How Gen Z Designers Are Smashing Conventions With “Creative Self-Exploration”
The next report in Material ConneXion’s insightful series on material trends focuses on the ultra-contemporary phenomena of expressionism among new generations of creators. Following on from their Eunomia report — which revealed insights into designers’ renewed passion for nature as a primary source of inspiration — their next release is entitled “Creative Self-Exploration”, and covers the rising trend for fluidity and dynamism with regards to everything from identity and aesthetics to occupation and innovation.
Learn More and Access the Full Report
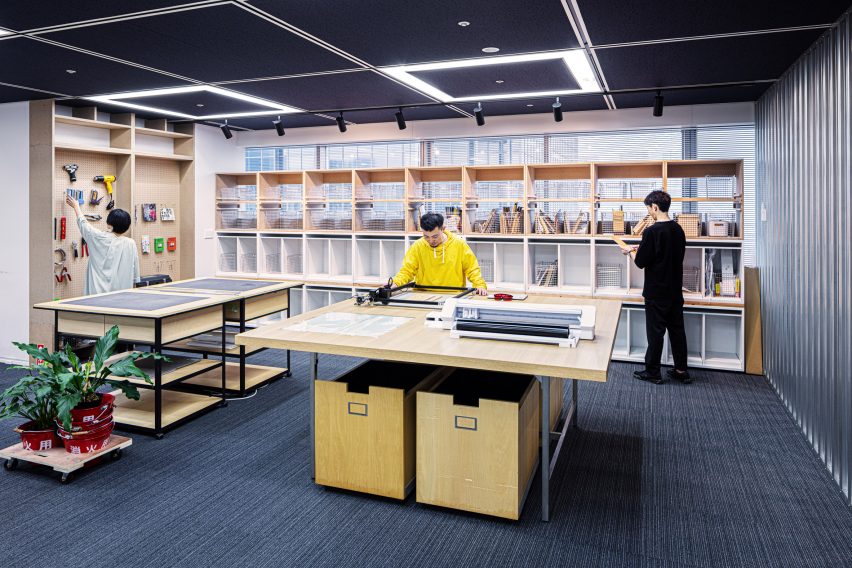
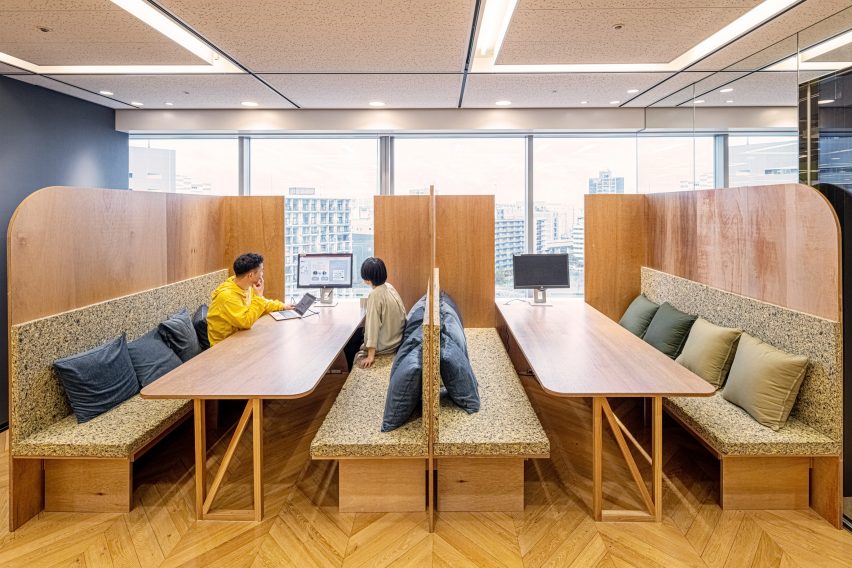
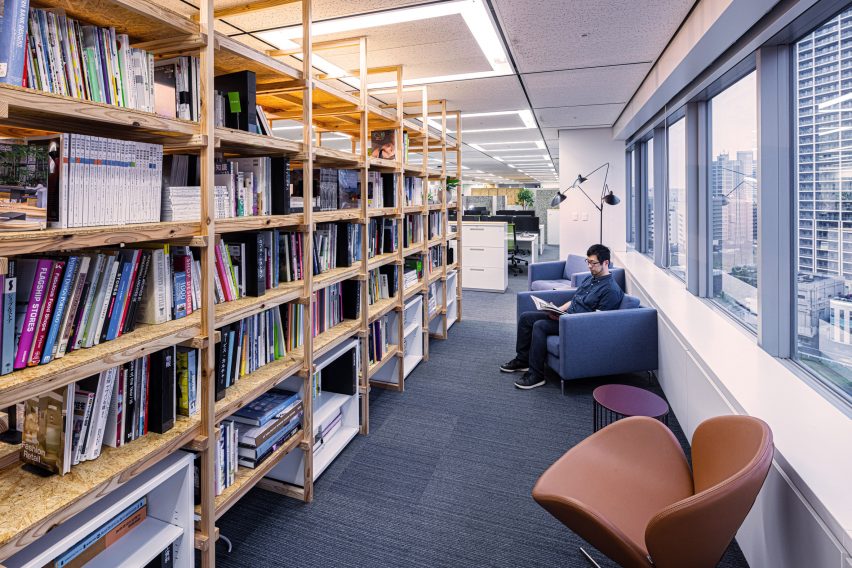
Illustrated with vibrant examples of creative individualism, the new trends “reflect a growing aspiration, especially among GEN Z and Alpha, to explore all the components that make up ‘the self’, from physical appearance to existential depth and emotions, overlooking established norms.” They also point towards a new wave of entrepreneurship, with young people breaking free from conventional occupations. Instead, they are harnessing the maturing landscape of social media to create their own opportunities, as well as emerging realms such as the metaverse.
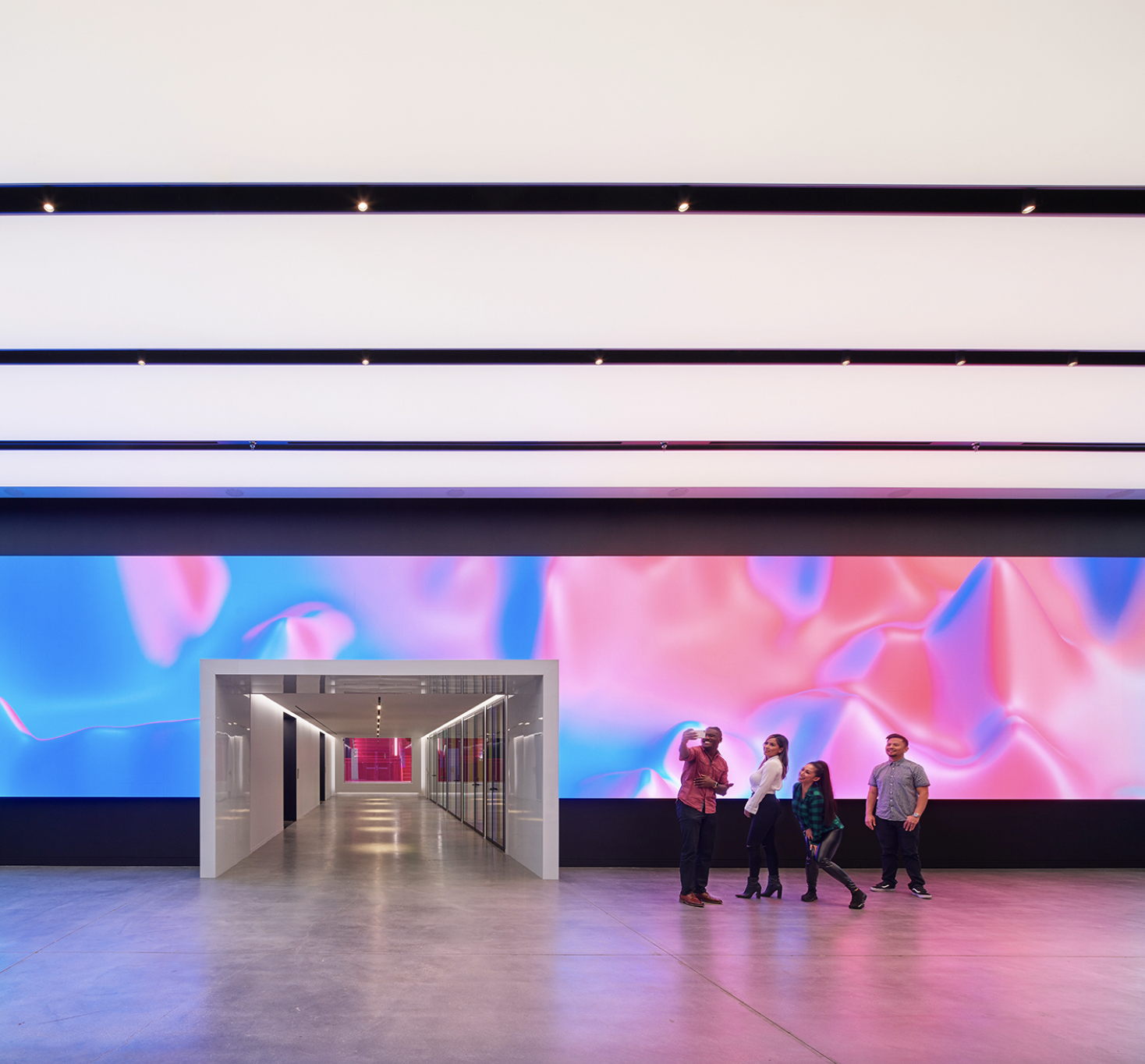

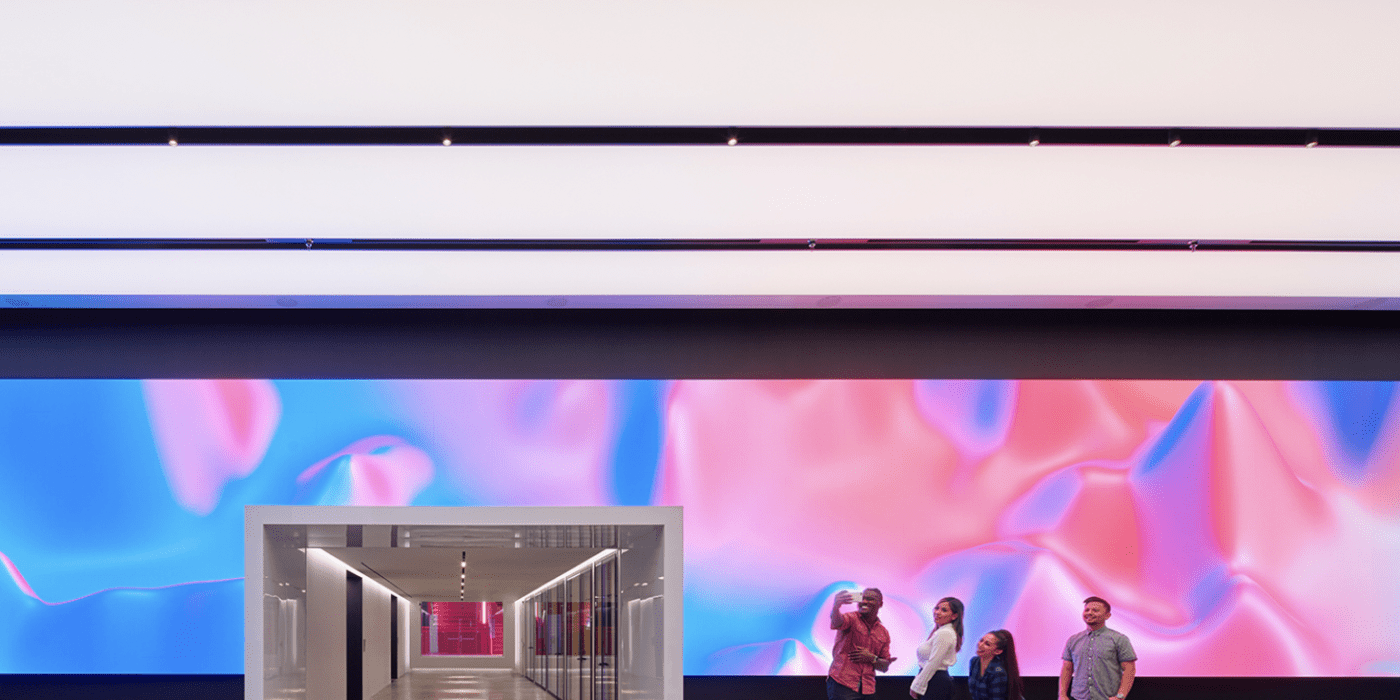
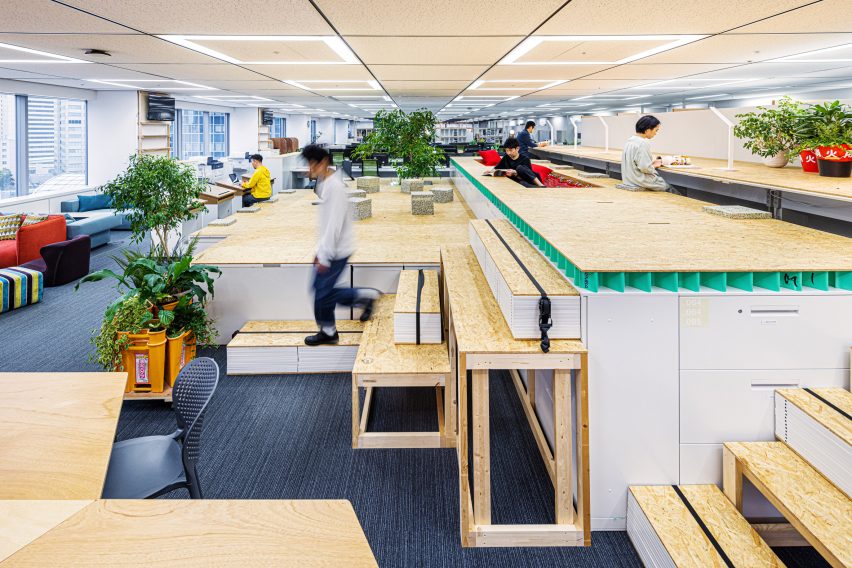
