Dekton Ukiyo: Cosentino’s New Material Collection Celebrates the Aesthetic Wisdom of Japan
Most people who love design also love Japan. In fact, it is impossible to truly appreciate the modern history of Western art and design without recognizing Japan’s influence. From the woodblock prints of Hiroshige that inspired Van Gogh to the Zen tea rooms that laid the foundation for minimalist architecture, Japanese aesthetics paved the way for modernism.
It is not just that Japanese design is beautiful. The nation has a long tradition of thinking carefully about aesthetics, and how the contemplation of beauty contributes to human flourishing. Consider the concept of wabi-sabi, or the art of imperfection, that was recently explored in an Architzer op-ed. Centuries before American architects lamented the homogeneity of the clean and orderly suburbs, Japanese philosophers recognized the paradoxical truth about beauty: that it requires flaws.
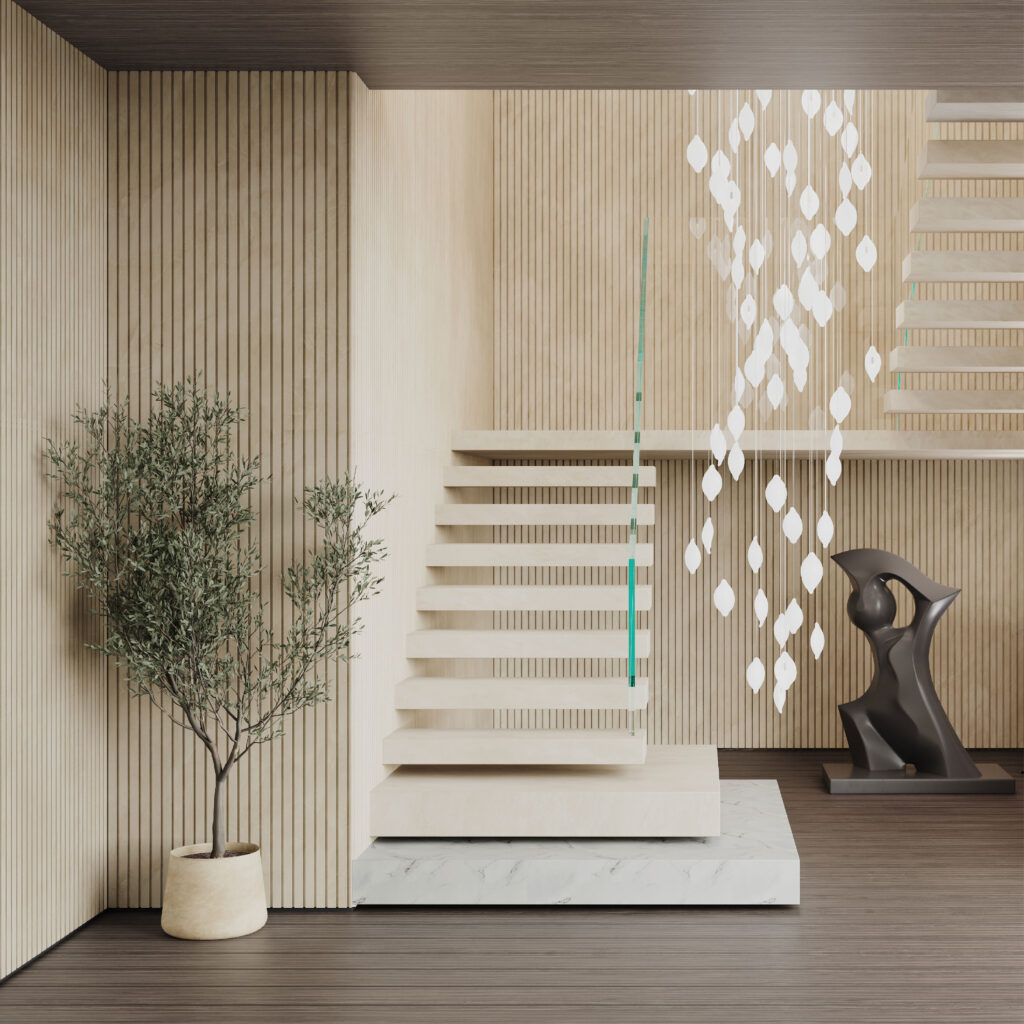

Dekton Ukiyo NACRE. Image courtesy Cosentino
It is this aspect of Japanese aesthetics — the theoretical side — that most inspired world-renowned interior designer Claudia Afshar in the development of her new collaborative collection with Cosentino, Ukiyo. The tagline for the series is “The Inner Texture,” which speaks to the Japanese understanding of interior design as an art that evokes a mental atmosphere of inner serenity. In the Japanese tradition, beauty and well-being go hand in hand.
The collaboration consists of a series of new patterns and textures for Cosentino’s versatile Dekton surfaces, a product we love and have profiled many times in the past. Scratch resistant, stain resistant, and able to endure the elements, Dekton is the surface of choice for designers looking for a material that is both resilient and visually alluring. The introduction of Dekton into the marketplace in 2013 completely upended the old conventional wisdom that natural materials are more beautiful than composites.
With Ukiyo, Claudia Afshar showcases the extraordinary potential of Dekton. Most Westerners recognize the term ukiyo as referring to a genre of woodblock prints that flourished in the 19th century, epitomized by the work of artists like Hokusai and Hiroshige. But in the promotional materials for this new collection, Afshar and Cosentino have chosen to emphasize the literal meaning of this term, listing the dictionary definition on the top of the collaboration webpage: “[u-key-yo], Japanese, (n). Living in the moment, detached from the bothers of life. ‘The floating world.’” The idea is drawn from Zen. It means that paradise is always at hand; all it takes is a choice to live in the moment.
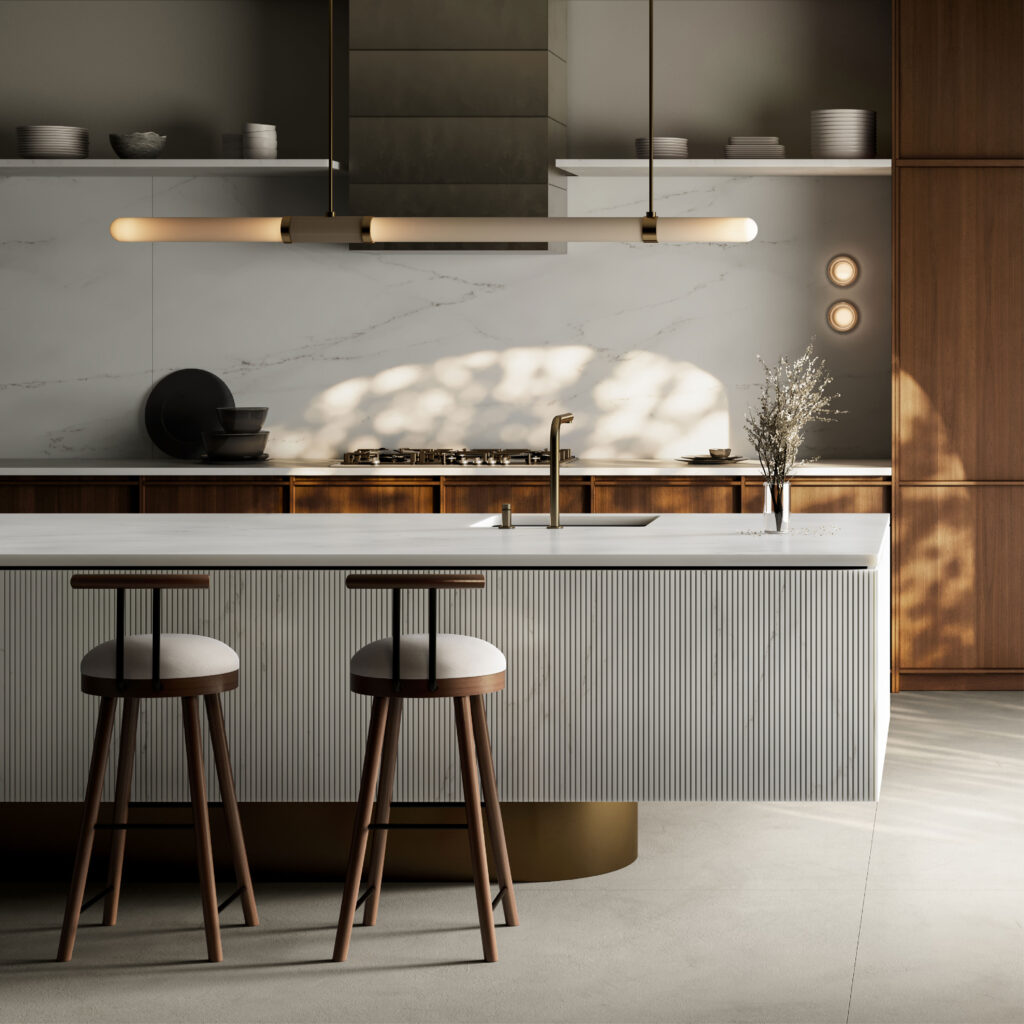

Dekton Ukiyo KRETA. Image courtesy Cosentino
In a recent webinar hosted by Architizer, Cosentino’s Lauren Dron quoted Coco Chanel’s statement that “An interior is the natural projection of the soul”, emphasizing the depth of the question architects and designers must ask every time they take on a project. “Meaningful design in the built environment continues to be rooted in our minds and in our emotions,” she declared. “Design is a reflection and enhancement of the human experience.”
This second part — enhancement — is key, and it is the place where architects can really have an impact on the world. In a social environment dominated by stress, conflict, and speed, architects can create environments of serenity and calm. They can remind people that “the floating world” is alway at hand if one is willing to adjust their perspective.
