Concrete grid defines Svendborg International Maritime Academy
Danish studios EFFEKT and CF Møller Architects have completed the Svendborg International Maritime Academy in Denmark, using an exposed concrete frame to echo its industrial surrounds.
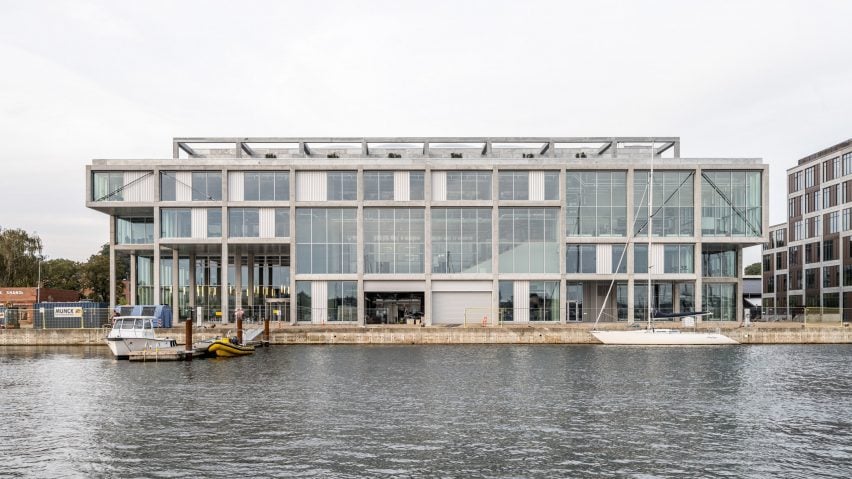
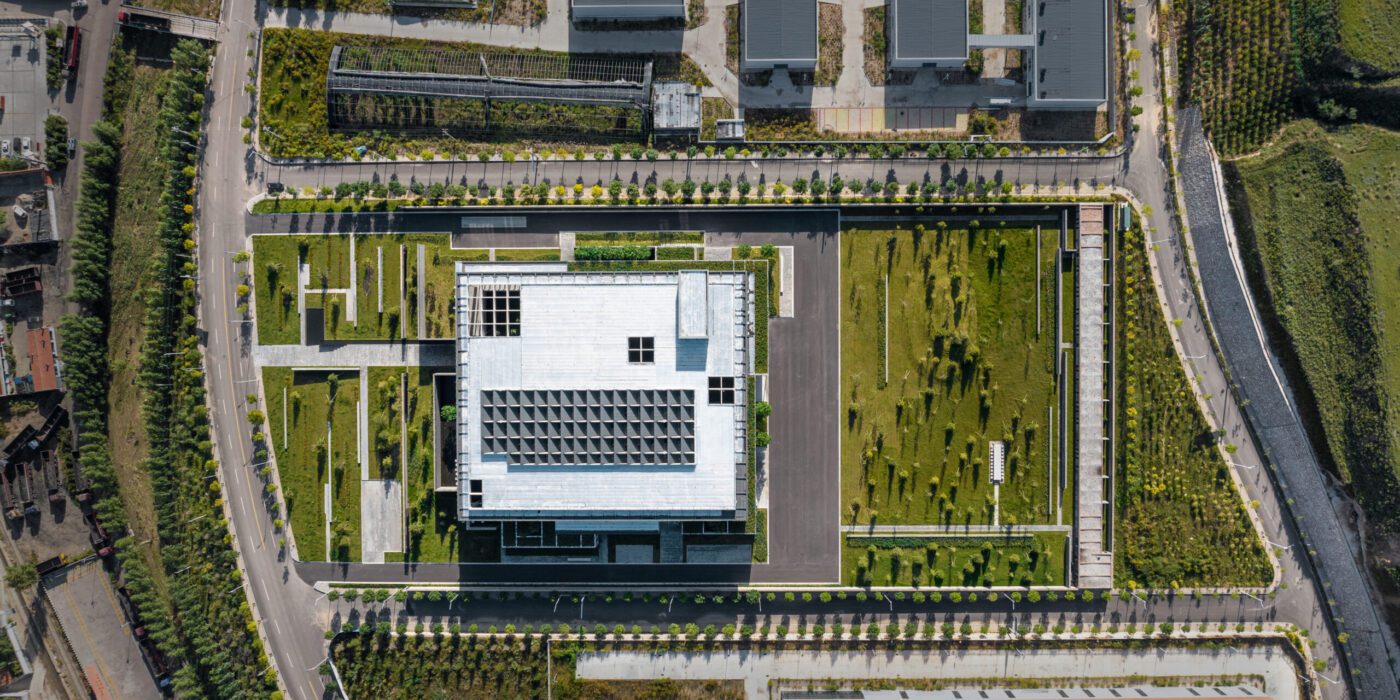
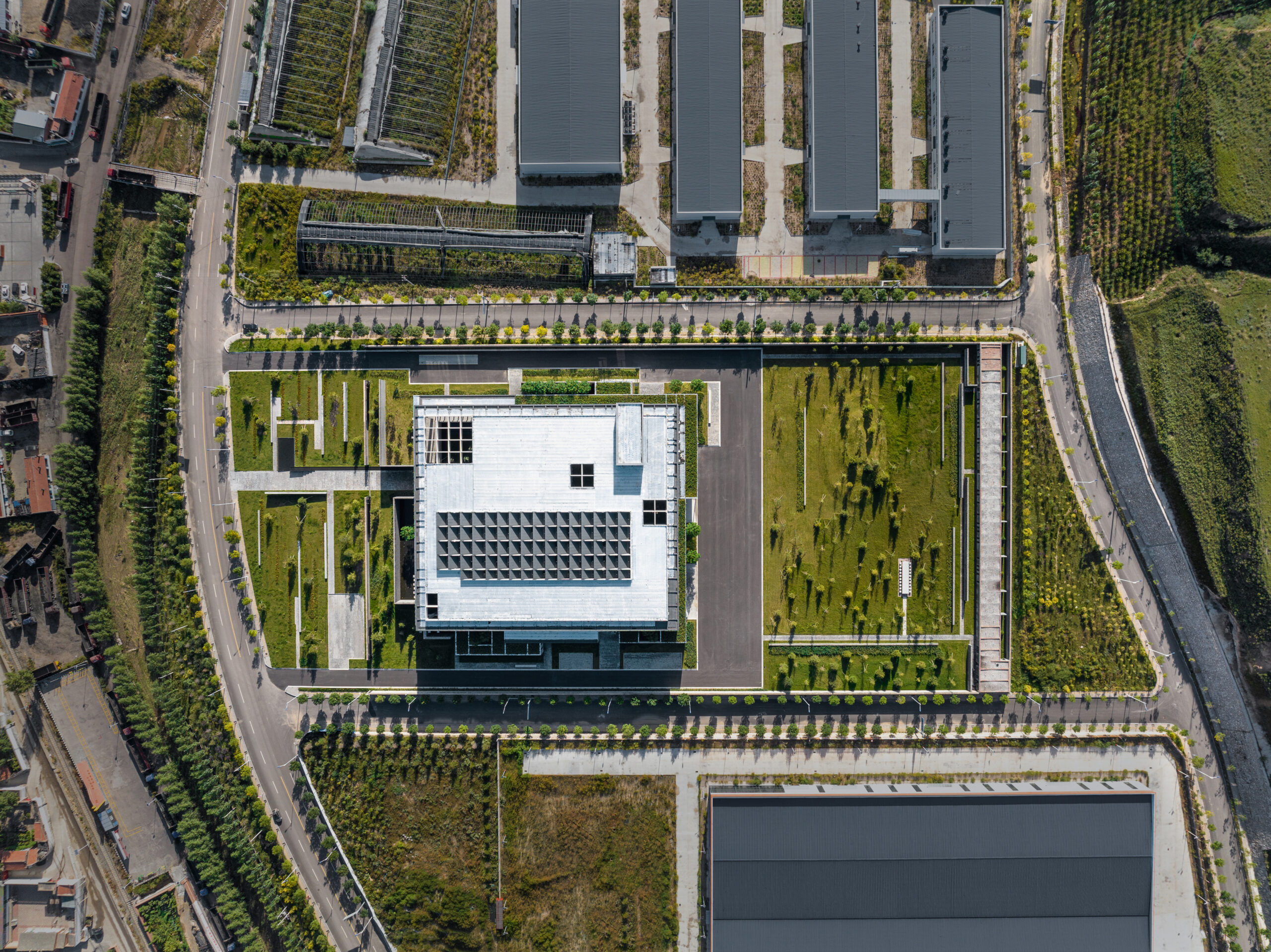
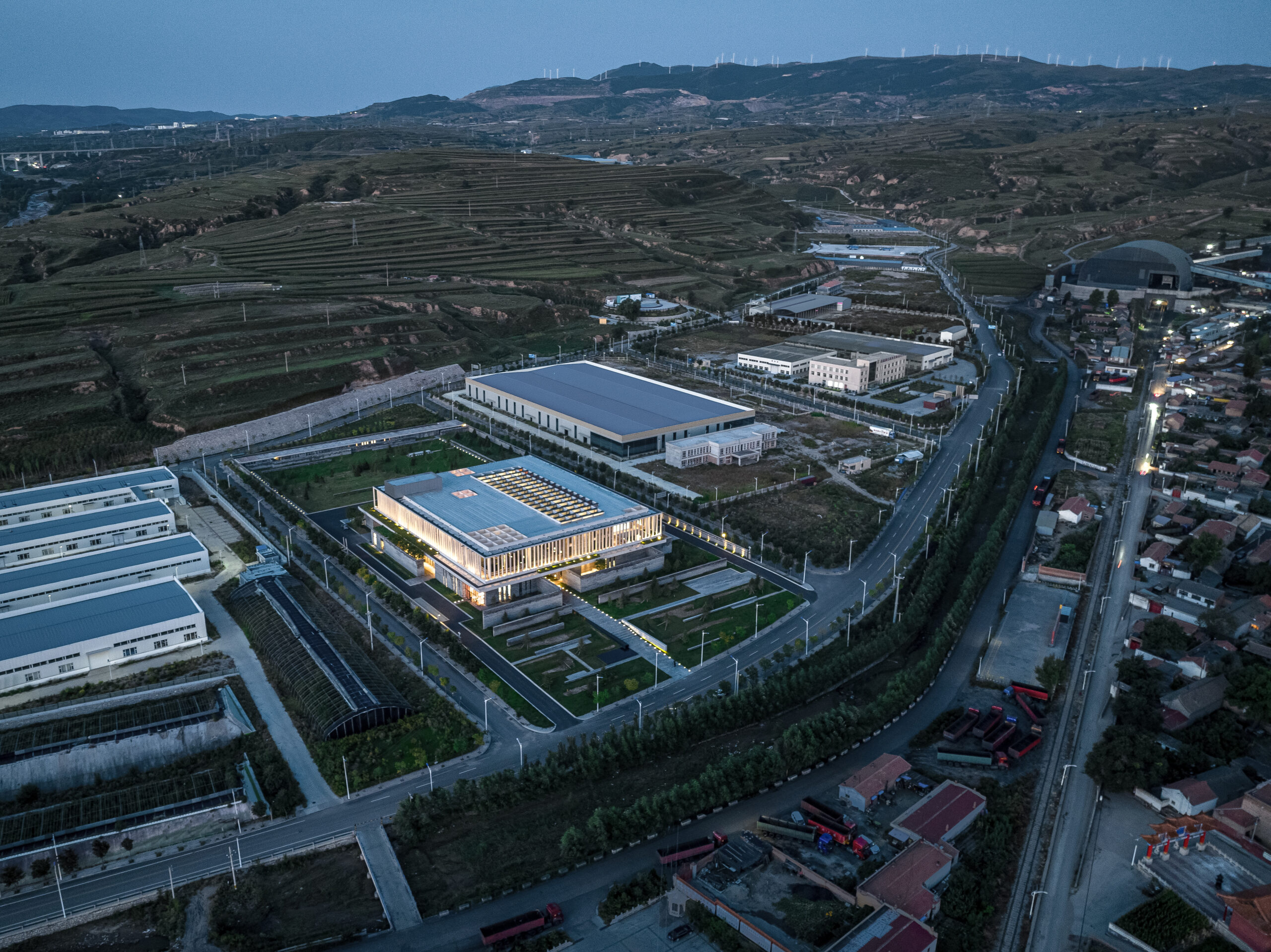
Overlooking the harbour in the North Quay of the former port city Svendborg, the 12,500-square-metre centre unites several previously separate departments of Svendborg International Maritime Academy (SIMAC), providing combined study spaces for 1,000 students.
