Architects: Want to have your project featured? Showcase your work through Architizer and sign up for our inspirational newsletter.
That nature can help cure people both physically and mentally is not a new concept. Architects are using greenery to help combat the sterility of modern healthcare facilities, yet it is not usually not easy to achieve the ideal result. Explore different approaches to ‘green healthcare’ with the following six projects of different sites and sizes.
Steno Diabetes Center Copenhagen
By Vilhelm Lauritzen Architects and MIKKELSEN Architects, Herlev, Denmark
Popular Choice, 10th Annual A+Awards, Hospitals & Healthcare Centers
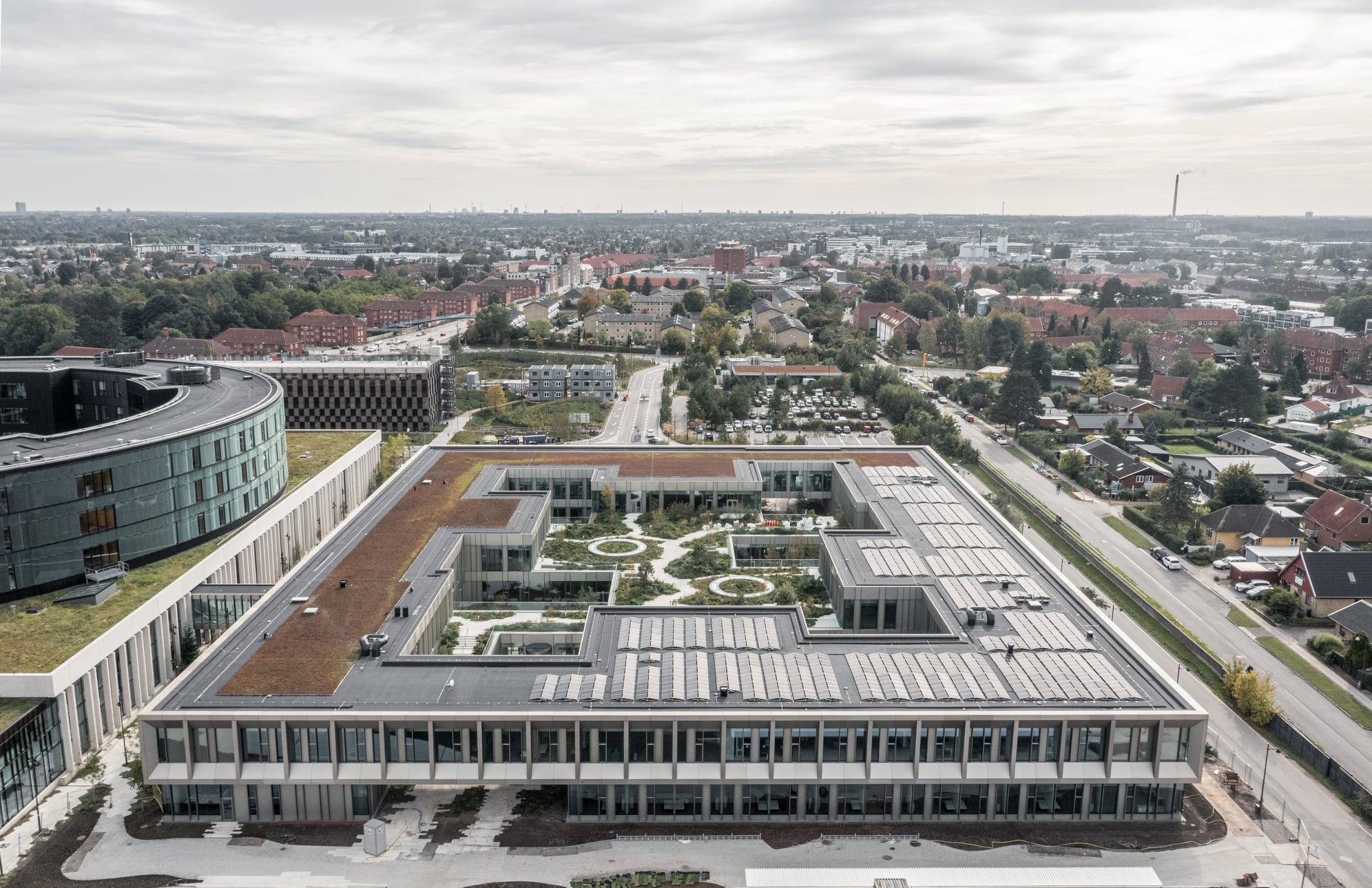
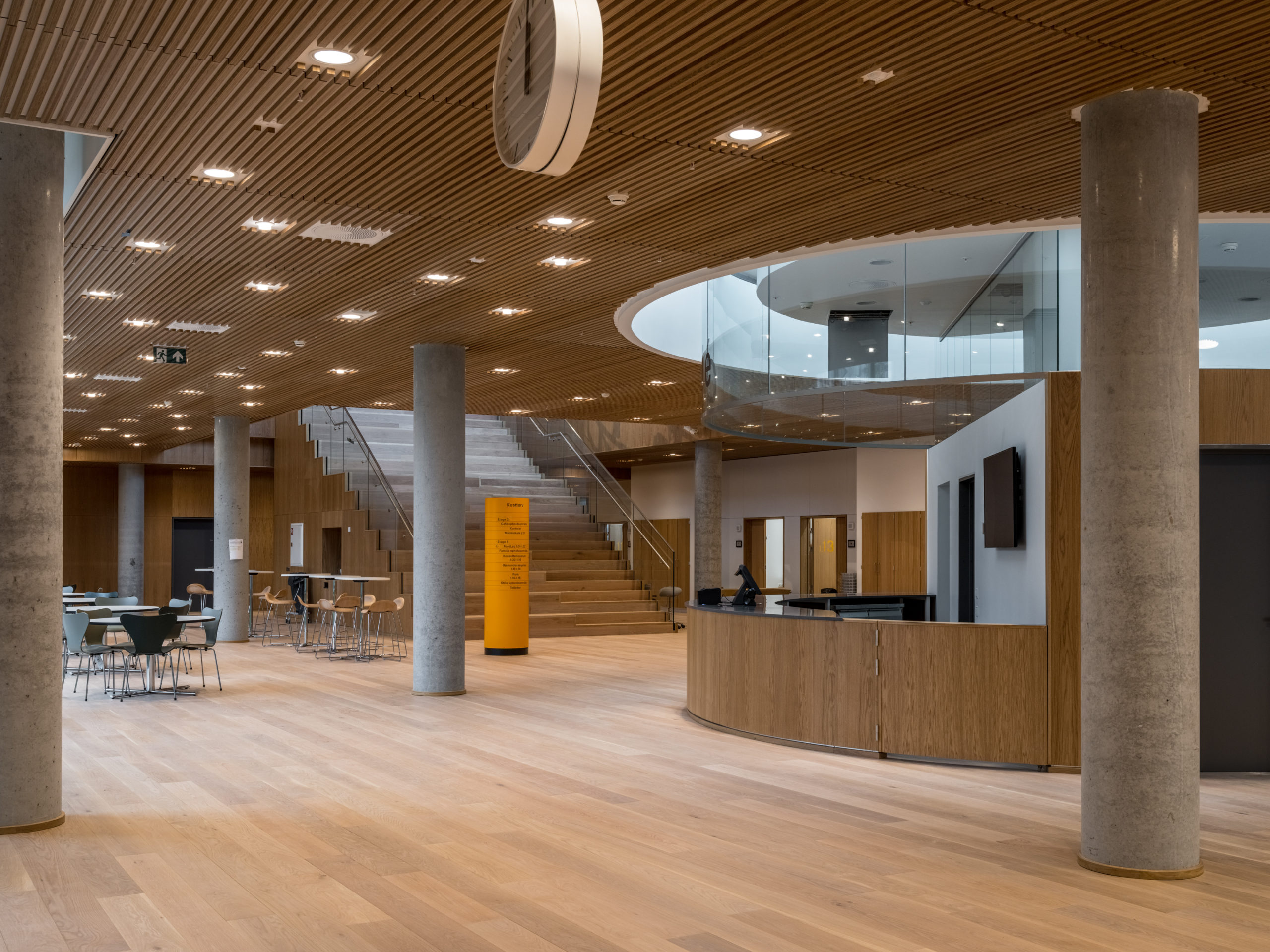
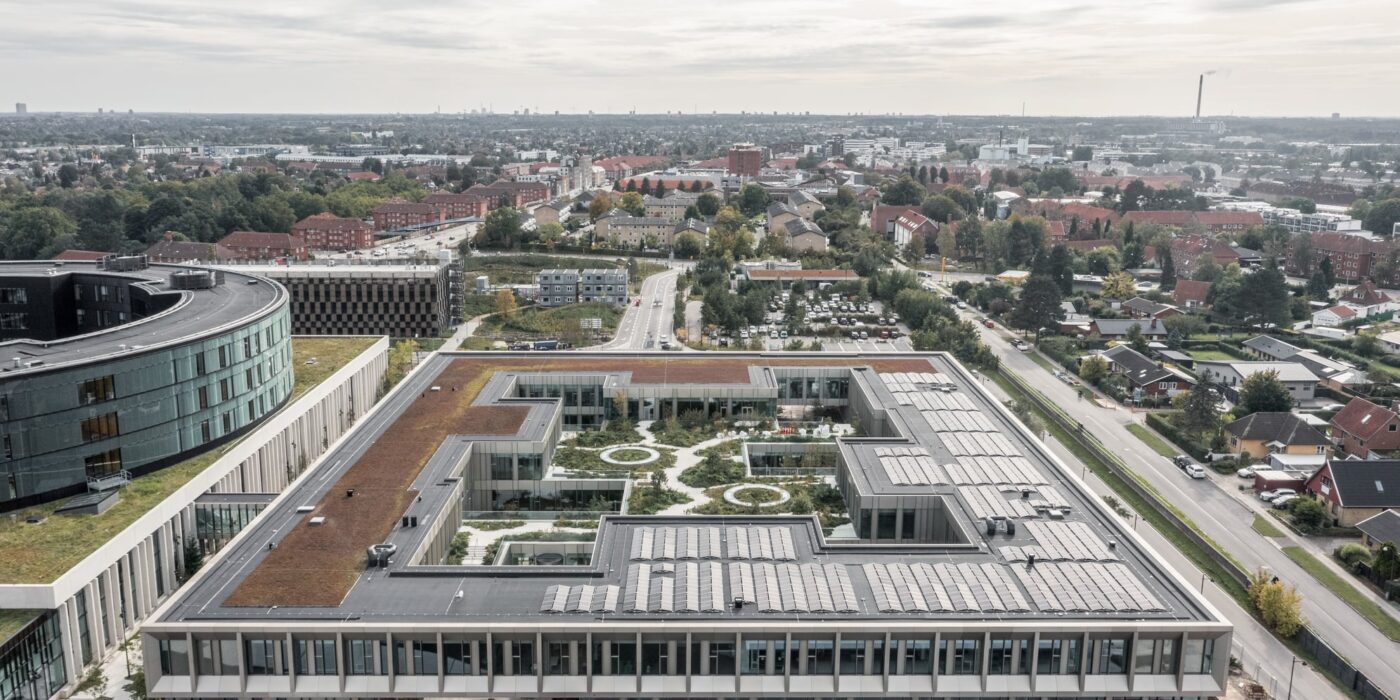
 Steno Diabetes Center Copenhagen is a hospital for preventing and treating diabetes. The hospital occupies a rectangular site with two entrances open on two opposite sides. There are four inner gardens on the first floor and two of them greet the visitors immediately upon their entry. Common areas such as circulation spaces and reception sit in the middle of the floor plan, while most individual rooms are lined on the outer ring.
Steno Diabetes Center Copenhagen is a hospital for preventing and treating diabetes. The hospital occupies a rectangular site with two entrances open on two opposite sides. There are four inner gardens on the first floor and two of them greet the visitors immediately upon their entry. Common areas such as circulation spaces and reception sit in the middle of the floor plan, while most individual rooms are lined on the outer ring.
The same layout continues to the second floor, replacing covered common areas with a continuous roof garden. Both vegetation and warm-color, wooden interior aim to build up a calming atmosphere for all visitors. Outside the rooms, a thin layer of vegetation shelters the rather private rooms from public view.