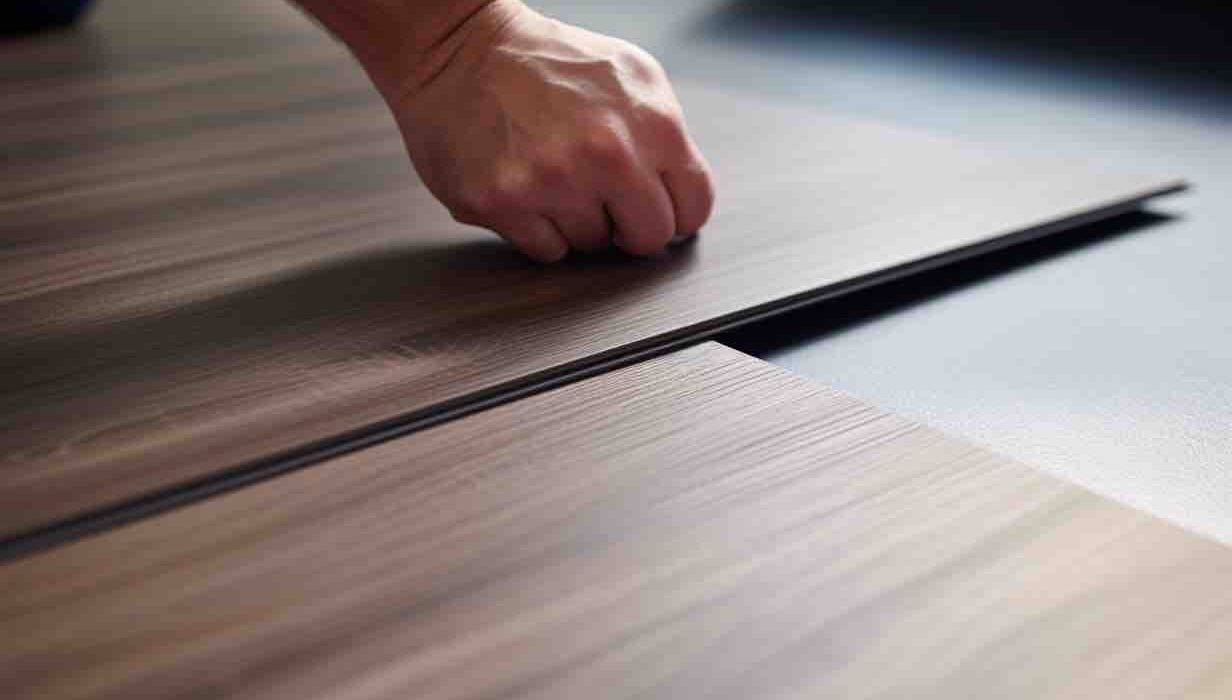
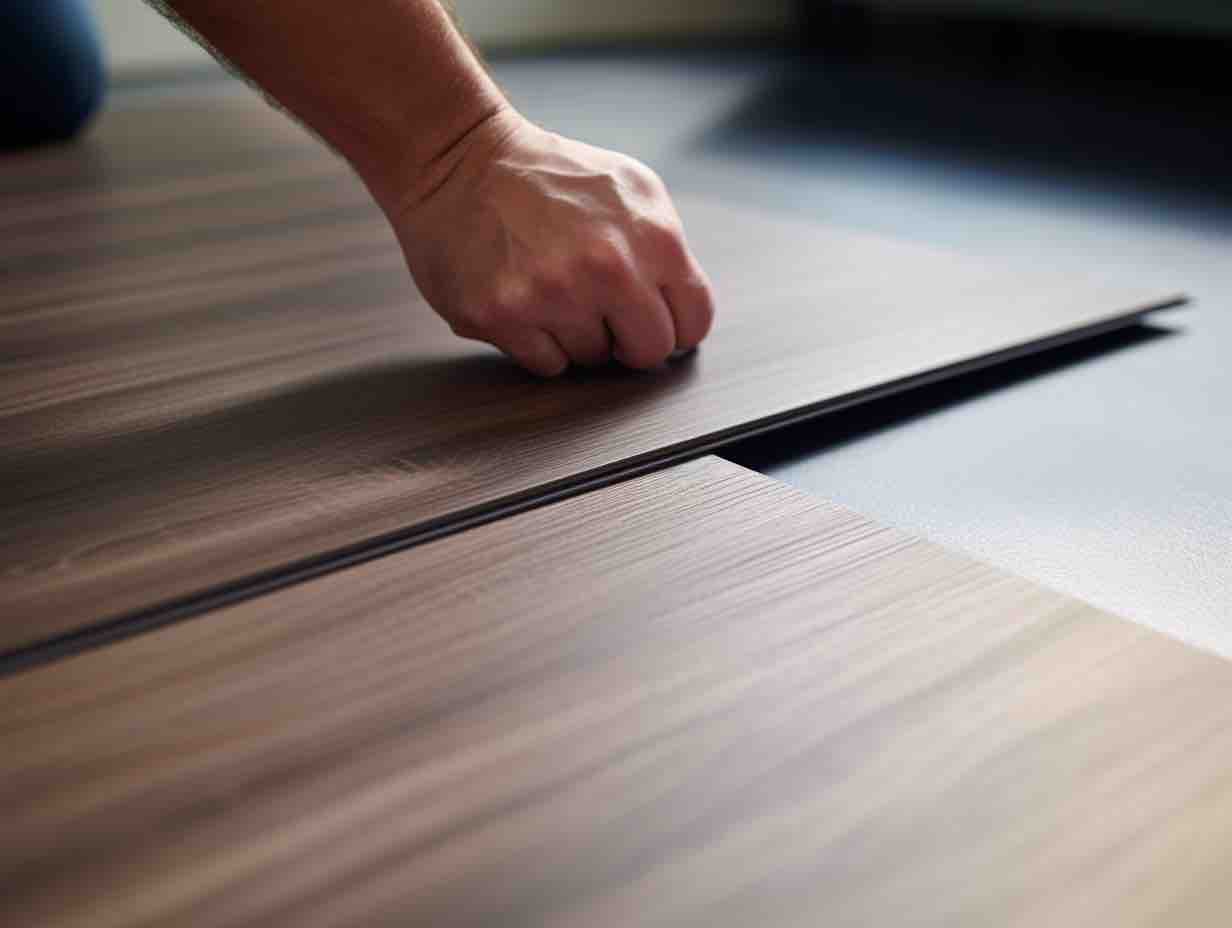
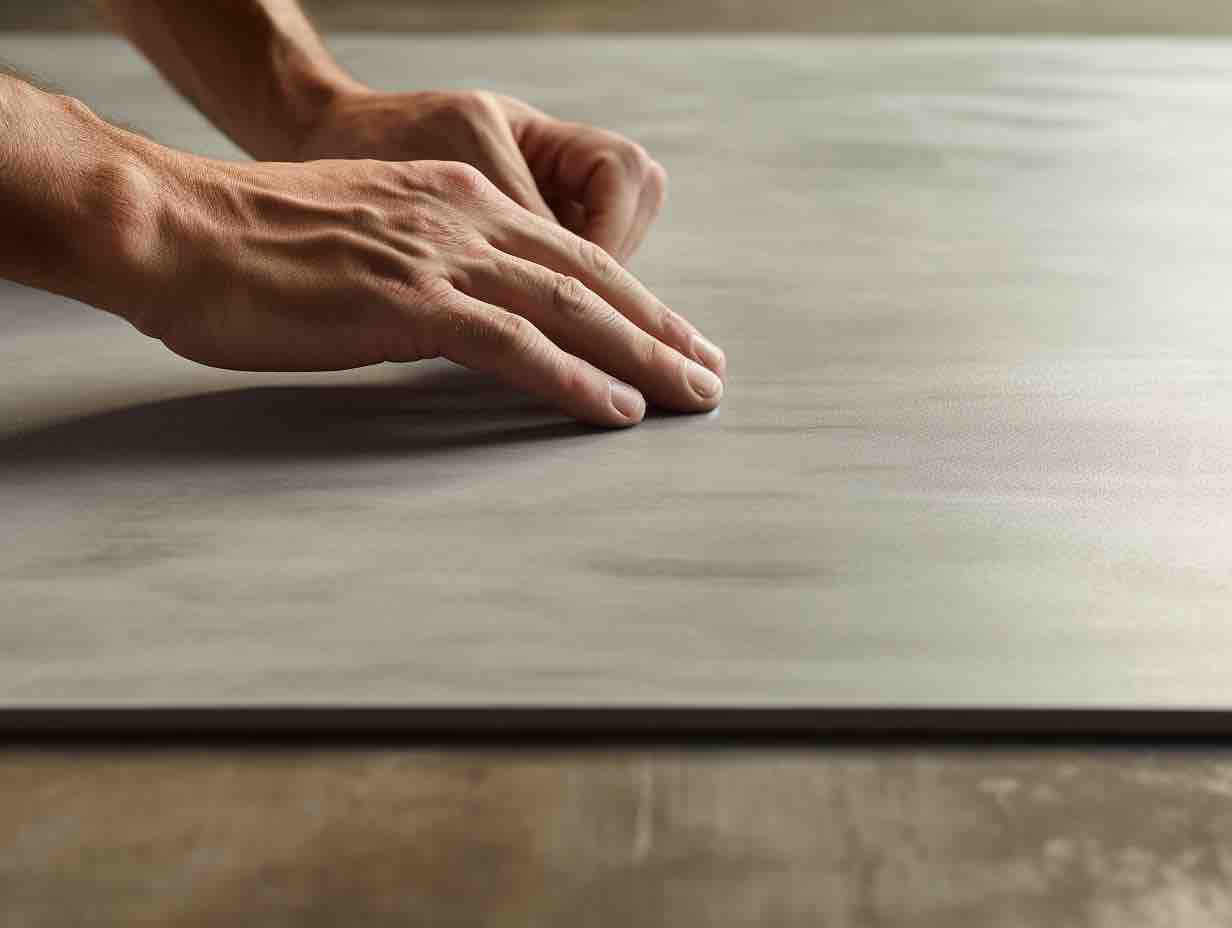
This, then, is the noble aim of Ukiyo, which features textures and colors that are simple, yet rich. As lush as any natural stone, and as meditative as a pool of still water, these surfaces bring serenity into all sorts of interiors, from domestic to commercial. Each Dekton color features the same delicate ribbed texture, which is reminiscent of the wood slats one often finds in Japanese homes. The texture also evokes the delicate patterns one finds raked into the sands of Zen gardens.
There are two different options when it comes to the size and spacing of the grooves. Ukiyo GV2 is wider, with 25 mm slats and grooves that are 5 mm wide and 3 mm deep. GV3 is finer, with 11 mm slats and grooves that are 4 mm wide and 4 mm deep.
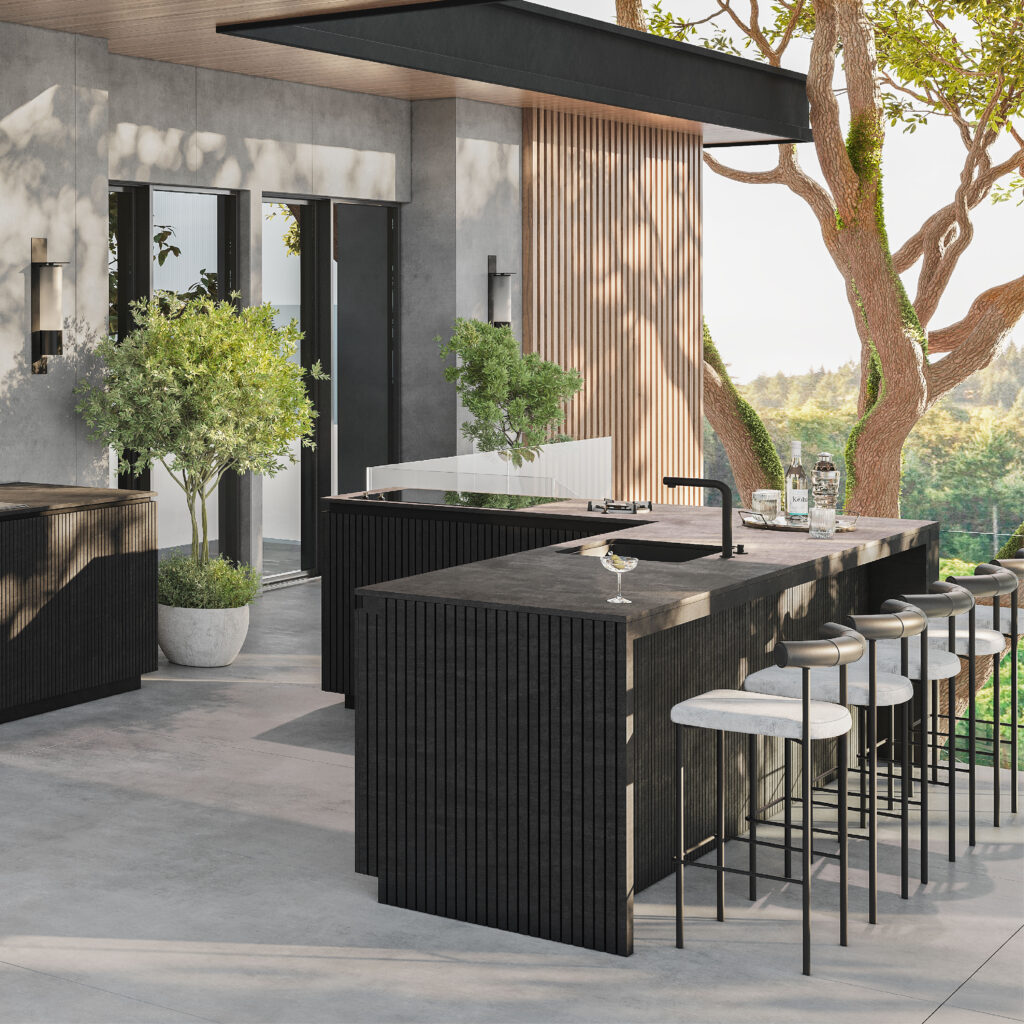

Dekton Ukiyo BROMO. Image courtesy Cosentino
BROMO is the first color in the series. It is described as “a dark gray shade inspired by slate featuring subtle faded graphics and a carefully crafted texture with a natural aesthetic.” The graphics are really key here. The material is actually deeper and richer than slate, yet it has the same soothing matte finish, exuding sophistication.
The next color, KRETA, is inspired by concrete, a material that retains modernist cache despite its ubiquity. Some of the most lyrical architecture ever made with raw concrete was created by Japanese architects, including Tadao Ando. Cosentino notes that KRETA can “create lighter or darker spaces.” In this way, it plays off the light conditions in its environment, just like real concrete — a true neutral.
NACRE and REM are both shades of cream or beige. NACRE is the lighter of the two, and can even be considered an off-white. It is a great choice for designers looking for a minimalist finish but wary of stark brightness. This tone is both light and warm. REM has a similar impact but is marked by more dramatic veining patterns. There is a luxe quality here that is perfect for commercial interiors.
