allow design firms of all sizes to showcase their practice and vie for the title of “World’s Best Architecture Firm”. Start an A+Firm Award Application today.
Architecture is shaped by form, transparency and light. Today, glass is one of the key materials specified to control what we experience inside a building, from views and daylight to heating and cooling. Glass has been used for thousands of years, holding both practical uses and cultural meaning. A major turning point came with the advent of the float glass process, invented by Sir Alastair Pilkington in 1952, which used a molten tin bath to produce a continuous ribbon of glass. Now, architects are working with manufacturers to rethink conventional building envelopes and construction techniques.
Bendheim is one of the world’s foremost resources for specialty architectural glass. Founded in New York City in 1927, the family-owned company offers in-stock and custom glass varieties for interior and exterior building applications. In the early 1980s, Bendheim began its Architectural Glass division with new tempering and lamination processes to transform hundreds of decorative glass varieties into safety architectural glass products. Bendheim now maintains production facilities in New Jersey and a Design Lab in New York City. The following projects showcase Bendheim’s products in architecture across the United States, from residential to cultural projects.
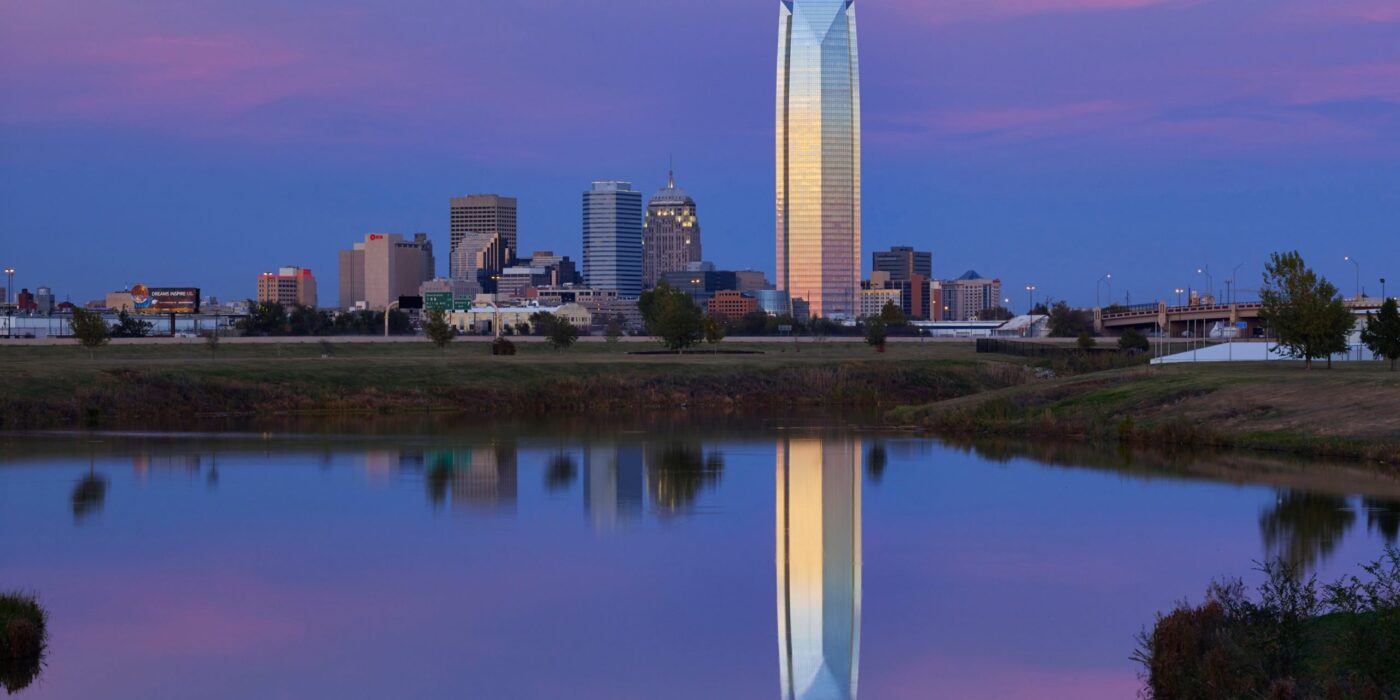
Devon Energy Center
By Pickard Chilton, Oklahoma City, OK, United States
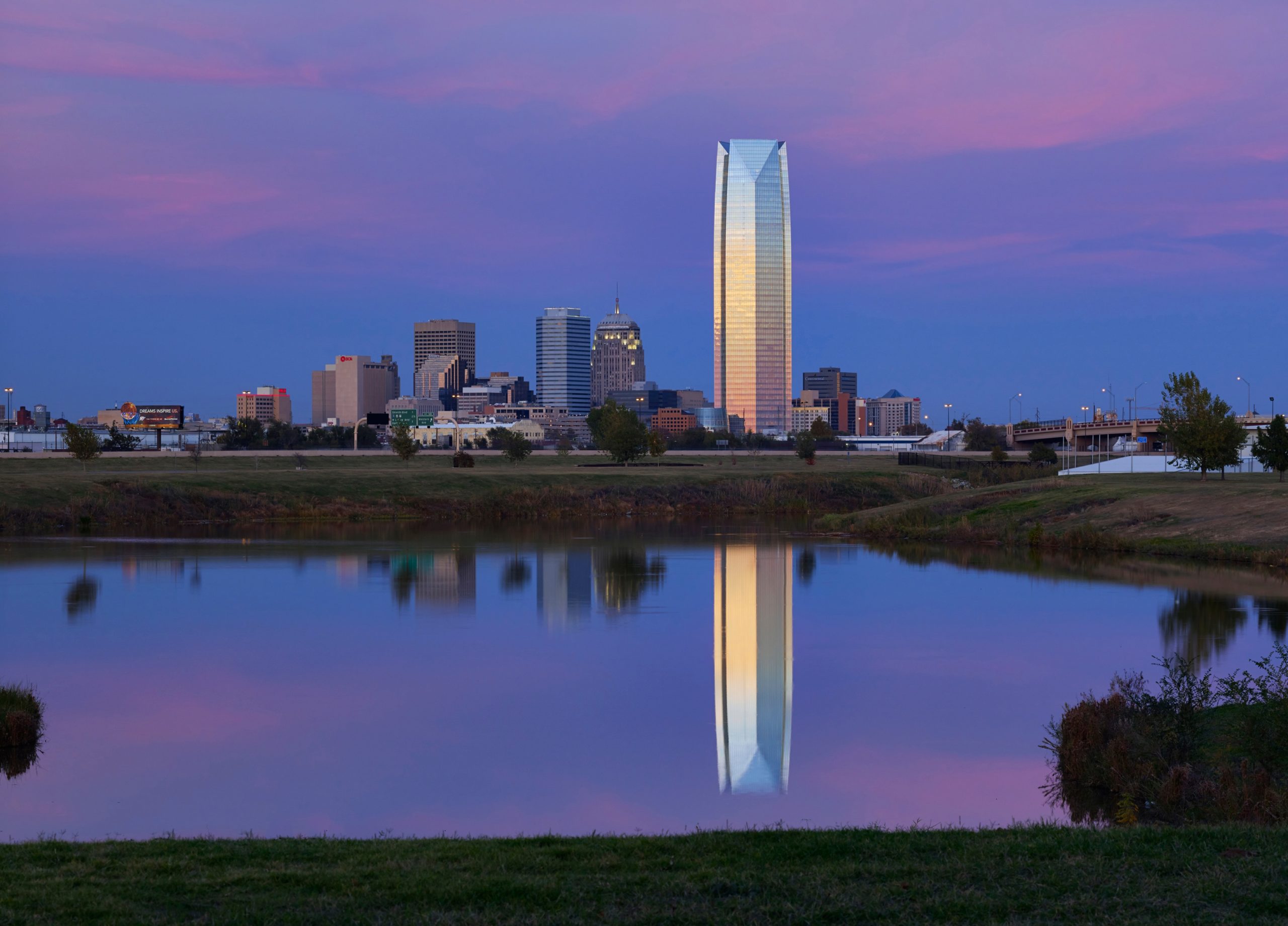
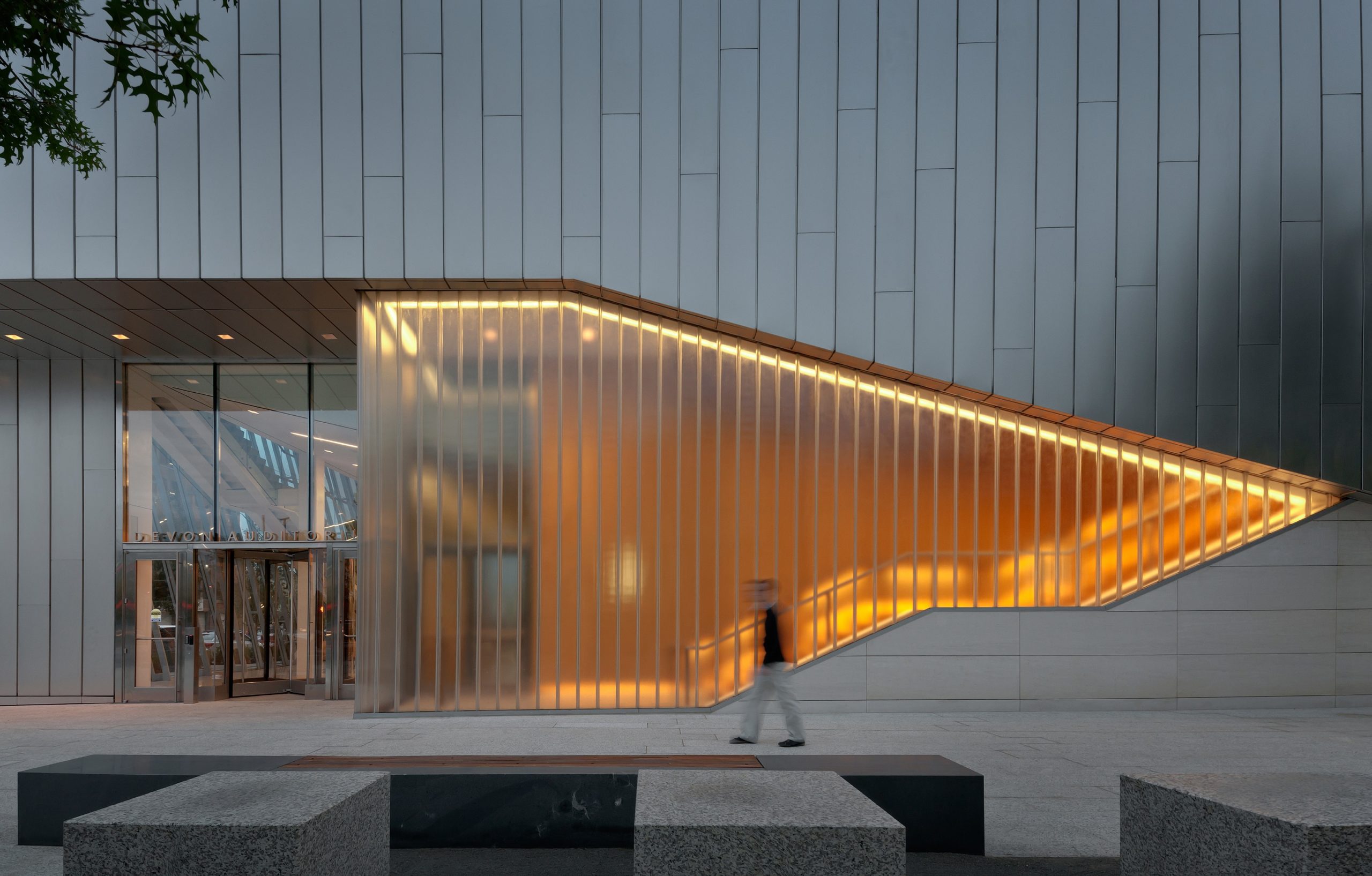
 The Devon Energy Center was designed to create a focal point for the company and the city by integrating civic-scaled spaces. The headquarters consolidates Devon’s Oklahoma City-based workforce into a single facility. Rising fifty floors, the tower’s unique three-sided footprint allows it to be viewed from all of greater Oklahoma City. The curtain wall is composed of state-of-the-art continuous floor-to-ceiling glazing and a highly articulated mullion system.
The Devon Energy Center was designed to create a focal point for the company and the city by integrating civic-scaled spaces. The headquarters consolidates Devon’s Oklahoma City-based workforce into a single facility. Rising fifty floors, the tower’s unique three-sided footprint allows it to be viewed from all of greater Oklahoma City. The curtain wall is composed of state-of-the-art continuous floor-to-ceiling glazing and a highly articulated mullion system.
Defining an urban edge between business and arts districts, the auditorium is a prominent, multi-use venue designed to support private and public events. Bendheim was brought on with double-glazed, solar channel glass to create feature exterior walls with angle cuts at the entrance. The SF-60 framing system was utilized for setting the glass.
Shaw Center for the Arts
By Schwartz/Silver Architects, Baton Rouge, LA, United States
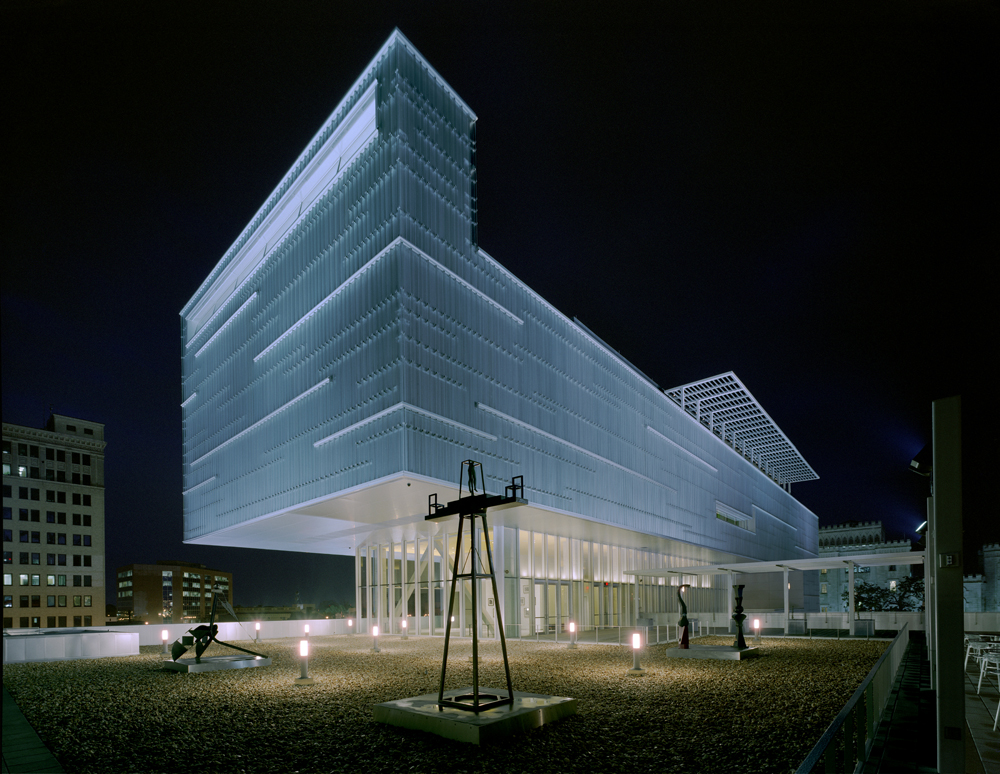
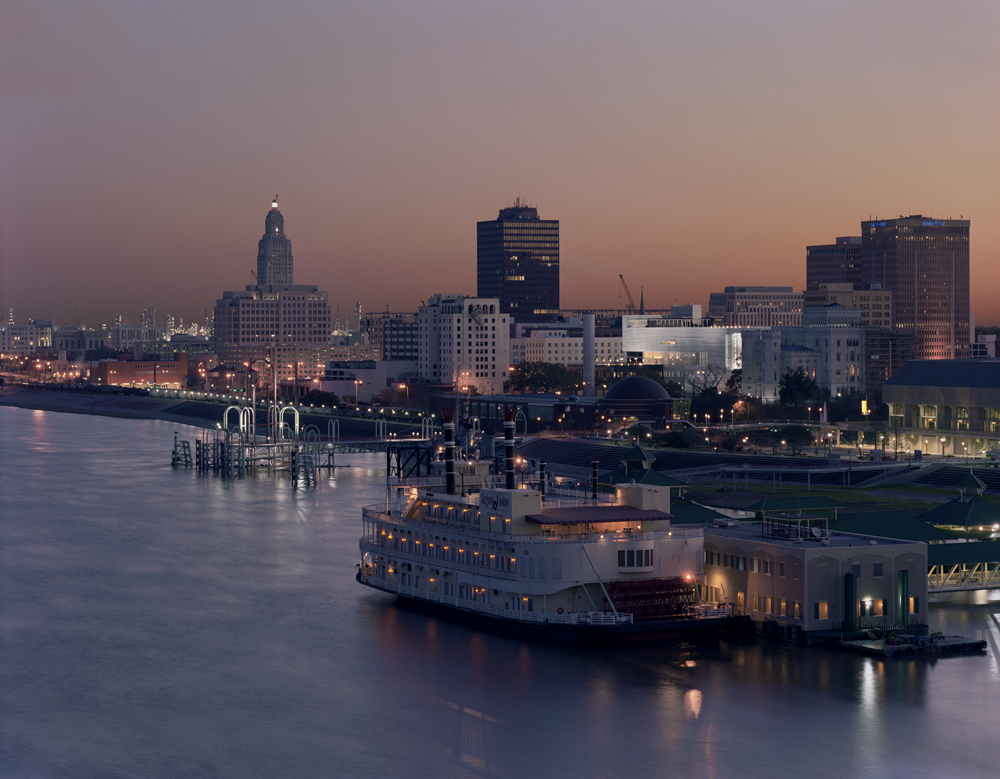
 Made to house Louisiana State University’s Museum of Art, this project also included studio art facilities, a regional performing arts facility with a 320 seat main stage, a hundred-seat black box theater, and a dance recital theater. An historic older building, the “Auto Hotel,” houses classrooms, offices, curatorial spaces, and a gallery for the LSU School of Art. The innovative Bendheim channel glass rainscreen creates a highly recognizable façade, while protecting the building and the works of art it houses from the elements.
Made to house Louisiana State University’s Museum of Art, this project also included studio art facilities, a regional performing arts facility with a 320 seat main stage, a hundred-seat black box theater, and a dance recital theater. An historic older building, the “Auto Hotel,” houses classrooms, offices, curatorial spaces, and a gallery for the LSU School of Art. The innovative Bendheim channel glass rainscreen creates a highly recognizable façade, while protecting the building and the works of art it houses from the elements.
The façade features approximately 40,000 square feet of the channel glass. Most of the flanges face outward, adding texture to the building. There are 2-inch gaps between the channels, and the glass rainscreen sits approximately 6 inches off a layer of waterproof aluminum. The resulting varied texture emulates the shimmering surface of the nearby Mississippi River. The unique flange-outward design adds visual complexity, while preventing wind and rain from accessing the metal panels behind the channel glass.
