7 Elegant Pools in the Great Outdoors
Browse the Architizer Jobs Board and apply for architecture and design positions at some of the world’s best firms. Click here to sign up for our Jobs Newsletter.
As a typology, outdoor pools are not necessarily exceptional. They sprinkle suburbs and cities throughout the world and are a statement of leisure almost as ubiquitous as well-groomed lawns. But in environments outside of the urban fabric of cities, where the absence of human infrastructure leaves us vulnerable to the unpredictability of the environment, pools become something greater: they are an assertion of human comfort, perhaps to remedy environmental extremes such as heat and humidity.
In such places, pools can become an artistic statement when they are freed from the physical constraints of the urban world. The seven designs below demonstrate how outdoor pools can interact with their adjacent home and surrounding landscape, acting as a reflection or as a contrast to that environment.
Desert Palisades
By WOODS + DANGARAN, Palm Springs, CA
10th Annual A+Awards, Jury Winner, Residential – Residential (>3000 sq ft) Interiors
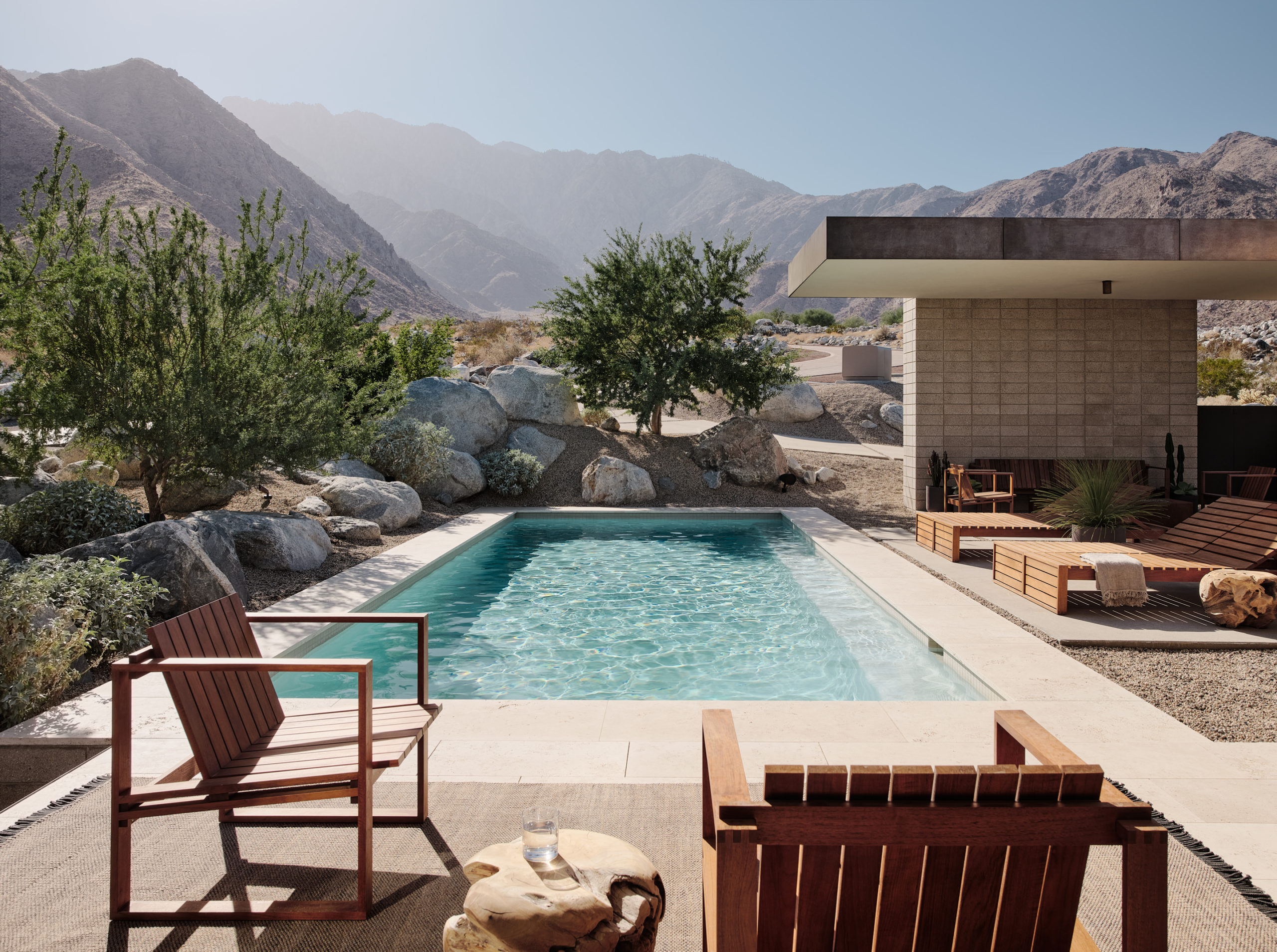
 Lightly perched above the floor of the La Quinta Valley, this home adopts a classic desert modernist aesthetic. The home’s exterior cladding of earth-toned plaster and textured concrete masonry puts it in harmony with the similarly brownish desert, but the structure’s simple and elegant rectangular compositions offer a balanced contrast with the valley’s rugged, uneven and hostile character. In similar fashion, the small outdoor pool, sheltered in one of the home’s two courtyards, pairs well in tone with the constant clear-blue sky, but provides instead a refreshing alternative to the arid climate.
Lightly perched above the floor of the La Quinta Valley, this home adopts a classic desert modernist aesthetic. The home’s exterior cladding of earth-toned plaster and textured concrete masonry puts it in harmony with the similarly brownish desert, but the structure’s simple and elegant rectangular compositions offer a balanced contrast with the valley’s rugged, uneven and hostile character. In similar fashion, the small outdoor pool, sheltered in one of the home’s two courtyards, pairs well in tone with the constant clear-blue sky, but provides instead a refreshing alternative to the arid climate.
Casa Malandra
By TAC, Puerto Escondido, Mexico
Popular Choice Winner, 10th Annual A+Awards, Private House (XS < 1000 sq ft)
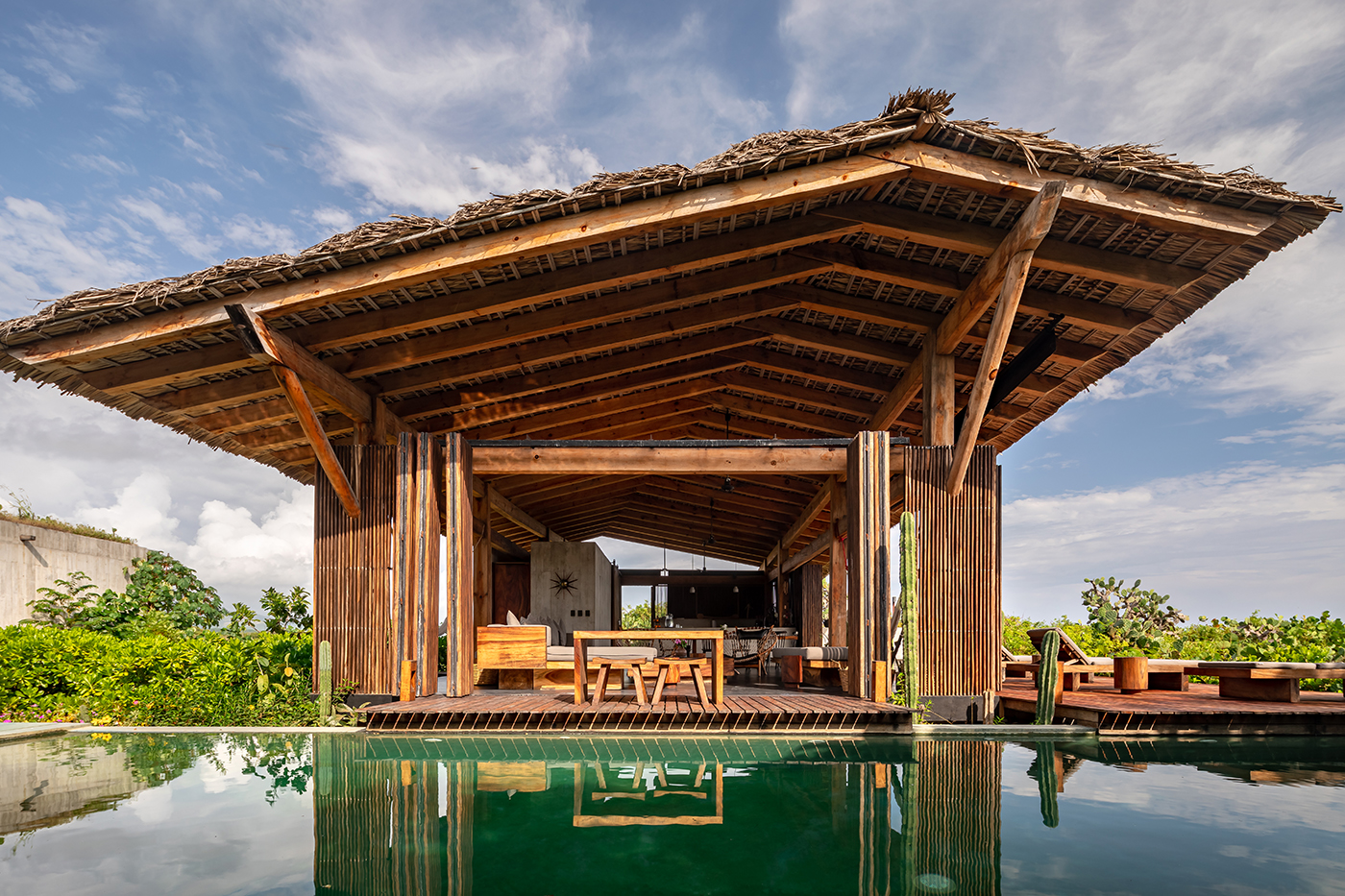

 This private home in the coastal town of Puerto Escondido uses vernacular materials to create a peaceful resort in line with the local architecture. But the concrete-cast pool which extends beyond the main room is undeniably modernist. It serves as its own micro-climate comfortably shielded by several canopies, both natural and man-made.
This private home in the coastal town of Puerto Escondido uses vernacular materials to create a peaceful resort in line with the local architecture. But the concrete-cast pool which extends beyond the main room is undeniably modernist. It serves as its own micro-climate comfortably shielded by several canopies, both natural and man-made.
Casa Meztitla
By EDAA | Estrategias para el Desarrollo de Arquitectura, Tepoztlán, Mexico
Jury Winner, 2016 A+Awards, Architecture +Water
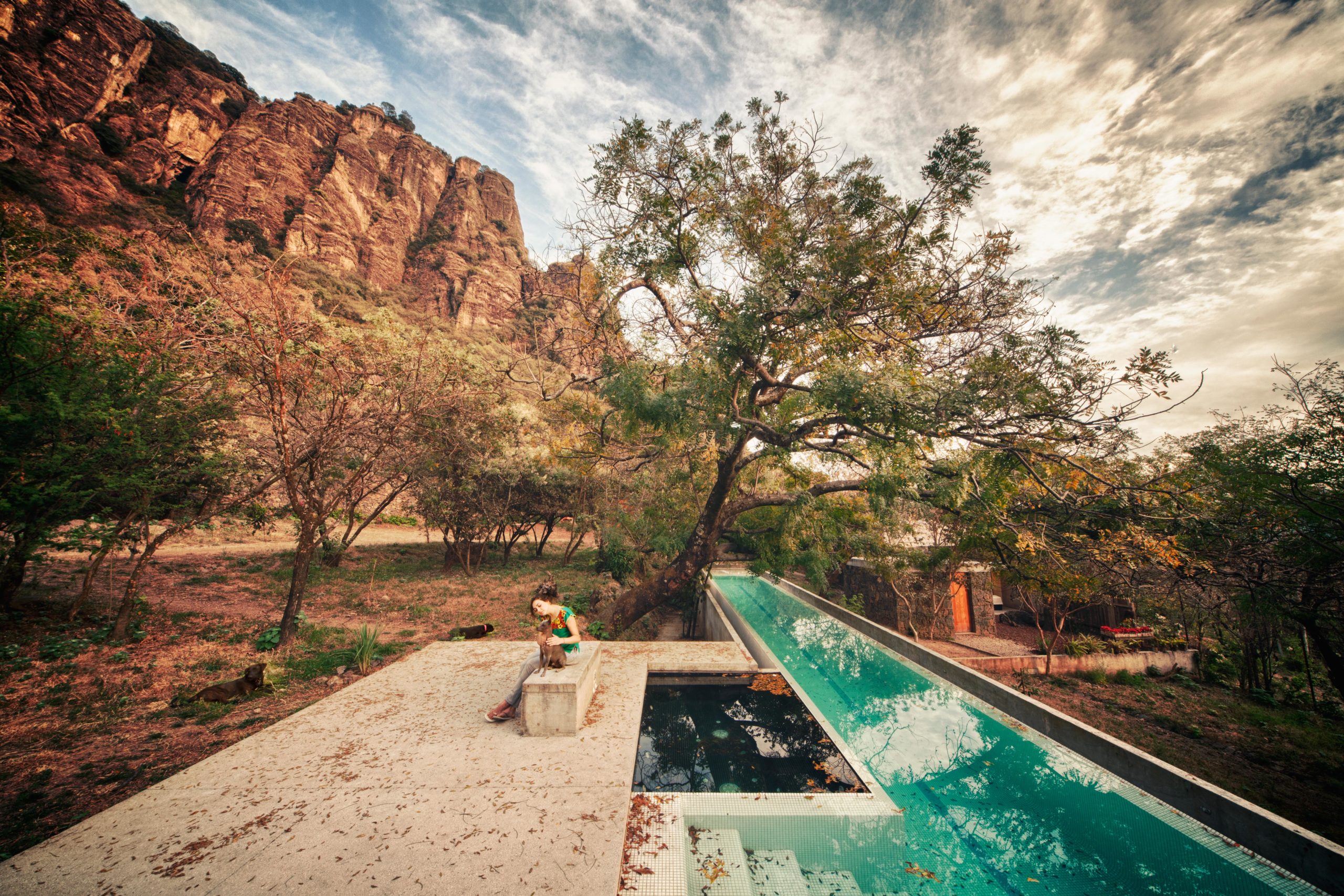
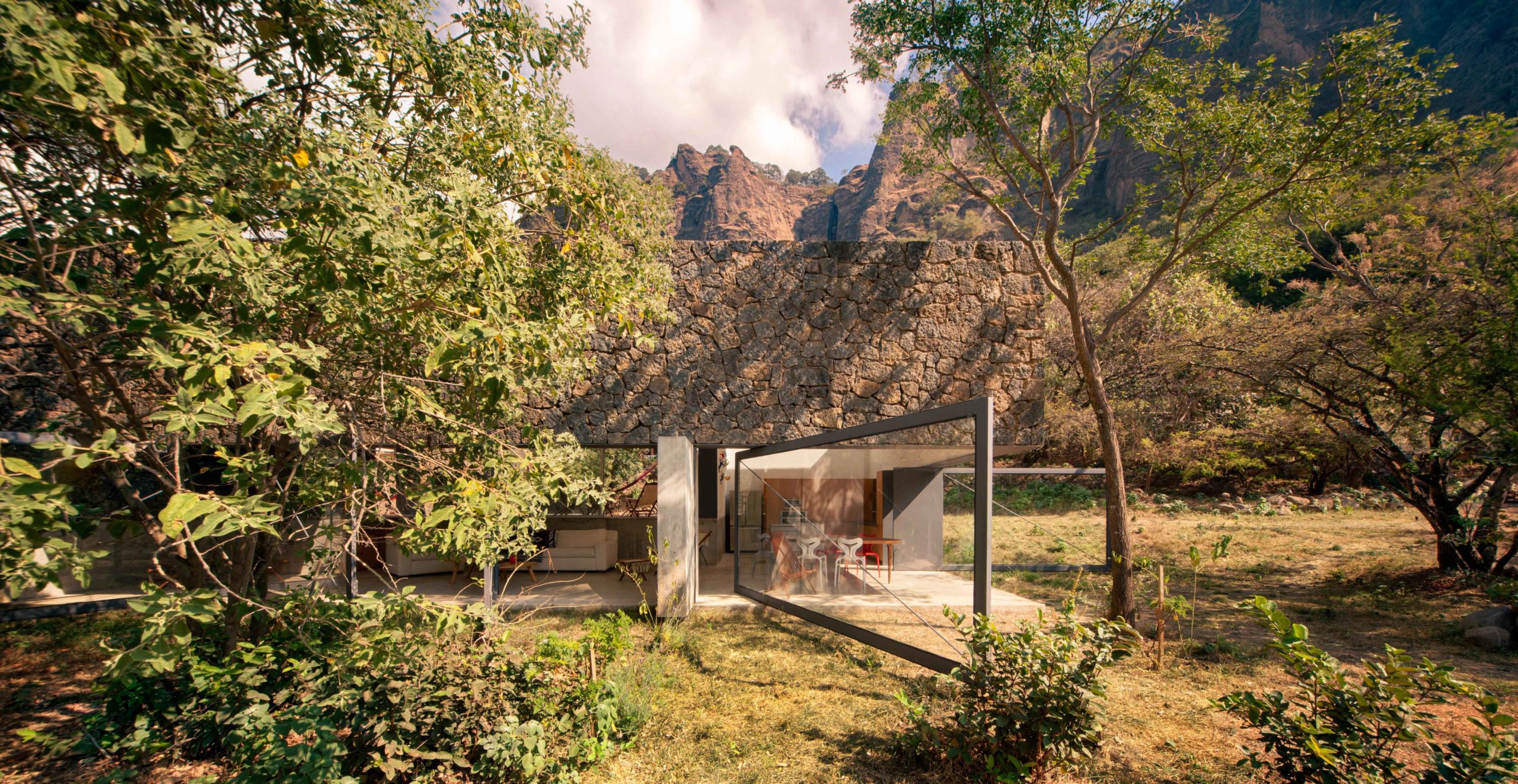
 This rural home in Tepoztlán, Mexico is a tranquil abode flanked by the imposing rock mountains of El Tepozteco. The house brings together monolithic white volumes with vernacular rough stone sections, allowing nature to project itself onto the structure. Meanwhile, a lap pool nearby acts like the house’s miniature desert oasis; it crawls under trees’ dense foliage like an emerald-tinted river breaking through an arid landscape. The pool offers a peaceful place to enjoy the nature that surrounds and blankets over it.
This rural home in Tepoztlán, Mexico is a tranquil abode flanked by the imposing rock mountains of El Tepozteco. The house brings together monolithic white volumes with vernacular rough stone sections, allowing nature to project itself onto the structure. Meanwhile, a lap pool nearby acts like the house’s miniature desert oasis; it crawls under trees’ dense foliage like an emerald-tinted river breaking through an arid landscape. The pool offers a peaceful place to enjoy the nature that surrounds and blankets over it.
Hale Lana
By Olson Kundig, Hawaii County, HI
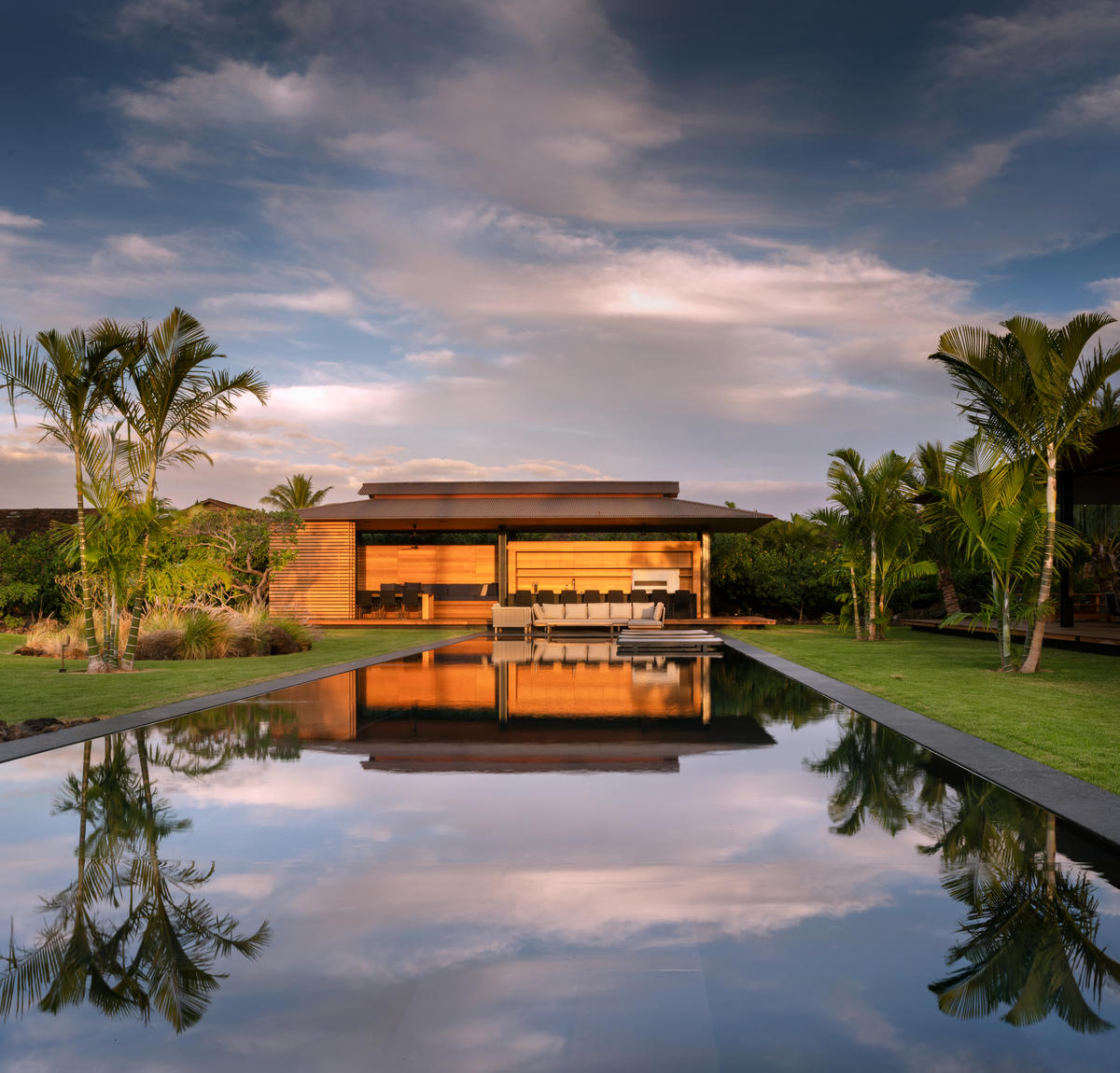


Photos by Nic Lehoux
This family retreat overlooking the sea in Hale Lana, Hawaii is a small manicured oasis amid the island’s volcanic rock. The collection of low-lying pavilions are connected by elevated wooden lanais and provide extended generous canopy for outdoor activity. A long rectangular pool imitates the elongated pavilions in their style and simplicity, and like the rest of the resort, exists in explicit contradiction to the natural landscape. On one end, the pool even extends beyond the edge of the volcanic slope. It’s a clear statement that purity of form will not be compromised for to adapt to the topographical reality.
Villa AT
By Saunders Architecture, Kristiansand, Norway


Photos by Bent René Synnevåg and Saunders Architecture
This elegantly curving home overlooking a rocky coast in Kristiansand, Norway seems to echo the waves of the sea below by its free-flowing nature. The new pool that separates these two elements, however, presents a controlled contrast to the choppy water of the sea. It’s a peaceful, safe swimming area framed by weathered wood that satisfies the urge to bathe without the perils of unchecked nature.
XXXL’s House
By Brengues Le Pavec architects, France
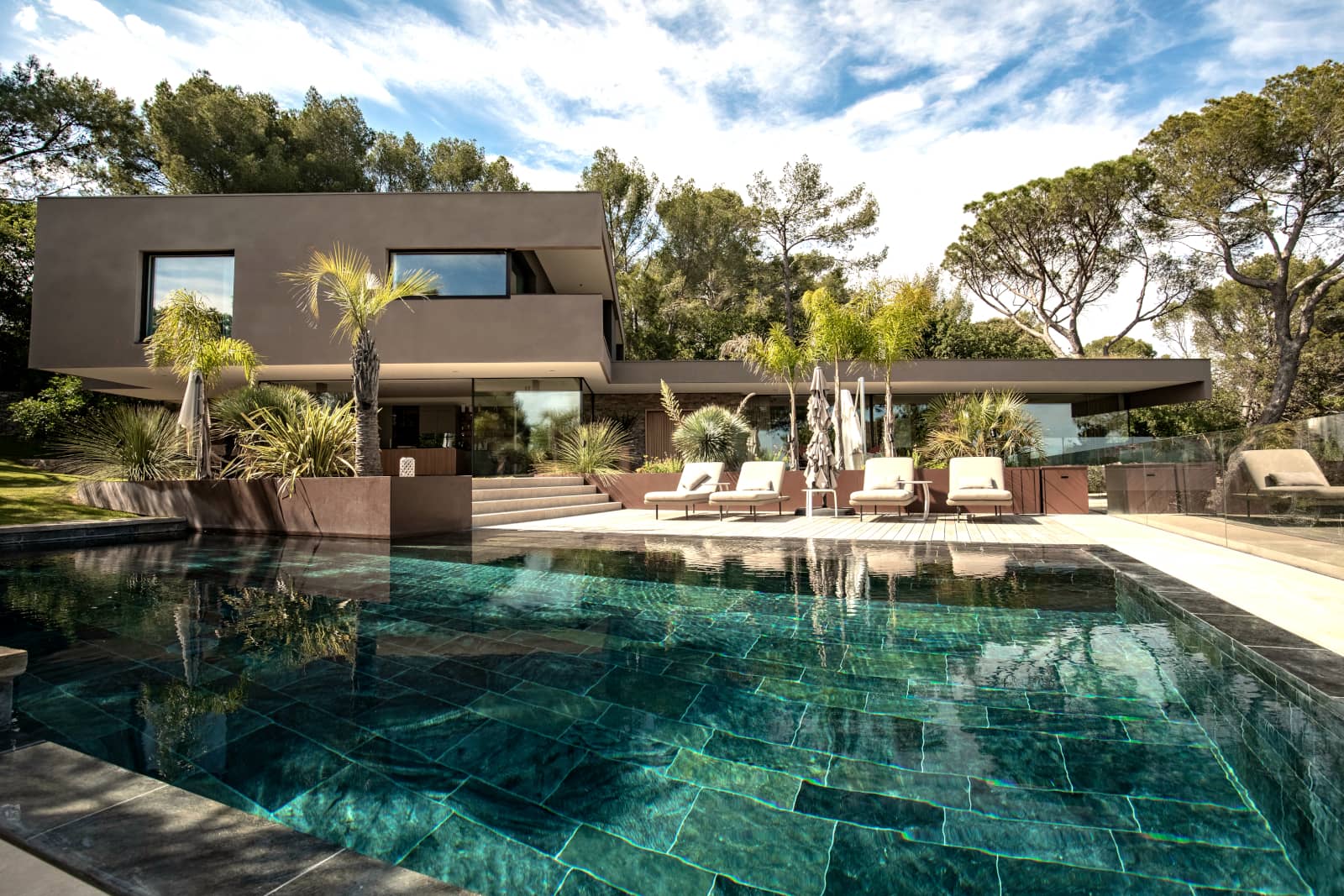

 Resting near the top of a hill in France, this new house takes advantage of the lot’s sloping angle to experiment with layering; from the house’s overlapping volumes to the stone walls guiding visitors down to it. As such, the house’s top floor acts like a belvedere overlooking the landscape further out. But right underneath it is the true surprise: a large tile-clad pool partly shaded by the diverse flora and from which visitors can continue enjoying the view in their bathing suits.
Resting near the top of a hill in France, this new house takes advantage of the lot’s sloping angle to experiment with layering; from the house’s overlapping volumes to the stone walls guiding visitors down to it. As such, the house’s top floor acts like a belvedere overlooking the landscape further out. But right underneath it is the true surprise: a large tile-clad pool partly shaded by the diverse flora and from which visitors can continue enjoying the view in their bathing suits.
Meditation Pavilion & Garden
By GMAA – GM Architectes Associés, Geneva, Switzerland

