Pearl Home Certification: Leading the Way to High Performance
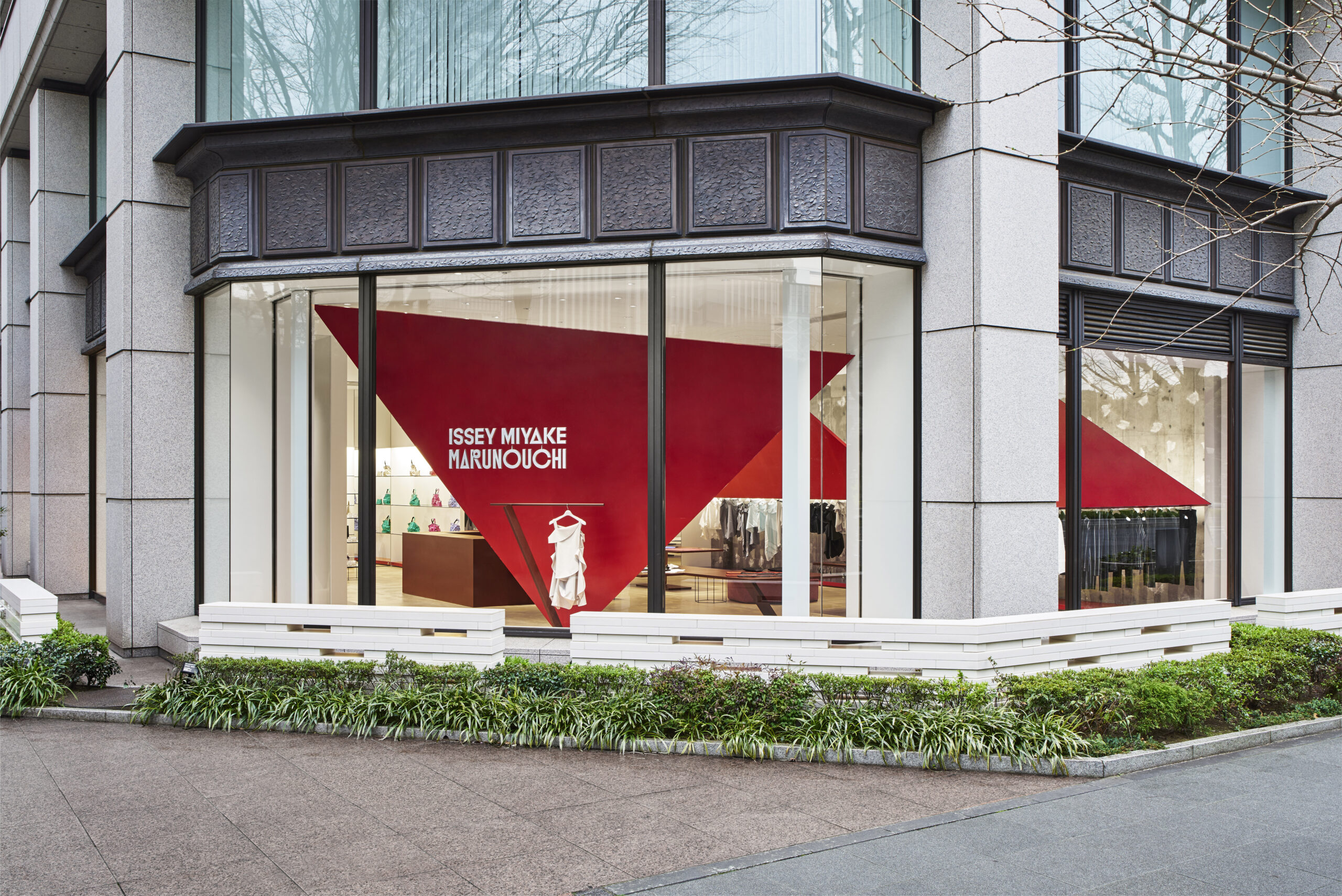
A Platinum-level Pearl Certification renovation in Long Island, NY, prioritized both comfort and cost savings. The homeowners installed heat pumps, ENERGY STAR certified windows and doors, advanced cellulose-dense insulation, as well as solar panels. Smart home technology helps them manage energy and monitor savings
Tracking home improvements
The journey towards a more sustainable, comfortable, and valuable home can be long and complex. In his renovations, Woodcock said he primarily takes advantage of Pearl Points, a scoring system designed to help homeowners recognize and track high-performing assets and potential improvements. “The scoring system is sort of addictive,” Patrick says. “By that, I mean it’s like the way you want to reach the next level in a video game.”