Swiss Embassy Residence
By Rüssli Architects AG, Washington, DC, United States
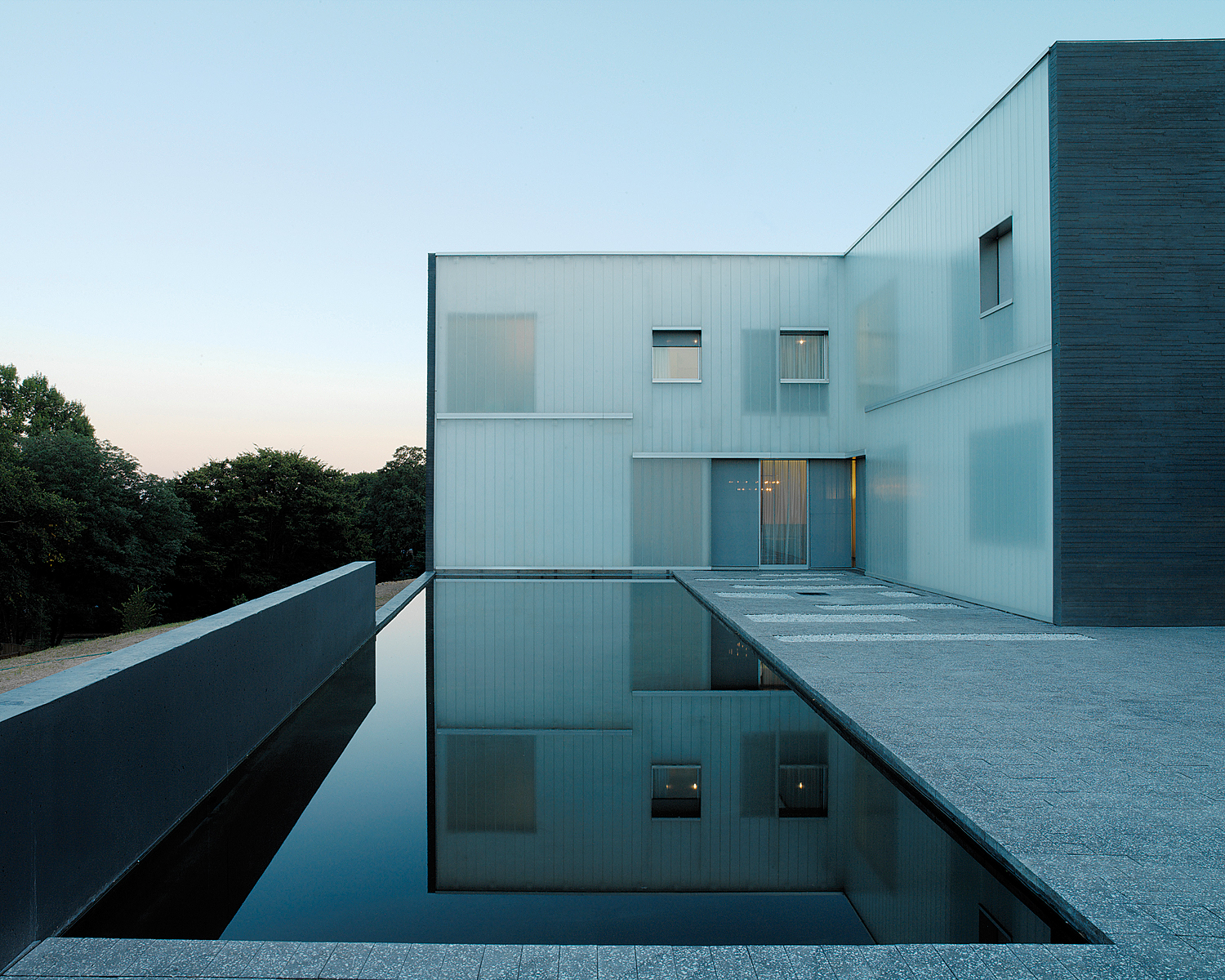
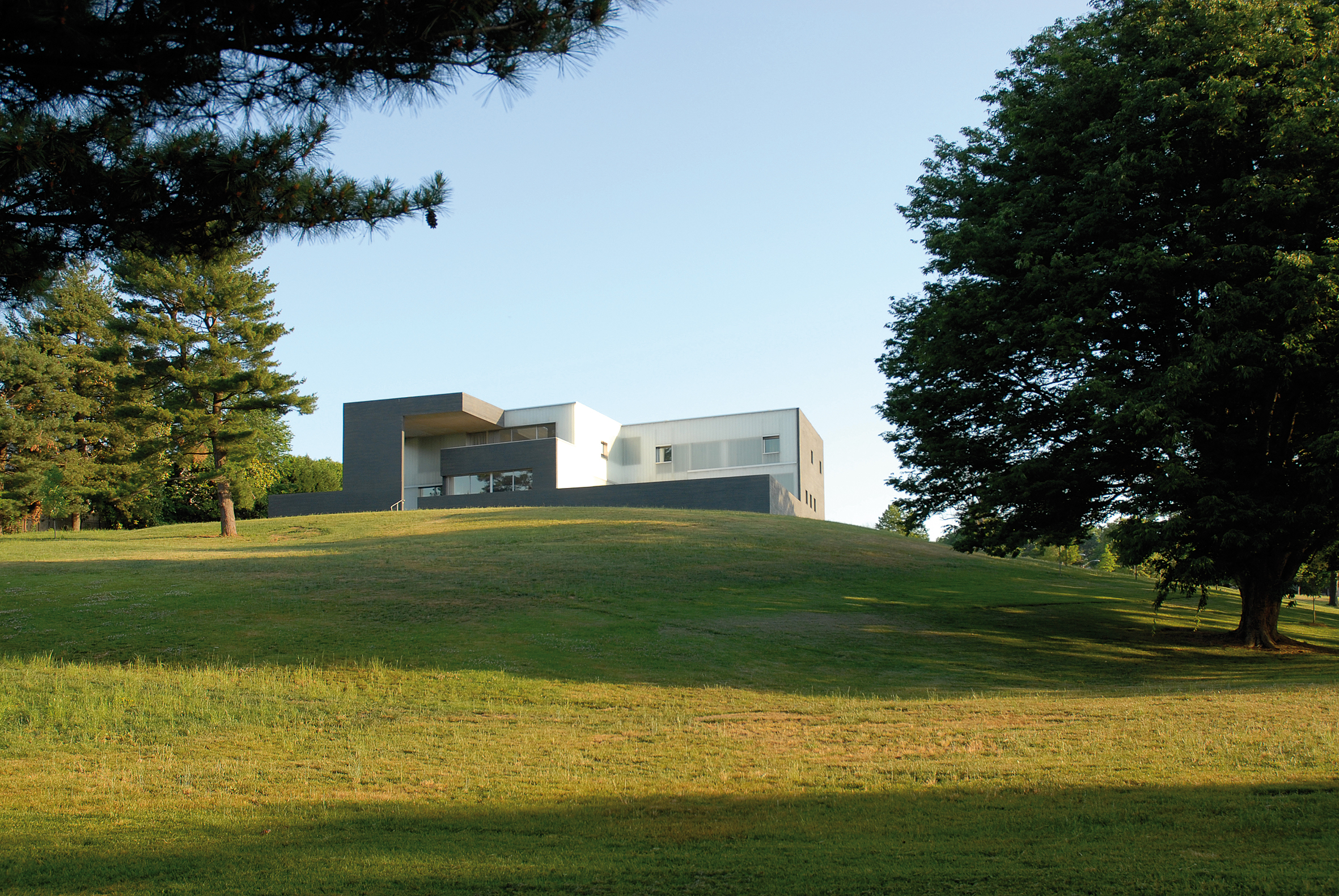
 Looking out with a view to the Washington Monument, this residence was made as a multifunctional microcosm of living and working space as well as rooms for official receptions and for the staff. The strictly geometrical structure of the Swiss Embassy is a cross-shaped volume on a massive, rectangular base. The outer sides of the cross, which are part of the base too, and the the resulting exterior spaces are allocated to adjacent areas.
Looking out with a view to the Washington Monument, this residence was made as a multifunctional microcosm of living and working space as well as rooms for official receptions and for the staff. The strictly geometrical structure of the Swiss Embassy is a cross-shaped volume on a massive, rectangular base. The outer sides of the cross, which are part of the base too, and the the resulting exterior spaces are allocated to adjacent areas.
Bendheim’s U-profile channel glass, contrasting with slate-trimmed grey concrete, produces a crisp, clean effect in this cross-shaped design. The complex features 10,000 square feet of tempered, low-iron, sandblasted, solar textured channel glass. The Swiss Embassy residence operates at high levels of efficiency, consuming half as much energy as a typical building structure. The project also conforms to the LEED Silver green building standard.
Institute of Contemporary Art
By Diller Scofidio + Renfro, Boston, MA, United States
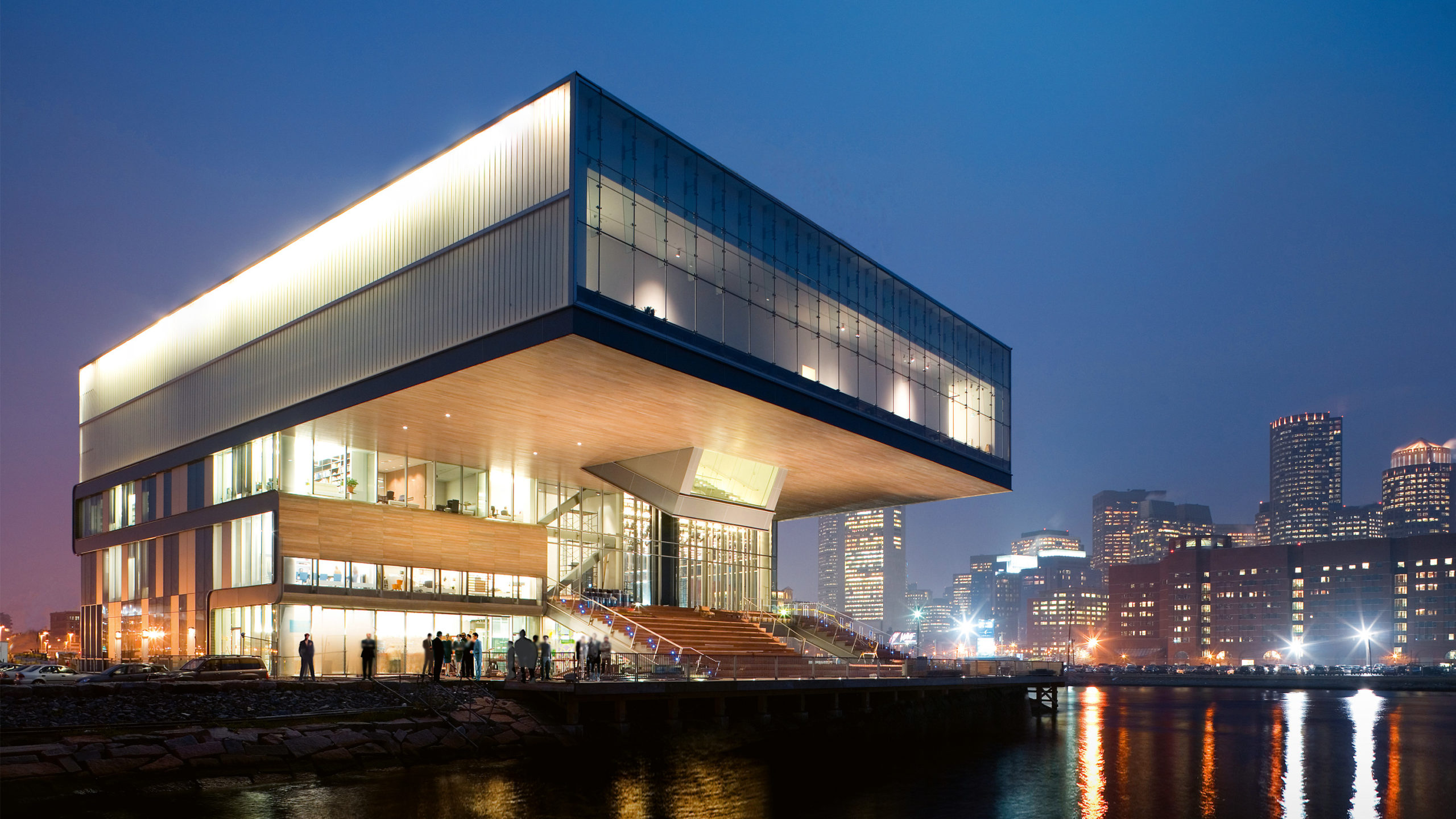
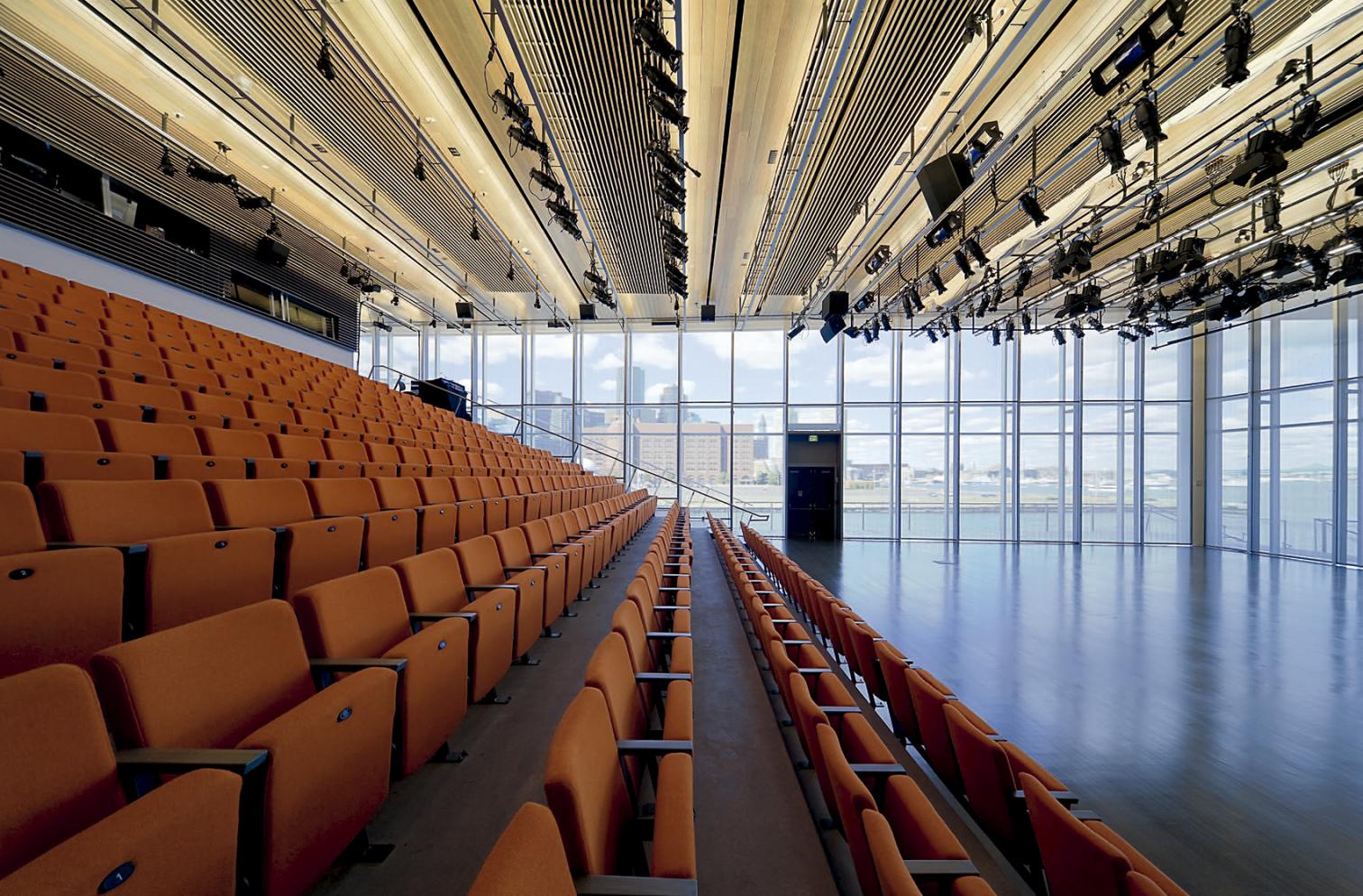
 The ICA was the first museum to be built in Boston in 100 years. The 65,000 square foot building includes temporary and permanent galleries, a 330 seat multi-purpose theater, a restaurant, bookstore, education/workshop facilities, and administrative offices. The site is bound on two sides by the Harbor Walk, a 47-mile public walkway at the water¹s edge reclaimed from Boston’s industrial past. The ICA offers the city some of its ground floor footprint in exchange for rights to cantilever over city property with a 18,000-square-foot gallery illuminated by an uninterrupted skylight.
The ICA was the first museum to be built in Boston in 100 years. The 65,000 square foot building includes temporary and permanent galleries, a 330 seat multi-purpose theater, a restaurant, bookstore, education/workshop facilities, and administrative offices. The site is bound on two sides by the Harbor Walk, a 47-mile public walkway at the water¹s edge reclaimed from Boston’s industrial past. The ICA offers the city some of its ground floor footprint in exchange for rights to cantilever over city property with a 18,000-square-foot gallery illuminated by an uninterrupted skylight.
A 504 Rough Cast channel glass façade envelopes the upper level of the Institute of Contemporary Art on three sides. The glass rainscreen is functional, protecting the building from harmful moisture damage, as well as being aesthetically pleasing. The glass is illuminated from the top, allowing the entire upper level to glow at night and to act as a beacon over the harbor.