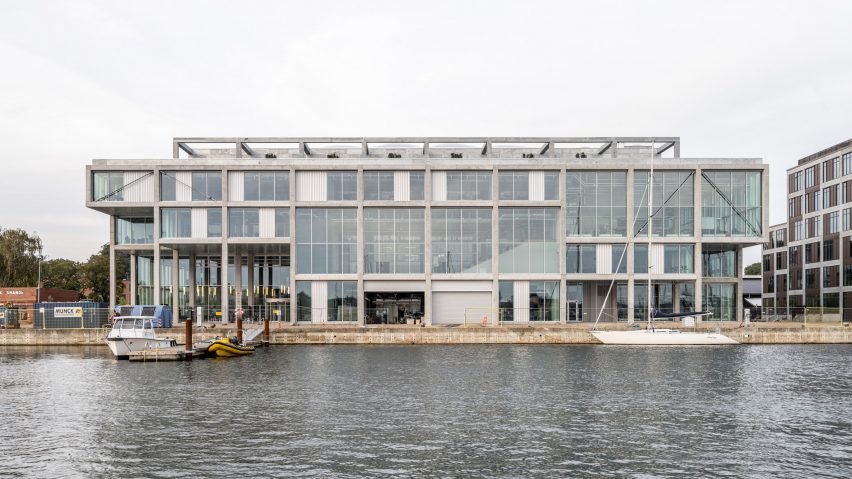


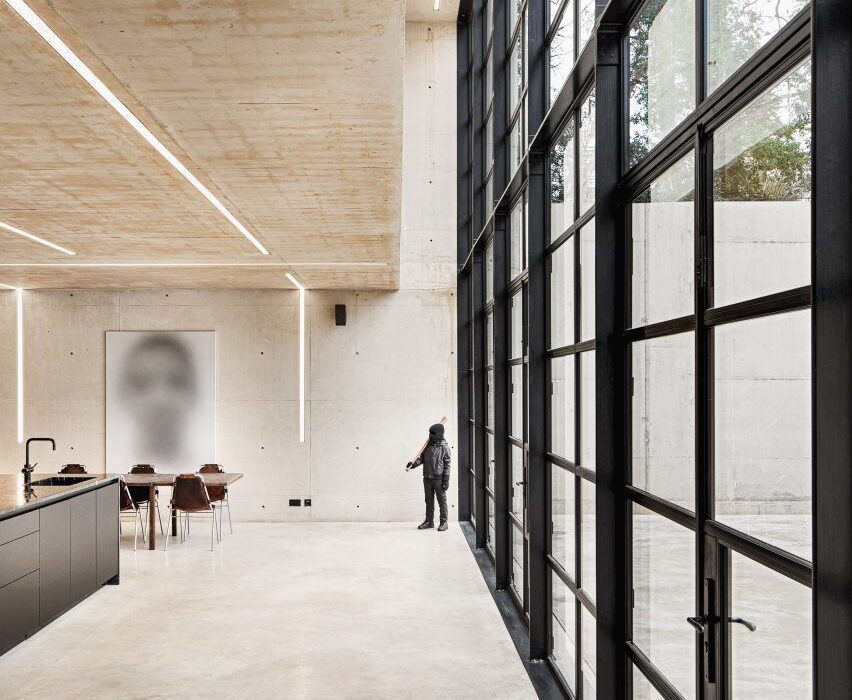
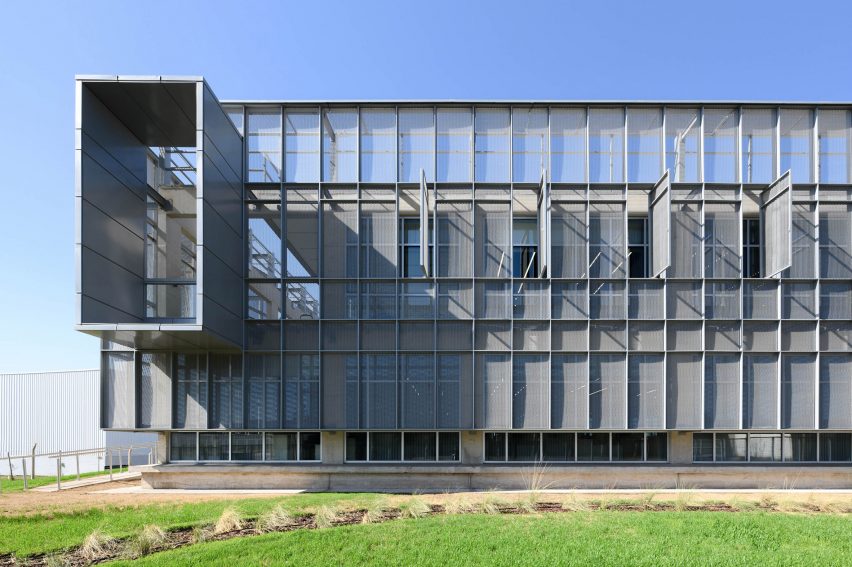
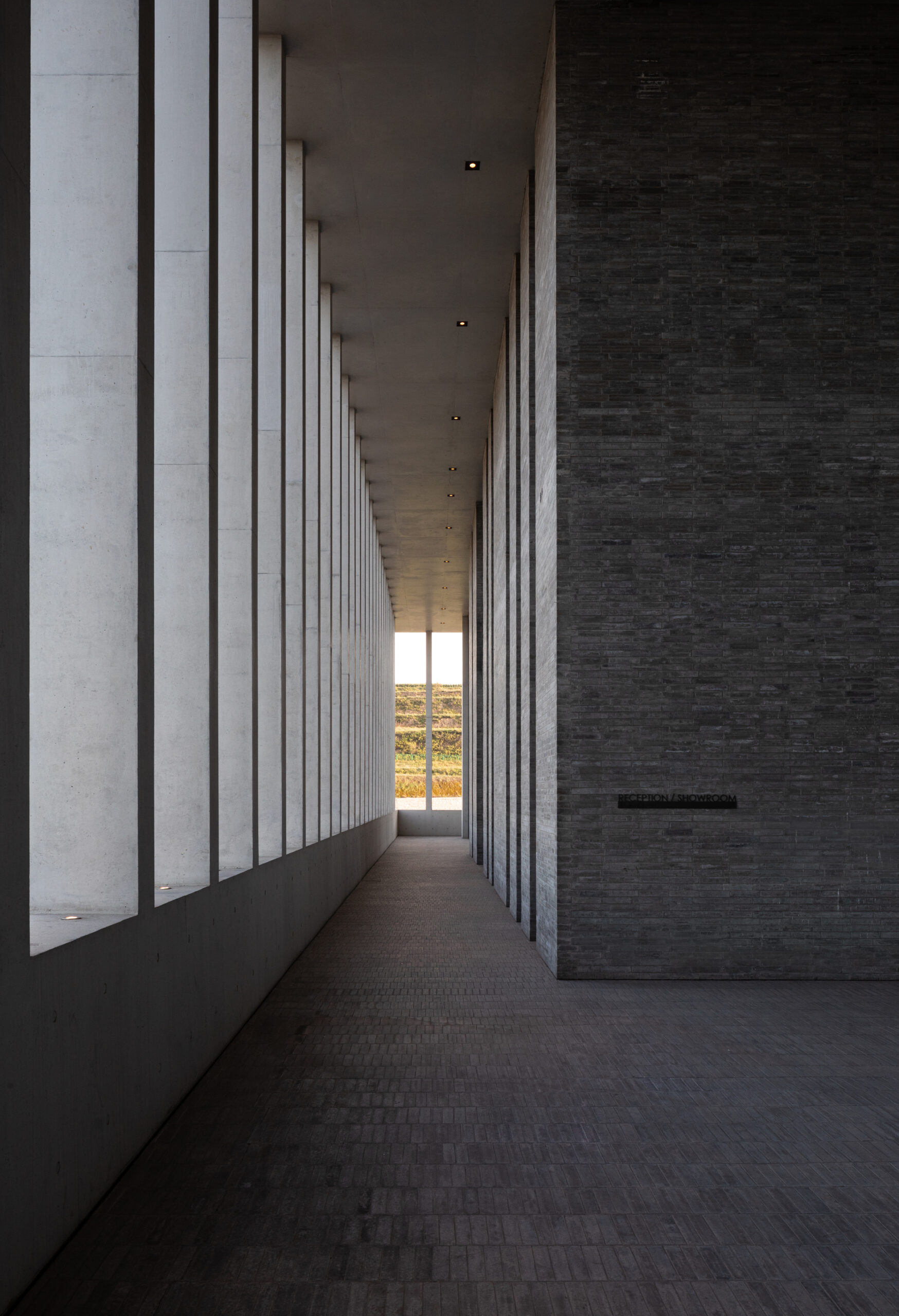
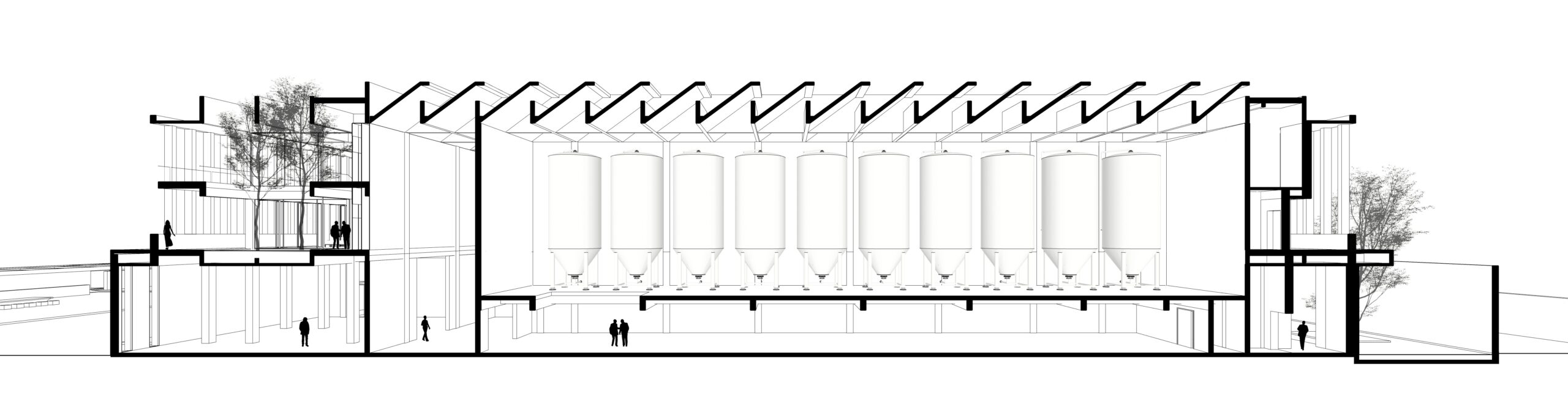
EFFEKT and CF Møller Architects designed a “resilient grid” for the building formed of prefabricated concrete elements, which nods to the surrounding architecture and is divided with glass partitions to create teaching spaces that can be easily modified or adapted in future.
“We set out with the desire to create an extremely raw and transparent grid structure, contextually adapted to its industrious setting while capable of staging the school’s workshop-based content,” explained CF Møller Architects partner Mads Mandrup.
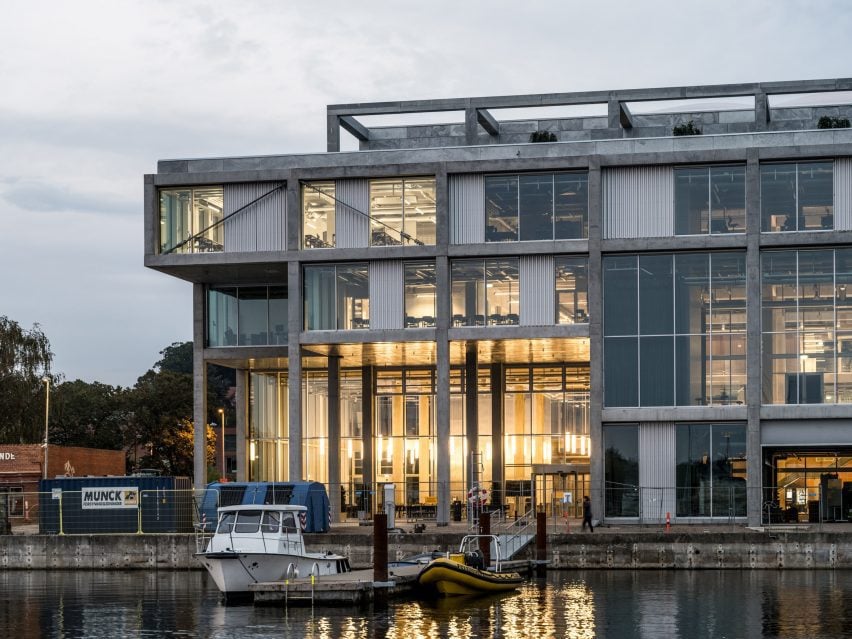


“[It is] a scaffolding of spatial possibilities, centred around encouraging young people to encounter and exchange ideas through informal meetings, both within and out towards its surroundings, activating the whole harbour front of Svendborg,” Mandrup added.