Maggie’s Leeds
By Heatherwick Studio, Leeds, United Kingdom
Jury Winner and Popular Choice, 9th Annual A+Awards, Hospitals & Healthcare Centers
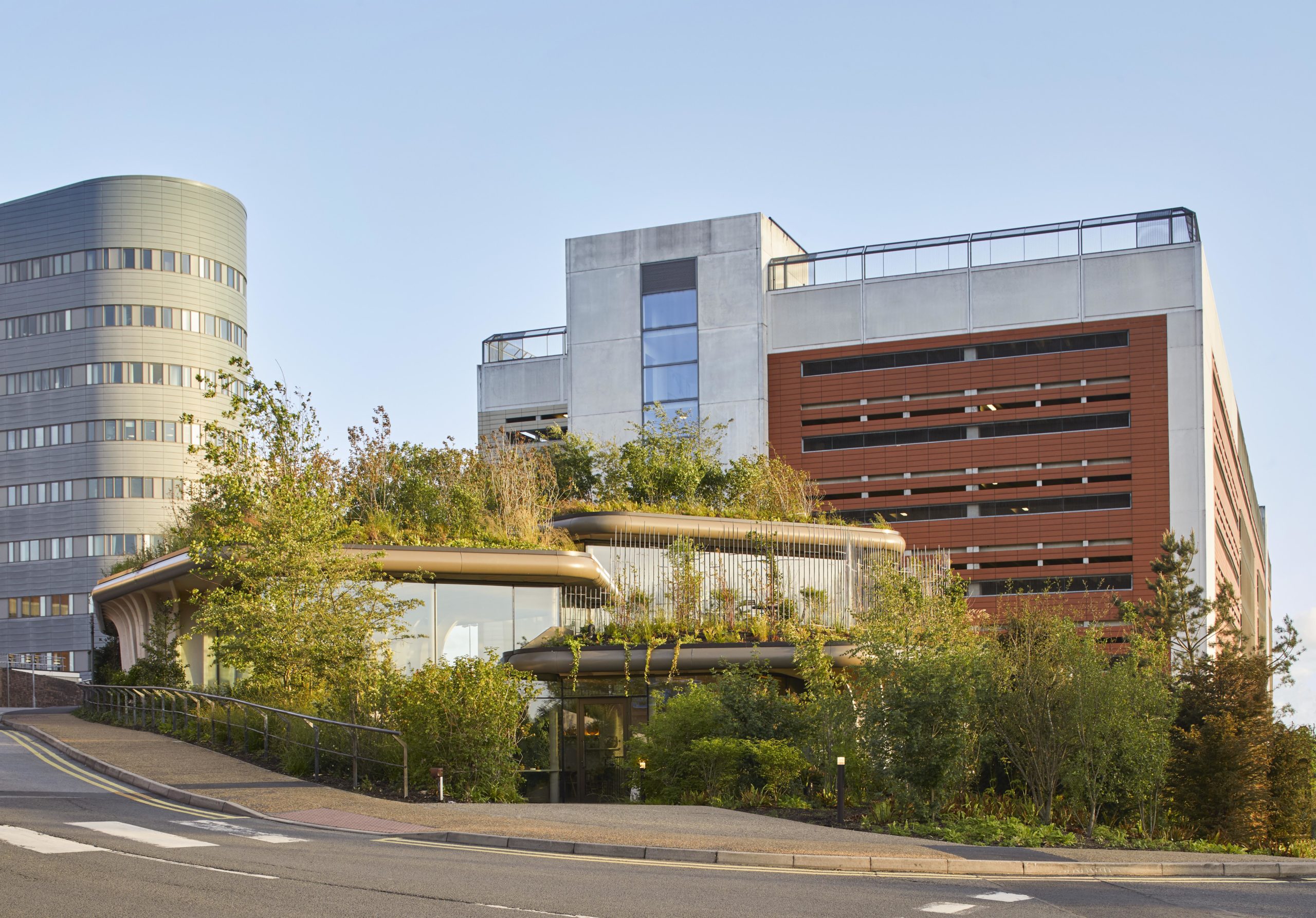
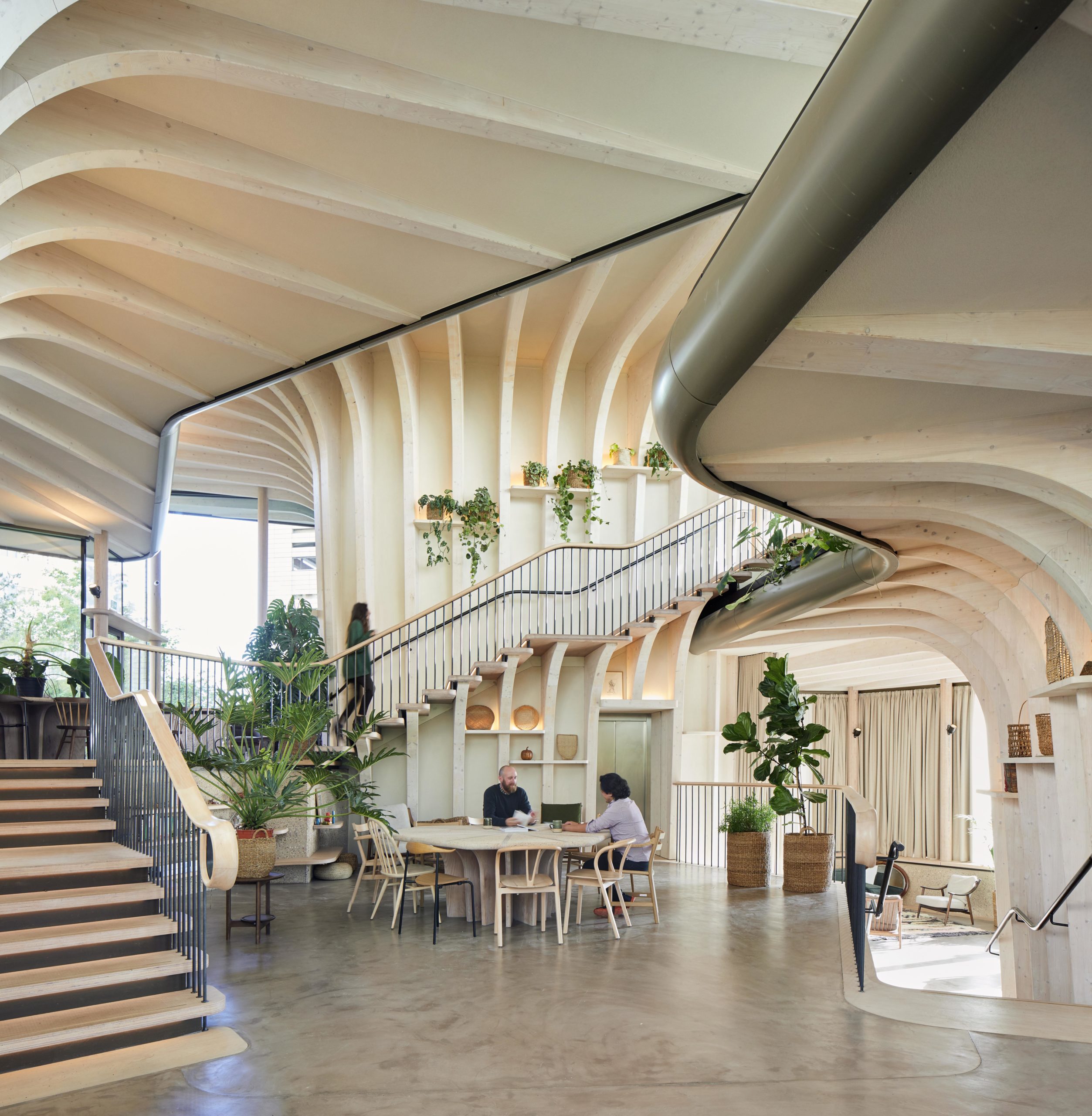
 Maggie’s centers provide free cancer support and information to patients and their friends and families. The centers are located across the UK, each in a unique style while all of them embrace nature as a way of healing. Maggie’s Leeds stands on the last patch of greenery at St James’s University Hospital. The sloping site is bounded by roads and a multi-story car park. Instead of flattening the landscape, the spaces descend along the landscape, creating views that vary from open to secluded.
Maggie’s centers provide free cancer support and information to patients and their friends and families. The centers are located across the UK, each in a unique style while all of them embrace nature as a way of healing. Maggie’s Leeds stands on the last patch of greenery at St James’s University Hospital. The sloping site is bounded by roads and a multi-story car park. Instead of flattening the landscape, the spaces descend along the landscape, creating views that vary from open to secluded.
Three tree-like structures articulate the common areas under their crowns and include the counseling rooms within the trunk. Plants are visible everywhere – on top of the roofs, around the buildings and inside the buildings. The building demonstrates the idea of shelter in a natural form.