C-Glass House
By deegan day design, Marin County, CA, United States
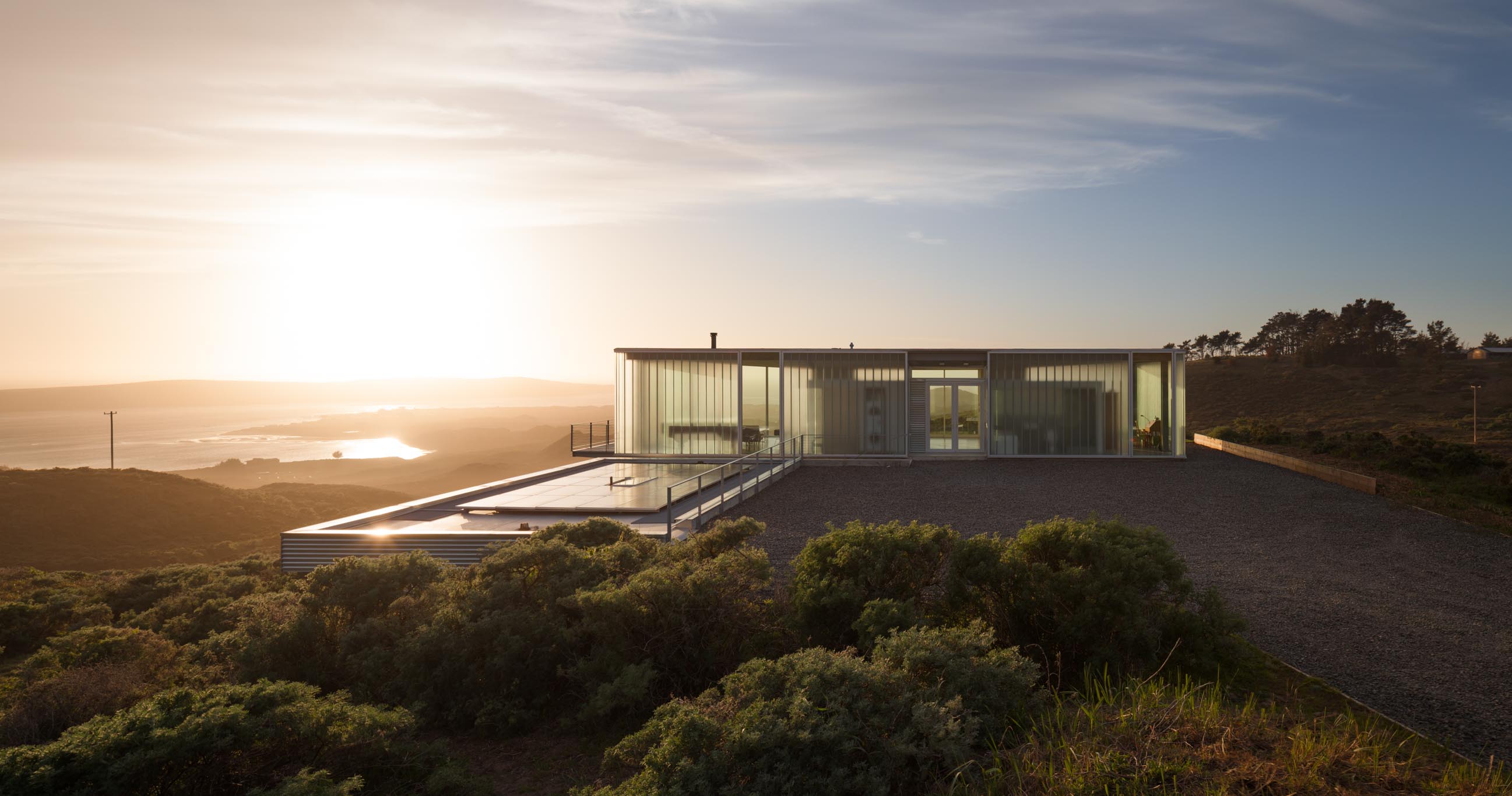
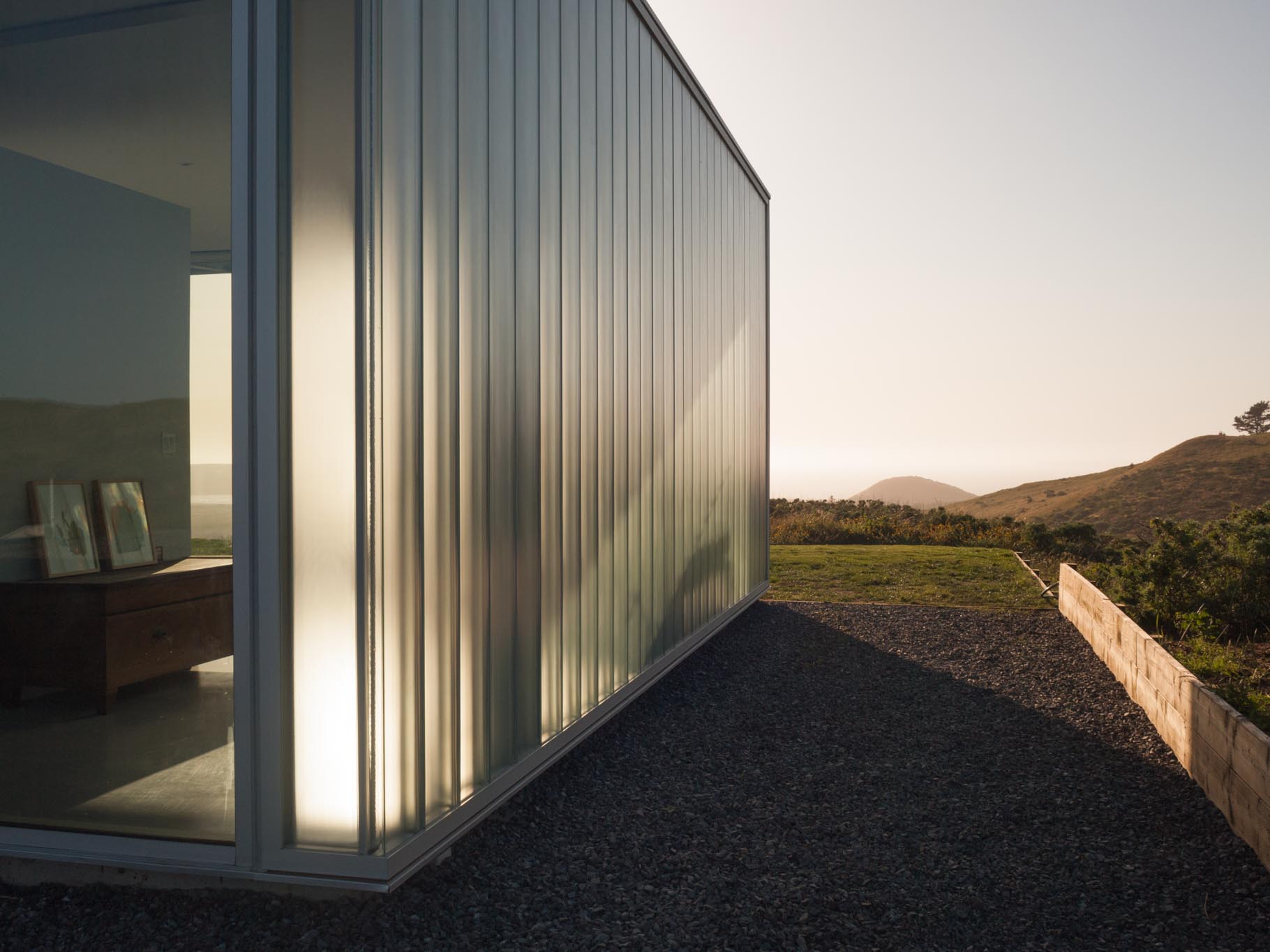
 The C-Glass House is an elegant retreat in northern California. Set on a spectacular site, the residence opens to a panoramic view of Tomales Bay and the open ocean, while bracing against winds from multiple directions. C-Glass House brokers between the Leica-like precision of high modern glass houses and the cinematic wireframe of the Case Study generation. The home was also inspired by artists’ explorations of glazed enclosures as much as it is to the precedents of Johnson and Mies.
The C-Glass House is an elegant retreat in northern California. Set on a spectacular site, the residence opens to a panoramic view of Tomales Bay and the open ocean, while bracing against winds from multiple directions. C-Glass House brokers between the Leica-like precision of high modern glass houses and the cinematic wireframe of the Case Study generation. The home was also inspired by artists’ explorations of glazed enclosures as much as it is to the precedents of Johnson and Mies.
The C-Glass House opens up to a panoramic vista but also modulates and reflects back on architecture’s evolving role in the American landscape. Affixed in Bendheim’s SF-60 framing system, solar textured channel glass defines the house’s exterior, creates privacy, and diffuses the strong Californian sunlight. Captured at the top and bottom, the tempered channel glass spans the height of the house, seamlessly turning corners without the need for extra metal supports.
Visual Arts Building, University of Iowa
By Steven Holl Architects and BNIM, Iowa City, IA, United States
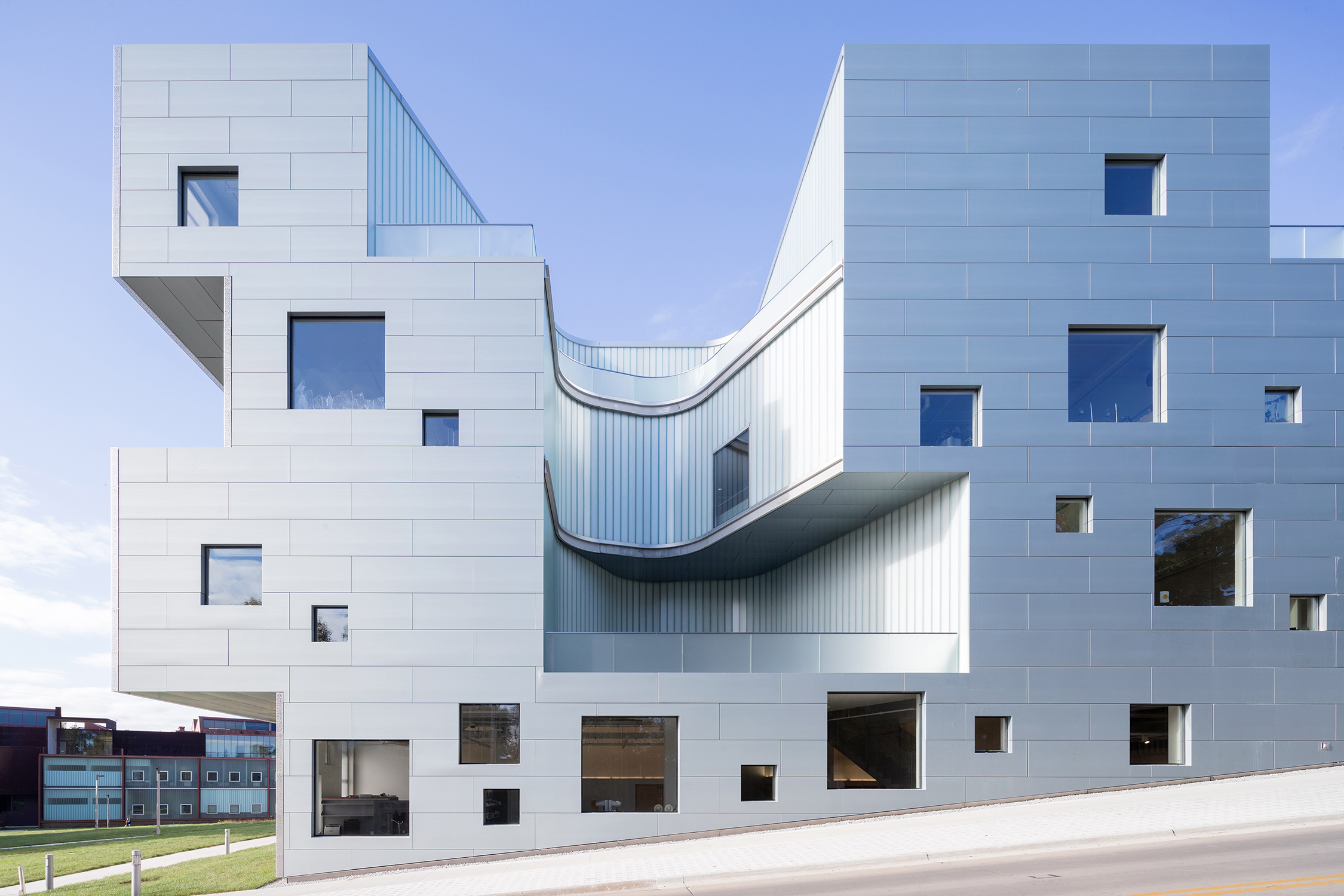
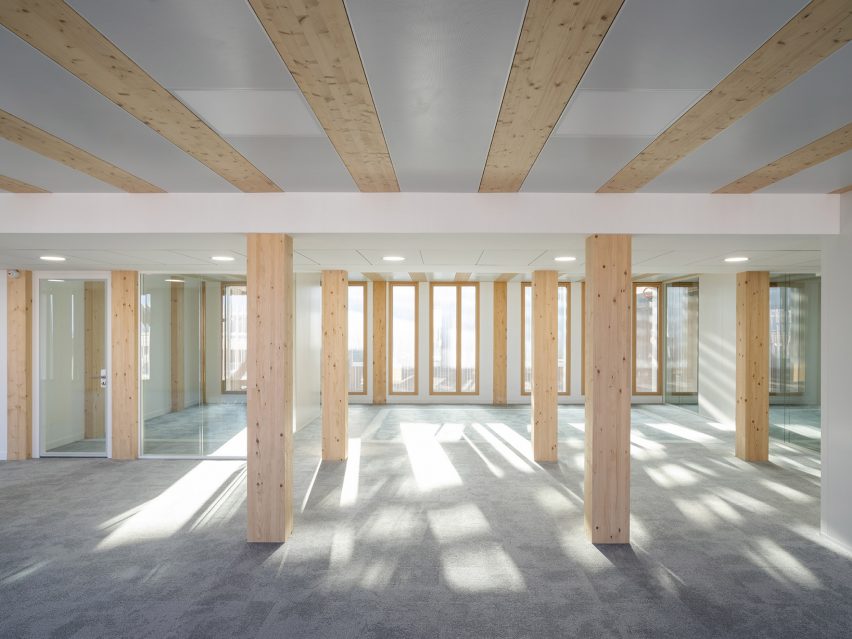
 SHA and BNIM designed the new Visual Arts Building for the University of Iowa’s School of Art and Art History. It provides 126,000 square feet of loft-like space for all visual arts media, from ancient metal-smithing techniques to the most advanced virtual reality technologies. The building replaces an original arts building from 1936, which was heavily damaged during the 2008 flood of the University of Iowa campus. Seven vertical “centers of light” are carved out of the building’s volume filling the interior with natural light and ventilation.
SHA and BNIM designed the new Visual Arts Building for the University of Iowa’s School of Art and Art History. It provides 126,000 square feet of loft-like space for all visual arts media, from ancient metal-smithing techniques to the most advanced virtual reality technologies. The building replaces an original arts building from 1936, which was heavily damaged during the 2008 flood of the University of Iowa campus. Seven vertical “centers of light” are carved out of the building’s volume filling the interior with natural light and ventilation.
Channel glass by Bendheim soars at 20 foot heights throughout the project. The combination of Bendheim’s 504 Rough Cast™ channel glass texture with translucent insulation inserts delivers ideal daylight, as if filtered through a translucent cloud. With no glare requiring shades or other window treatments to block it, classrooms, studios, and lounge spaces are flooded with natural light that appears to have no direct source. The idea was to create evenly dispersed light that would make the best possible atmosphere in which to work and create.
Architizer’s A+Awards Best Firm categories allow design firms of all sizes to showcase their practice and vie for the title of “World’s Best Architecture Firm”. Start an A+Firm Award Application today.