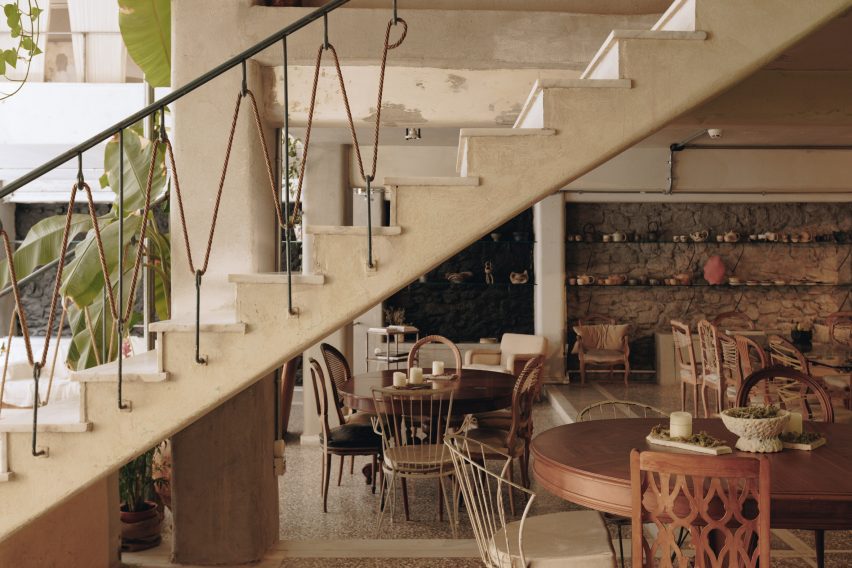
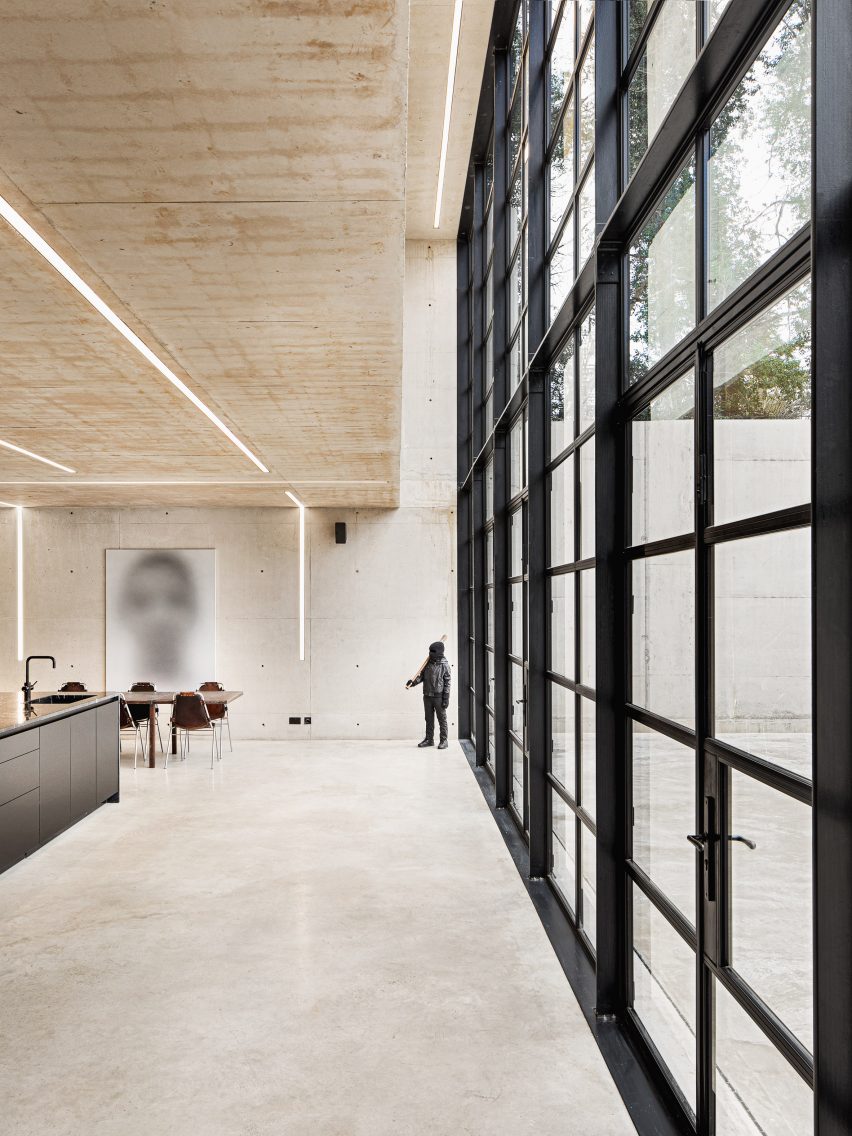
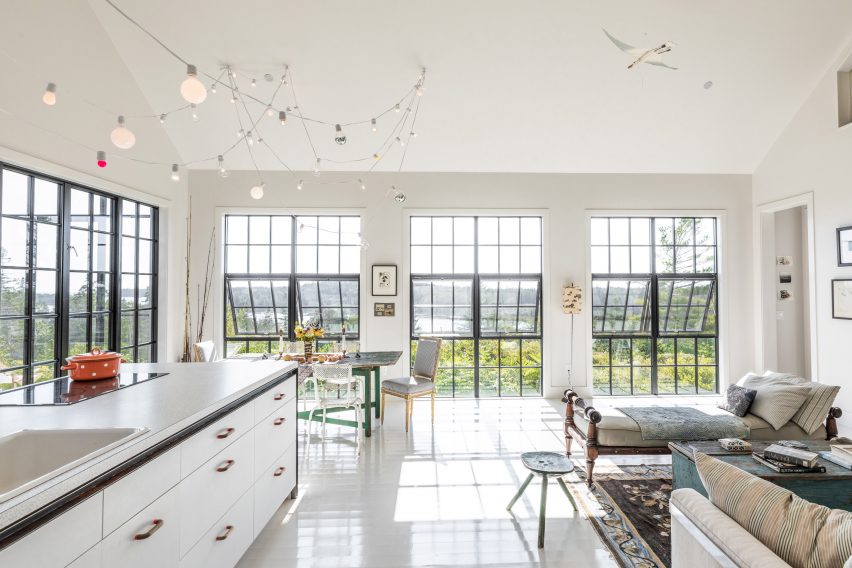
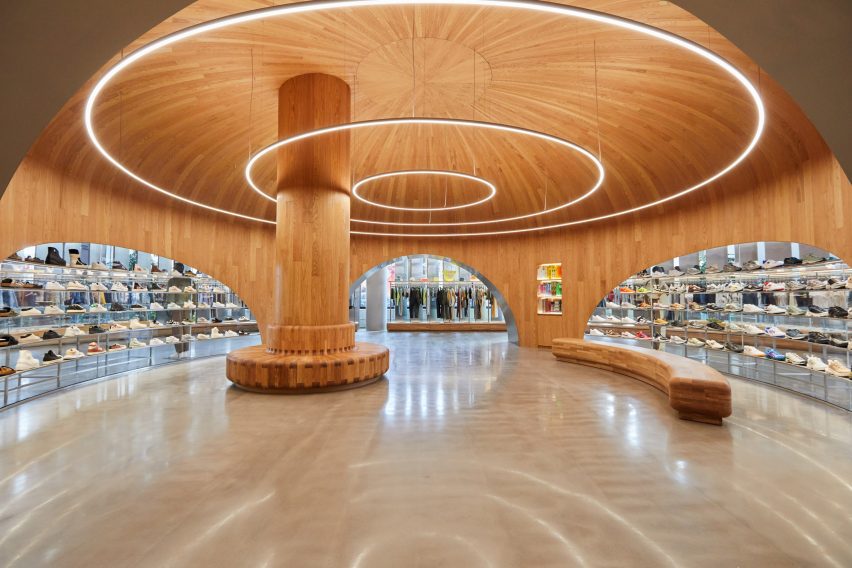
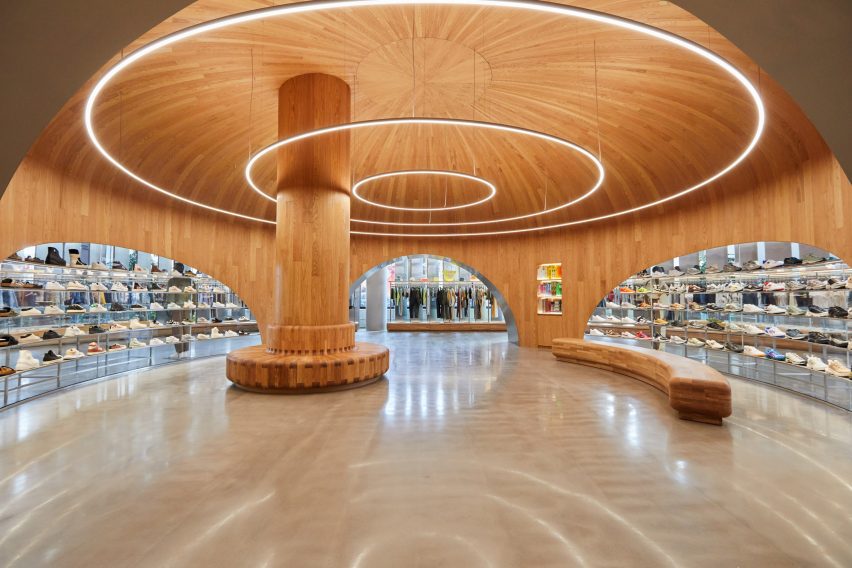
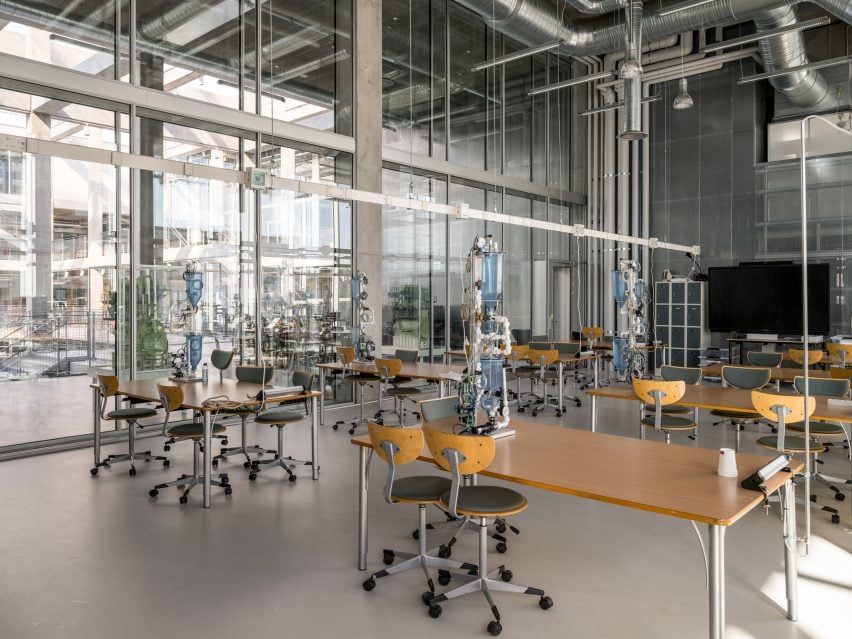
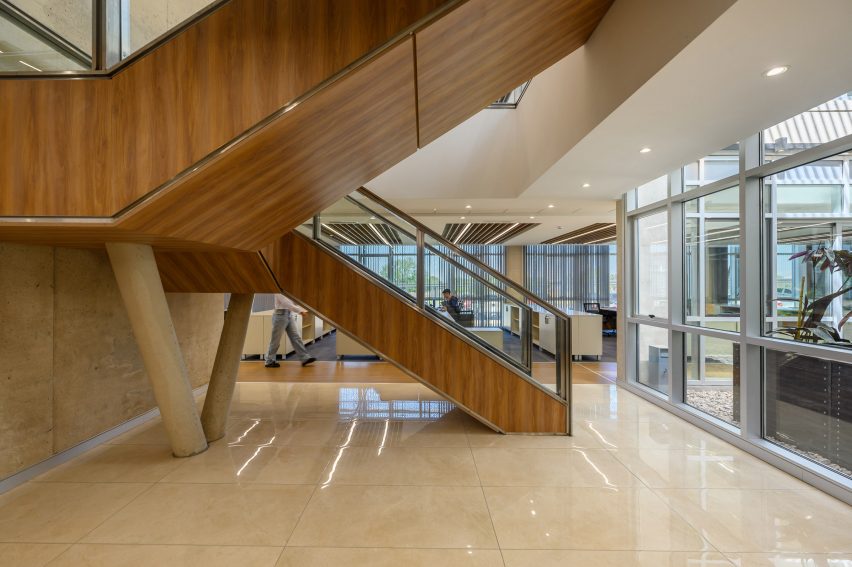
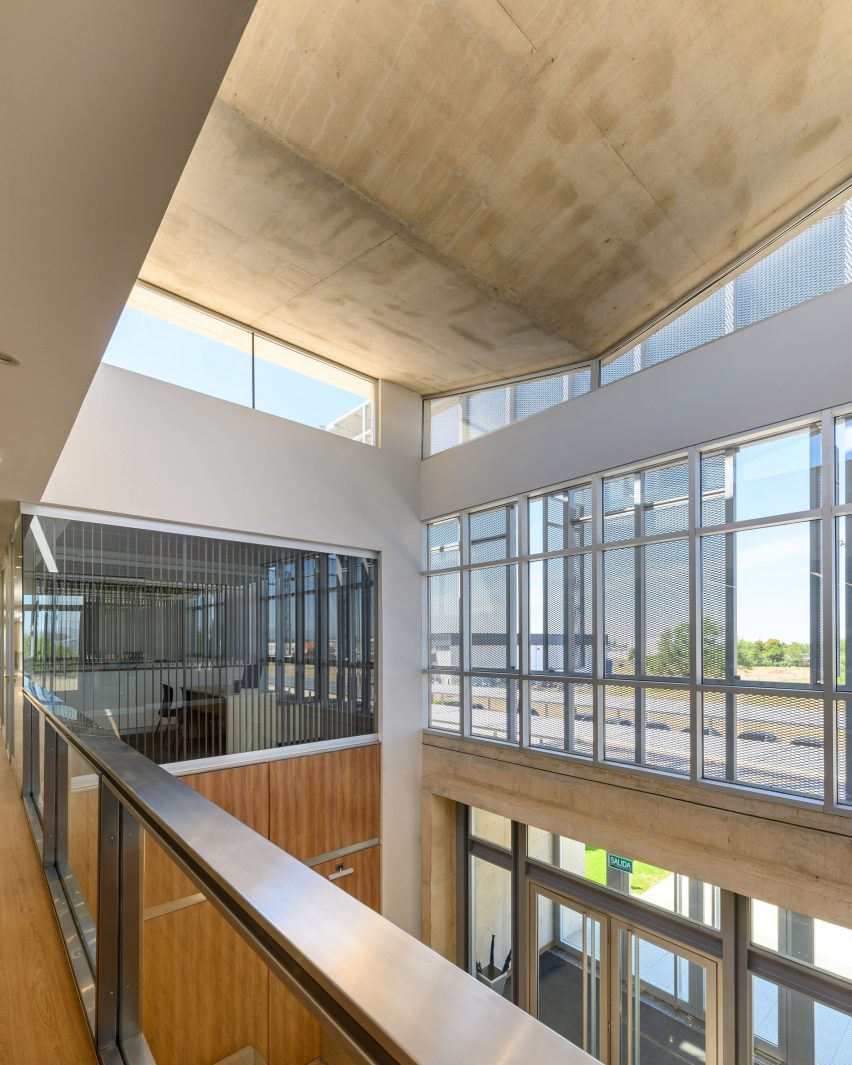
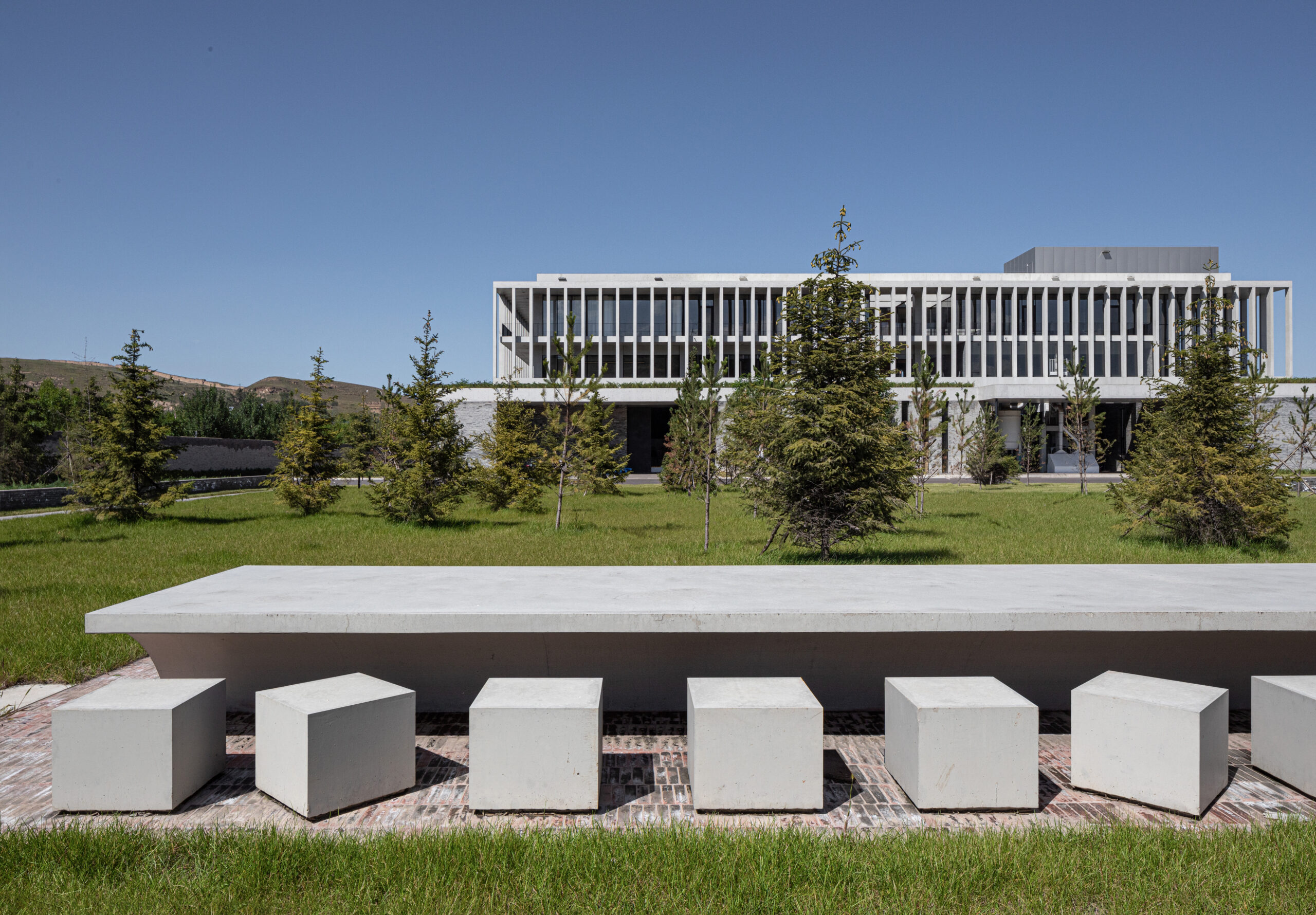
SIMAC’s teaching spaces are organised across five storeys around a central 20-metre-high atrium. Lined with balconies, this atrium visually connects each level to a communal seating area on the ground floor.
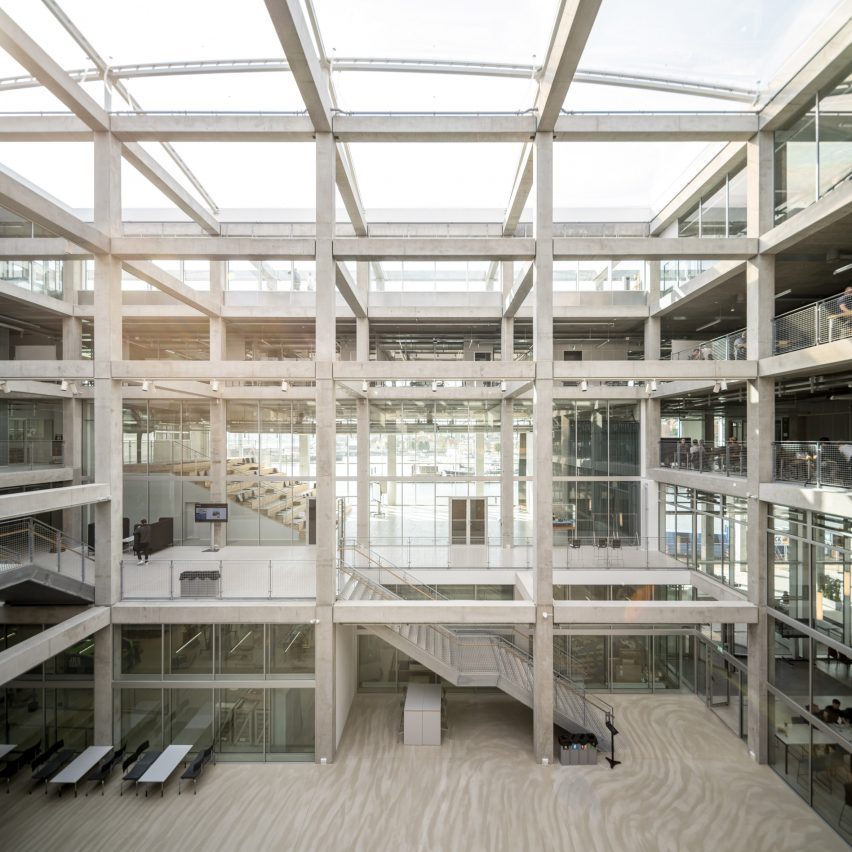


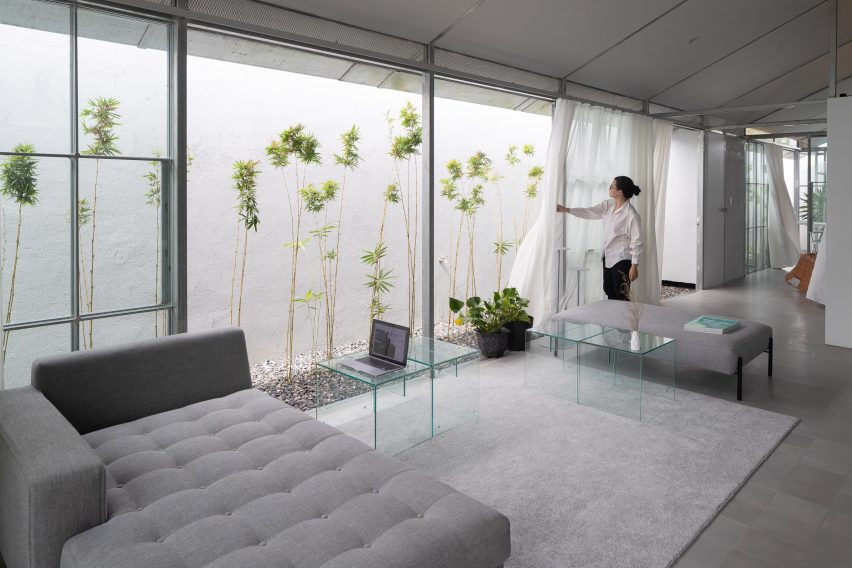
Double-height spaces house specialist workshops alongside conventional offices and classrooms, with the glass partitions intended to “stimulate communication and informal exchange” between areas, said the studios.
On the roof is a communal terrace for students and staff, providing both internal and external spaces with expansive views out across the harbour framed by the hollow concrete grid.