 For this new pavilion in Geneva, GMAA – GM Architectes Associés had envisioned a wooden volume gently hovering above a water surface. Their final project achieves this vision with a subtly integrated pool — more closely akin to a pond — that turns into a perfect mirror on windless days. As opposed to the natural ponds on the pavilions’ grounds, this artificial one is kept spotless; a pure and perfect counterpart to the surrounding nature, reflecting and emphasizing the beauty around.
For this new pavilion in Geneva, GMAA – GM Architectes Associés had envisioned a wooden volume gently hovering above a water surface. Their final project achieves this vision with a subtly integrated pool — more closely akin to a pond — that turns into a perfect mirror on windless days. As opposed to the natural ponds on the pavilions’ grounds, this artificial one is kept spotless; a pure and perfect counterpart to the surrounding nature, reflecting and emphasizing the beauty around.
Browse the Architizer Jobs Board and apply for architecture and design positions at some of the world’s best firms. Click here to sign up for our Jobs Newsletter.
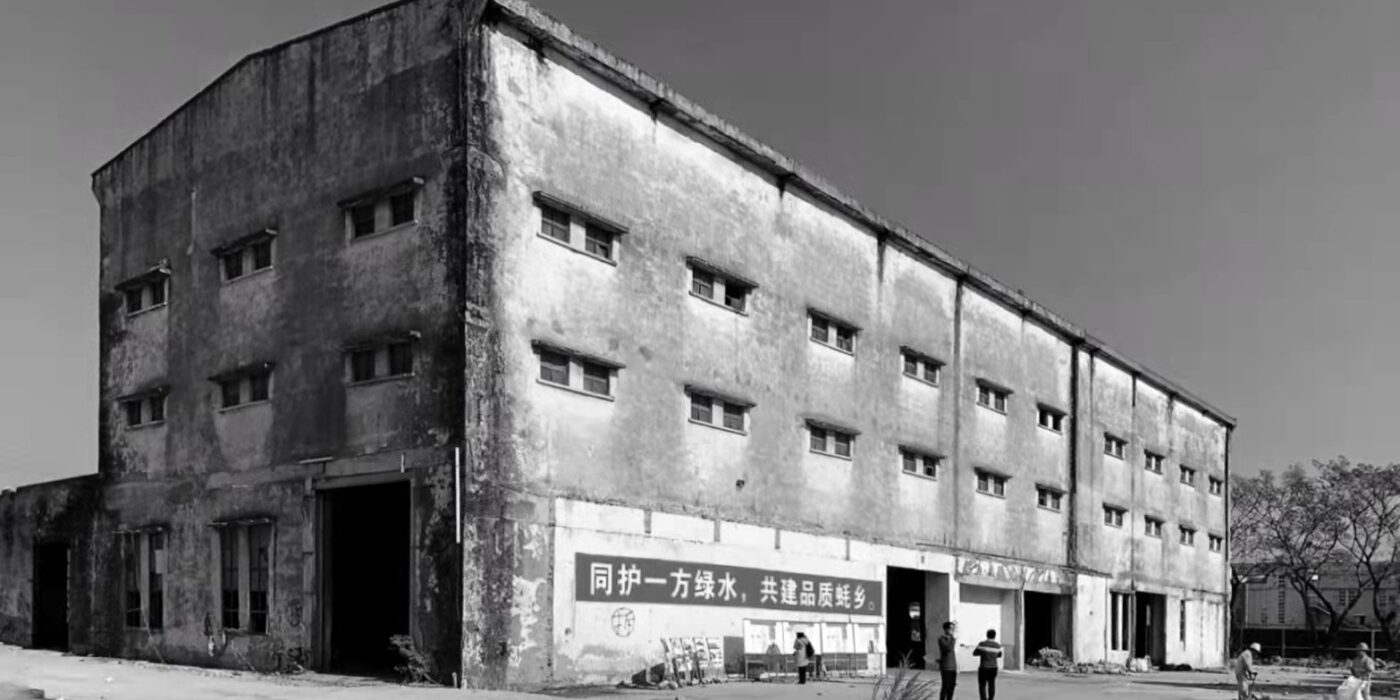
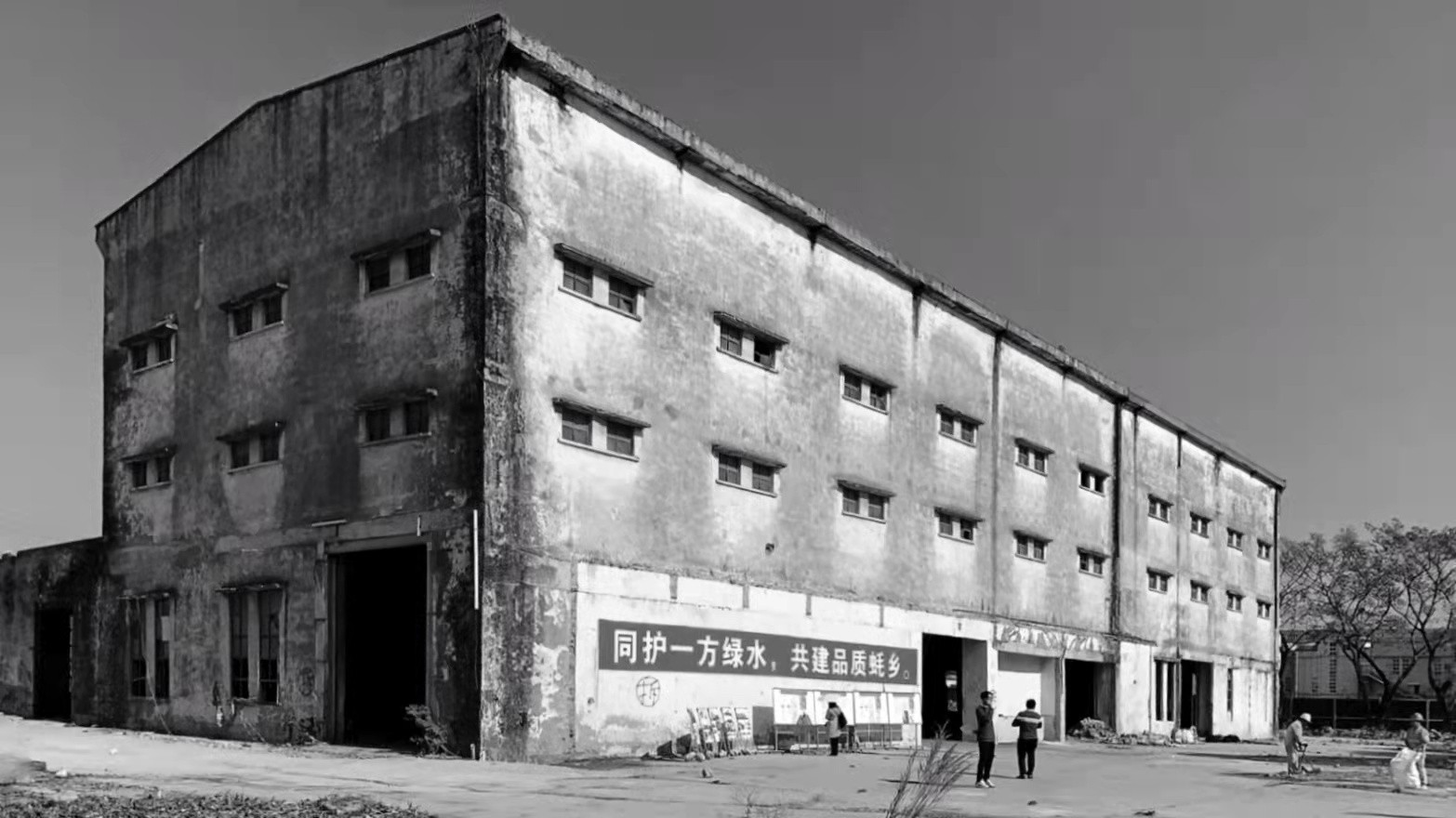
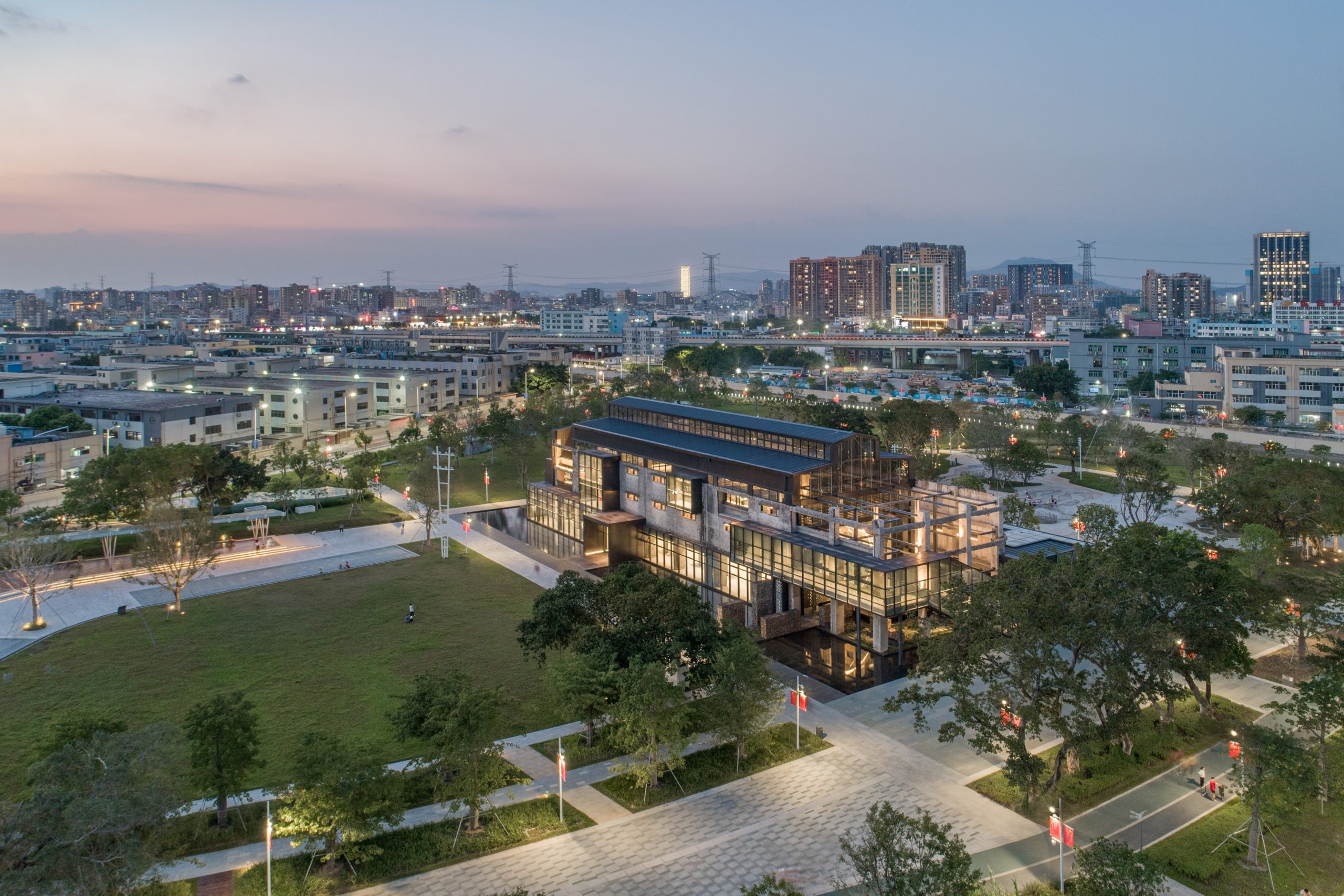
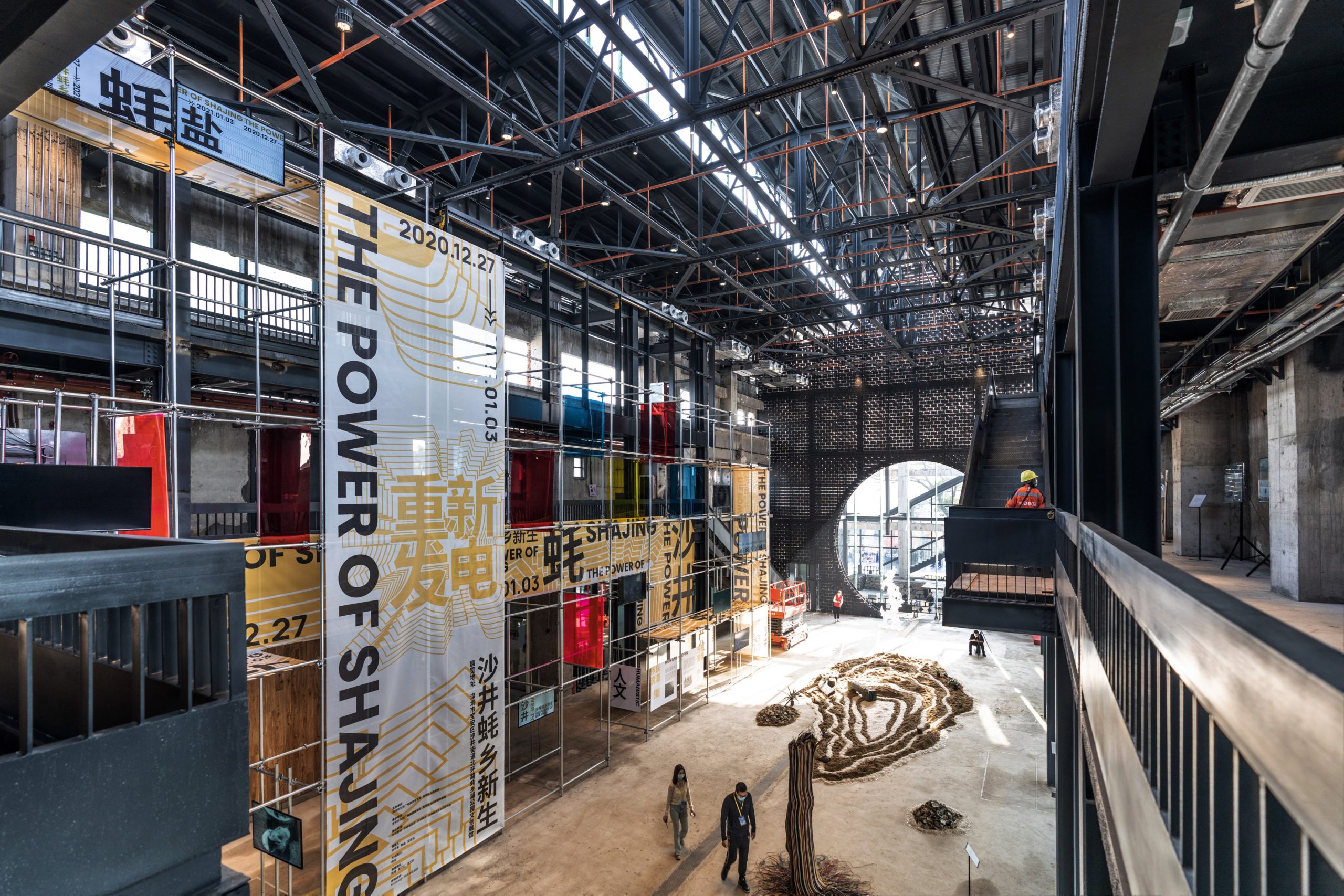
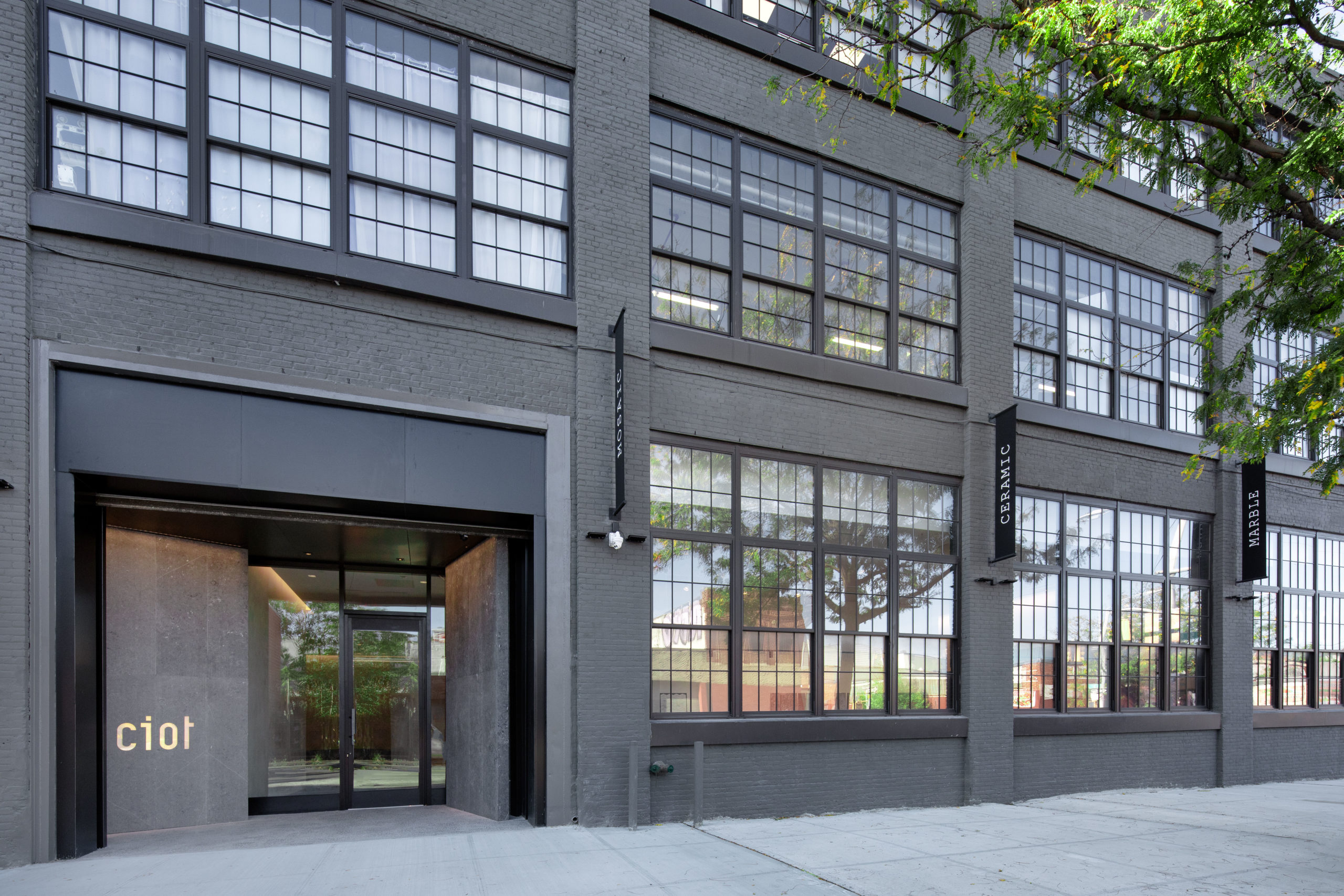
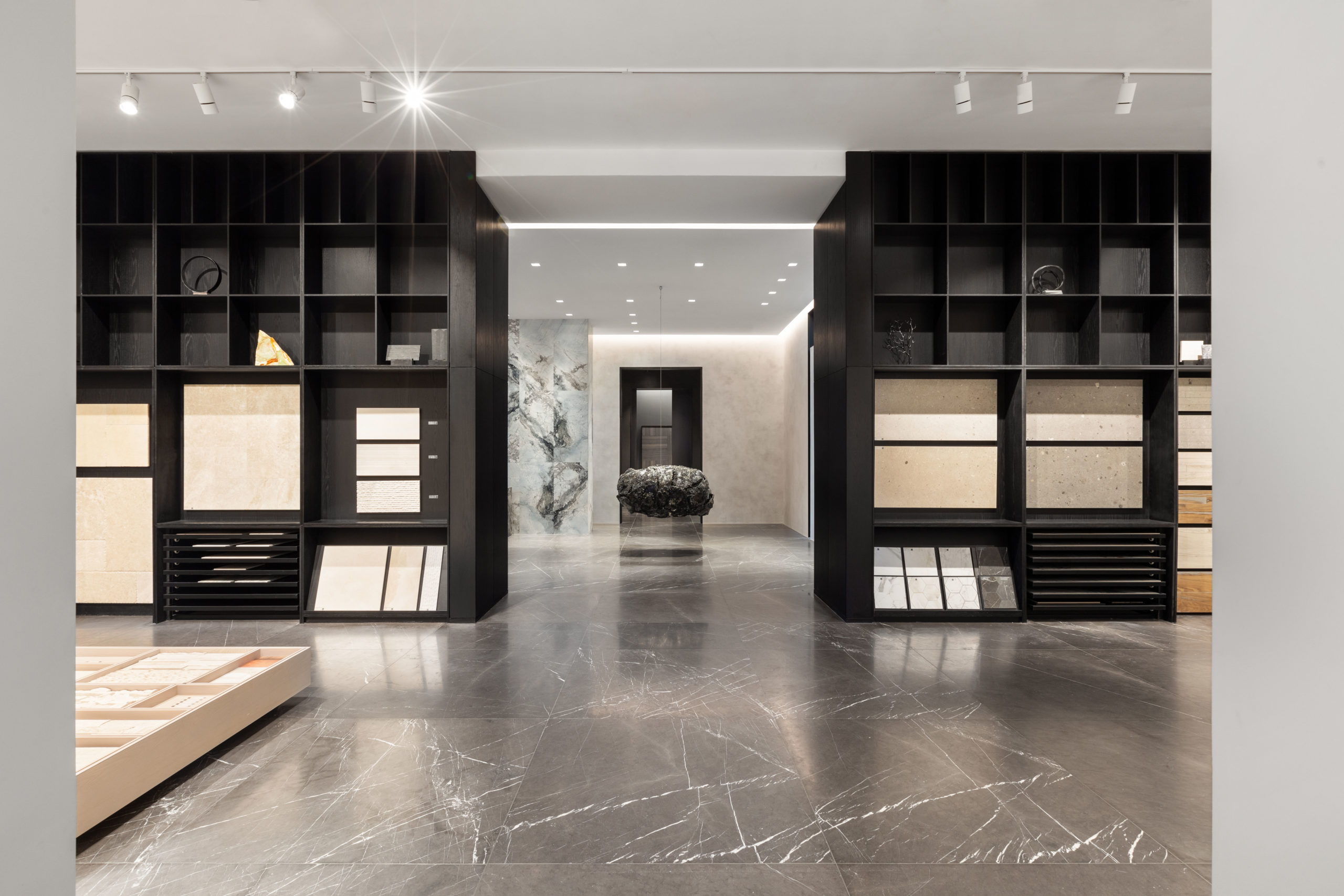






 In a former armaments factory on the Brooklyn waterfront, Montreal-based stone supplier Ciot has a new home designed by Bando x Seidel Meersseman. The beautiful slab gallery is unrecognizable from its past life, with a bright and meticulous showroom and gallery gaining an air of drama and sophistication under its mono-chromatic refurbishment.
In a former armaments factory on the Brooklyn waterfront, Montreal-based stone supplier Ciot has a new home designed by Bando x Seidel Meersseman. The beautiful slab gallery is unrecognizable from its past life, with a bright and meticulous showroom and gallery gaining an air of drama and sophistication under its mono-chromatic refurbishment.
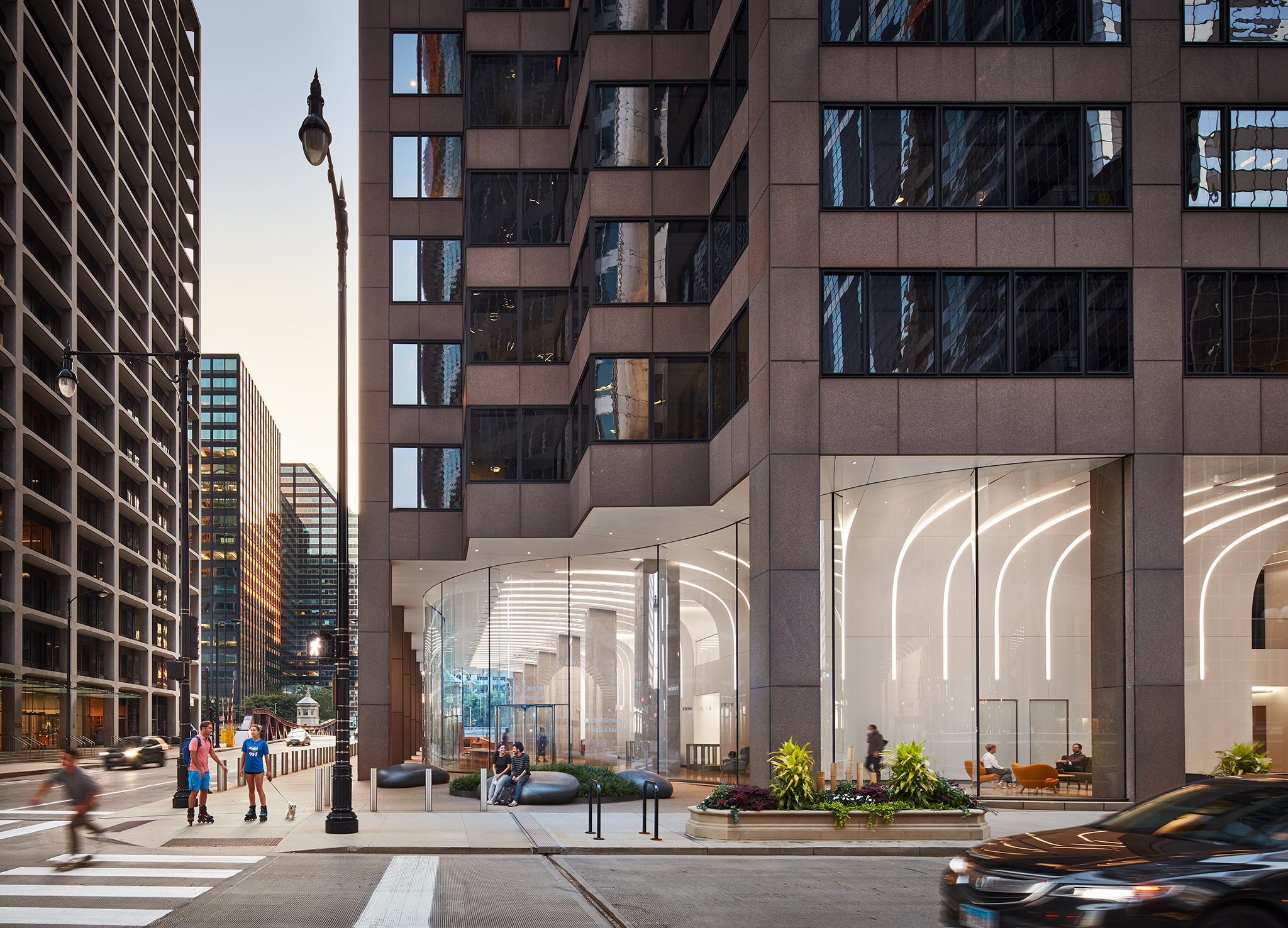
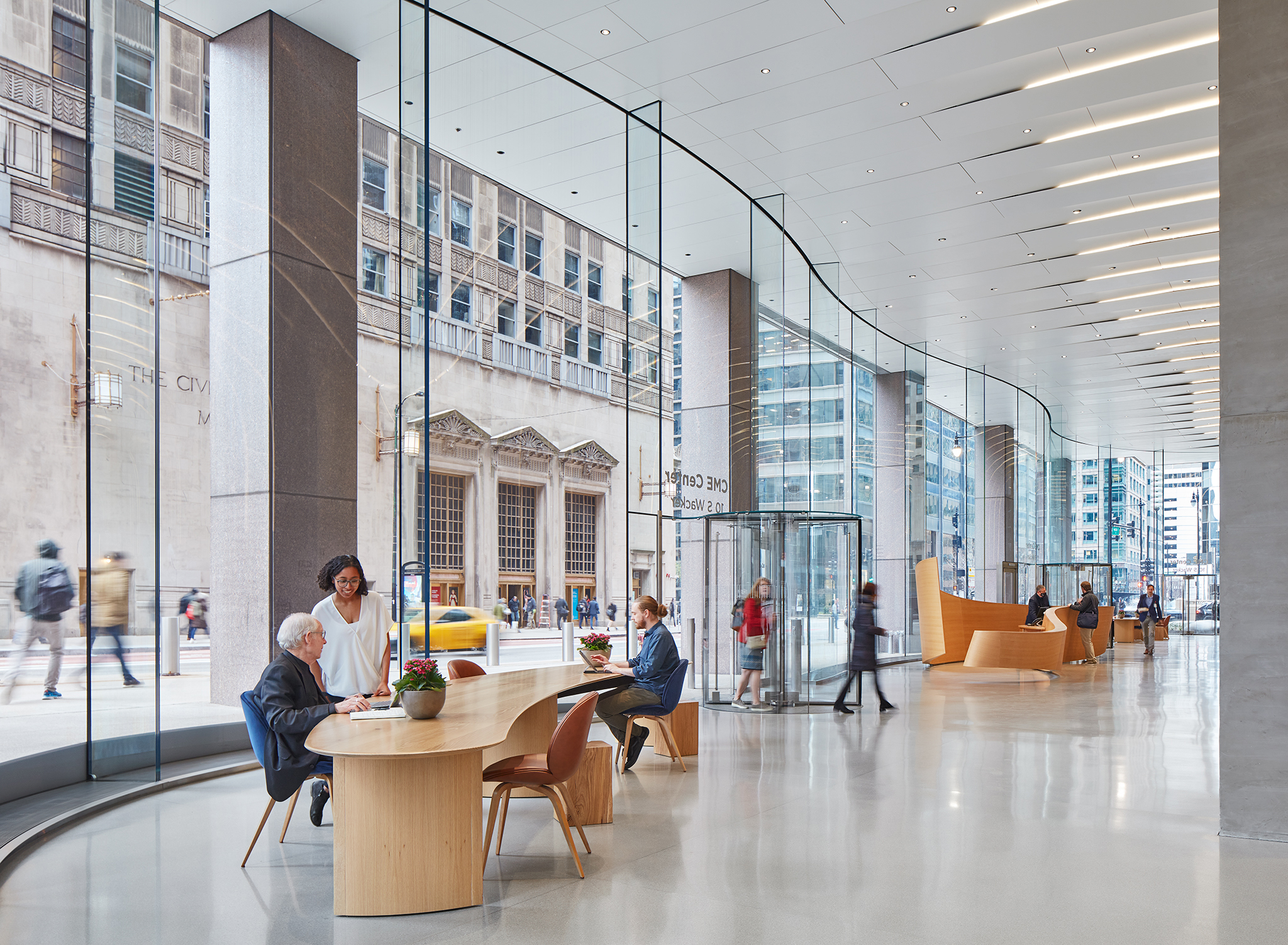
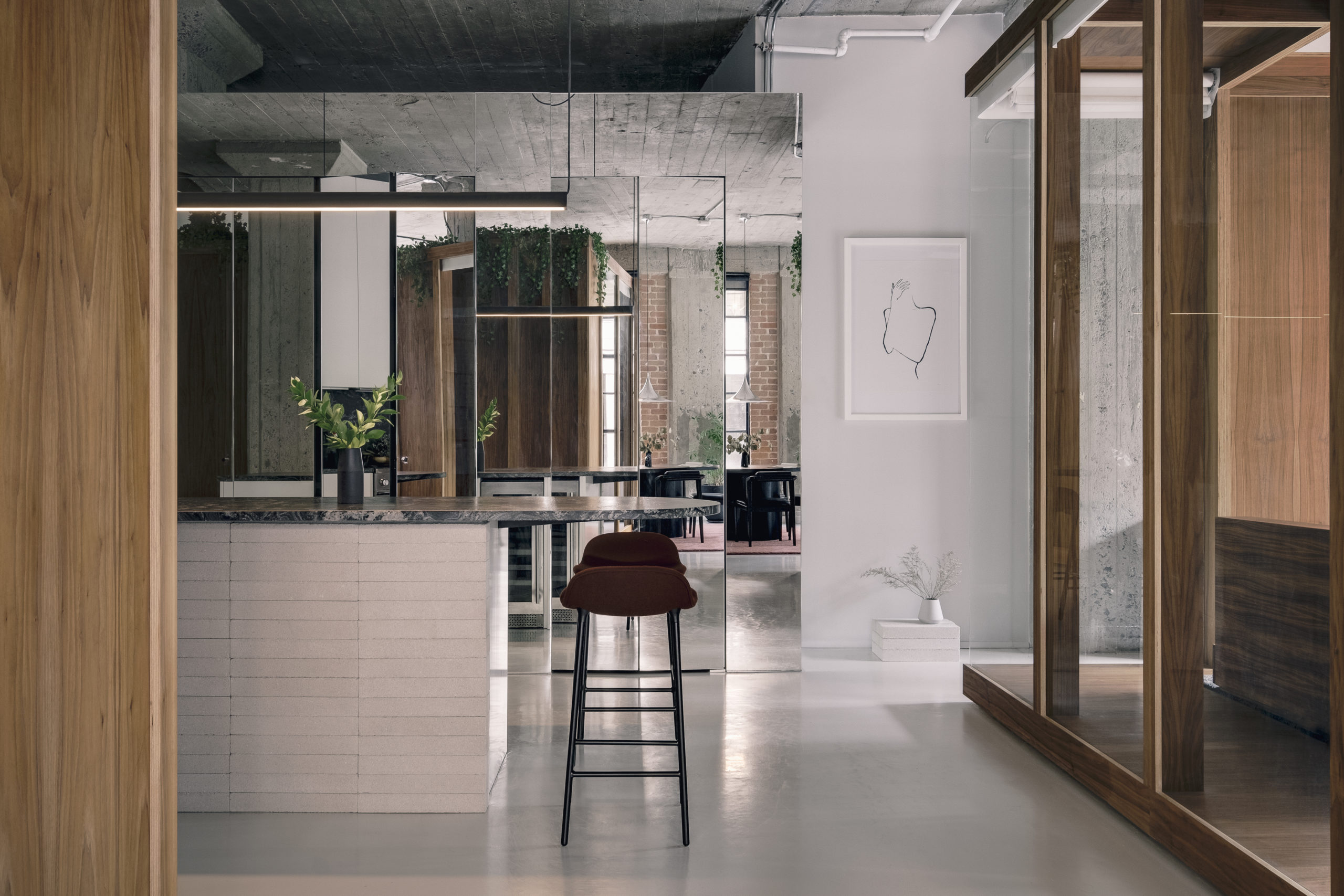
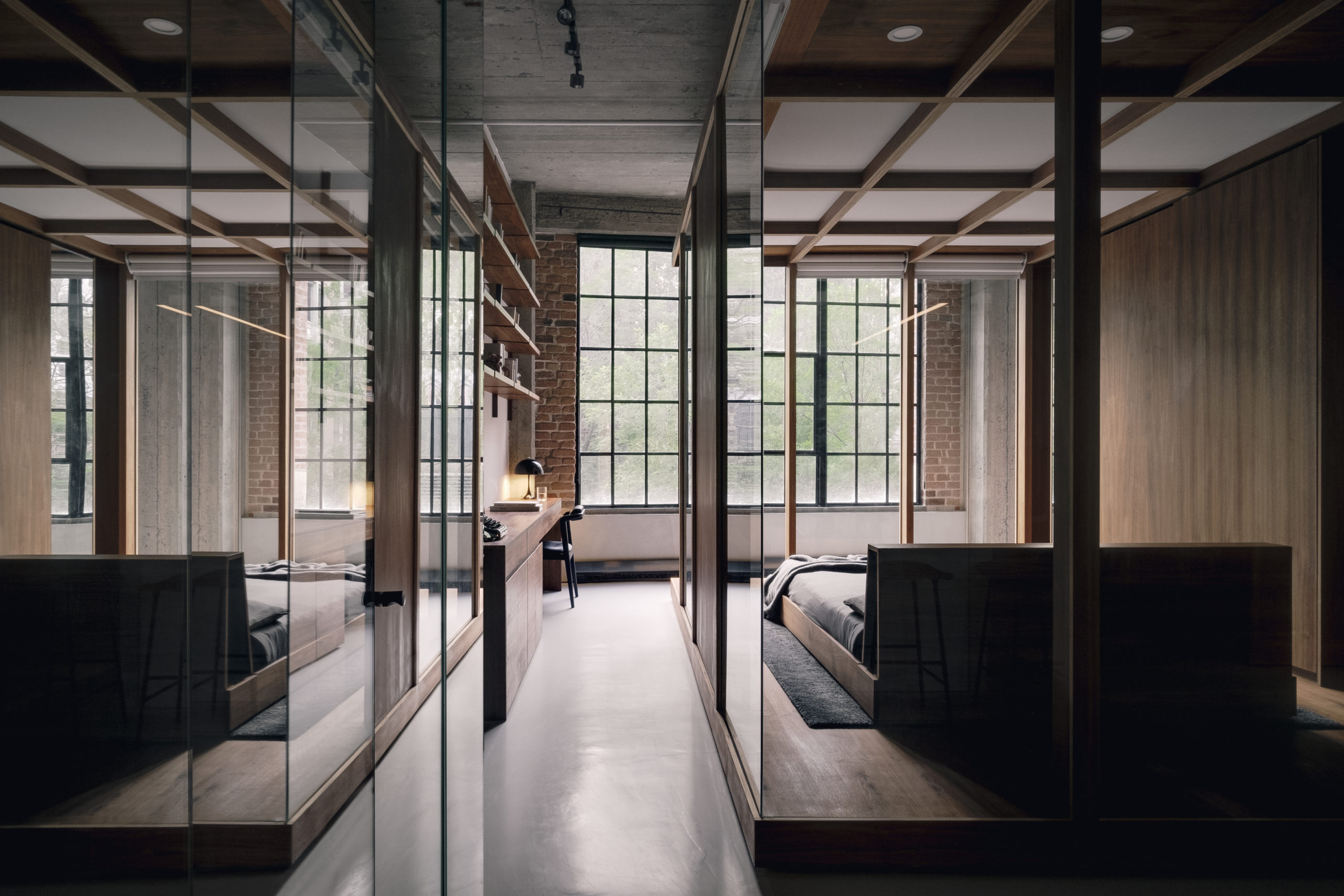
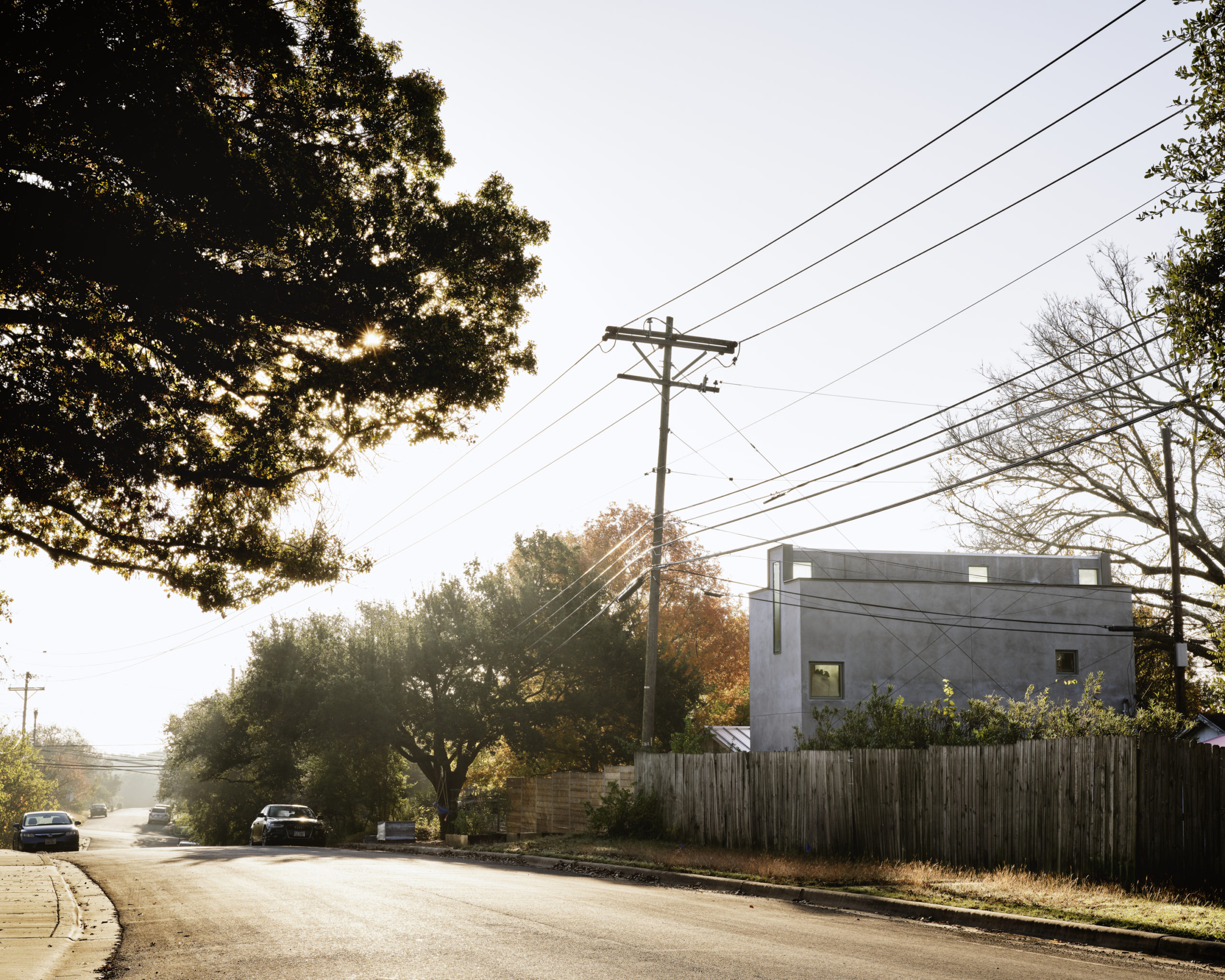
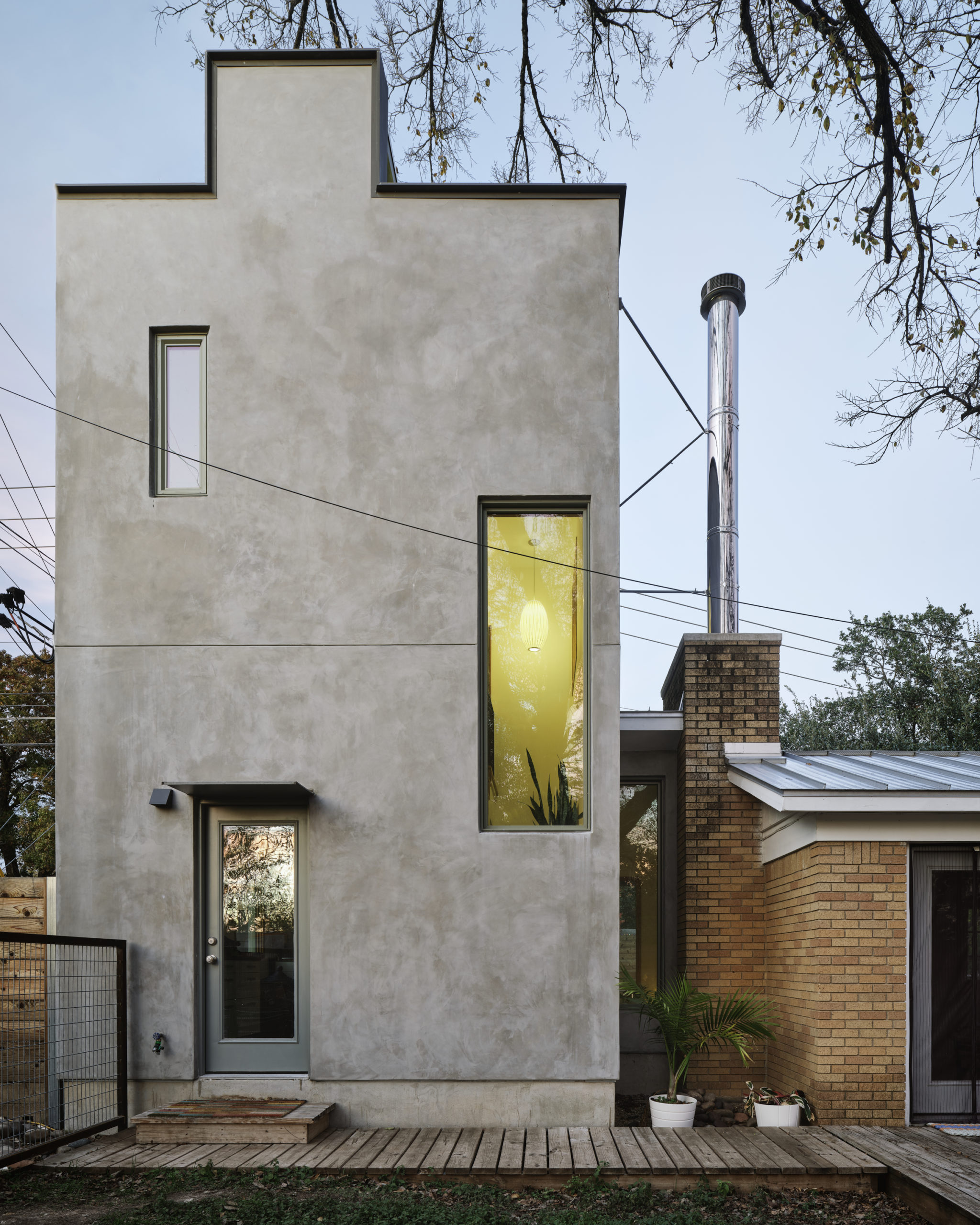