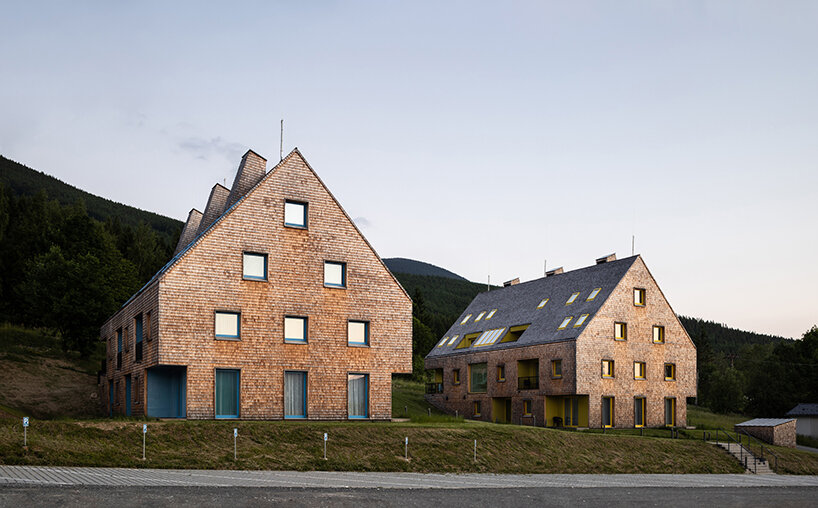
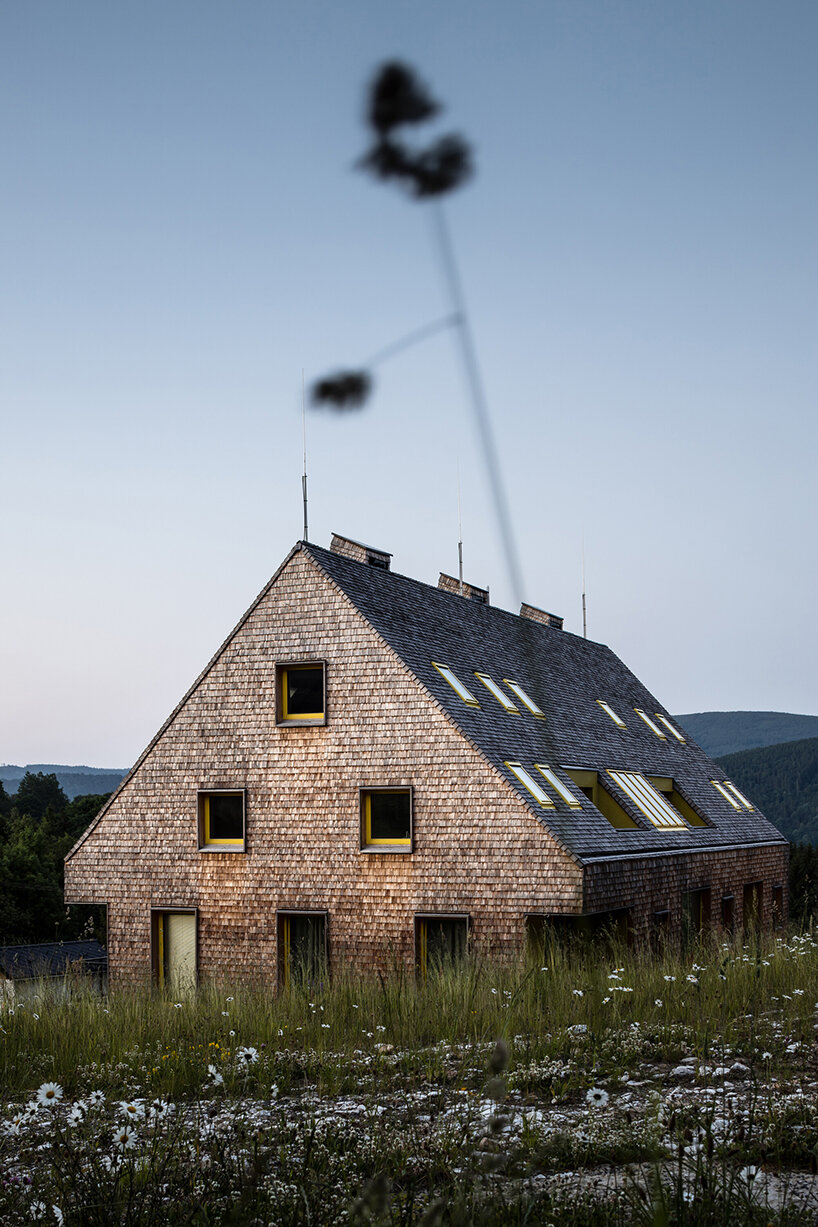
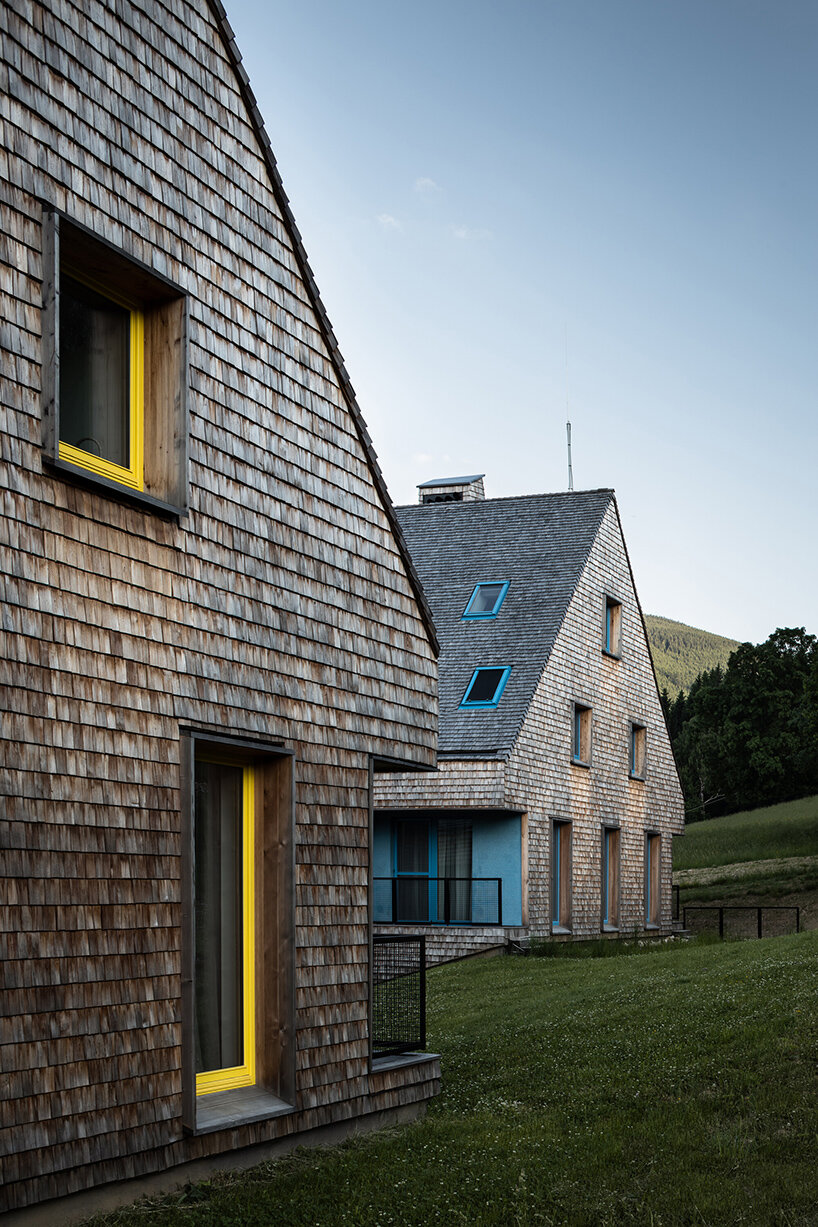
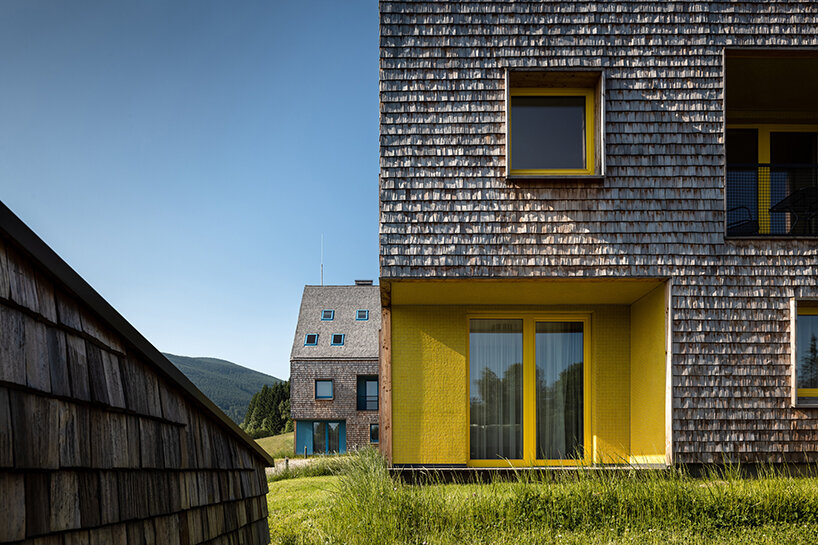
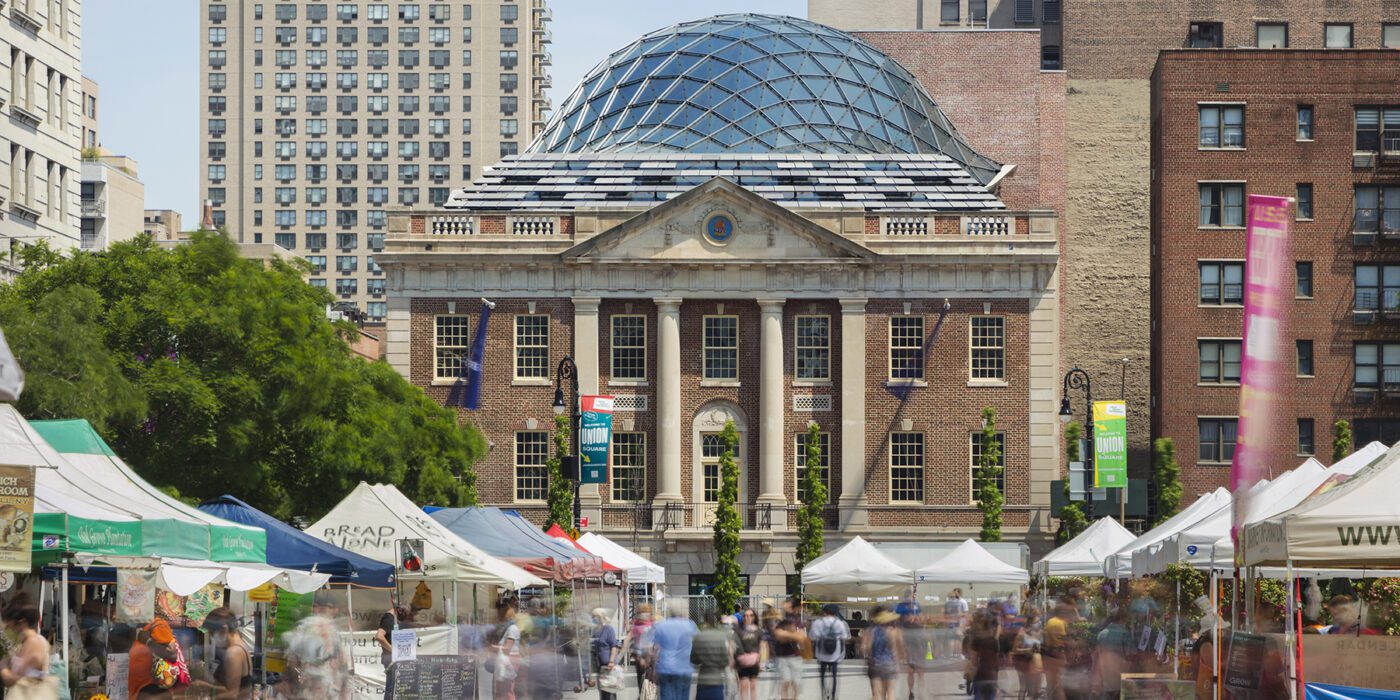
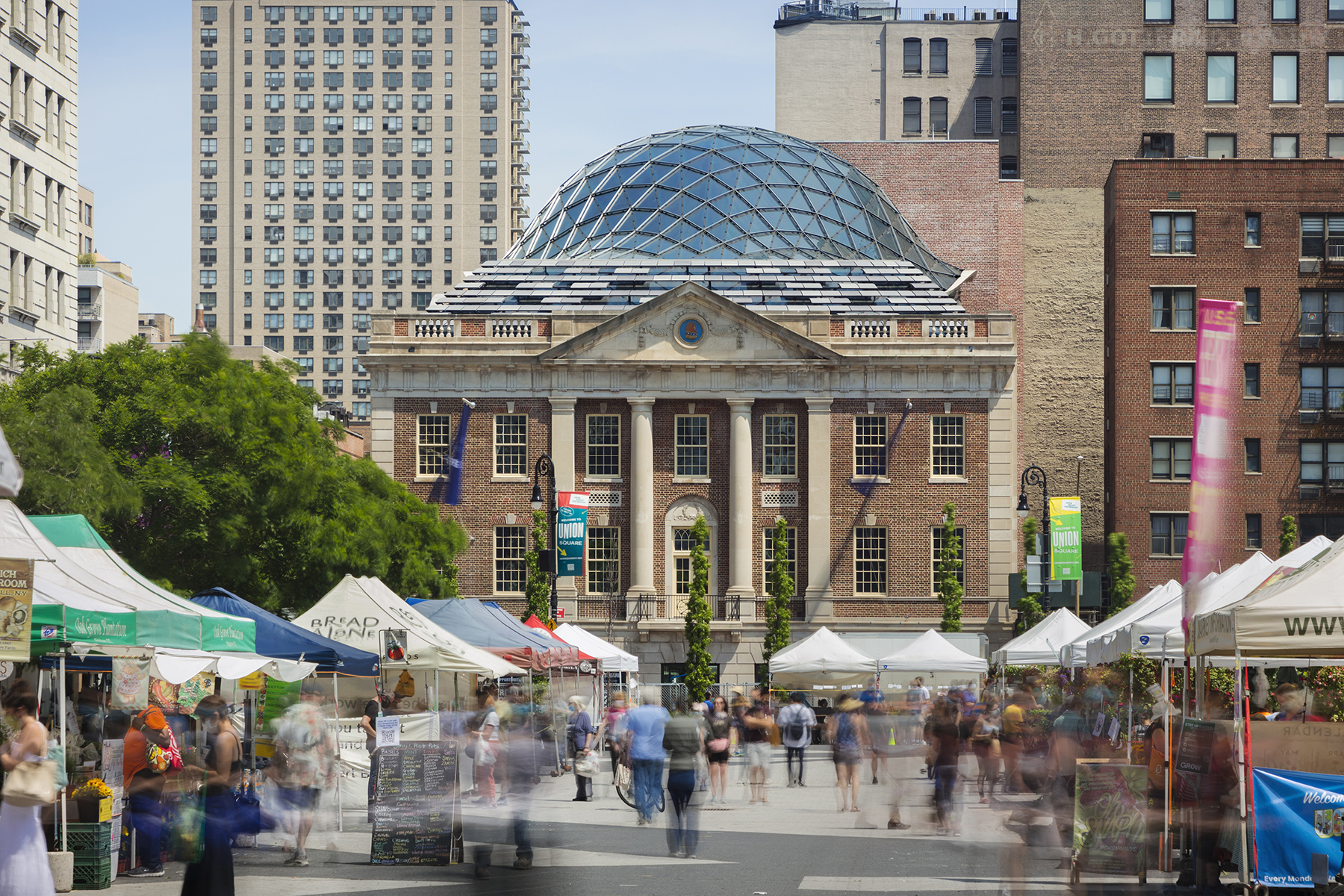
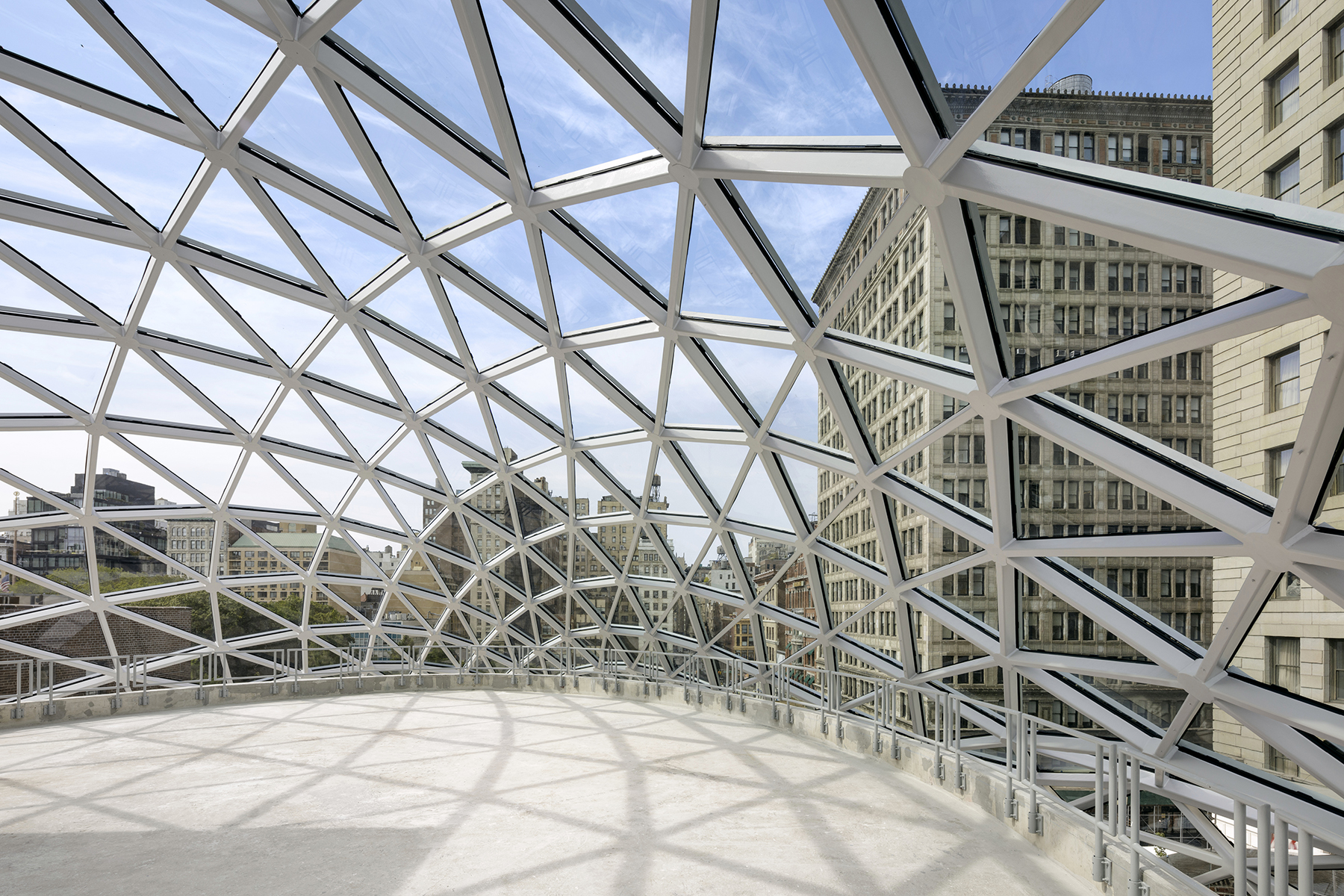













 This redevelopment in Budapest seeks to reconnect the urban landscape with the adjacent Danube River with an aquatic-inspired glass addition to an old commercial center. Most noticeably, the curving glass dome imitates a streamlined body of a whale. But the design is subtle enough that the glass addition takes a life of its own, beyond its biomorphic origins.