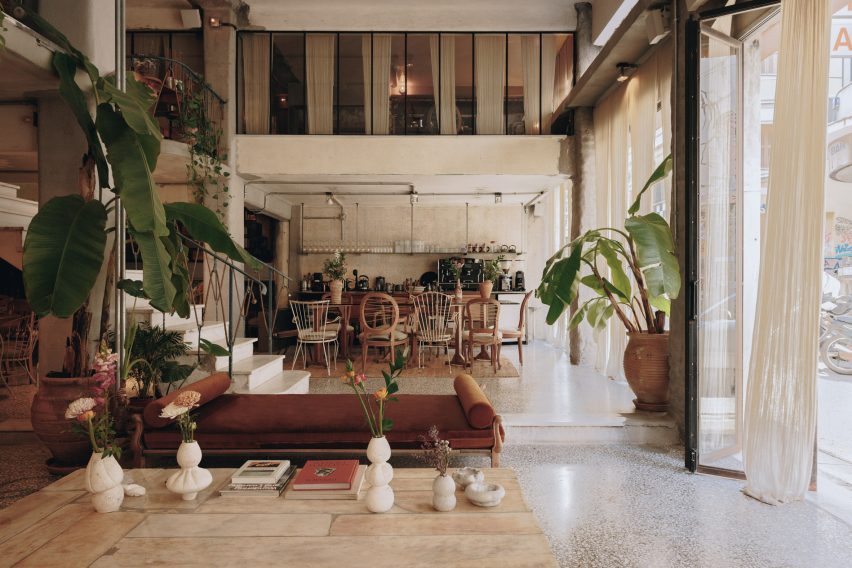
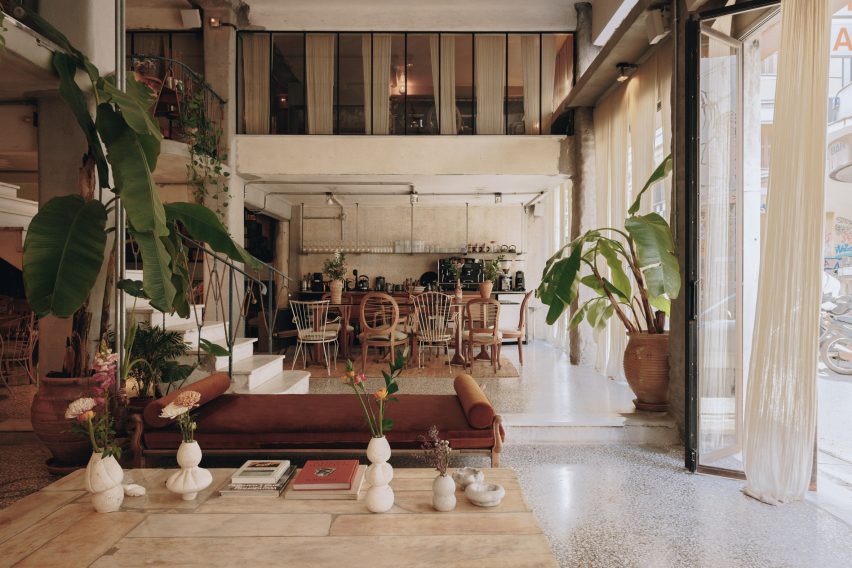
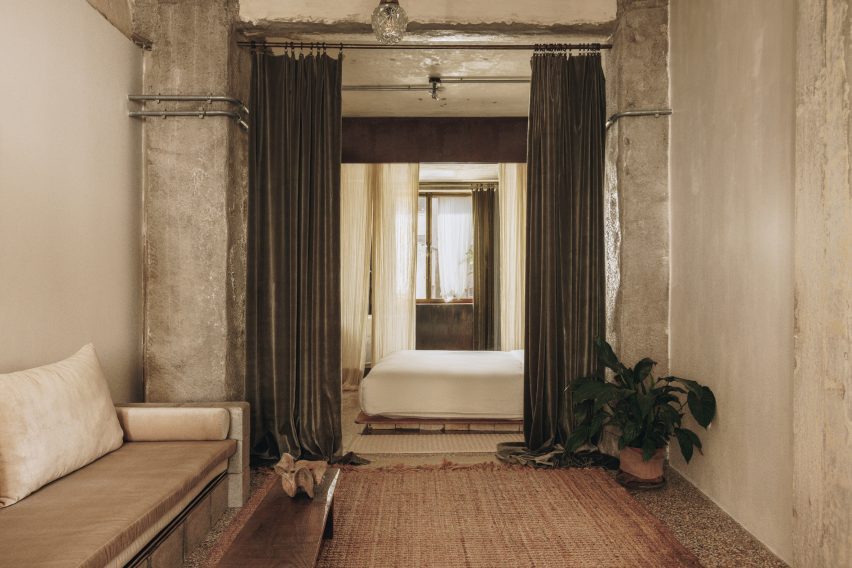
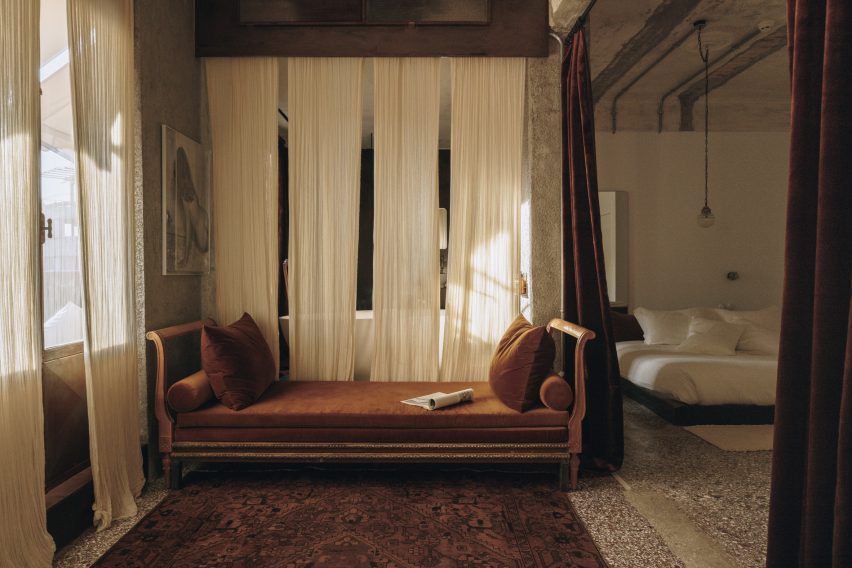
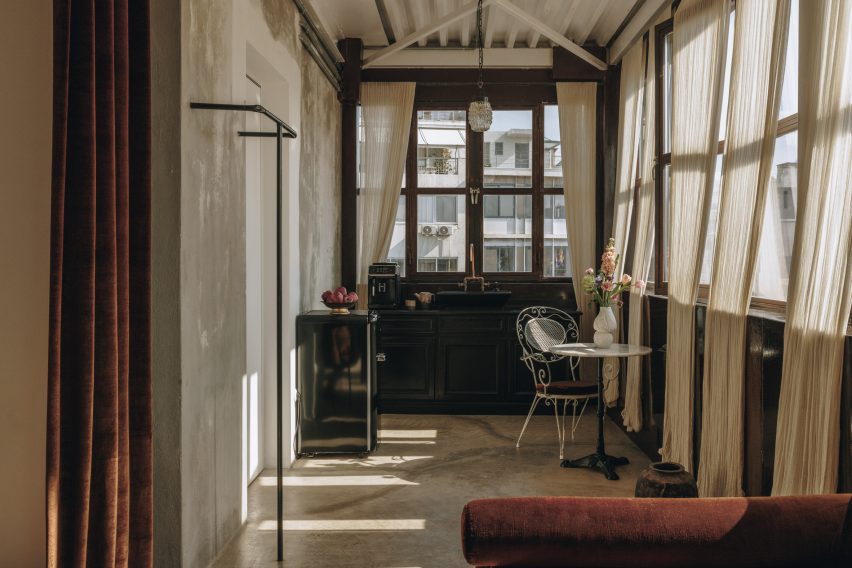
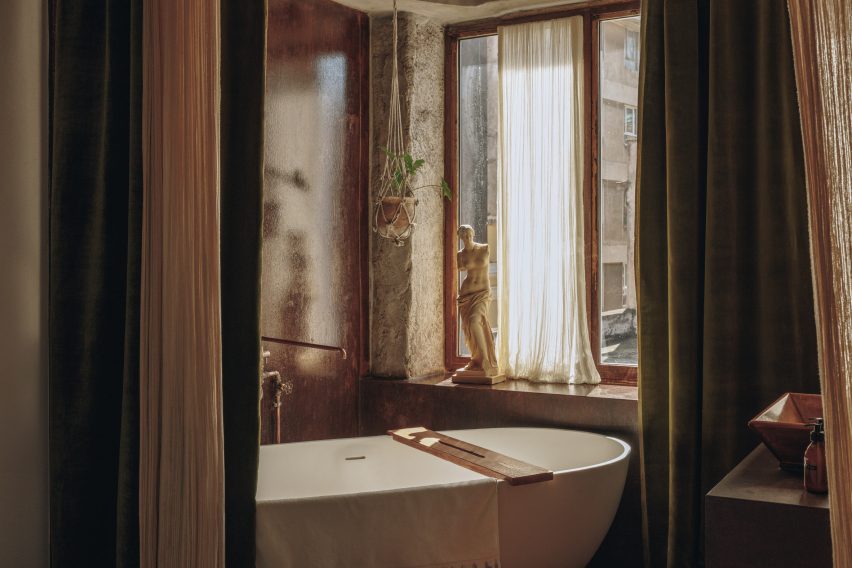
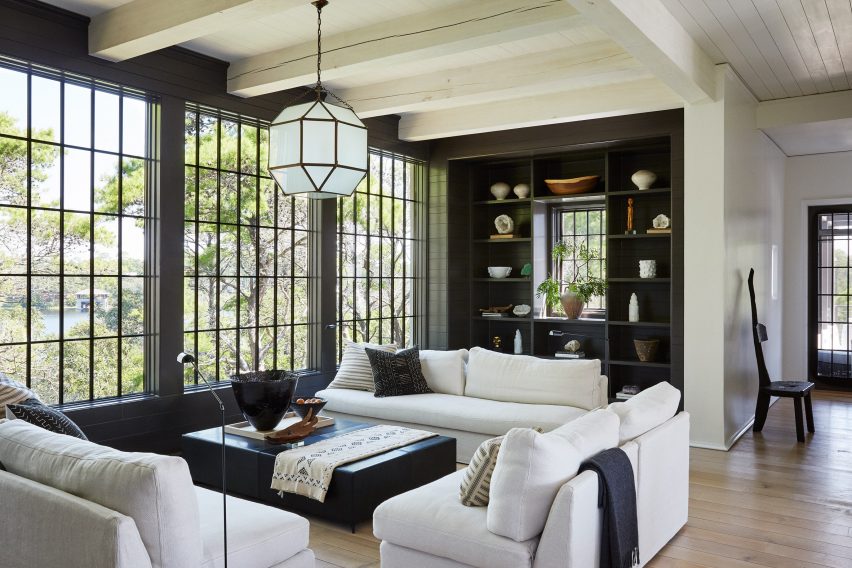
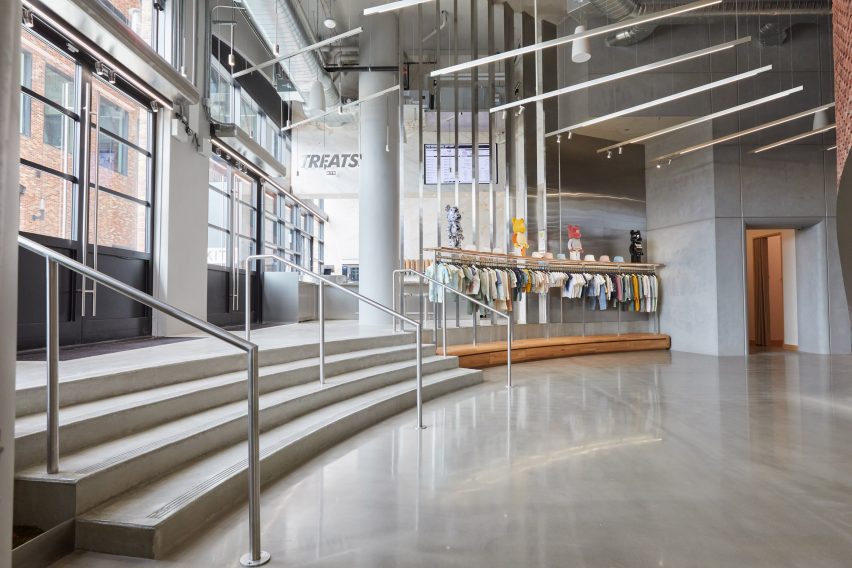
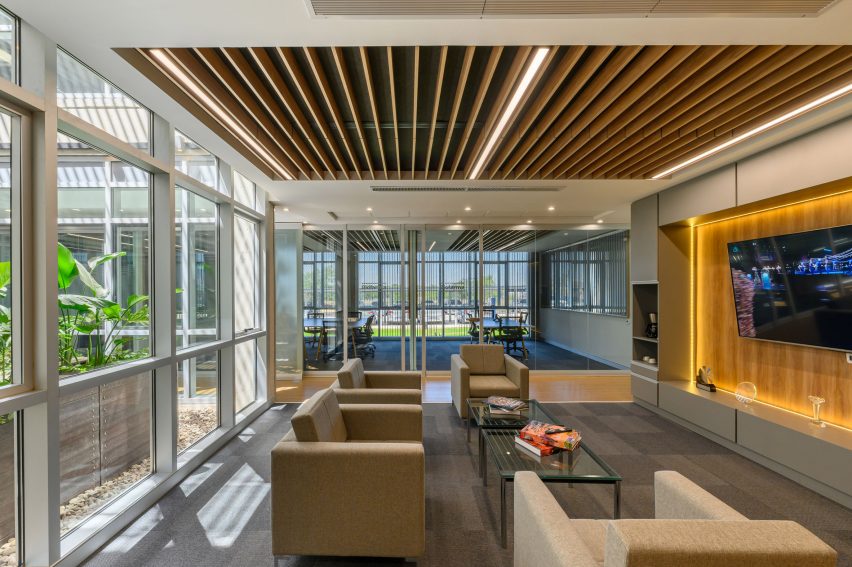
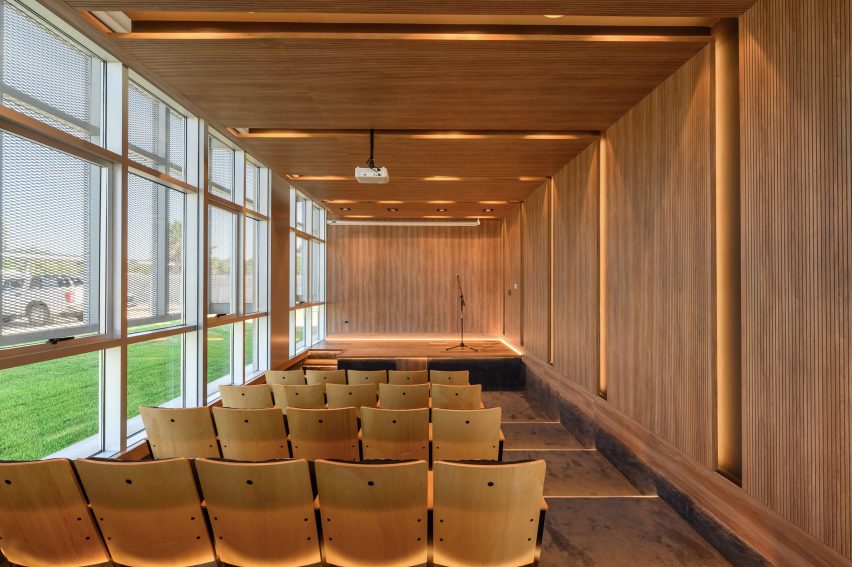
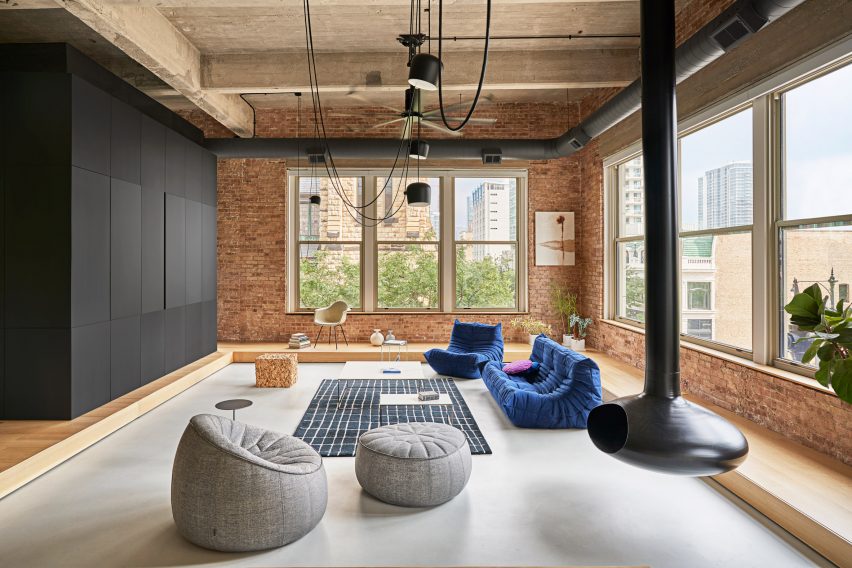
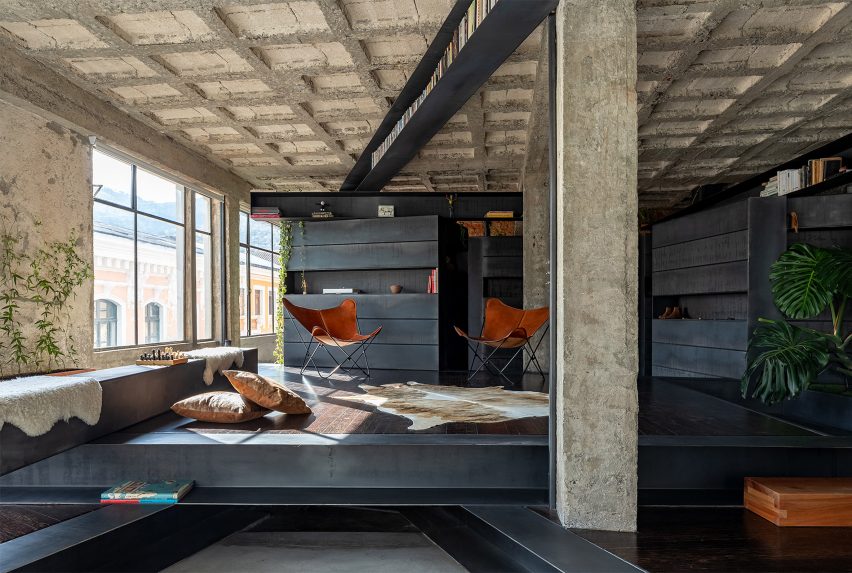
Taking cues from the raw concrete structure, interior finishes have been kept minimal and unfinished, with exposed ducting and steel balustrades. Social areas are visually softened by wooden details, including an area of tiered seating.
