Material and spatial contrasts define Barwon Heads House
Australian studio Adam Kane Architects has renovated a cottage on a quiet coastal street in Barwon Heads and connected it to a barn-like extension by a glazed link.
Named Barwon Heads House, the project was designed by Melbourne studio Adam Kane Architects as a contemporary dwelling that embodied a “relaxed, coastal lifestyle”.
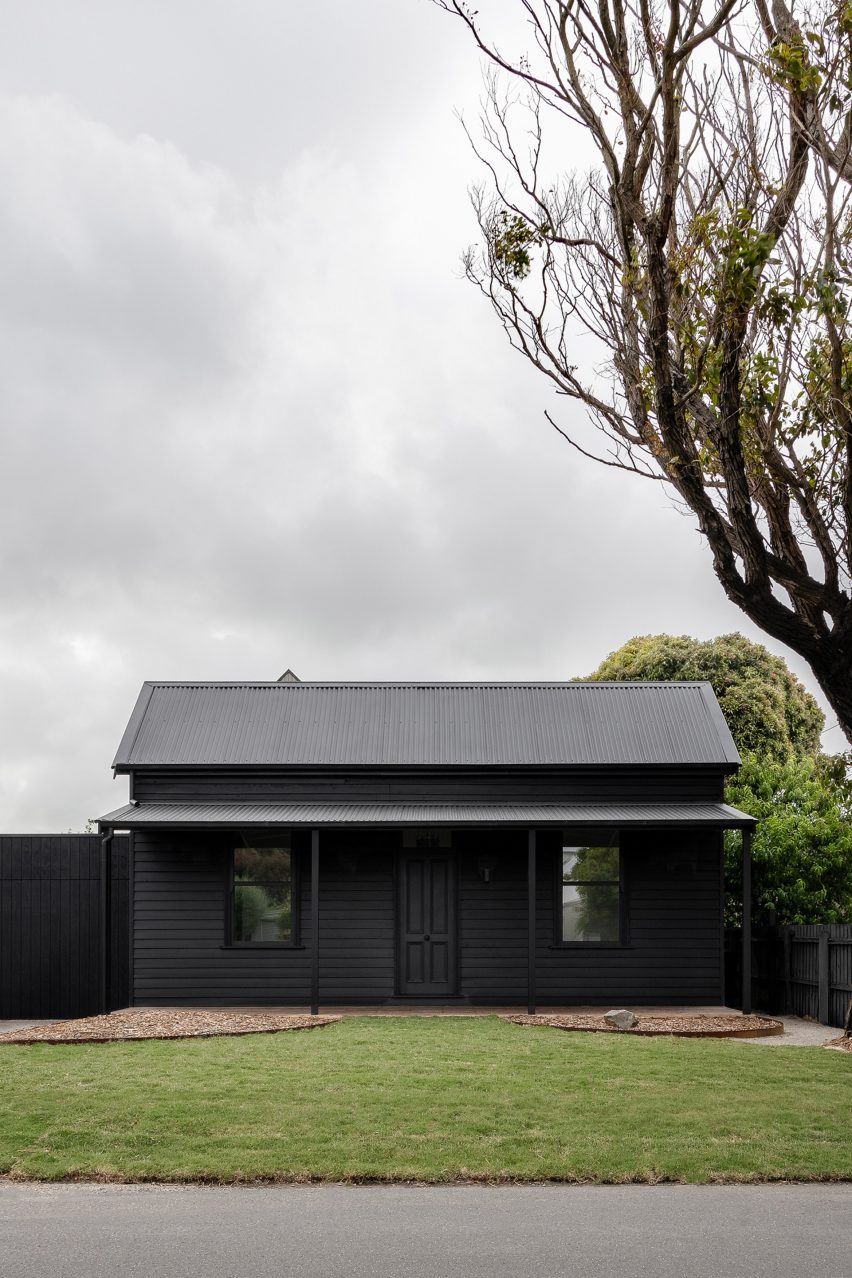

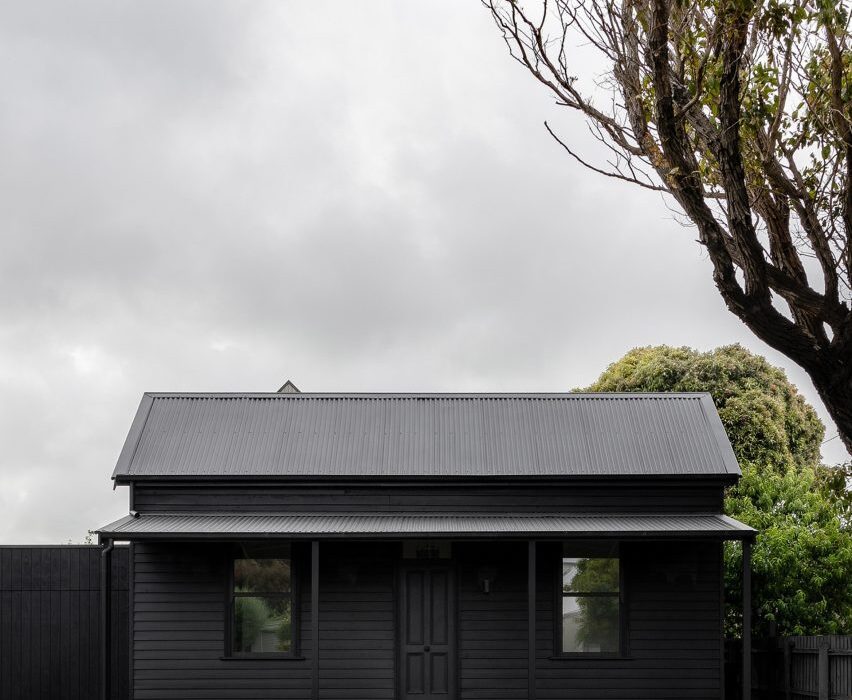