This redevelopment in Budapest seeks to reconnect the urban landscape with the adjacent Danube River with an aquatic-inspired glass addition to an old commercial center. Most noticeably, the curving glass dome imitates a streamlined body of a whale. But the design is subtle enough that the glass addition takes a life of its own, beyond its biomorphic origins.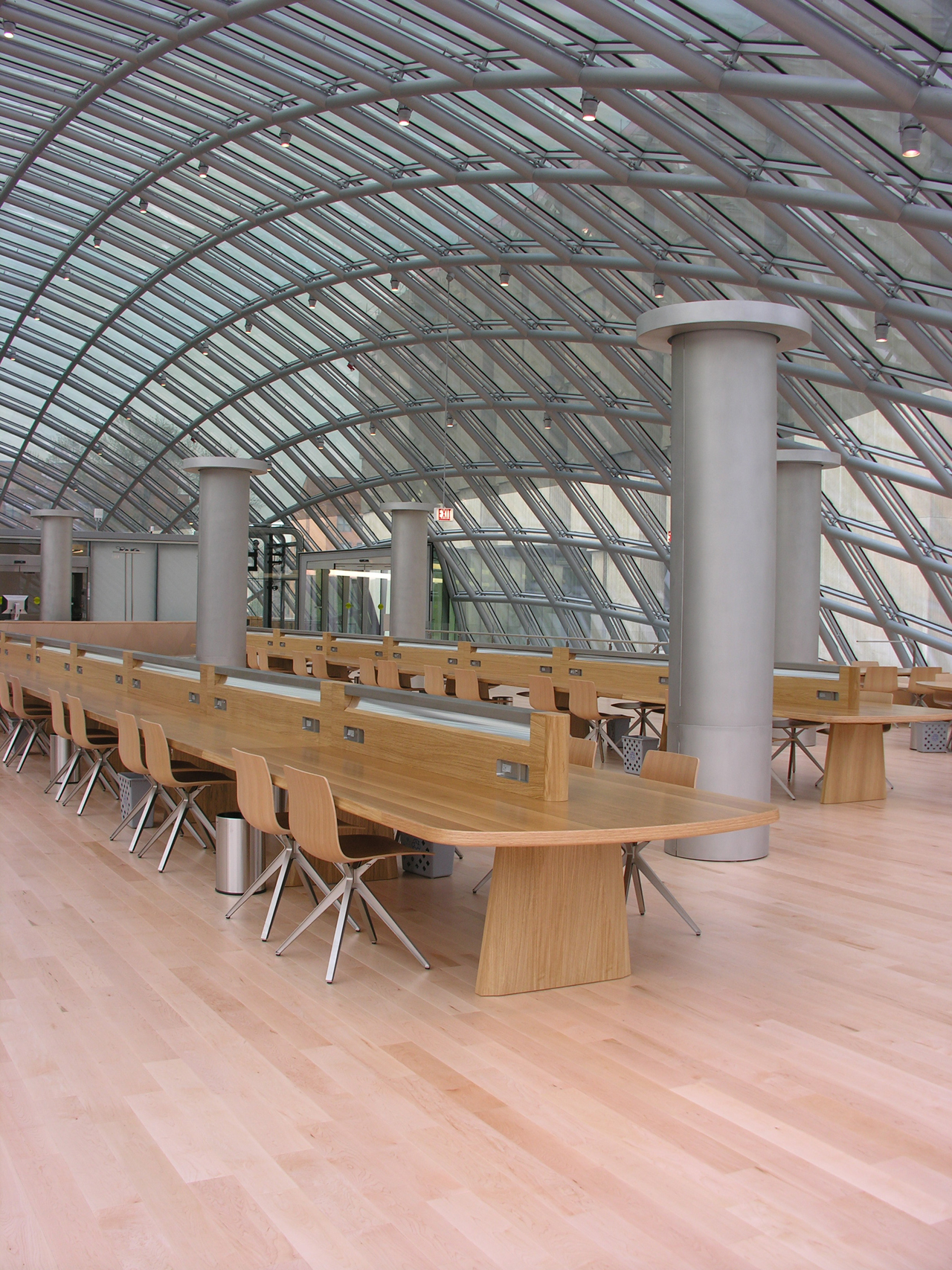
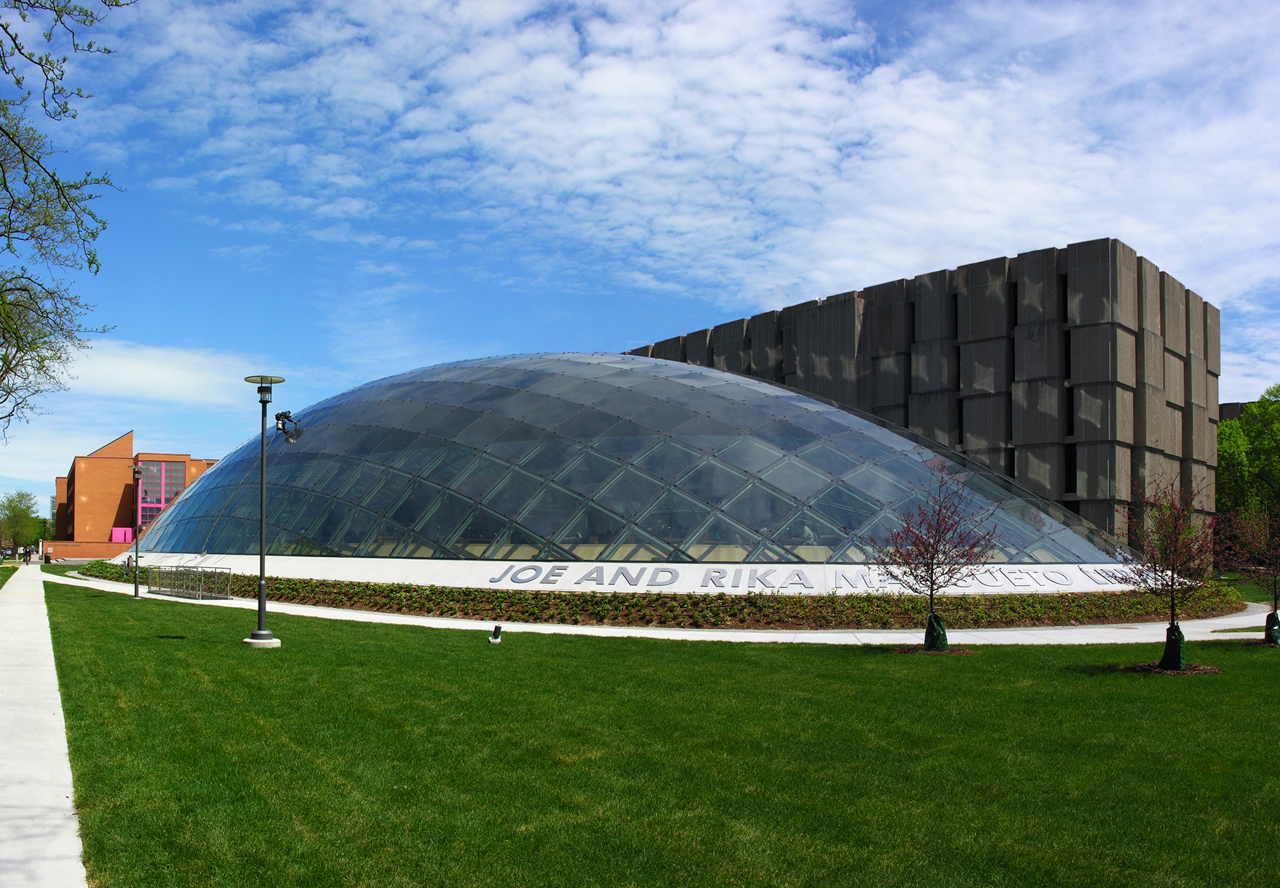 Given the eclectic mix of architecturally distinct campus buildings in its vicinity, it was fitting that this new library at the University of Chicago should stand out as well. The elliptical glass dome design elegantly rejects the common utilitarian box-shaped university libraries; in doing so creates a more natural and people-friendly place to do studies. Like a biodome, the library’s reading room offers a sunny, outdoor-like atmosphere without the inconveniences of being outside.
Given the eclectic mix of architecturally distinct campus buildings in its vicinity, it was fitting that this new library at the University of Chicago should stand out as well. The elliptical glass dome design elegantly rejects the common utilitarian box-shaped university libraries; in doing so creates a more natural and people-friendly place to do studies. Like a biodome, the library’s reading room offers a sunny, outdoor-like atmosphere without the inconveniences of being outside.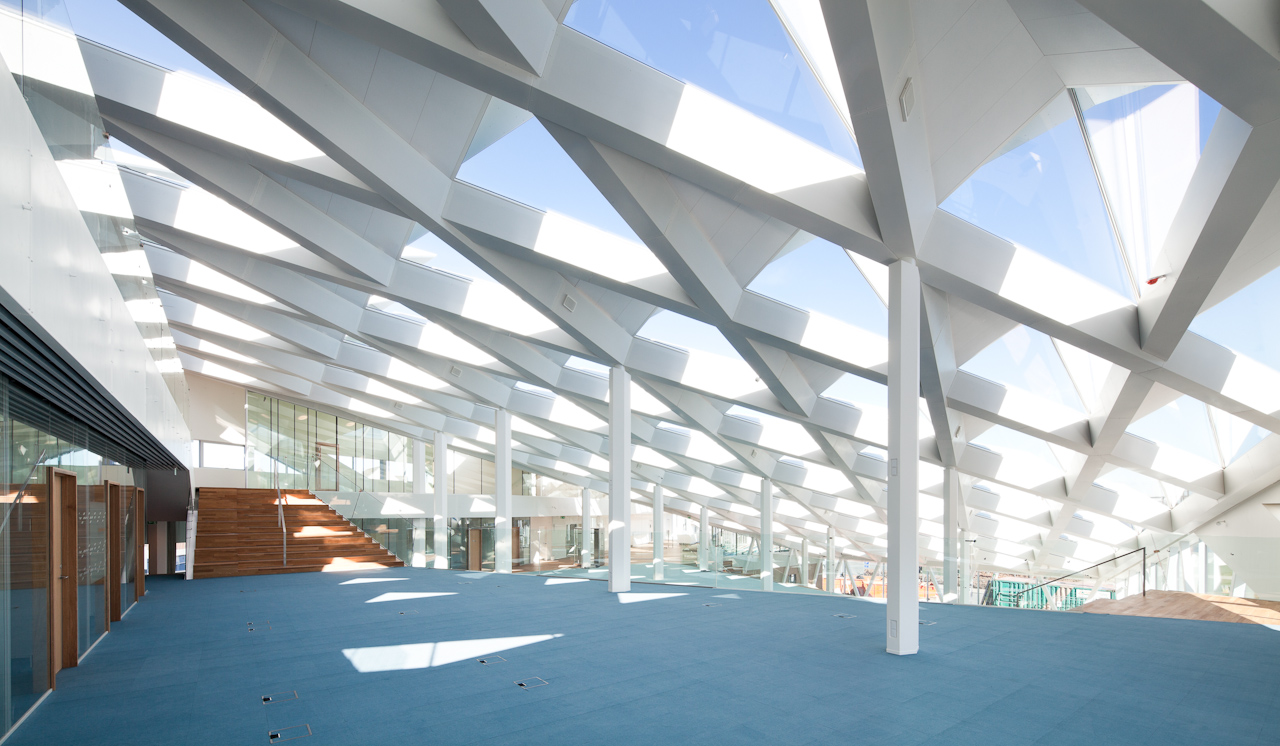
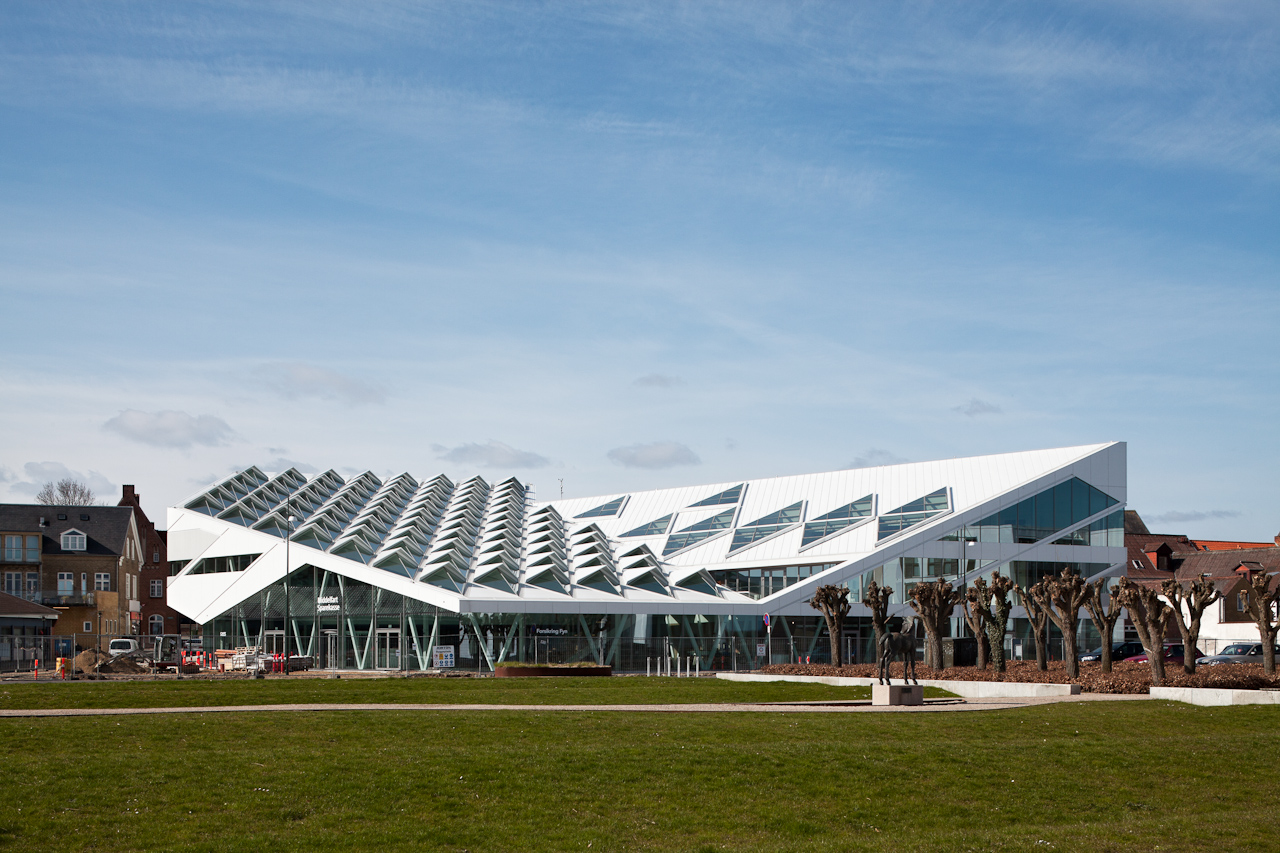 This new multi-purpose commercial space in the seaside town of Middelfart, Denmark brings a brisk change to the architectural cityscape, without excessively sticking out. The white slanted roofs offer a sharp contrast to the old town’s color palette, but the structure’s scale and proportions are not out of line with the neighborhood. Similarly, the triangular-shaped cornices that adorn the roof — which cleverly double as skylights — are a bold architectural choice, yet they simultaneously offer an imitation of ocean waves. It’s not a coincidence that those very windows provide a direct view of the Lillebælt seaside.
This new multi-purpose commercial space in the seaside town of Middelfart, Denmark brings a brisk change to the architectural cityscape, without excessively sticking out. The white slanted roofs offer a sharp contrast to the old town’s color palette, but the structure’s scale and proportions are not out of line with the neighborhood. Similarly, the triangular-shaped cornices that adorn the roof — which cleverly double as skylights — are a bold architectural choice, yet they simultaneously offer an imitation of ocean waves. It’s not a coincidence that those very windows provide a direct view of the Lillebælt seaside.
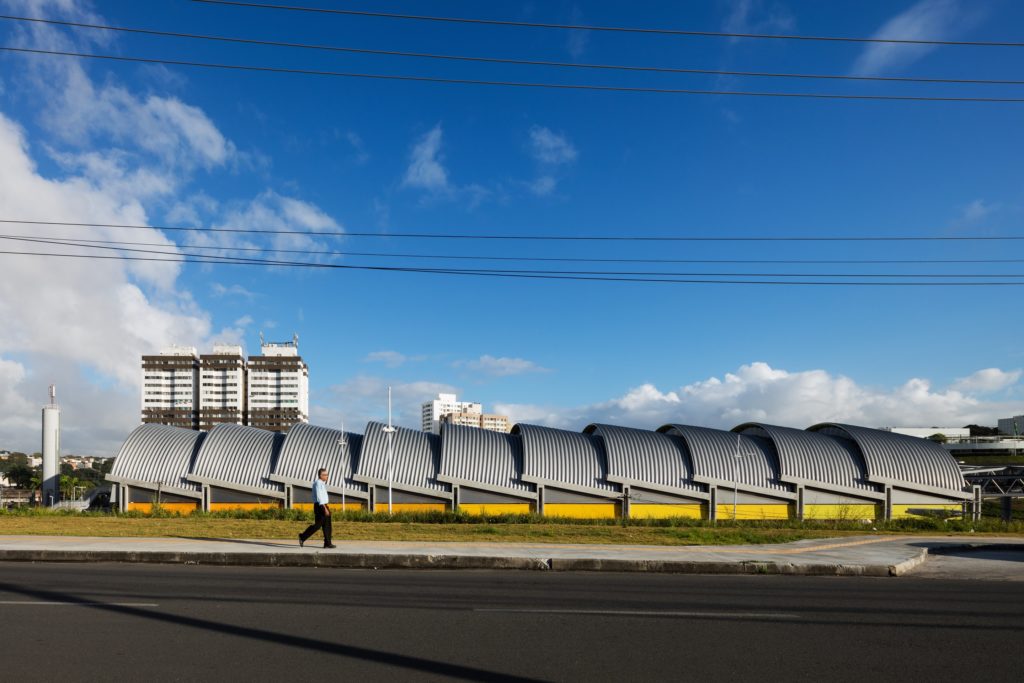
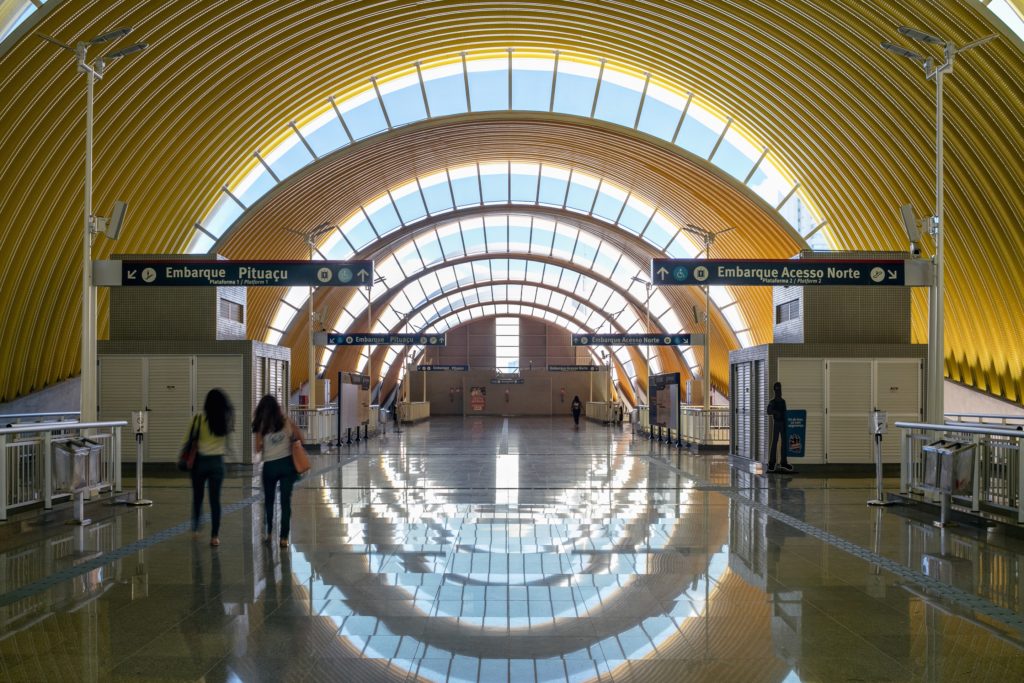

 The central motif of this new transport hub in Salvador, Brazil consists in large overlapping semi-cylinders stacked like fallen dominoes. Conveniently enough, this slanted pattern allows for slivers of sun to pass through concealed, arching skylights, brightening the main station considerably.