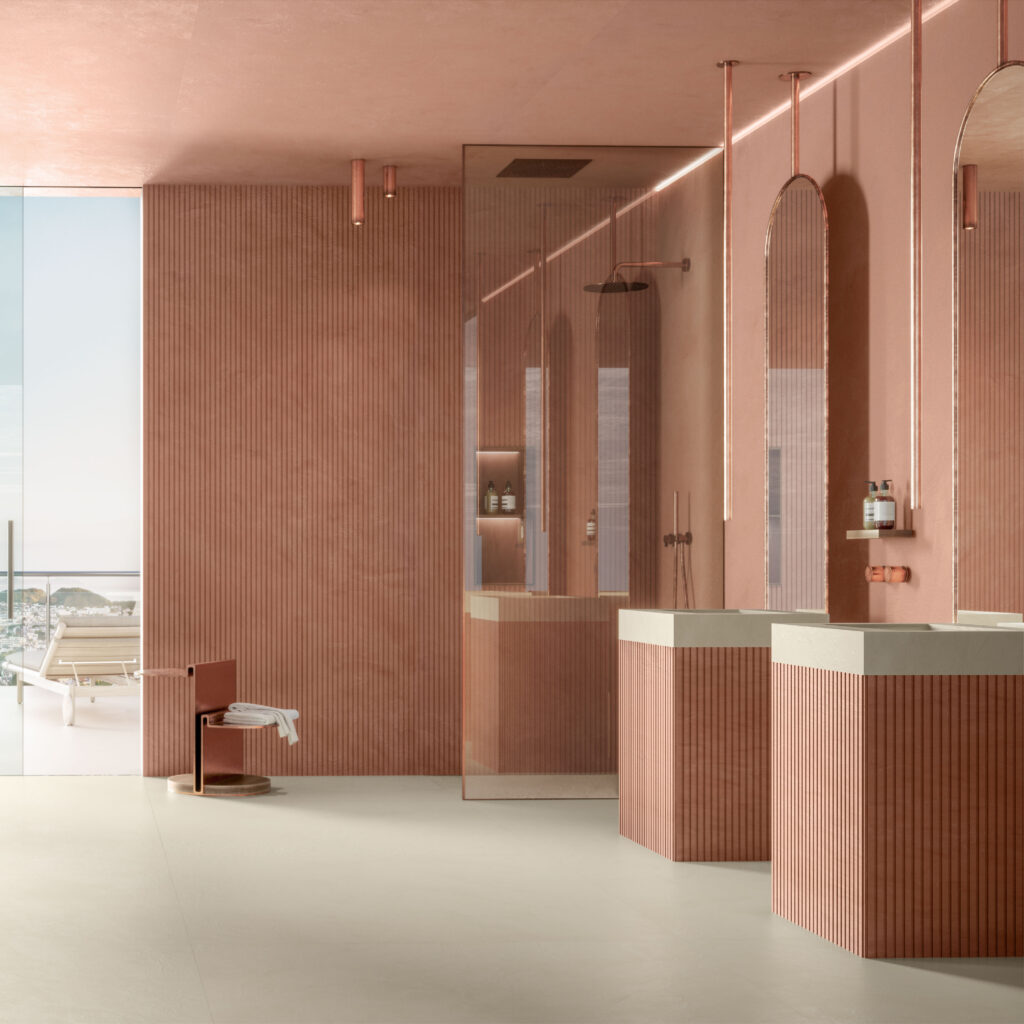

Dekton Ukiyo UMBER. Image courtesy Cosentino
Finally there is UMBER, the most adventurous and unique color in the series. It is hard to look at this delicately textured terracotta without imagining the rooms one could create with this tone. Unlike the other colors, which are notable for their versatility, UMBER is a showstopper. It is the kind of color you build a room around.
Ukiyo is a truly inspiring series of surfaces. It is also ethically manufactured. Dekton is the only “Cradle-to-Grave Carbon Neutral surface” as Cosentino offsets 100% of their CO2 emissions over the product’s life cycle. This too is very Zen. Dekton exists in harmony with its surroundings.
To learn more about Dekton Ukiyo and talk with Cosentino about how to integrate it into your next project, visit their website.
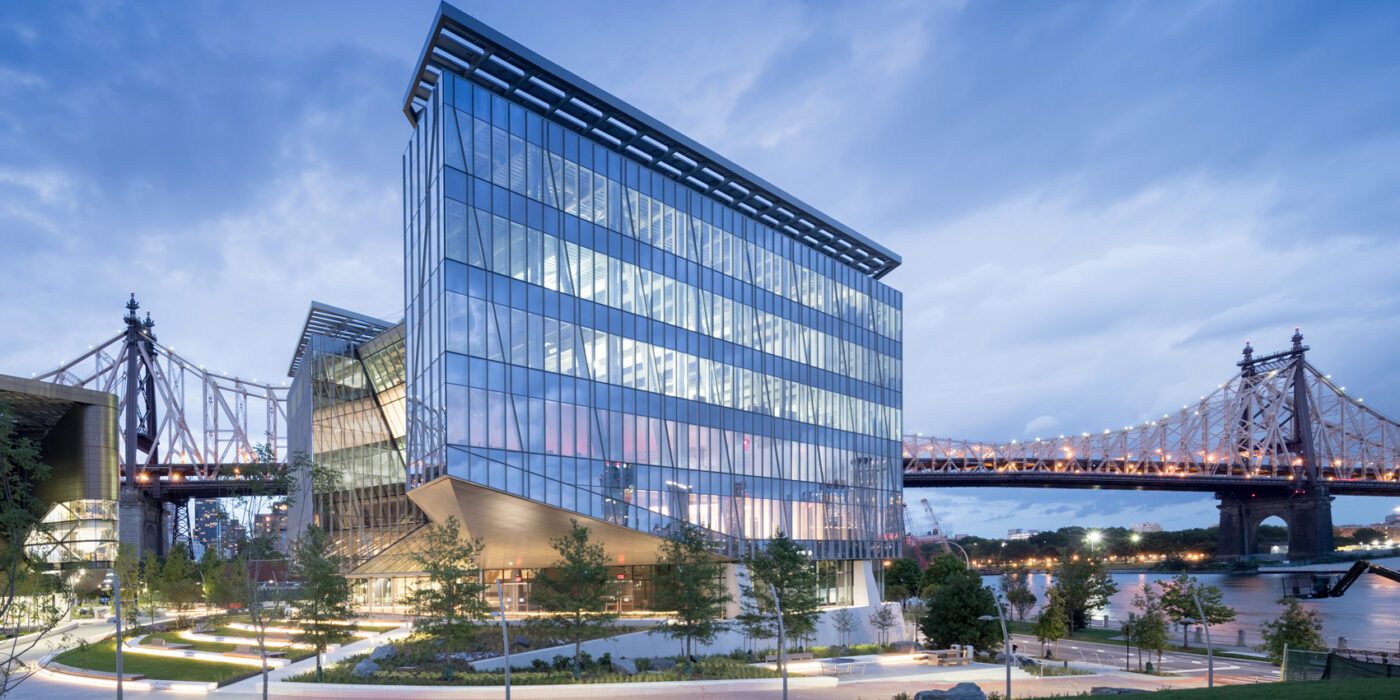
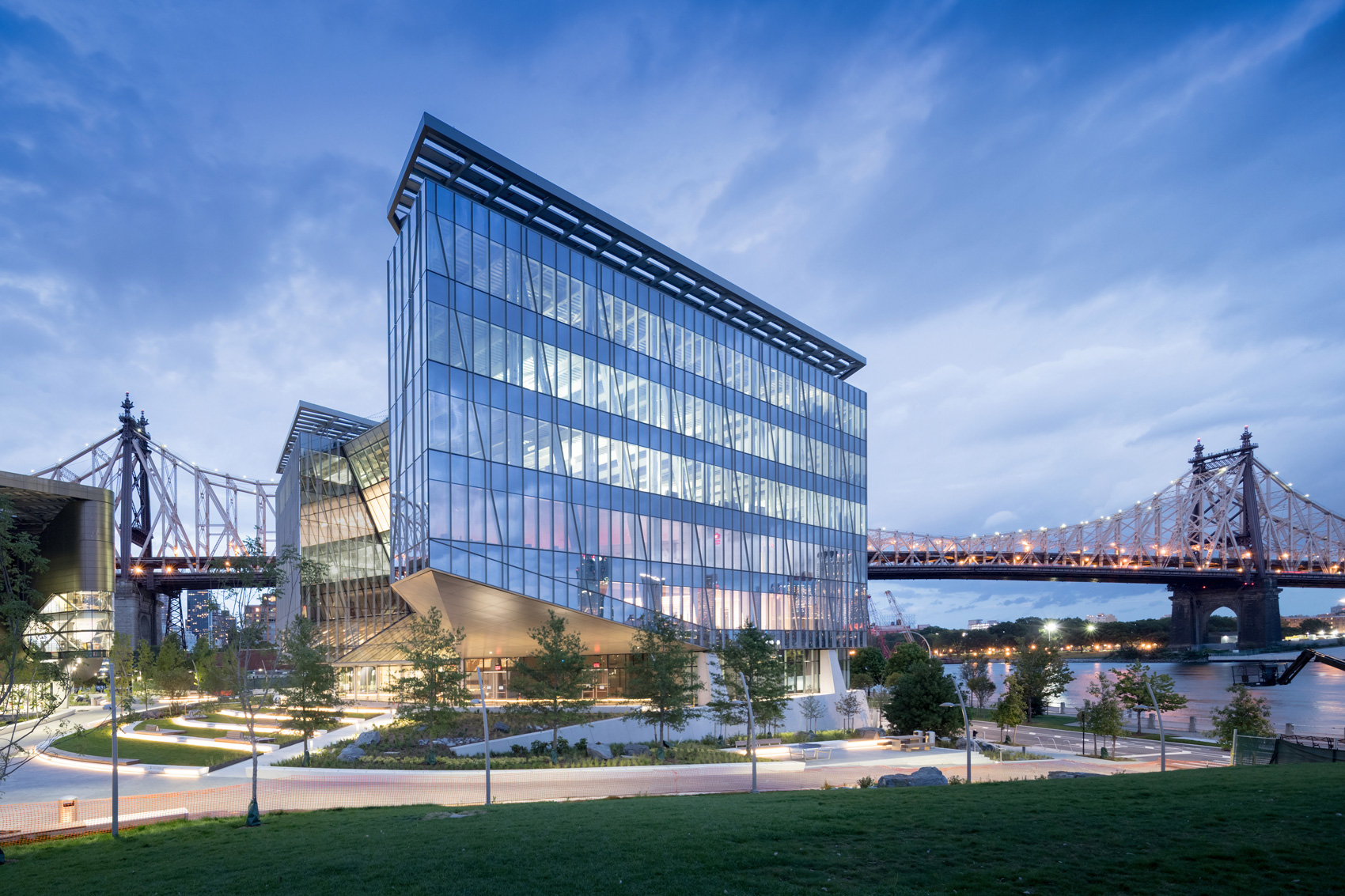
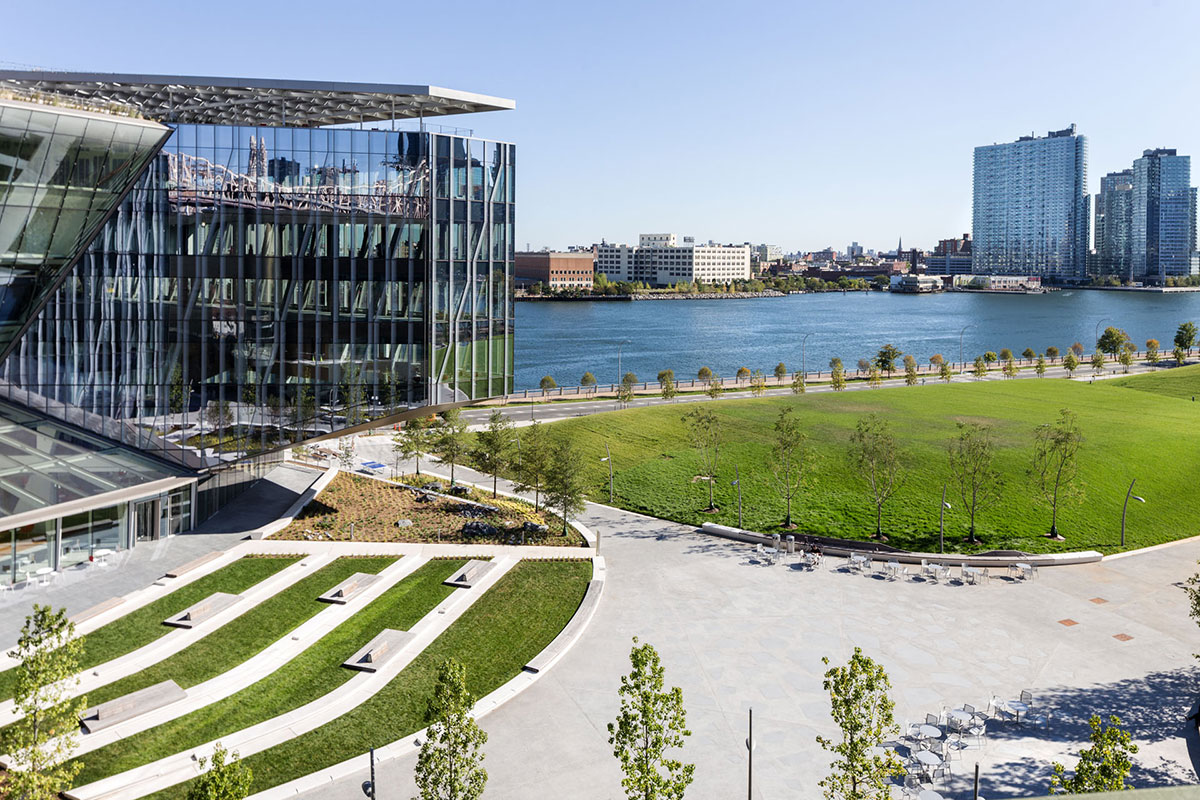
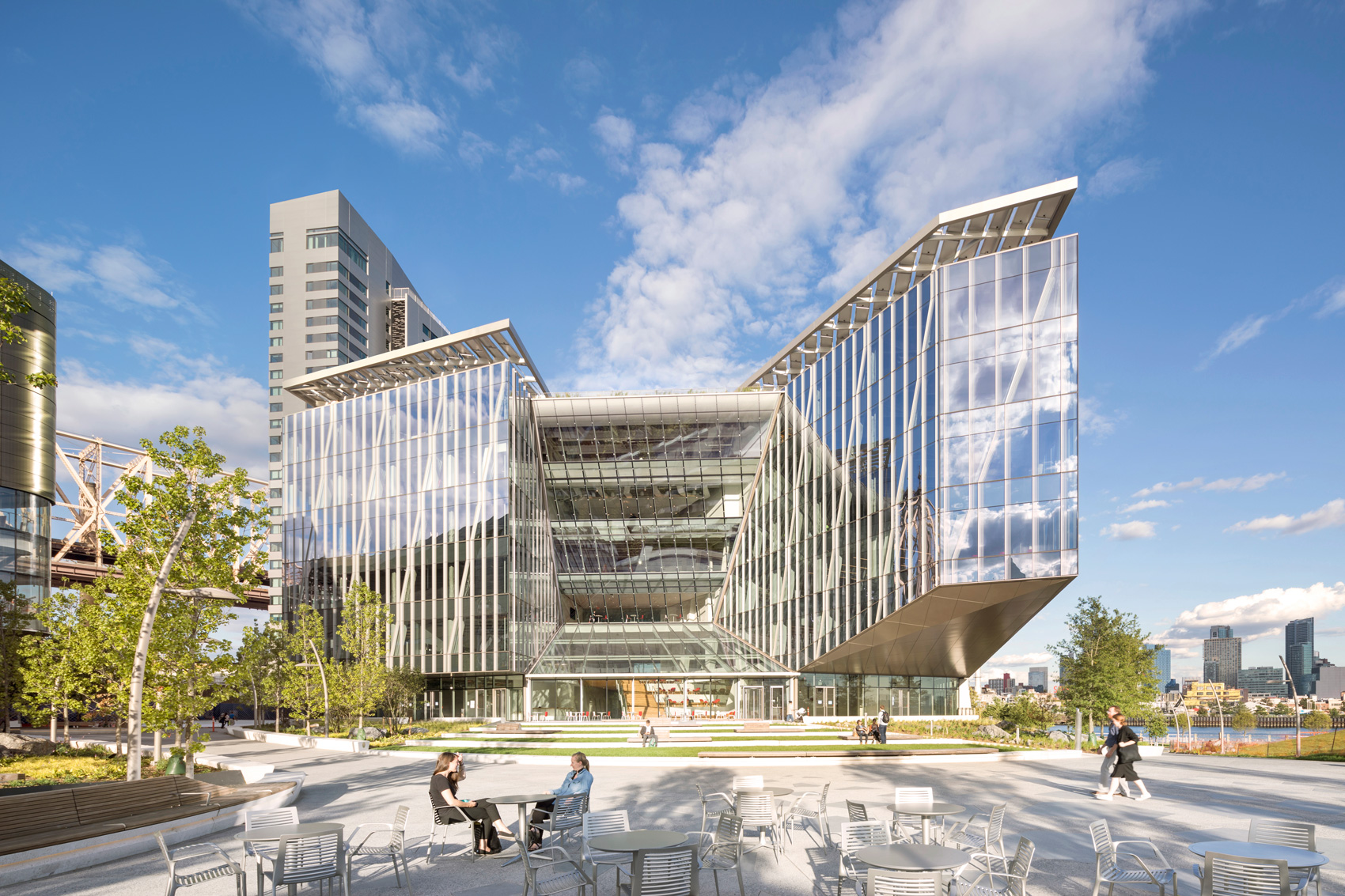




 Outside the Tata Innovation Center and the surrounding grounds on Roosevelt Island, ABC provided a series of granite stone pavers. The project itself was developed by Forest City New York to supports Cornell Tech’s