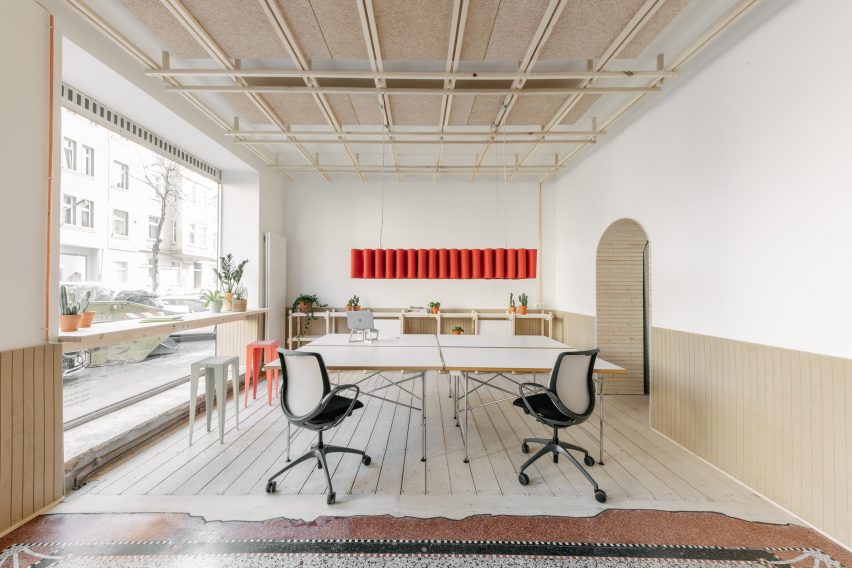
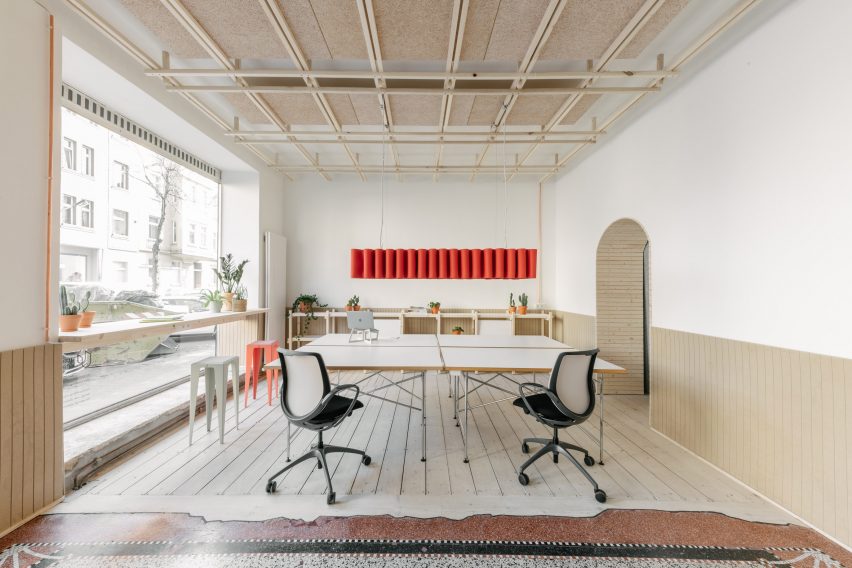
Tiktok Headquarters by Gensler, 9th Annual A+Awards Finalist in the Large Office Interiors category.
In terms of architecture and design, these trends are manifested in avant-garde projects that challenge traditional ideas pertaining to the function, program and typology of buildings. One example is the “Tiktok Beauty Hub”. As described in the report, “Tiktokers now have a creative hub in the heart of LA, hosted by Fenty Beauty, Rhianna’s brand. The concept behind this collaborative space is to help influencers on the platform by offering a fully stocked ‘Make-up Pantry’ in a camera-ready, creative space as well as community building amongst participants.”
One of a number of innovation concepts in the report is named “Phygital Experiences”, highlighting new investments in “marvelous, magical worlds and bewitching inspirations that boost the imagination” and “immersive and multisensorial experiences that create the sensation of lucid dreaming.” This form of design, with its emphasis on interactivity, engagement and dynamic mediums is undoubtedly permeating architecture and design — one such example is the work of Turkish digital artist, Refik Anadol, whose installation “Quantum Memories” was a recent A+Awards Finalist in the Architecture +New Technology category.

Quantum Memories by Refik Anadol, 9th Annual A+Awards Finalist in the Architecture +New Technology category.