The central motif of this new transport hub in Salvador, Brazil consists in large overlapping semi-cylinders stacked like fallen dominoes. Conveniently enough, this slanted pattern allows for slivers of sun to pass through concealed, arching skylights, brightening the main station considerably.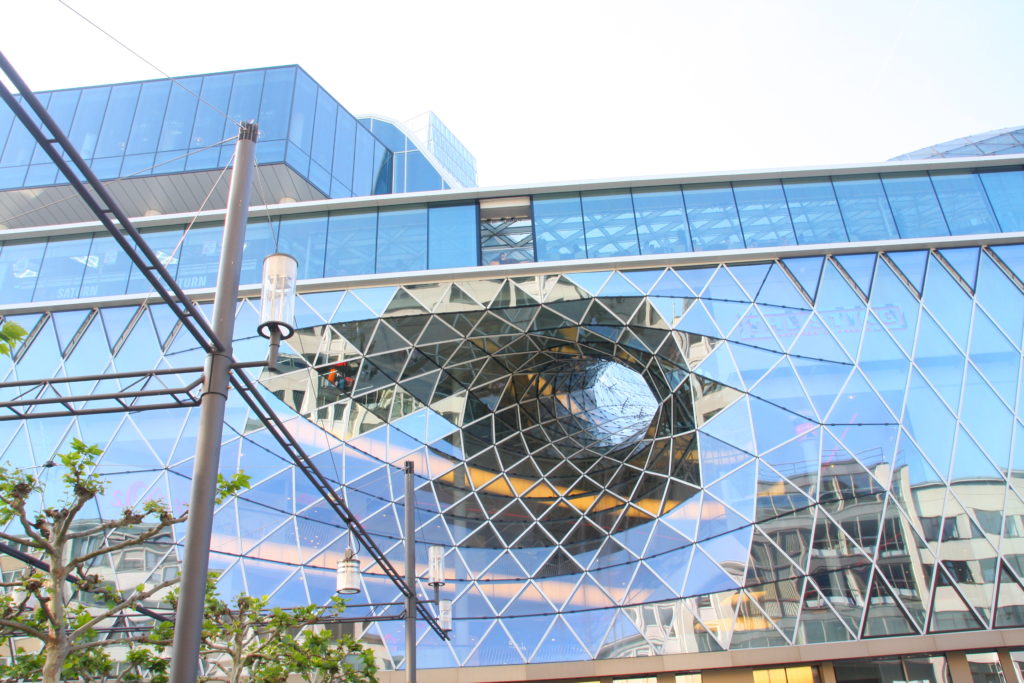
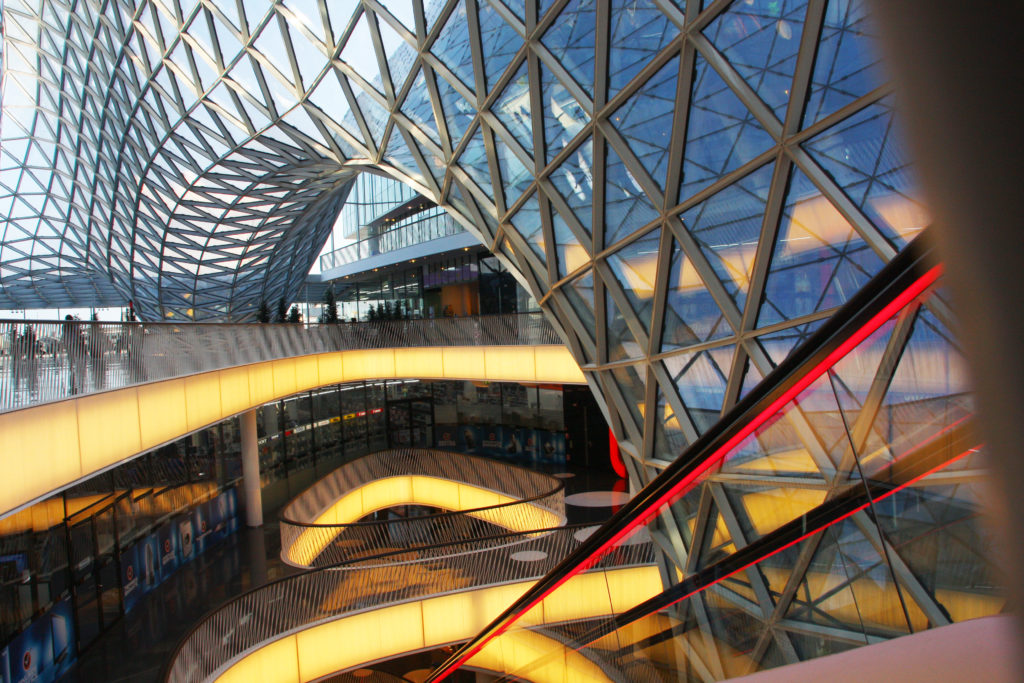 While the design concept for the roofing on this project was supposedly based on the shape of a canyon, this retail center in Frankfurt turns curving glass on its head very literally. The resulting concoction, a light and airy shell, appears like a water funnel, a vortex or a portal into another dimension.
While the design concept for the roofing on this project was supposedly based on the shape of a canyon, this retail center in Frankfurt turns curving glass on its head very literally. The resulting concoction, a light and airy shell, appears like a water funnel, a vortex or a portal into another dimension.
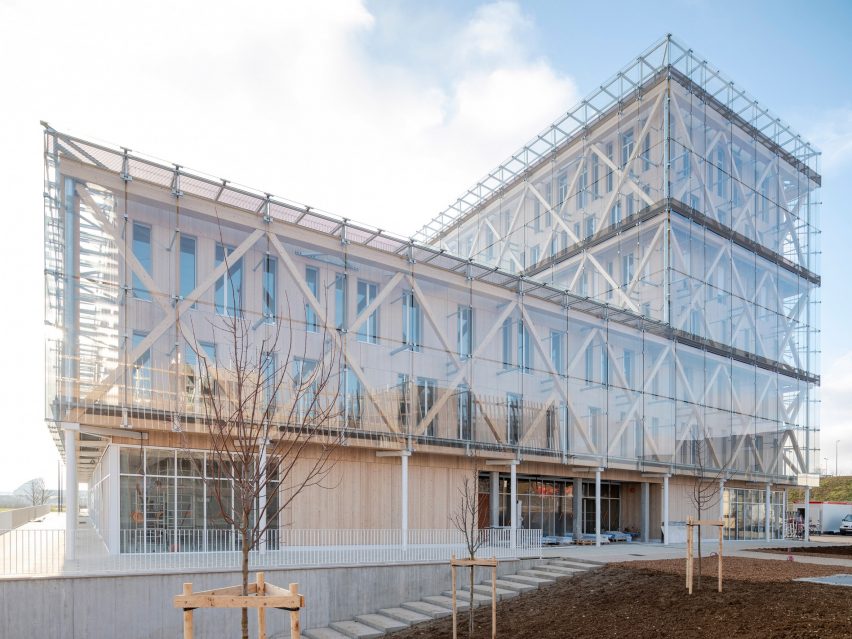
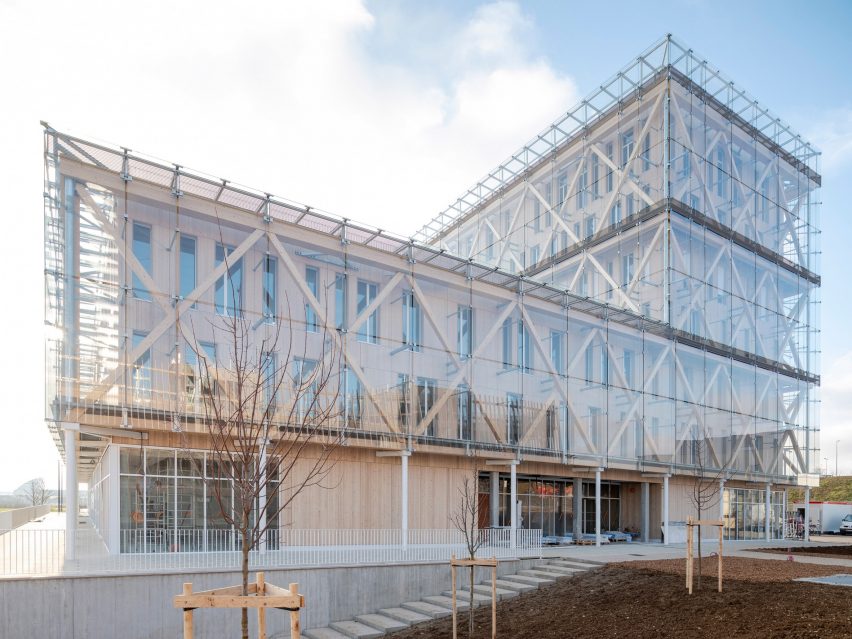
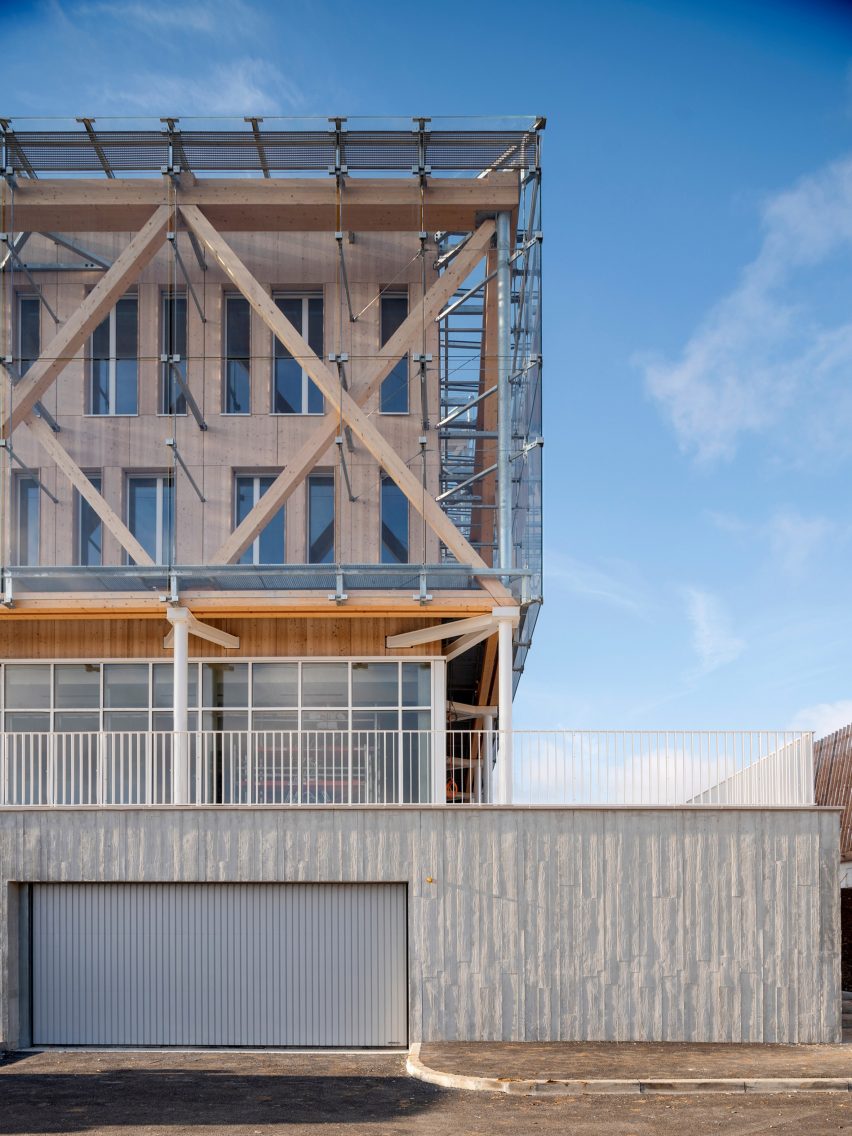
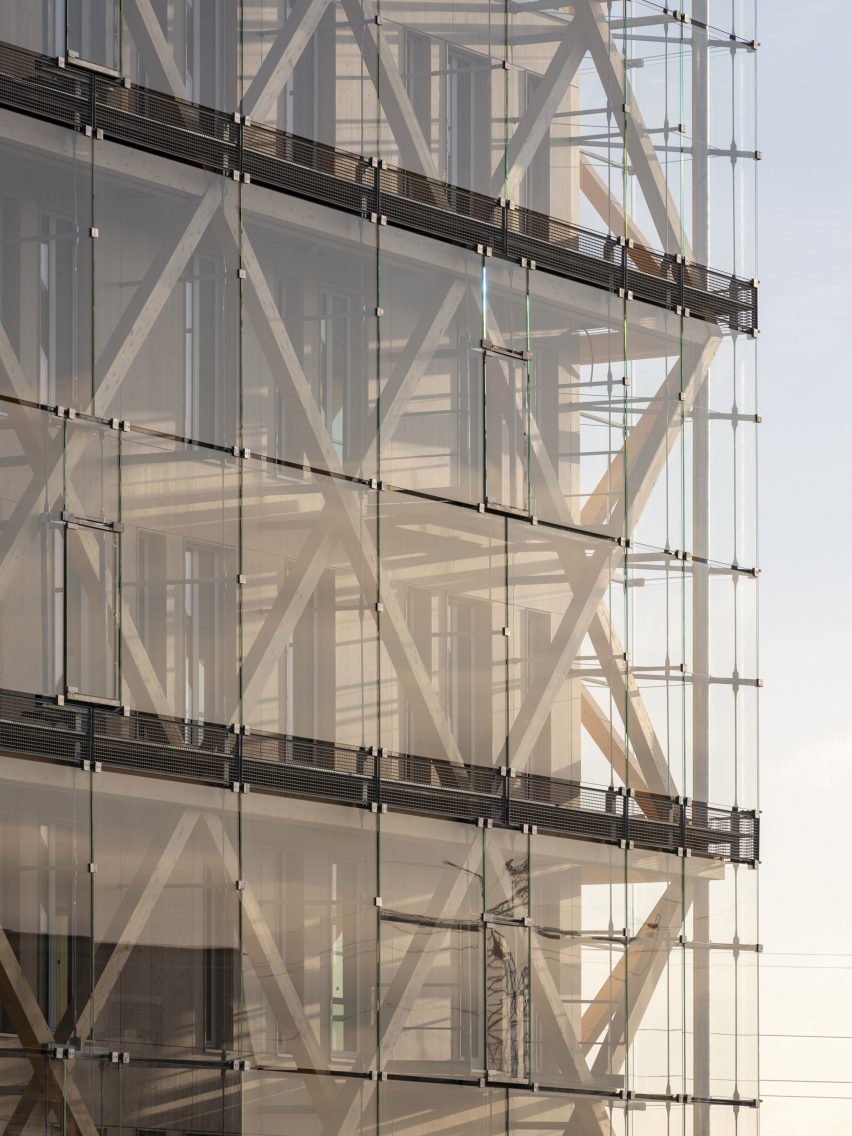











 At the heart of the FADS building is the idea of bringing diverse ideas and art practices together. The building was made to exemplify the notion of learning by doing, drawing together disciplines that were previously dispersed across campus: graphic design, sculpture, ceramics, metals, painting, drawing, photography and filmmaking. The architecture was designed to provide a framework for new synergies and enhanced collaboration and, in doing so, inspire creativity and new forms of art making.