efforts to fuse entrepreneurial and academic ambitions on its new Roosevelt Island campus in New York City. One-third of the 235,000-square-foot building hosts Cornell Tech studios, labs, classrooms, and event spaces, while the upper levels are dedicated to a mix of technology-focused companies and start-ups.
Outside the Tata Innovation Center and the surrounding grounds on Roosevelt Island, ABC provided a series of granite stone pavers. The project itself was developed by Forest City New York to supports Cornell Tech’s efforts to fuse entrepreneurial and academic ambitions on its new Roosevelt Island campus in New York City. One-third of the 235,000-square-foot building hosts Cornell Tech studios, labs, classrooms, and event spaces, while the upper levels are dedicated to a mix of technology-focused companies and start-ups.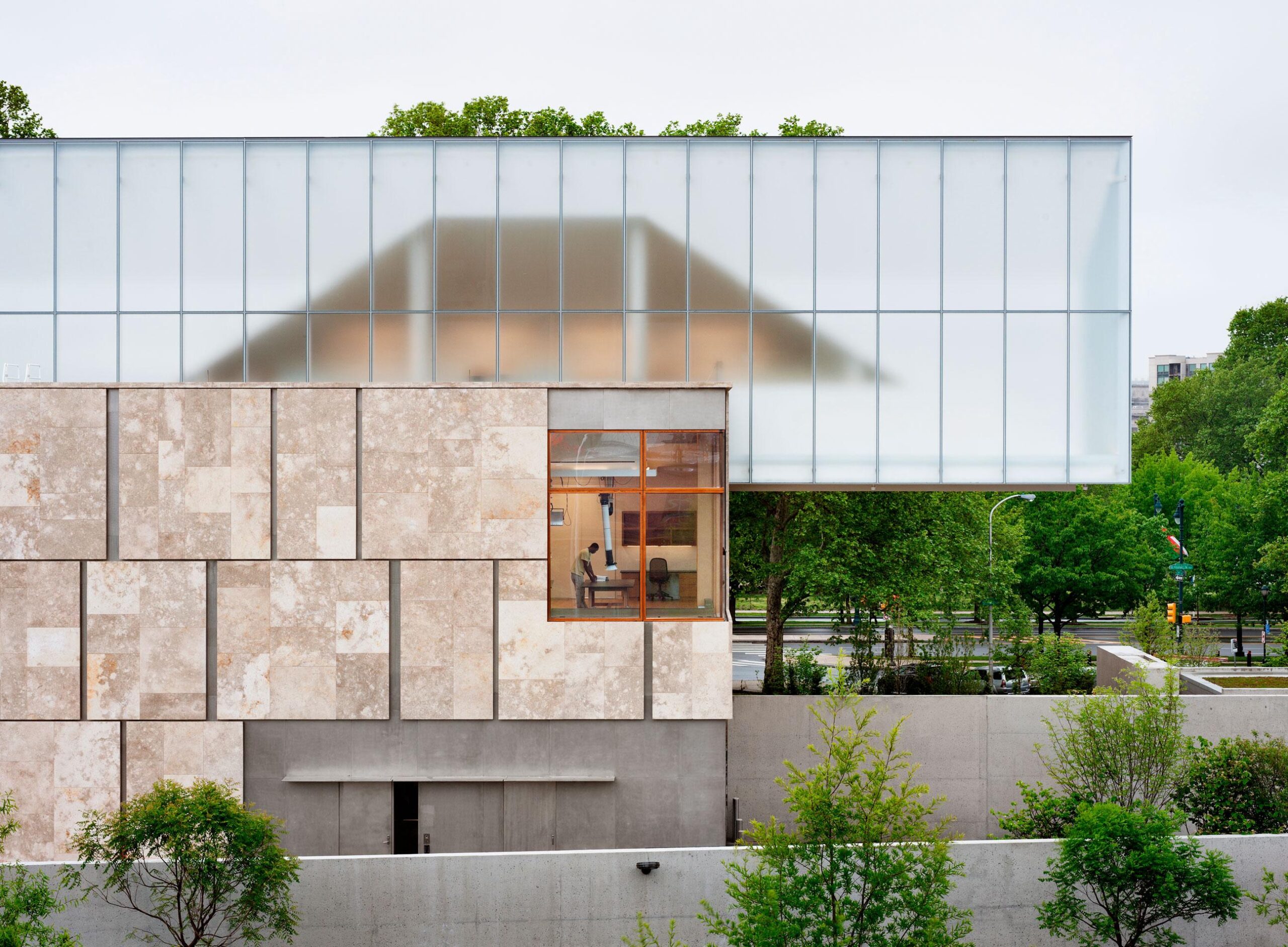
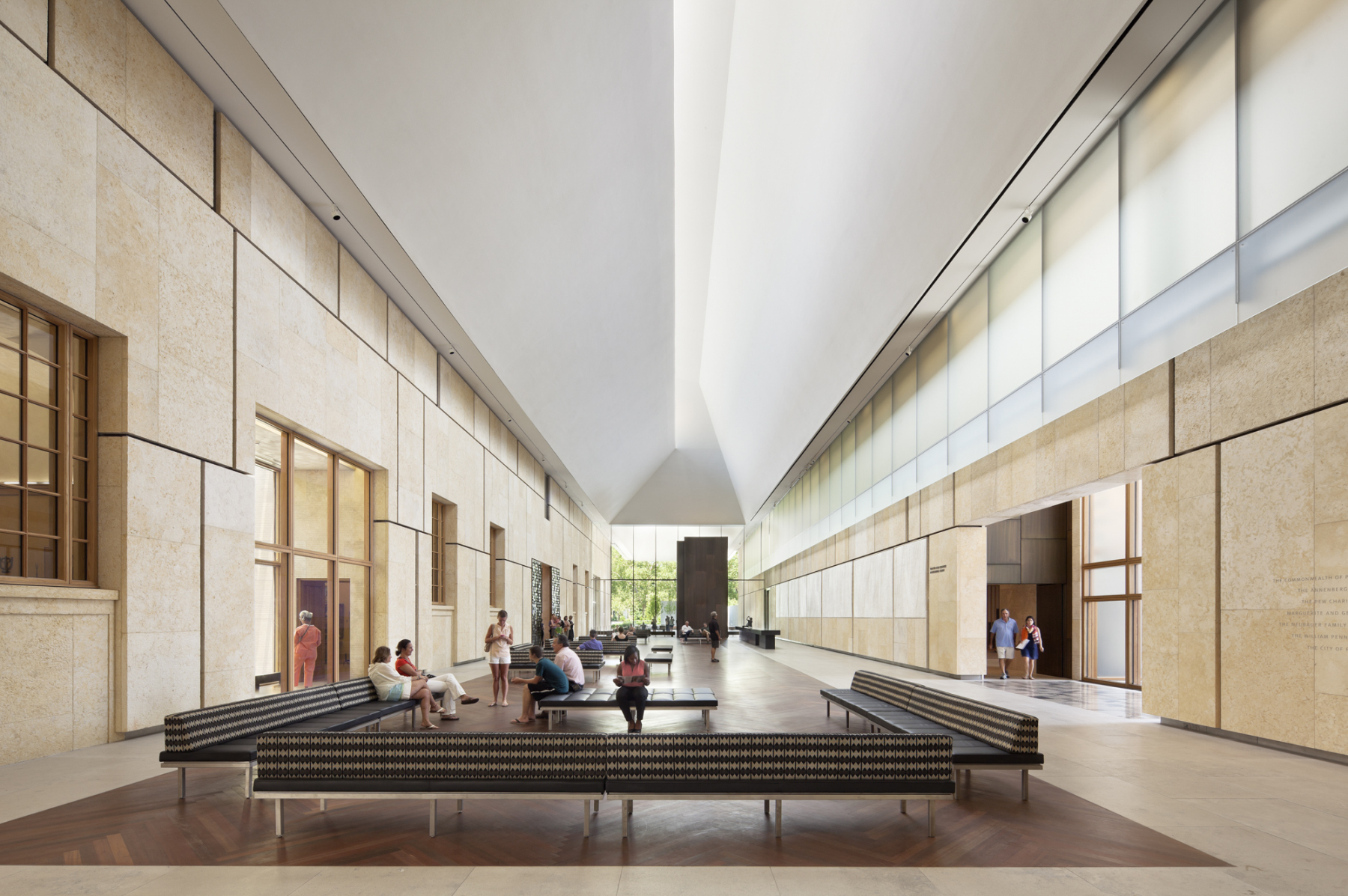
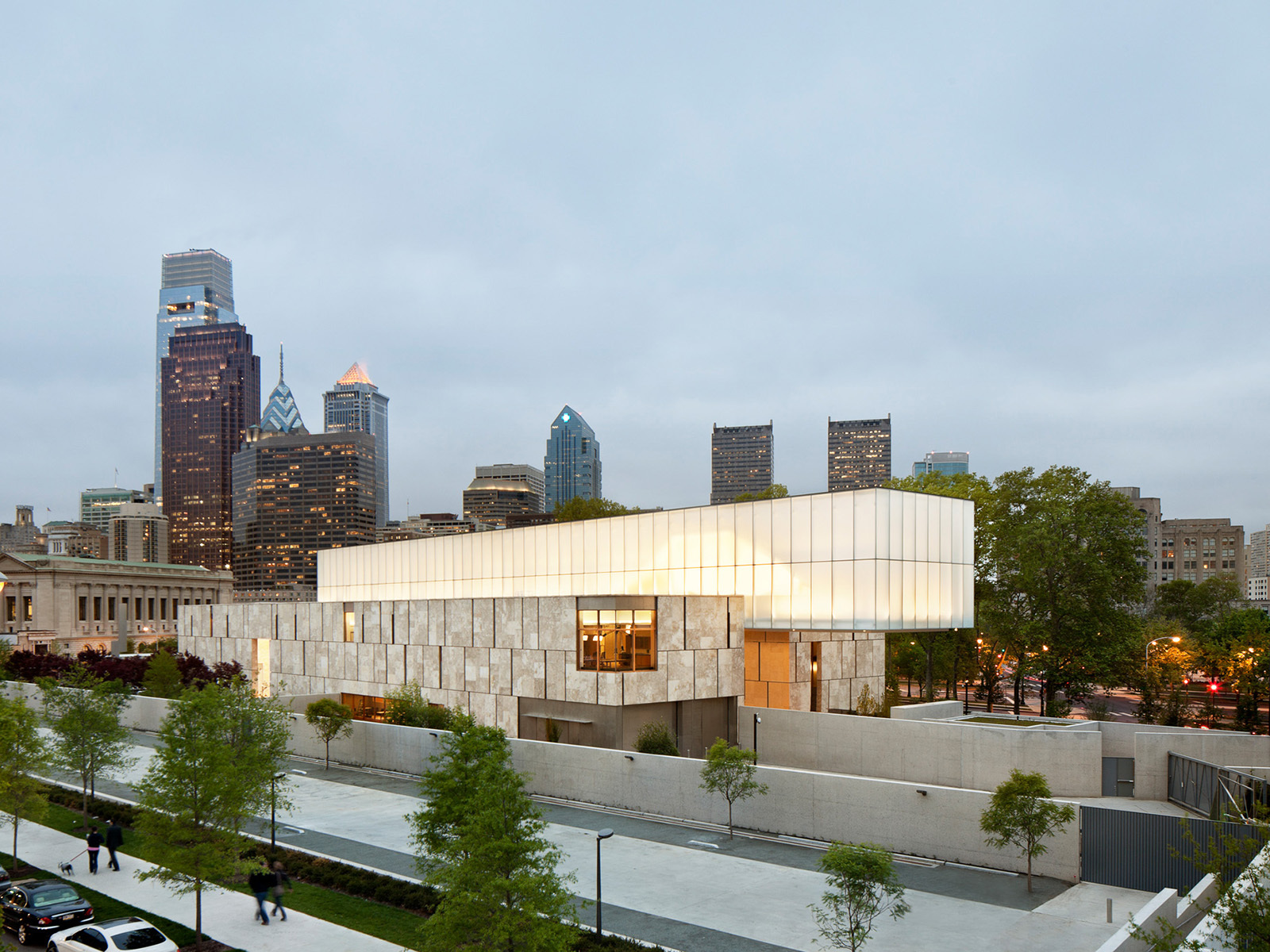
 The Barnes Foundation collection was relocated to a 93,000 square foot, LEED Platinum building on the Benjamin Franklin Parkway in downtown Philadelphia. Conceived as “a gallery in a garden and a garden in a gallery,” the new building honors the past Merion facility