Is Graphene the Next Revolutionary Building Material?
Browse the Architizer Jobs Board and apply for architecture and design positions at some of the world’s best firms. Click here to sign up for our Jobs Newsletter.
What is Graphene? Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, making it the thinnest material known to man. Despite its thin composition, graphene is incredibly strong — two hundred times stronger and 6 times lighter than steel. First isolated by researchers Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov from the University of Manchester in 2004, the material received the 2010 Nobel Prize in Physics, garnering increased global attention and interest. Graphene is durable and malleable, and scientists see promising architectural potential in the new material.
Graphene is also highly conductive and equally holds unique light-absorbing qualities. When it comes to conducting electricity, graphene rivals copper; when it comes to conducting heat, it trumps all other known materials. Meanwhile, graphene is nearly transparent, making it a suitable material for products such as touch screen devices, as well as light and solar panels. When mixed with plastic, graphene becomes a strong conductor of electricity, making it a potentially useful product in the satellite, aviation and automotive industries.
Although it is still in the early stages of research and development, there are many companies and research initiatives already dedicated to understanding the potential uses of graphene. Due to its unique property makeup, graphene can be used and applied in a plethora of ways, making it a worthwhile and lucrative material to research, study and develop commercially. This certainly holds true in the architecture and construction industry. Will this material have a revolutionary role in the design world?
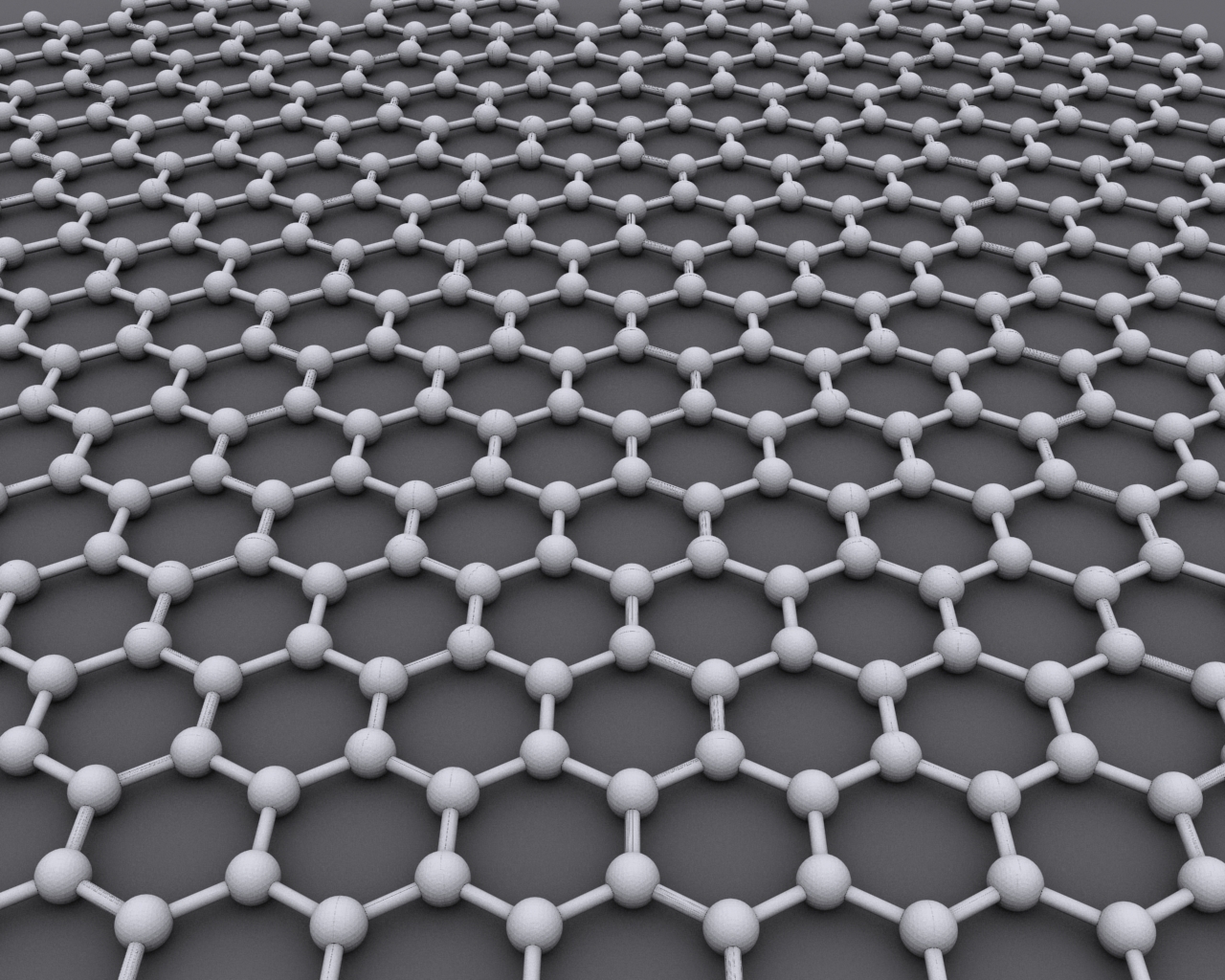 Properties of Graphene:
Properties of Graphene:
- Thermal and electrical conductivity
- Flexible and malleable
- Extremely durable
- Ability to generate electricity through exposure to sunlight
- Transparent and lightweight
- Antibacterial & resistant to ionizing radiation
Graphene as a Concrete Additive
In 2018, researchers at the University of Exeter found that incorporating graphene into concrete can produce a durable and water-resistant concrete composite. Researchers at the university suggest this composite material is two times strong and four times more water-resistant than any existing concrete. Through a new nano-engineering technology, the researchers suspended thin graphene in water, which produced an extremely resistant and usable concrete composite. Seeing that concrete releases high levels of CO2 into the air, this new composite material perhaps promises a greener alternative to traditional concrete.