At the heart of the FADS building is the idea of bringing diverse ideas and art practices together. The building was made to exemplify the notion of learning by doing, drawing together disciplines that were previously dispersed across campus: graphic design, sculpture, ceramics, metals, painting, drawing, photography and filmmaking. The architecture was designed to provide a framework for new synergies and enhanced collaboration and, in doing so, inspire creativity and new forms of art making.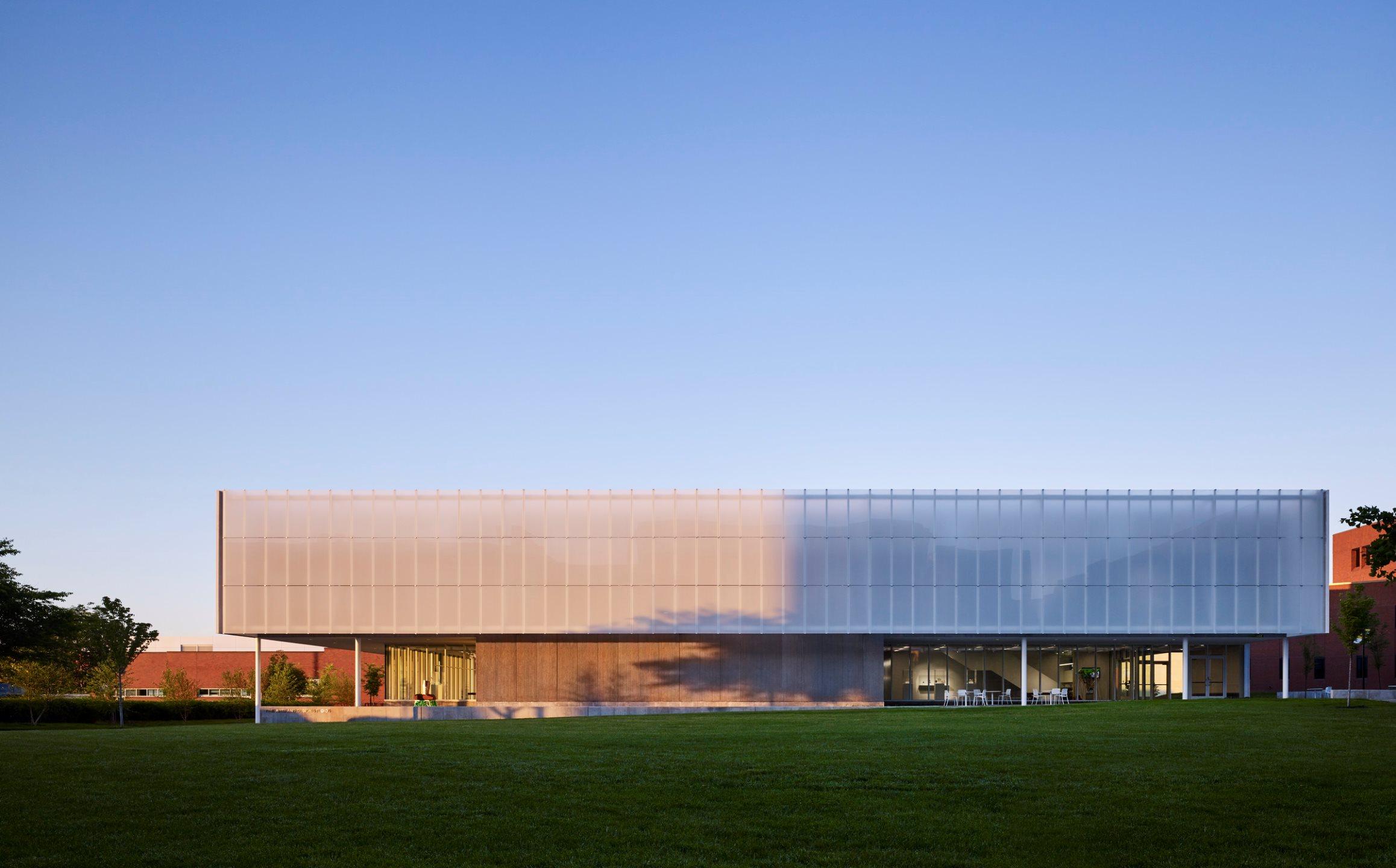
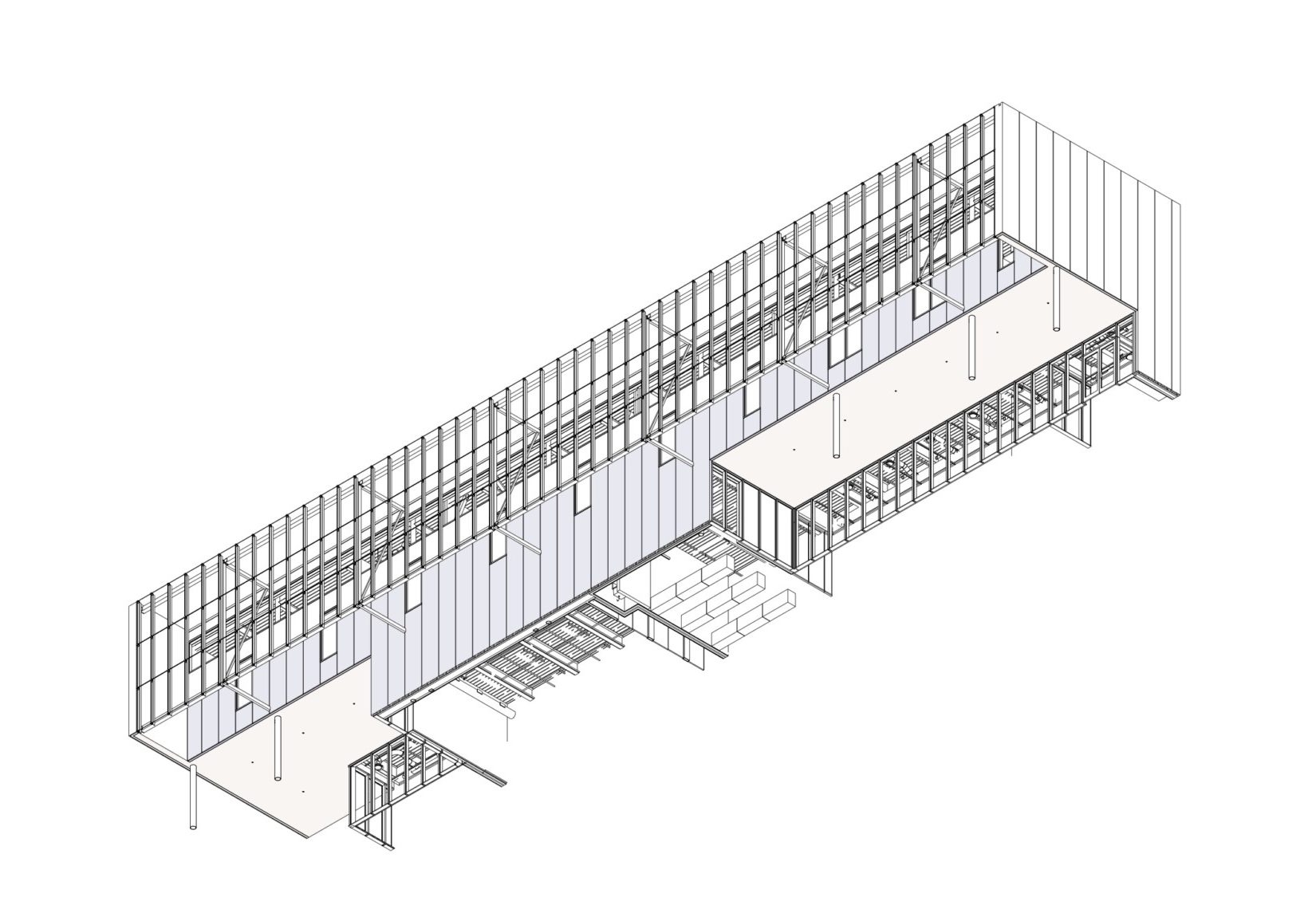 The FADS building was completed with
The FADS building was completed with 
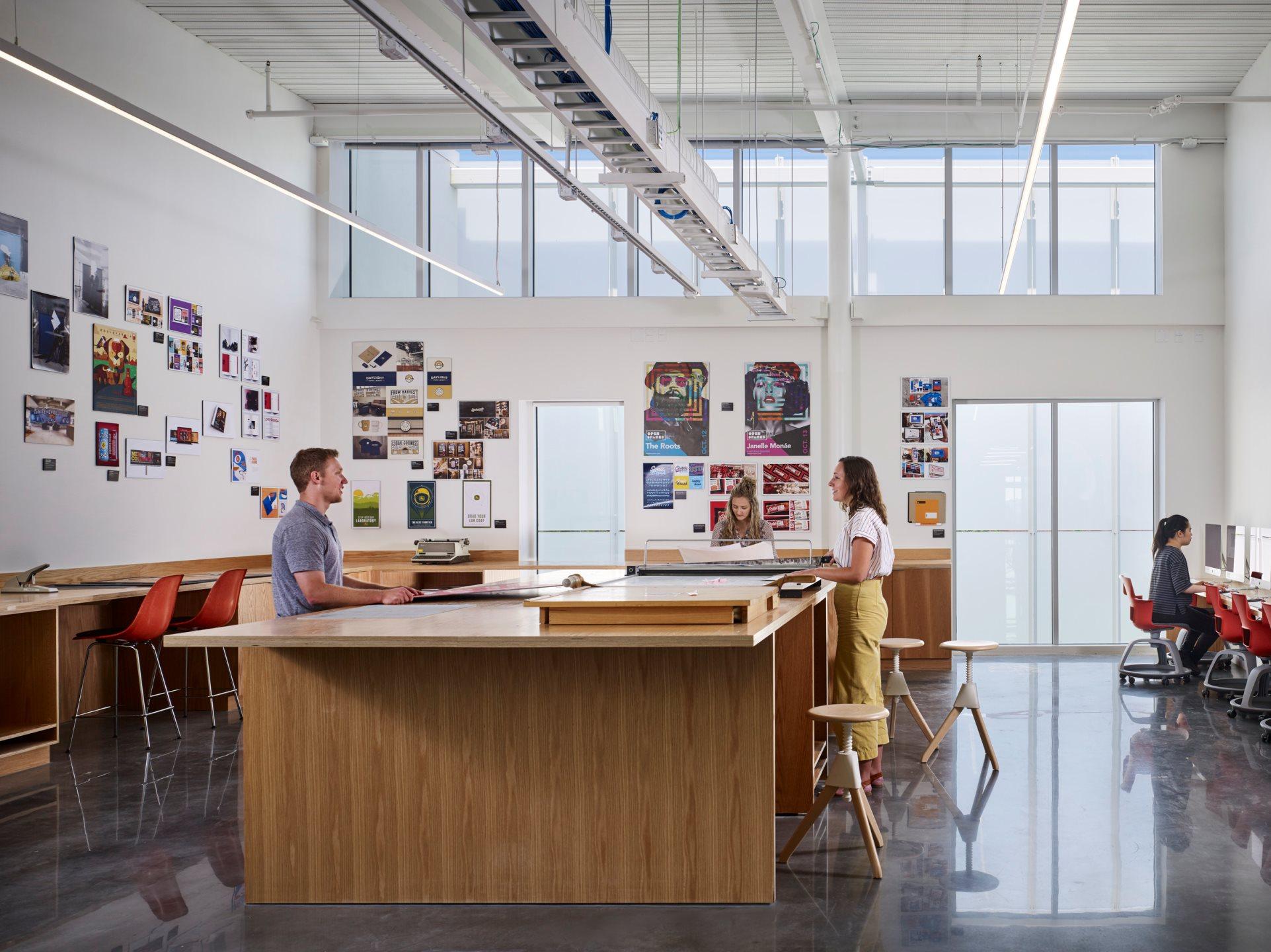
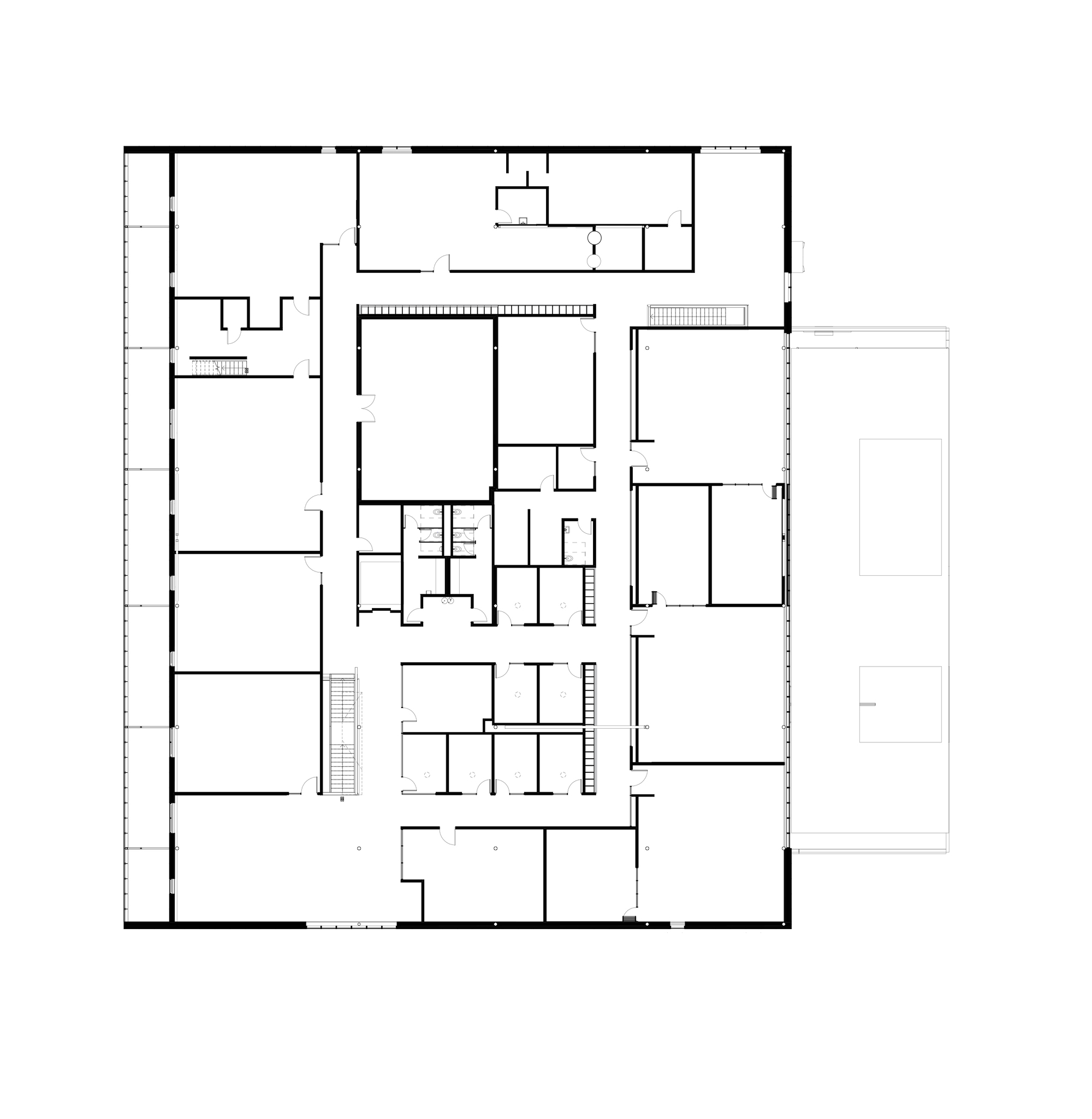
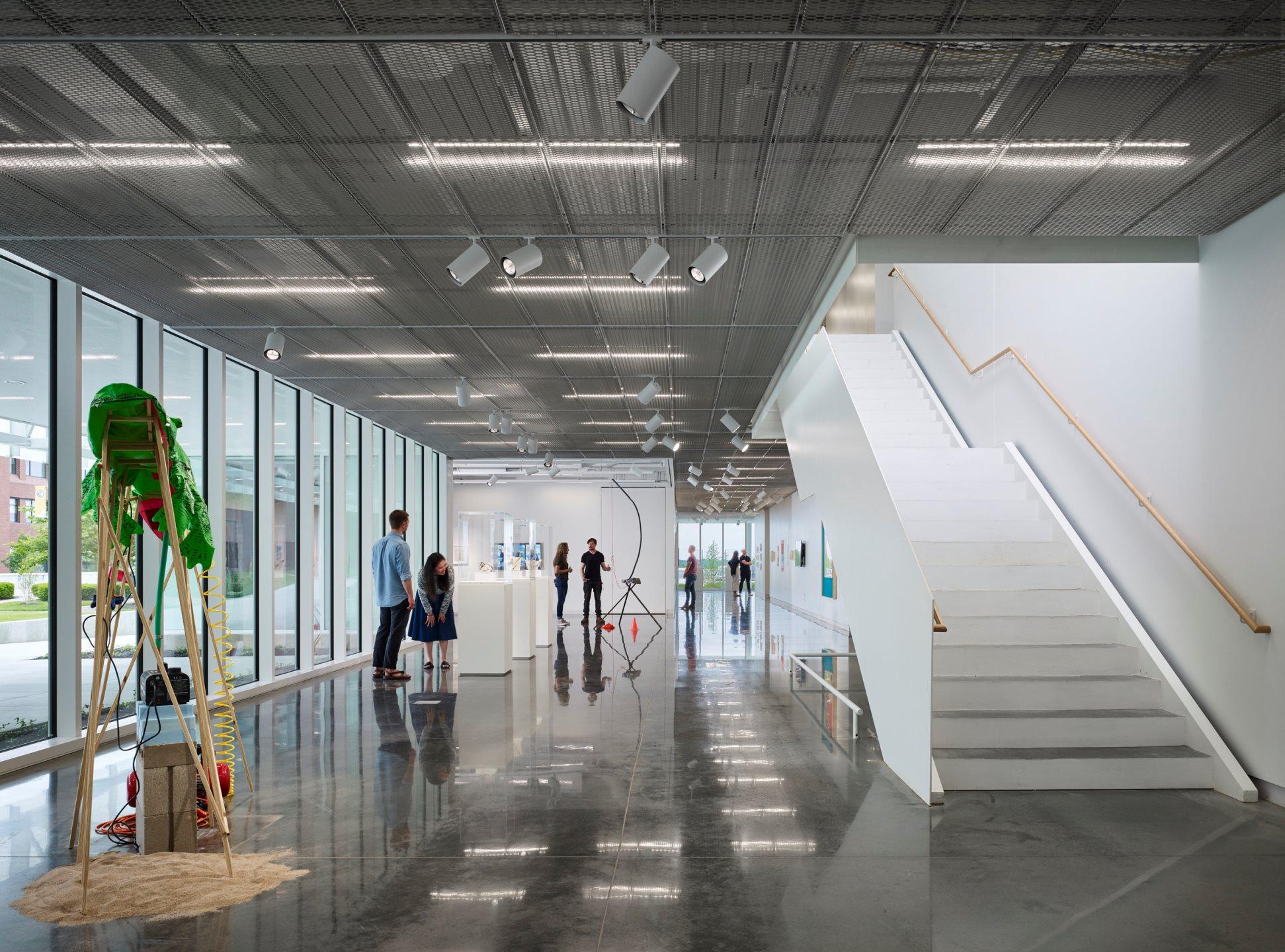 As the design team notes, the FADS building included classrooms and studio space, material storage, multi-use common spaces, as well as display and collaboration spaces throughout building corridors. Fueling a desire to create, FADS includes these hallway gallery spaces and a covered outdoor courtyard, which functions as a year-round workspace for student and faculty artists alike.