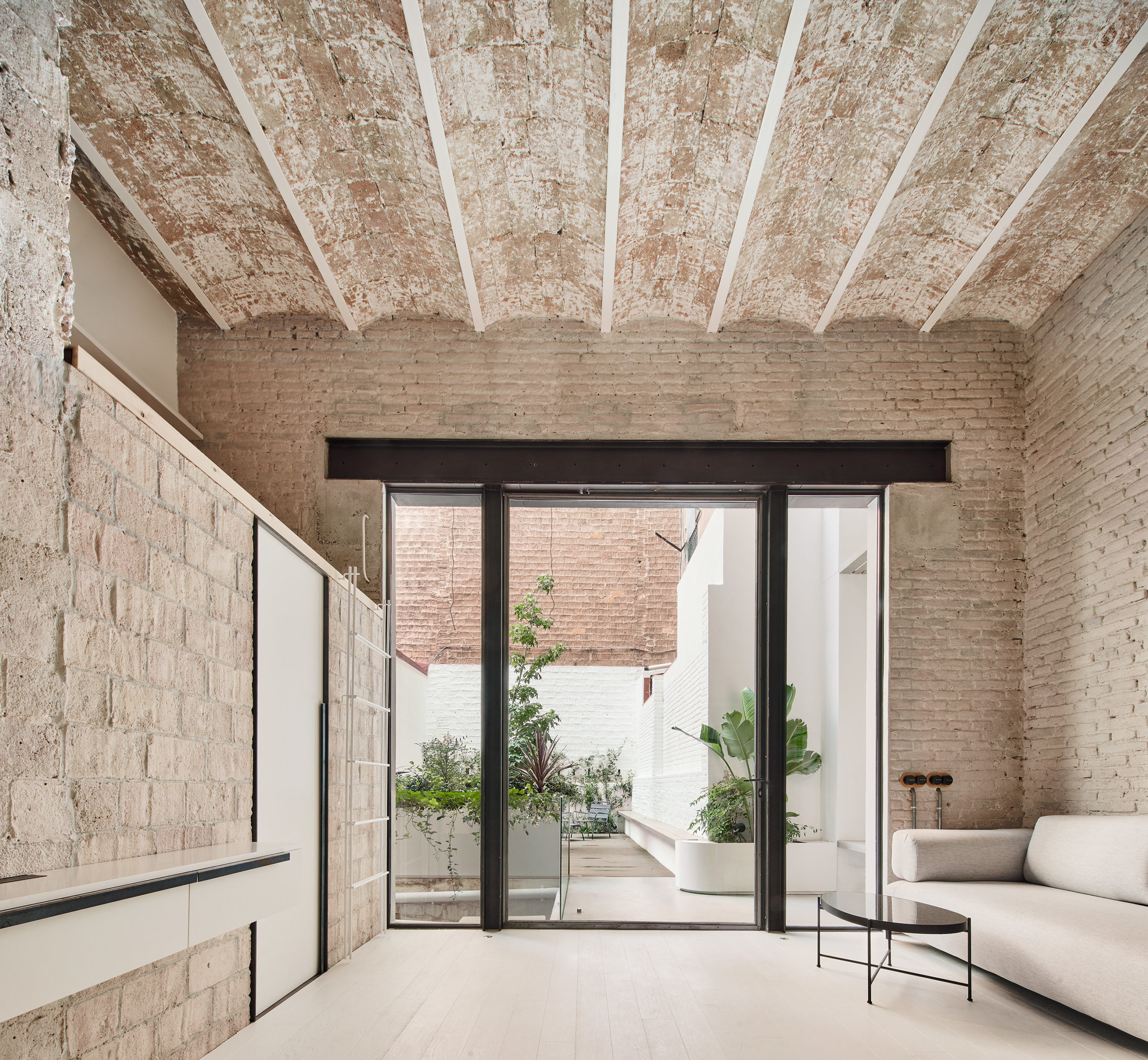
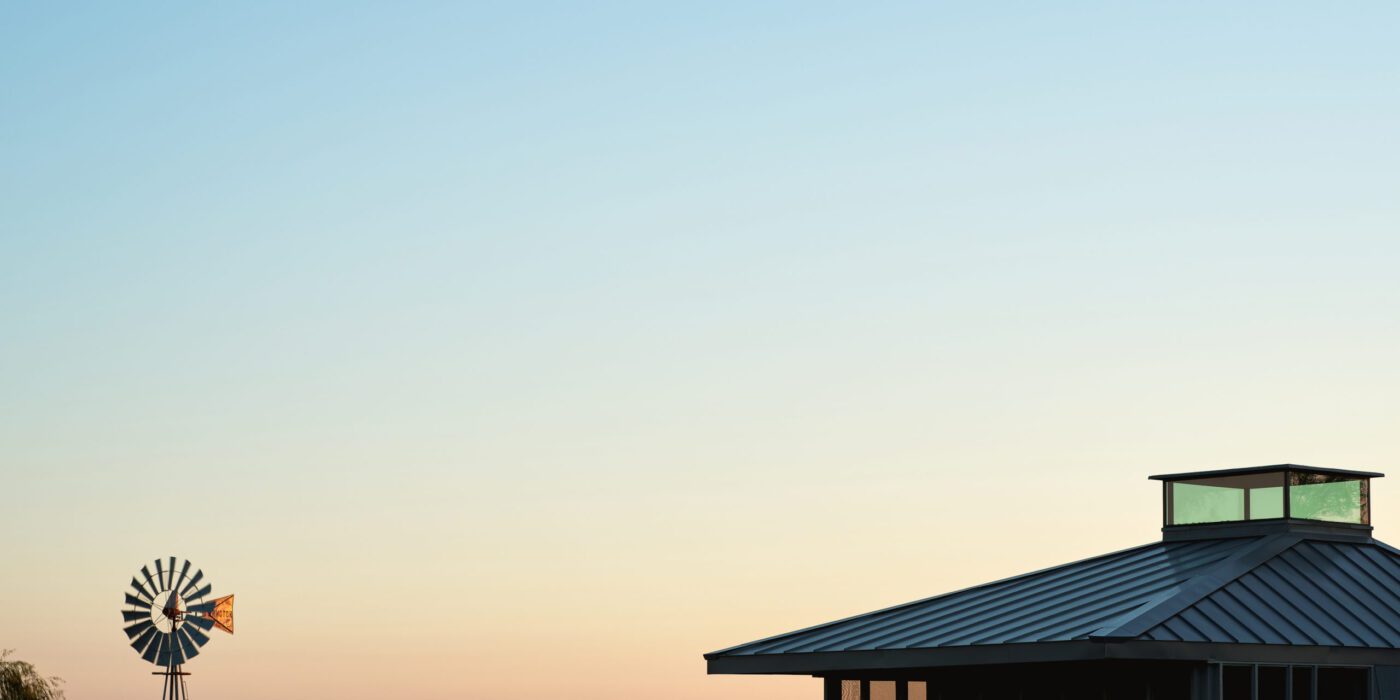
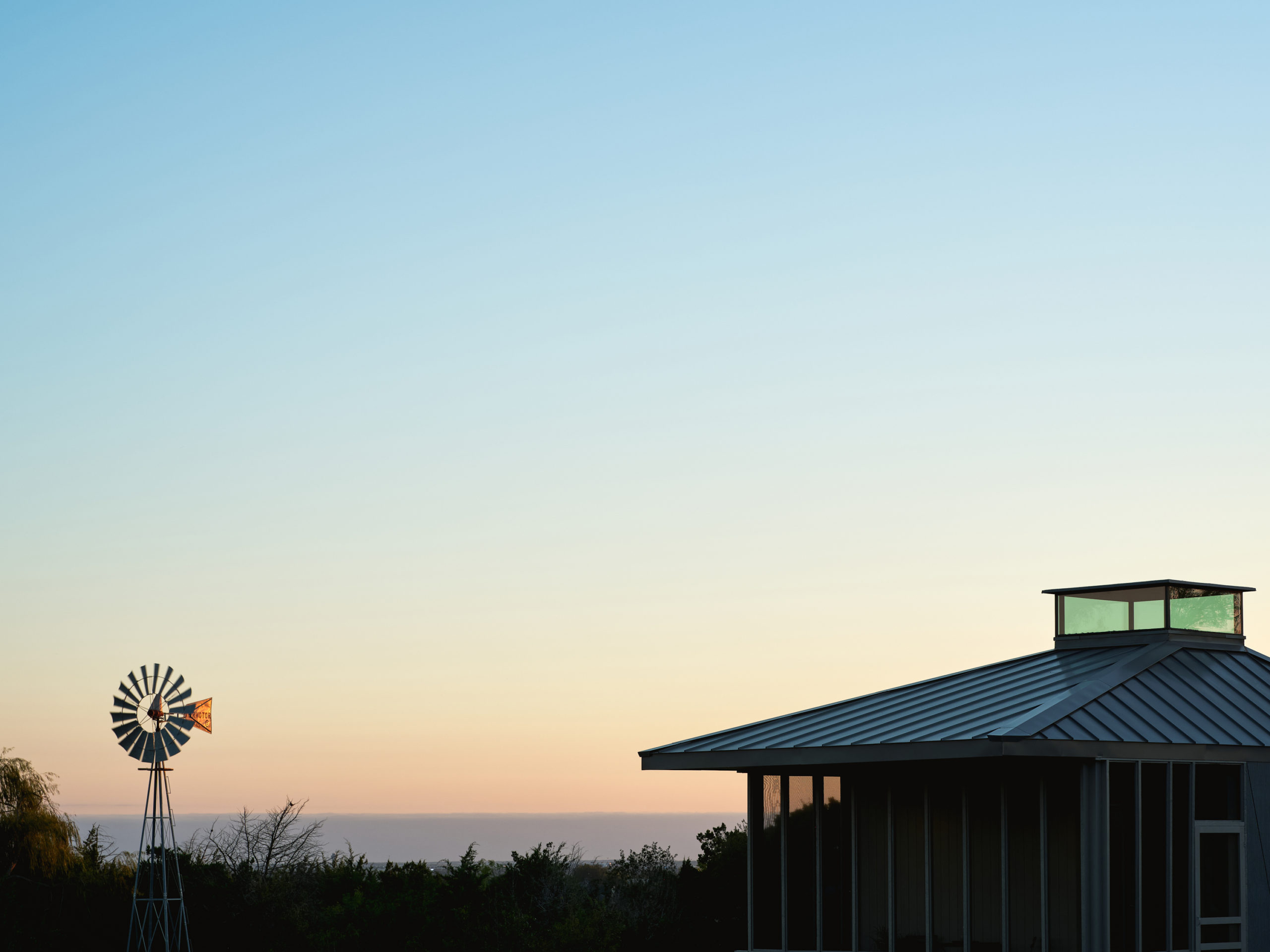
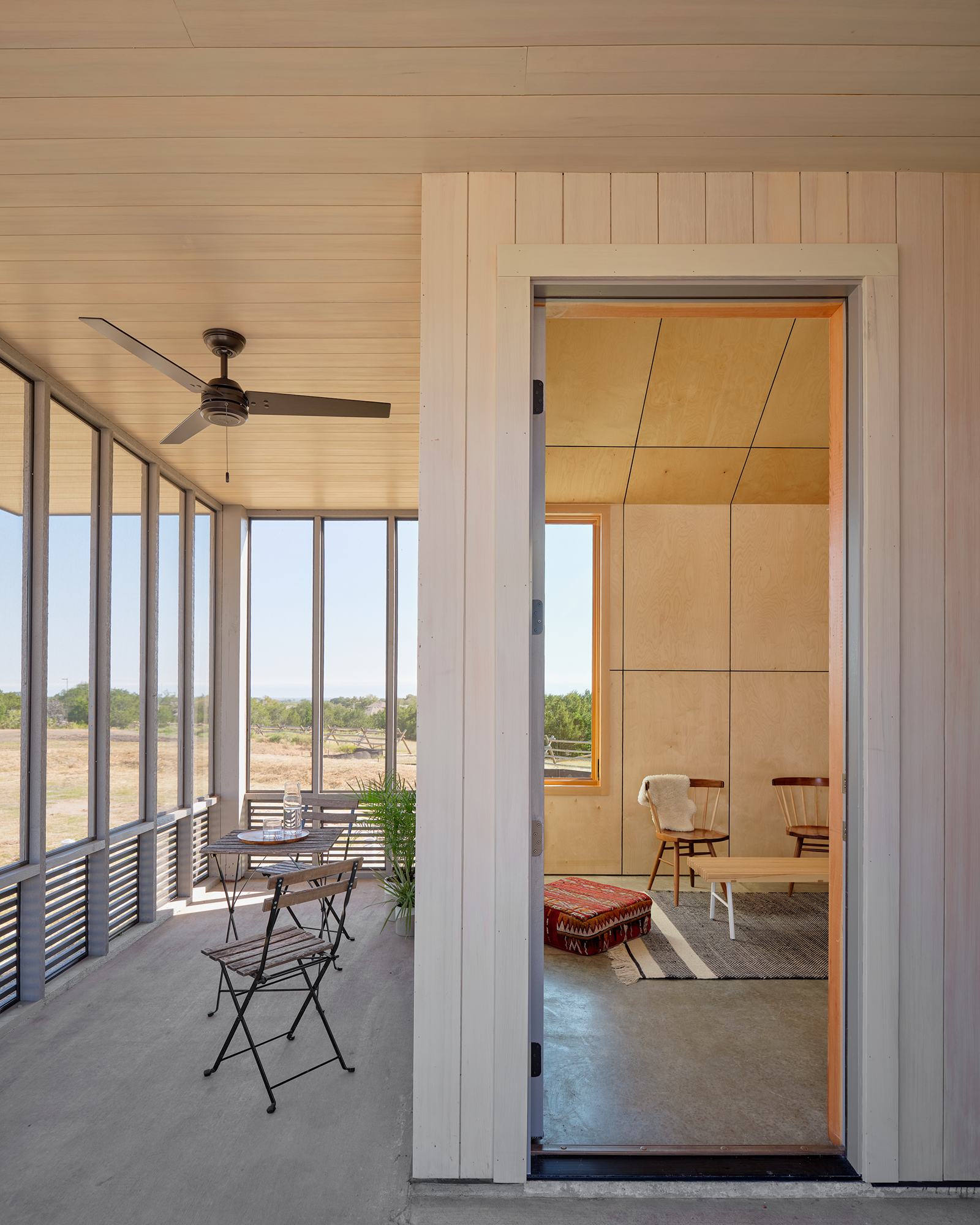
 South 2nd is a surprising addition to an existing single-story American ranch house. The new 900-square-foot building is connected to the current house through an adjacent link and contains home offices on the ground floor and a further bedroom and bathroom suite above.
South 2nd is a surprising addition to an existing single-story American ranch house. The new 900-square-foot building is connected to the current house through an adjacent link and contains home offices on the ground floor and a further bedroom and bathroom suite above.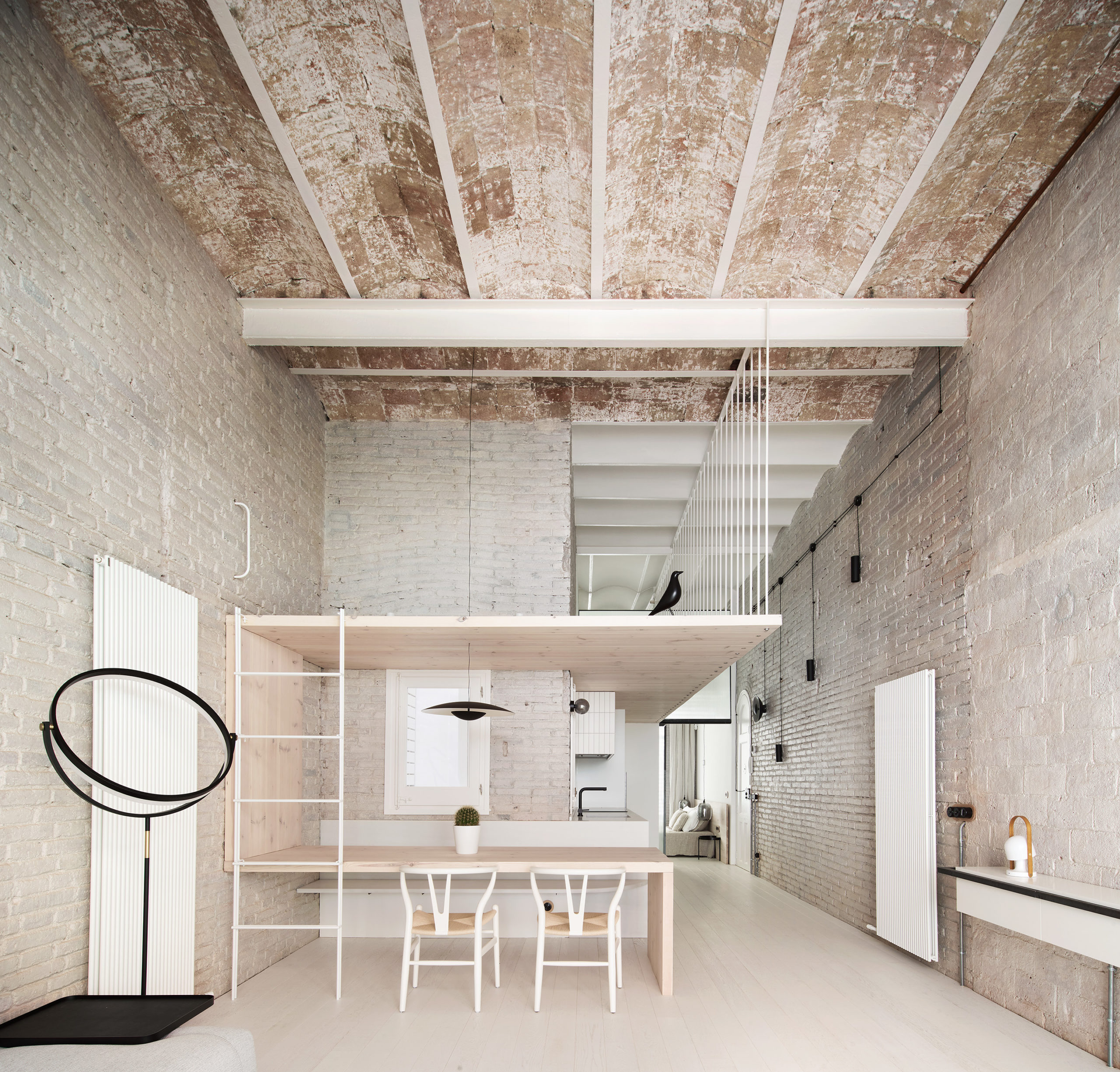
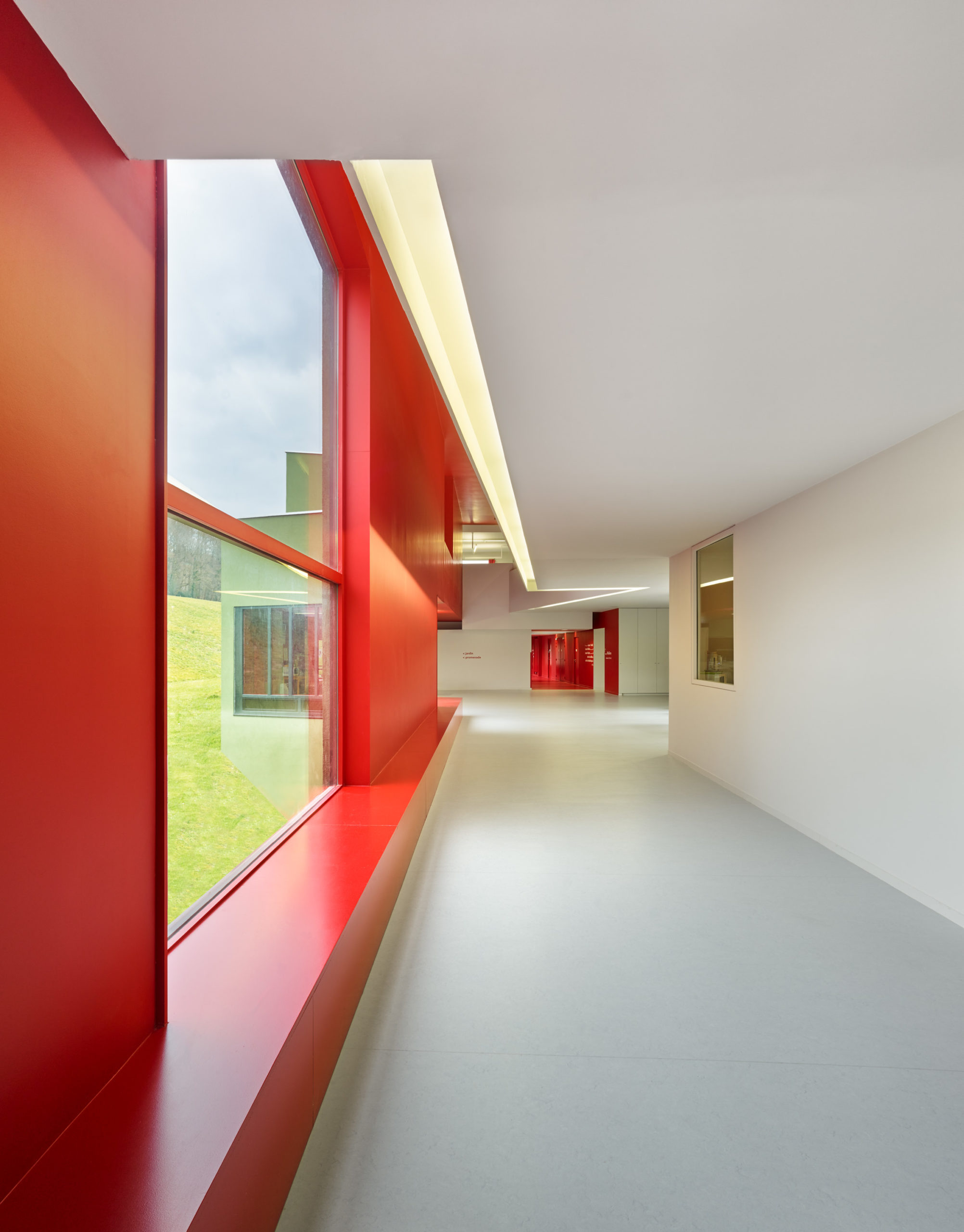
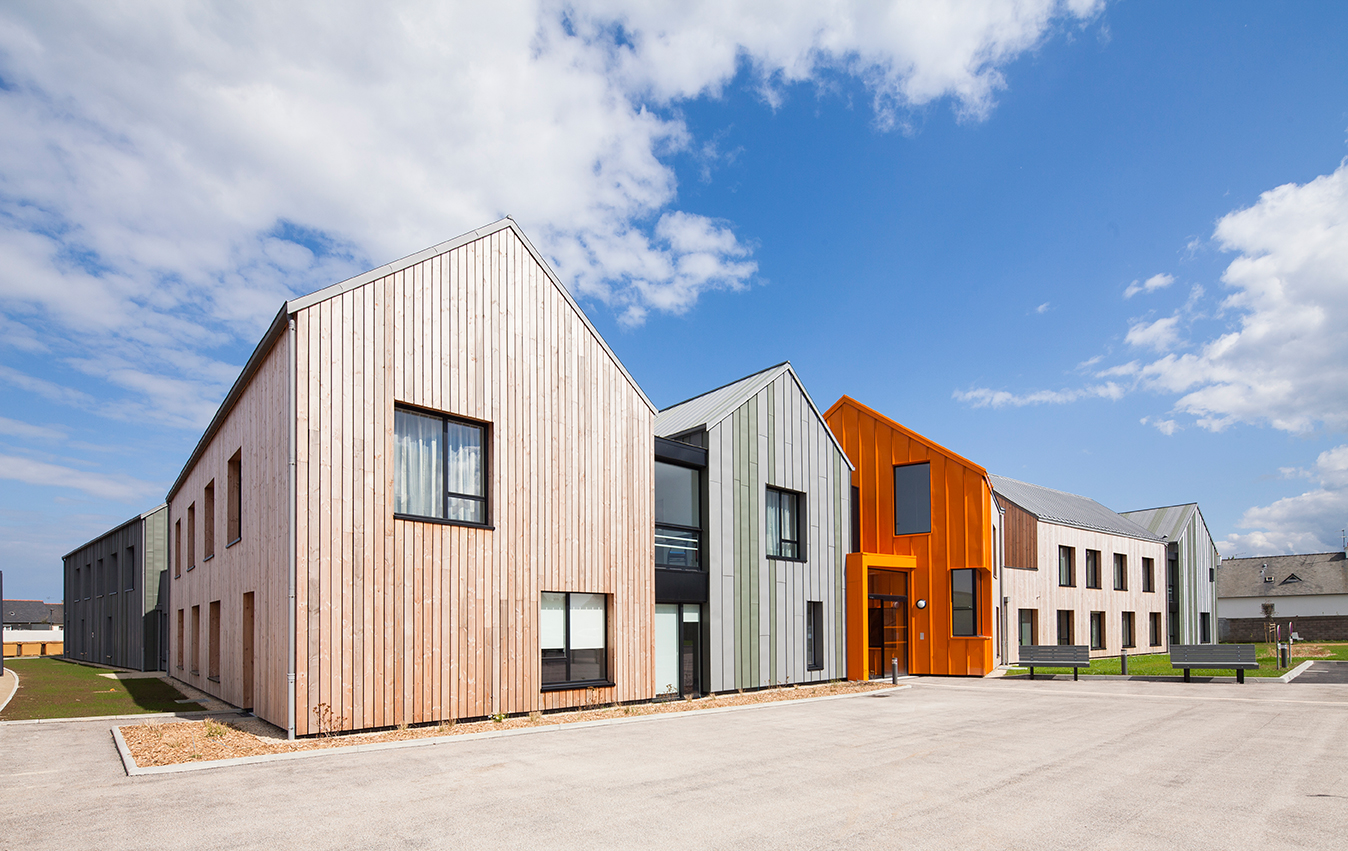
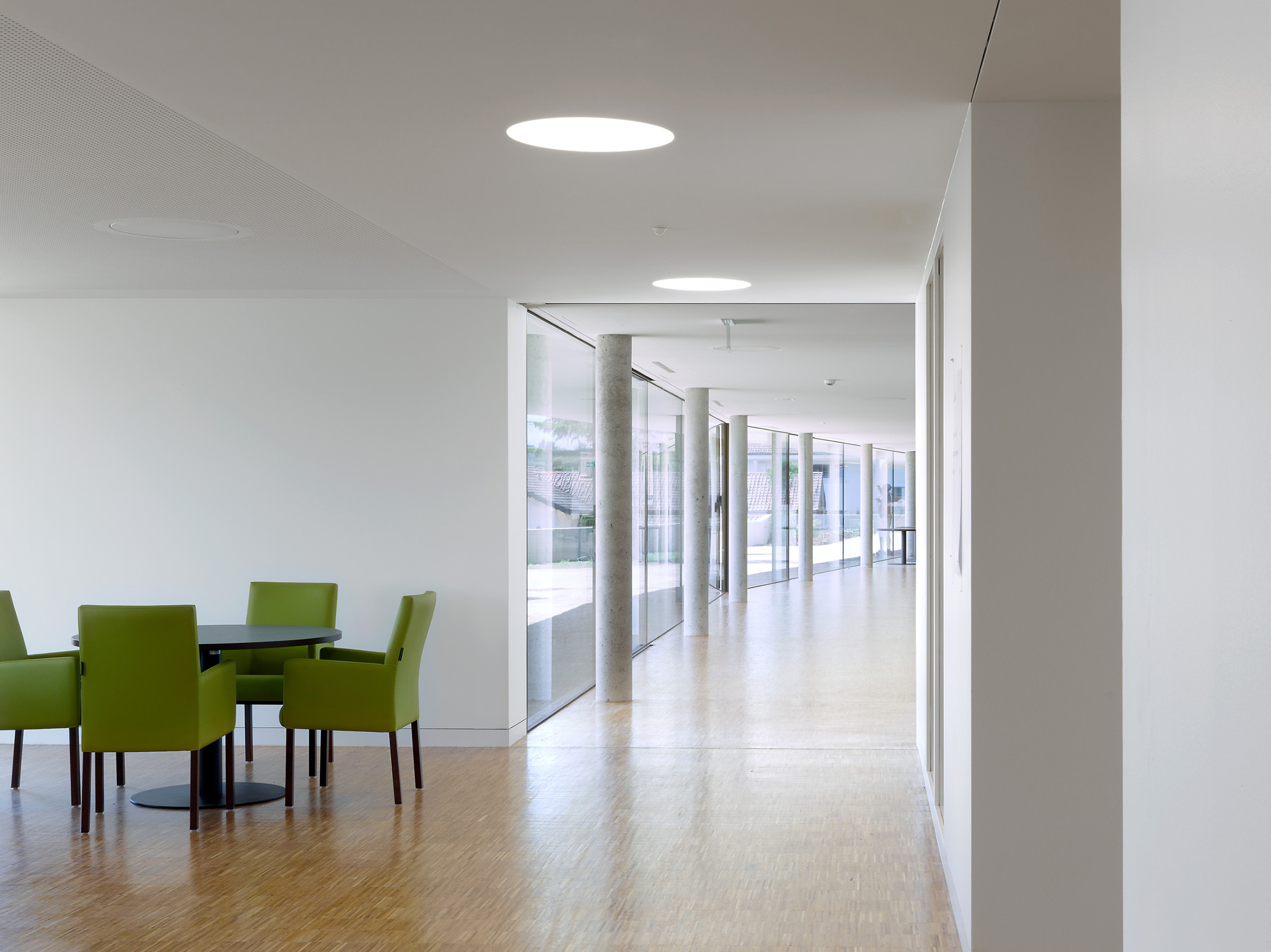
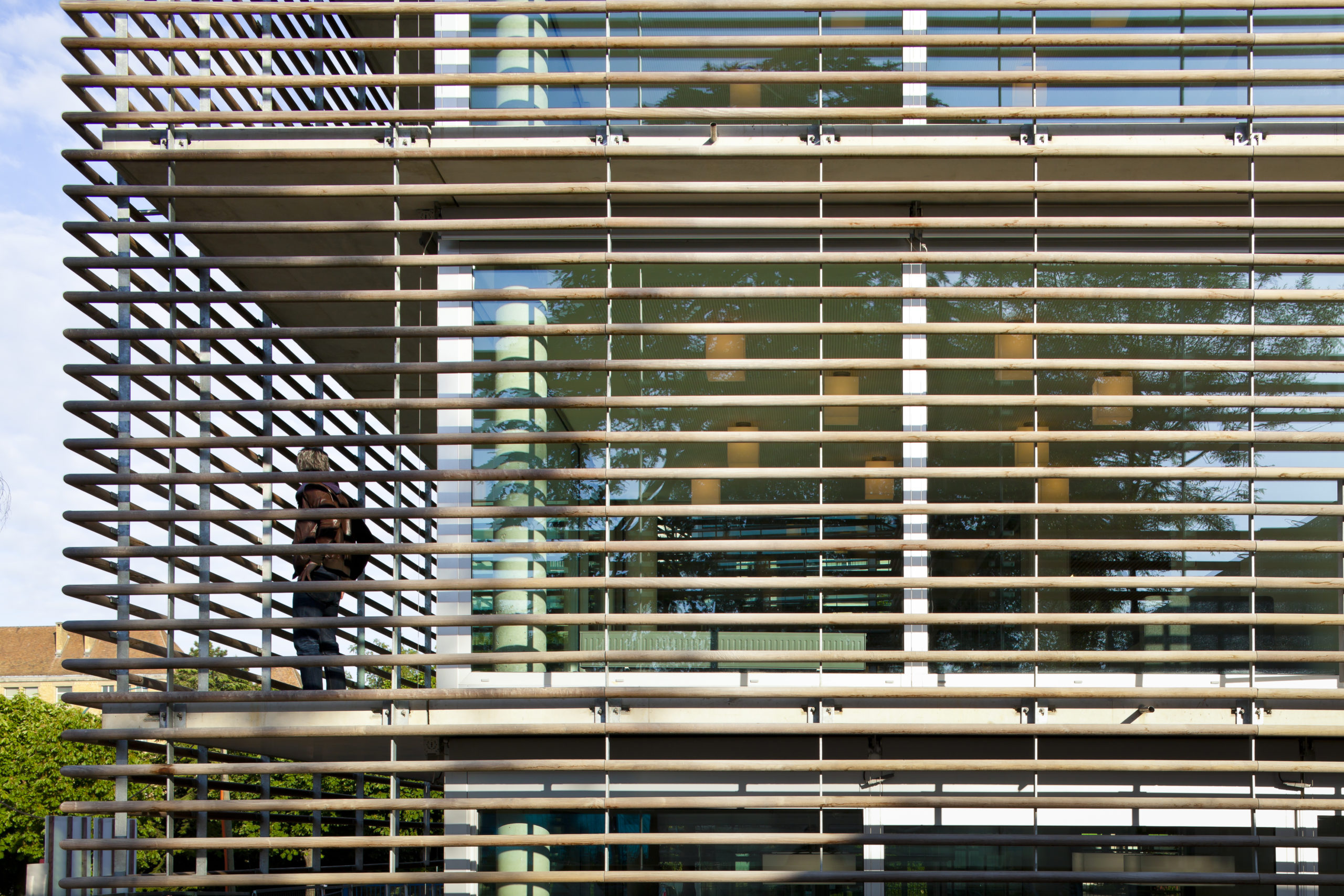
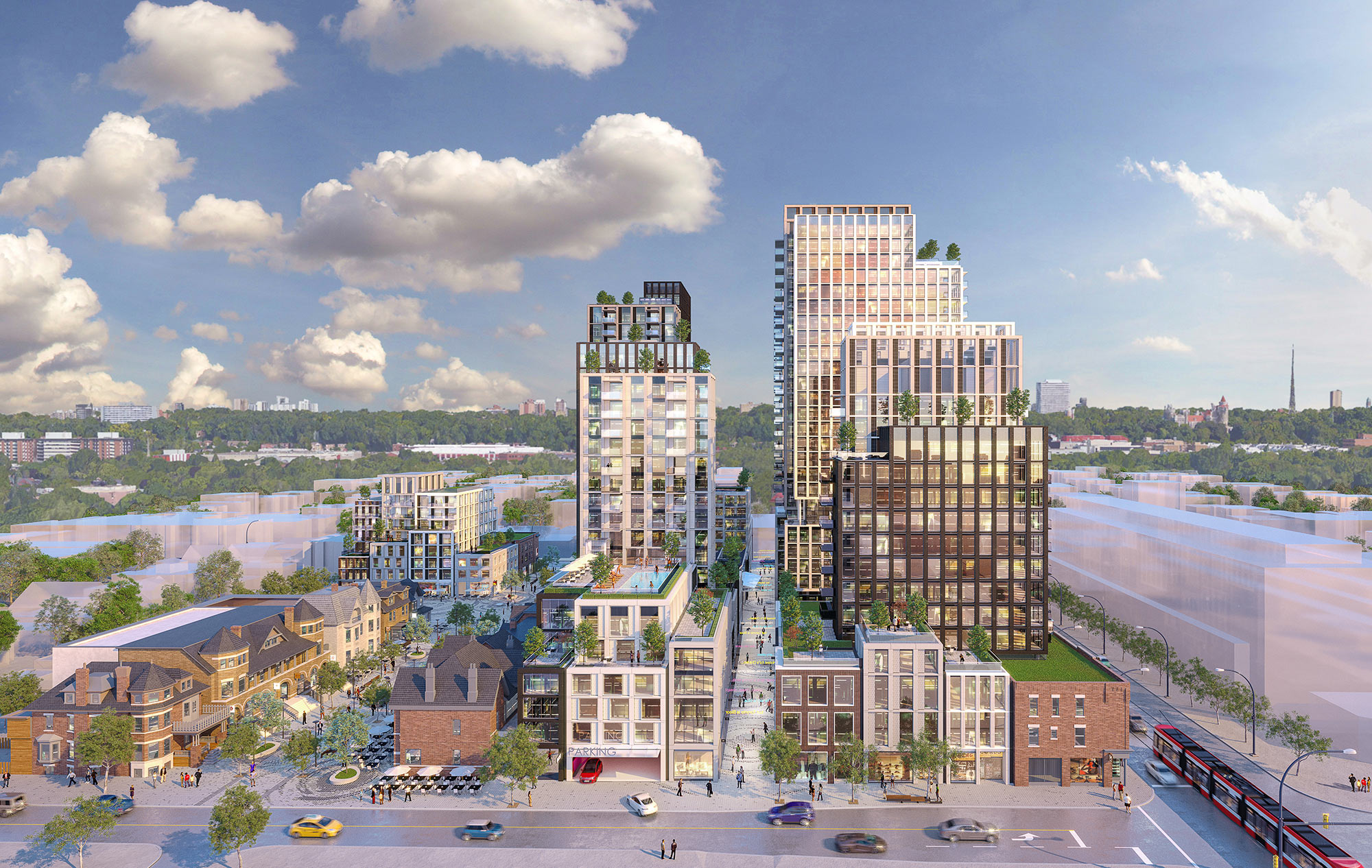
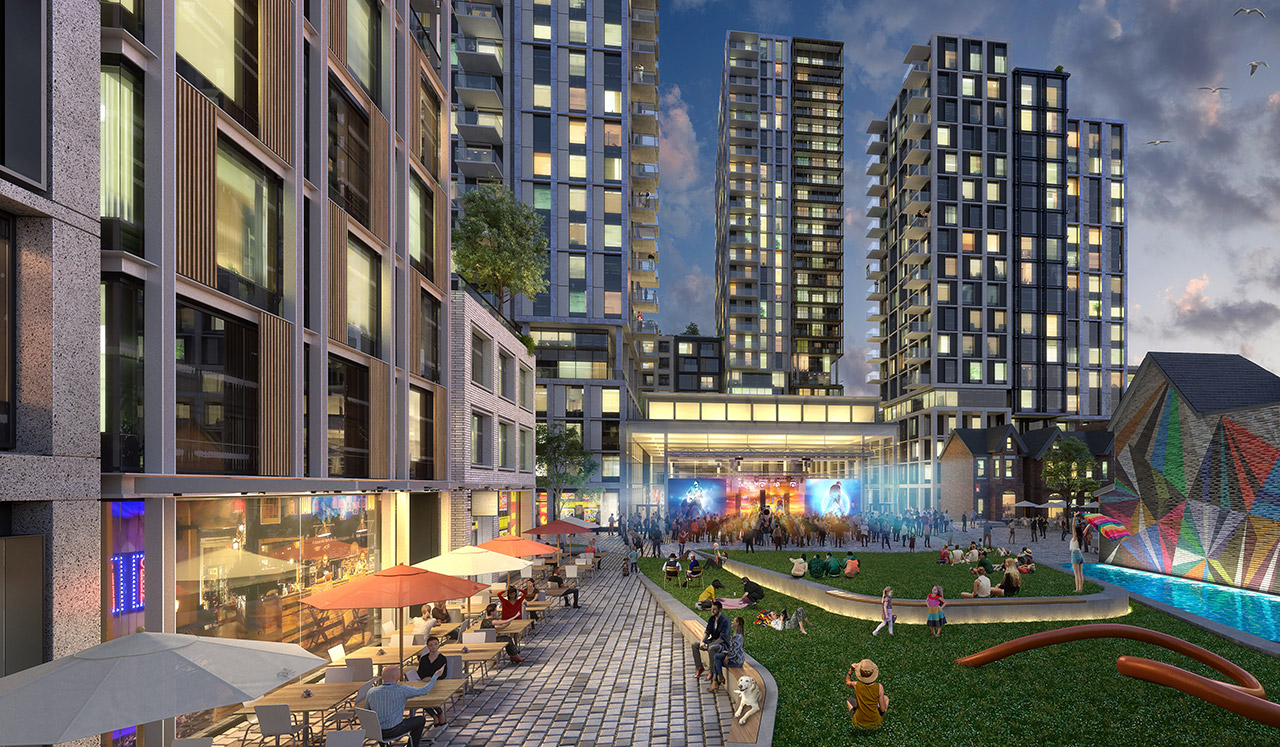