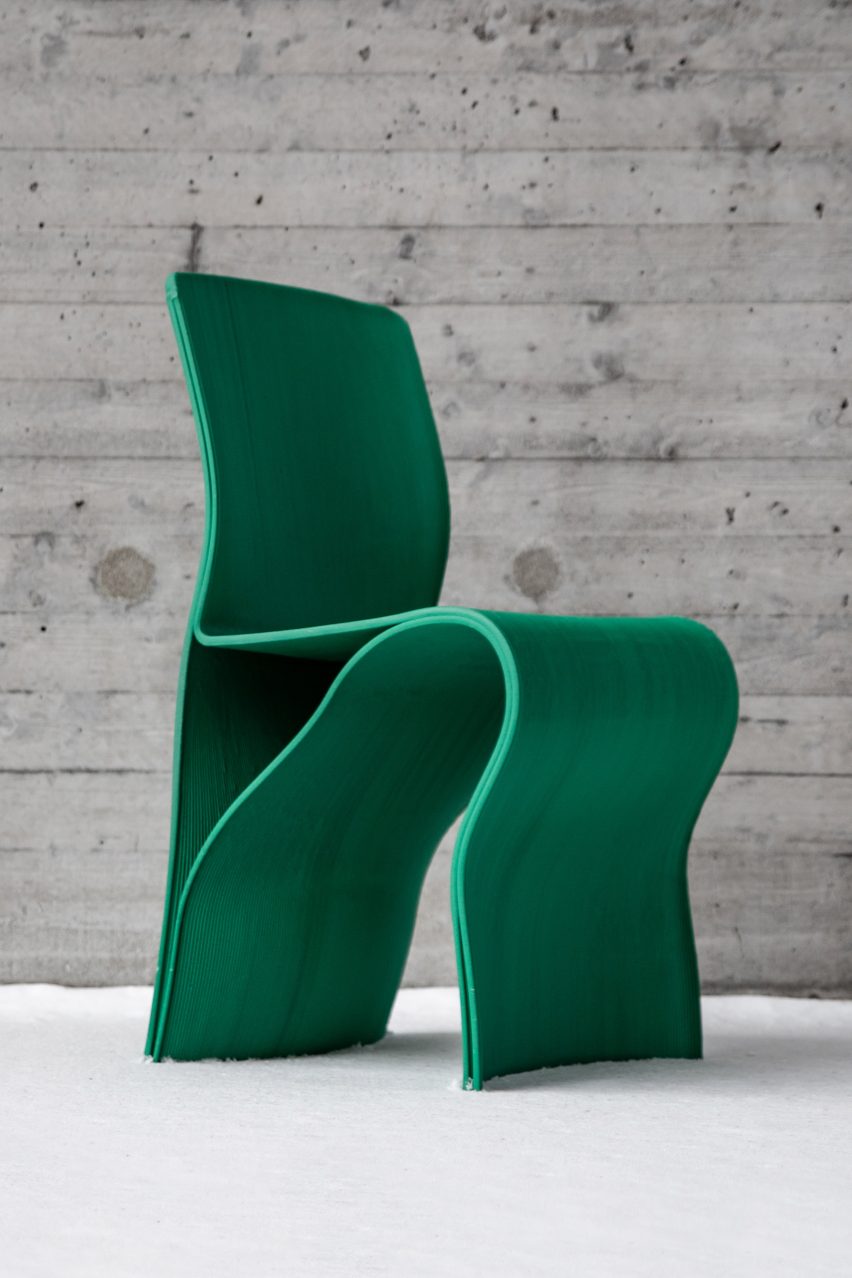
In the report’s ‘Design Ideations’ section, a series of multichromatic mood boards visualizes how the rise of creative self-exploration can be translated into real-world spaces, textures, materials, products and beyond. The bold range of colors, forms and finishes on display encapsulates the overriding takeaway from this report — that emerging creatives are not concerned in the slightest with the social or aesthetic “rules” of prior generations. In fact, they embrace the unconventional, and revel in its unlimited creative potential.