Prior to Adam Kane Architects‘ renovation and extension, the neglected weatherboarded cottage was known locally as “the dump”.
Its transformation led it to be shortlisted house interior of the year in the Dezeen Awards 2022 and win the public vote for the same category.
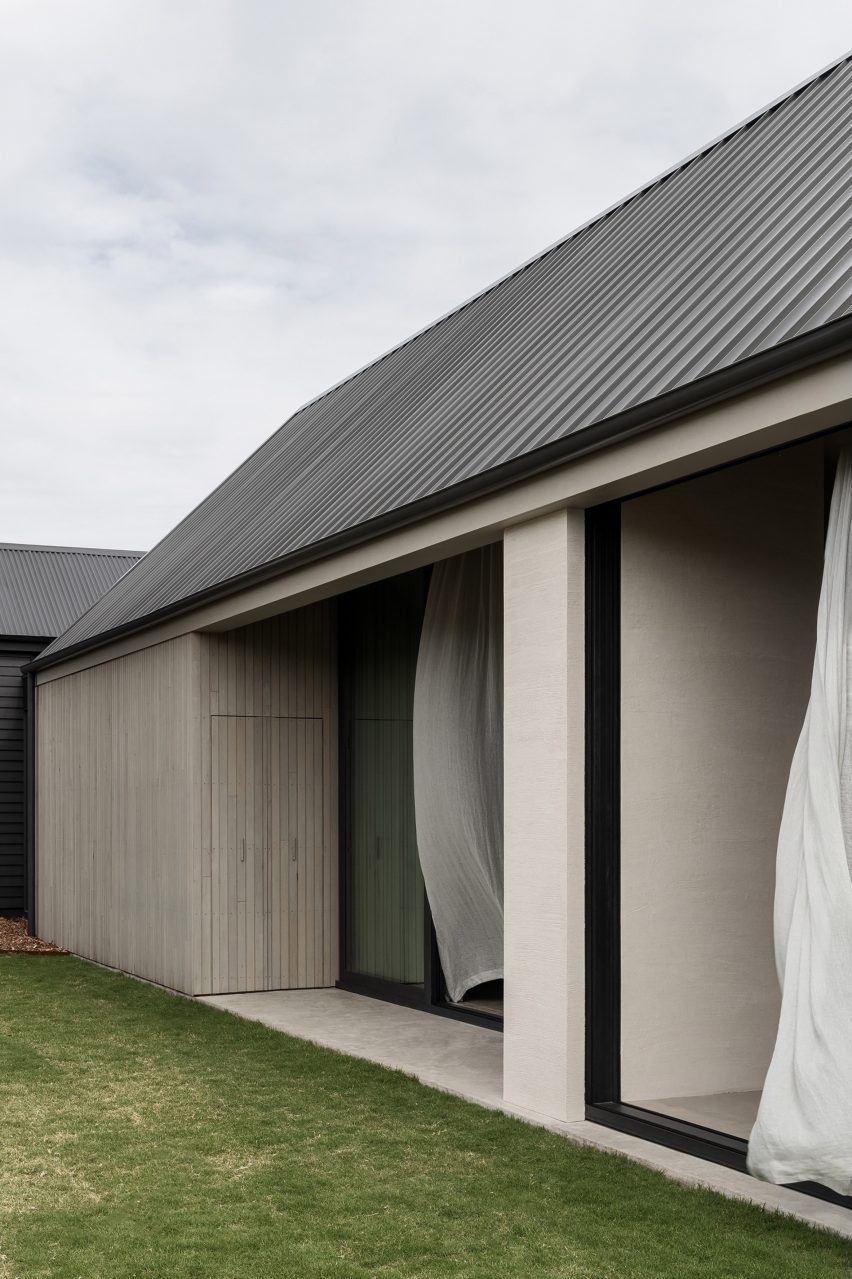

Adopting a minimal palette of monochrome contrasts, the studio painted the existing cottage’s exterior entirely black, pairing it with a lighter extension clad in silvery-grey weathered wooden planks.
