Global innovation spotlight: Singapore – Springwise
Global innovation spotlight: Singapore
Global Innovation Spotlight
Reflecting our global Springwise readership, we explore the innovation landscape and freshest thinking from a new country each week. This week, we’ve headed to Southeast Asia…
Singapore Innovation Facts
Global Innovation Index ranking: 8th
Climate targets: reduce GHG emissions intensity by 36% by 2030 (compared to 2005), net zero by 2050
Sustainability challenges
Dependence on food imports – Over 90 per cent of the food consumed in Singapore is imported. This not only incurs carbon emissions from transportation – it also makes the city-state vulnerable to supply problems and price hikes.
Waste management – Despite its reputation for cleanliness and investment in waste management, Singapore faces unique challenges when it comes to waste. Recycling rates are low, and more than 40 per cent of rubbish produced by the city-state is incinerated.
Energy security – Around 95 per cent of Singapore’s domestic electricity is generated from imported natural gas. Natural gas is a fossil fuel, and Singapore’s reliance on imports makes it vulnerable to high energy prices. In response, the government recently announced targets to import around 30 per cent of the country’s electricity from low-carbon sources by 2035.
Sector specialisms
Deep tech
E-commerce
Fintech
Source: Startup Universal
Three exciting innovations from Singapore

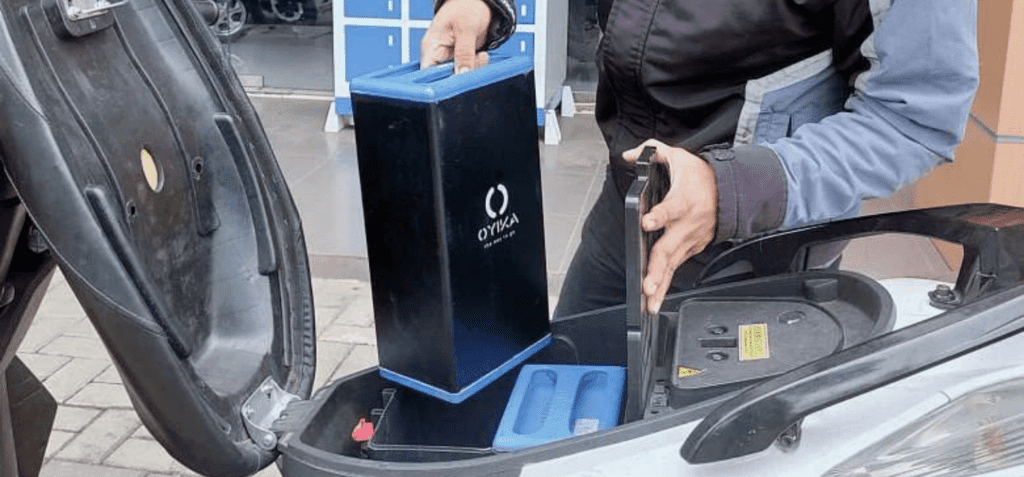
A BATTERY SWAP STARTUP TURNS PETROL-POWERED MOTORBIKES INTO EVS
In Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia, and Malaysia between 83 and 87 per cent of households own motorbikes. Despite being smaller than cars, the sheer numbers of these vehicles on the road contribute to ongoing air pollution problems in many urban areas. Seeking to change that, startup Oyika has created a battery swapping service that turns petrol-powered motorbikes into electric vehicles (EVs). Read more.

A CSR PLATFORM ENABLES COMPANIES TO CHOOSE AND TRACK VERIFIED IMPACT PROJECTS
Singaporean startup Handprint is providing businesses with an easy way to improve their planetary impact. The Handprint platform offers companies a choice of pre-verified impact projects grouped into themes such as social justice, clean water, and deforestation. Each company can then choose to support the ones that best align with its brand and values. Software tools allow client companies to integrate contributions to those projects into core business processes such as e-commerce. Read more.

NANOFILTRATION REDUCES INDUSTRIAL CHEMICAL SEPARATION EMISSIONS
An invisible polluter, industrial chemical separation is a necessity in many industries, including pharmaceuticals, oil refinement, and semiconductor and vegetable oil production. The process of separating chemicals for commercial and industrial accounts for up to 15 per cent of the world’s energy use. In response, Singapore-based Seppure has built a membrane capable of separating even the harshest chemicals at the molecular level without using heat. Read more.
Words: Matthew Hempstead
To keep up with the latest innovations, sign up to our free newsletters or email info@springwise.com to get in touch.
27th May 2022







 All said and done, this process produces ZERO water waste. That’s right, zero with a Z. In 2022, this is welcome news indeed. The past few years have seen new attention given to the issue of water conservation as global water shortages have become a mounting problem.
All said and done, this process produces ZERO water waste. That’s right, zero with a Z. In 2022, this is welcome news indeed. The past few years have seen new attention given to the issue of water conservation as global water shortages have become a mounting problem. Cosentino believes that consumers need not compromise quality in the name of sustainability. In fact, those Silestone surfaces that have been produced with HybriQ+ technology are among the most beautiful the company has ever produced. The company explains that “the new mineral composition enables never before-seen effects in color depth, texture and tone.” Indeed, Cosentino has long proven that synthetic materials can be just as elegant and intricate as natural materials.
Cosentino believes that consumers need not compromise quality in the name of sustainability. In fact, those Silestone surfaces that have been produced with HybriQ+ technology are among the most beautiful the company has ever produced. The company explains that “the new mineral composition enables never before-seen effects in color depth, texture and tone.” Indeed, Cosentino has long proven that synthetic materials can be just as elegant and intricate as natural materials. We recommend spending time on the
We recommend spending time on the