Waldkliniken Eisenberg
By Matteo Thun & Partners, Germany
Popular Choice, 9th Annual A+Awards, Architecture + Health
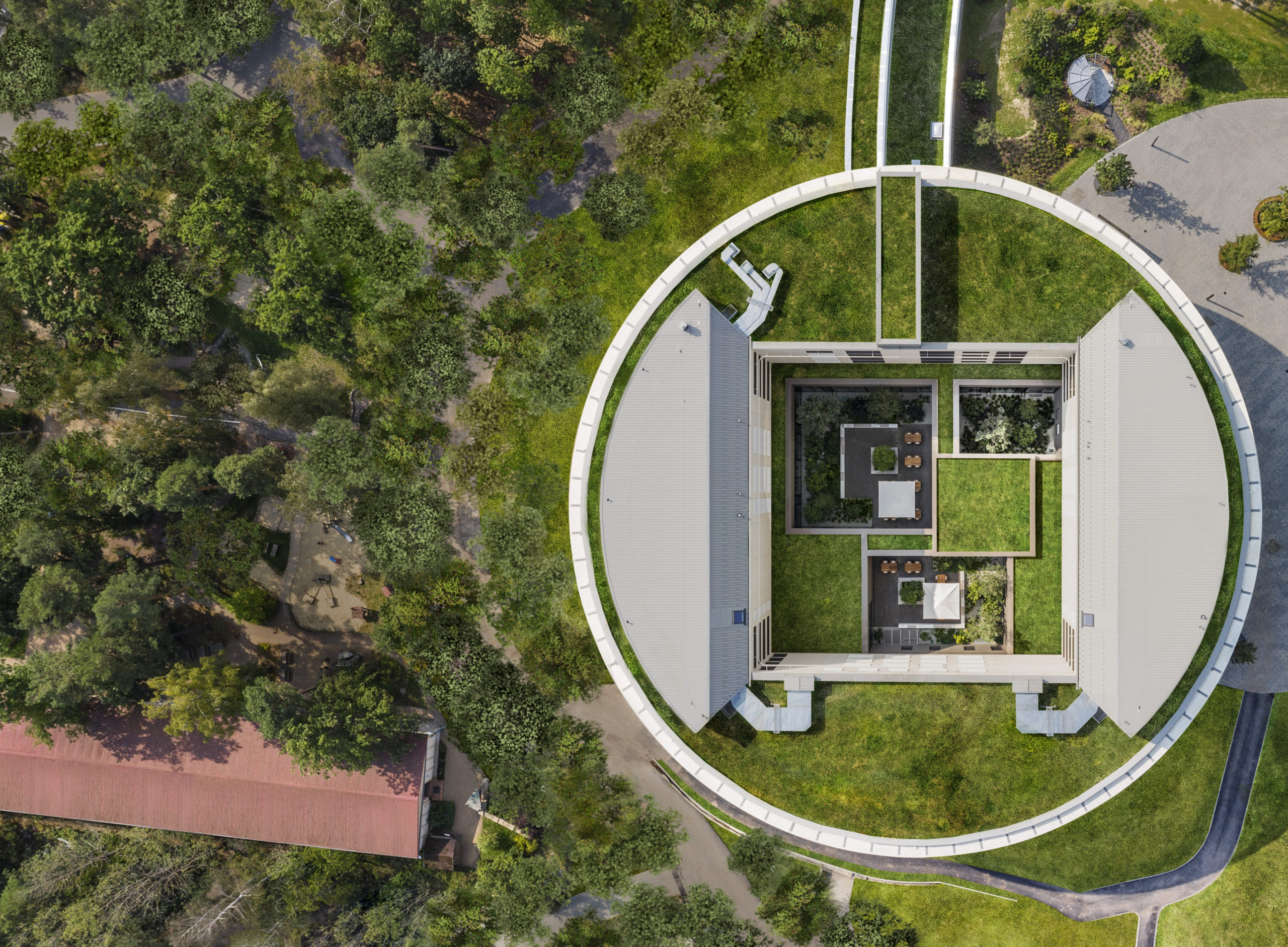
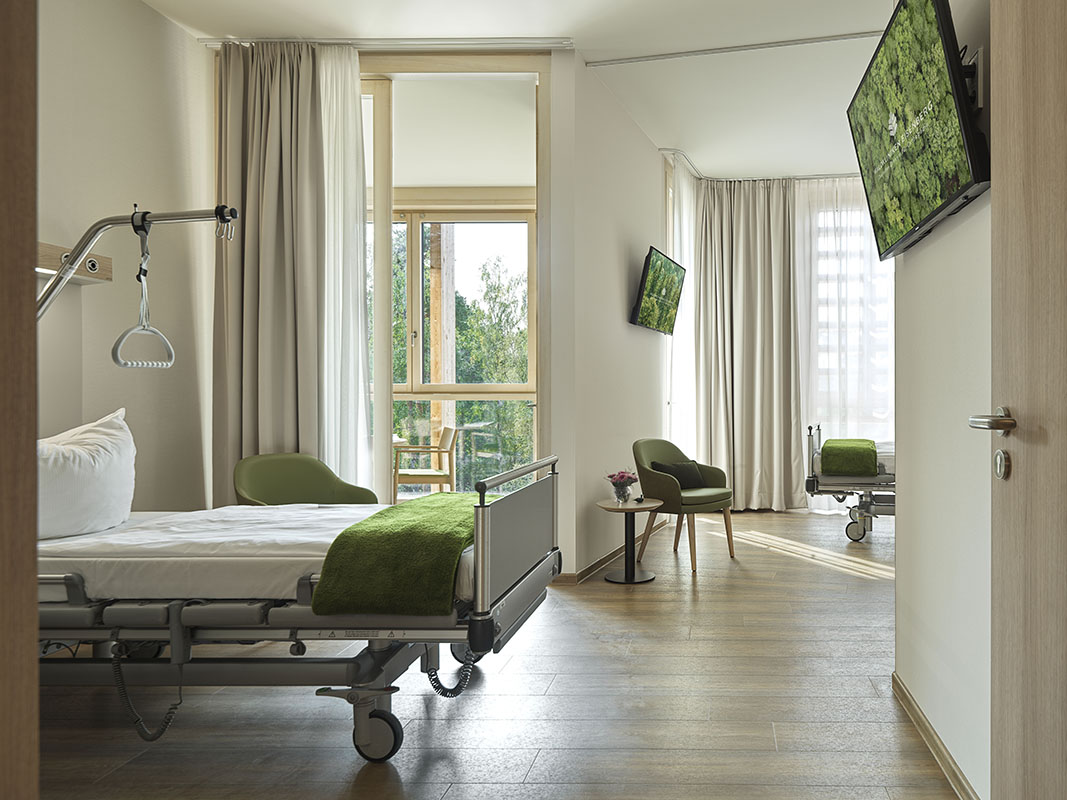
 This new hospital wing of the orthopedic center Waldkliniken Eisenberg enjoys an immersive view of the Thuringian Forest. The six-story building has 128 patient rooms, all located on the outer ring of the circular floor plans. Floor-to-ceiling windows invite unblocked views of the natural landscape into the rooms while providing natural light and fresh air to the rooms.