and provides visitors with a personal experience. Clad in fossilized limestone and crowned by a luminous light box, the two-story building, with an additional level below grade, is set in a public garden.
The Barnes Foundation collection was relocated to a 93,000 square foot, LEED Platinum building on the Benjamin Franklin Parkway in downtown Philadelphia. Conceived as “a gallery in a garden and a garden in a gallery,” the new building honors the past Merion facility and provides visitors with a personal experience. Clad in fossilized limestone and crowned by a luminous light box, the two-story building, with an additional level below grade, is set in a public garden.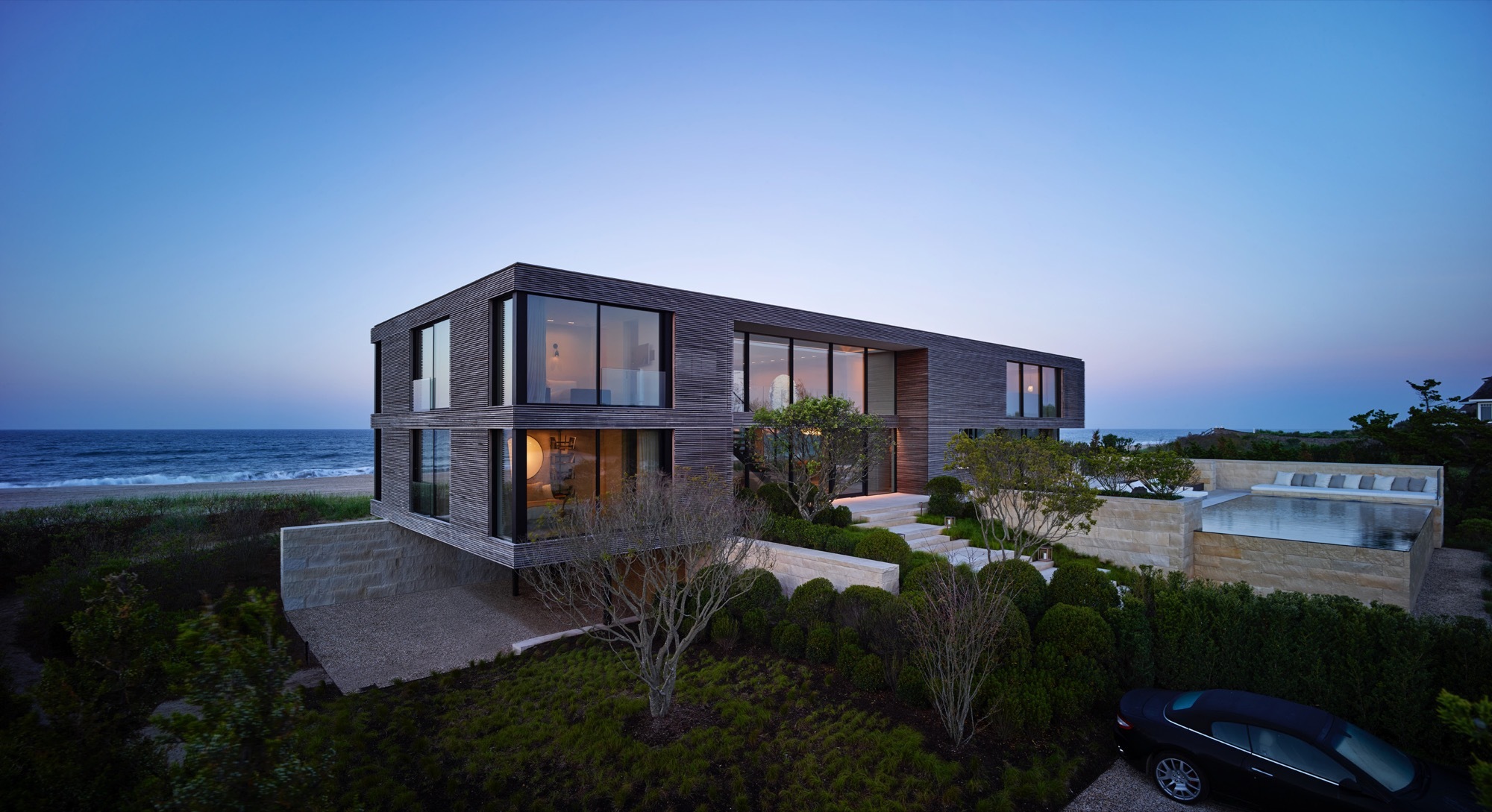
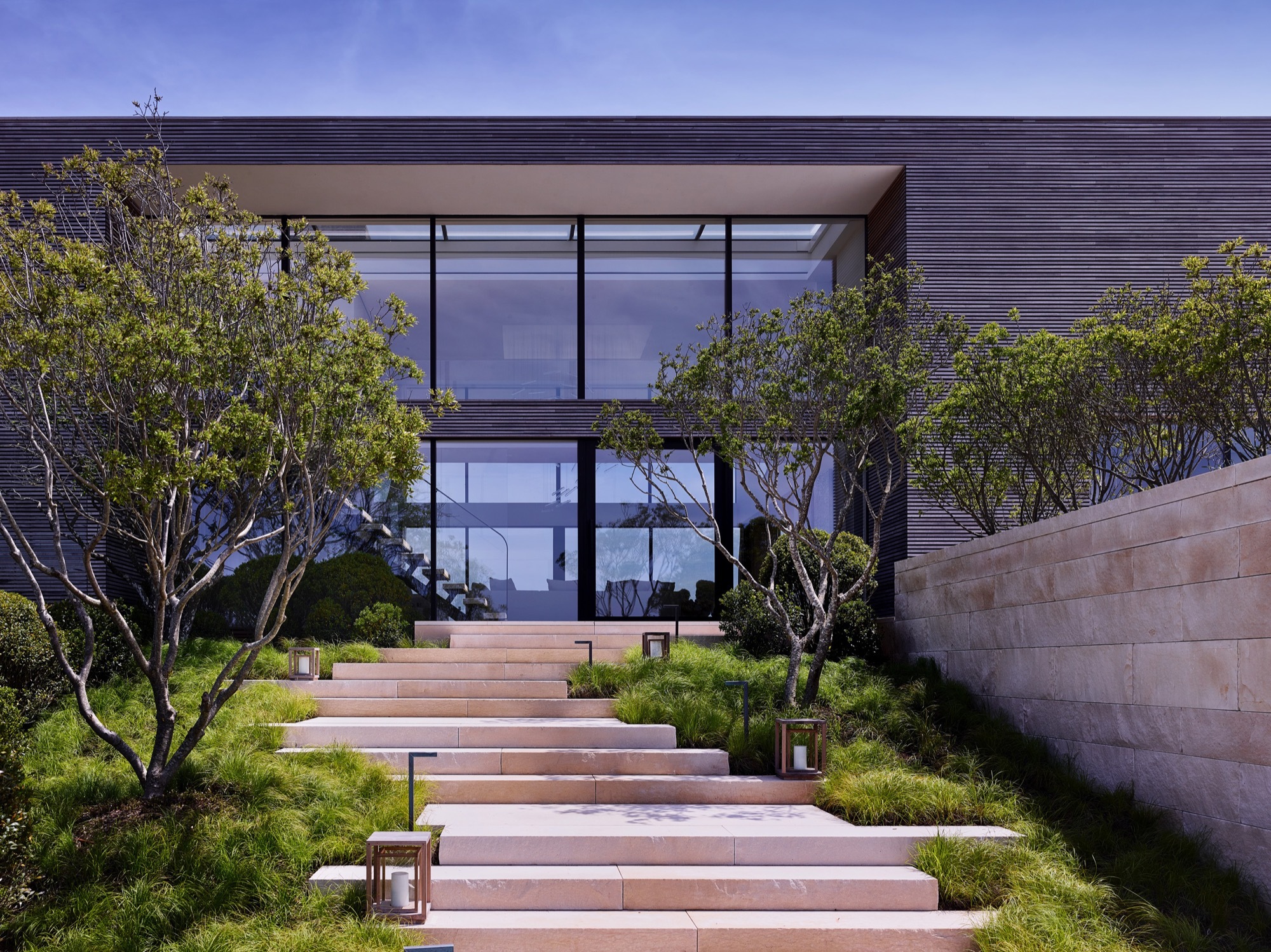
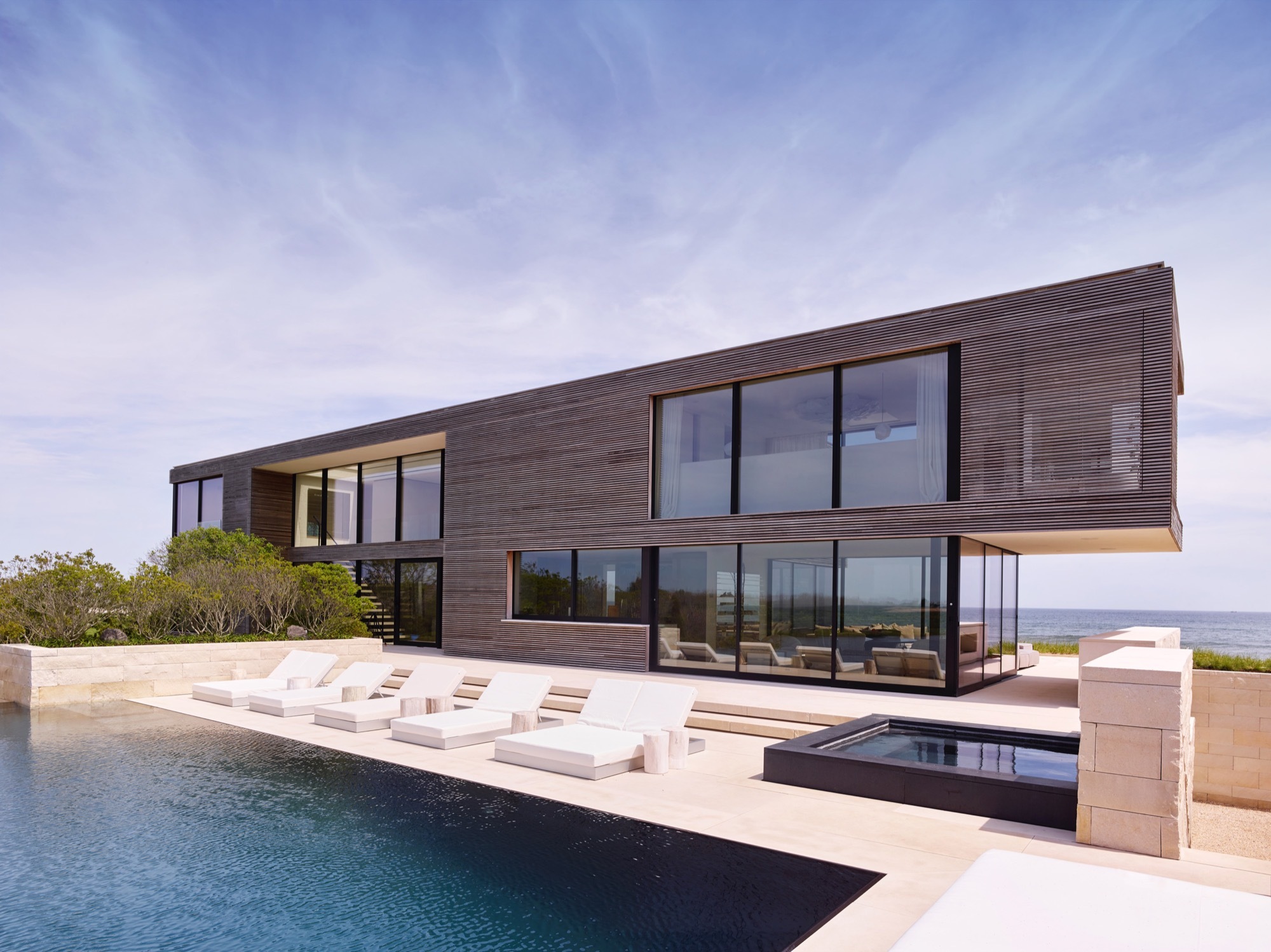
 Field House was built between ocean and pond. With the landscape seemingly running through it, the house was designed around flooding and wind. It was constructed on piles with a steel frame and high density limestone. The house is approached through a terraced set of stairs, and the interior palette matches the exterior, with the limestone extending throughout the main level and reappearing as solid blocks in bathrooms.