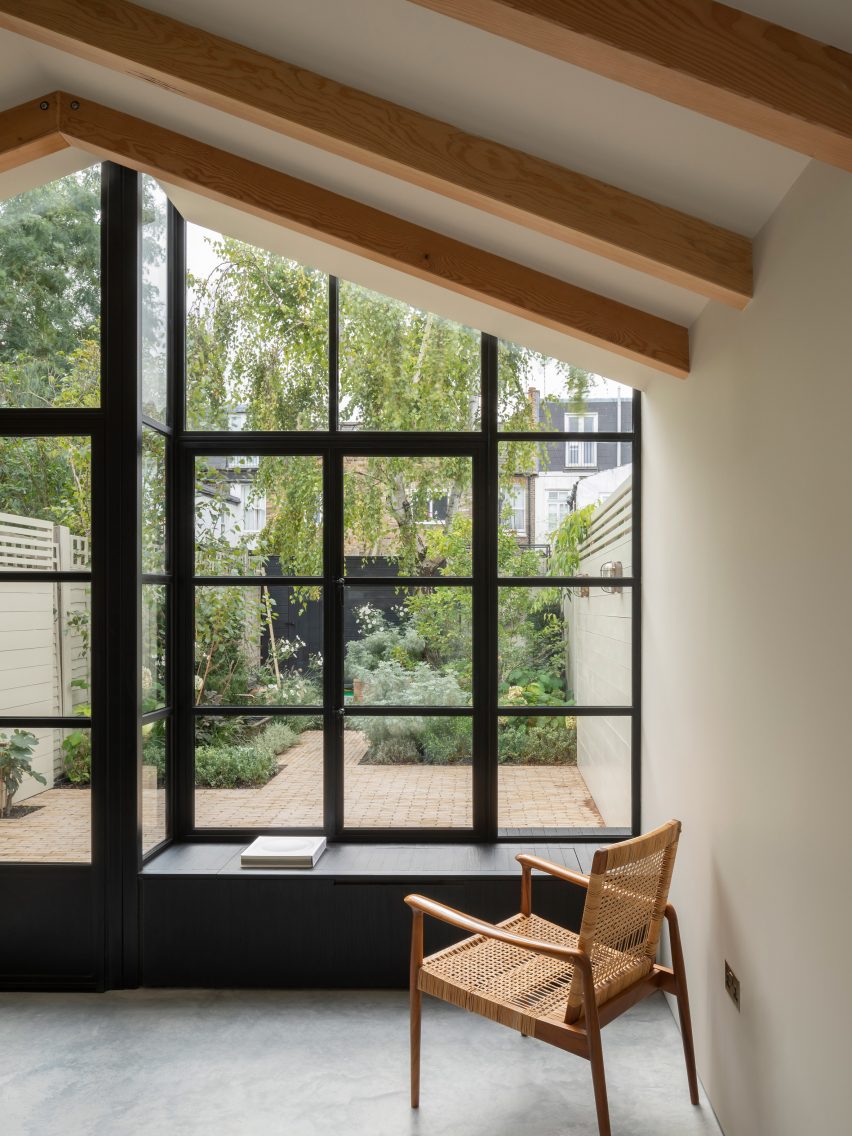
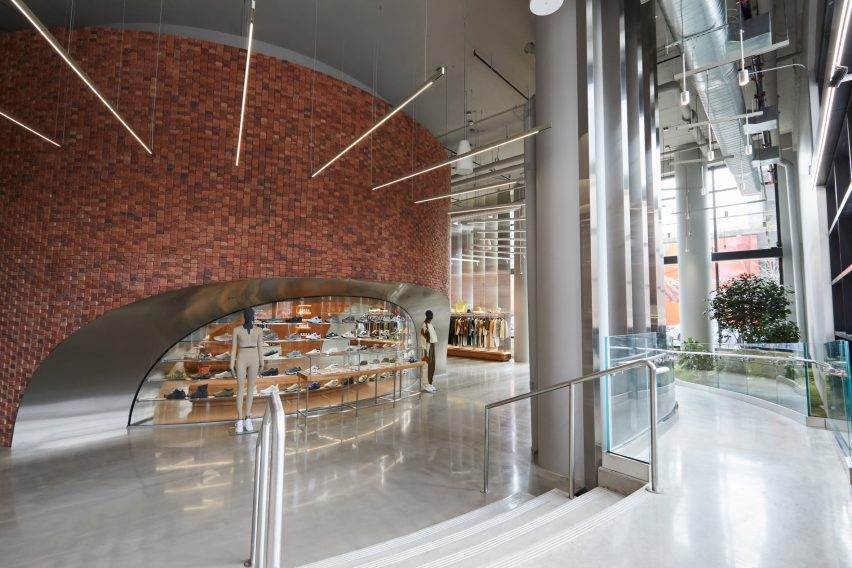
On the building’s exterior, panels of glazing and corrugated metal have been pulled back to express the concrete structure. In each corner, the grid is cut away to create sheltered external areas for the cafe and canteen, which are open to the public.
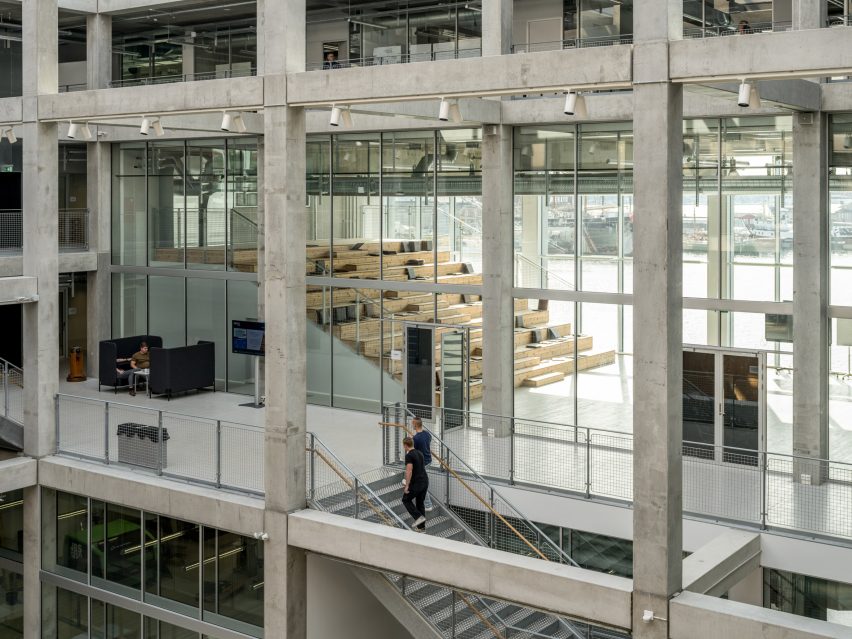


“You see the same raw, minimalist exposed column-girder structure both from the outside and the inside,” said EFFEKT co-founder Sinus Lynge.
“The space essentially flows through the building’s structure, and the intriguing aspect concerning the concrete elements is that SIMAC’s structure is the architecture,” he added.


SIMAC is the first project to be completed as part of a wider masterplan for a new district in Svendborg, which is set to transform 5.5 hectares of industrial area with new education, business and residential buildings.
Elsewhere, EFFEKT also recently completed Denmark’s first treetop walkway at the Hamaren Activity Park in Fyresdal and CF Møller Architects created the headquarters for Lego in Billund with a bright yellow atrium.
The photography is by Rasmus Hjortshøj.
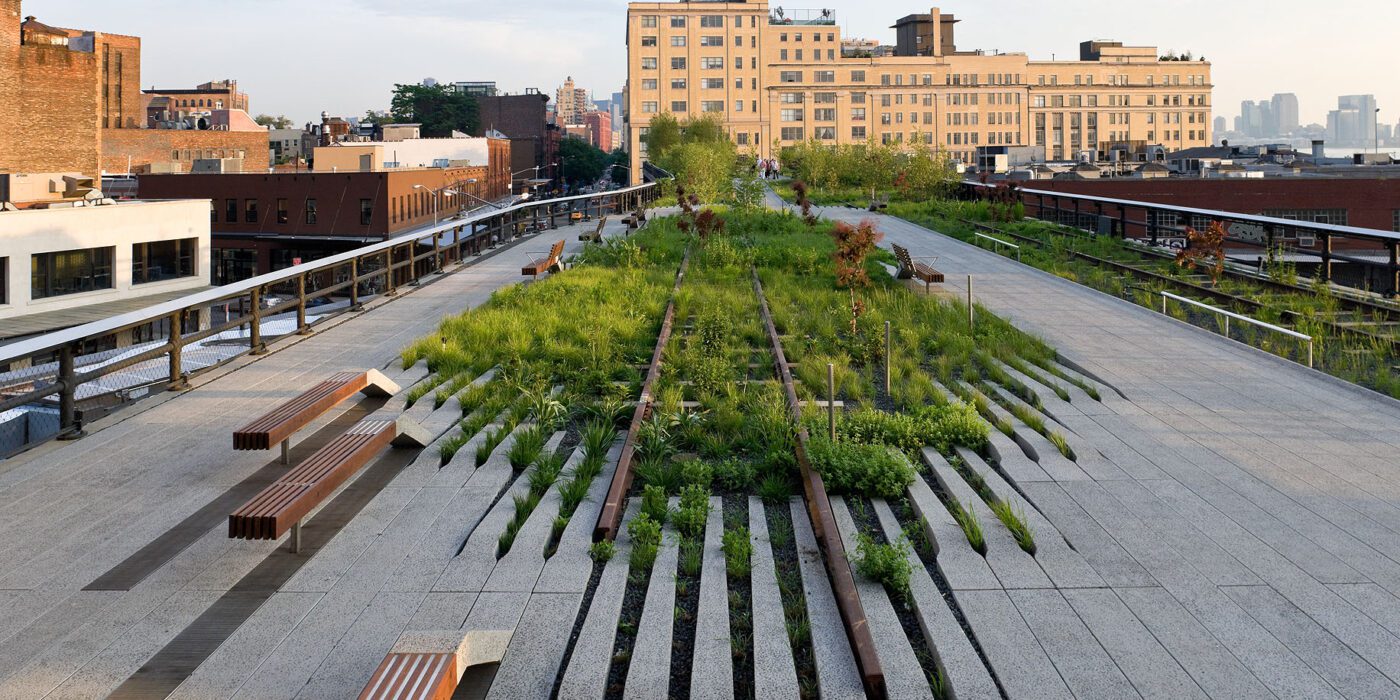
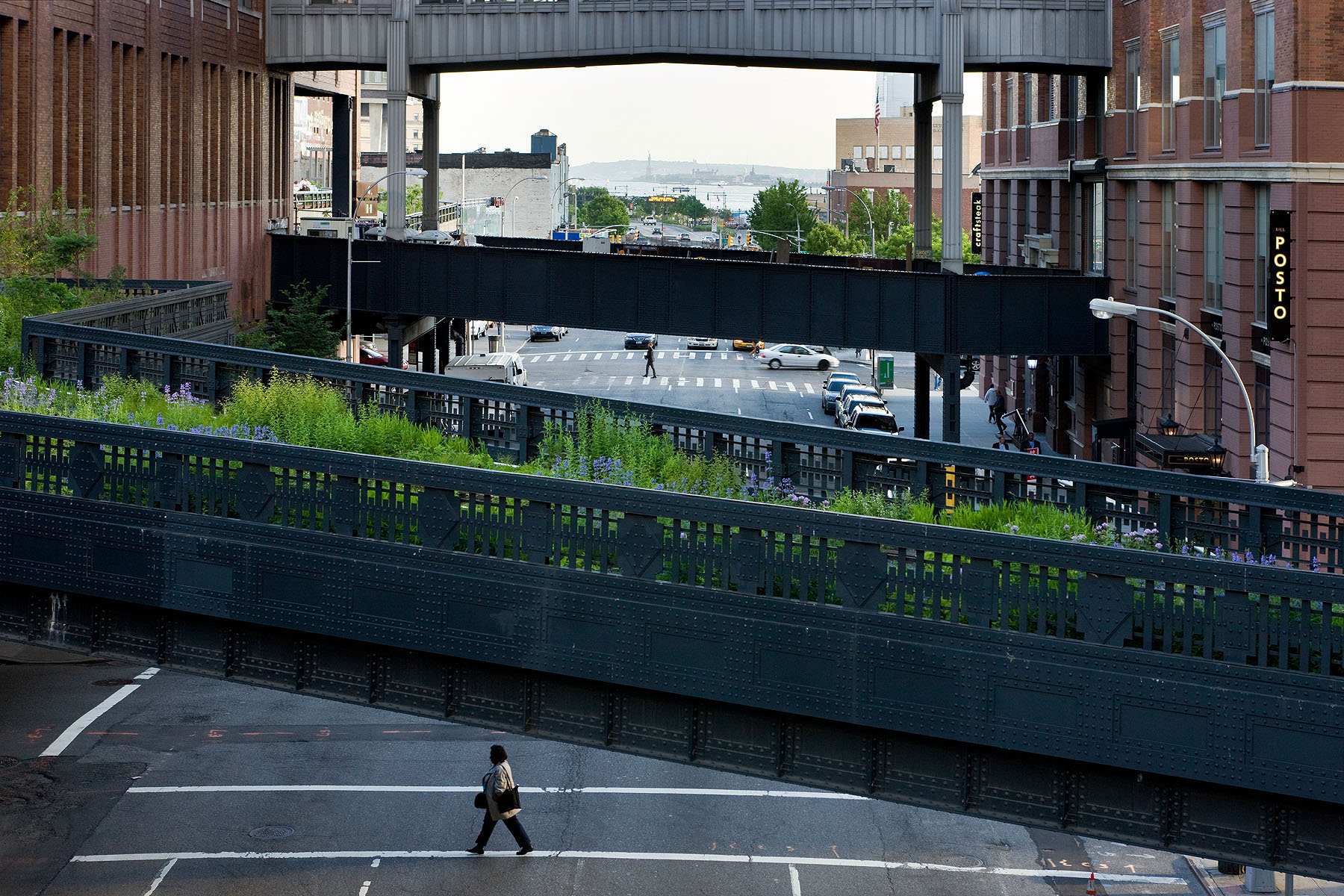





























 How can an abandoned railroad be reused by the citizens of New York City? Connecting the Meatpacking District with the Hudson Railyards, 1.5 miles (2.5 kilometers) of elevated rail tracks have been transformed into the High Line project: a public park that stands as an agricultural oasis amidst the franticness of the big city. Prior to the project’s realisation, the deserted railroad had already been “reclaimed” by nature. Consequently, when James Corner Field Operations and Diller Scofidio + Renfro designed the High Line they celebrated these natural diversities, by employing the strategy of “agri-tecture”. Irregular paving patterns and planting beds form a series of asymmetrical pathways, allowing the people of New York to experience the city through a different, more impromptu, type of lens.