This new hospital wing of the orthopedic center Waldkliniken Eisenberg enjoys an immersive view of the Thuringian Forest. The six-story building has 128 patient rooms, all located on the outer ring of the circular floor plans. Floor-to-ceiling windows invite unblocked views of the natural landscape into the rooms while providing natural light and fresh air to the rooms.
Common areas such as the lobby and the cafeteria for patients are in the middle of the floor plans, framed by the wards. Inner gardens are carefully cultivated so that the common areas are also visually connected to pleasing greenery. The interior is finished largely in warm-color timber and lighted up by colorful fabrics. Rich textures and colors create a cozy and cheerful atmosphere for the patients.
Expansion of Santa Fe de Bogotá Foundation
By EL EQUIPO MAZZANTI, Bogota, Colombia
Popular Choice, 8th Annual A+Awards, Health Care & Wellness
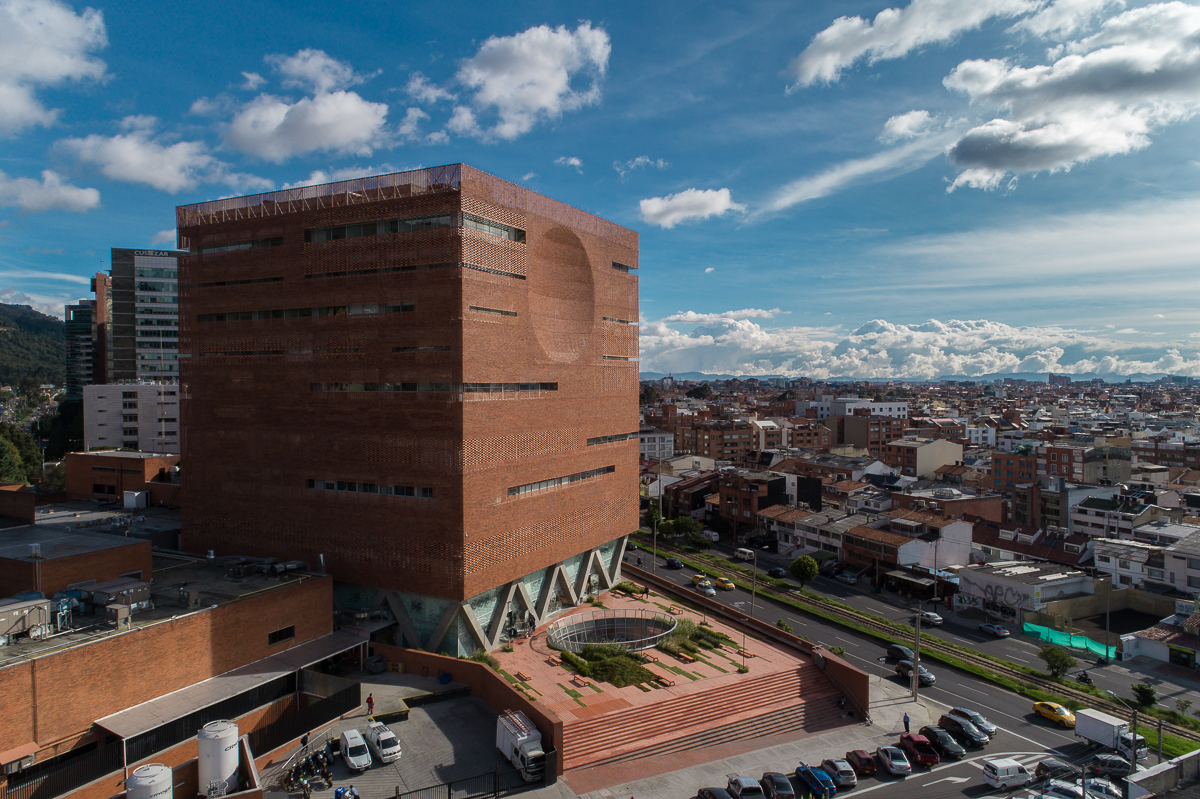
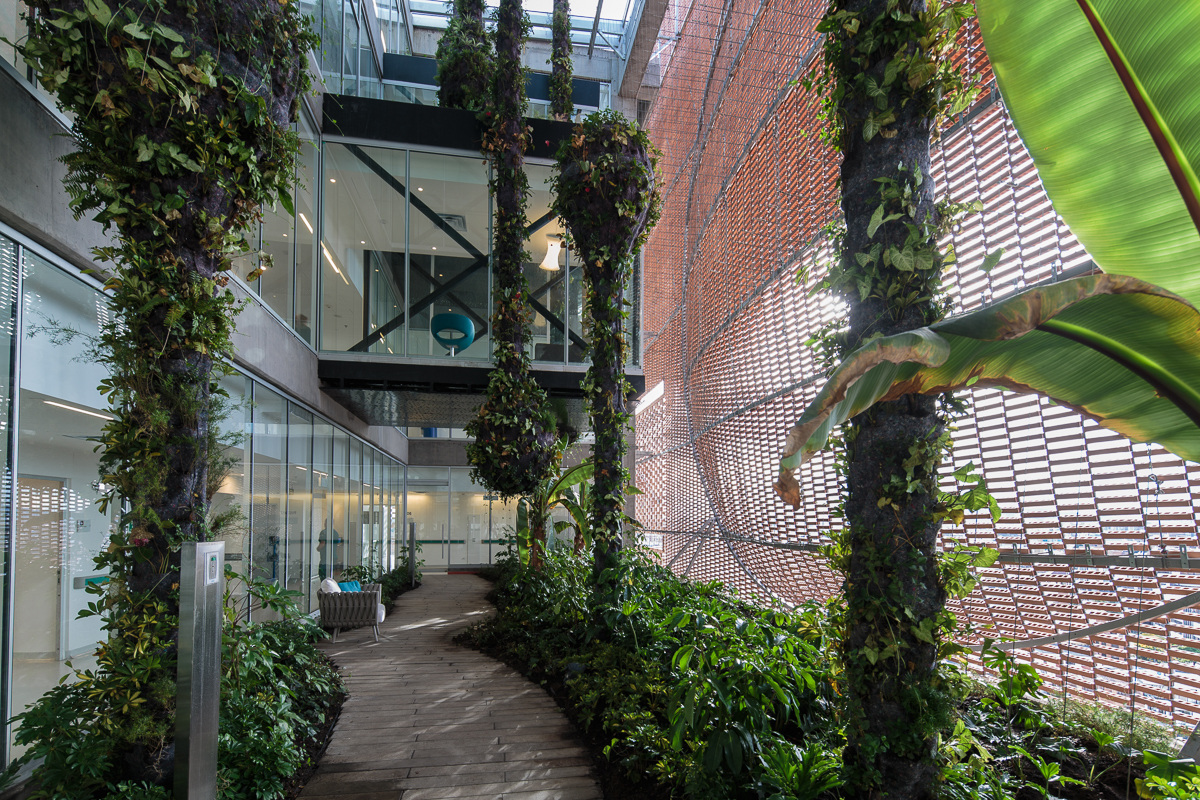
 The expansion of Santa Fe de Bogotá Foundation is sited in the compact urban context of the city of Bogotá. It comprises an eleven-story block and a single-story base. The roof of the base becomes a plaza opening to the roads, with staircases inviting people onto it. Red bricks cover the expansion as a response to the existing buildings around. Strips of pavement on the plaza are replaced by plants. Different types of plants vary in height, breaking the flatness and solidity of the brick plaza.