The research was carried out in accordance with the British and European standards for construction, which ensures a safe material for architects to build with. Moreover, graphene’s water-resistant properties could equally be beneficial for sites that are difficult to reach and properly maintain — making this concrete composite not only durable but practical. It is possible that graphene-reinforced composites could be the future.

National Graphene Institute by Jestico + Whiles, Manchester United Kingdom. © Hufton+Crow Photography
Intelligent Cities
Some have suggested that graphene can easily up building’s intelligence. Architect Chenthur Raaghav Naagendran explains his research in a TEDx talk in Vienna, where he explores the possibilities of implementing graphene as a flexible skin for architecture. He proposes that graphene can be used to make architecture interactive, intelligent and adaptable. Chenthur’s research suggests that graphene could be used to replace traditional building materials and wires to create smart structures that respond to societal threats, such as global warming. Essentially, graphene can turn static structures into responsive agents.
Graphene in Paint
In 2017, paint manufacturer Graphenstone released a lime-based paint infused with graphene. Limewash paint has been around for centuries and has been revered for its breathable, bacteria-resistant, odor-absorbing and hypoallergenic properties. The company incorporated graphene into its renowned lime-based paint to create a thermal-regulating product. To resist heat from radiating through walls, the graphene present in the paint assists in capturing heat and thus improves a room’s insulation. Graphene’s thin makeup and durable properties mean less paint is required to achieve a corrosion-resistant and durable finish.

National Graphene Institute by Jestico + Whiles, Manchester United Kingdom. © Hufton+Crow Photography
Summary
Understandings of the role that graphene can play in the architecture and construction sphere are still in the early stages of research. However, there are promising concepts and graphene-present materials in development today. Equally, there are countless research initiatives and institutions dedicated to the commercialization of graphene. For example, the National Graphene Institute at the University of Manchester, designed by architecture firm Jestico + Whiles, is a world-leading research center dedicated to the research and development of graphene. Located at the very same institution where the material was first isolated, this institute demonstrates the UK’s dedication to remaining at the forefront of graphene commercialization.
Although there are still factors standing in the way of graphene commercialization — such as cost and maintaining quality during large-scale production — graphene could lead to more durable and thermally-regulated constructions in the future and is not to be overlooked.
Browse the Architizer Jobs Board and apply for architecture and design positions at some of the world’s best firms. Click here to sign up for our Jobs Newsletter.

 The core of a kitchen setup is always the counter or island. Today’s homeowners are looking for surfaces that are utilitarian without compromising the overall aesthetic. Plain surfaces with flushed drawers, concealed joints and even hidden electric stoves or sinks are making rounds on social media and in homes.
The core of a kitchen setup is always the counter or island. Today’s homeowners are looking for surfaces that are utilitarian without compromising the overall aesthetic. Plain surfaces with flushed drawers, concealed joints and even hidden electric stoves or sinks are making rounds on social media and in homes. No perfect counter is complete without the right stove. A recessed stovetop not only makes the kitchen seem more spacious but also makes movement and cleaning easier. Traditional burners can come with the headache of cleaning out grime and spillovers and using burner covers can mar the clean look of a kitchen.