Pearl’s multiple certification levels present your home’s overall performance, Silver, Gold, and Platinum. Plus, it deep-dives into specific categories of assets:
- Building Shell, including insulation
- Heating & Cooling systems
- Baseload appliance energy use
- Home Management, like smart thermostats and dashboards
- Solar, EV & Energy Storage
A home that doesn’t reach Pearl Silver (yet!) can qualify for Pearl Asset Certification, highlighting one or more high-performing features: high-performance windows and doors, heat pumps, ENERGY STAR appliances, etc. Assets that interact more with your local climate will earn more points. For instance, a high-efficiency air conditioner will be worth more points in Phoenix than in the Midwest.
This helps identify the most impactful home upgrades, from temperature and humidity control to reducing energy bills and resilience in the face of climate change, including well-being issues like indoor air quality. These “hidden” systems have no curb appeal but do represent valuable, long-lasting home investments.
The Green Door app will recommend priority tasks and update your plan as you bring assets online, earning Pearl Points toward higher home certification. Maintenance reminders help you ensure your investments continue to save on your energy bill and retain their value. Finally, the app stores the documentation and warranties on upgraded systems.
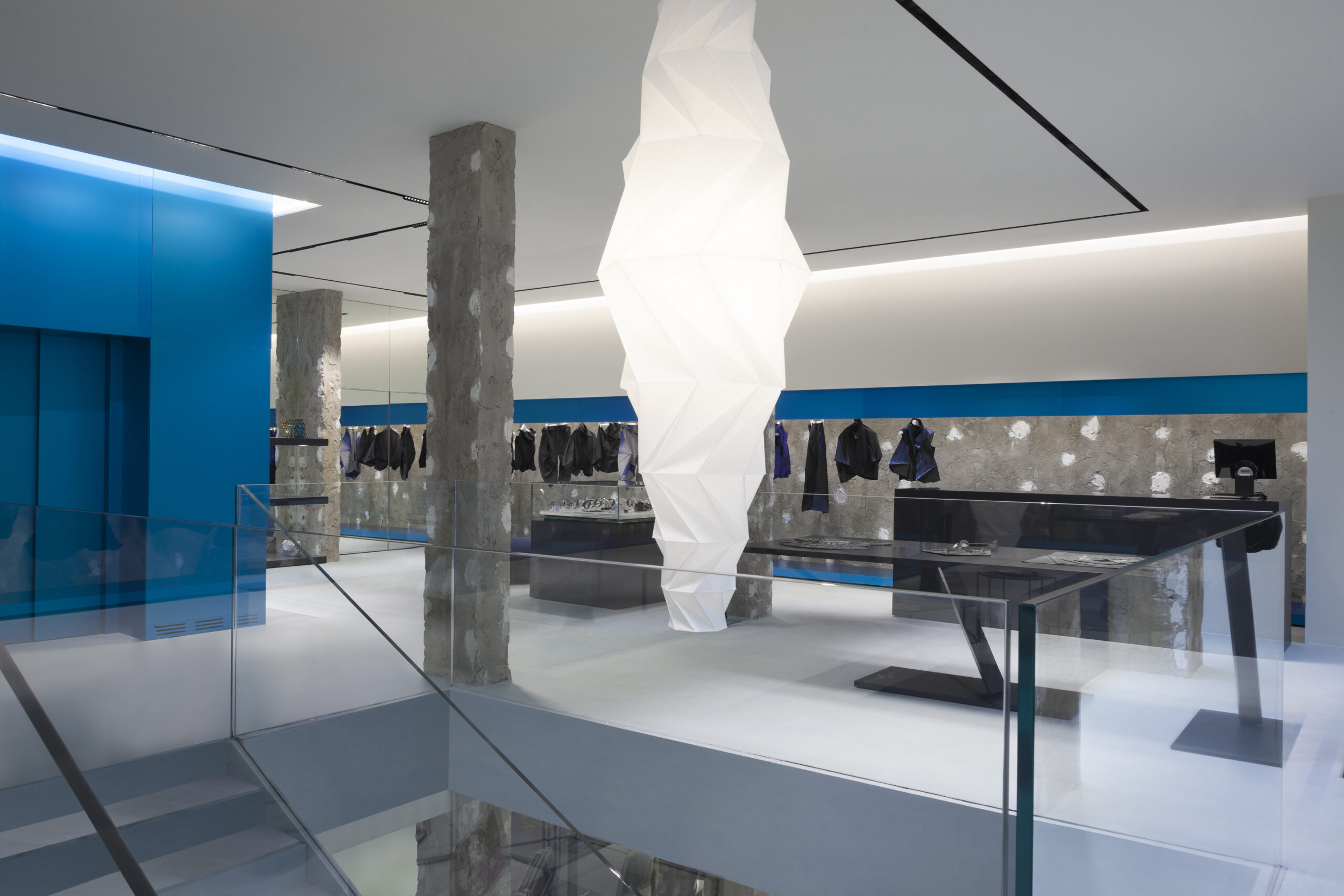
To achieve Gold-level Pearl Certification, this renovation in Phoenix included solar panels, AeroSealing, an EV charger, and ENERGY STAR certified appliances.
Contractor connection
Jan Green, a realtor and certified eco-broker, transformed her 1979 dilapidated Phoenix home, purchased in 2015, into a net-zero, energy-efficient residence, earning a Pearl Gold Certification. “A lot of people probably don’t know this—I certainly didn’t—but if the contractor who does your energy audit is also a certified contractor, with the capabilities to handle whatever fixes or replacements the audit revealed, it’s fairly standard practice for them to waive the cost of the energy audit as long as you contract with them for services,” said Green.