Field House was built between ocean and pond. With the landscape seemingly running through it, the house was designed around flooding and wind. It was constructed on piles with a steel frame and high density limestone. The house is approached through a terraced set of stairs, and the interior palette matches the exterior, with the limestone extending throughout the main level and reappearing as solid blocks in bathrooms.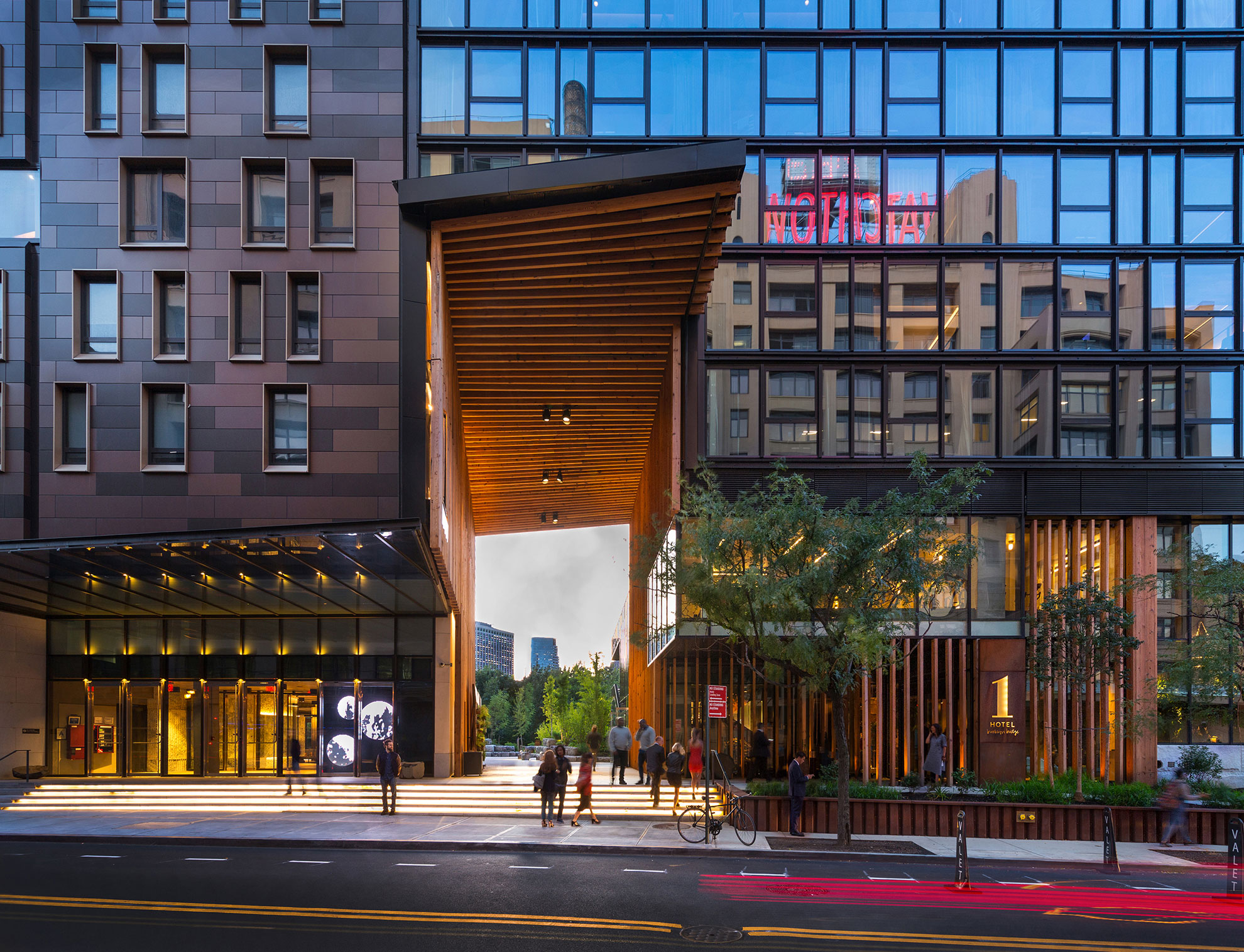
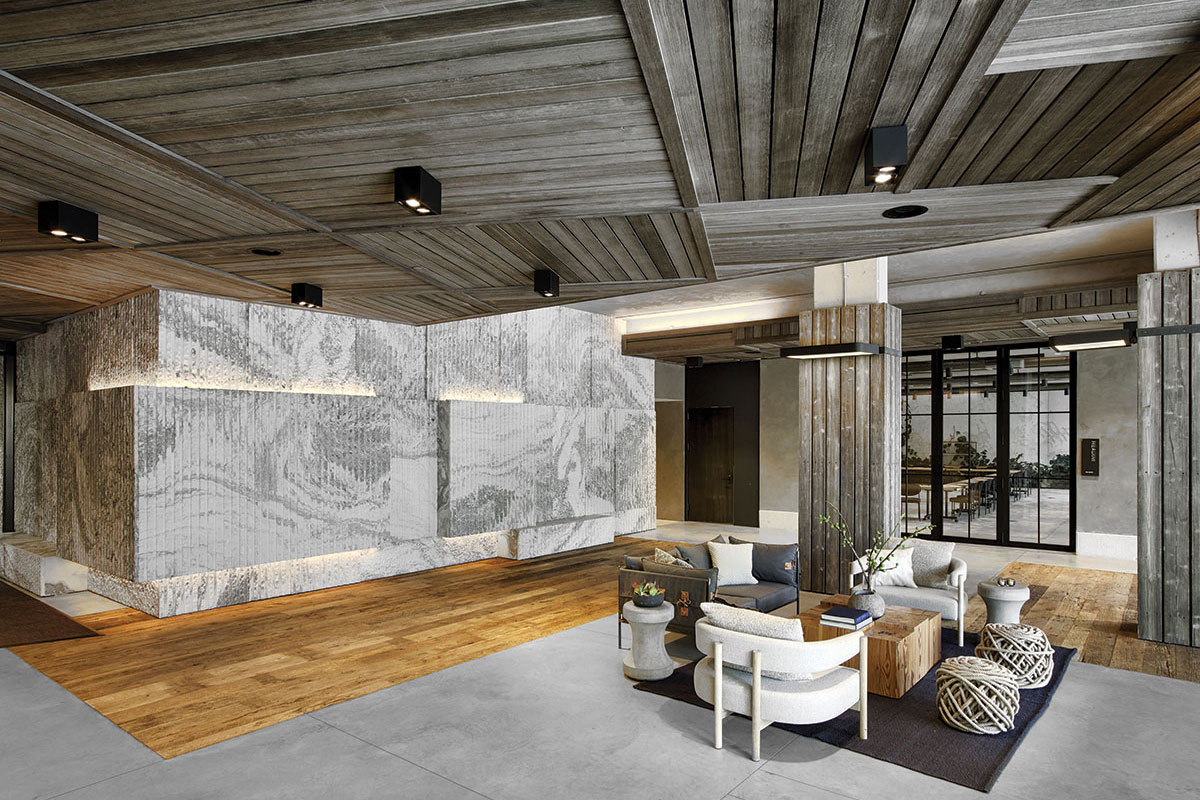
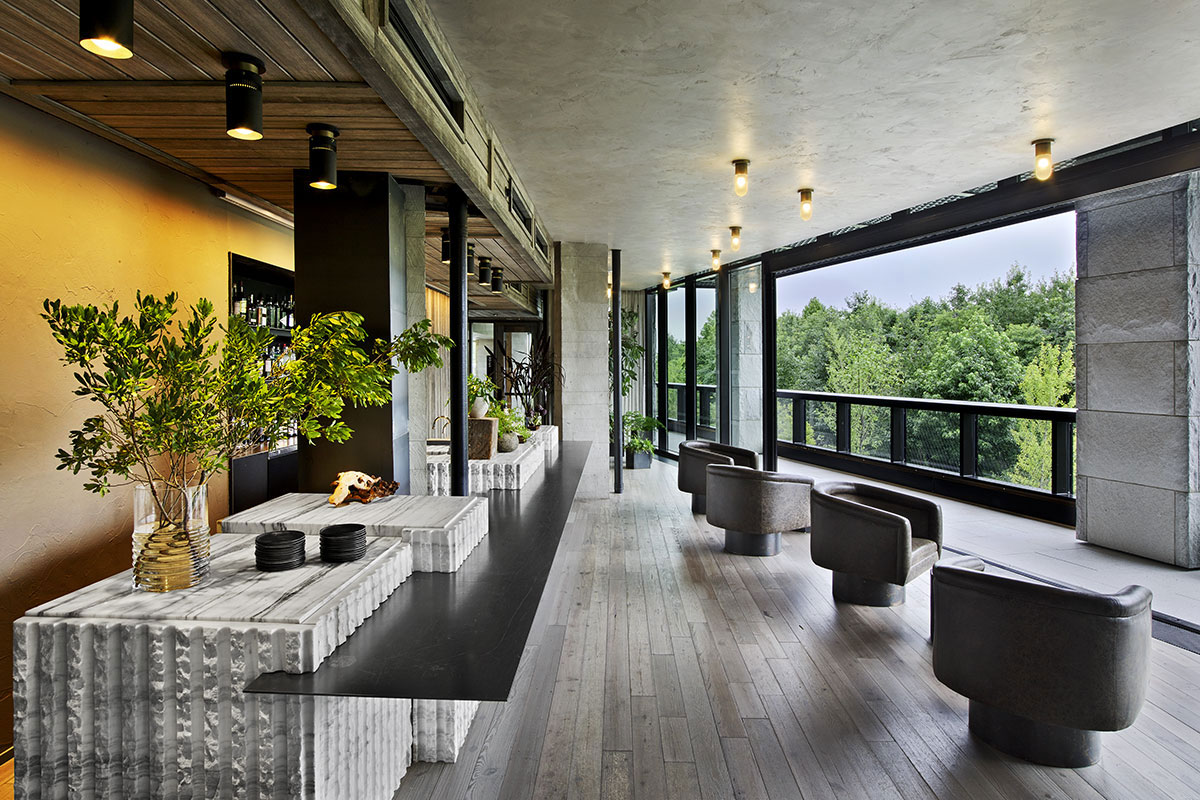
 1 Hotel overlooks the East River in Brooklyn’s DUMBO neighborhood and features more than 10,000 square feet ABC’s Montclair Danby Vein Cut, Mountain White Danby, and Crystal Grey Danby. The Pierhouse and 1 Hotel Brooklyn Bridge building echoes the park’s simplified use of stone and steel. It steps down to meet the green lawns with planted roofs. Using stone from a Vermont quarry helped the project achieve the designation of LEED Gold certification.