To see the full trend report and receive new material insights each month, become a member of Material ConneXion. Learn more >
Top image: 100 colors no.35 by emmanuelle moureaux architecture + design, 9th Annual A+Awards Finalist in the Architecture +Color category.
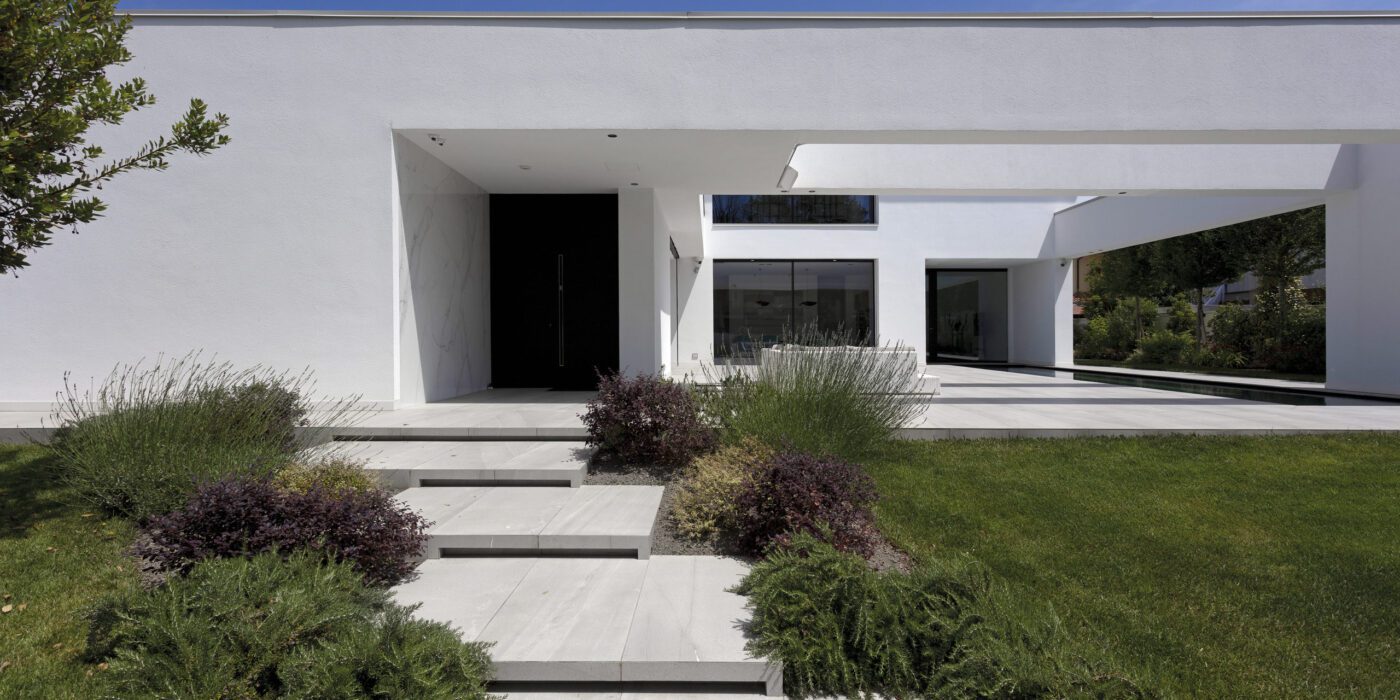
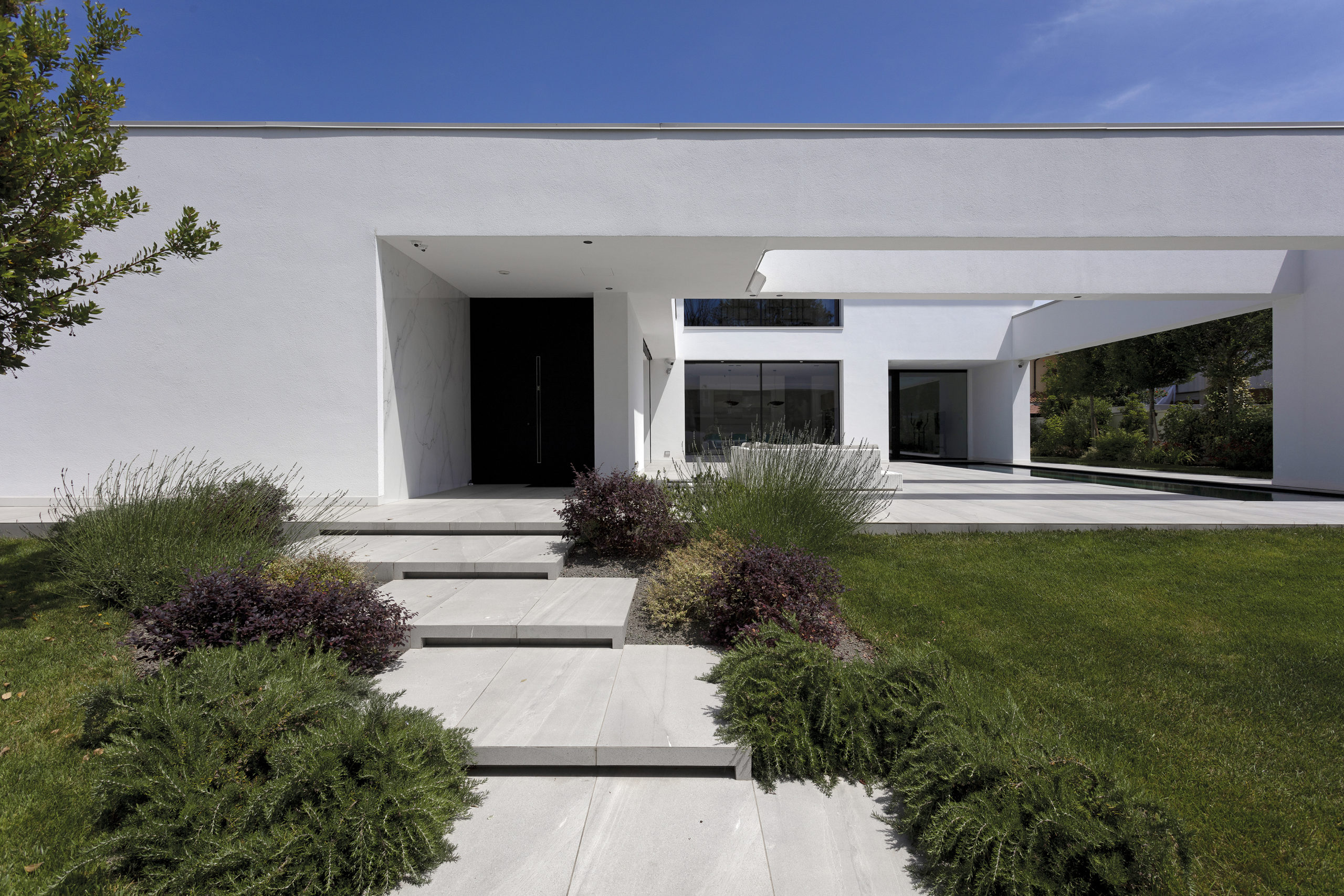
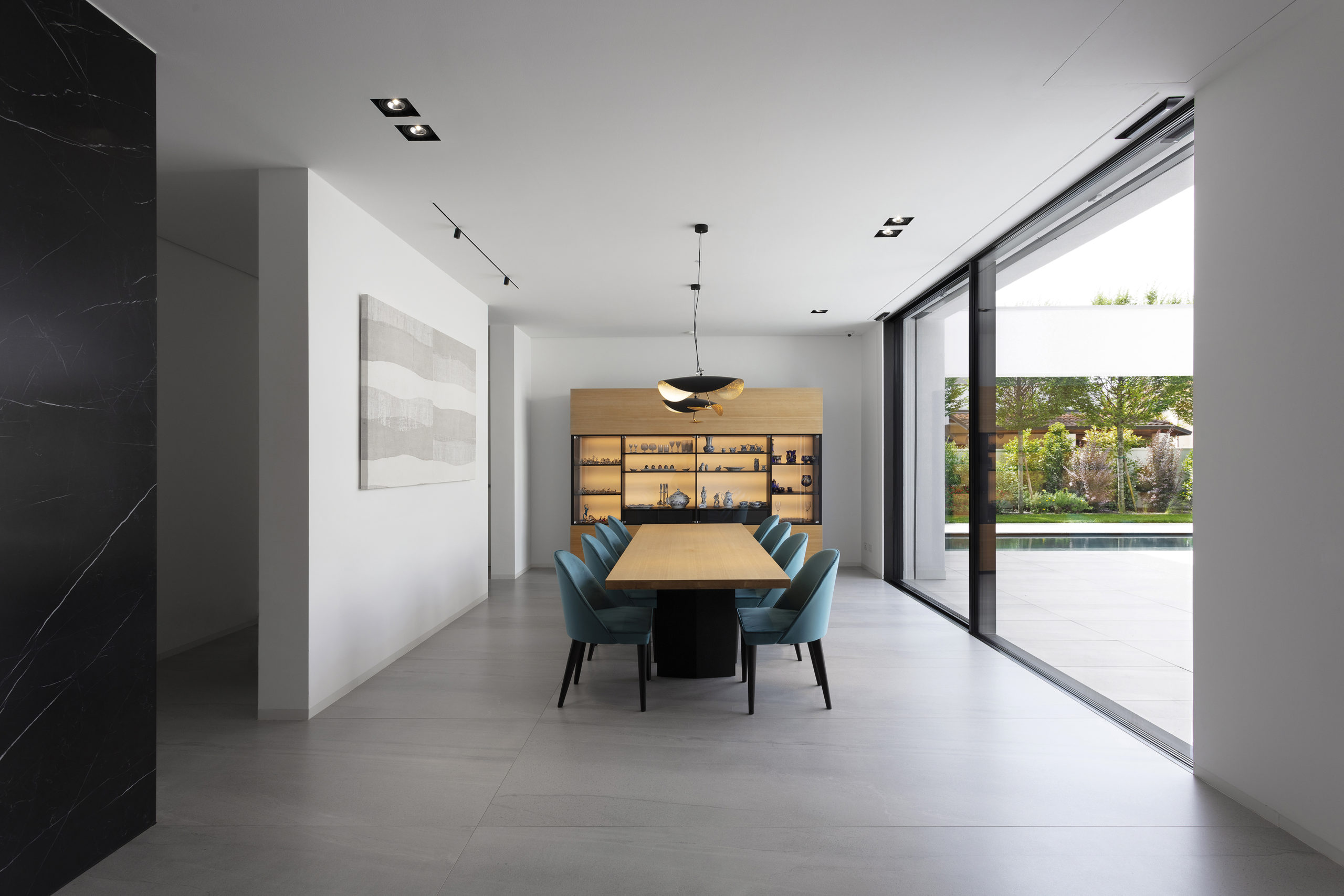
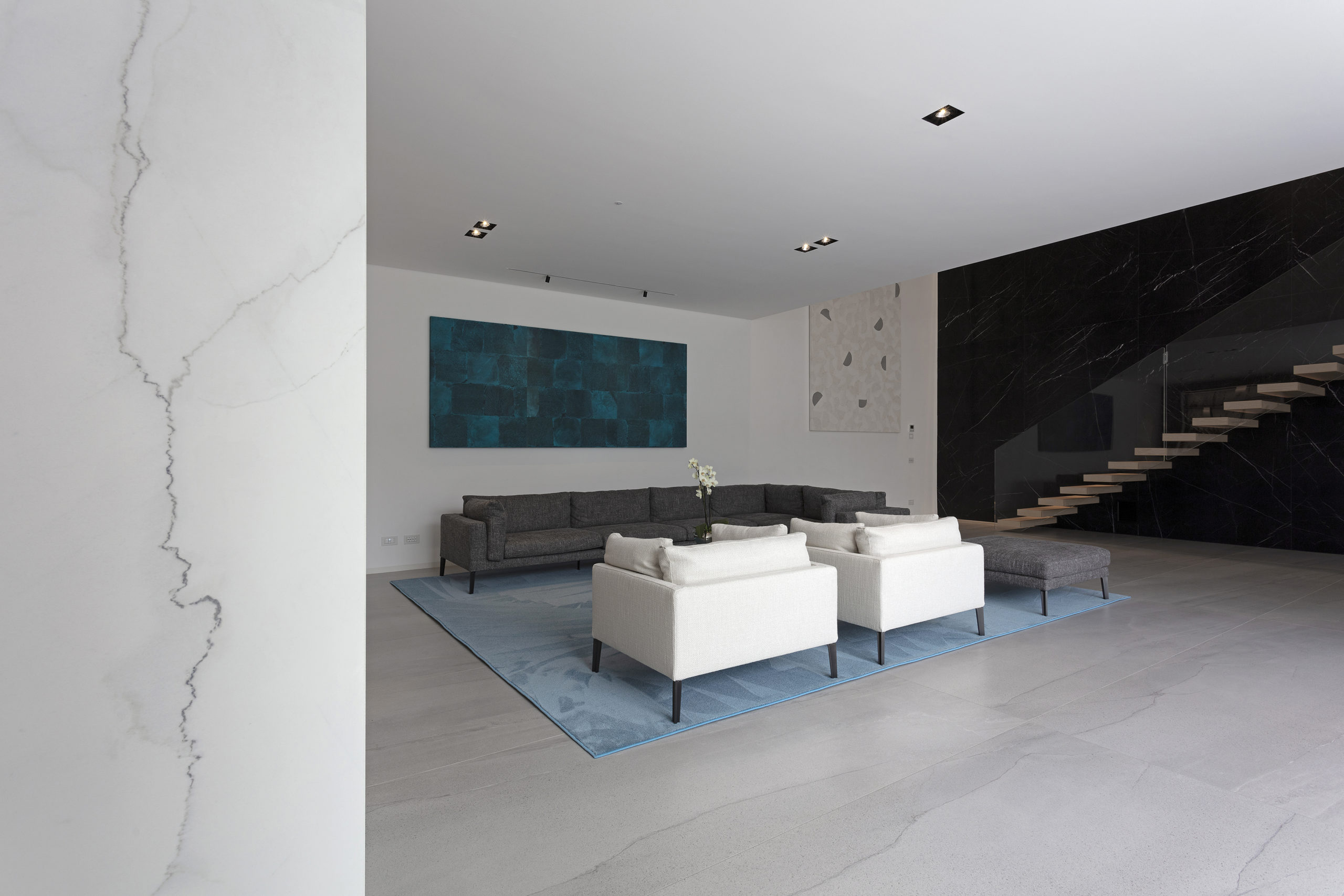
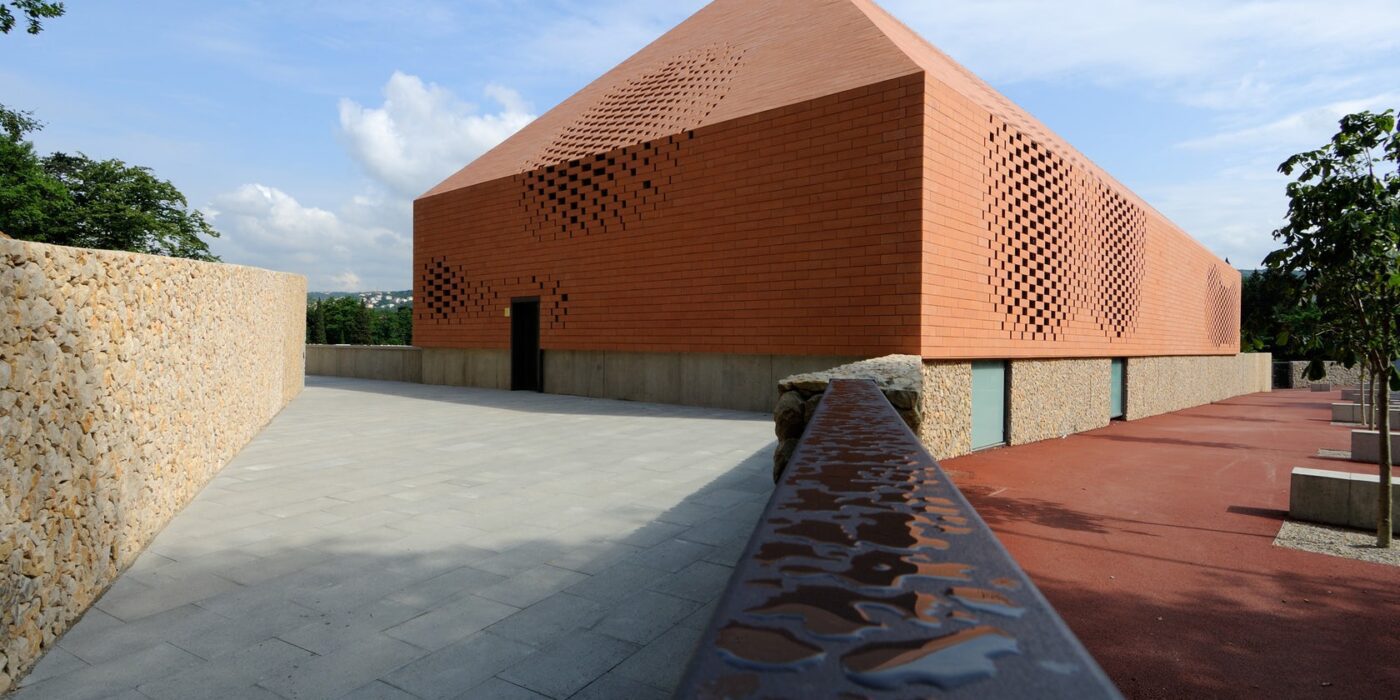