No perfect counter is complete without the right stove. A recessed stovetop not only makes the kitchen seem more spacious but also makes movement and cleaning easier. Traditional burners can come with the headache of cleaning out grime and spillovers and using burner covers can mar the clean look of a kitchen. The next step in assembling a minimal kitchen is finding the perfect sink — one that stands out but also blends in. Fewer seams and streamlined fittings can help prevent excess soap and grime buildup and also create the appearance of more room. In line with these needs, designers are now moving away from traditional metal sinks and opting for stone or ceramic options that are more geometric and modern.
The next step in assembling a minimal kitchen is finding the perfect sink — one that stands out but also blends in. Fewer seams and streamlined fittings can help prevent excess soap and grime buildup and also create the appearance of more room. In line with these needs, designers are now moving away from traditional metal sinks and opting for stone or ceramic options that are more geometric and modern.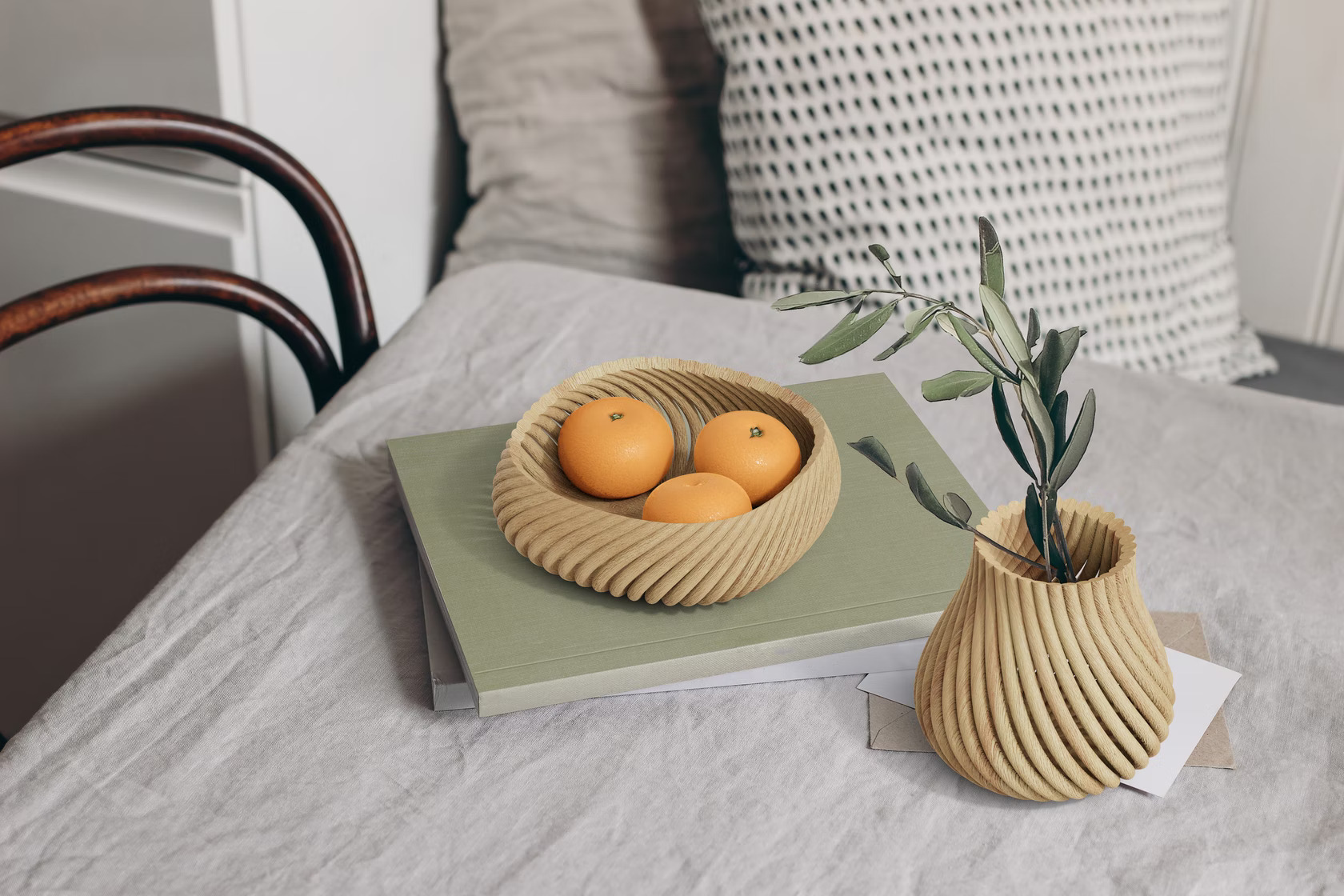 In addition to pots, pans and utensils, displayware is also becoming increasingly popular in kitchen décor. From ornate flower vases to decorative signs and stands, there are options for every kitchen aesthetic. Forust recently developed a 3D printing system that uses wood waste to craft home goods. The sustainable Vine range, designed by fuseproject, includes a vessel, bowl, basket and tray — all of which can be used for a variety of schemes ranging from whimsical cottagecore to minimal monochrome. These pieces are made up of 3D-printed rods that twist and come together to create curved forms without any adhesives. Their simple and versatile design language makes them an easy option to add some warmth to simple spaces.
In addition to pots, pans and utensils, displayware is also becoming increasingly popular in kitchen décor. From ornate flower vases to decorative signs and stands, there are options for every kitchen aesthetic. Forust recently developed a 3D printing system that uses wood waste to craft home goods. The sustainable Vine range, designed by fuseproject, includes a vessel, bowl, basket and tray — all of which can be used for a variety of schemes ranging from whimsical cottagecore to minimal monochrome. These pieces are made up of 3D-printed rods that twist and come together to create curved forms without any adhesives. Their simple and versatile design language makes them an easy option to add some warmth to simple spaces.
 All said and done, this process produces ZERO water waste. That’s right, zero with a Z. In 2022, this is welcome news indeed. The past few years have seen new attention given to the issue of water conservation as global water shortages have become a mounting problem.
All said and done, this process produces ZERO water waste. That’s right, zero with a Z. In 2022, this is welcome news indeed. The past few years have seen new attention given to the issue of water conservation as global water shortages have become a mounting problem. Cosentino believes that consumers need not compromise quality in the name of sustainability. In fact, those Silestone surfaces that have been produced with HybriQ+ technology are among the most beautiful the company has ever produced. The company explains that “the new mineral composition enables never before-seen effects in color depth, texture and tone.” Indeed, Cosentino has long proven that synthetic materials can be just as elegant and intricate as natural materials.