The expansion of Santa Fe de Bogotá Foundation is sited in the compact urban context of the city of Bogotá. It comprises an eleven-story block and a single-story base. The roof of the base becomes a plaza opening to the roads, with staircases inviting people onto it. Red bricks cover the expansion as a response to the existing buildings around. Strips of pavement on the plaza are replaced by plants. Different types of plants vary in height, breaking the flatness and solidity of the brick plaza.
Bricks are held by metal cables and form an airy net over the tall block. Light penetrates the breeze-wall façade during the day, nurturing the plants in the solarium on the ninth floor. Patients can feel connected to the outside world in the solarium while remaining sheltered and protected.
Maggie’s Gartnavel
By OMA, Glasgow, United Kingdom
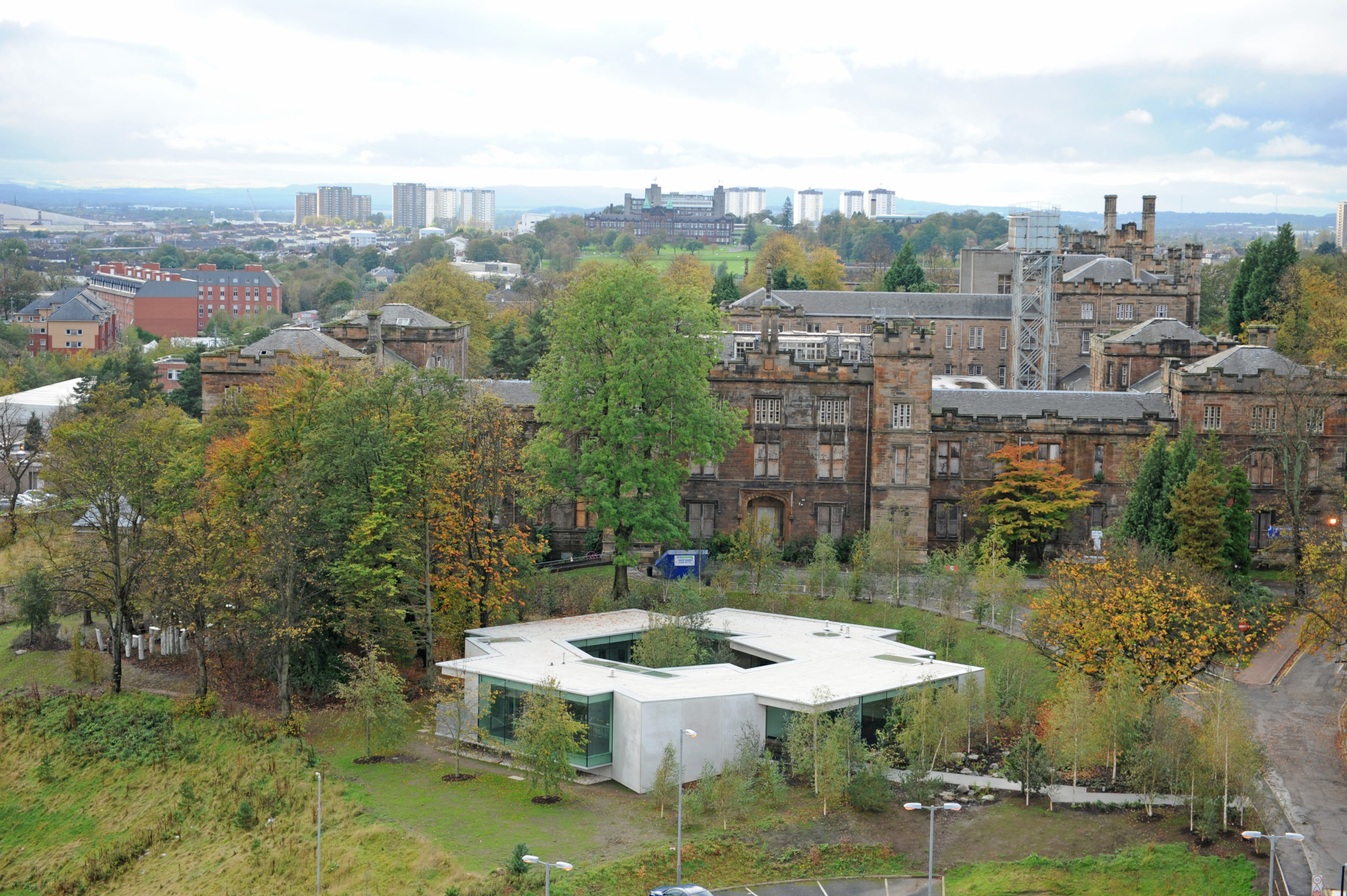
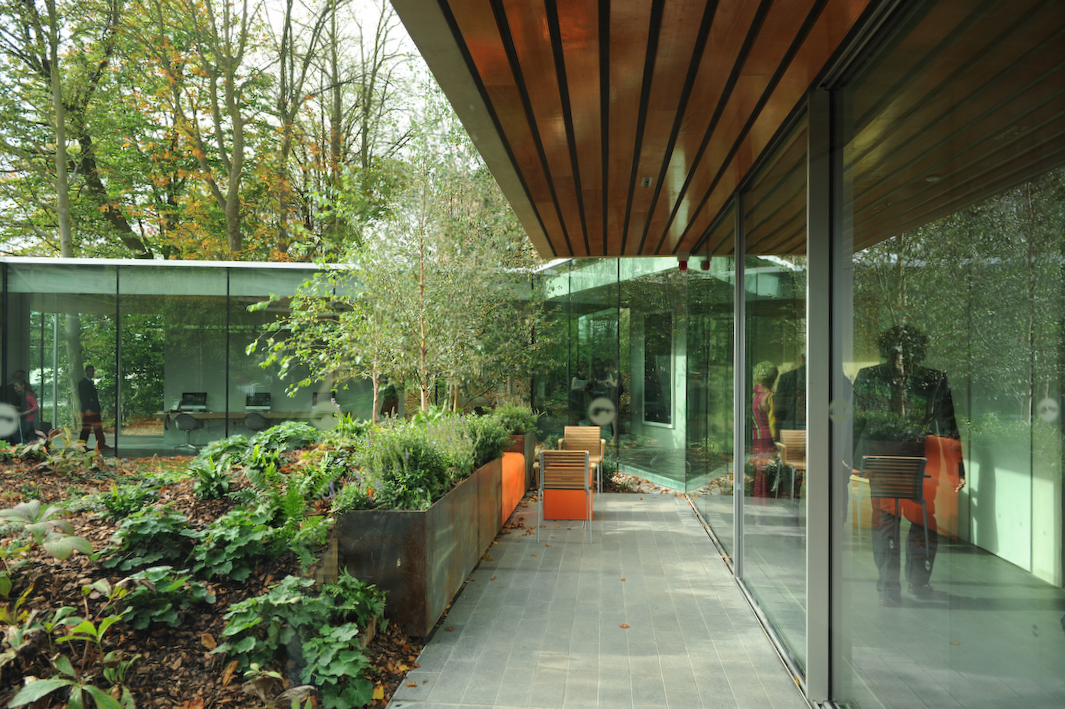
 Maggie’s Gartnavel sits humbly on the land of the Gartnavel hospital in Glasgow, close to the Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre. The single-level volume comprises a series of interlocking rooms, with an inner garden in the middle of the ring of rooms. With a flat roof and floor levels that respond to the natural topography, the rooms vary in height. Common areas including the dining room, kitchen, library and a large activity room are on the side with taller ceilings and the counseling rooms are more intimate.