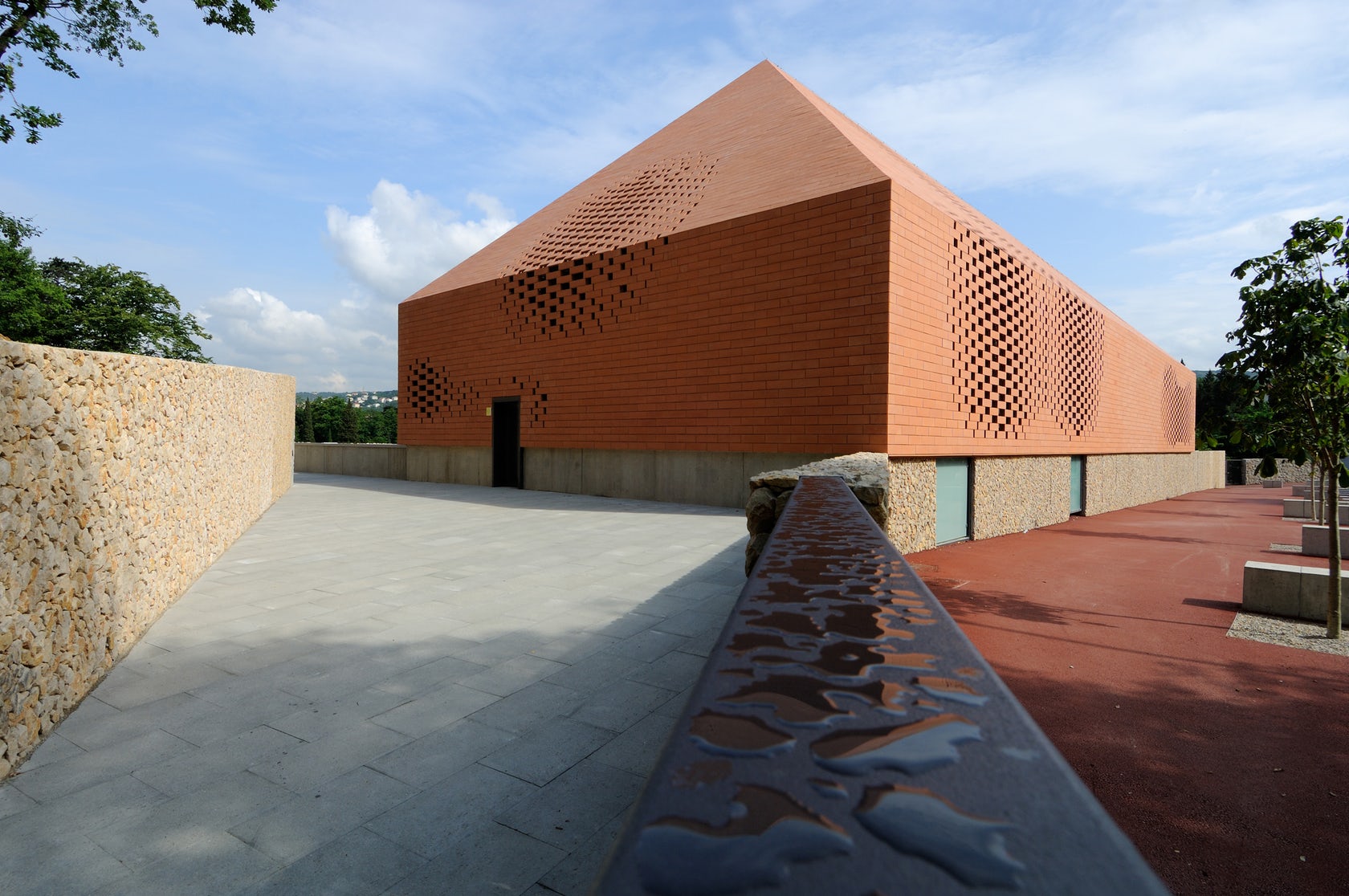
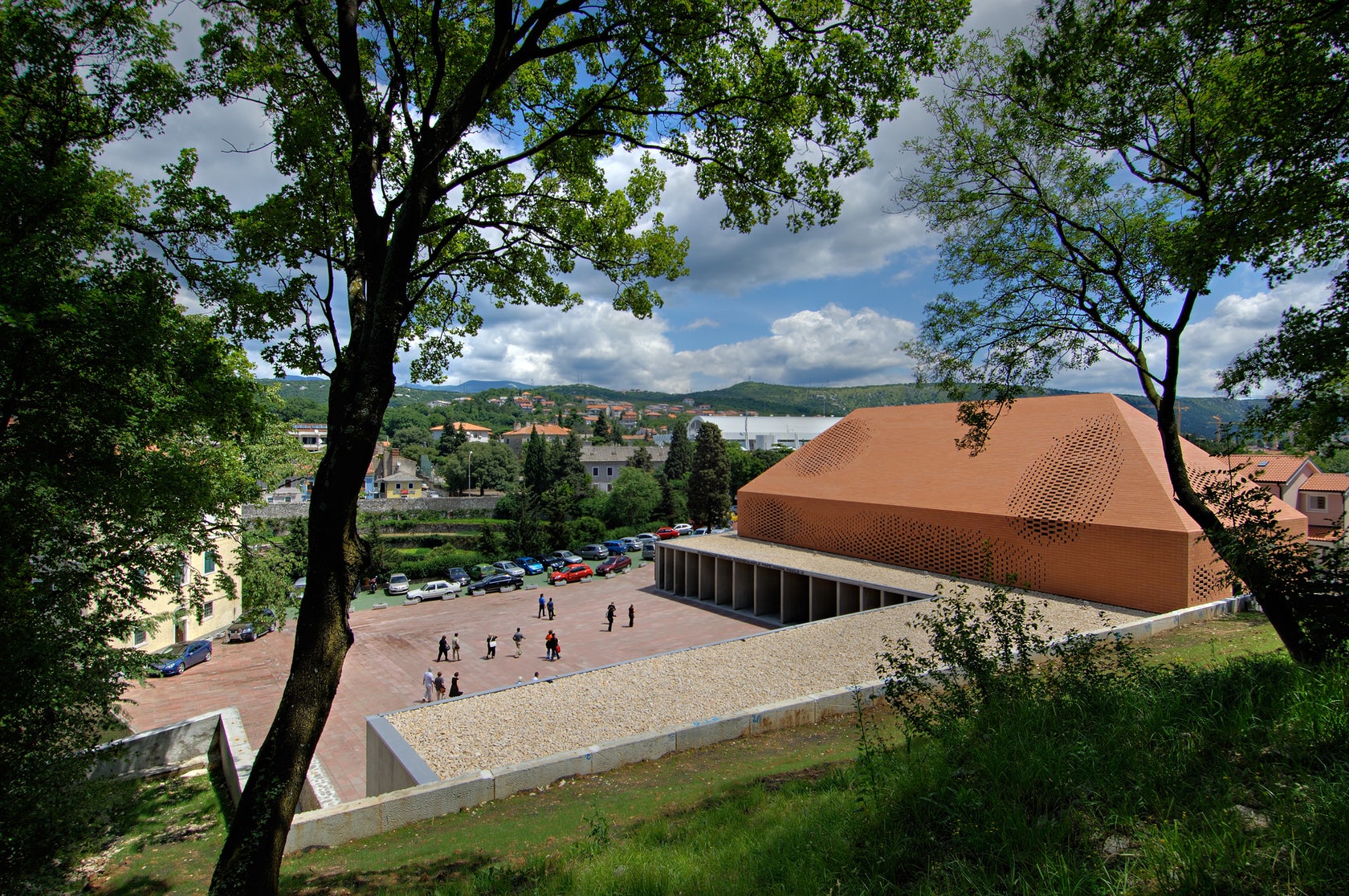





















































 Sited in one of the most important pilgrimage sites in Croatia, this Great Hall was designed alongside the Pope’s visit to Rijeka. Housing cultural activities of the monastery, the project also creates a new major entrance for the pilgrims and a large public walk. A pixel-ized terracotta volume was designed to filter light inside the structure while a columned portico forms a new public square outside.