 Built on the site of Honest Ed’s, an eclectic discount store that was once a landmark to the people of Toronto, the newly imagined Mirvish Village will be a comprehensive purpose-built community for rental apartments and innovative retail. Mirvish Village will comprise 32 micro buildings and eventually be home to over 2,000 Torontonians. All 800 suites will be rented, with some apartments available below-market rates and almost half designed for families.
Built on the site of Honest Ed’s, an eclectic discount store that was once a landmark to the people of Toronto, the newly imagined Mirvish Village will be a comprehensive purpose-built community for rental apartments and innovative retail. Mirvish Village will comprise 32 micro buildings and eventually be home to over 2,000 Torontonians. All 800 suites will be rented, with some apartments available below-market rates and almost half designed for families.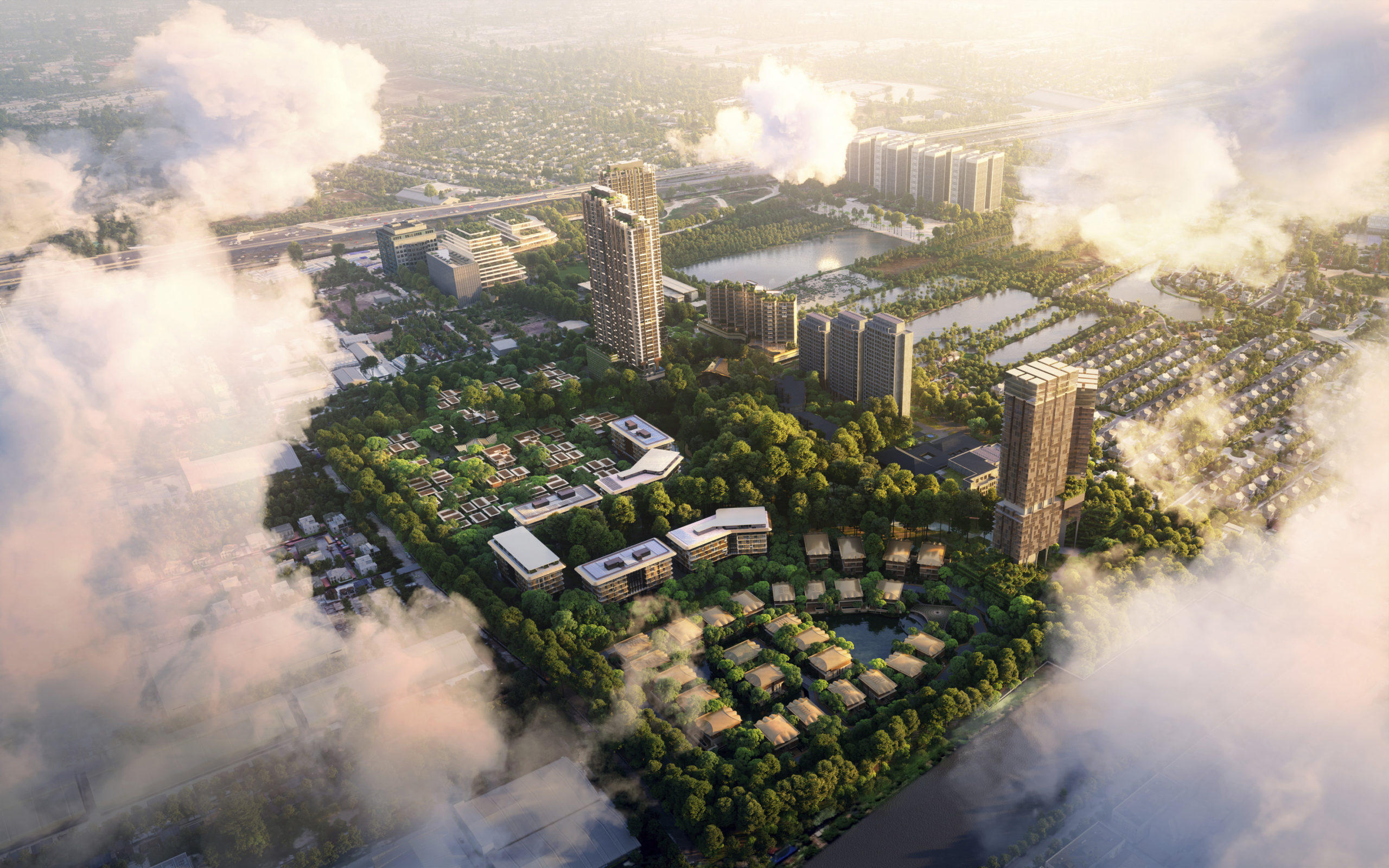 Situated on the outskirts of Bangkok, The Forestias is a residential-led masterplan with a substantial forest at its heart. The pioneering development aims to become an example and a template for future urban living in Thailand and globally. Lush greenery dissects the urban development that hosts a variety of housing types. The development creates shared facilities that encourage community interaction by visually reducing boundary walls and hedges.
Situated on the outskirts of Bangkok, The Forestias is a residential-led masterplan with a substantial forest at its heart. The pioneering development aims to become an example and a template for future urban living in Thailand and globally. Lush greenery dissects the urban development that hosts a variety of housing types. The development creates shared facilities that encourage community interaction by visually reducing boundary walls and hedges.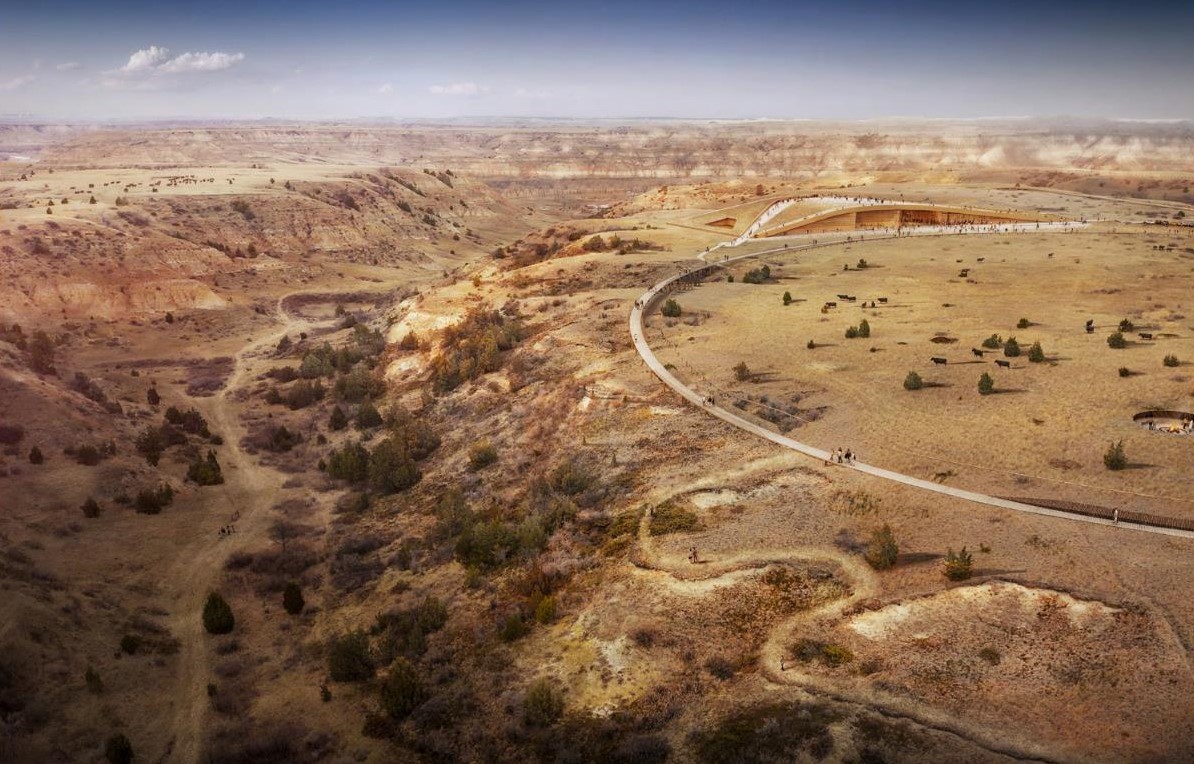
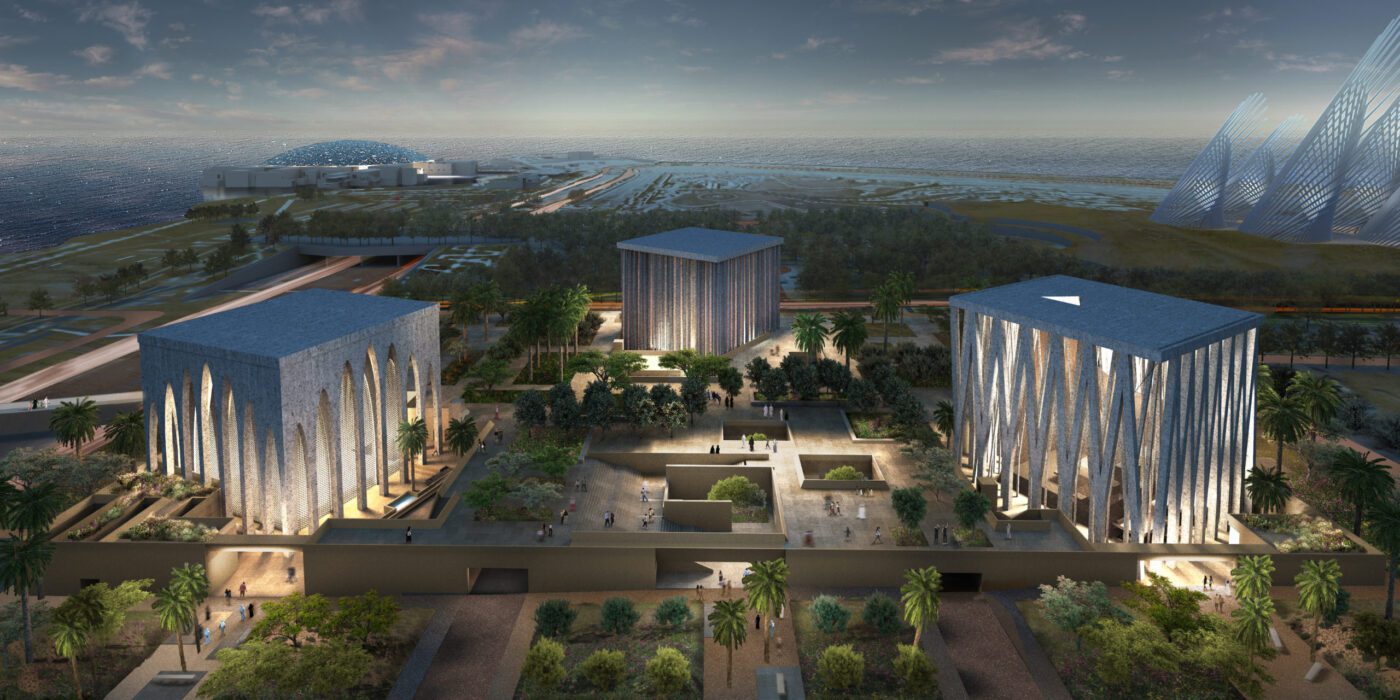
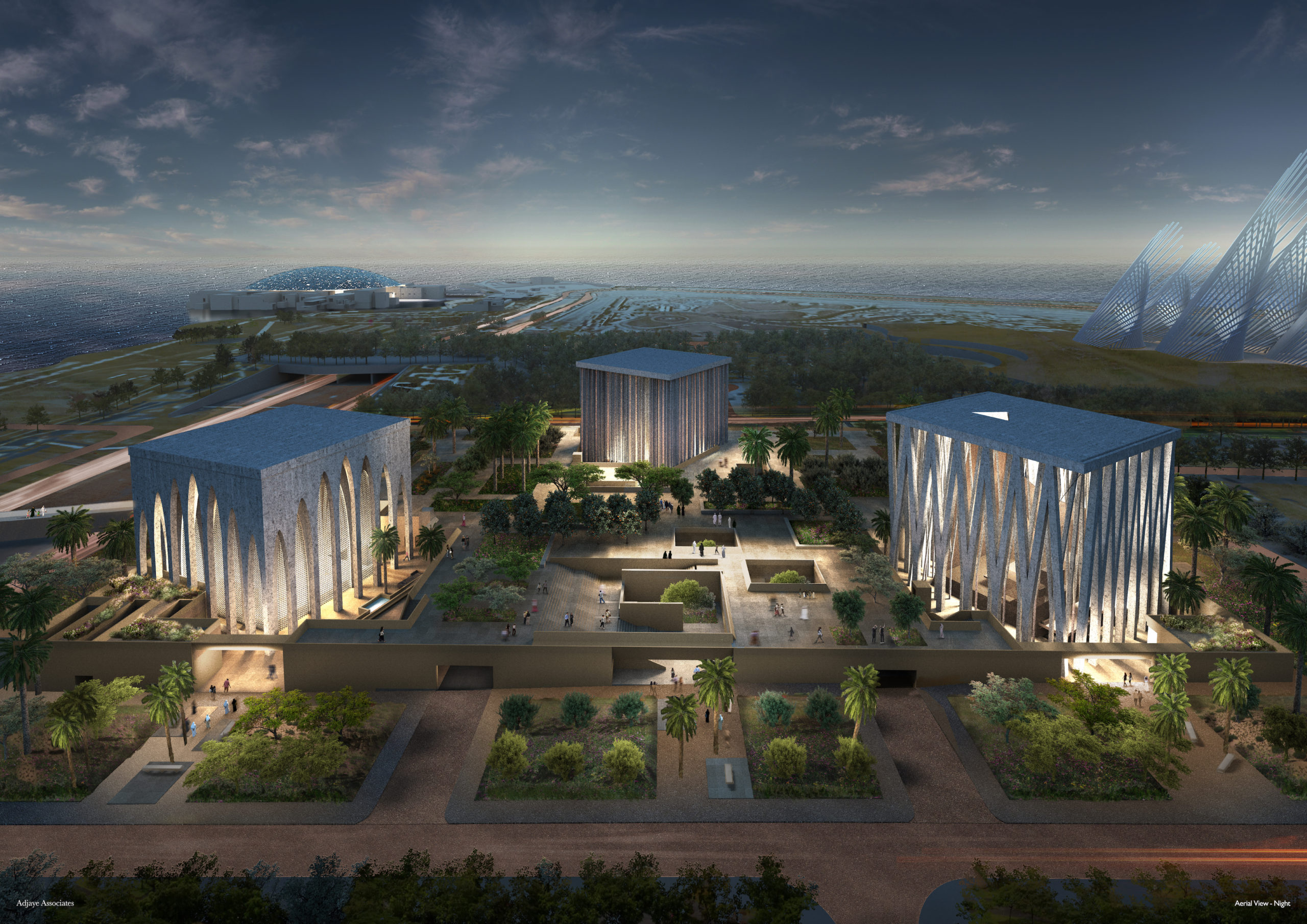
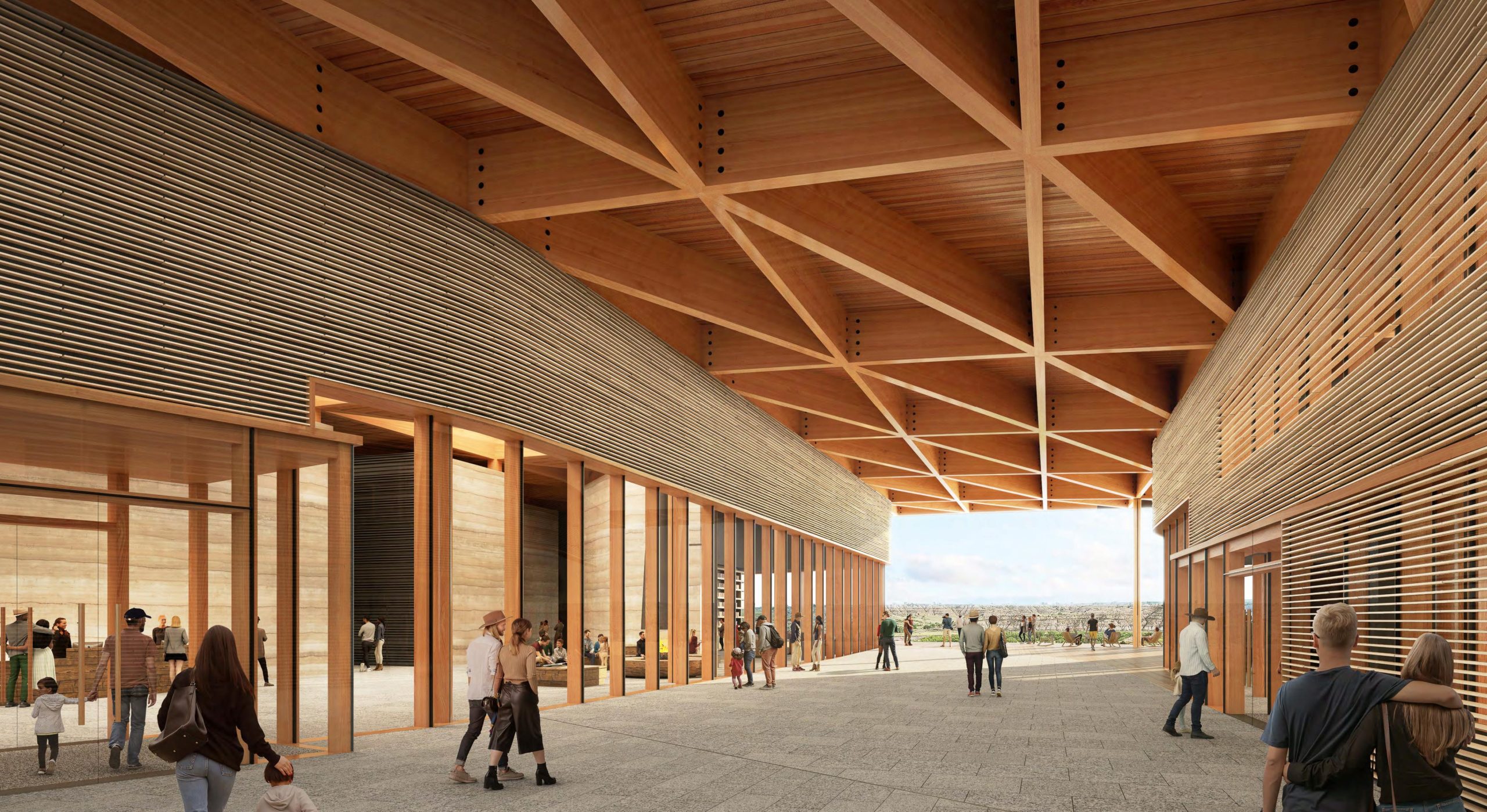 A challenge was set for the design of the much-anticipated Library of the 26th President of the United States: “Build an awe-inspiring, architecturally significant destination that works with, not against, nature.” Of all the competitors, JLG was chosen to work hand-in-hand with Snøhetta to develop a destination that strives to continue the legacy of Roosevelt and his pursuit and creation of conservation ideas that have shaped the country.
A challenge was set for the design of the much-anticipated Library of the 26th President of the United States: “Build an awe-inspiring, architecturally significant destination that works with, not against, nature.” Of all the competitors, JLG was chosen to work hand-in-hand with Snøhetta to develop a destination that strives to continue the legacy of Roosevelt and his pursuit and creation of conservation ideas that have shaped the country.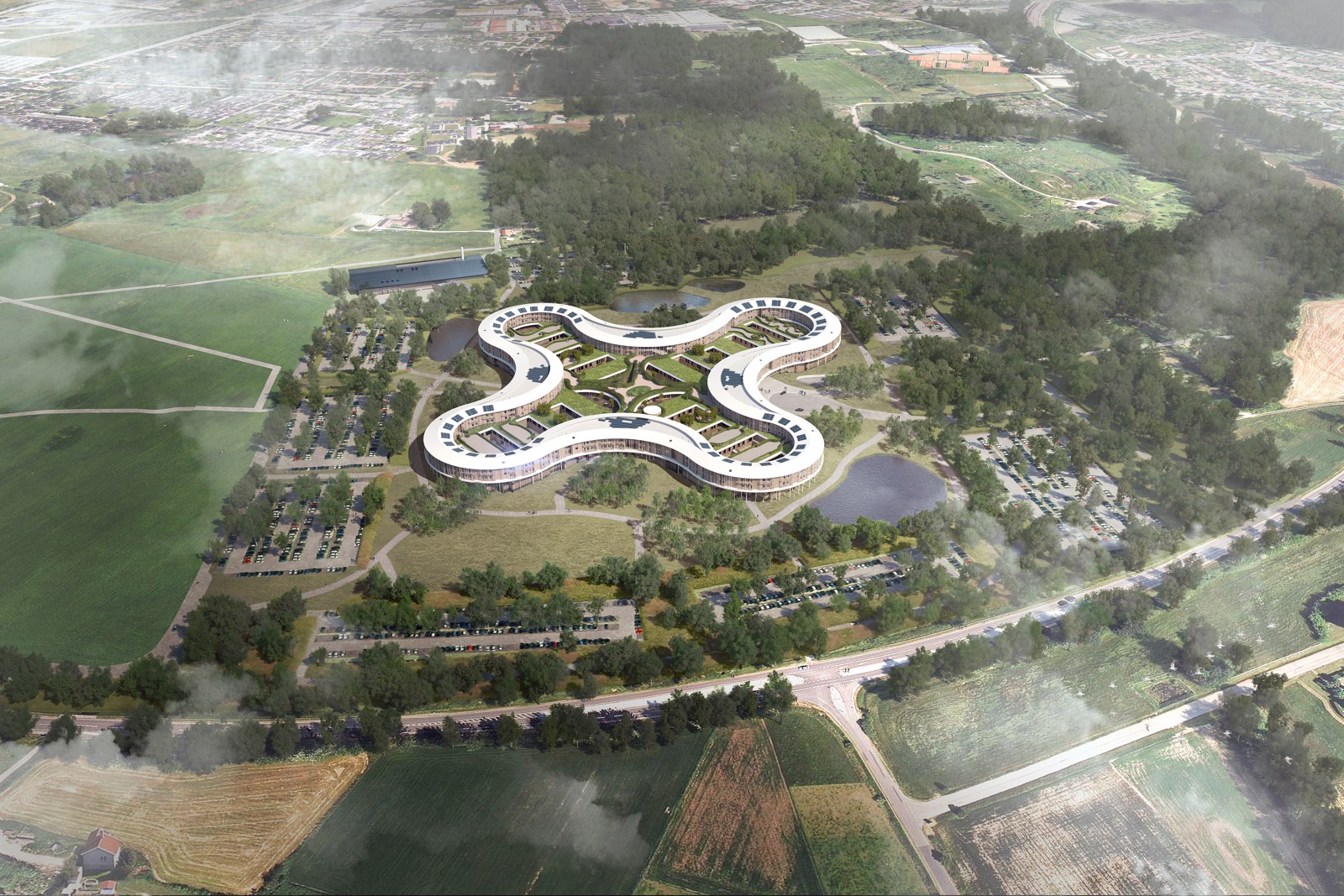
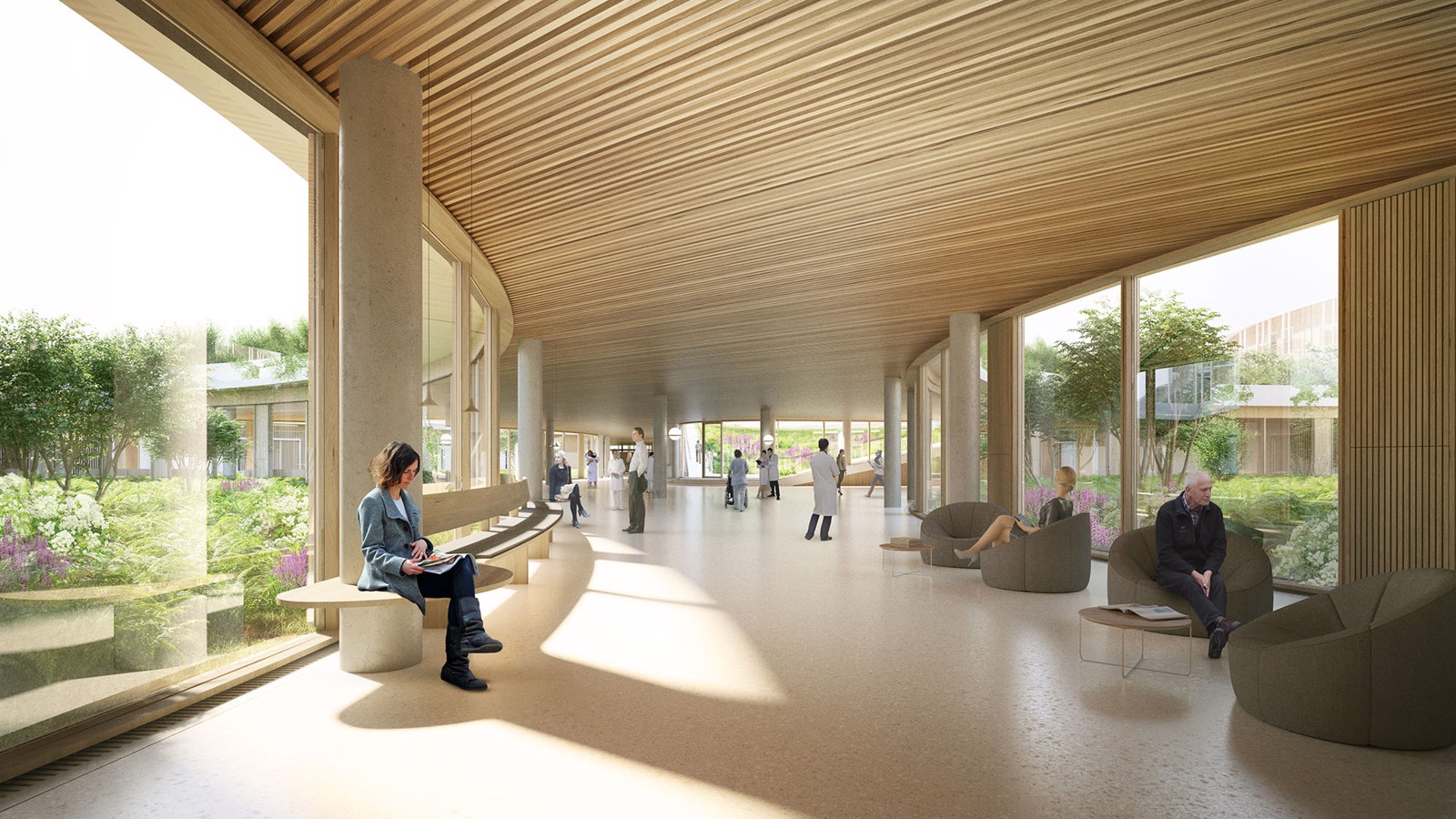 The New Hospital in North Zealand, Hillerød, has been planned to be the central hospital resource for more than 310,000 citizens in the northern part of the Capital Region of Denmark. The hospital merges three existing hospitals: Hillerød Hospital, Elsinore Hospital and Frederikssund Hospital. Focusing on questioning how we facilitate healthcare, Herzog & de Meuron and Vilhelm Lauritzen Architects’ design ambition is to redefine how we perceive a hospital and how we design and construct them.
The New Hospital in North Zealand, Hillerød, has been planned to be the central hospital resource for more than 310,000 citizens in the northern part of the Capital Region of Denmark. The hospital merges three existing hospitals: Hillerød Hospital, Elsinore Hospital and Frederikssund Hospital. Focusing on questioning how we facilitate healthcare, Herzog & de Meuron and Vilhelm Lauritzen Architects’ design ambition is to redefine how we perceive a hospital and how we design and construct them.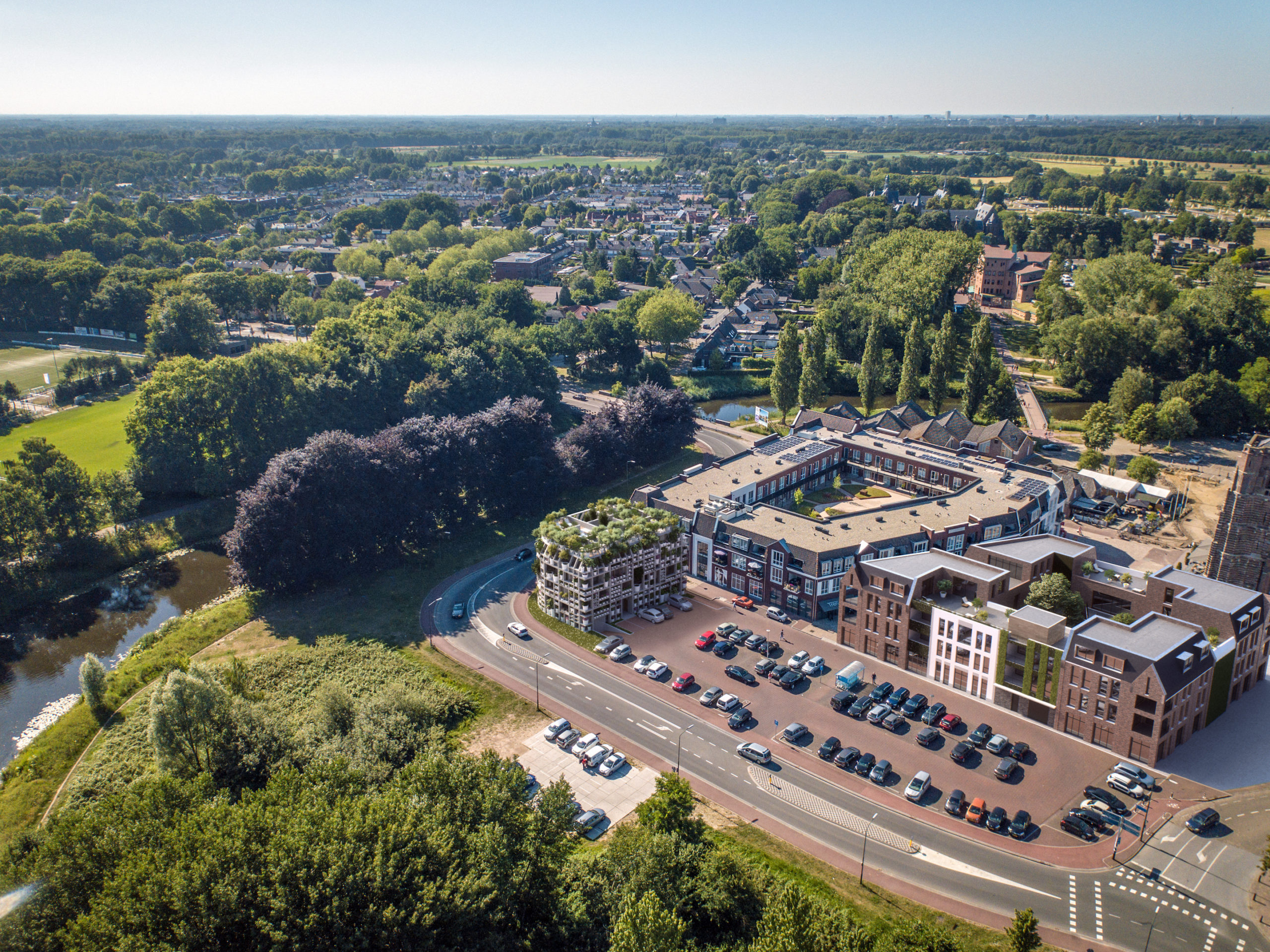
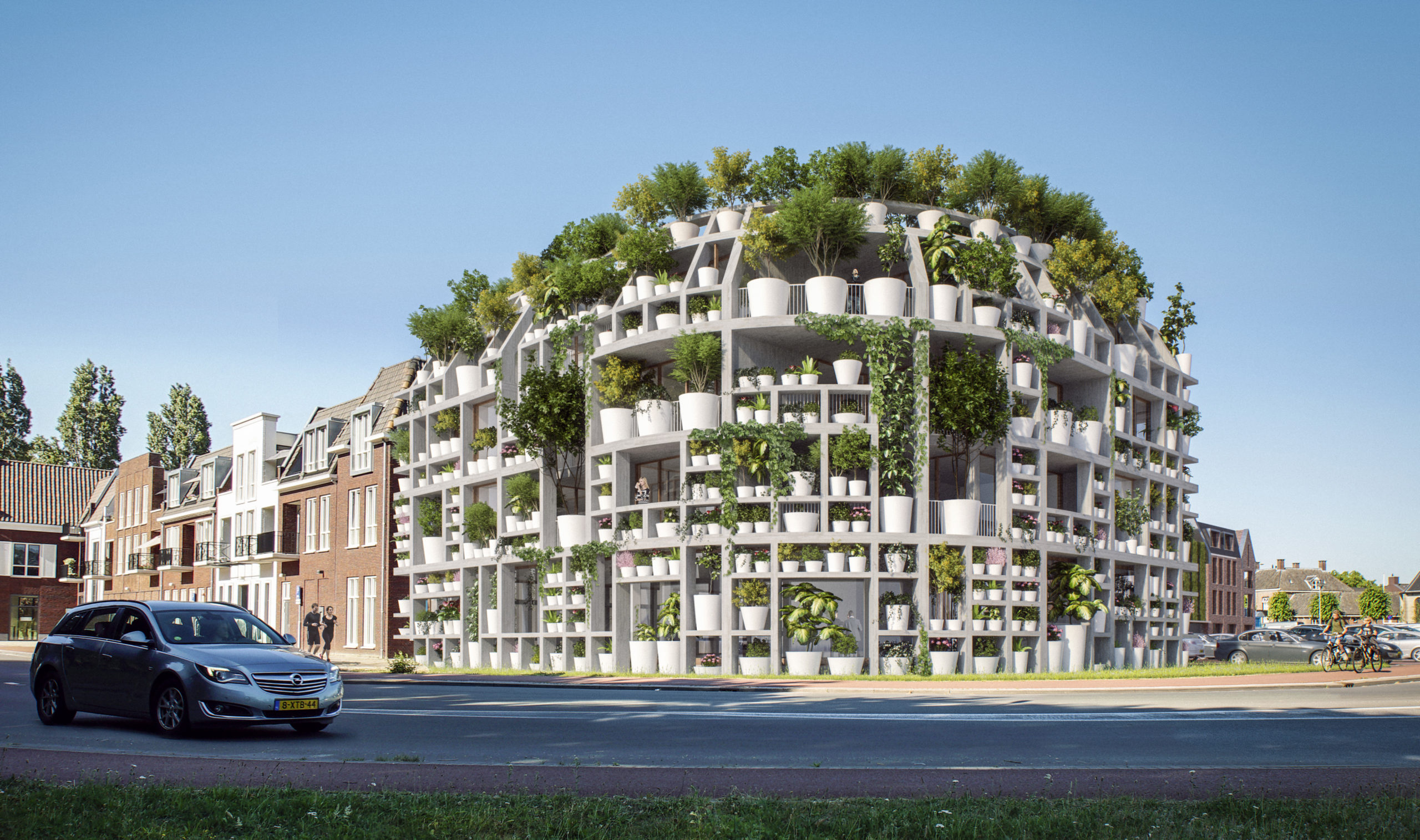 Located on the southern edge of the Dutch village of Sint-Michielsgestel, the four-story Green Villa by MVRDV and Van Boven Architecten is a unique and exciting proposal that explores the potential of ‘façade-less’ buildings and ‘radical greening.’ The inner and outer skin is made up of a “rack” of shelves, varying in depth, that hosts an abundance of potted plants, bushes, and trees such as forsythias, jasmine, pine, and birch, all labeled and cataloged. The forward-thinking approach stems from MVRDV’s belief that sustainability implies a technological challenge and a positive change in lifestyle, where urban areas should be considered a part of the natural landscape. The flexible mixed-use development will be home to adaptable residential and commercial spaces.
Located on the southern edge of the Dutch village of Sint-Michielsgestel, the four-story Green Villa by MVRDV and Van Boven Architecten is a unique and exciting proposal that explores the potential of ‘façade-less’ buildings and ‘radical greening.’ The inner and outer skin is made up of a “rack” of shelves, varying in depth, that hosts an abundance of potted plants, bushes, and trees such as forsythias, jasmine, pine, and birch, all labeled and cataloged. The forward-thinking approach stems from MVRDV’s belief that sustainability implies a technological challenge and a positive change in lifestyle, where urban areas should be considered a part of the natural landscape. The flexible mixed-use development will be home to adaptable residential and commercial spaces.
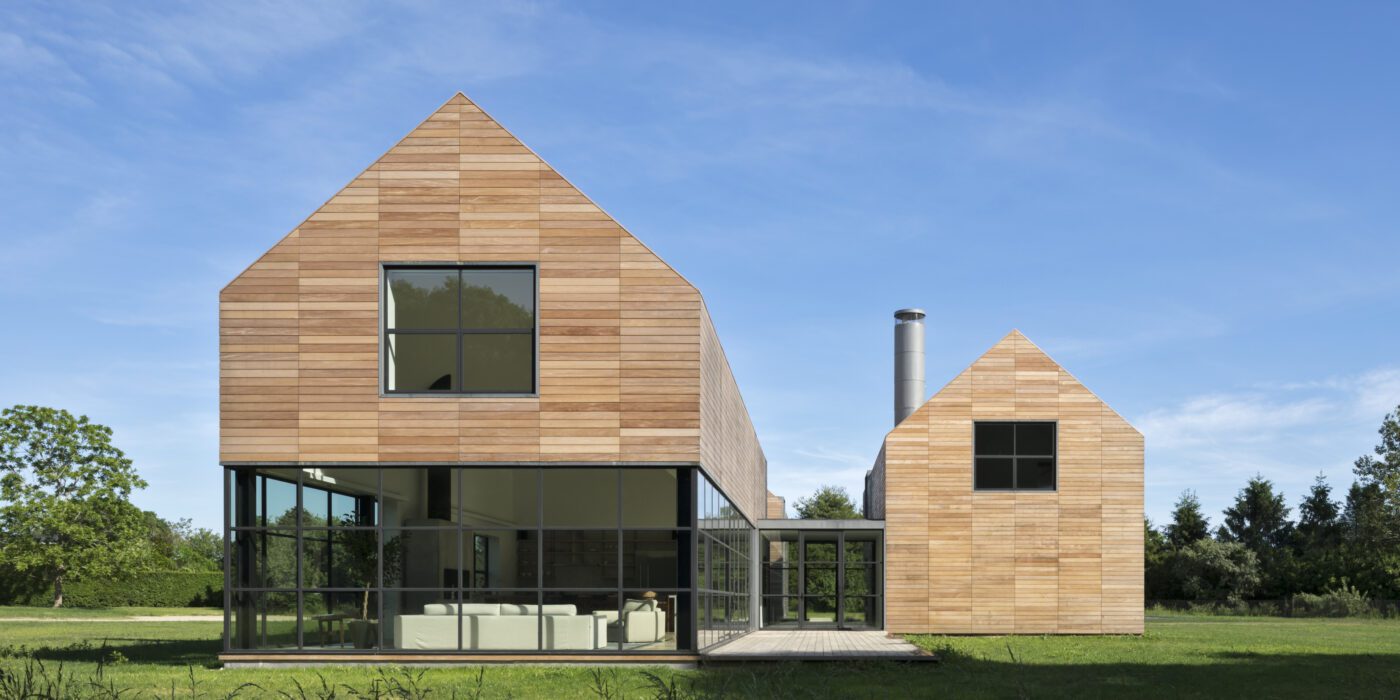