As the design team notes, the FADS building included classrooms and studio space, material storage, multi-use common spaces, as well as display and collaboration spaces throughout building corridors. Fueling a desire to create, FADS includes these hallway gallery spaces and a covered outdoor courtyard, which functions as a year-round workspace for student and faculty artists alike.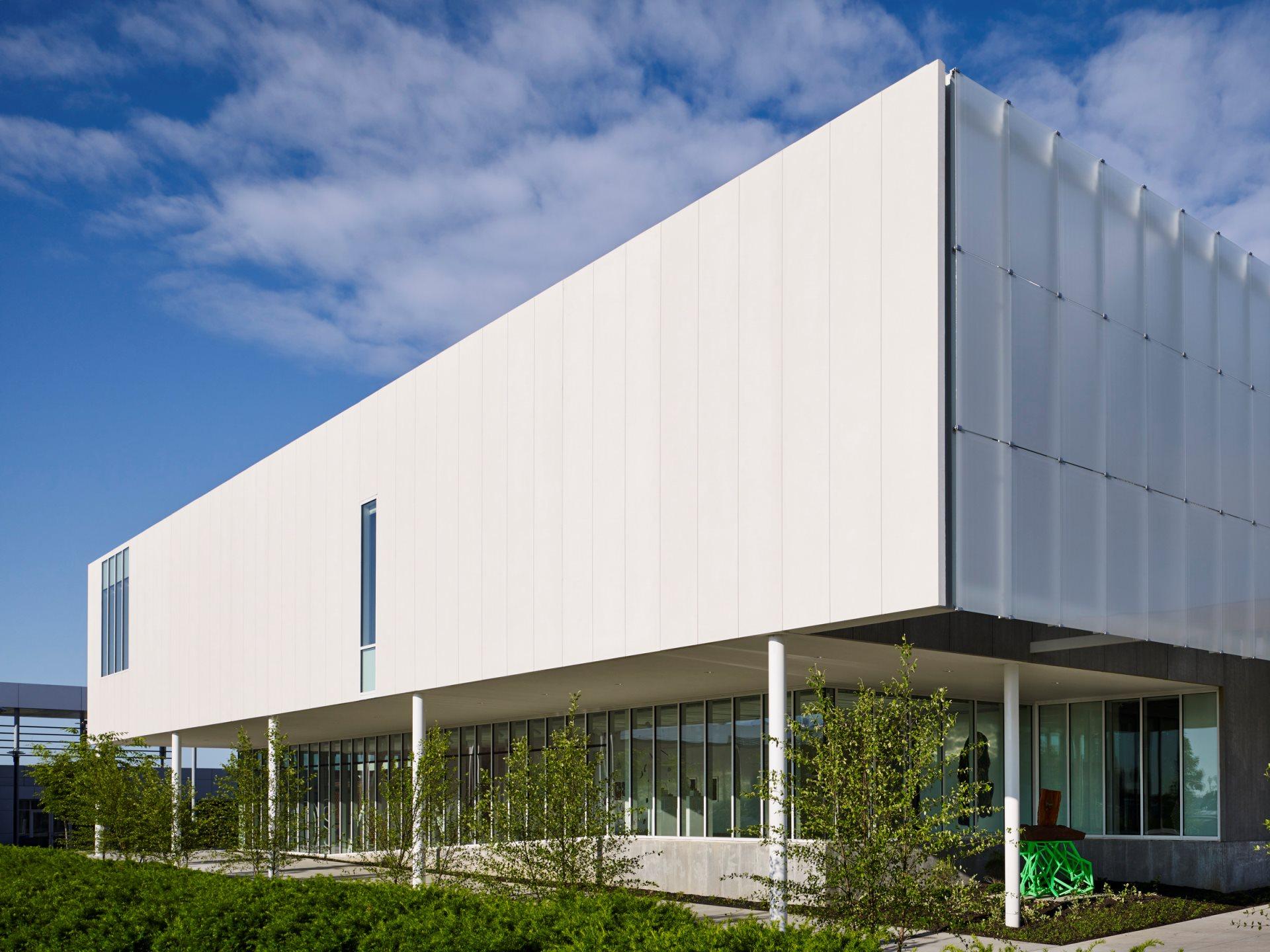
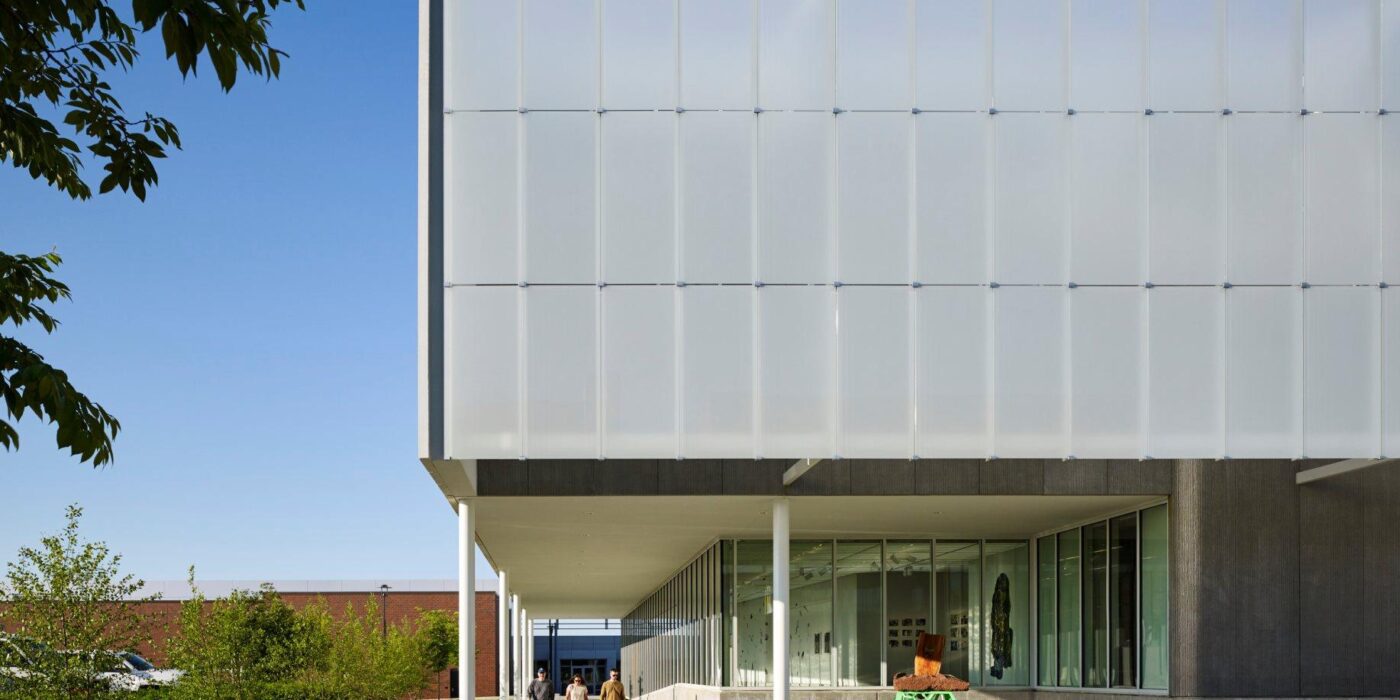
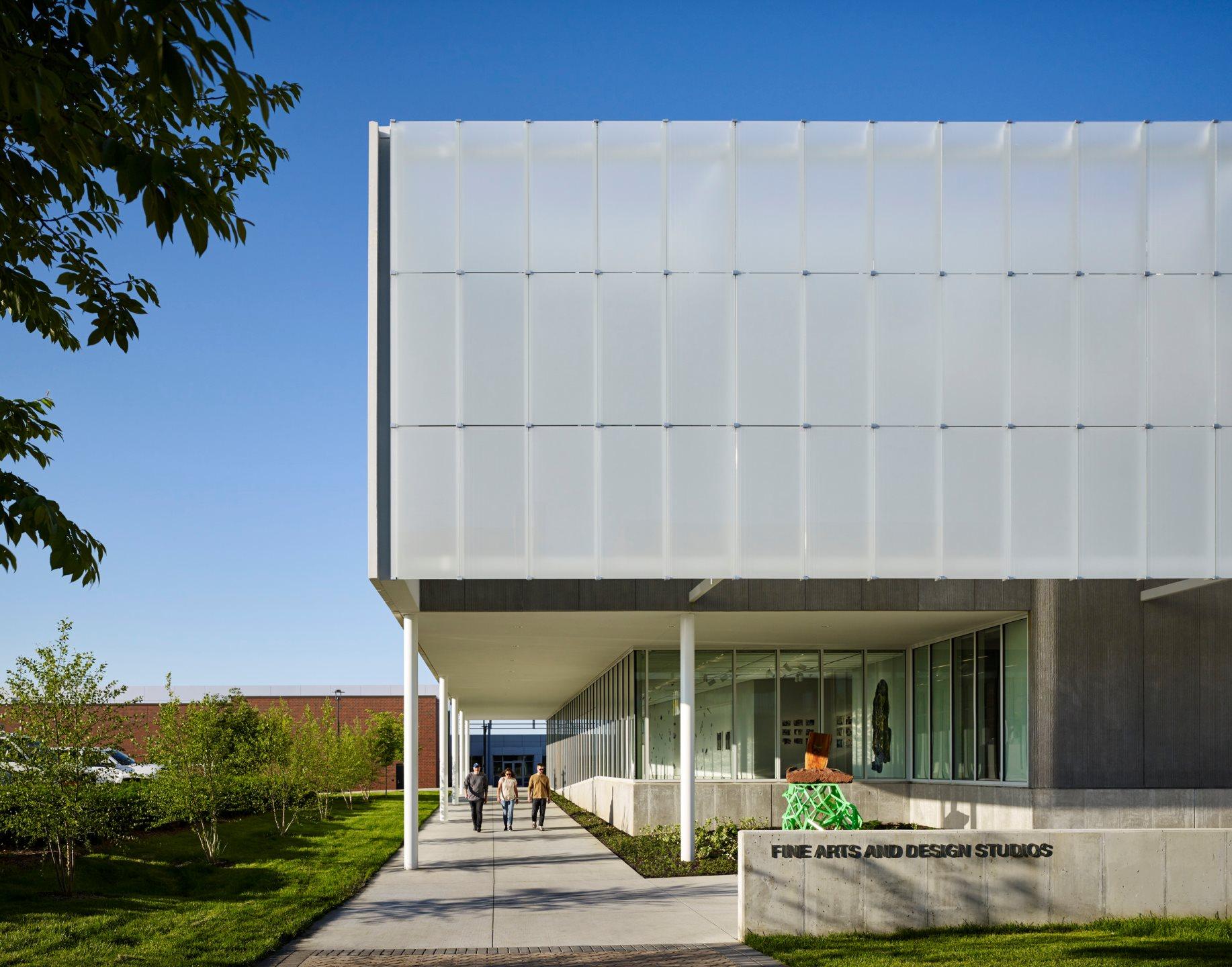
 BNIM’s design features a rectangular volume lifted off the ground by a concrete podium and pilotis. In turn, the building volume is offset by acid-etched and ceramic-fritted glass panels. They worked with architectural glass and systems manufacturer Bendheim to bring the glass panels to life.
BNIM’s design features a rectangular volume lifted off the ground by a concrete podium and pilotis. In turn, the building volume is offset by acid-etched and ceramic-fritted glass panels. They worked with architectural glass and systems manufacturer Bendheim to bring the glass panels to life.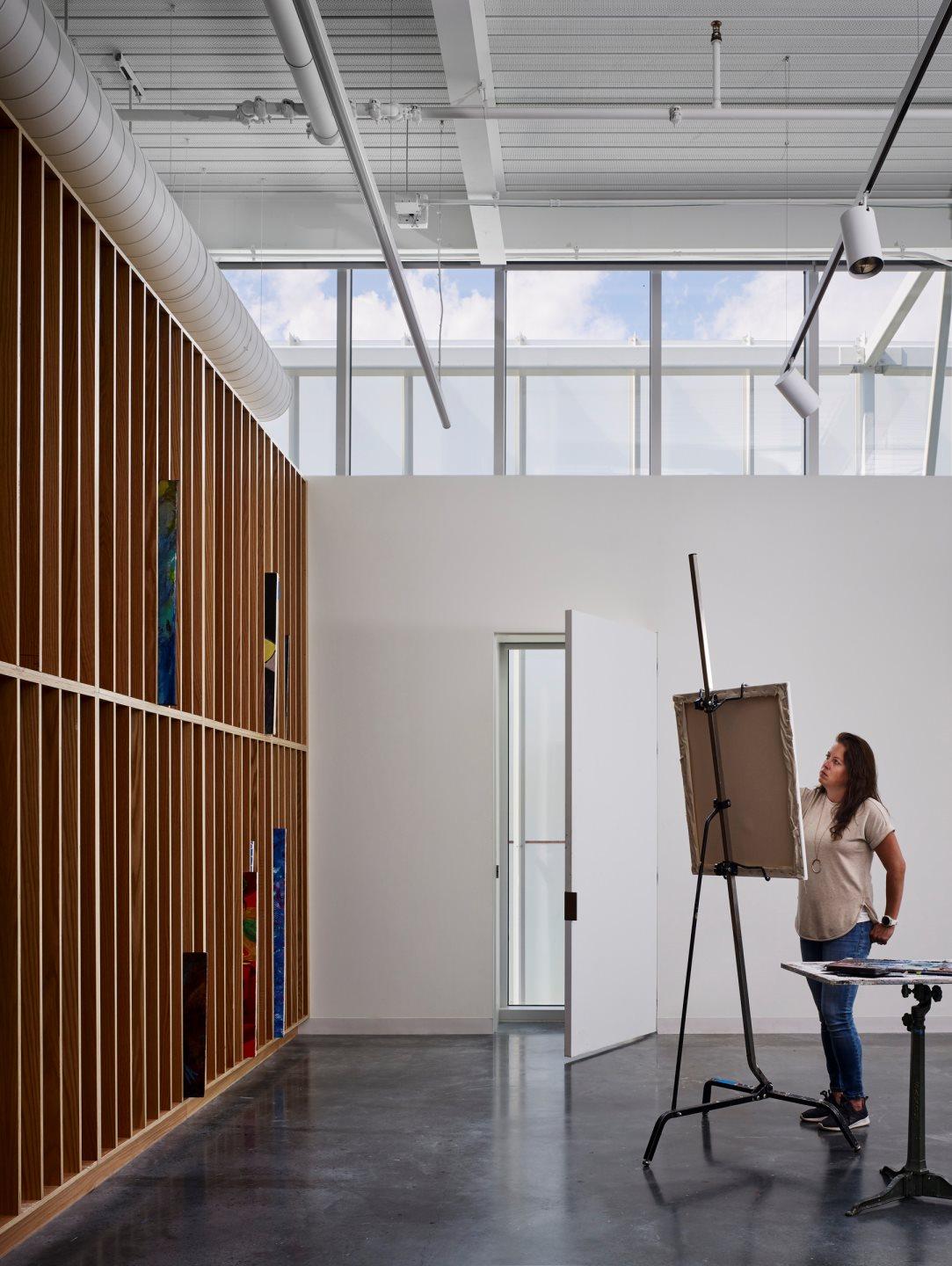
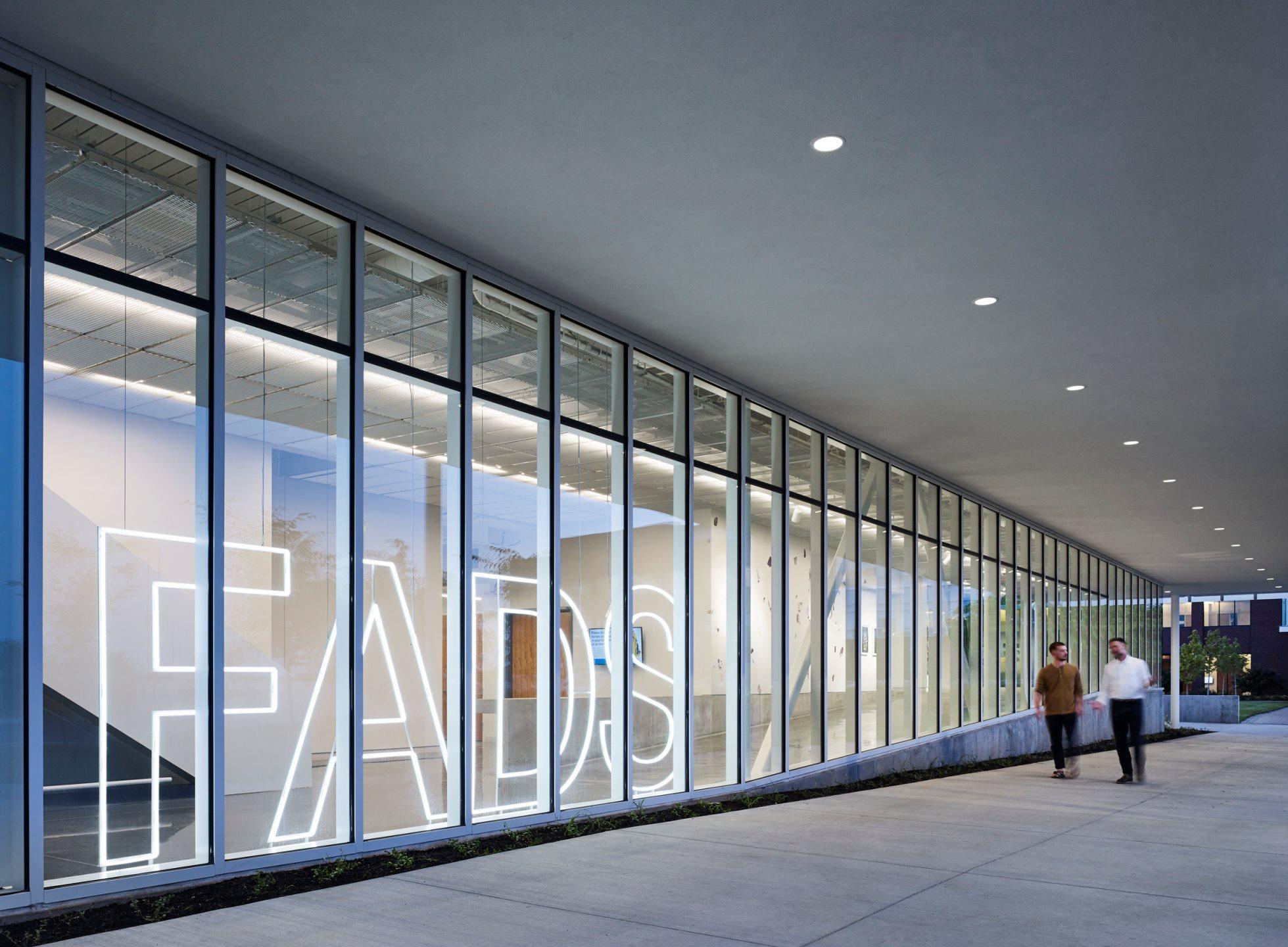 Just steps away from the Midwest Trust Center, the Wylie Hospitality and Culinary Academy, and the Nerman Museum of Contemporary Art, the Fine Arts & Design Studios (FADS) facility was made to anchor a new arts neighborhood on campus. The FADS strengthens these connections and provides space to reimagine how art is made.
Just steps away from the Midwest Trust Center, the Wylie Hospitality and Culinary Academy, and the Nerman Museum of Contemporary Art, the Fine Arts & Design Studios (FADS) facility was made to anchor a new arts neighborhood on campus. The FADS strengthens these connections and provides space to reimagine how art is made.
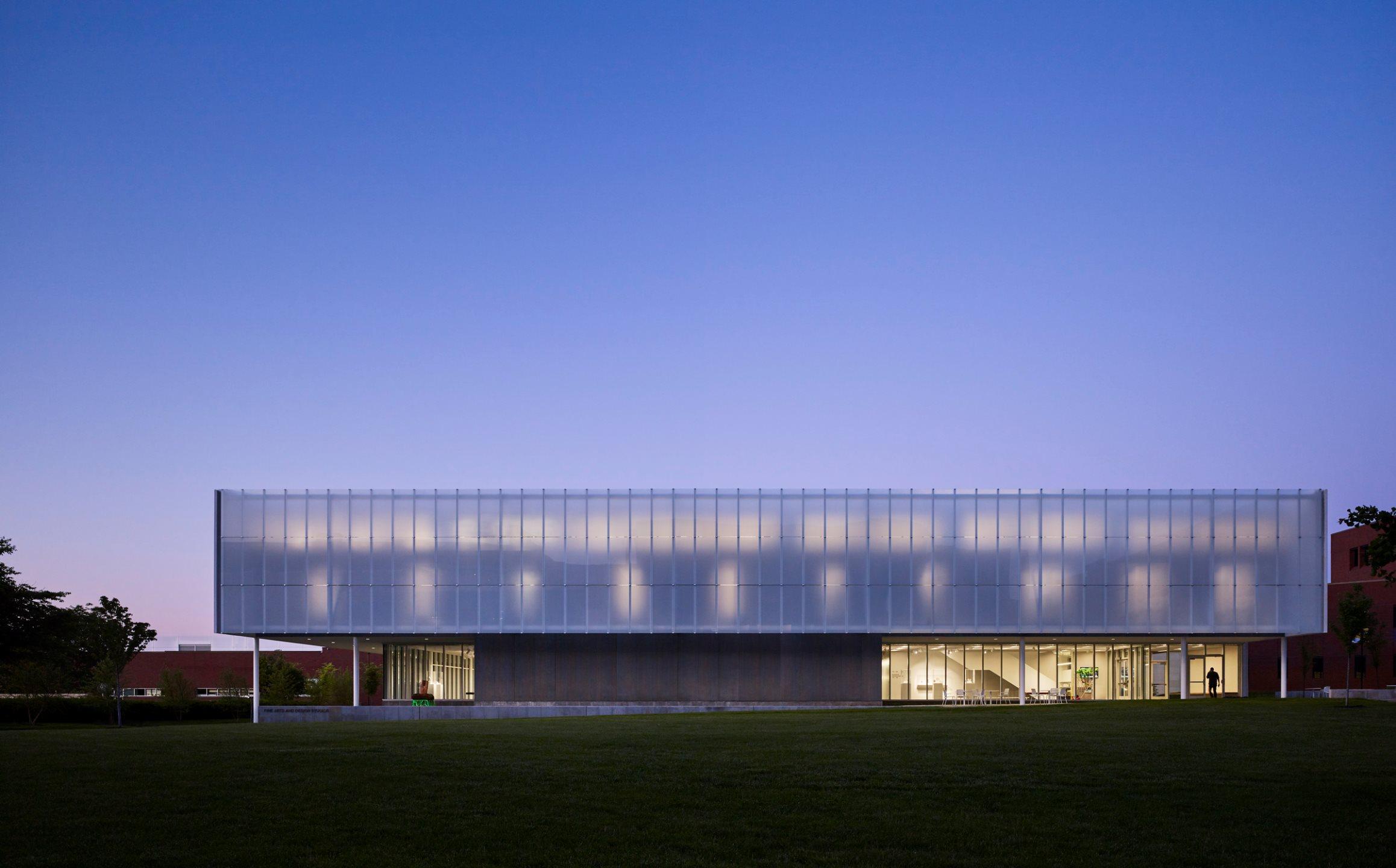 “In the fine arts are these silos of specialties, but the trend is to break through those silos,” says Fine Arts Professor Mark Cowardin. “Painters are embracing more materials, and sculptors are working with ceramics and drawing. We want that sort of cross-pollination, not only with our students but with our professors. We are encouraging a creativity zone where we can build on our reputation and present to our students the opportunity for innovation.”
“In the fine arts are these silos of specialties, but the trend is to break through those silos,” says Fine Arts Professor Mark Cowardin. “Painters are embracing more materials, and sculptors are working with ceramics and drawing. We want that sort of cross-pollination, not only with our students but with our professors. We are encouraging a creativity zone where we can build on our reputation and present to our students the opportunity for innovation.”