How can an abandoned railroad be reused by the citizens of New York City? Connecting the Meatpacking District with the Hudson Railyards, 1.5 miles (2.5 kilometers) of elevated rail tracks have been transformed into the High Line project: a public park that stands as an agricultural oasis amidst the franticness of the big city. Prior to the project’s realisation, the deserted railroad had already been “reclaimed” by nature. Consequently, when James Corner Field Operations and Diller Scofidio + Renfro designed the High Line they celebrated these natural diversities, by employing the strategy of “agri-tecture”. Irregular paving patterns and planting beds form a series of asymmetrical pathways, allowing the people of New York to experience the city through a different, more impromptu, type of lens.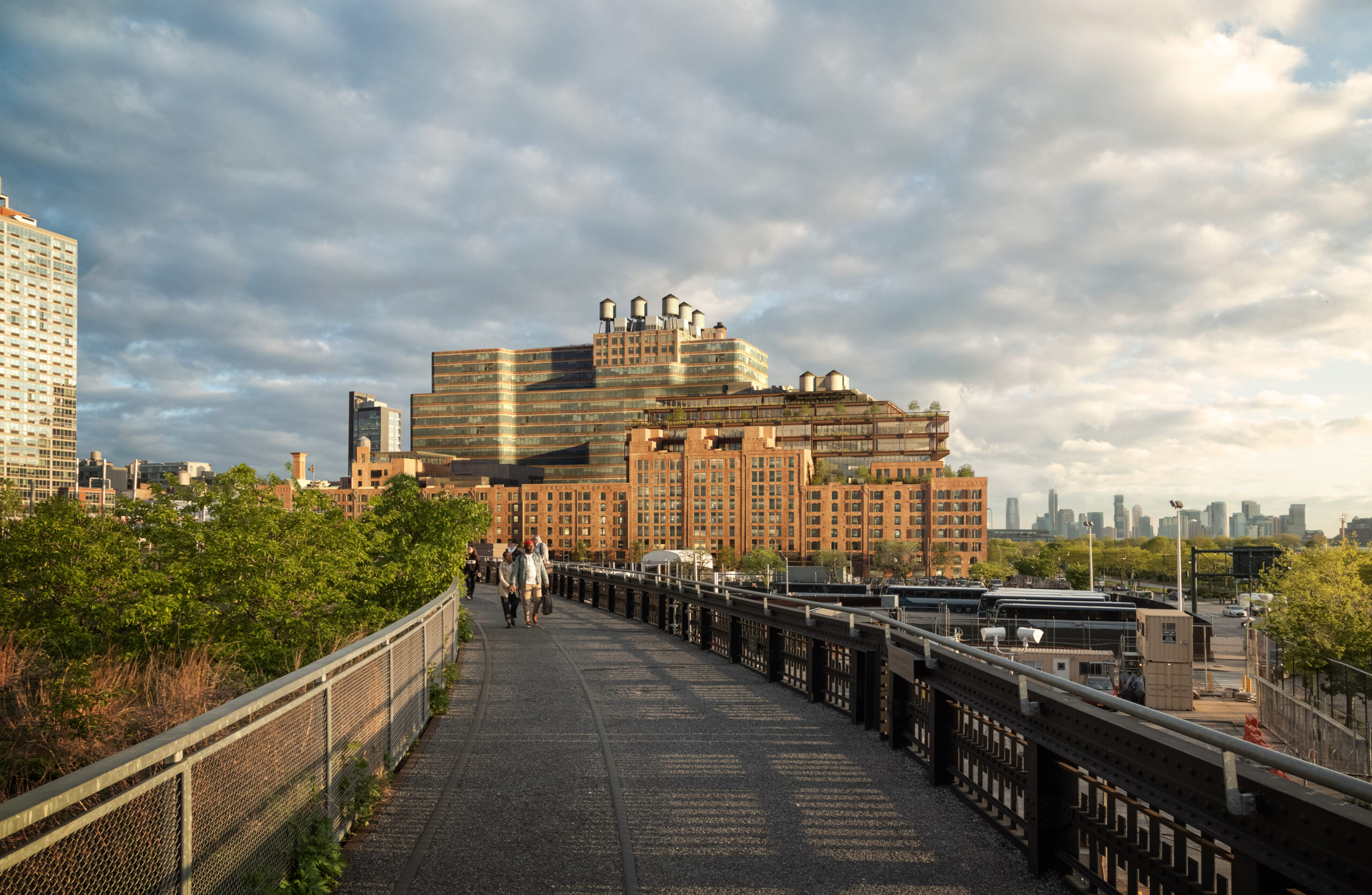
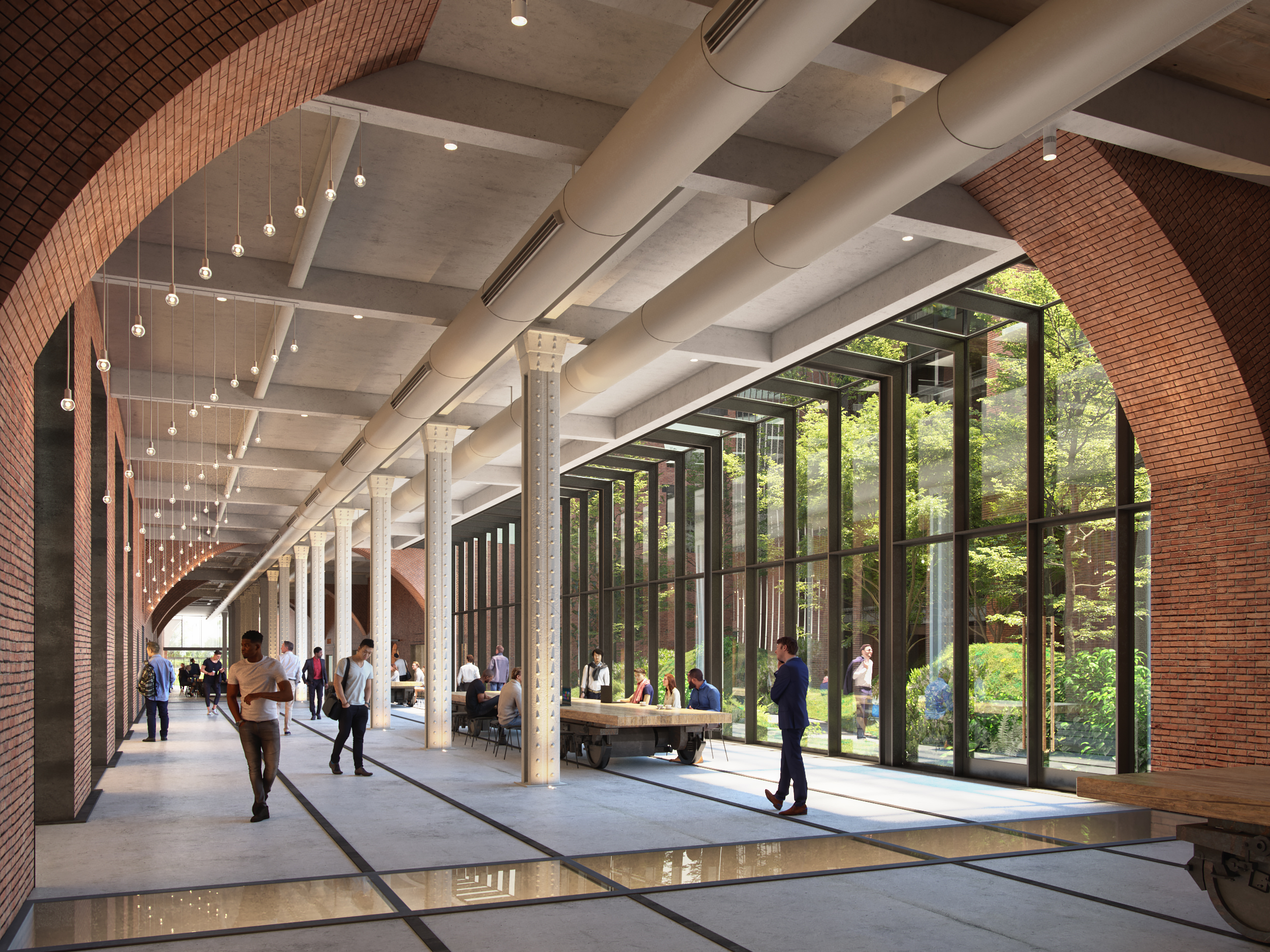 Built in 1891, the Terminal Warehouse is an iconic post-industrial ruin of New York. No longer needing the traditional warehouse in West Chelsea district, the Terminal Warehouse is gradually being transformed into a collection of biophilic office spaces. As part of their design strategy, COOKFOX Architects have preserved the building’s historic architectural typology and used its masonry structure as an infrastructure for supporting a series of gardens and green terraces. Additionally, through a set of rail tracks, the Terminal Warehouse is directly linked with Hudson river. The disregarded railroad becomes an opportunity for reuse and is transformed into a pedestrian route that reestablishes the link between city and water.
Built in 1891, the Terminal Warehouse is an iconic post-industrial ruin of New York. No longer needing the traditional warehouse in West Chelsea district, the Terminal Warehouse is gradually being transformed into a collection of biophilic office spaces. As part of their design strategy, COOKFOX Architects have preserved the building’s historic architectural typology and used its masonry structure as an infrastructure for supporting a series of gardens and green terraces. Additionally, through a set of rail tracks, the Terminal Warehouse is directly linked with Hudson river. The disregarded railroad becomes an opportunity for reuse and is transformed into a pedestrian route that reestablishes the link between city and water.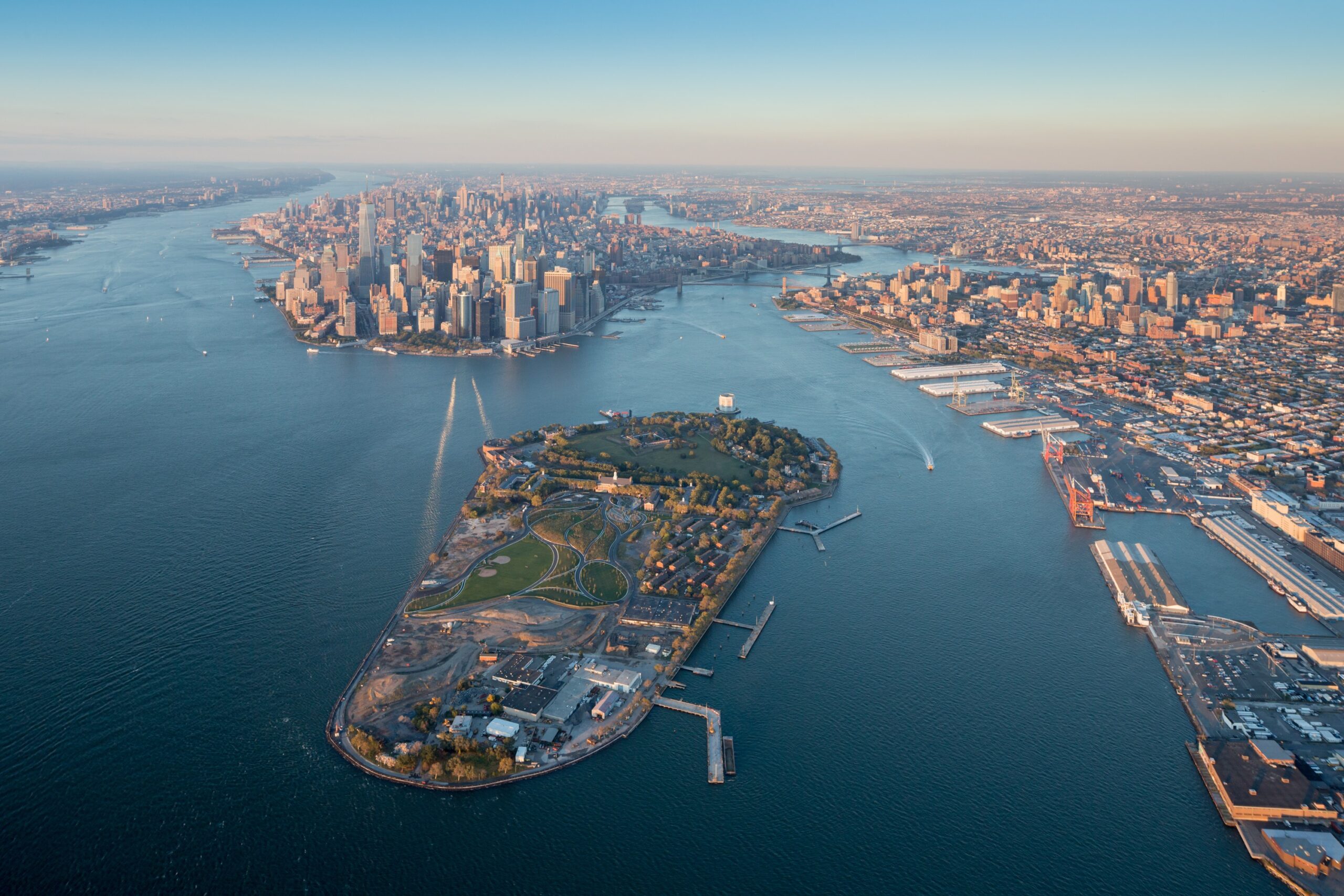