Homeowners can access Pearl’s network of contractors through the Green Door app. Importantly, any work done by a Pearl Contractor is automatically Pearl Certified upon successful completion. This ensures that the improvements contribute towards the home’s certification and overall value.
Green began with an energy audit, and then step-by-step upgraded her home with efficiency renovations: air sealing, LED lighting, energy-efficient appliances, and solar panels. She was able to offset some costs with a 26% federal tax credit and state incentives. Her approach aligns with the Inflation Reduction Act’s (IRA) incentives for high-performing home improvements. Homeowners can determine which specific funds are available for different upgrades utilizing Pearl’s IRA Rebates Calculator.
Looking to sell?
Pearl hosts a nationwide network of real estate agents who are trained to identify and certify high-performing home features. They can then leverage the marketing materials provided with Pearl Certification to highlight a home’s high-performance qualities and capitalize on their added value.
More and more new homes include high-performing features. And as more cities adopt stricter energy codes, this is where the market is headed. An eco-savvy real estate agent can ensure you get the most value for your efficiency renovations by optimizing the green fields in MLS databases and filling out the Appraisal Institute’s Green and Energy Efficient Addendum. They know how to market individual energy efficiency, home automation, and solar features, as well as connect whole-home performance to value and comfort.
Home certification is a gateway to a higher standard of living and a testament to the value of sustainability investments in our homes. In an evolving real estate market, Pearl Certification recognizes what’s already working and helps unlock the full potential of our homes to create a better, greener future.