Maggie’s Gartnavel sits humbly on the land of the Gartnavel hospital in Glasgow, close to the Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre. The single-level volume comprises a series of interlocking rooms, with an inner garden in the middle of the ring of rooms. With a flat roof and floor levels that respond to the natural topography, the rooms vary in height. Common areas including the dining room, kitchen, library and a large activity room are on the side with taller ceilings and the counseling rooms are more intimate.
Although the rooms are of different levels of privacy, there are hardly continuous walls that enclose a room. Most spaces have at least one side open or transparent. As a result, the spaces are separated by functions yet visually continuous. Meanwhile, views of the gardens enter the spaces freely through the transparent façades.
SDC
By Takeru Shoji Architects.Co.,Ltd., Niigata, Japan
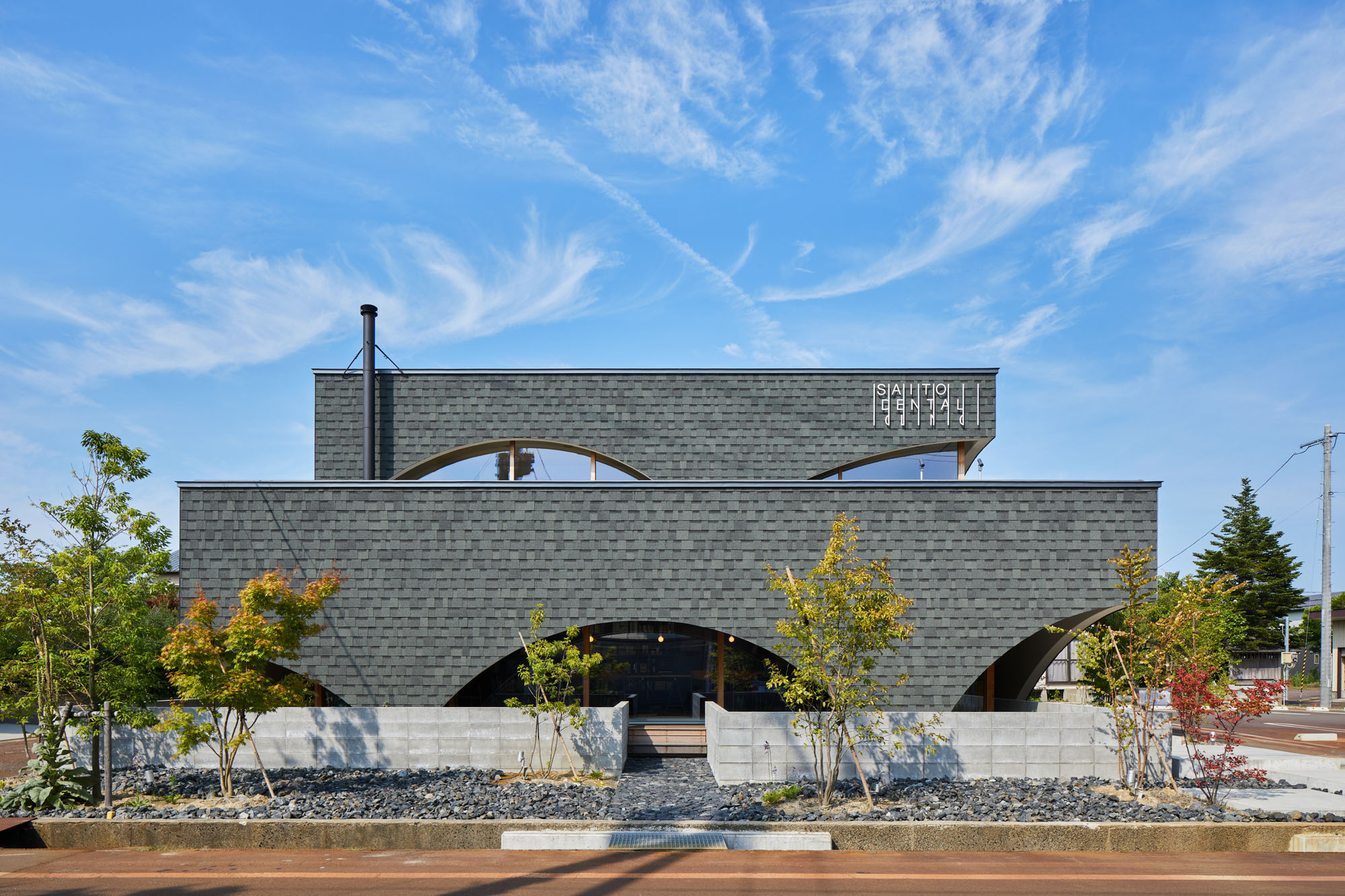
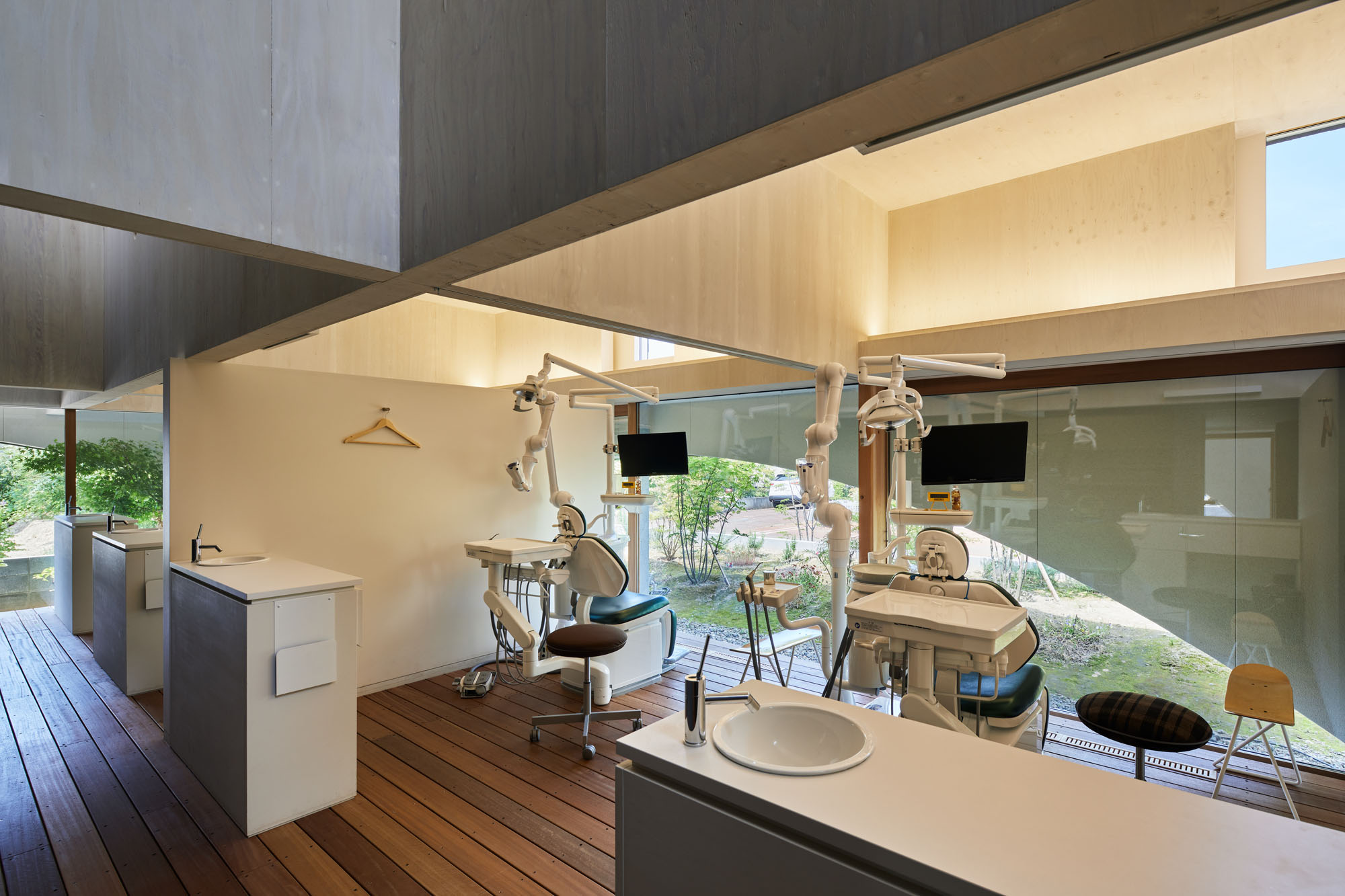
 Neighboring a nursery, elementary school and junior high school, this dental clinic is designed as an enjoyable place for both children and parents. This two-story timber building accommodates not only a clinic but also a bookstore and daycare center. By combining programs, the design team wishes to encourage people to come not just for their appointment.
Neighboring a nursery, elementary school and junior high school, this dental clinic is designed as an enjoyable place for both children and parents. This two-story timber building accommodates not only a clinic but also a bookstore and daycare center. By combining programs, the design team wishes to encourage people to come not just for their appointment.
A long garden surrounds the building. The view of the garden passes through the sheltered corridors and enters the interior spaces. The garden is a buffer between the clinic and the roads as well as a showcase for changing weather and seasons.
Architects: Want to have your project featured? Showcase your work through Architizer and sign up for our inspirational newsletter.








 Steno Diabetes Center Copenhagen is a hospital for preventing and treating diabetes. The hospital occupies a rectangular site with two entrances open on two opposite sides. There are four inner gardens on the first floor and two of them greet the visitors immediately upon their entry. Common areas such as circulation spaces and reception sit in the middle of the floor plan, while most individual rooms are lined on the outer ring.
Steno Diabetes Center Copenhagen is a hospital for preventing and treating diabetes. The hospital occupies a rectangular site with two entrances open on two opposite sides. There are four inner gardens on the first floor and two of them greet the visitors immediately upon their entry. Common areas such as circulation spaces and reception sit in the middle of the floor plan, while most individual rooms are lined on the outer ring.
 Maggie’s centers provide free cancer support and information to patients and their friends and families. The centers are located across the UK, each in a unique style while all of them embrace nature as a way of healing. Maggie’s Leeds stands on the last patch of greenery at St James’s University Hospital. The sloping site is bounded by roads and a multi-story car park. Instead of flattening the landscape, the spaces descend along the landscape, creating views that vary from open to secluded.
Maggie’s centers provide free cancer support and information to patients and their friends and families. The centers are located across the UK, each in a unique style while all of them embrace nature as a way of healing. Maggie’s Leeds stands on the last patch of greenery at St James’s University Hospital. The sloping site is bounded by roads and a multi-story car park. Instead of flattening the landscape, the spaces descend along the landscape, creating views that vary from open to secluded.