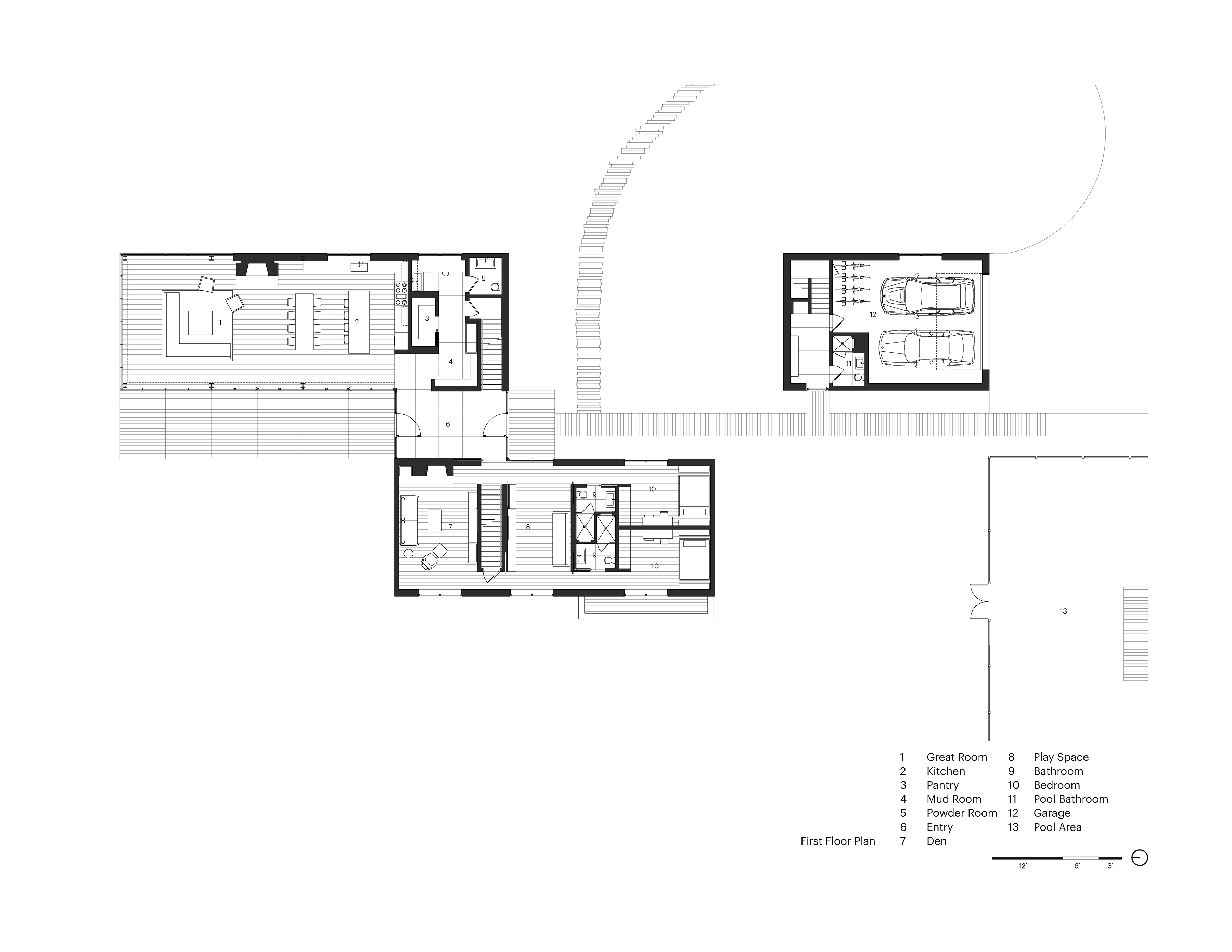 This private Hamptons residence was designed as an immersive retreat. Situated along a natural ravine and protected wetlands, the residence consists of three simple gable-shaped volumes, creating a dialogue between the natural grasslands and the built environment. A contemporary interpretation of a common New England building form, each volume is shrouded in horizontal wood slats which seamlessly wrap all wall and roof surfaces. A public great room is centrally located, acting as a social hub for family and guest interaction. Within the great room, special attention was taken to the design of the architectural concrete fireplace, countertops and black steel sash windows.
This private Hamptons residence was designed as an immersive retreat. Situated along a natural ravine and protected wetlands, the residence consists of three simple gable-shaped volumes, creating a dialogue between the natural grasslands and the built environment. A contemporary interpretation of a common New England building form, each volume is shrouded in horizontal wood slats which seamlessly wrap all wall and roof surfaces. A public great room is centrally located, acting as a social hub for family and guest interaction. Within the great room, special attention was taken to the design of the architectural concrete fireplace, countertops and black steel sash windows.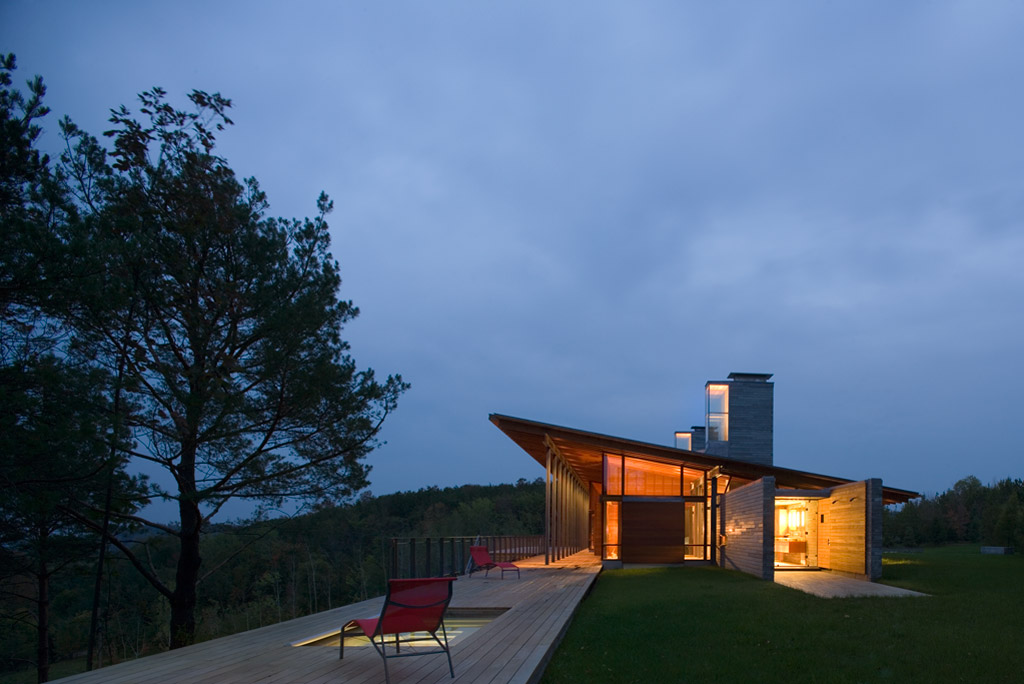
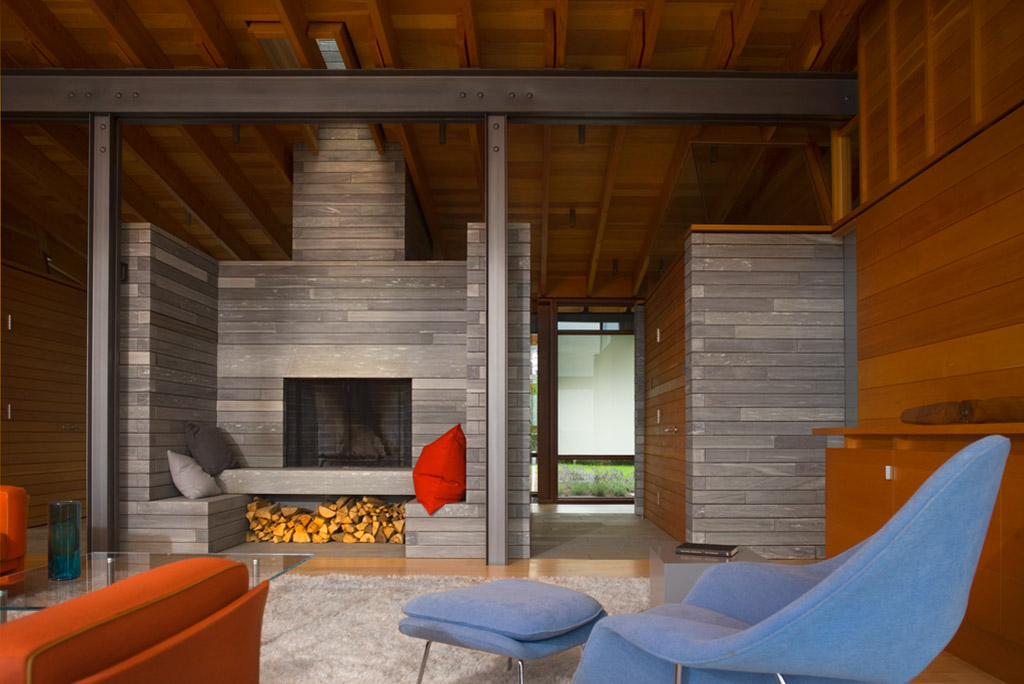

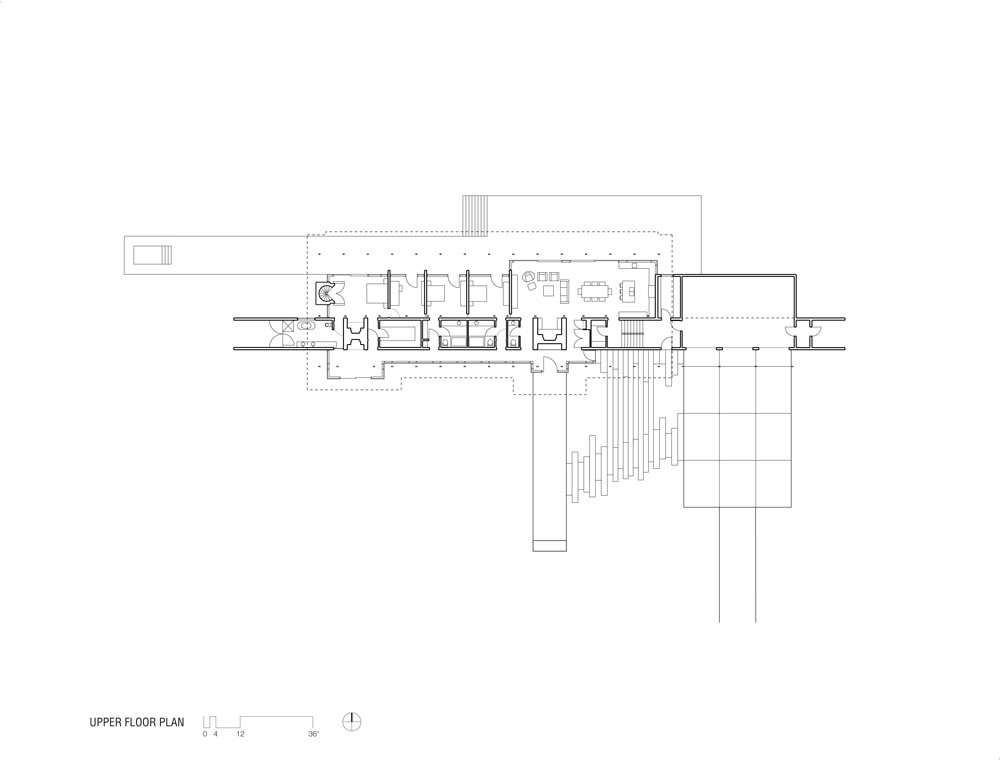 This retreat was conceived as a place for gathering family and friends as well as solitude. Located along the crest of a narrow ridge overlooking a broad valley, the drive that connects to the home turns to reveal a long, linear core of sawn stone that parallels the ridge, sliding under a single-slope roof through a steel-framed glass volume. The stone core, marked by two large fireplace masses, organizes the spaces, with primary circulation along its south face, while gaps in the stone provide access to each of the living spaces. In turn, clear and translucent glass along the south wall creates a play of light and shadow at the circulation spine.
This retreat was conceived as a place for gathering family and friends as well as solitude. Located along the crest of a narrow ridge overlooking a broad valley, the drive that connects to the home turns to reveal a long, linear core of sawn stone that parallels the ridge, sliding under a single-slope roof through a steel-framed glass volume. The stone core, marked by two large fireplace masses, organizes the spaces, with primary circulation along its south face, while gaps in the stone provide access to each of the living spaces. In turn, clear and translucent glass along the south wall creates a play of light and shadow at the circulation spine.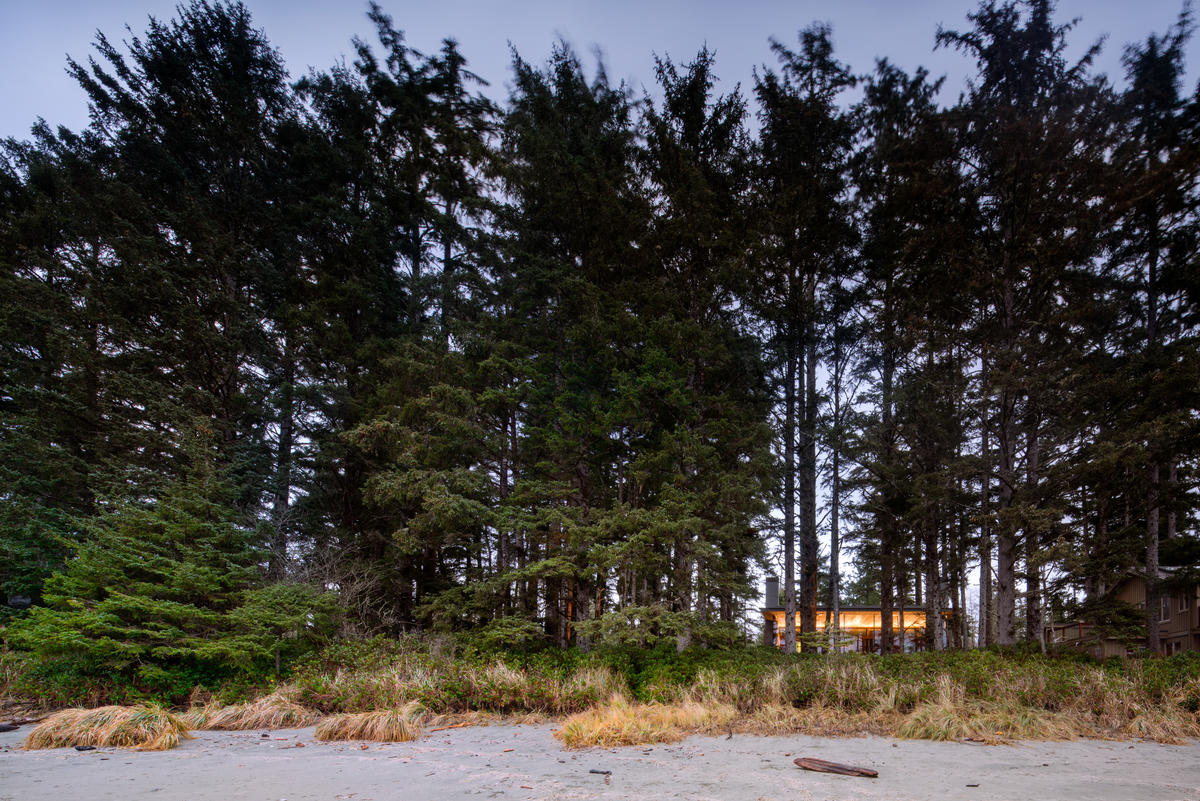
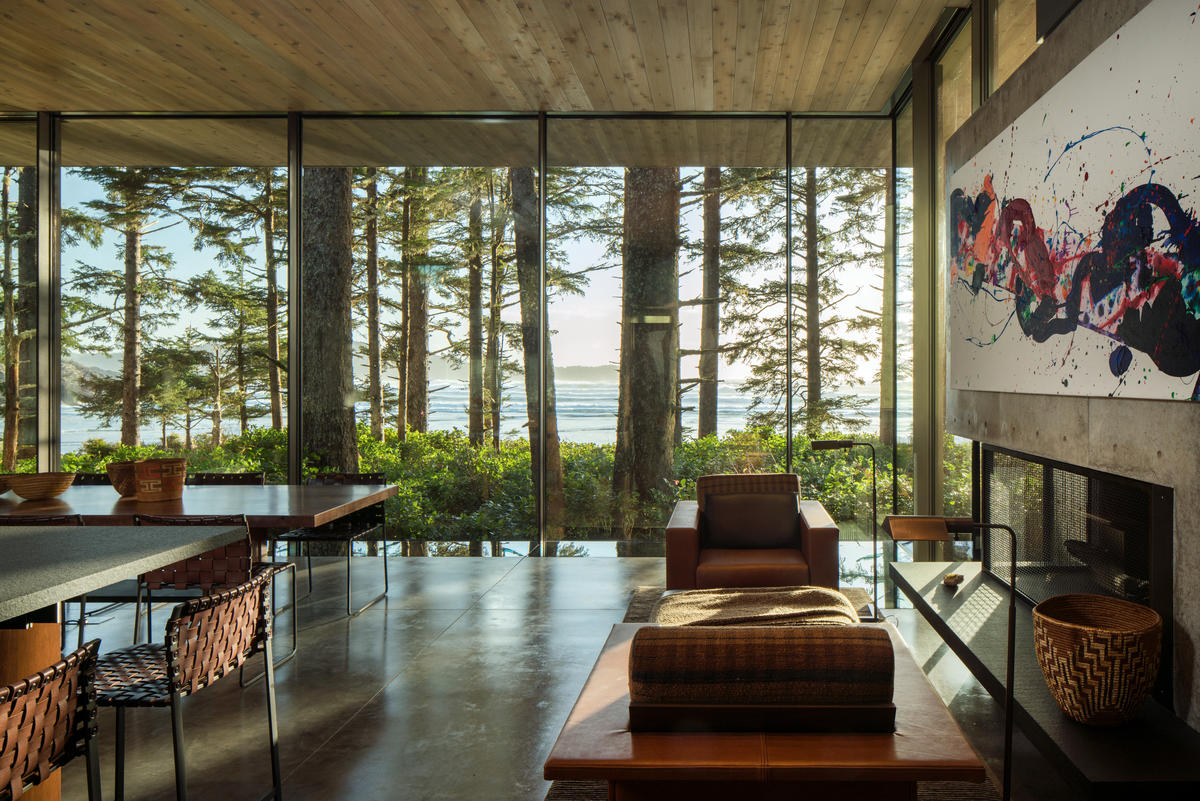