Cosentino believes that consumers need not compromise quality in the name of sustainability. In fact, those Silestone surfaces that have been produced with HybriQ+ technology are among the most beautiful the company has ever produced. The company explains that “the new mineral composition enables never before-seen effects in color depth, texture and tone.” Indeed, Cosentino has long proven that synthetic materials can be just as elegant and intricate as natural materials. We recommend spending time on the
We recommend spending time on the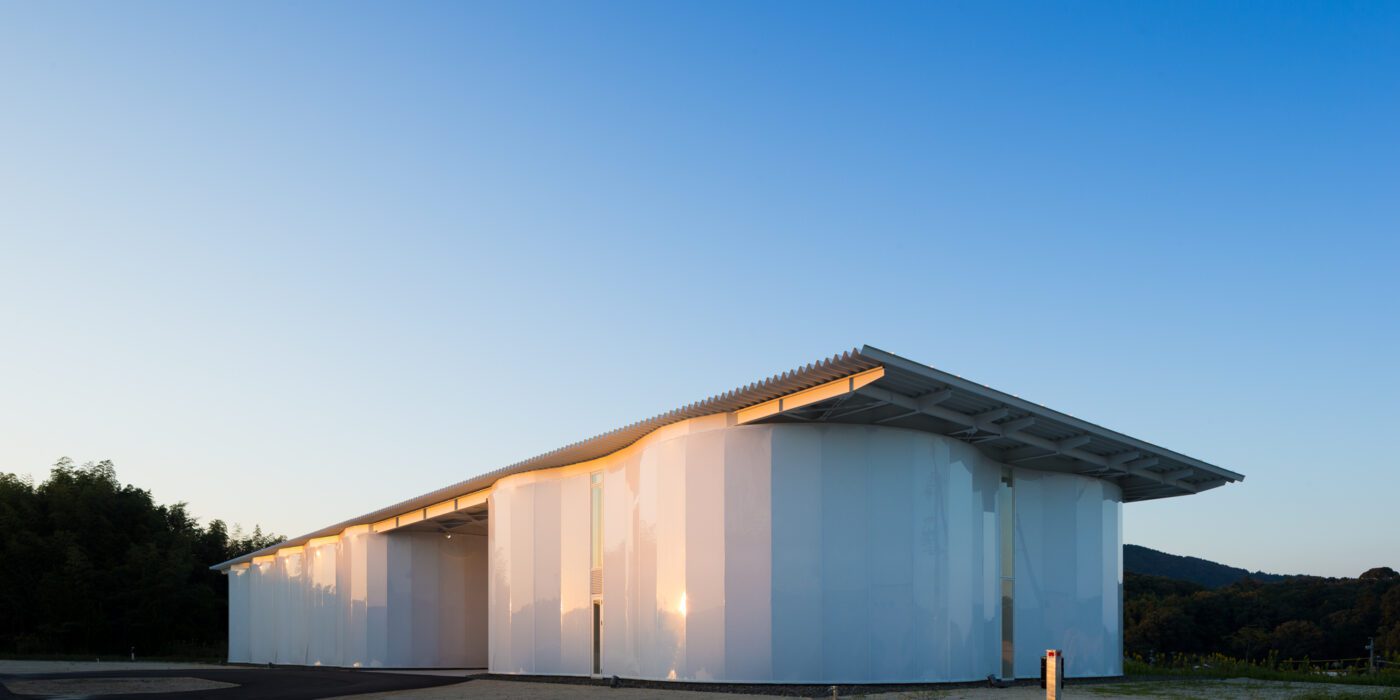 
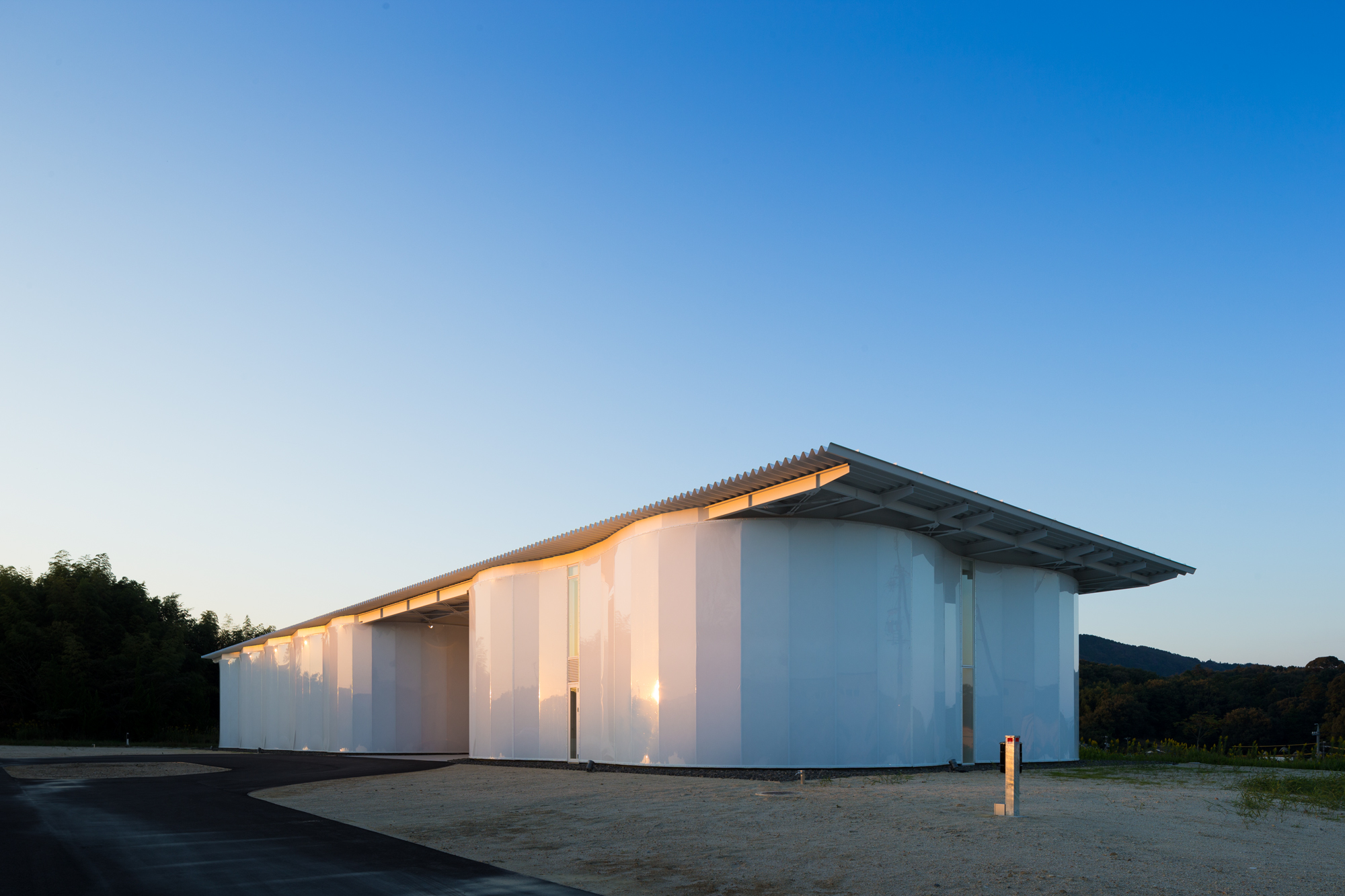
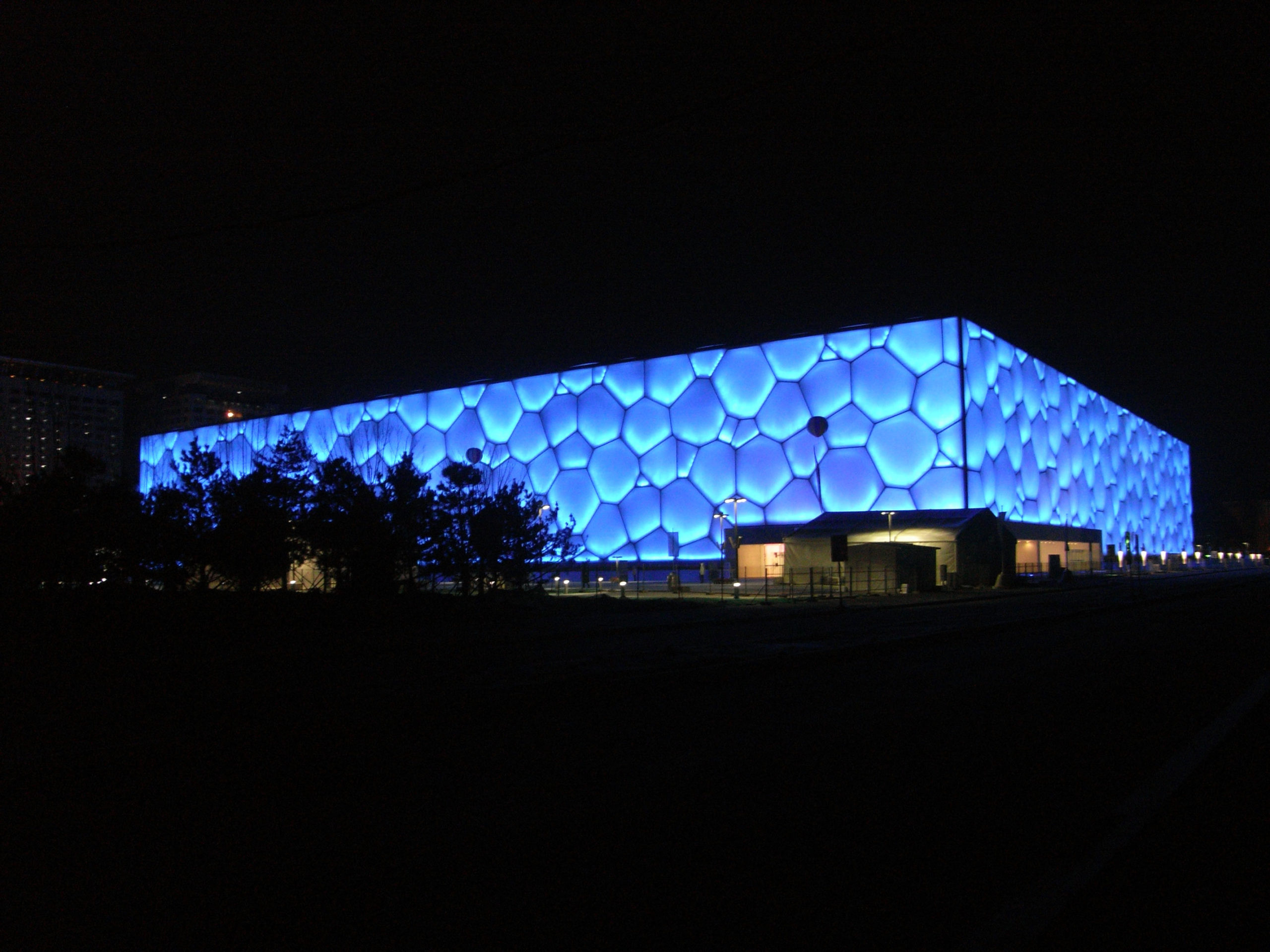
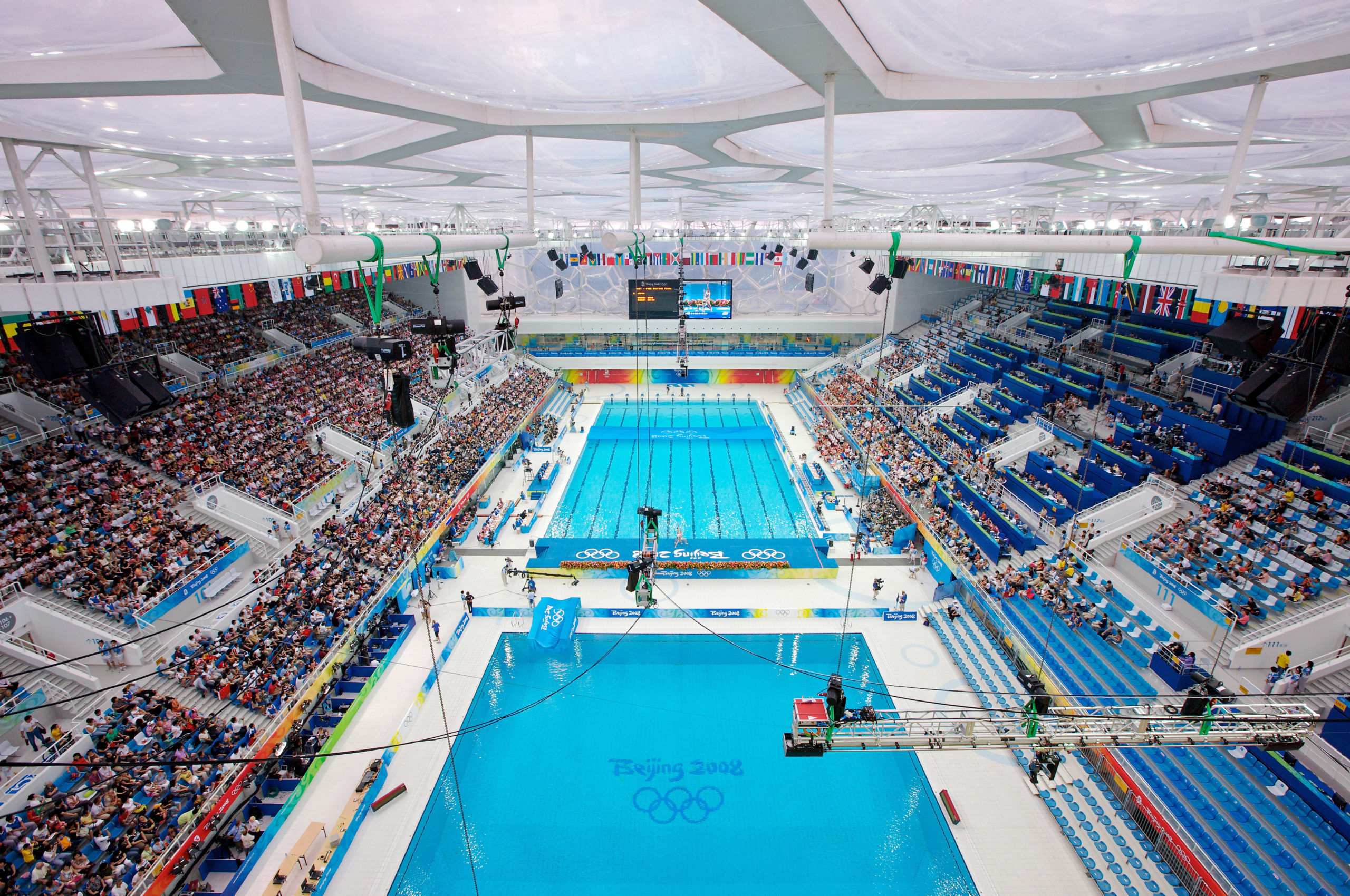