1 Hotel overlooks the East River in Brooklyn’s DUMBO neighborhood and features more than 10,000 square feet ABC’s Montclair Danby Vein Cut, Mountain White Danby, and Crystal Grey Danby. The Pierhouse and 1 Hotel Brooklyn Bridge building echoes the park’s simplified use of stone and steel. It steps down to meet the green lawns with planted roofs. Using stone from a Vermont quarry helped the project achieve the designation of LEED Gold certification.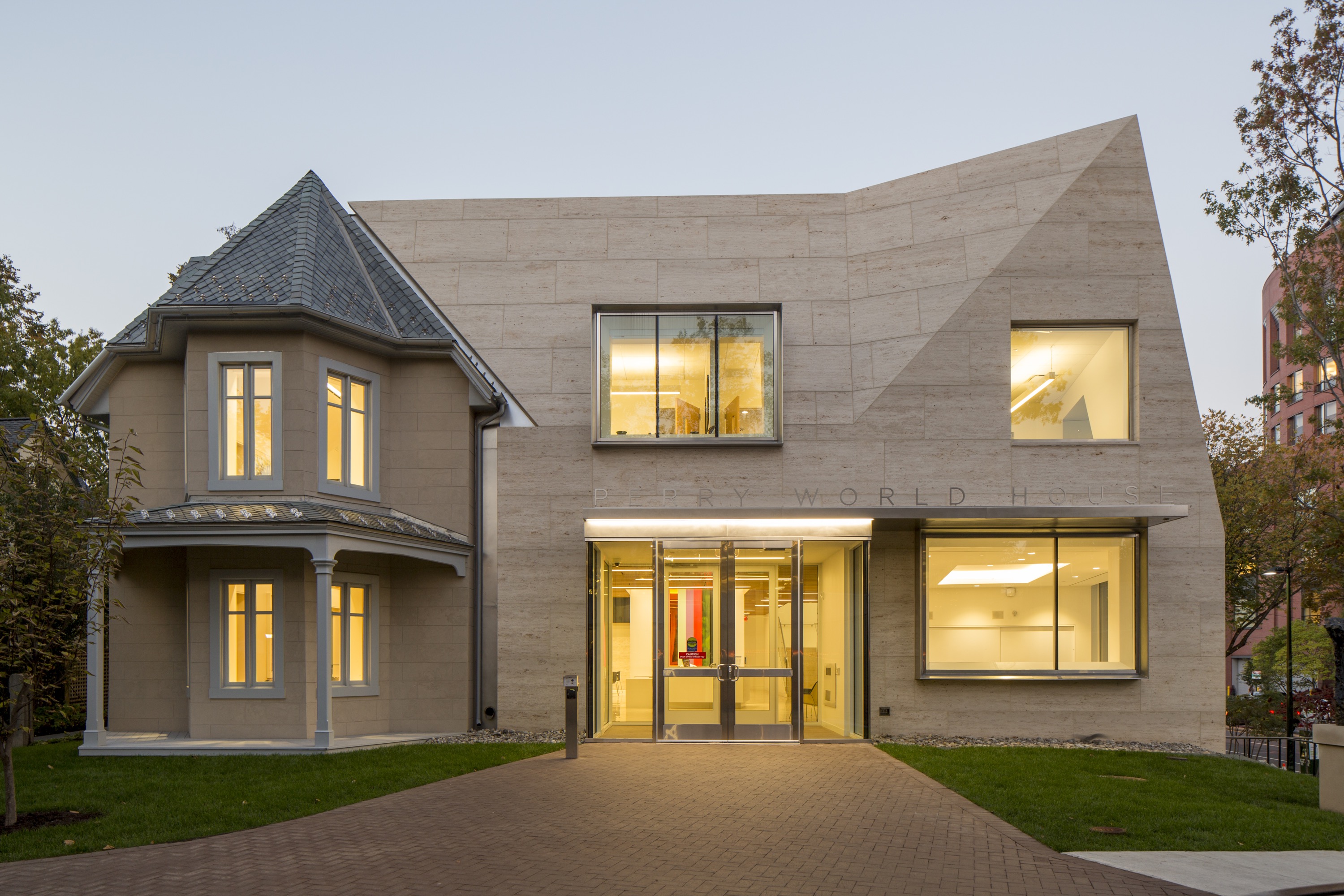
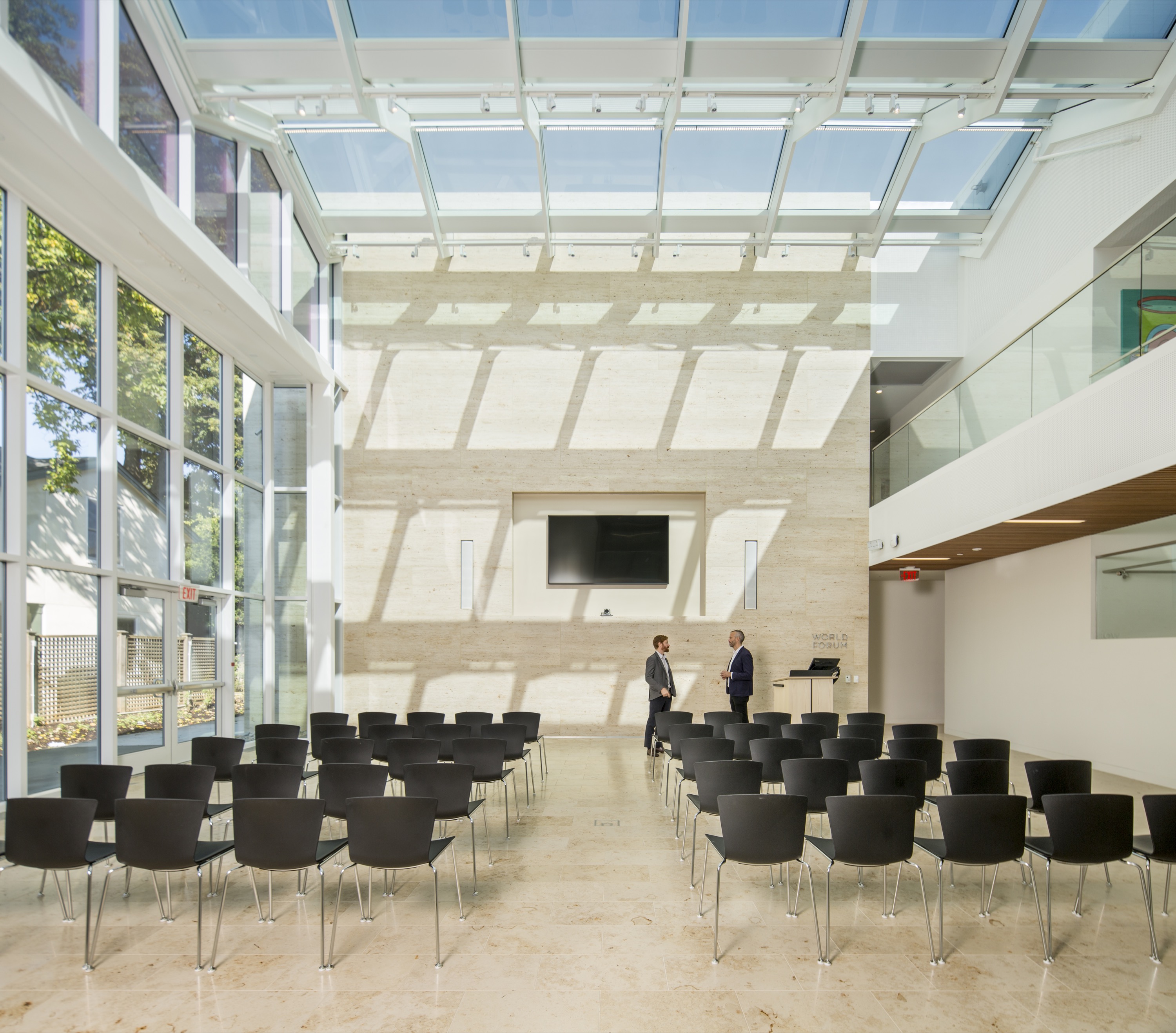
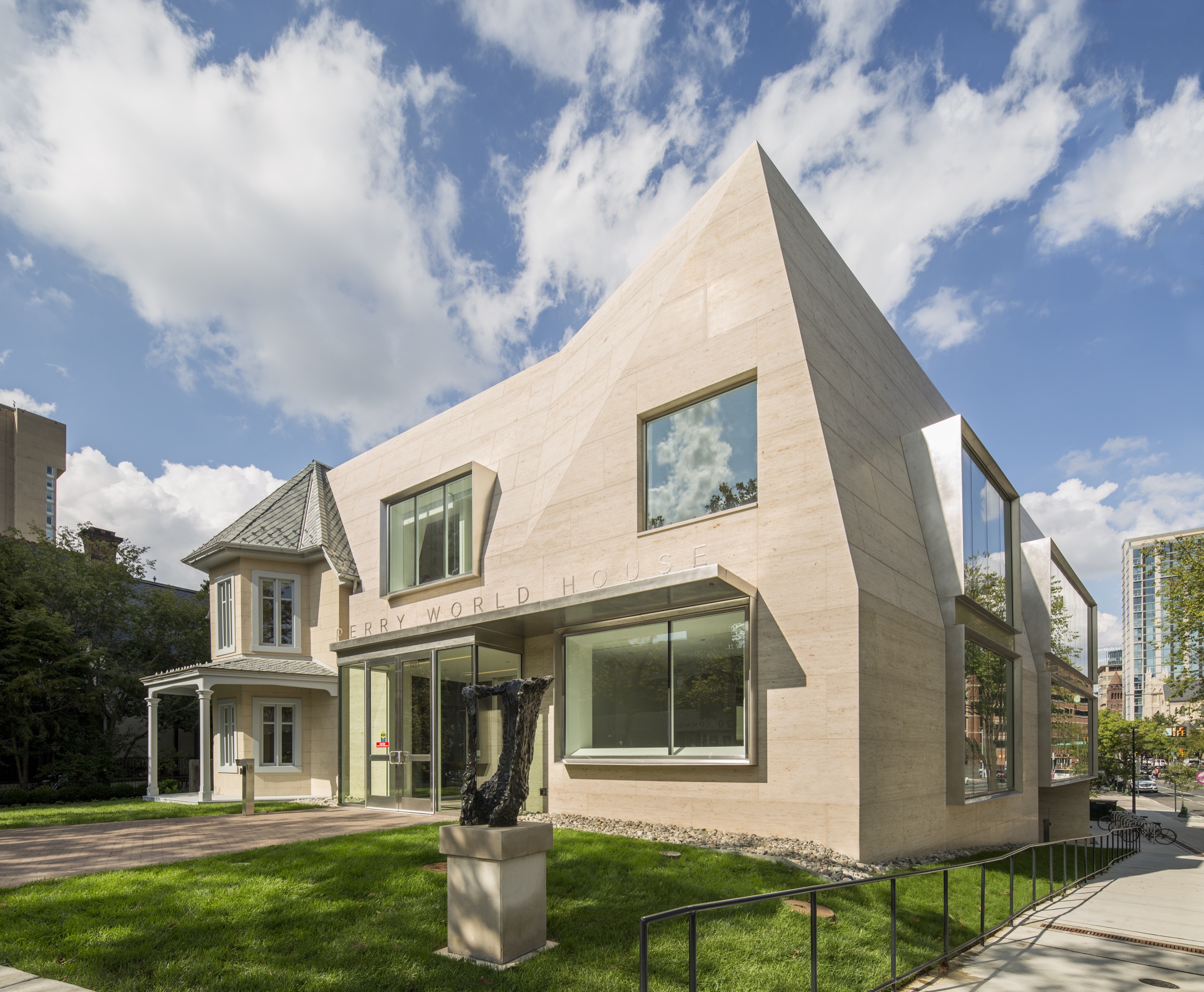
 For the Perry World House, the University of Pennsylvania needed a space for its new institute that would aggregate all its international activities. This became a renovated cottage that was originally built in 1851. Designed by 1100 Architect, the team preserved the house while transforming the site into a 21st century flagship for this newly formed institute. ABC Worldwide Stone was responsible for sourcing, selecting, quality checks, logistics and fabrication approvals on all the project’s 1,850 cubic feet of Renaissance Beige limestone.