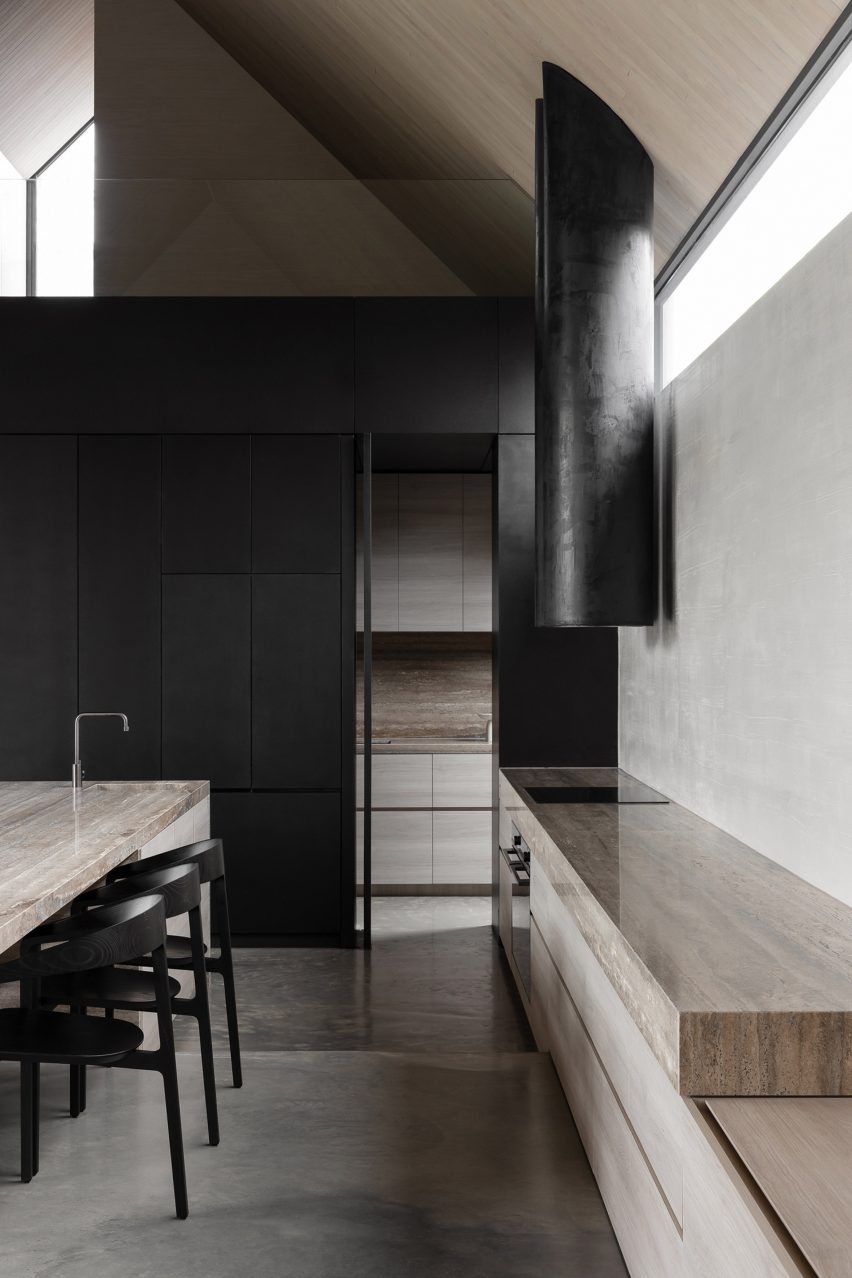
Beneath steeply pitched black metal roofs, this play of contrasts continues to the interiors, creating a spatial journey of “compression and release” that begins in the more compartmentalised cottage containing three bedrooms and a bathroom.
