Using fallen city trees for greener urban building – Springwise

Spotted: According to one study, rural and urban communities across the US lose around 36 million trees every year, whether that’s due to felling, disease, or weather-related damages. Once they’ve fallen or been cut down, the majority of these trees are chipped, burnt, or simply sent to rot in landfill. This represents a huge waste of potential resources and economic opportunity. One startup that’s hoping to change that is Washington-based Cambium Carbon.
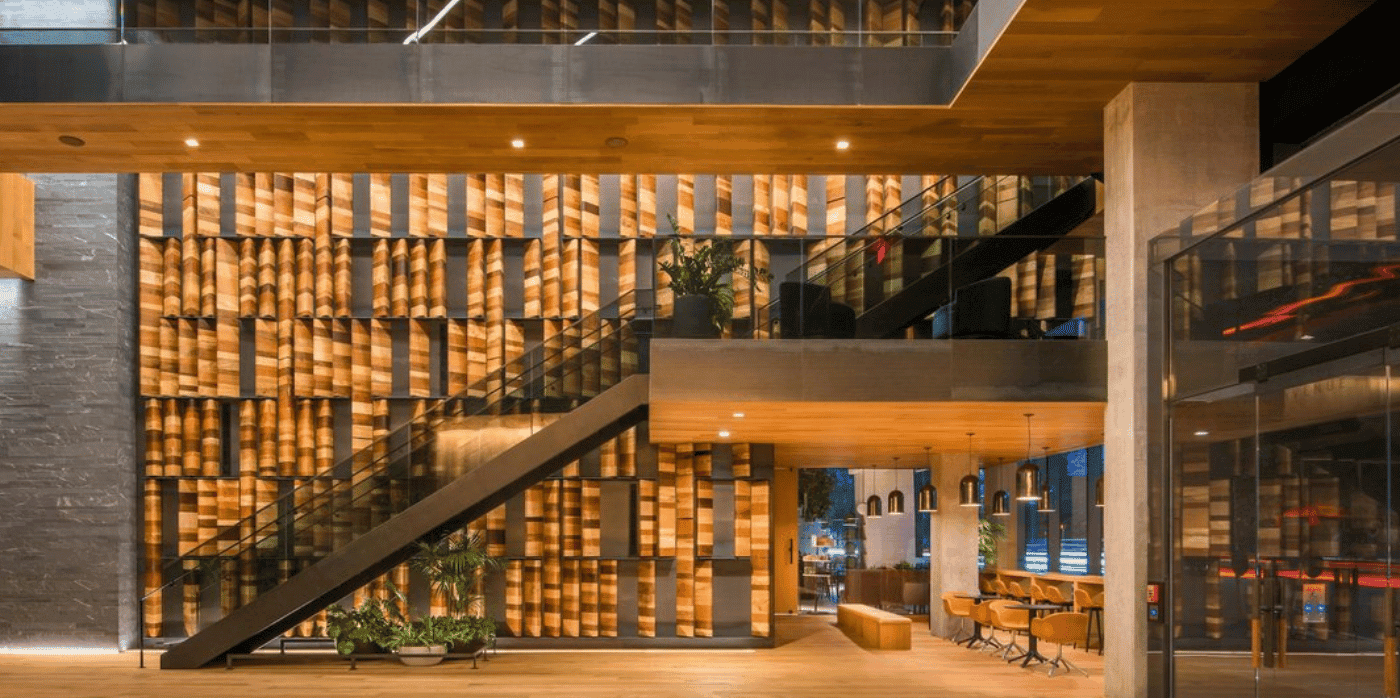
Instead of allowing fallen or cut-down trees to go to waste, Cambium partners with local sawmills and other organisations to turn them into Carbon Smart Wood – a high-quality, carbon-negative building material with various purposes, including decking, siding, fencing, millwork, and lumber. To regenerate land and ensure the long-term of America’s forests, the company allocates 15 per cent of its profits to the planting of new trees, targeting historically underserved and low-canopy areas.
Cambium Carbon also tracks all incoming material through its transparent supply chain software, Traece. With the Traece system, end users can also access information on their Carbon Smart Wood manufacturing, as well as helpful data on the carbon impact, which can be used in a company’s climate reporting as they work to meet sustainability goals.
Numerous companies have seen the potential in Cambium, with Carbon Smart Wood already incorporated across various sites like Maryland’s Guinness Brewery, the Patagonia store in Baltimore, and the National Geographic headquarters in Washington. Furniture retailer Room & Board has also used the material to craft unique coffee and side tables.
There are many other innovators making use of wood to create beautiful, eco-friendly products – including a waterproof wood composite for use in bathrooms and another material made from wood waste.
Written By: Lauryn Berry and Matilda Cox