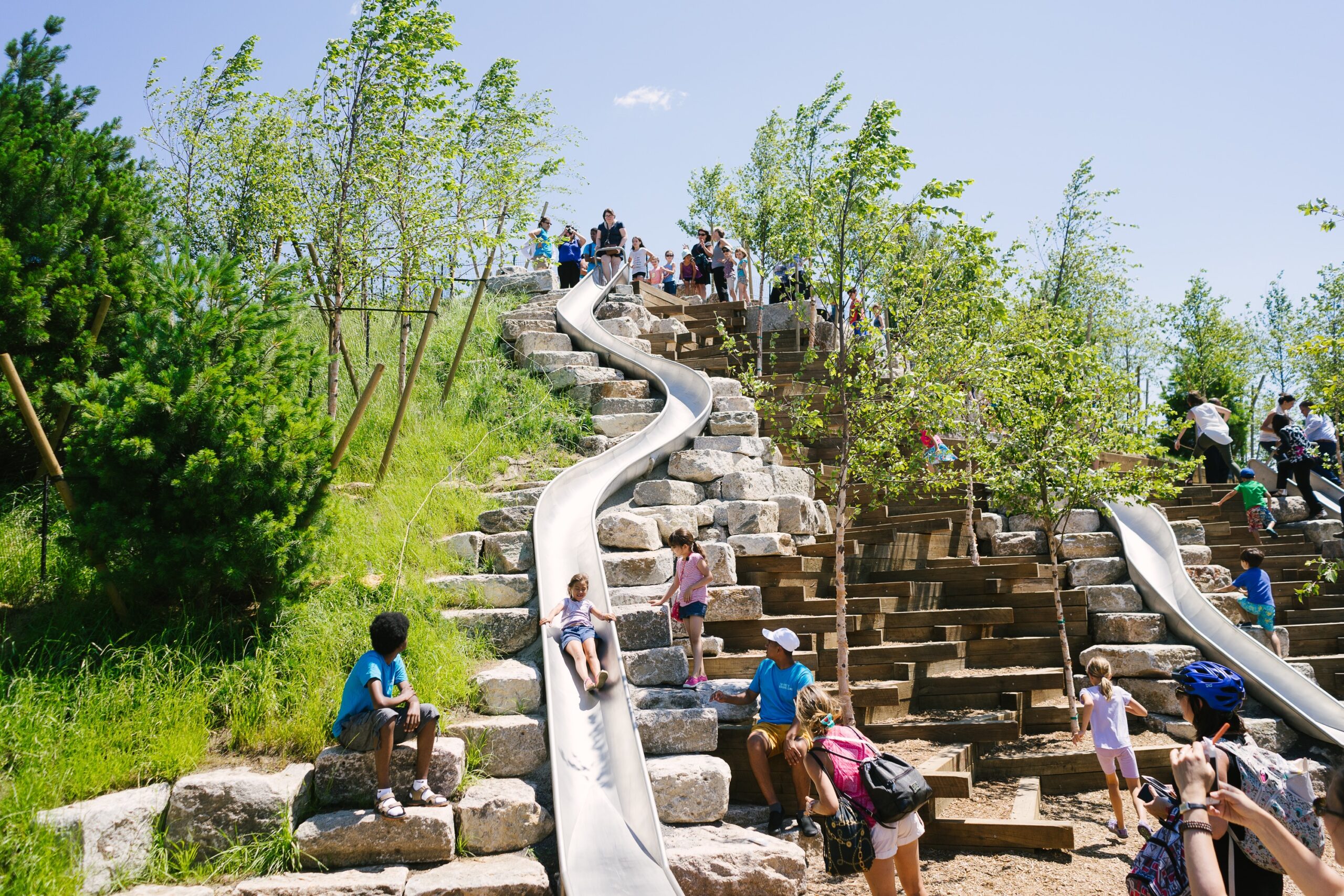
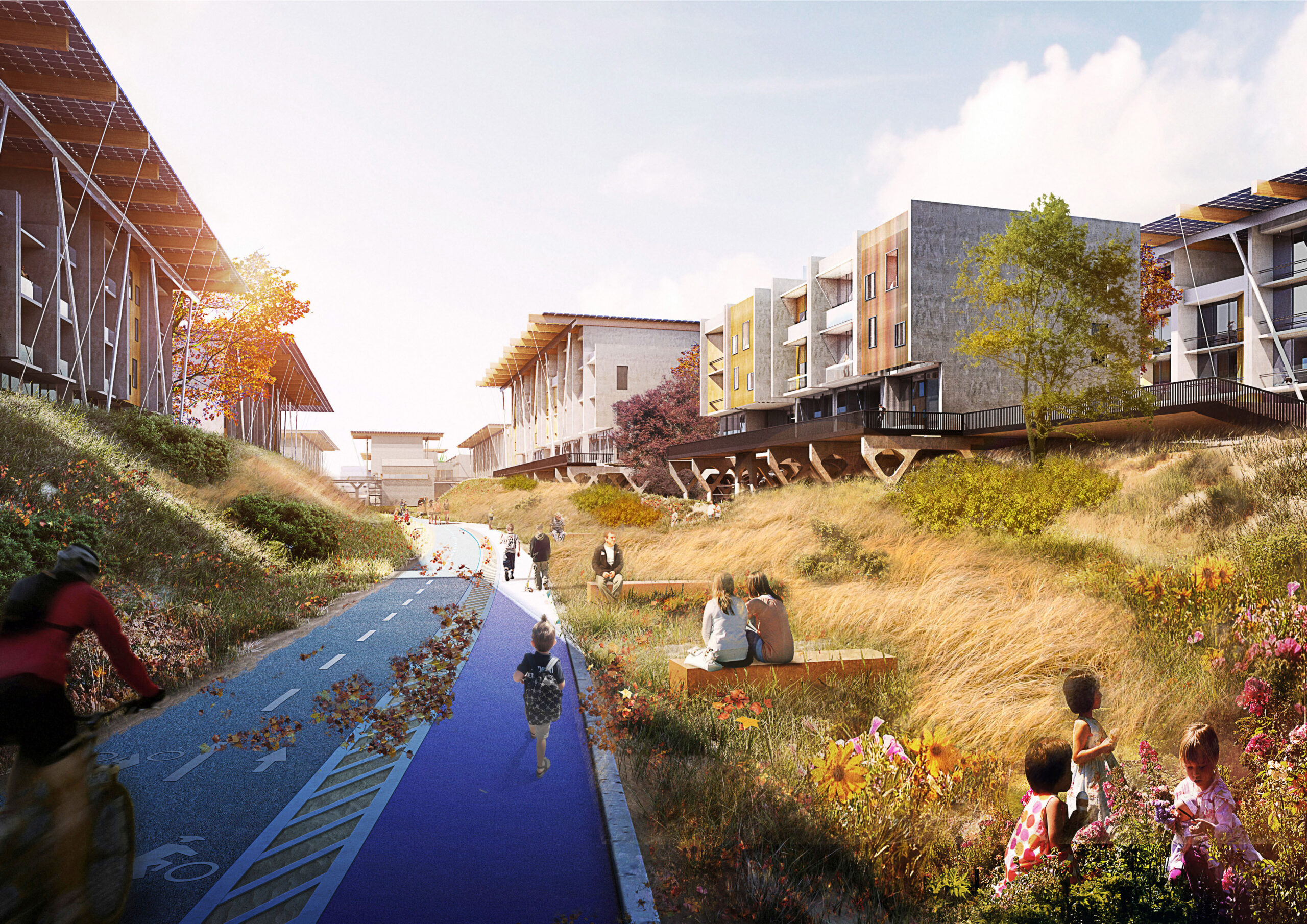
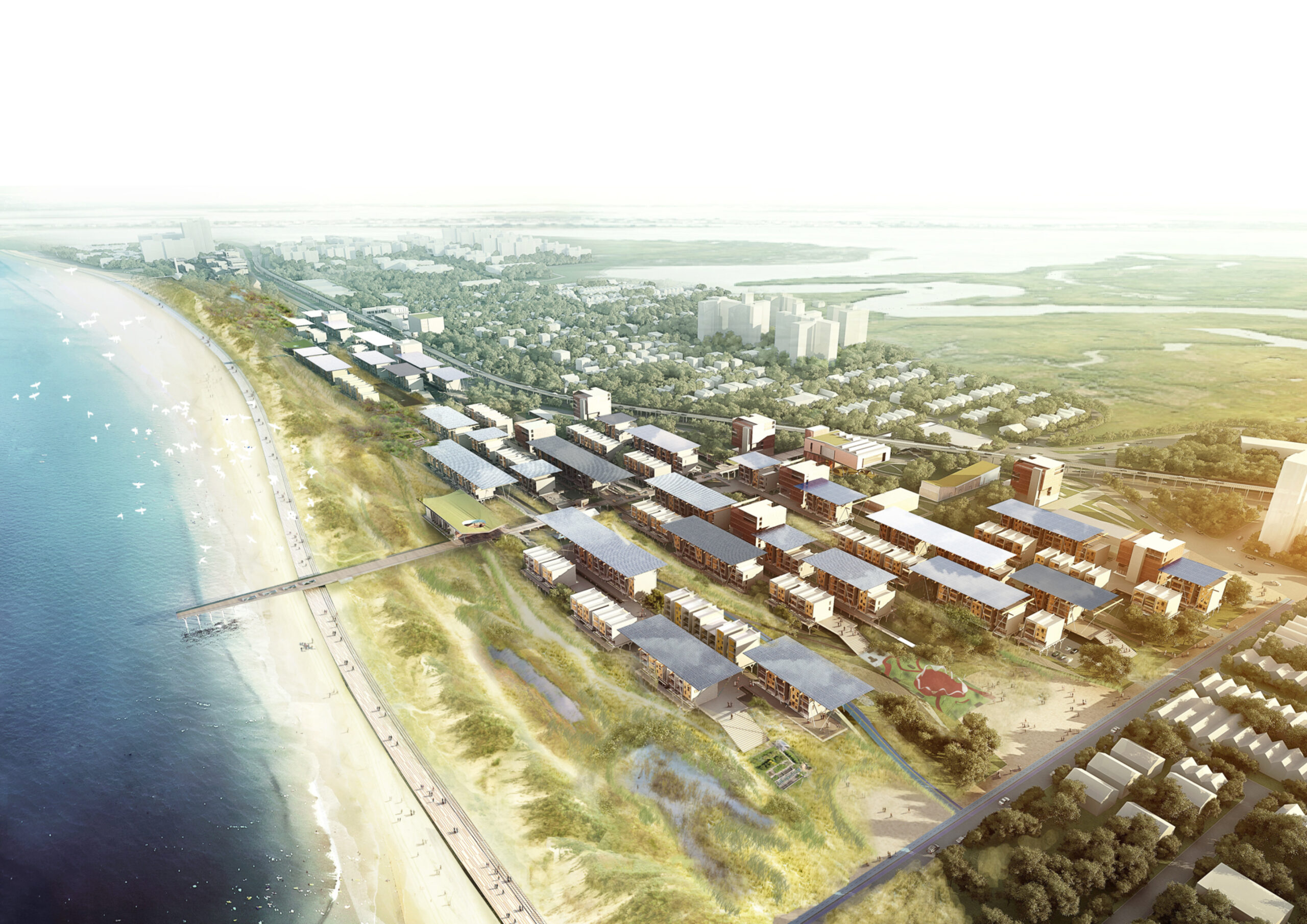

 Located in a beach-front site in the Rockaways, the F.R.E.D. proposal introduces a new type of pairing between nature and infrastructure. Ennead Architects used the iconic Row House typology and the local sand dunes as the two components for designing a resilient infrastructure system. Their aim was to create a flexible strategy, which could be easily repurposed for other waterfront sites with the same characteristics and expand upon the research on “infrastructuring nature”.
Located in a beach-front site in the Rockaways, the F.R.E.D. proposal introduces a new type of pairing between nature and infrastructure. Ennead Architects used the iconic Row House typology and the local sand dunes as the two components for designing a resilient infrastructure system. Their aim was to create a flexible strategy, which could be easily repurposed for other waterfront sites with the same characteristics and expand upon the research on “infrastructuring nature”.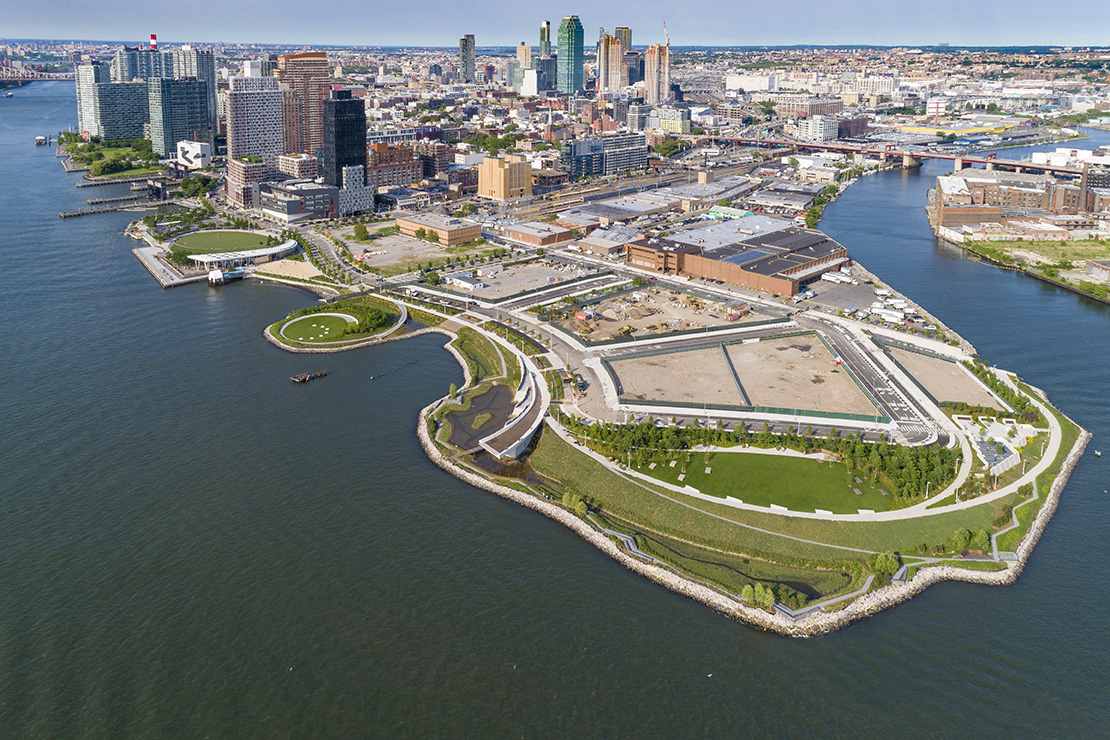
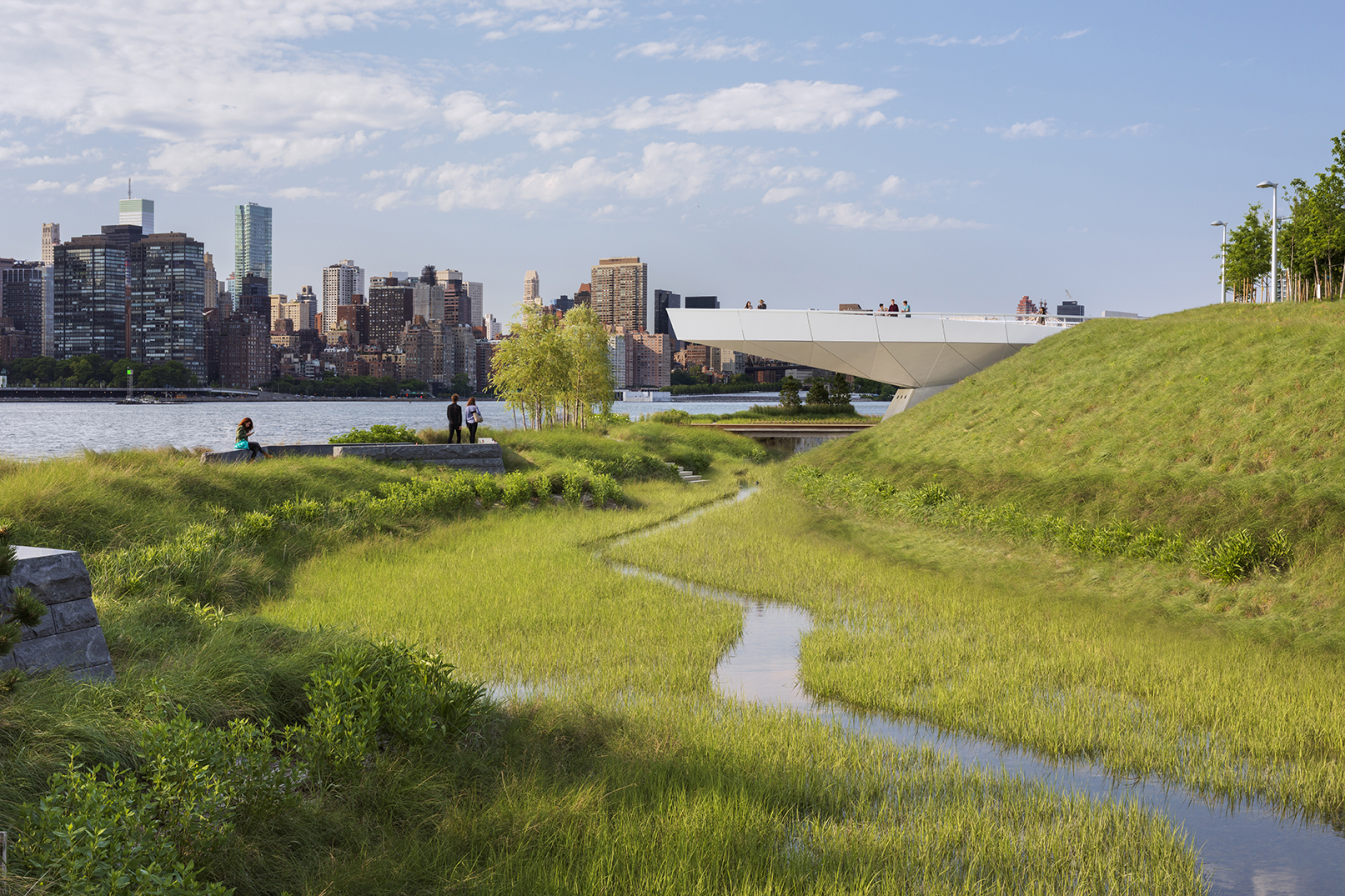 For two hundred years, Hunter’s Point was a series of wetlands on the East river. Later on, the site was turned into an industrial hub and rail station. Eventually, it was diminished to a post-industrial ruin filled with decaying piers and steep landfills, inaccessible to the wider public. Finally, in 2018 it became one of the most transformative and ecologically driven projects in the city. A coastal park, a footbridge, a cantilevered overlook and even a landfill peninsula transformed what used to be an empty industrial site into an adaptable infrastructural system that reinvented the once iconic water edge.