 Designed by PTW Architects, the National Swimming Centre in Beijing, also called Water Cube, has an iconic “bubbling” façade made of ETFE. To achieve this appearance, ETFE films are first welded together, then installed onto the steel frames and lastly filled with inert gases using the piped embedded in the steel frames to form cushions. The swimming pool is lit by natural light during the daytime and very little artificial lighting is needed, thanks to the transparency of ETFE.
Designed by PTW Architects, the National Swimming Centre in Beijing, also called Water Cube, has an iconic “bubbling” façade made of ETFE. To achieve this appearance, ETFE films are first welded together, then installed onto the steel frames and lastly filled with inert gases using the piped embedded in the steel frames to form cushions. The swimming pool is lit by natural light during the daytime and very little artificial lighting is needed, thanks to the transparency of ETFE.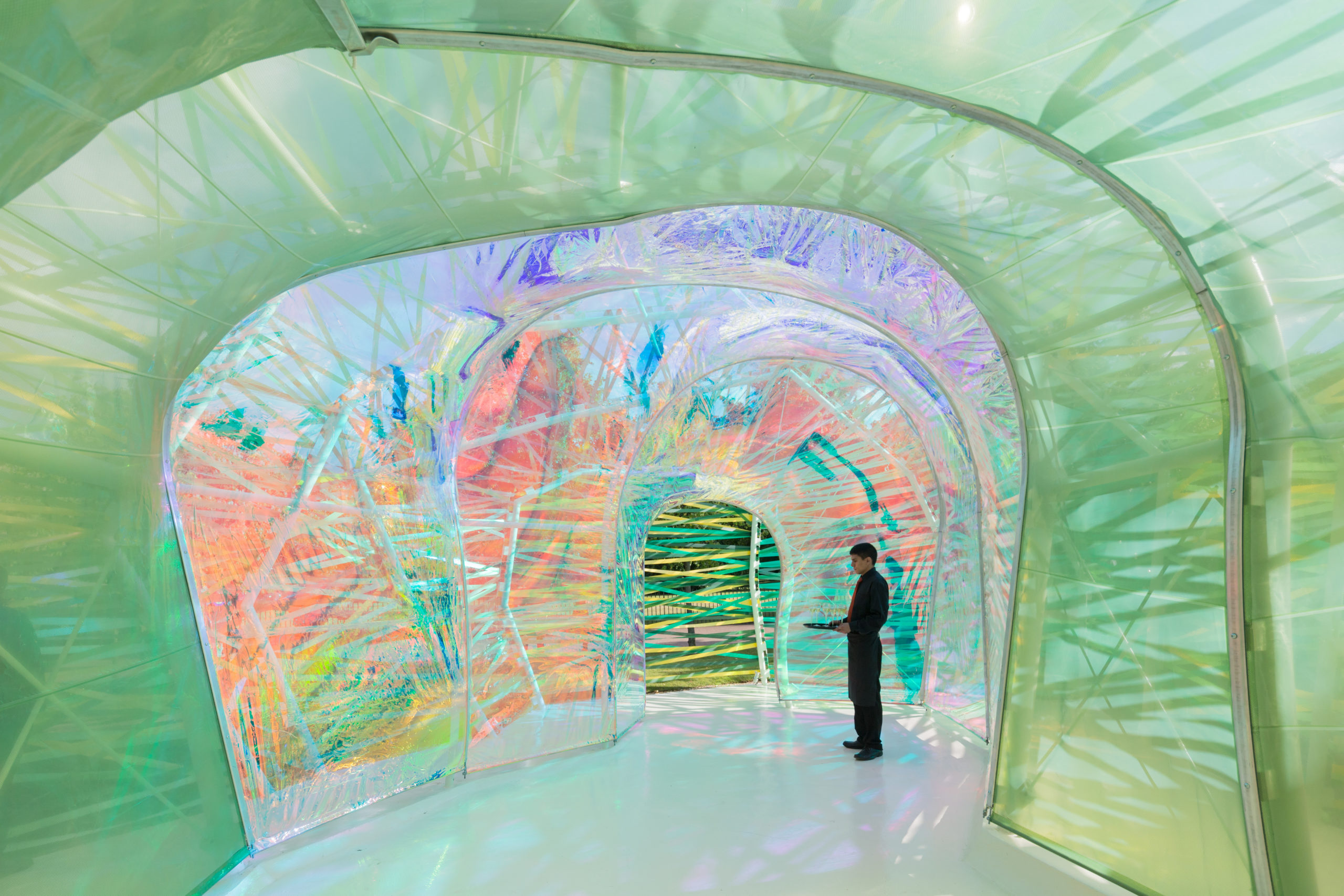 While Water Cube employs ETFE cushions for their environmental performance, the Serpentine Pavilion 2015 designed by SelgasCano plays with the material’s transparency. Using colored and color-diffusing ETFE films, joined by colored ribbons, the design team created a surreally colorful spatial experience. ETFE films and ribbons of different shades are attached to the steel skeleton, forming a double skin system where shades overlay building new shades and forms penetrate forming dreamy shadows. The lightness of the material allowed all skin sections to be installed by hand.
While Water Cube employs ETFE cushions for their environmental performance, the Serpentine Pavilion 2015 designed by SelgasCano plays with the material’s transparency. Using colored and