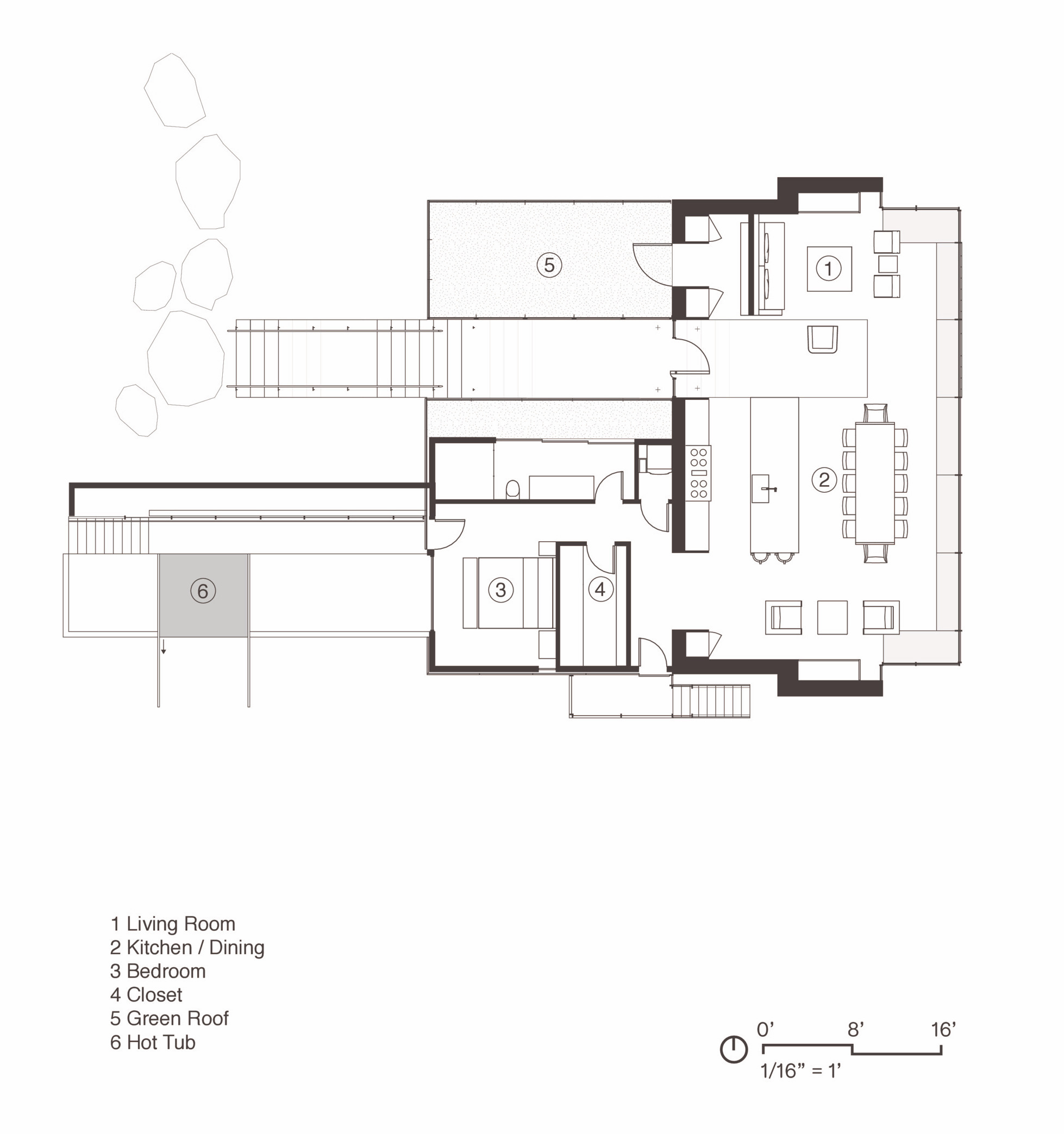 Designed as a beach house within the forest, this home creates a connection between the drama of the nearby ocean and the sense of sanctuary provided by the trees. Composed primarily of one large room, the house is light-filled on the south side facing the ocean, while remaining insular and protected on the other side. Glass walls open the living area to panoramic views of forest and ocean with two fireplaces on either end anchor that the space and provide a feeling of refuge. Artworks were incorporated into the design of the home, with the fireplace walls specially designed to fit paintings by Sam Francis and Diego Singh.
Designed as a beach house within the forest, this home creates a connection between the drama of the nearby ocean and the sense of sanctuary provided by the trees. Composed primarily of one large room, the house is light-filled on the south side facing the ocean, while remaining insular and protected on the other side. Glass walls open the living area to panoramic views of forest and ocean with two fireplaces on either end anchor that the space and provide a feeling of refuge. Artworks were incorporated into the design of the home, with the fireplace walls specially designed to fit paintings by Sam Francis and Diego Singh.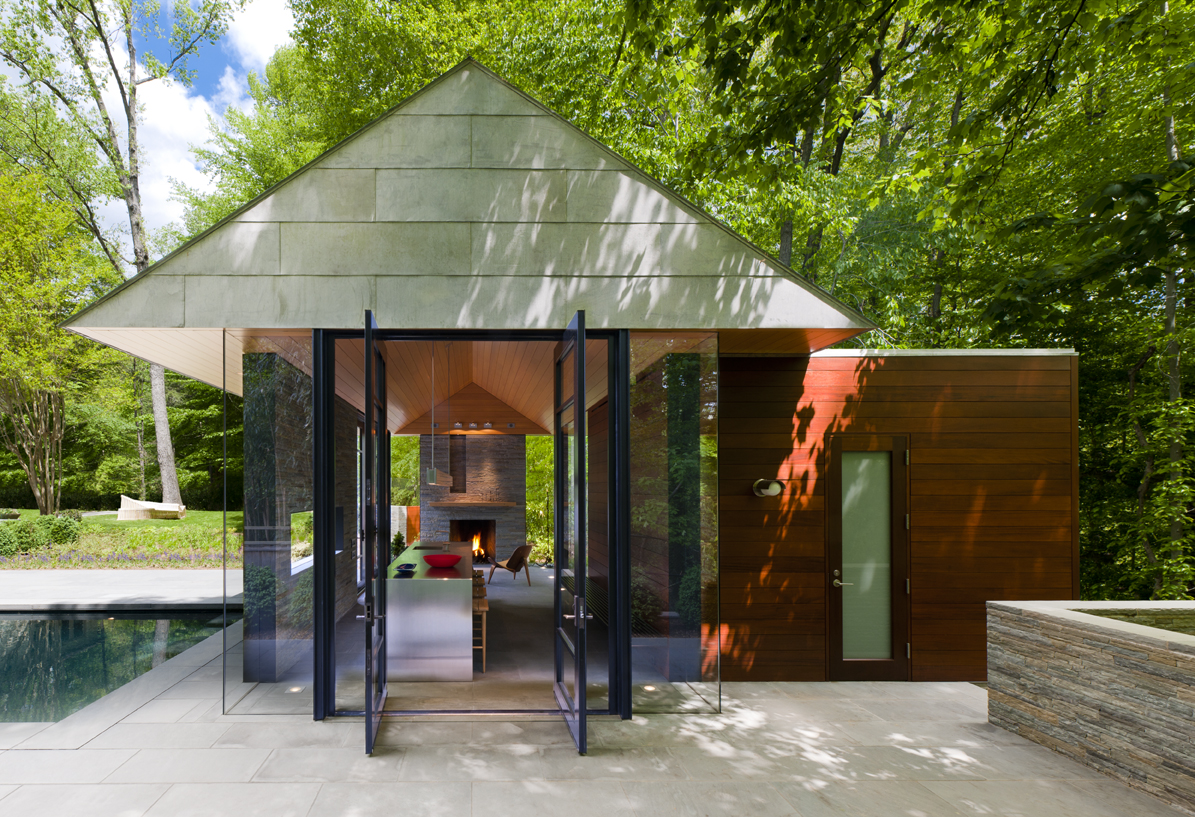
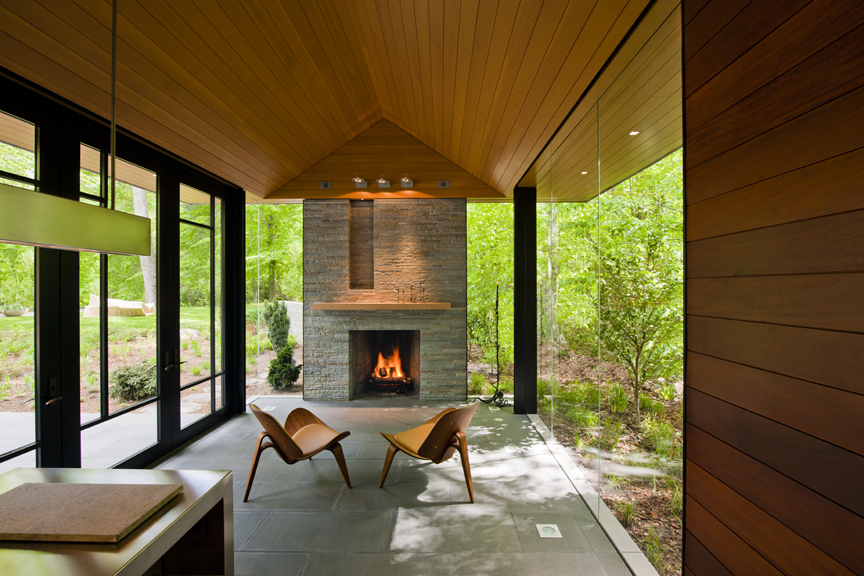

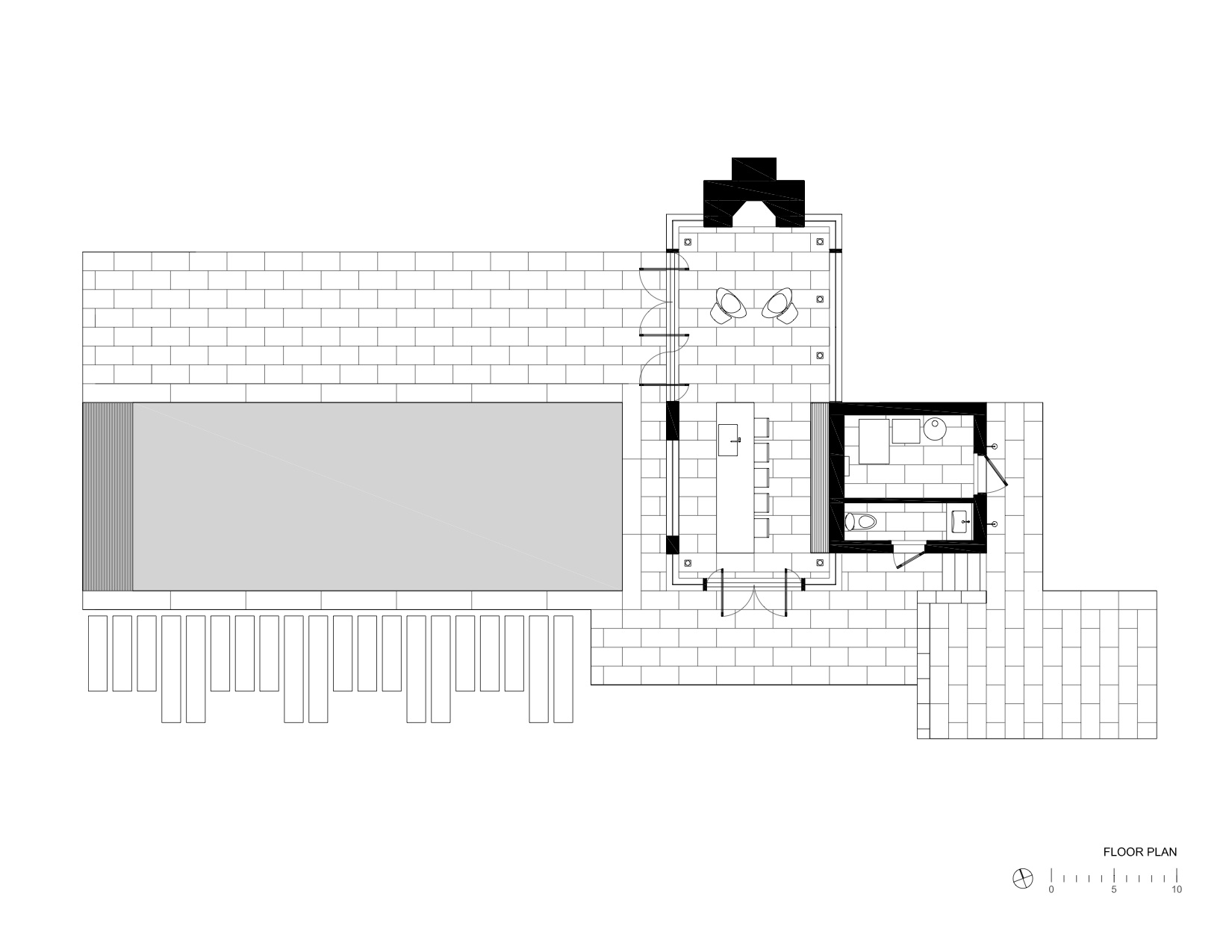 This suburban pavilion is located adjacent to woodlands. A contemporary house surrounded by mature trees and manicured gardens anchors the site. A new swimming pool, stone walls and terraces located behind the existing house organize the rear yard and establishes a dialogue between the existing house and a new pavilion. New paths, trees and structured plantings reinforce the geometry. The new pavilion, intended for year round use, is strategically located to provide a threshold between the structured landscape and adjacent woodland. The doors pivot to open the space much of the year while a large Rumford fireplace and heated floors provide a cozy counterpoint in winter months.
This suburban pavilion is located adjacent to woodlands. A contemporary house surrounded by mature trees and manicured gardens anchors the site. A new swimming pool, stone walls and terraces located behind the existing house organize the rear yard and establishes a dialogue between the existing house and a new pavilion. New paths, trees and structured plantings reinforce the geometry. The new pavilion, intended for year round use, is strategically located to provide a threshold between the structured landscape and adjacent woodland. The doors pivot to open the space much of the year while a large Rumford fireplace and heated floors provide a cozy counterpoint in winter months.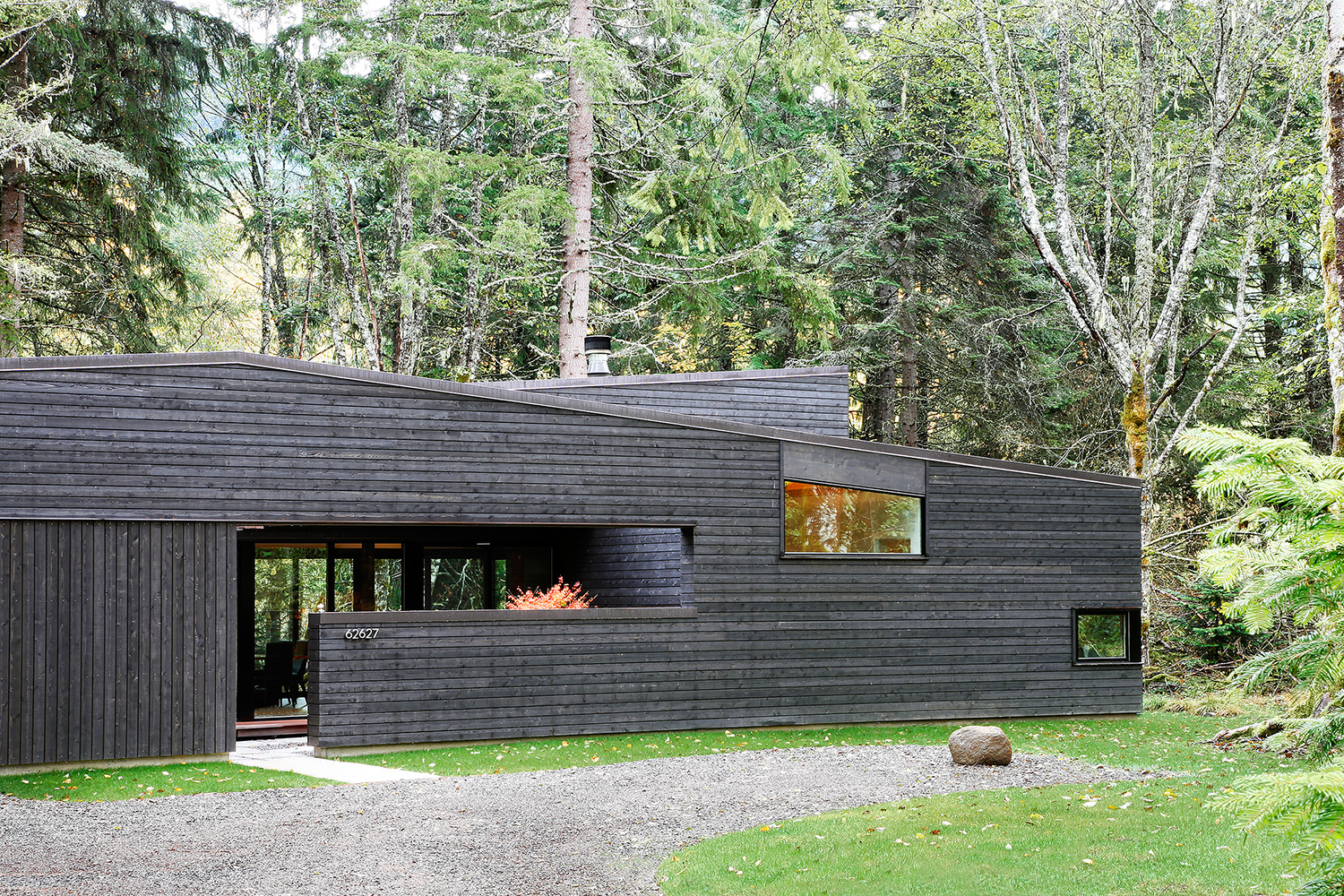
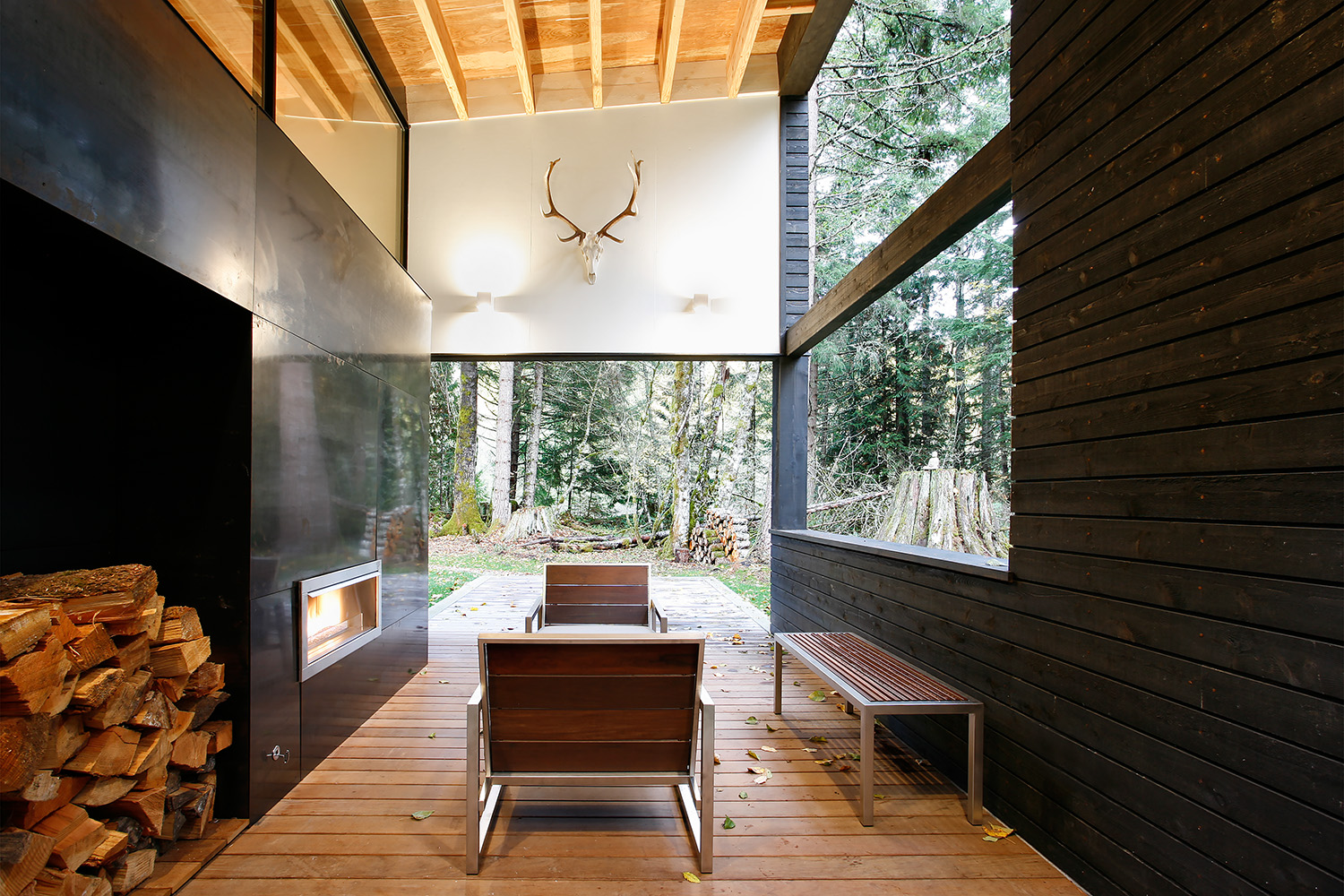

 This small residence is sited on the banks of the White River five miles from Mt. Rainier. The project was designed to quietly blend into the surrounding forest. An entry courtyard serves as a transition space from outdoors to indoors and keeps the ubiquitous elk herds at bay. A steel-clad fireplace mass separates the living room from a covered outdoor patio. By working diligently with the client (who also served as General Contractor for the project), the building footprint was kept as compact as possible to minimize site disturbance. The residence was made to epitomize the small home living movement.
This small residence is sited on the banks of the White River five miles from Mt. Rainier. The project was designed to quietly blend into the surrounding forest. An entry courtyard serves as a transition space from outdoors to indoors and keeps the ubiquitous elk herds at bay. A steel-clad fireplace mass separates the living room from a covered outdoor patio. By working diligently with the client (who also served as General Contractor for the project), the building footprint was kept as compact as possible to minimize site disturbance. The residence was made to epitomize the small home living movement.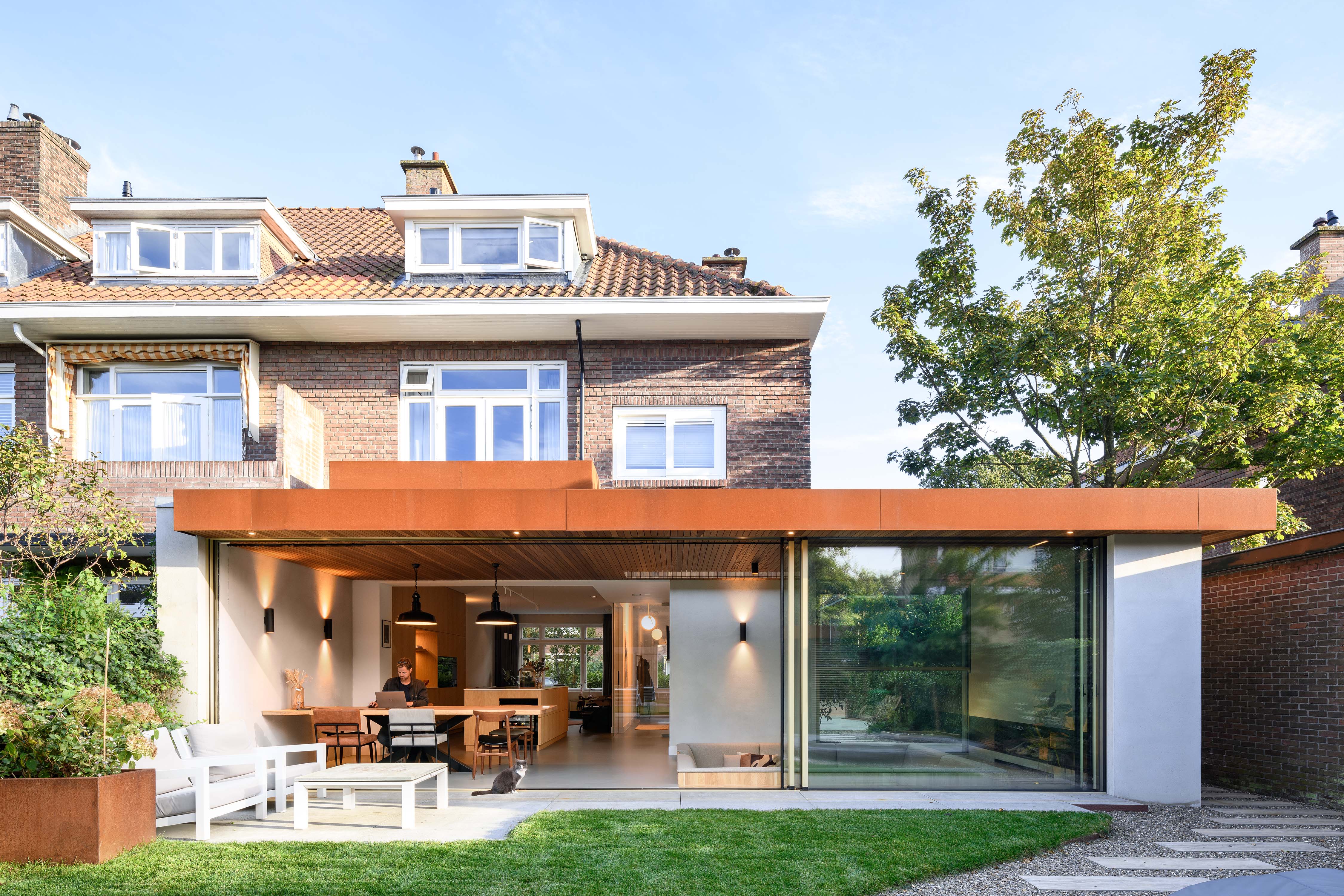
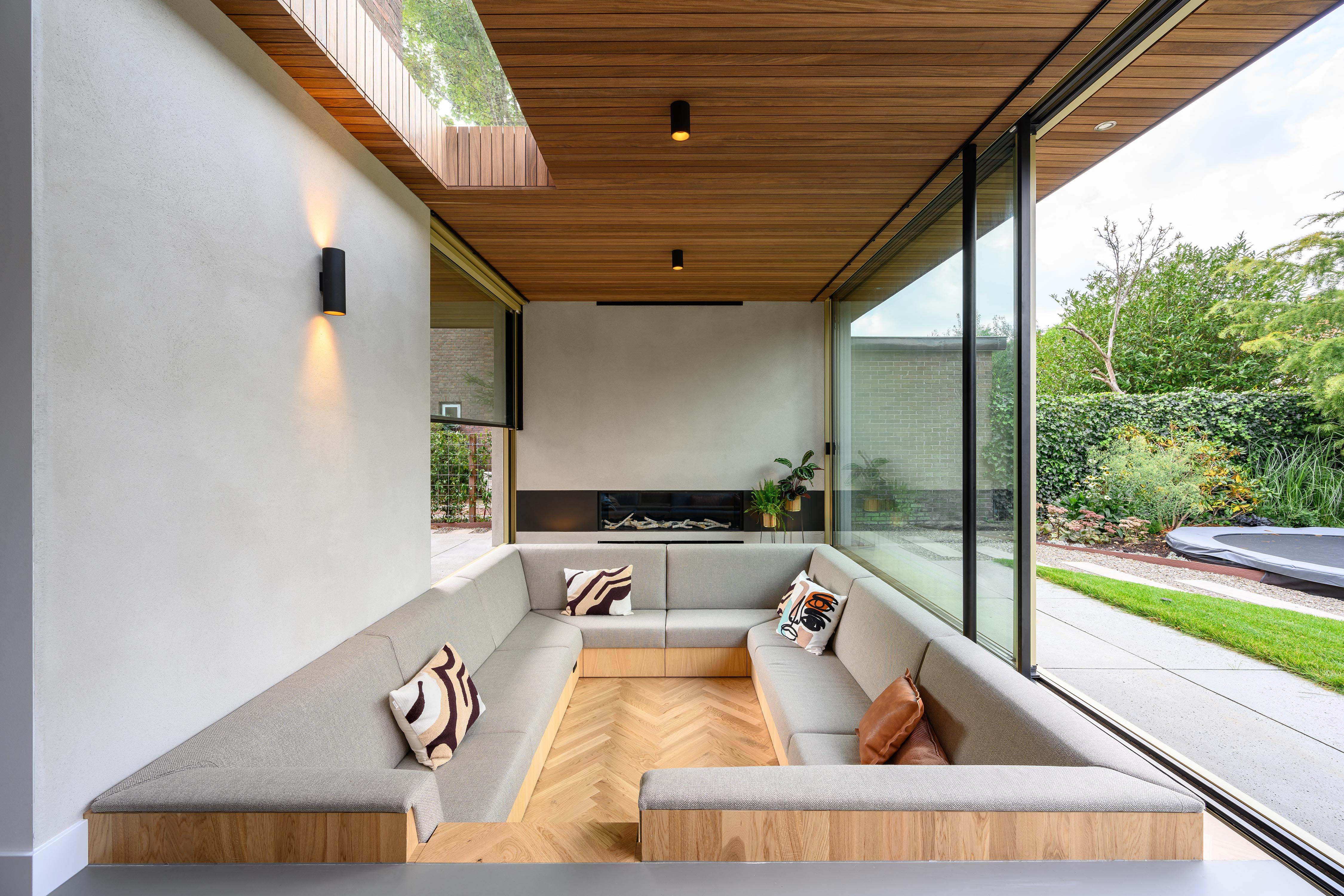

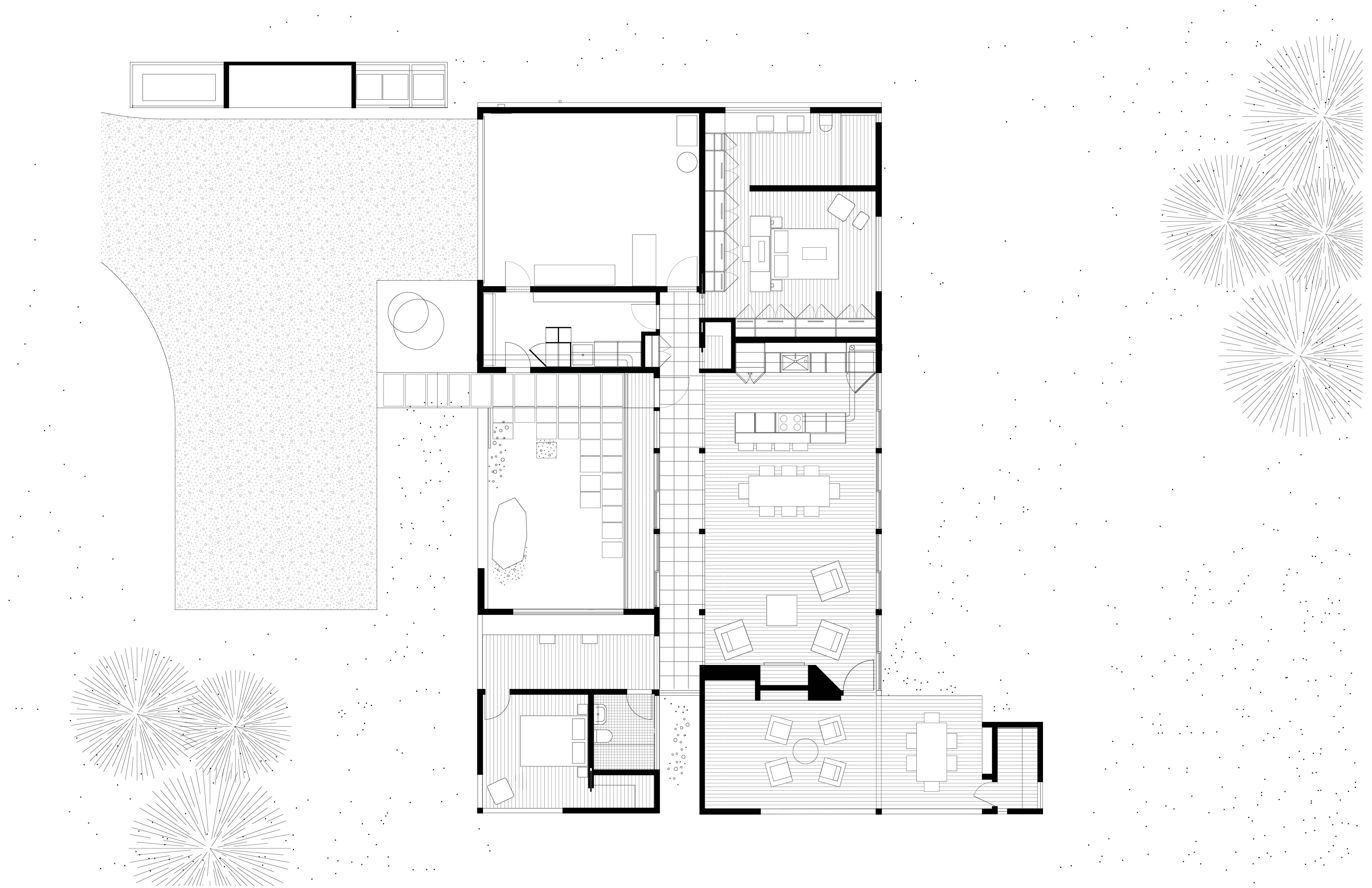
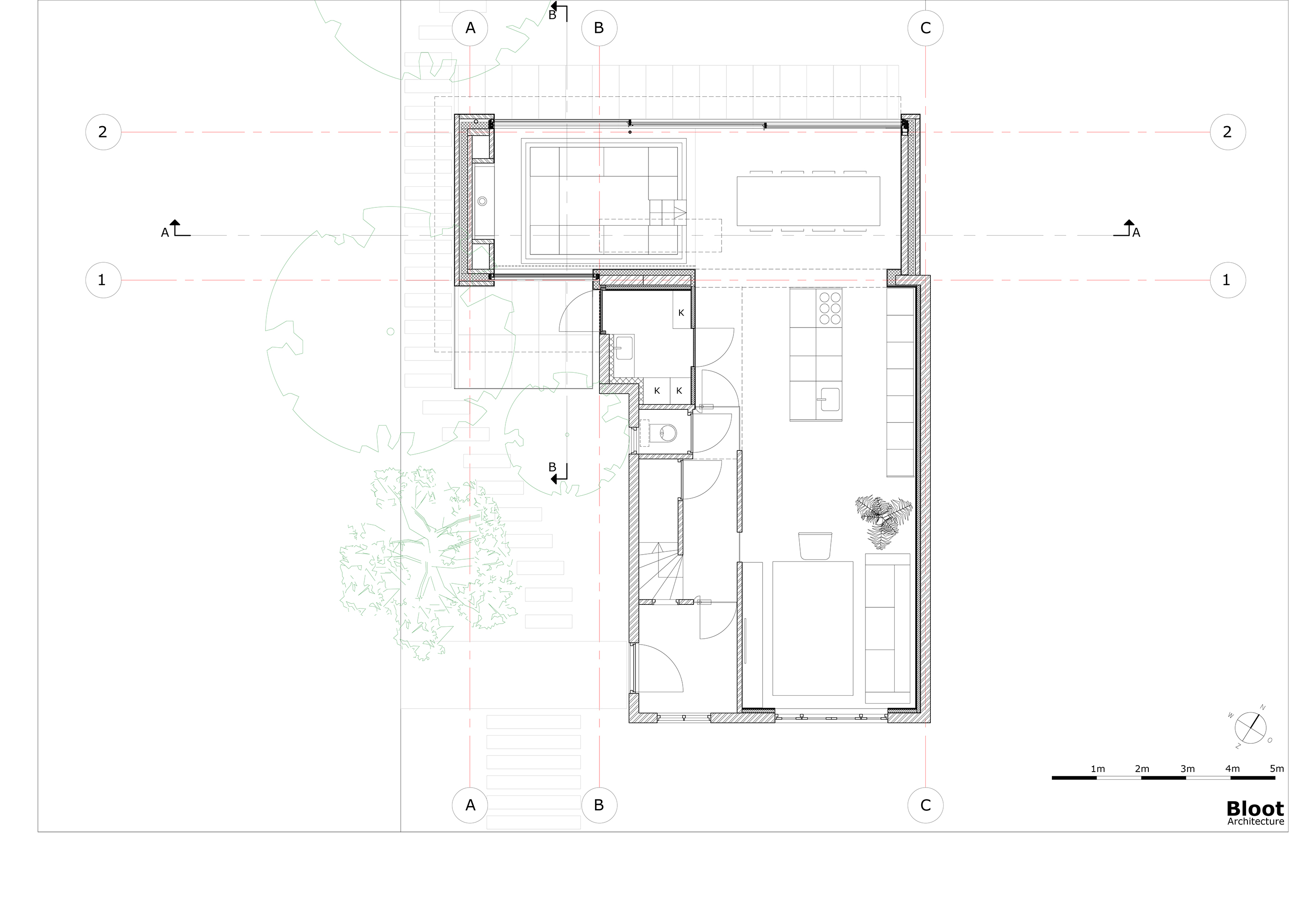 The heart of a dilapidated brick corner house from 1929 was completely renovated and extended, incorporating an inviting sitting pit. The clients asked for more space, an open kitchen and a more direct relationship to the garden. The sitting pit forms a playful space around the fireplace, where the owners are able to stay together with each other, friends and family. Seen at eye level from the seating pit, there is a vertically sliding window on the street side. By sliding this open as well as the large sliding doors at the rear, visitors find themselves outside in a sitting pit, at a fireplace and under a roof. The fireplace sits in a solid block that, together with a thick wall on the other side and a wall parallel to the seating pit, supports the roof.
The heart of a dilapidated brick corner house from 1929 was completely renovated and extended, incorporating an inviting sitting pit. The clients asked for more space, an open kitchen and a more direct relationship to the garden. The sitting pit forms a playful space around the fireplace, where the owners are able to stay together with each other, friends and family. Seen at eye level from the seating pit, there is a vertically sliding window on the street side. By sliding this open as well as the large sliding doors at the rear, visitors find themselves outside in a sitting pit, at a fireplace and under a roof. The fireplace sits in a solid block that, together with a thick wall on the other side and a wall parallel to the seating pit, supports the roof.