For two hundred years, Hunter’s Point was a series of wetlands on the East river. Later on, the site was turned into an industrial hub and rail station. Eventually, it was diminished to a post-industrial ruin filled with decaying piers and steep landfills, inaccessible to the wider public. Finally, in 2018 it became one of the most transformative and ecologically driven projects in the city. A coastal park, a footbridge, a cantilevered overlook and even a landfill peninsula transformed what used to be an empty industrial site into an adaptable infrastructural system that reinvented the once iconic water edge.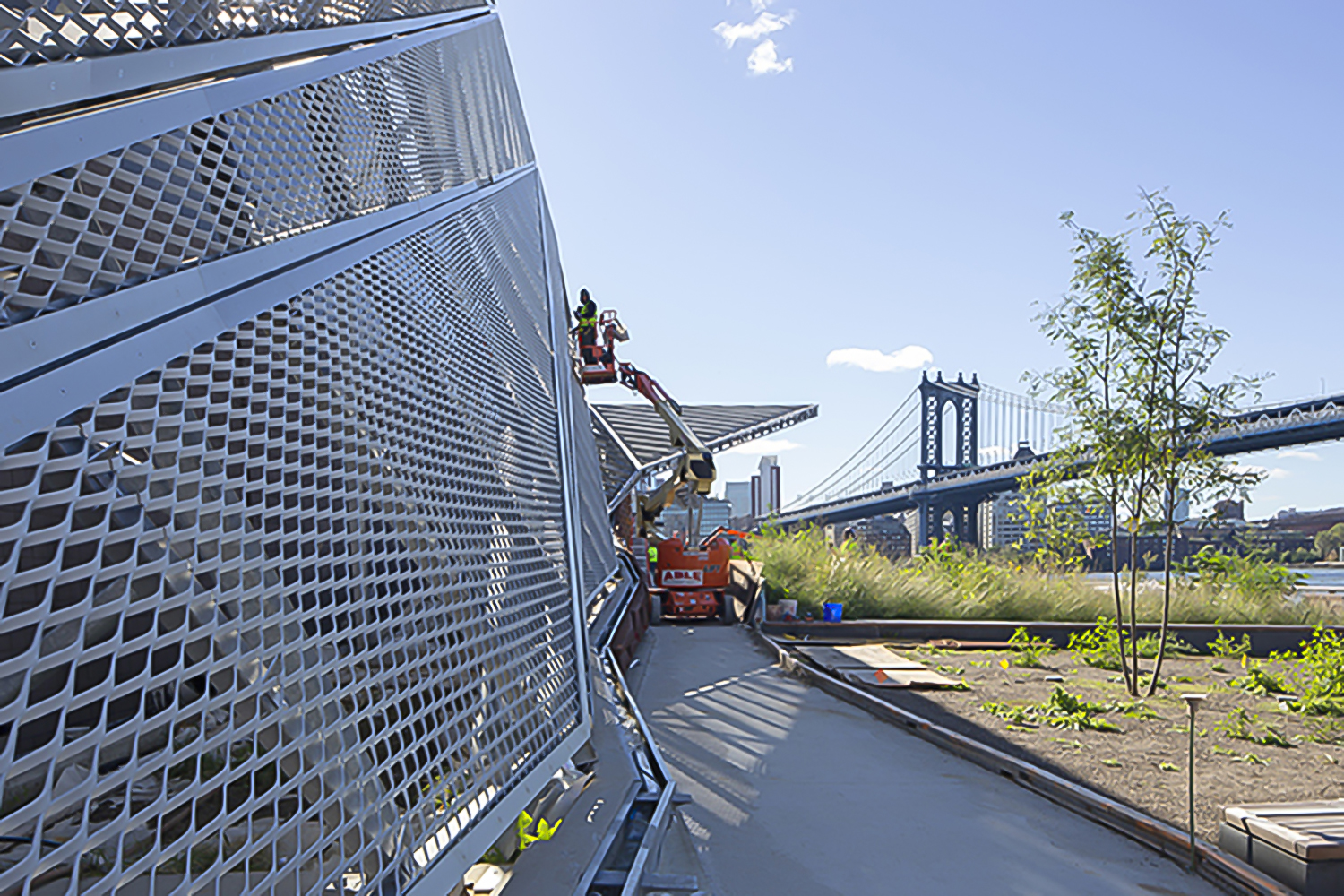
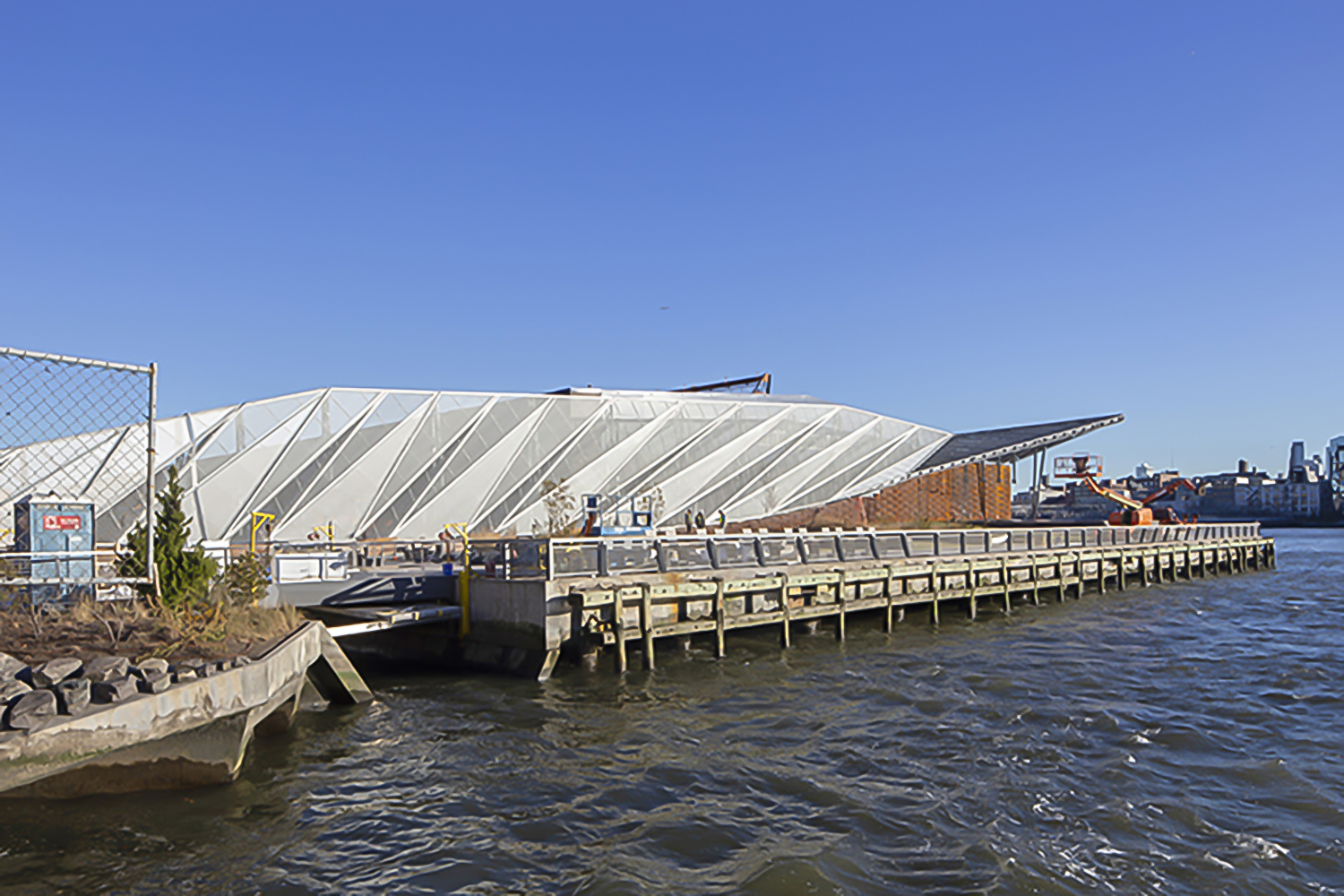 Enclosed by the Hudson and East rivers, the island of Manhattan is naturally surrounded by many raw, uninviting concrete piers. Fortunately, the Pier 35 proposal transformed one of these flat blocks of artificial land into a much needed esplanade project. Pier 35 is literary “infrastructuring nature”. It consists of a folded landscape that gradually slopes down to the surface of the water. Its crinkled form interacts with the varying tidal currents, while replicating the physical characteristics of the East river shoreline. Above the water, a series of landscape lawns, dunes and inclined plant-covered screens form pedestrian walkways filled with vantage points towards Brooklyn and Manhattan bridge.
Enclosed by the Hudson and East rivers, the island of Manhattan is naturally surrounded by many raw, uninviting concrete piers. Fortunately, the Pier 35 proposal transformed one of these flat blocks of artificial land into a much needed esplanade project. Pier 35 is literary “infrastructuring nature”. It consists of a folded landscape that gradually slopes down to the surface of the water. Its crinkled form interacts with the varying tidal currents, while replicating the physical characteristics of the East river shoreline. Above the water, a series of landscape lawns, dunes and inclined plant-covered screens form pedestrian walkways filled with vantage points towards Brooklyn and Manhattan bridge.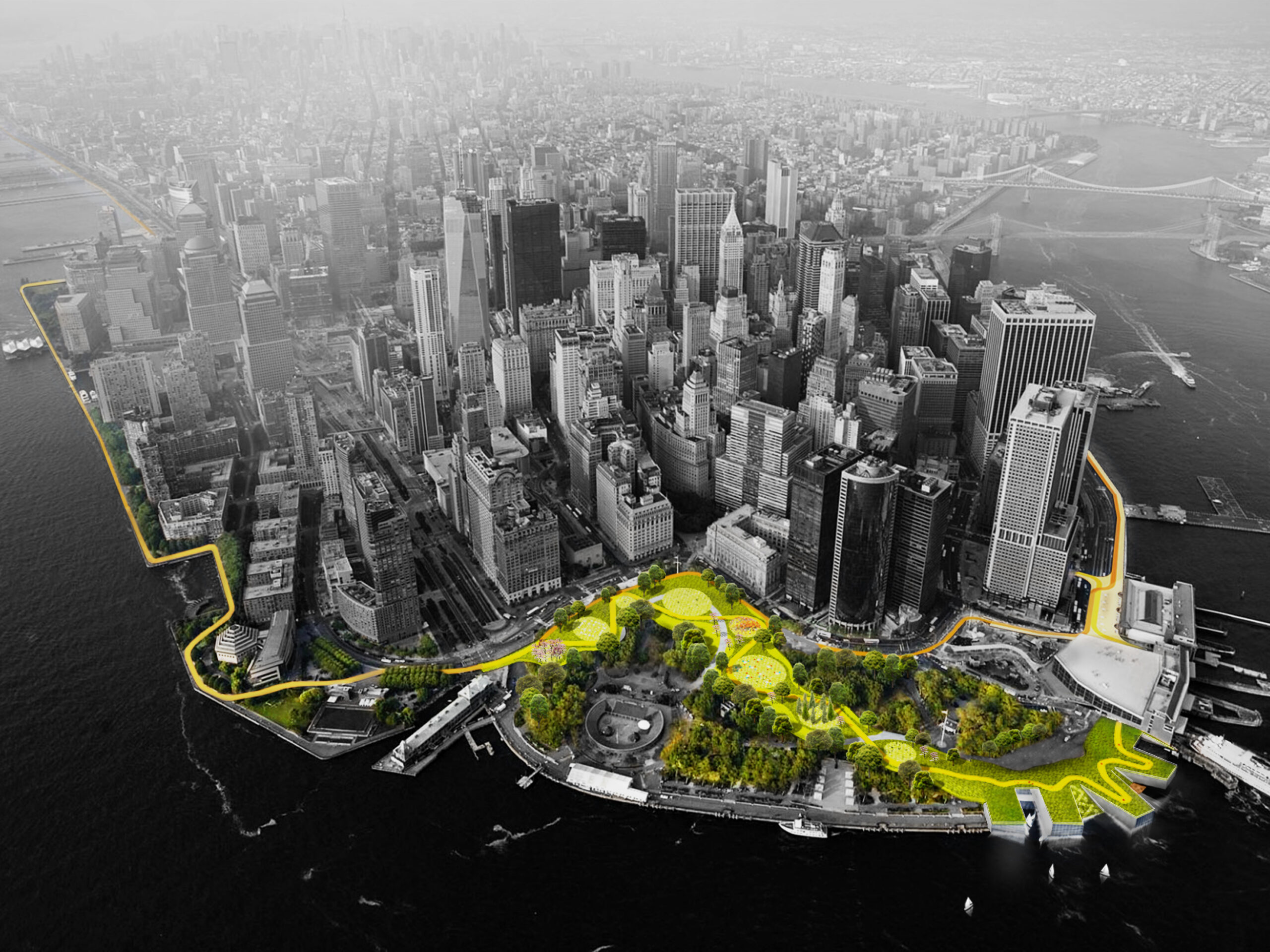
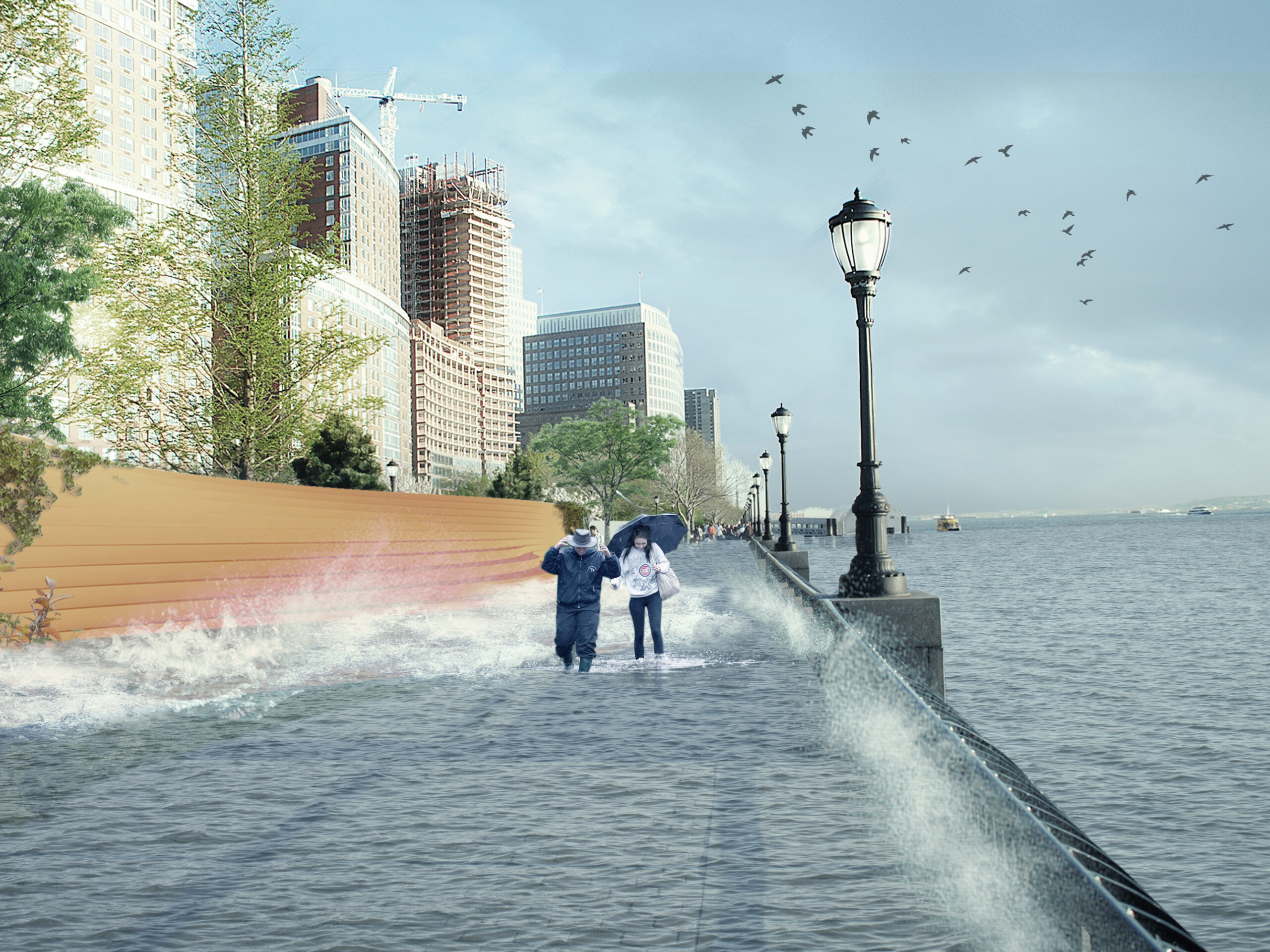 Also known as “The Big U,” this conceptual 10-mile-long (16 kilometer) protective ribbon around Manhattan was imagined in the wake of Superstorm Sandy. Ultimately, it was deemed unfit to respond to the challenging weather conditions that increasingly threaten the city. Subsequently, the Dryline is a project that redesigns lower Manhattan’s water edge, proposing a series of components that will aid to both the physical and social infrastructure requirements of the neighboring districts. More specifically, the project consist of a continuous protective element that also operates as playful street furniture, an elevated pathway and finally, a series of overarching greenways. In short, the Dryline project has essentially become the blueprint for effectively designing social as well as physical infrastructure strategies for coastal cities, providing new insights for “infra structuring nature” practices.
Also known as “The Big U,” this conceptual 10-mile-long (16 kilometer) protective ribbon around Manhattan was imagined in the wake of Superstorm Sandy. Ultimately, it was deemed unfit to respond to the challenging weather conditions that increasingly threaten the city. Subsequently, the Dryline is a project that redesigns lower Manhattan’s water edge, proposing a series of components that will aid to both the physical and social infrastructure requirements of the neighboring districts. More specifically, the project consist of a continuous protective element that also operates as playful street furniture, an elevated pathway and finally, a series of overarching greenways. In short, the Dryline project has essentially become the blueprint for effectively designing social as well as physical infrastructure strategies for coastal cities, providing new insights for “infra structuring nature” practices.






