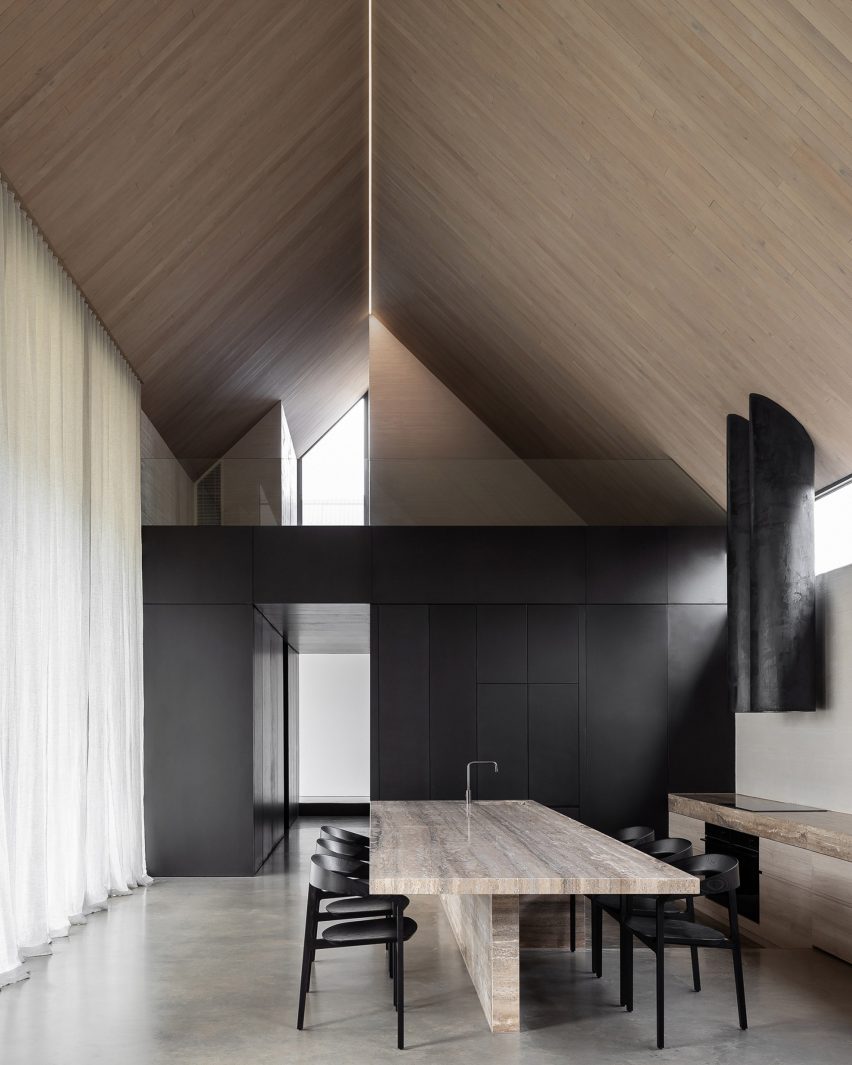

Moving through the existing cottage into the small glazed link and a dark corridor, Barwon Heads House’s extension opens up into a large living and dining space, overlooked by the main bedroom on a mezzanine above.
Full-height windows look out to Barwon Heads House’s garden to the north, while a narrow clerestory-level window opposite draws in light above its kitchen.
“Access to the extension is via an enclosed corridor, lined with black mottled joinery panels on walls and ceilings, and is used to conceal doorways into the rumpus, laundry and storage areas,” said Adam Kane Architects.
“The ‘journey’ through this dark corridor with a lower ceiling creates a sense of compression before a sense of release when walking towards the living room, where the gable opens up into the main space,” it continued.