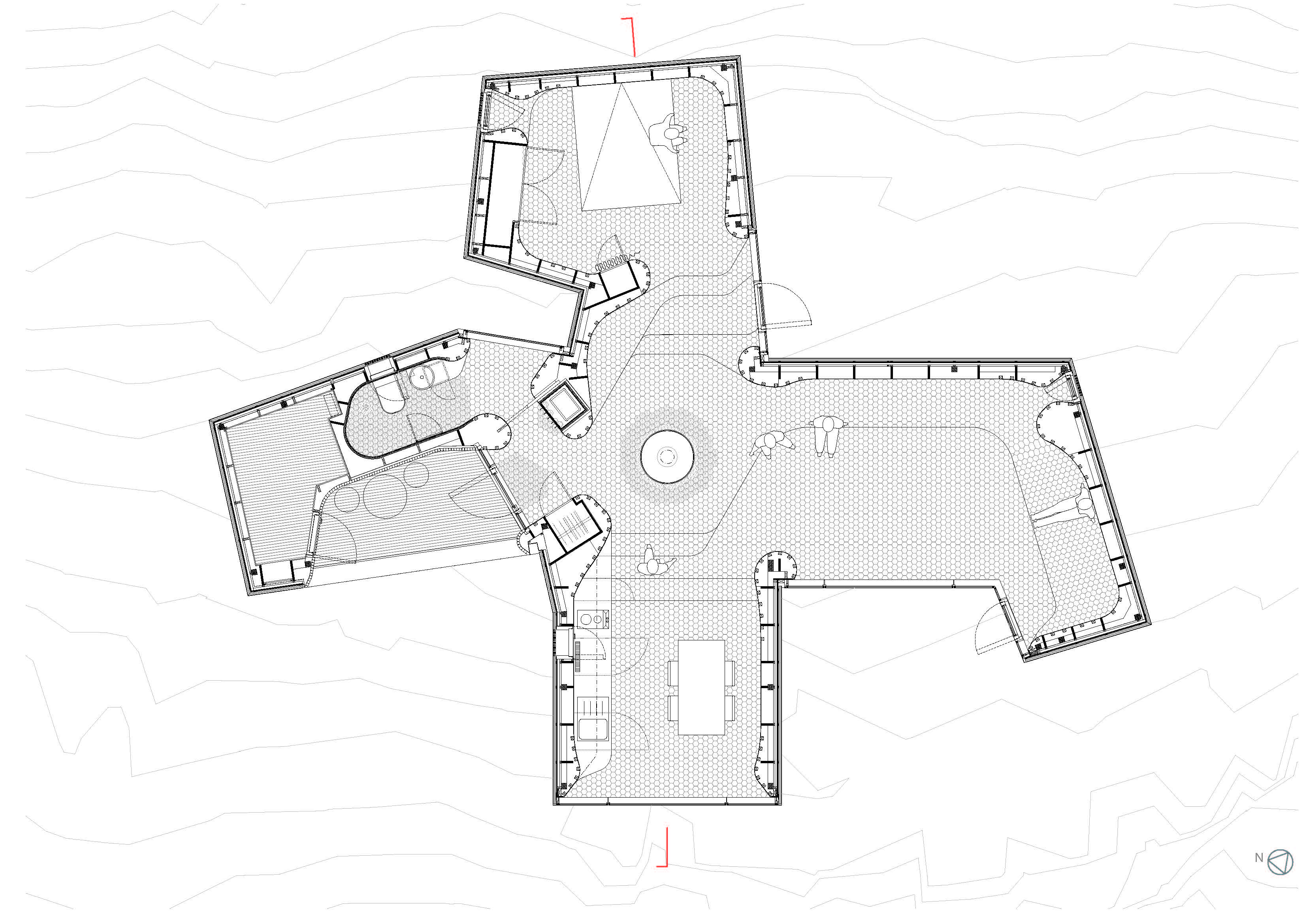 This residential cabin project is located in Krokskogen forests, outside the town of Hønefoss. The site is very exposed to the wind and the cabin is shaped to create several outdoors spaces that provide shelter from the wind and sun at different times of day. The interior is a continuous space finished in a thin layer of curved birch plywood. The fireplace is located at the center of the cabin. The fireplace mantel is hanging from the ceiling, while the fire is down at the floor of the access level. This provides the feeling of a campfire in the landscape that can be seen from different places.
This residential cabin project is located in Krokskogen forests, outside the town of Hønefoss. The site is very exposed to the wind and the cabin is shaped to create several outdoors spaces that provide shelter from the wind and sun at different times of day. The interior is a continuous space finished in a thin layer of curved birch plywood. The fireplace is located at the center of the cabin. The fireplace mantel is hanging from the ceiling, while the fire is down at the floor of the access level. This provides the feeling of a campfire in the landscape that can be seen from different places.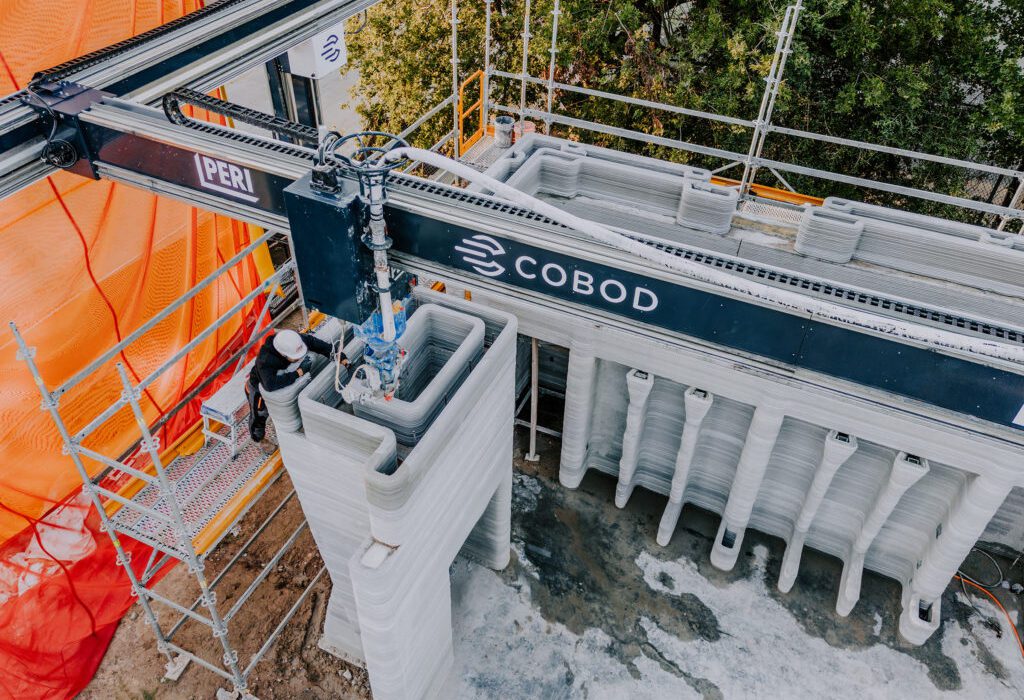
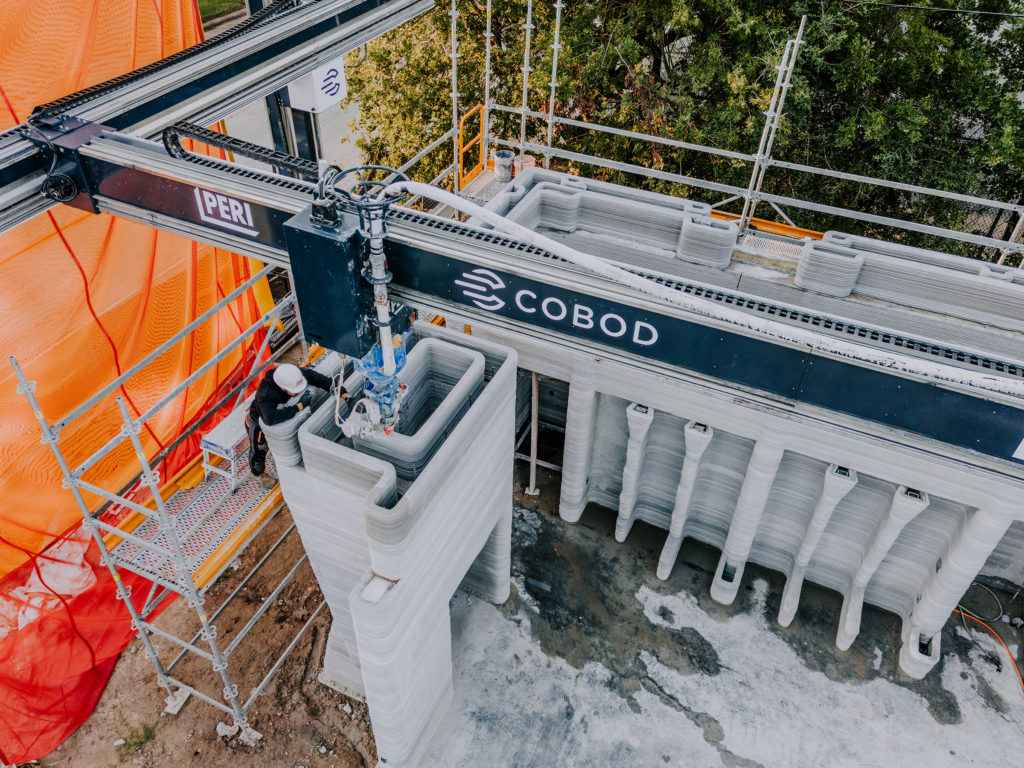 Spearheaded by Leslie Lok and Sasa Zivkovic, assistant professors at the College of Architecture, Art, and Planning at Cornell University and principals at HANNAH, the project began with the objective of developing a 3D printed construction system that could be scalable and applicable for multi-family housing the future — not an easy feat given the additional structural challenges when printing beyond a single story. As such, Lok explains that it was necessary to develop the design in relationship to the material and construction process.
Spearheaded by Leslie Lok and Sasa Zivkovic, assistant professors at the College of Architecture, Art, and Planning at Cornell University and principals at HANNAH, the project began with the objective of developing a 3D printed construction system that could be scalable and applicable for multi-family housing the future — not an easy feat given the additional structural challenges when printing beyond a single story. As such, Lok explains that it was necessary to develop the design in relationship to the material and construction process.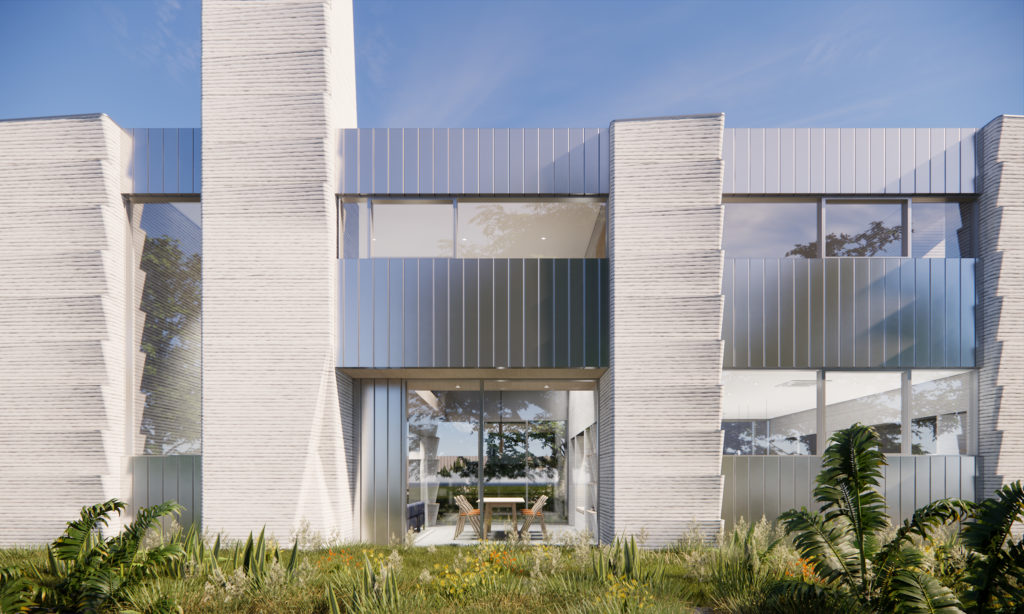
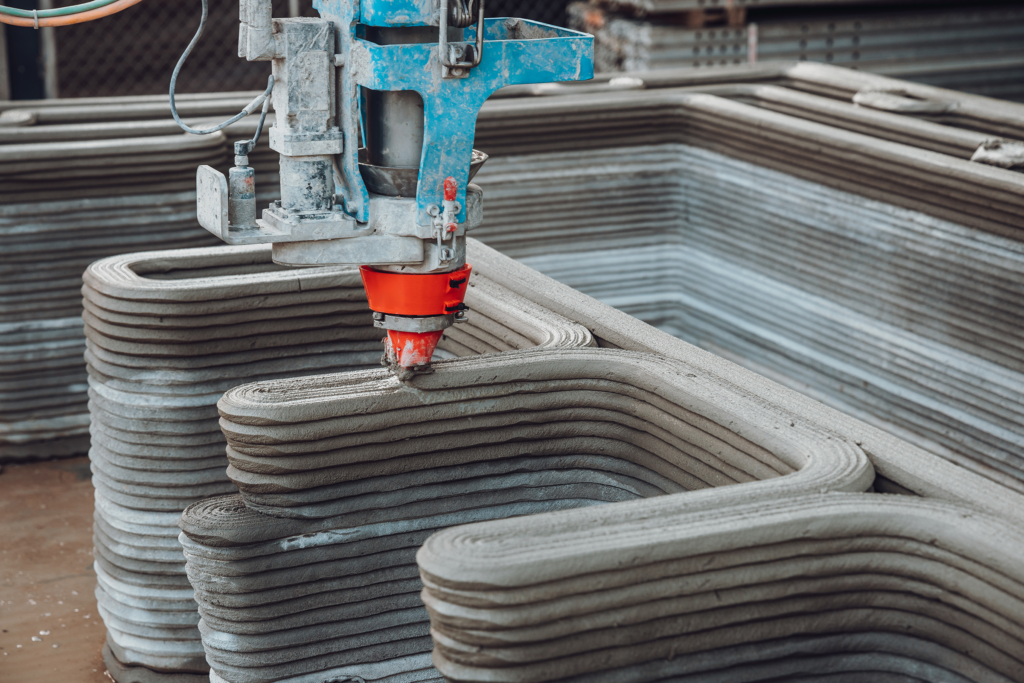
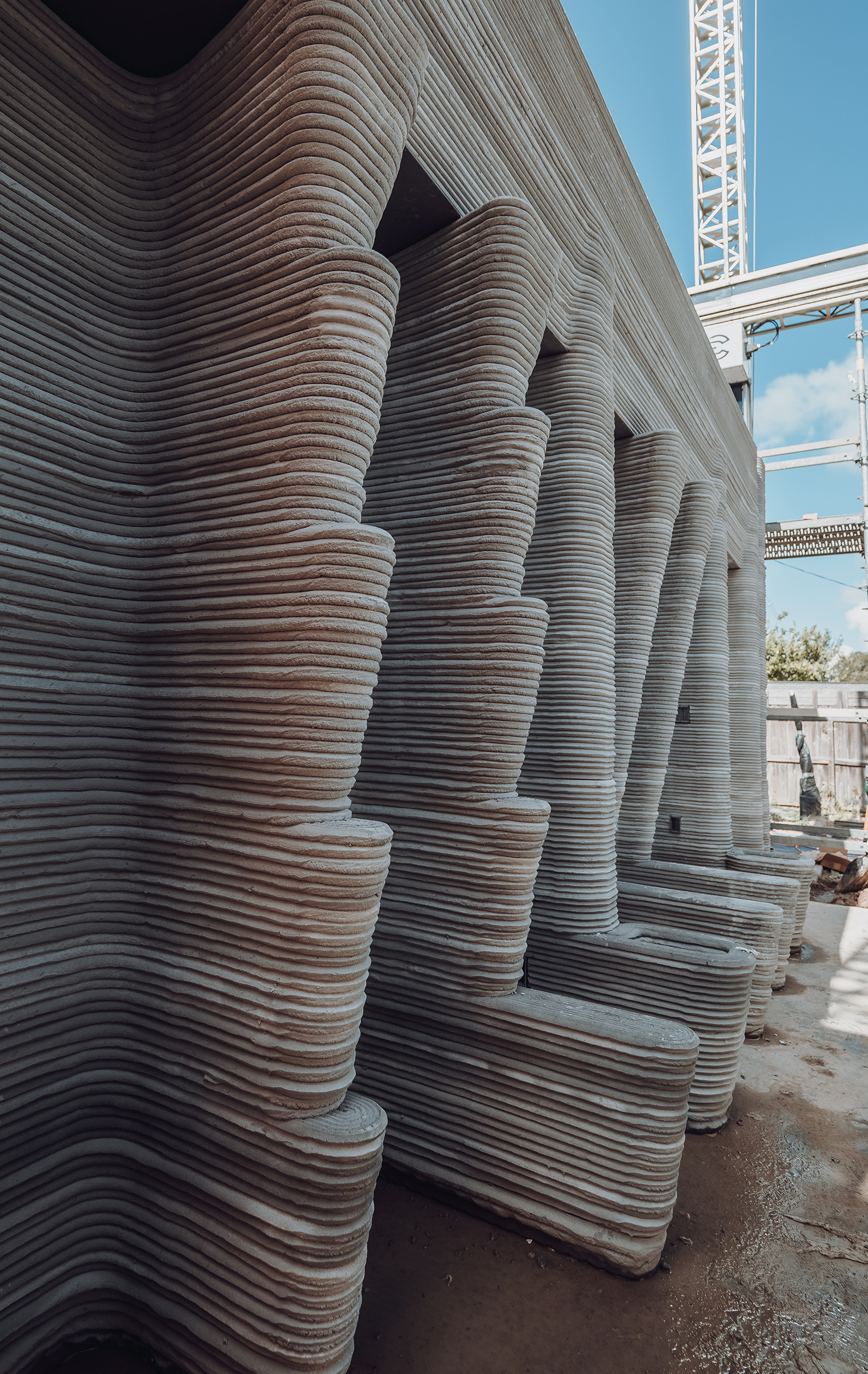
 Far from letting this complex process limit their design, HANNAH used the printing toolpath as an opportunity to push the design possibilities of 3D-printed structures. The repeated use of incremental cantilevers within the concrete modules serves as an architectural motif that is both ornamental and functional. Paired with the distinct horizontal layers of printed concrete, HANNAH creates a bold stylistic statement about 3D printed architecture; hinting at the opportunities of new design language for printed projects.
Far from letting this complex process limit their design, HANNAH used the printing toolpath as an opportunity to push the design possibilities of 3D-printed structures. The repeated use of incremental cantilevers within the concrete modules serves as an architectural motif that is both ornamental and functional. Paired with the distinct horizontal layers of printed concrete, HANNAH creates a bold stylistic statement about 3D printed architecture; hinting at the opportunities of new design language for printed projects.
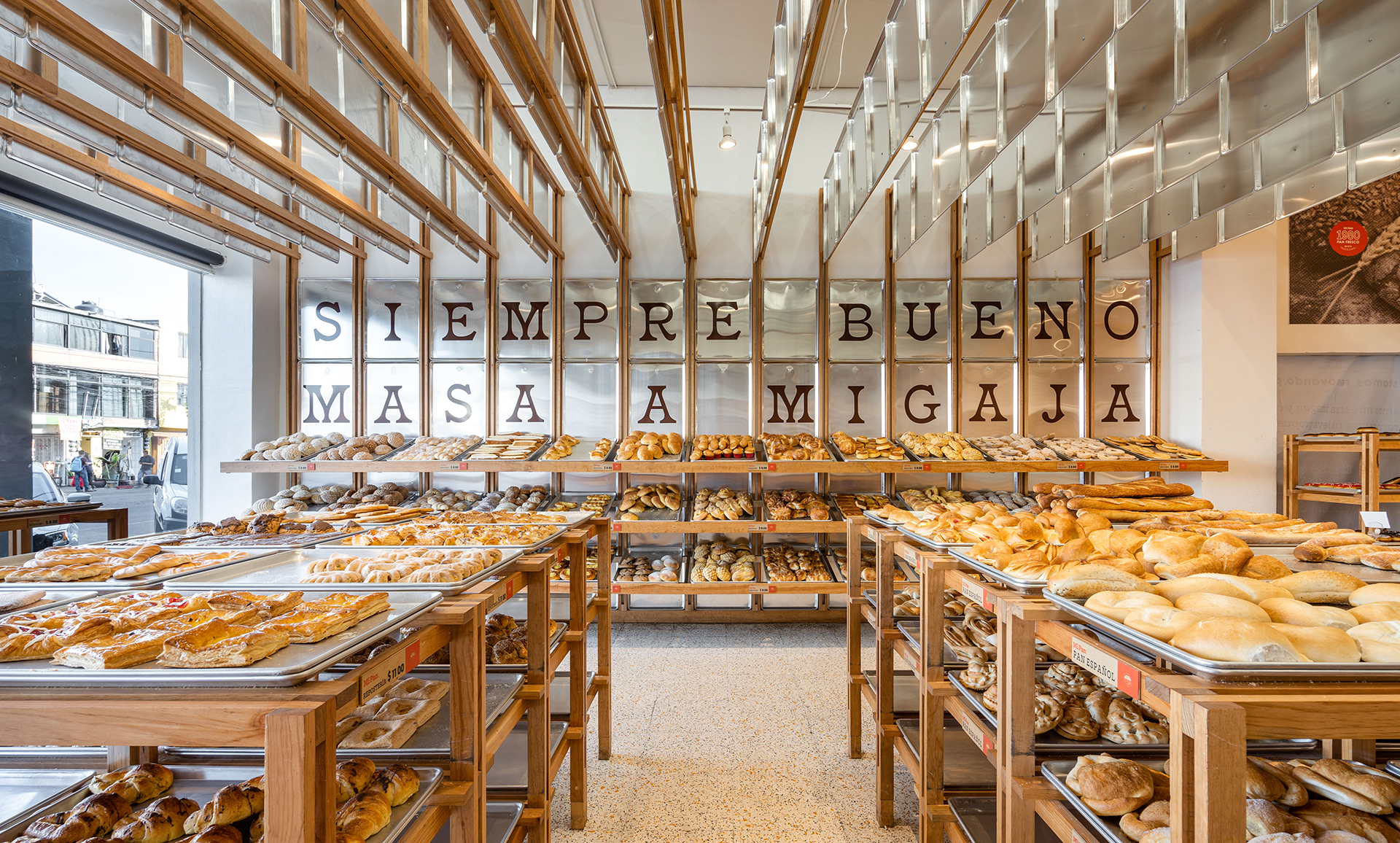
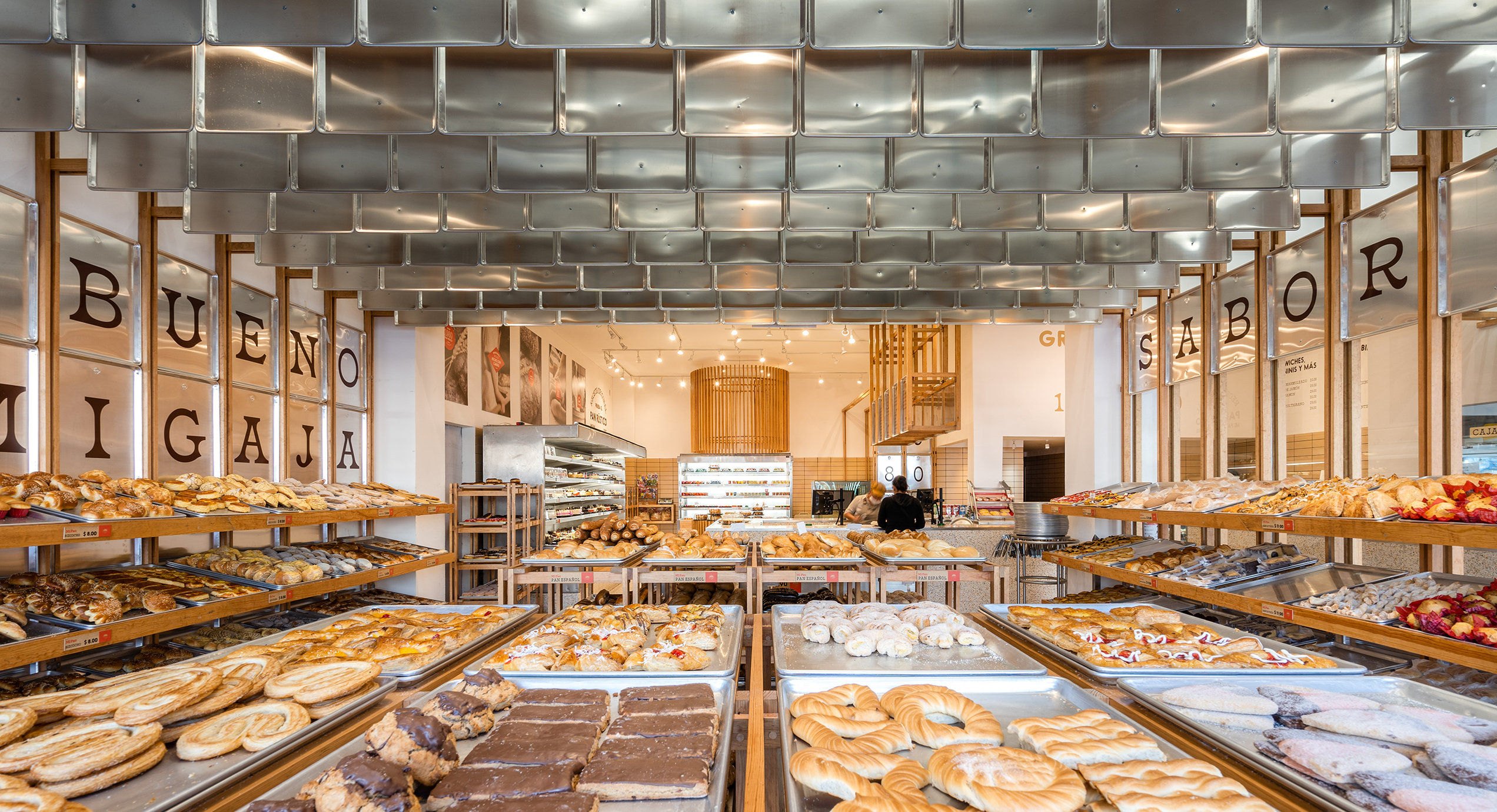
 The bakery Mi Pan celebrates bakers’ hard work in making delicious bread. Metal trays reoccur on the shelves, wall cladding and ceiling decorations. These are the same type of tray used for bread production, reminding people of the heart of Mi Pan – the kitchen.
The bakery Mi Pan celebrates bakers’ hard work in making delicious bread. Metal trays reoccur on the shelves, wall cladding and ceiling decorations. These are the same type of tray used for bread production, reminding people of the heart of Mi Pan – the kitchen.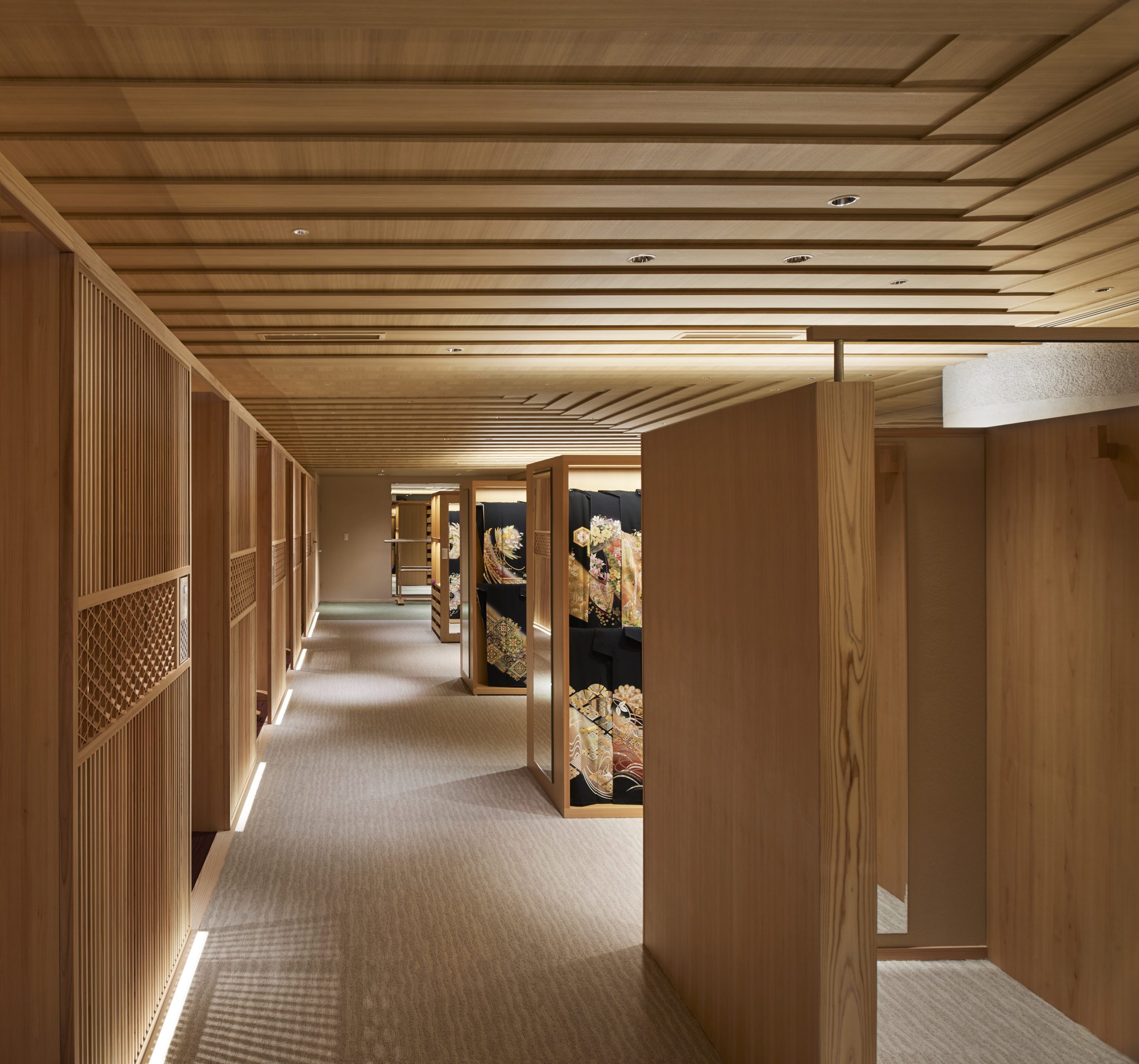