Sited in one of the most important pilgrimage sites in Croatia, this Great Hall was designed alongside the Pope’s visit to Rijeka. Housing cultural activities of the monastery, the project also creates a new major entrance for the pilgrims and a large public walk. A pixel-ized terracotta volume was designed to filter light inside the structure while a columned portico forms a new public square outside.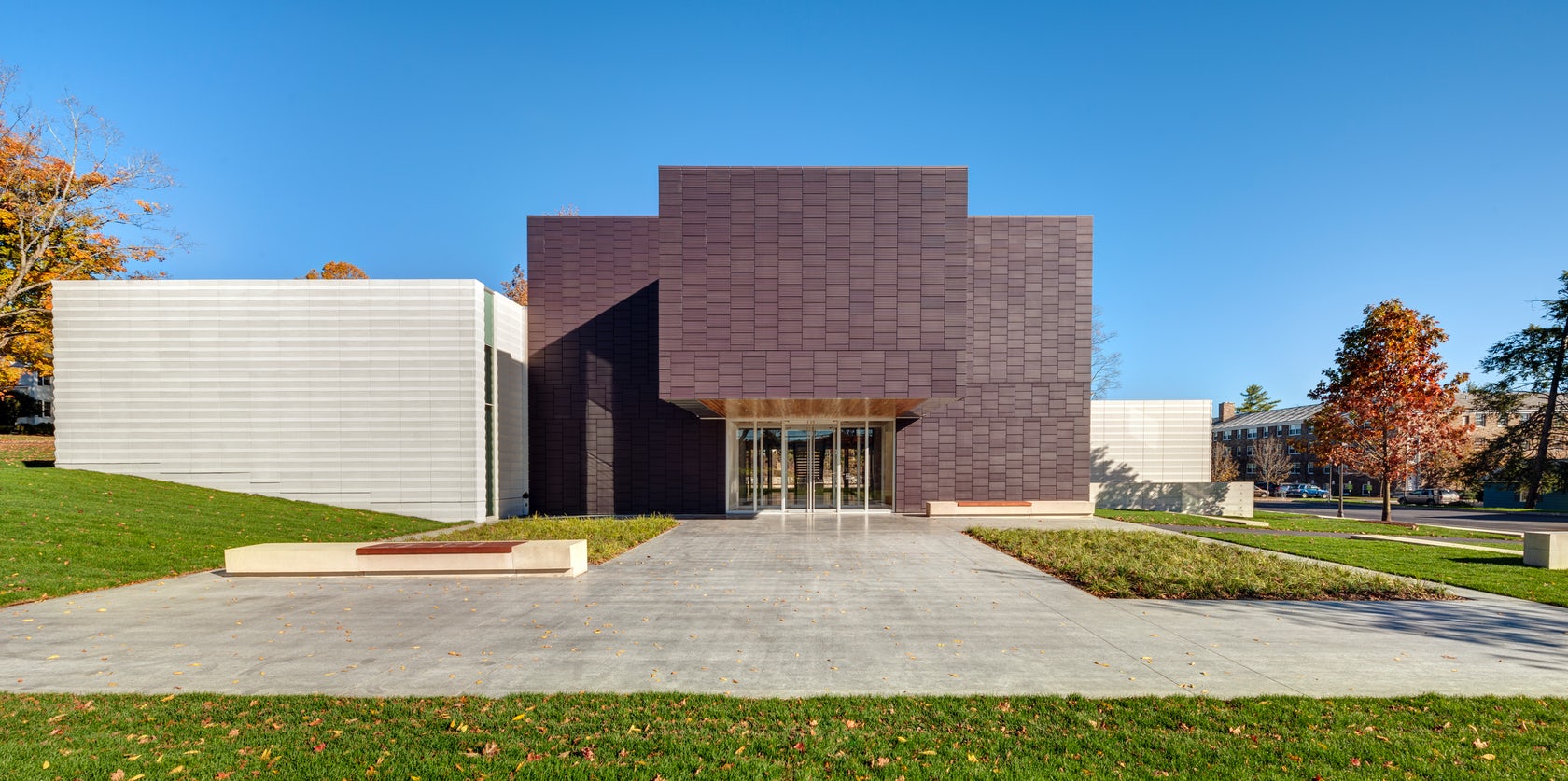
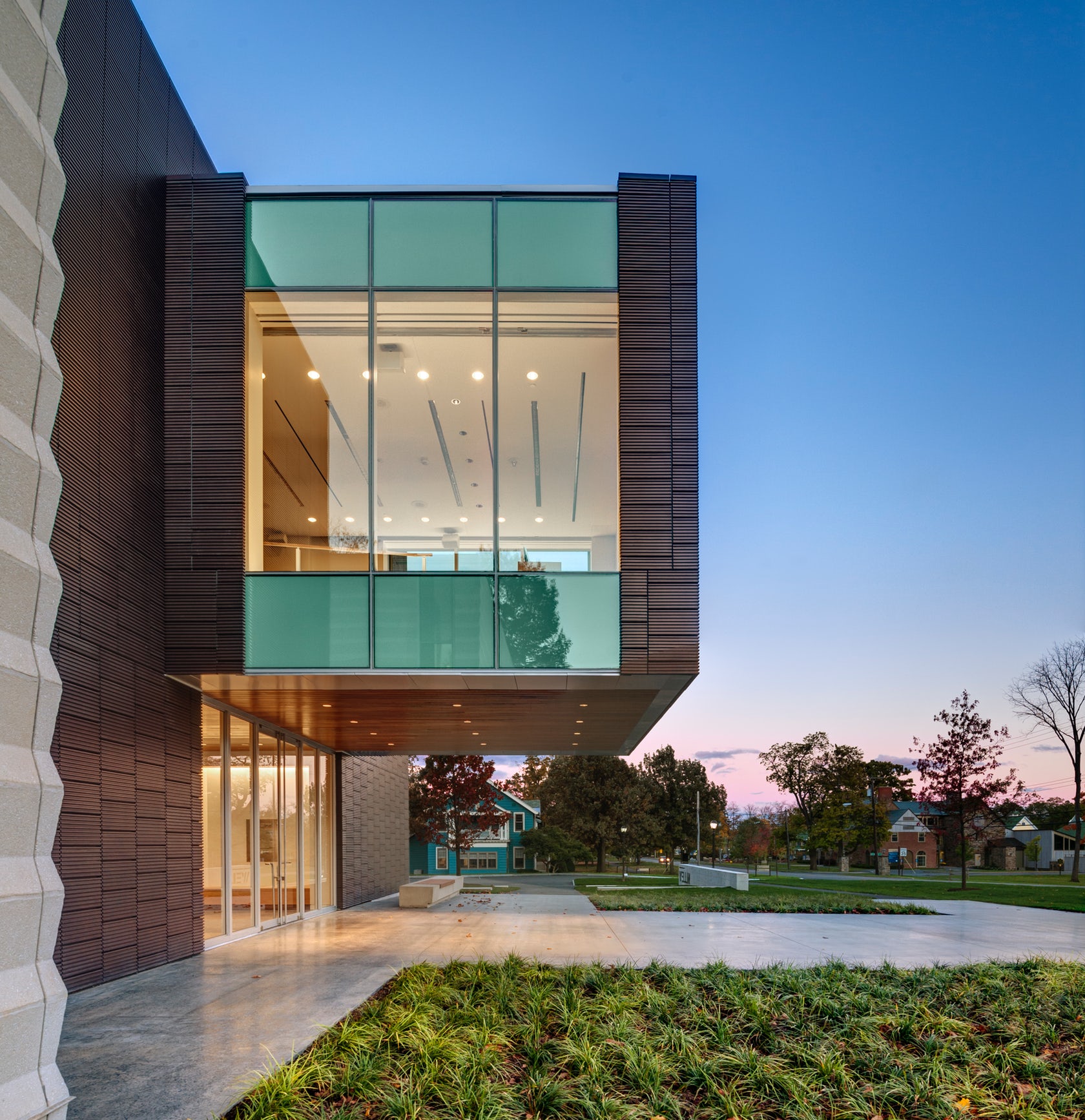 Located on the Hamilton College campus, the Wellin Museum of art was designed as part of a new arts quad. The building includes admin offices, seminar rooms, galleries, and a monumental two-story glass archive hall. Dark terracotta cladding was used along the central volume to reinforce its role programmatically and organizationally.
Located on the Hamilton College campus, the Wellin Museum of art was designed as part of a new arts quad. The building includes admin offices, seminar rooms, galleries, and a monumental two-story glass archive hall. Dark terracotta cladding was used along the central volume to reinforce its role programmatically and organizationally.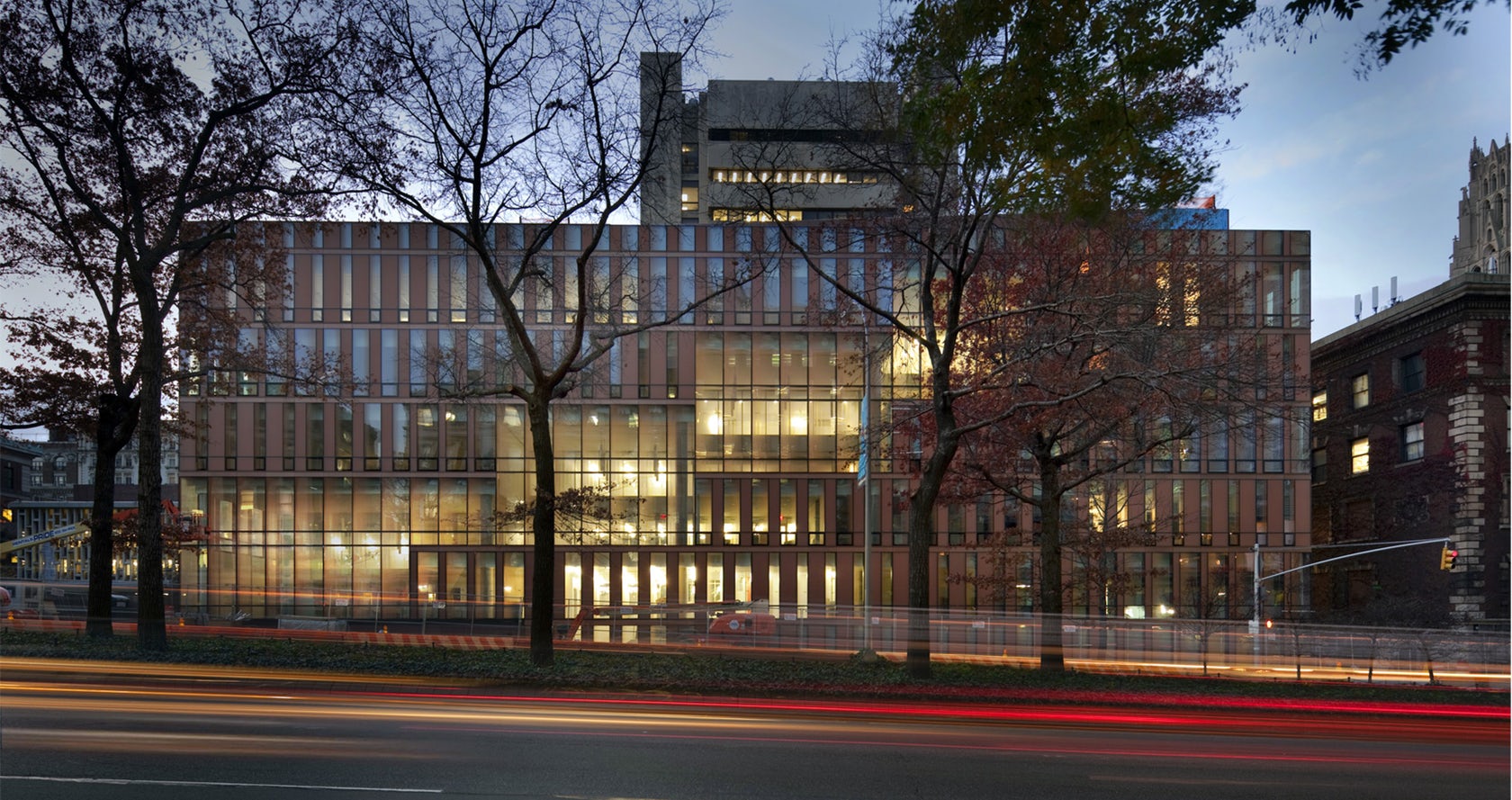