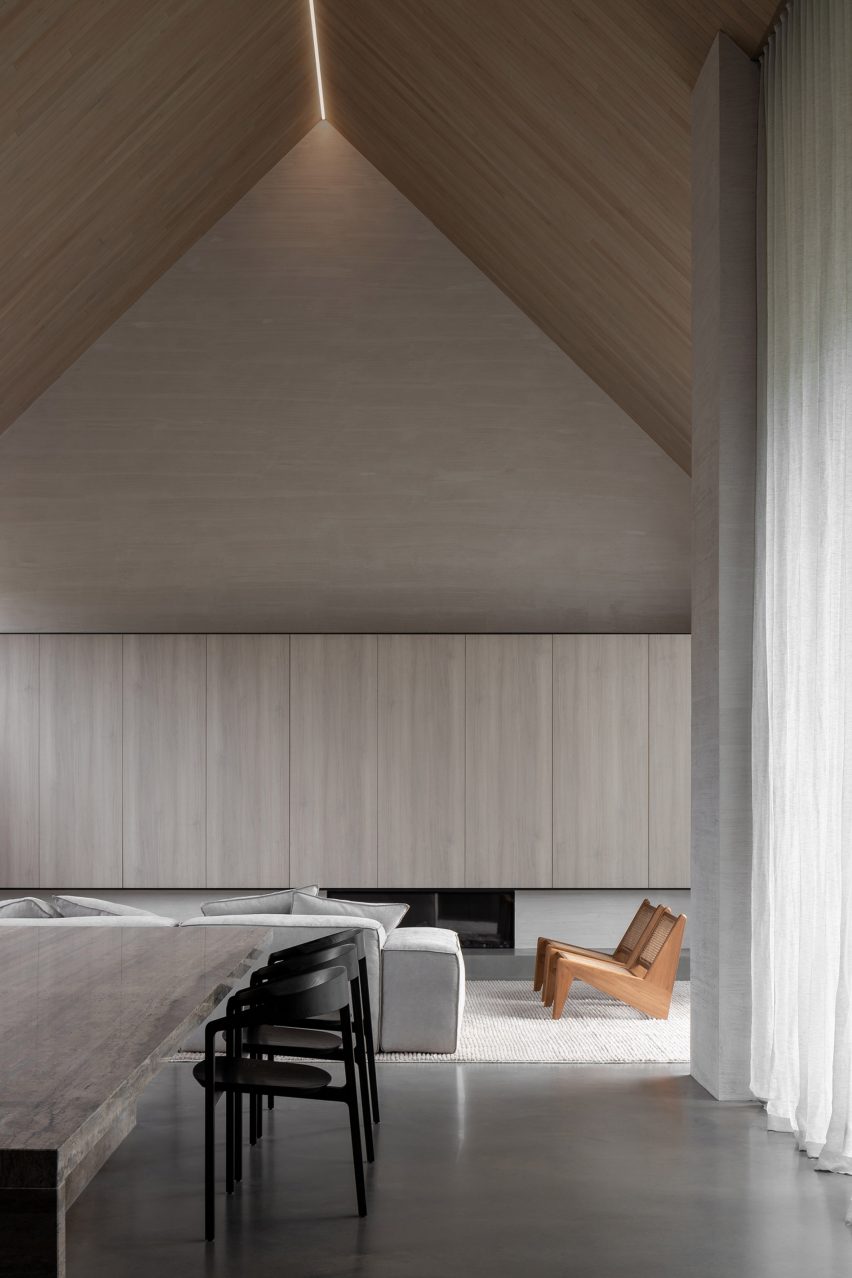

Existing features were retained in the cottage, while the extension has a deliberately simple interior finished with oak panelling and exposed concrete. Slabs of travertine marble are used as countertops, coffee tables and a large dining table.
“Heritage features are maintained through the use of the original lining board ceilings, as well as period skirting and architraves, which fit perfectly with the renewed tones,” said the studio.
“The timber lining helps blur the threshold between inside and out, delineating zones, making spaces feel more generous and contributing to the relaxed feel of the home.”

Adam Kane Architects was founded in 2015, and its previous projects include a bridal boutique in Melbourne with minimal finishes of concrete and marble.
Alongside Barwon Heads House, other projects shortlisted in the house interior category of Dezeen Awards 2022 include a home in Melbourne with a palette of “organic” materials by Brave New Eco and the renovation of a 120-year-old townhouse in Kyoto by Td-Atelier and Endo Shojiro Design.
The photography is by Timothy Kaye.


 Properties of Graphene:
Properties of Graphene:


 All said and done, this process produces ZERO water waste. That’s right, zero with a Z. In 2022, this is welcome news indeed. The past few years have seen new attention given to the issue of water conservation as global water shortages have become a mounting problem.
All said and done, this process produces ZERO water waste. That’s right, zero with a Z. In 2022, this is welcome news indeed. The past few years have seen new attention given to the issue of water conservation as global water shortages have become a mounting problem. Cosentino believes that consumers need not compromise quality in the name of sustainability. In fact, those Silestone surfaces that have been produced with HybriQ+ technology are among the most beautiful the company has ever produced. The company explains that “the new mineral composition enables never before-seen effects in color depth, texture and tone.” Indeed, Cosentino has long proven that synthetic materials can be just as elegant and intricate as natural materials.
Cosentino believes that consumers need not compromise quality in the name of sustainability. In fact, those Silestone surfaces that have been produced with HybriQ+ technology are among the most beautiful the company has ever produced. The company explains that “the new mineral composition enables never before-seen effects in color depth, texture and tone.” Indeed, Cosentino has long proven that synthetic materials can be just as elegant and intricate as natural materials. We recommend spending time on the
We recommend spending time on the