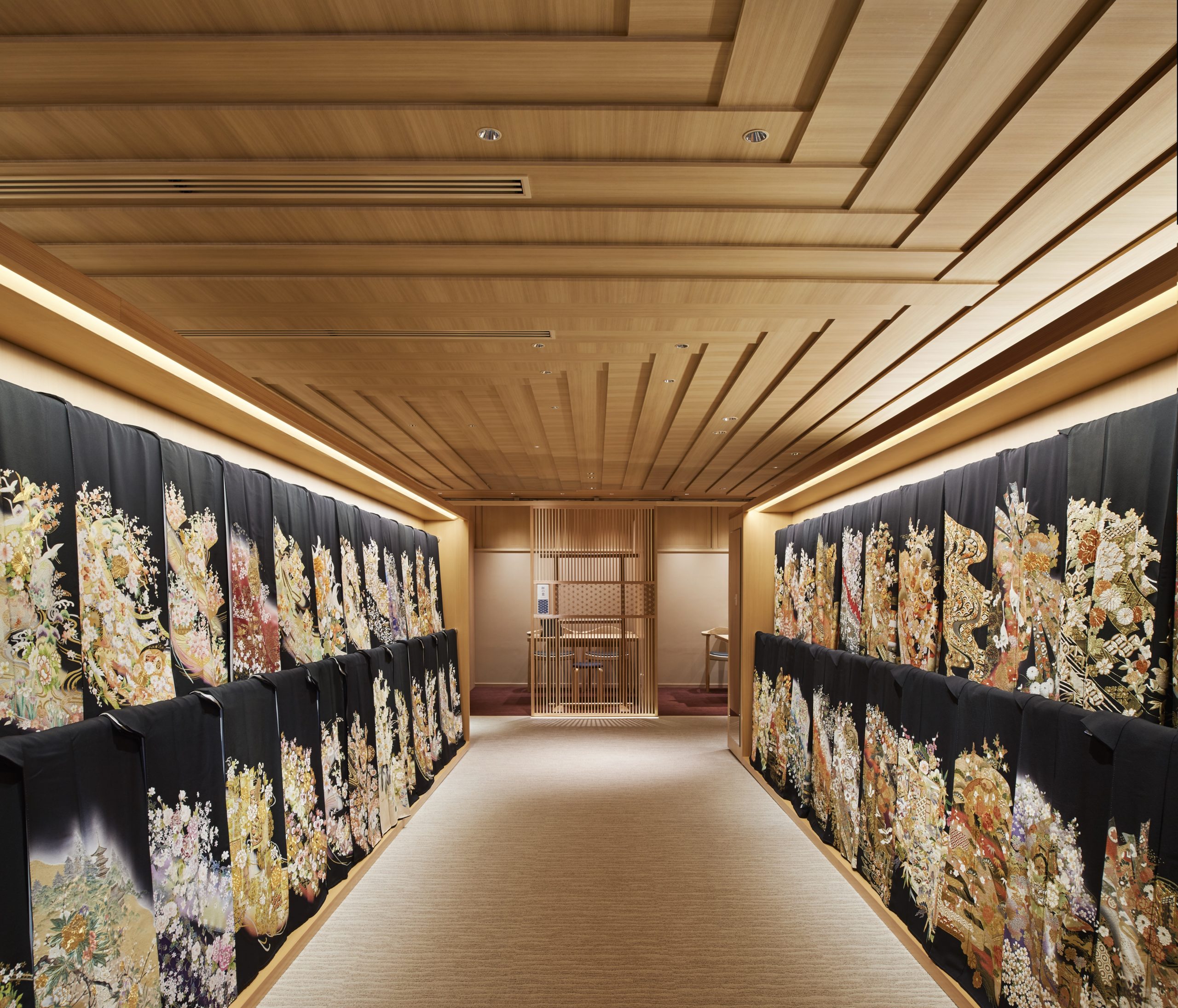 The design team refurbished the floor of the wedding Kimono in the traditional Japanese clothing shop Haregino Marusho and themed it with wood. Many spatial components, including display shelves, partitions and the ceiling, are in warm-color wood of similarly soft patterns. The space becomes an elegant wooden display box that does not take any spotlight from the kimono fabrics.
The design team refurbished the floor of the wedding Kimono in the traditional Japanese clothing shop Haregino Marusho and themed it with wood. Many spatial components, including display shelves, partitions and the ceiling, are in warm-color wood of similarly soft patterns. The space becomes an elegant wooden display box that does not take any spotlight from the kimono fabrics.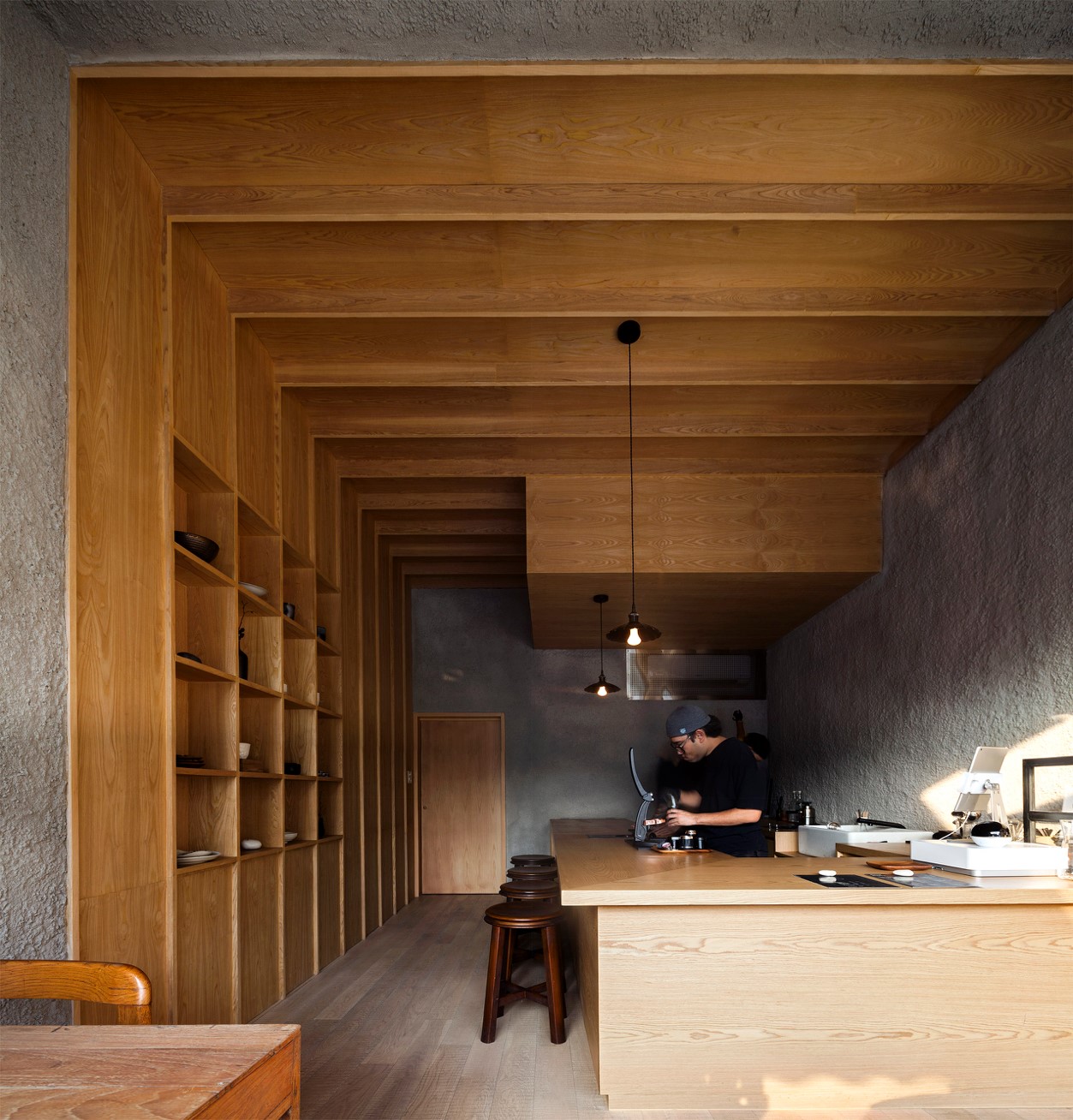
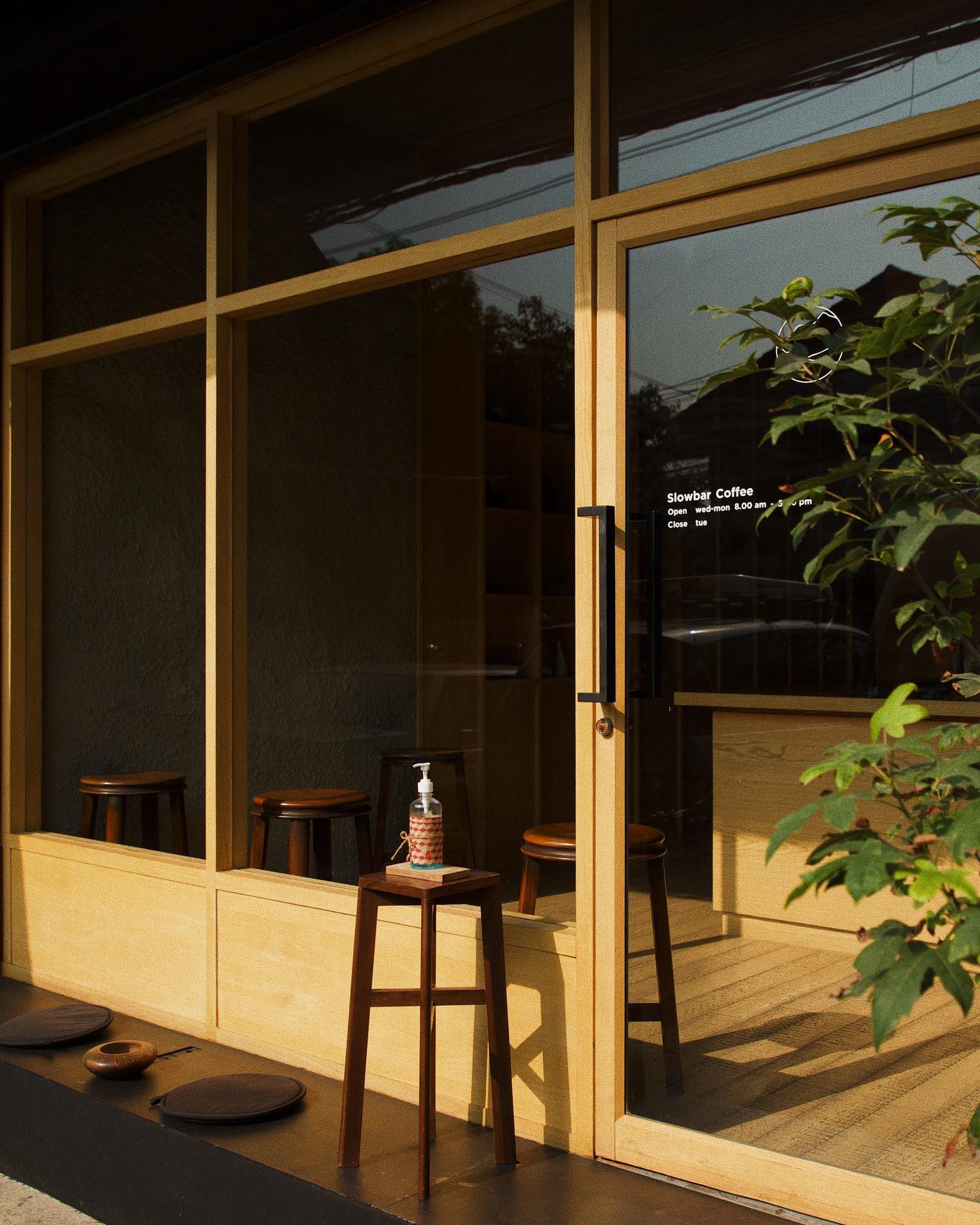 In the coffee bar Blackhill, smooth wooden surfaces are put in conjunction with rough concrete surfaces. They together create a zen space for enjoying a moment away from the busy central Bangkok. In contrast to the colorful urban environment outside, the materials used in the coffee shop are limited to only wood and concrete. The simplicity of the design makes it almost a meditative space.
In the coffee bar Blackhill, smooth wooden surfaces are put in conjunction with rough concrete surfaces. They together create a zen space for enjoying a moment away from the busy central Bangkok. In contrast to the colorful urban environment outside, the materials used in the coffee shop are limited to only wood and concrete. The simplicity of the design makes it almost a meditative space.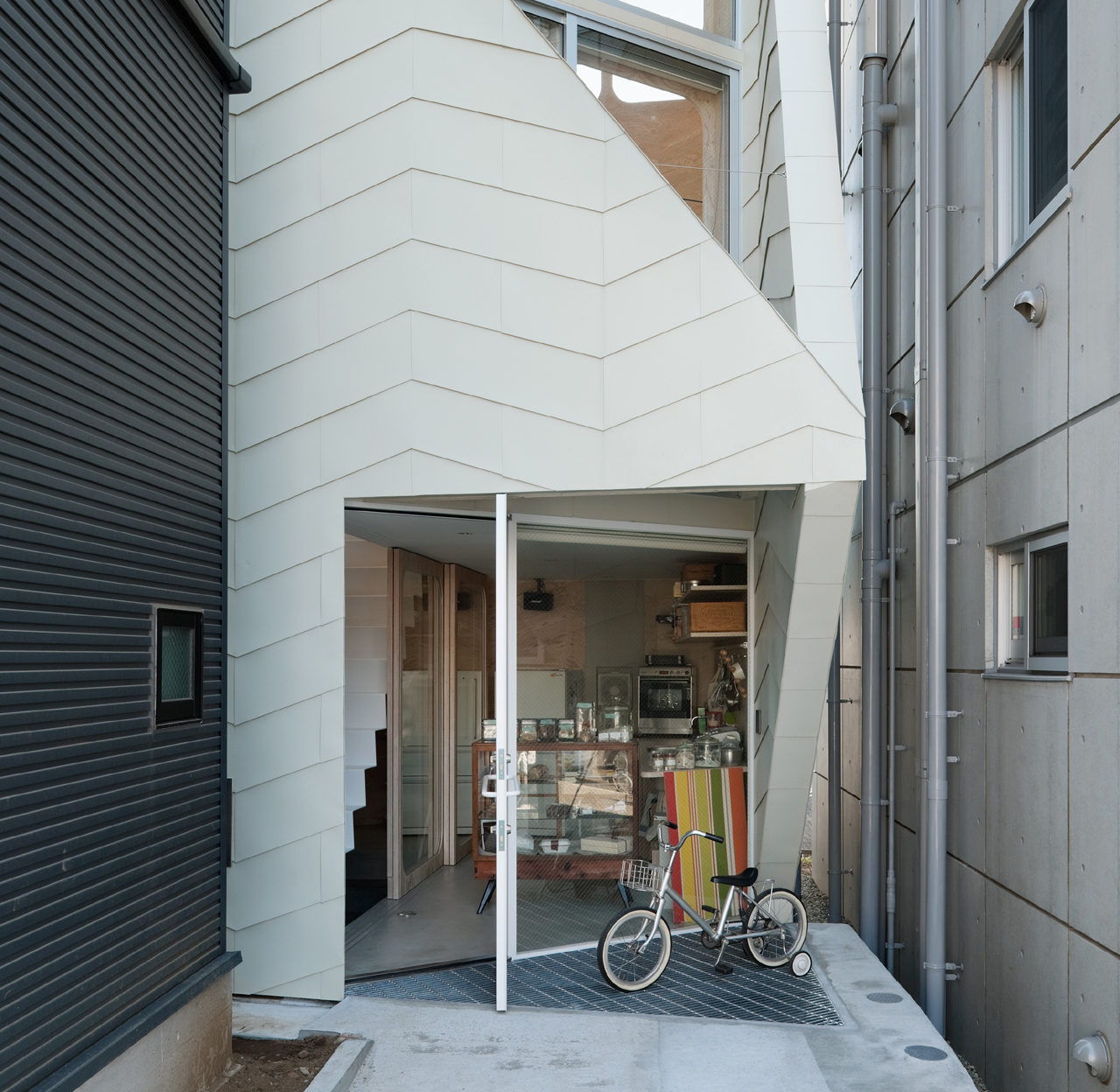
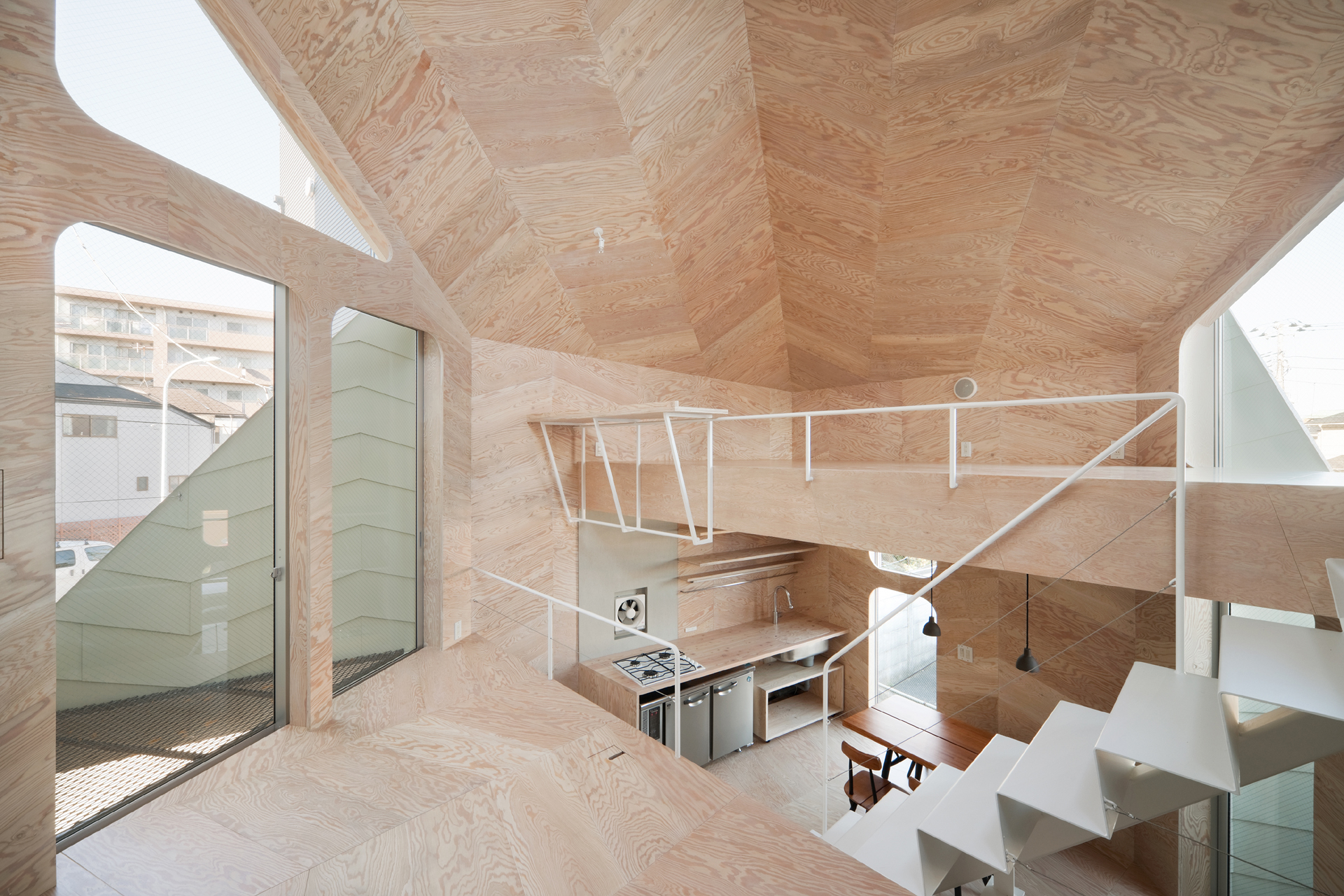 This small house has a footprint of only 280 square feet, yet it accommodates a biscuit shop and the shop owner’s family. Tsubomi House has seven different levels with no solid partitions between them. Each level is half a story higher/lower than the next one. Without walls separating each functional area, residents can move quickly from one space to another.
This small house has a footprint of only 280 square feet, yet it accommodates a biscuit shop and the shop owner’s family. Tsubomi House has seven different levels with no solid partitions between them. Each level is half a story higher/lower than the next one. Without walls separating each functional area, residents can move quickly from one space to another.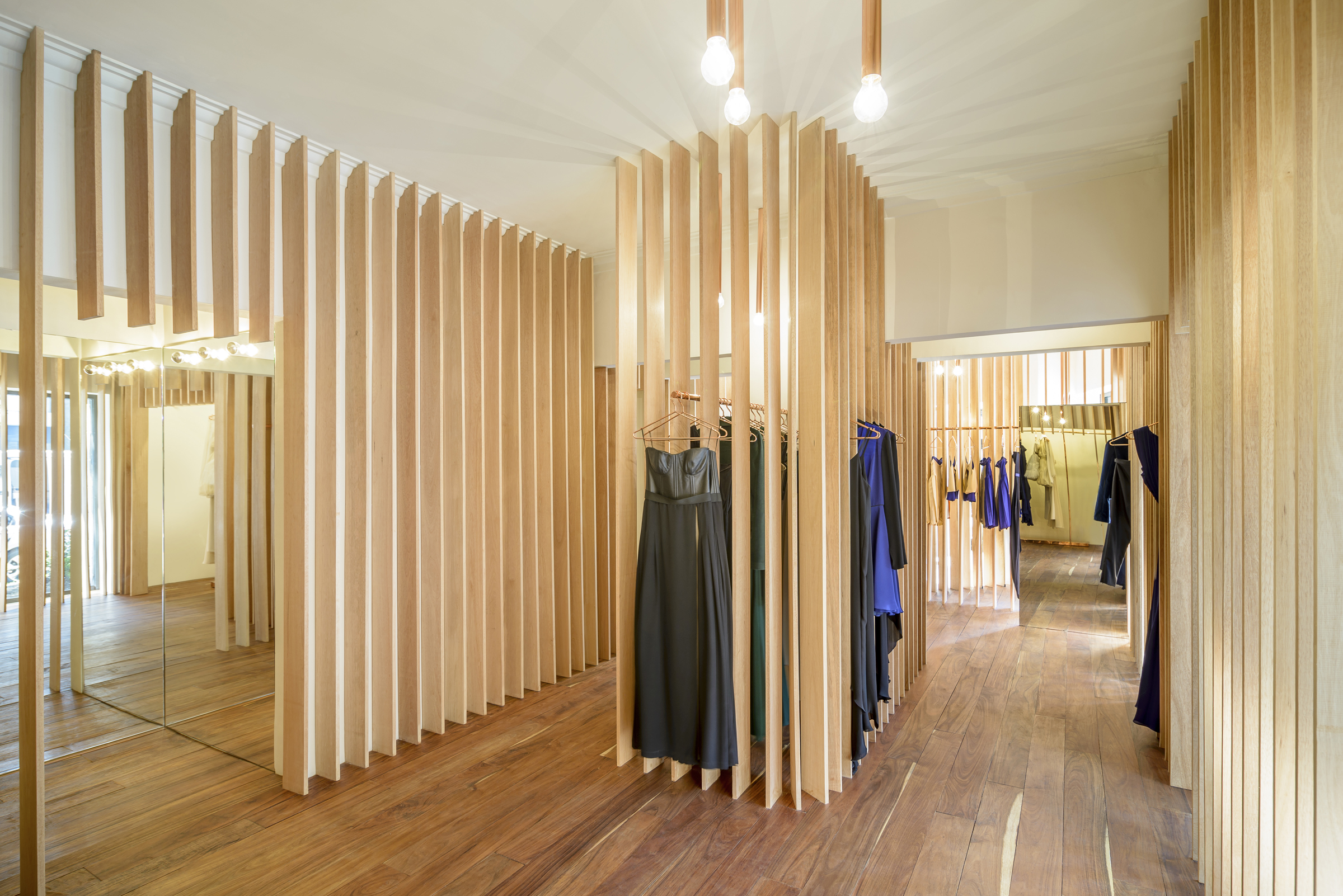
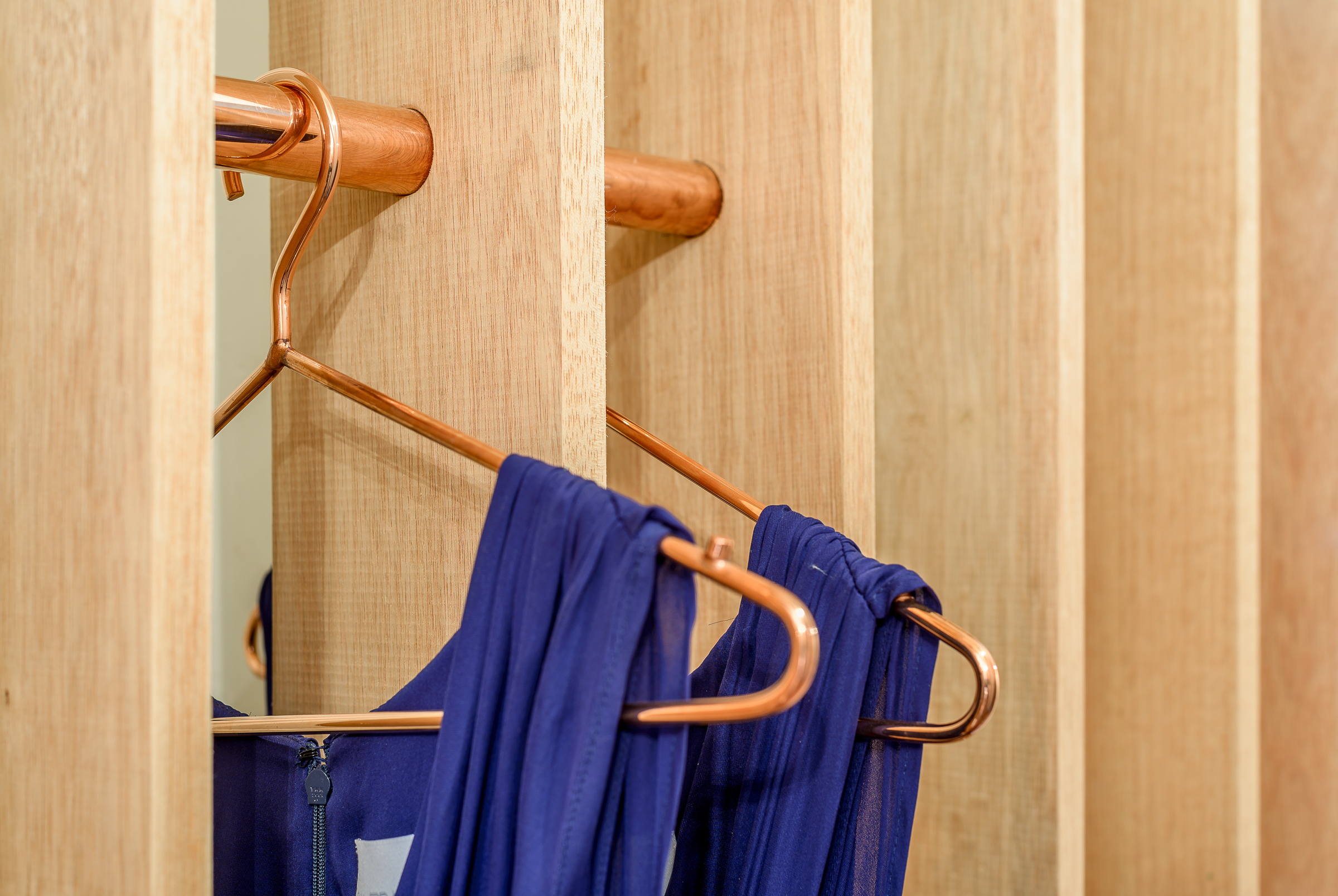 Instead of presenting the garments all at once, Sandra Weil Store’s design gradually reveals the collections as customers walk around. Floor-to-ceiling slats made of local tropical wood stand in line with equal intervals between them. They form rhythmic partitions that are visually permeable only from certain angles. This allows a comfortable level of privacy in the shop without cutting the small store space into tiny fragments.
Instead of presenting the garments all at once, Sandra Weil Store’s design gradually reveals the collections as customers walk around. Floor-to-ceiling slats made of local tropical wood stand in line with equal intervals between them. They form rhythmic partitions that are visually permeable only from certain angles. This allows a comfortable level of privacy in the shop without cutting the small store space into tiny fragments.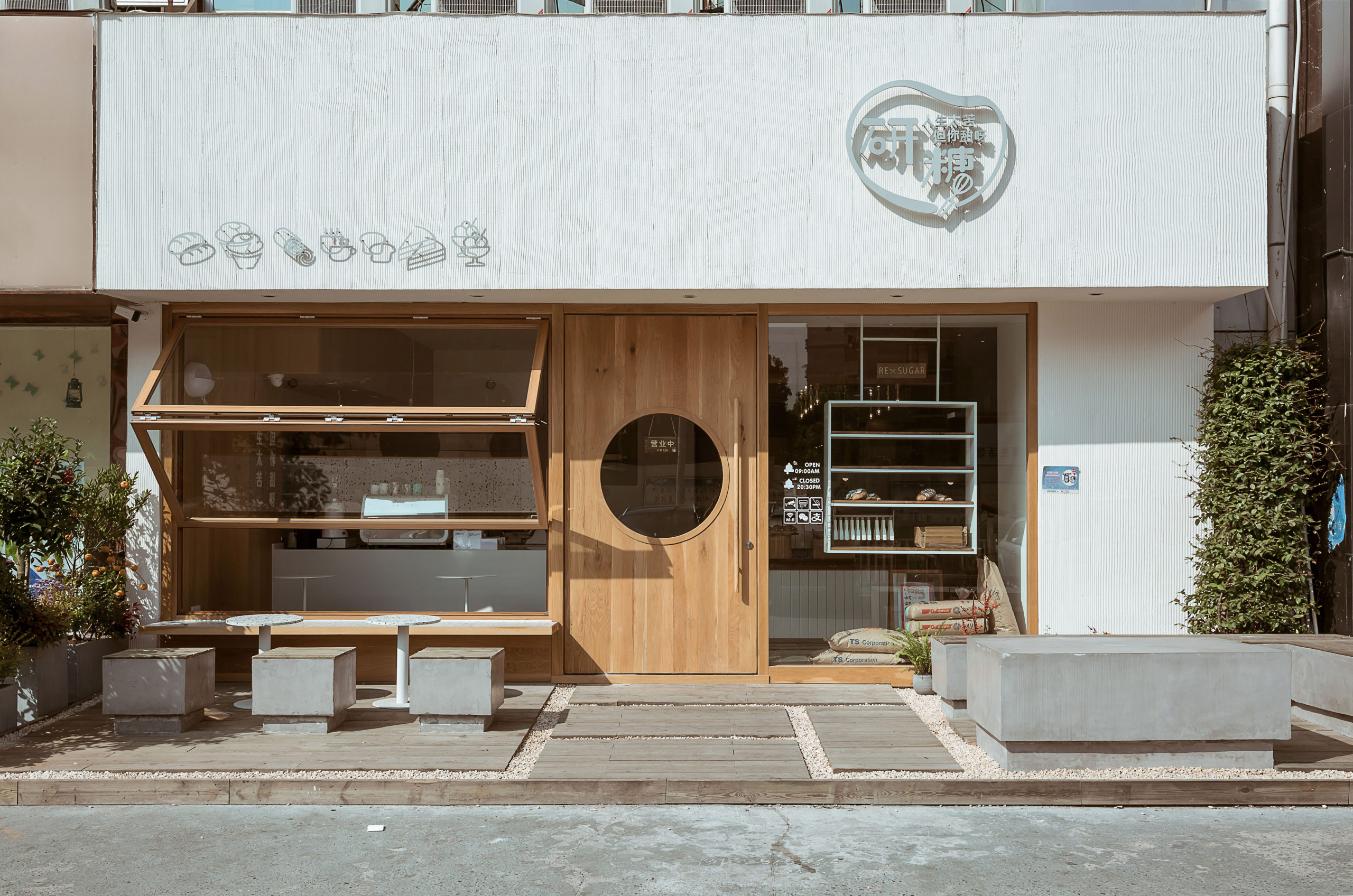
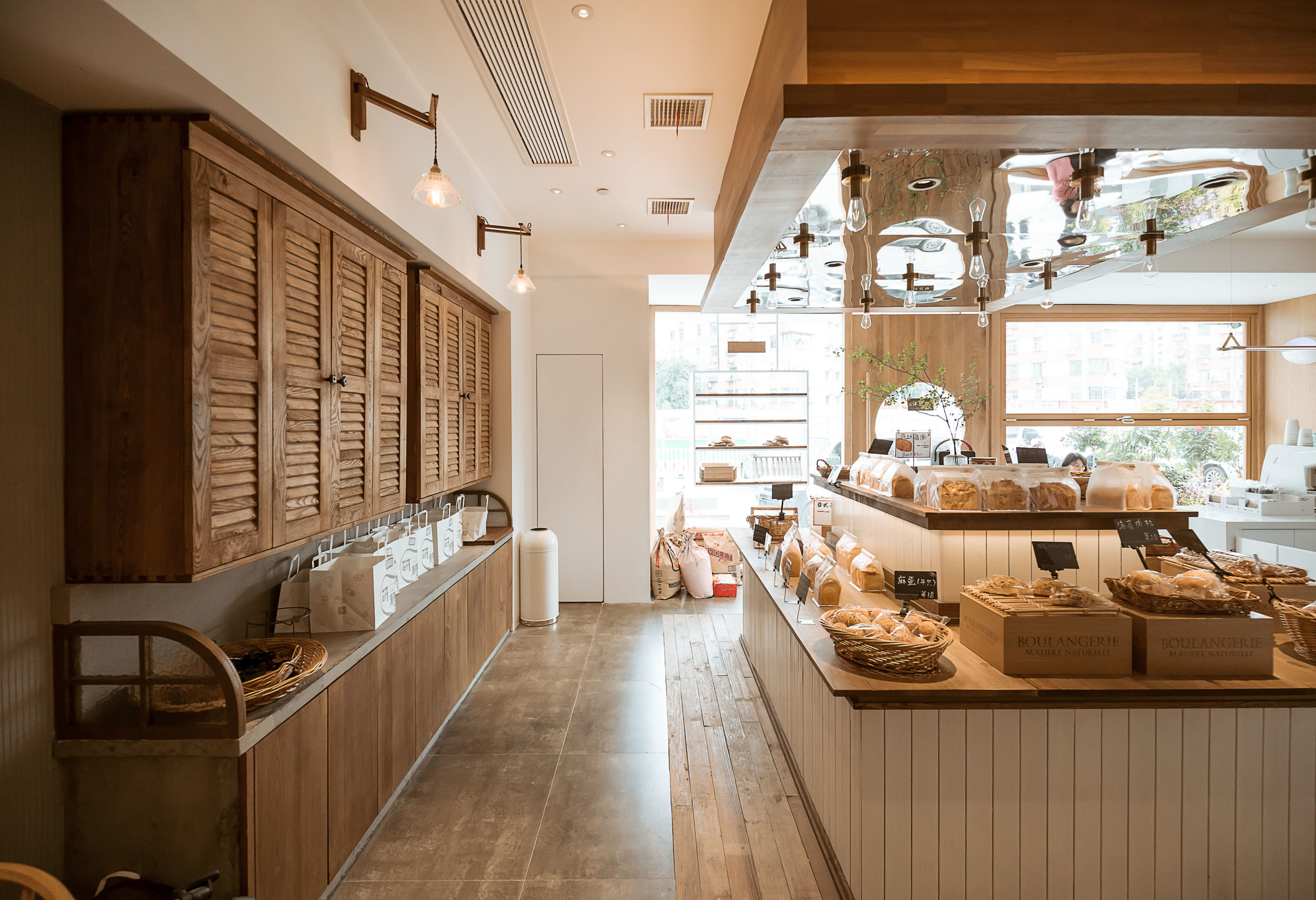 This community bakery uses large areas of warm-color timber to create a relaxing atmosphere. Like Blackhills Café, RE x SUGAR also has a transparent shop front that embraces the sunlight. A large folding window connects indoors and outdoors while the window sills become seats.
This community bakery uses large areas of warm-color timber to create a relaxing atmosphere. Like Blackhills Café, RE x SUGAR also has a transparent shop front that embraces the sunlight. A large folding window connects indoors and outdoors while the window sills become seats.