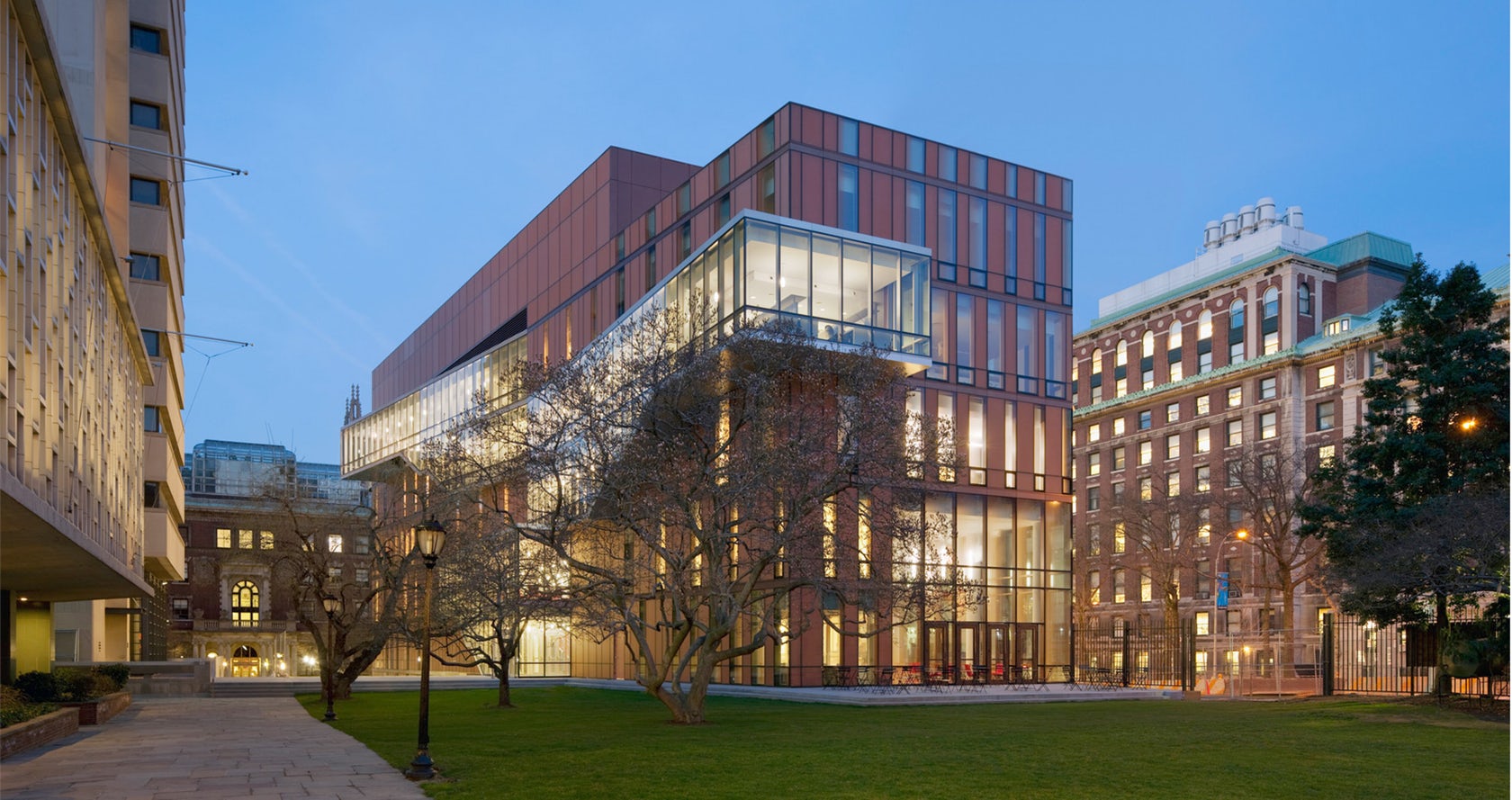 Located at Barnard College, the Diana Center includes a gallery space, a library, classrooms, dining, and a black box theater. A slipped atria links spaces vertically and becomes connected through ascending stairs. Luminous terracotta glass panels were used throughout the building envelope. Surrounded by a campus defined by brick and terracotta, the Diana translates the static opacity of masonry into a luminous curtain wall.
Located at Barnard College, the Diana Center includes a gallery space, a library, classrooms, dining, and a black box theater. A slipped atria links spaces vertically and becomes connected through ascending stairs. Luminous terracotta glass panels were used throughout the building envelope. Surrounded by a campus defined by brick and terracotta, the Diana translates the static opacity of masonry into a luminous curtain wall.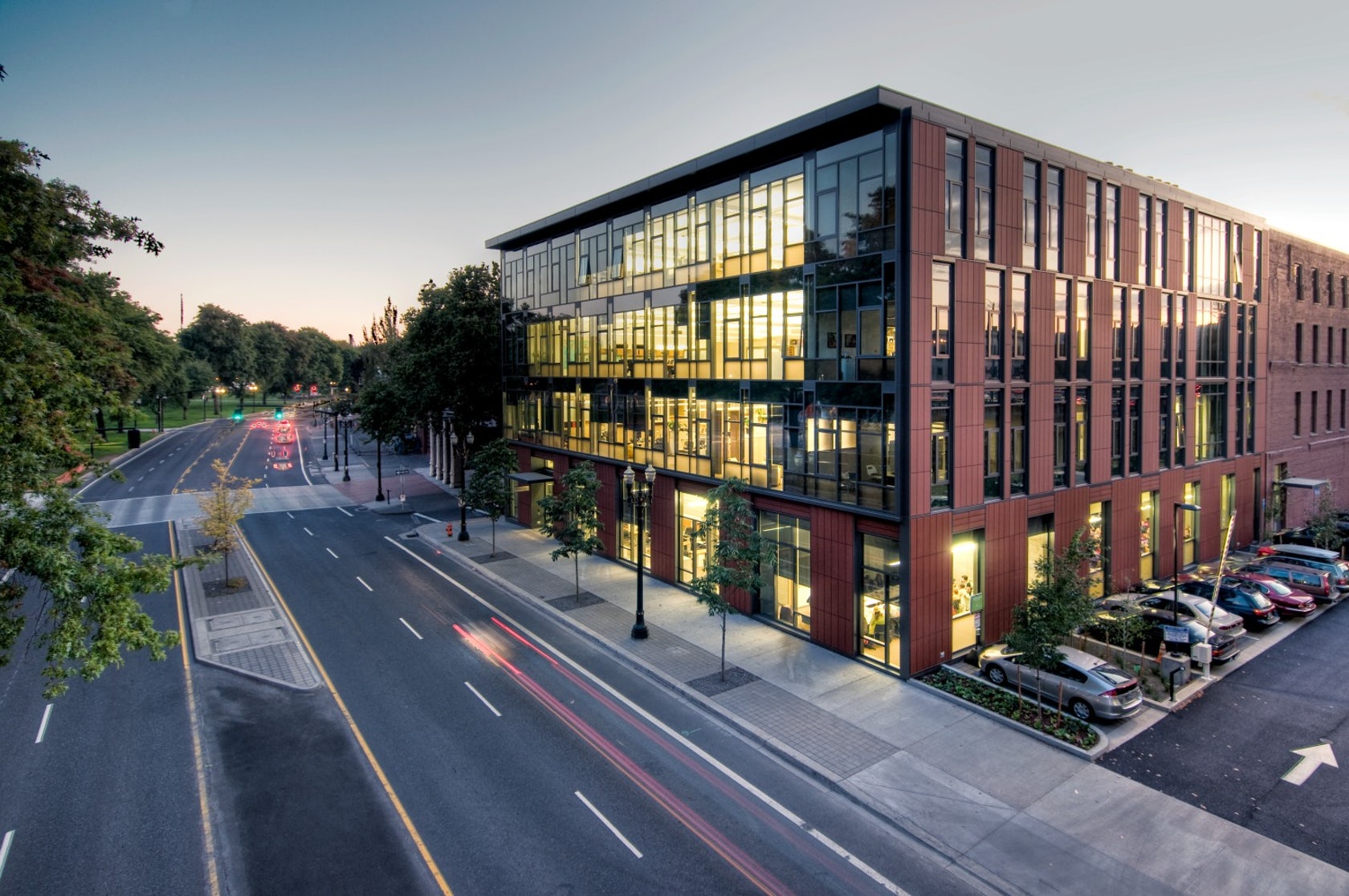
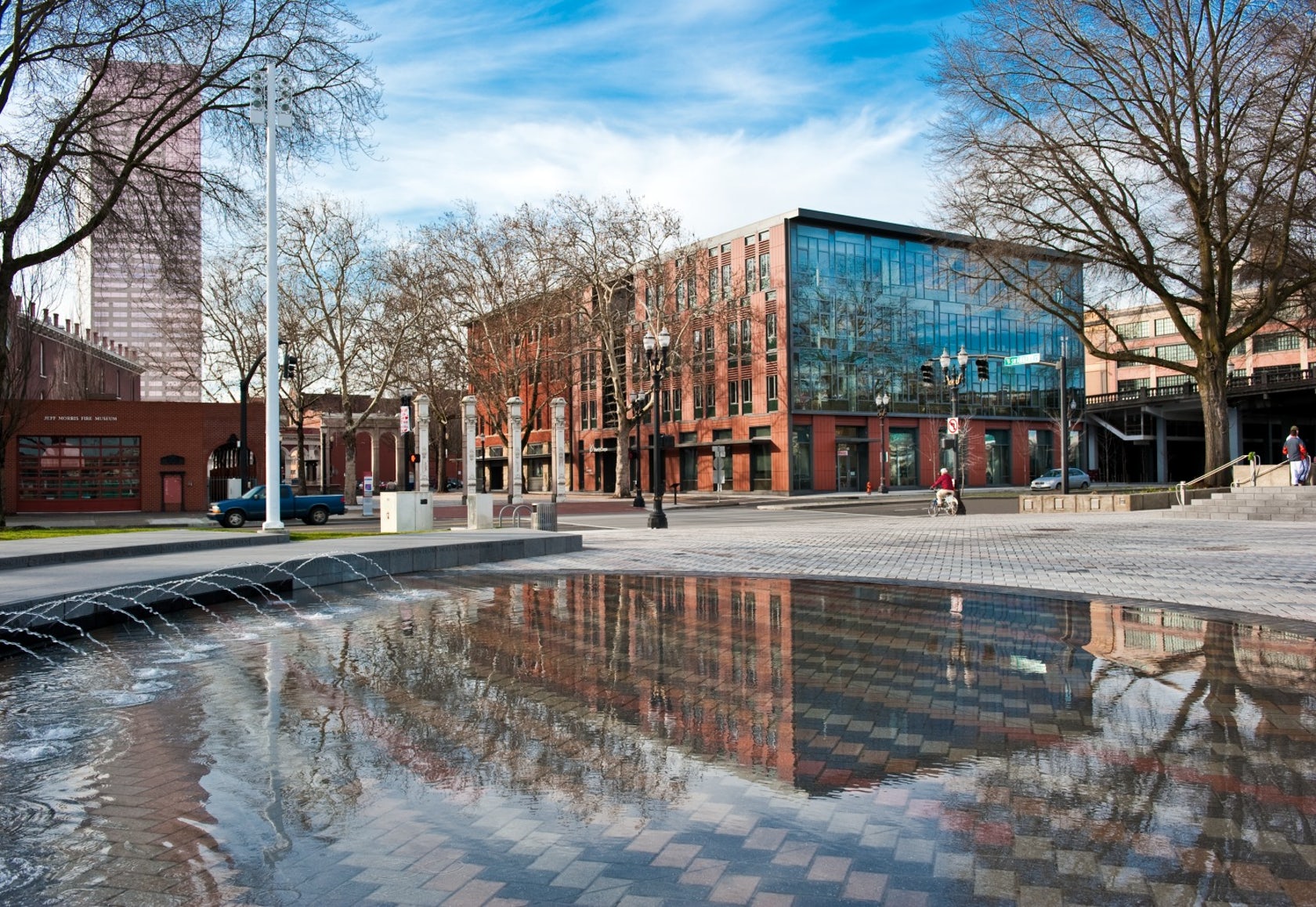 The Mercy Corps building was built to exemplify a sustainable, community-focused approach while encouraging visitors to engage with contemporary issues. Doubling the size of the historic Portland Packer-Scott Building, the landmark project combined a green roof, with resource-friendly landscaping and a glass and terracotta envelope.