 This new hospital wing of the orthopedic center Waldkliniken Eisenberg enjoys an immersive view of the Thuringian Forest. The six-story building has 128 patient rooms, all located on the outer ring of the circular floor plans. Floor-to-ceiling windows invite unblocked views of the natural landscape into the rooms while providing natural light and fresh air to the rooms.
This new hospital wing of the orthopedic center Waldkliniken Eisenberg enjoys an immersive view of the Thuringian Forest. The six-story building has 128 patient rooms, all located on the outer ring of the circular floor plans. Floor-to-ceiling windows invite unblocked views of the natural landscape into the rooms while providing natural light and fresh air to the rooms.
 The expansion of Santa Fe de Bogotá Foundation is sited in the compact urban context of the city of Bogotá. It comprises an eleven-story block and a single-story base. The roof of the base becomes a plaza opening to the roads, with staircases inviting people onto it. Red bricks cover the expansion as a response to the existing buildings around. Strips of pavement on the plaza are replaced by plants. Different types of plants vary in height, breaking the flatness and solidity of the brick plaza.
The expansion of Santa Fe de Bogotá Foundation is sited in the compact urban context of the city of Bogotá. It comprises an eleven-story block and a single-story base. The roof of the base becomes a plaza opening to the roads, with staircases inviting people onto it. Red bricks cover the expansion as a response to the existing buildings around. Strips of pavement on the plaza are replaced by plants. Different types of plants vary in height, breaking the flatness and solidity of the brick plaza.
 Maggie’s Gartnavel sits humbly on the land of the Gartnavel hospital in Glasgow, close to the Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre. The single-level volume comprises a series of interlocking rooms, with an inner garden in the middle of the ring of rooms. With a flat roof and floor levels that respond to the natural topography, the rooms vary in height. Common areas including the dining room, kitchen, library and a large activity room are on the side with taller ceilings and the counseling rooms are more intimate.
Maggie’s Gartnavel sits humbly on the land of the Gartnavel hospital in Glasgow, close to the Beatson West of Scotland Cancer Centre. The single-level volume comprises a series of interlocking rooms, with an inner garden in the middle of the ring of rooms. With a flat roof and floor levels that respond to the natural topography, the rooms vary in height. Common areas including the dining room, kitchen, library and a large activity room are on the side with taller ceilings and the counseling rooms are more intimate.
 Neighboring a nursery, elementary school and junior high school, this dental clinic is designed as an enjoyable place for both children and parents. This two-story timber building accommodates not only a clinic but also a bookstore and daycare center. By combining programs, the design team wishes to encourage people to come not just for their appointment.
Neighboring a nursery, elementary school and junior high school, this dental clinic is designed as an enjoyable place for both children and parents. This two-story timber building accommodates not only a clinic but also a bookstore and daycare center. By combining programs, the design team wishes to encourage people to come not just for their appointment.