color-diffusing ETFE films, joined by colored ribbons, the design team created a surreally colorful spatial experience. ETFE films and ribbons of different shades are attached to the steel skeleton, forming a double skin system where shades overlay building new shades and forms penetrate forming dreamy shadows. The lightness of the material allowed all skin sections to be installed by hand.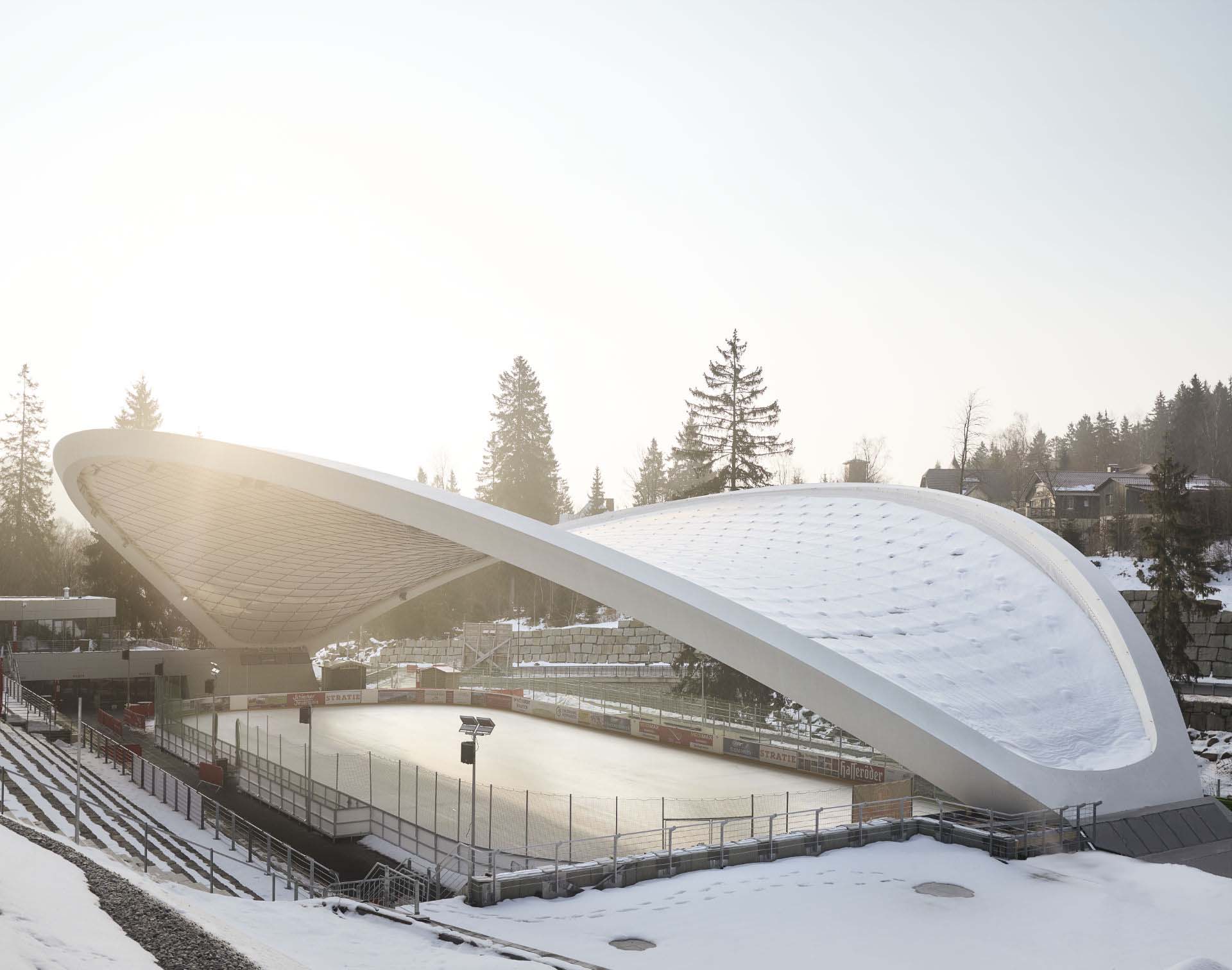
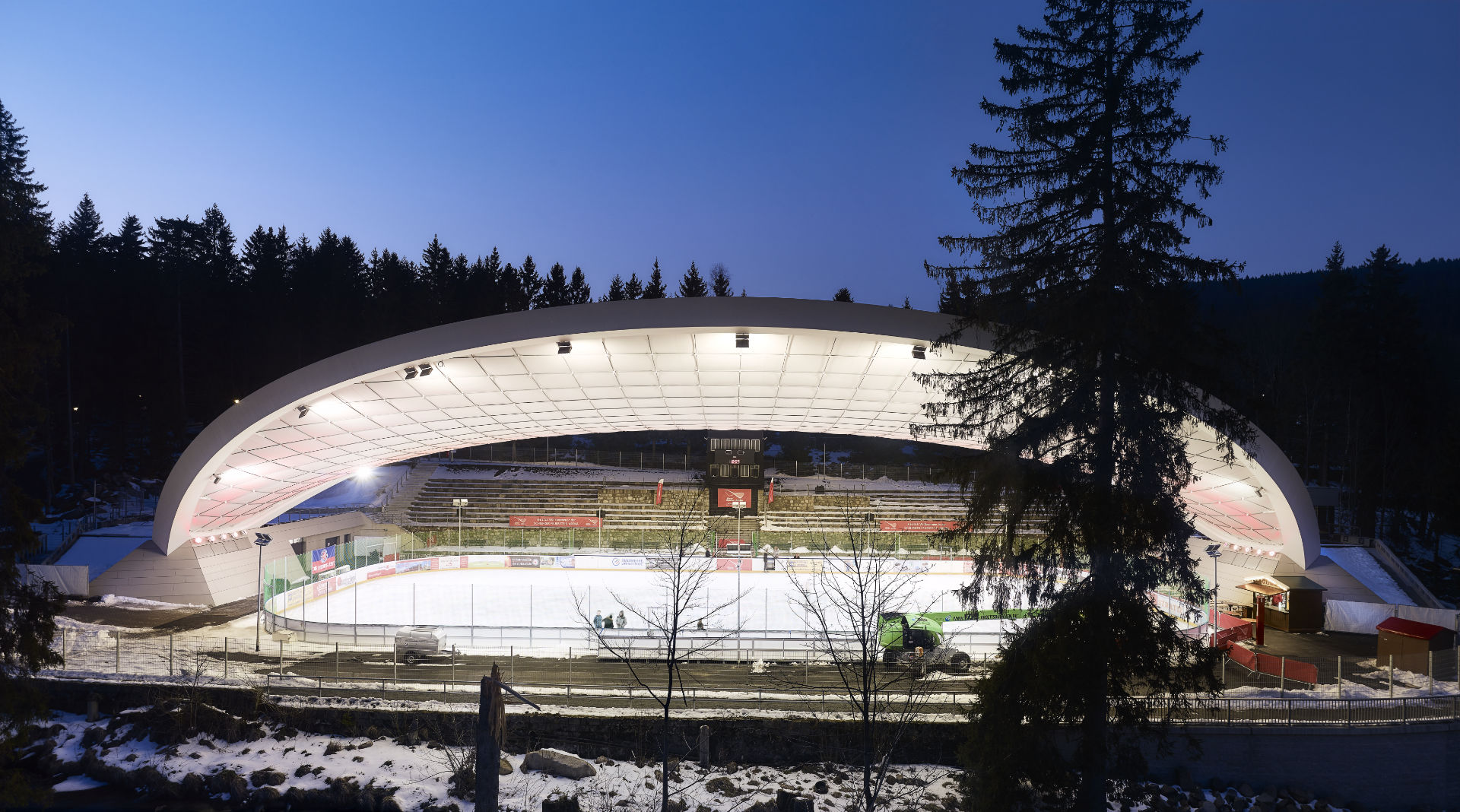 The Ice Stadium Schierker Feuerstein-Arena designed by GRAFT stands out in the competition to renovate the stadium for its unique roof. The roof of over 29,000 square feet (2, 700 sq. m) spans across the ice rink, meeting the ground at its two ends. The lightweight yet strong PTFE membrane rests on a net of steel ropes which is then fixed to the outer steel frame. The structure bears wind, rain and snow and sheltered the stadium from direct sunlight by diffusing it. During the night, the reflectivity of the material spreads lights across the whole roof, multiplying the artificial lighting.
The Ice Stadium Schierker Feuerstein-Arena designed by GRAFT stands out in the competition to renovate the stadium for its unique roof. The roof of over 29,000 square feet (2, 700 sq. m) spans across the ice rink, meeting the ground at its two ends. The lightweight yet strong PTFE membrane rests on a net of steel ropes which is then fixed to the outer steel frame. The structure bears wind, rain and snow and sheltered the stadium from direct sunlight by diffusing it. During the night, the reflectivity of the material spreads lights across the whole roof, multiplying the artificial lighting.