The Mercy Corps building was built to exemplify a sustainable, community-focused approach while encouraging visitors to engage with contemporary issues. Doubling the size of the historic Portland Packer-Scott Building, the landmark project combined a green roof, with resource-friendly landscaping and a glass and terracotta envelope.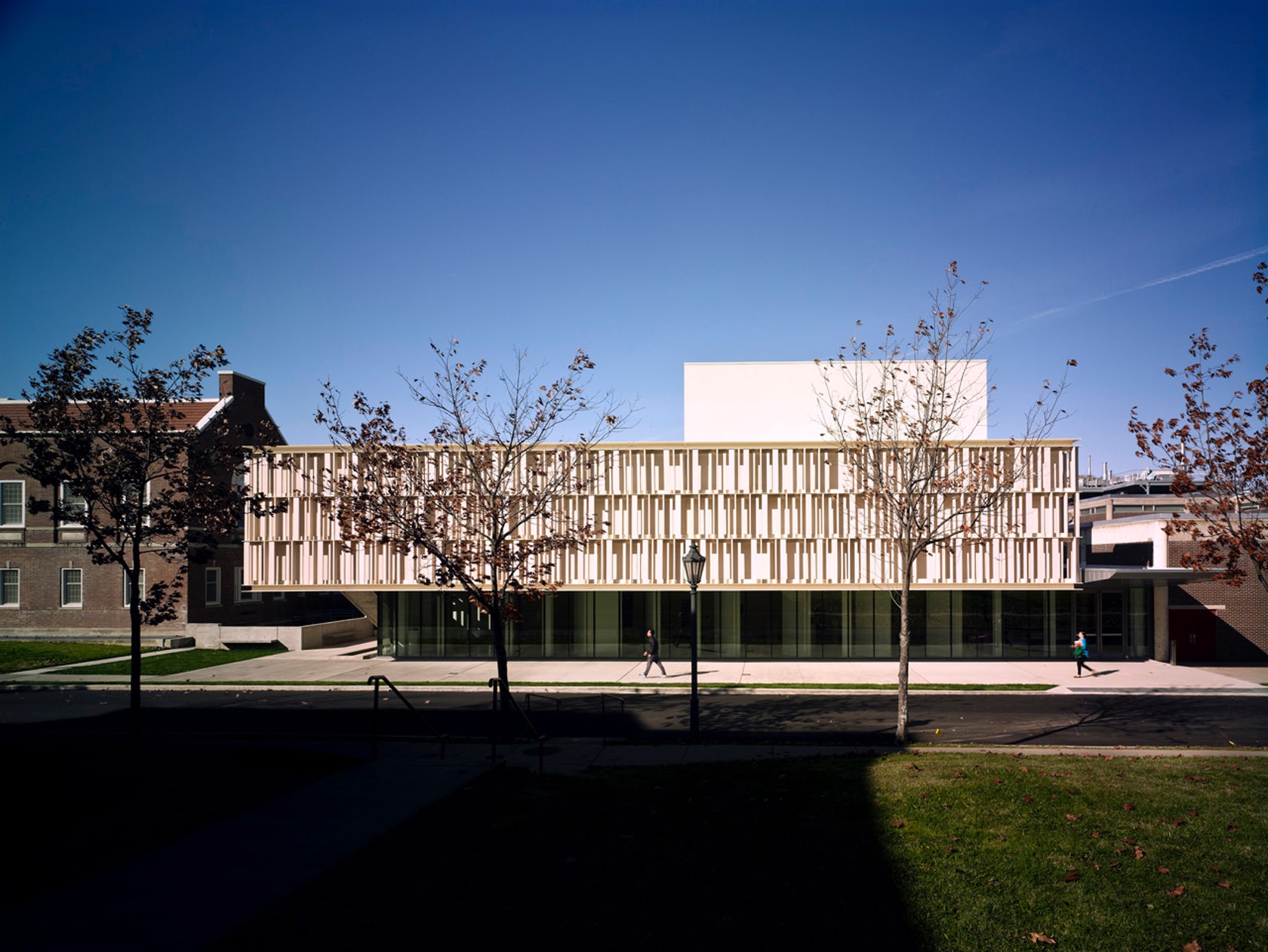
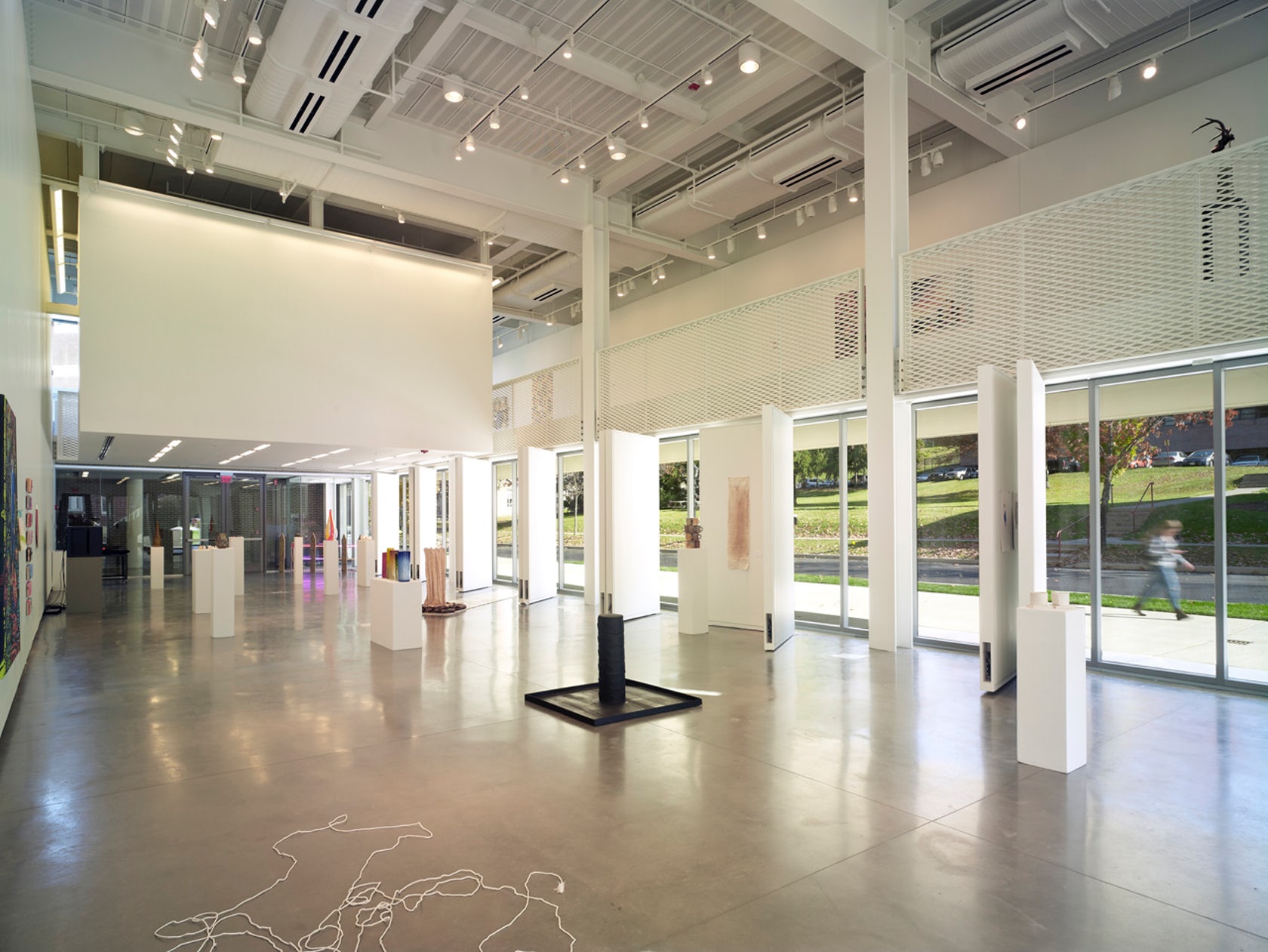 The terracotta tube façade for this ceramics pavilion screens both rain and solar heat, while its staggered pattern was inspired by pottery racks. The Art Pavilion was created as a “ceramic vessel” holding both light and art. The design was inspired by the region’s history of manufacturing ceramics, and incorporates the unglazed, hollow tubes with an off-white pigment.
The terracotta tube façade for this ceramics pavilion screens both rain and solar heat, while its staggered pattern was inspired by pottery racks. The Art Pavilion was created as a “ceramic vessel” holding both light and art. The design was inspired by the region’s history of manufacturing ceramics, and incorporates the unglazed, hollow tubes with an off-white pigment.