For the Perry World House, the University of Pennsylvania needed a space for its new institute that would aggregate all its international activities. This became a renovated cottage that was originally built in 1851. Designed by 1100 Architect, the team preserved the house while transforming the site into a 21st century flagship for this newly formed institute. ABC Worldwide Stone was responsible for sourcing, selecting, quality checks, logistics and fabrication approvals on all the project’s 1,850 cubic feet of Renaissance Beige limestone.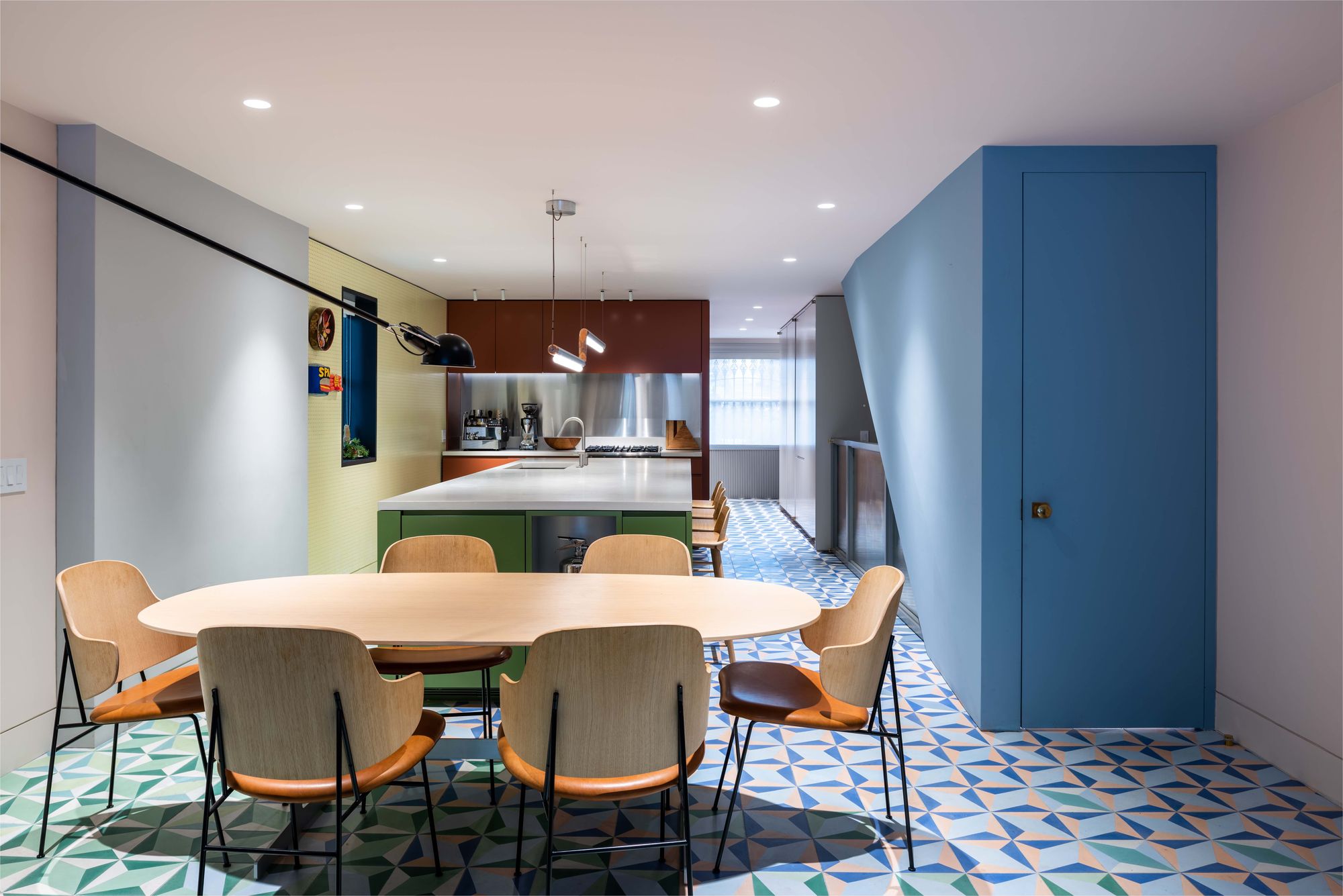
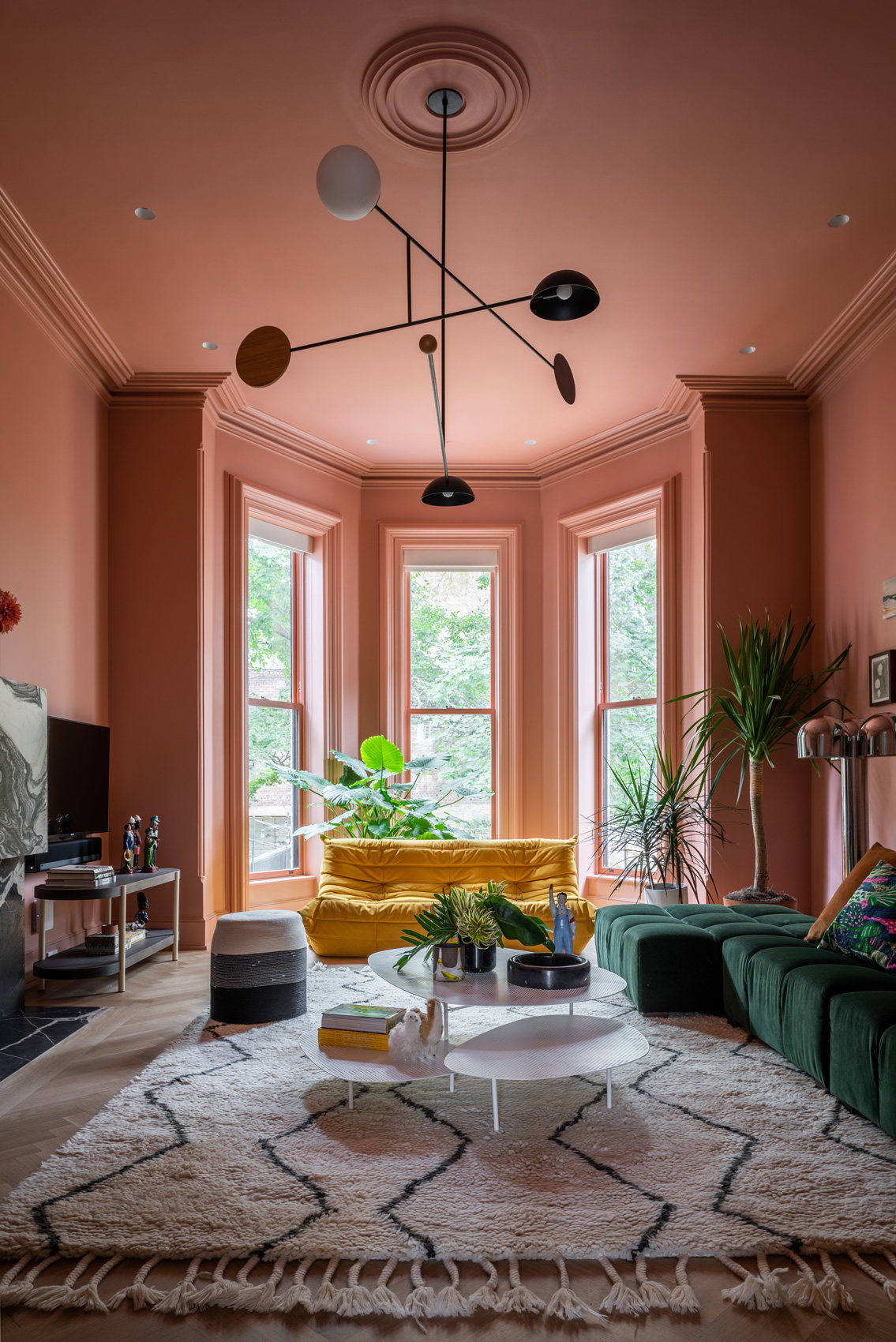
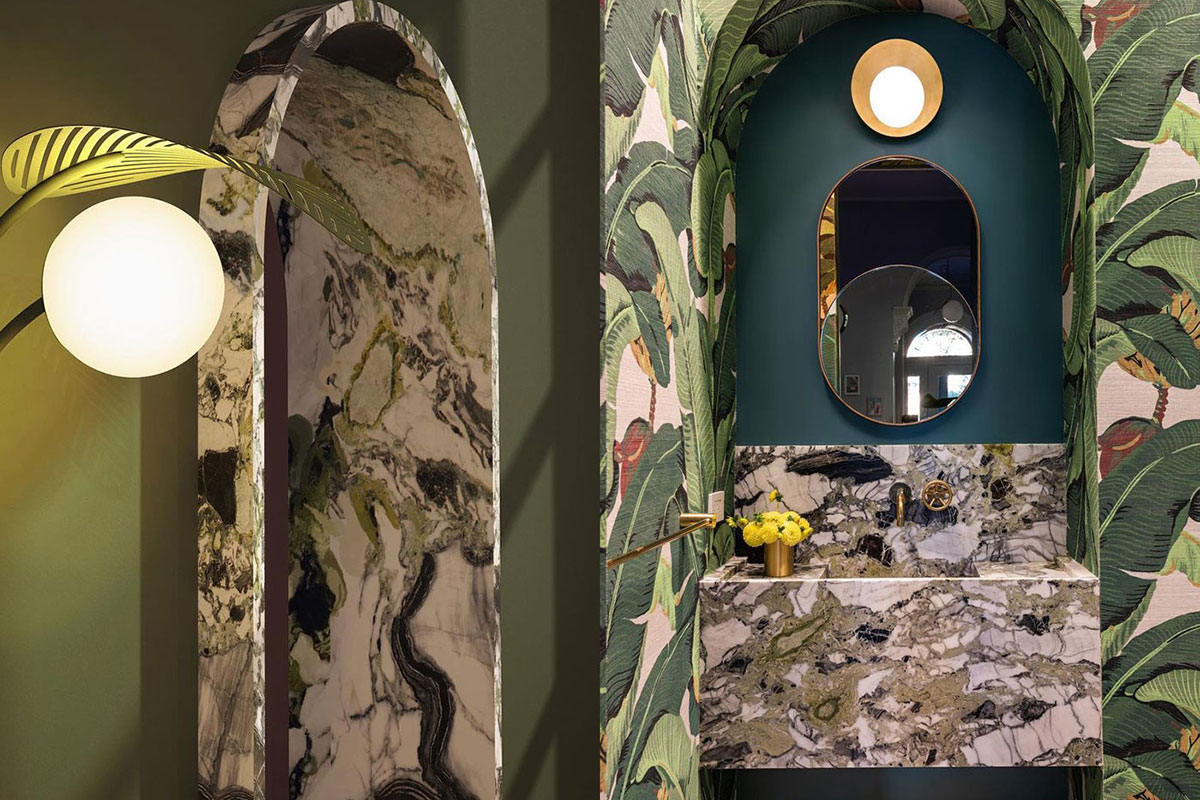
 MKCA’s gut renovation and exterior restoration of a landmark Brooklyn brownstone balances history with a playful intervention. Located in the historic Clinton Hill neighborhood, the original structure was abandoned to decay for twenty years. The design of the house balances stabilizing the building and recapturing its original details with efforts to create a new home in an adventurous, innovative manner, producing an appealing aesthetic between the historic elements and the new additions.
MKCA’s gut renovation and exterior restoration of a landmark Brooklyn brownstone balances history with a playful intervention. Located in the historic Clinton Hill neighborhood, the original structure was abandoned to decay for twenty years. The design of the house balances stabilizing the building and recapturing its original details with efforts to create a new home in an adventurous, innovative manner, producing an appealing aesthetic between the historic elements and the new additions.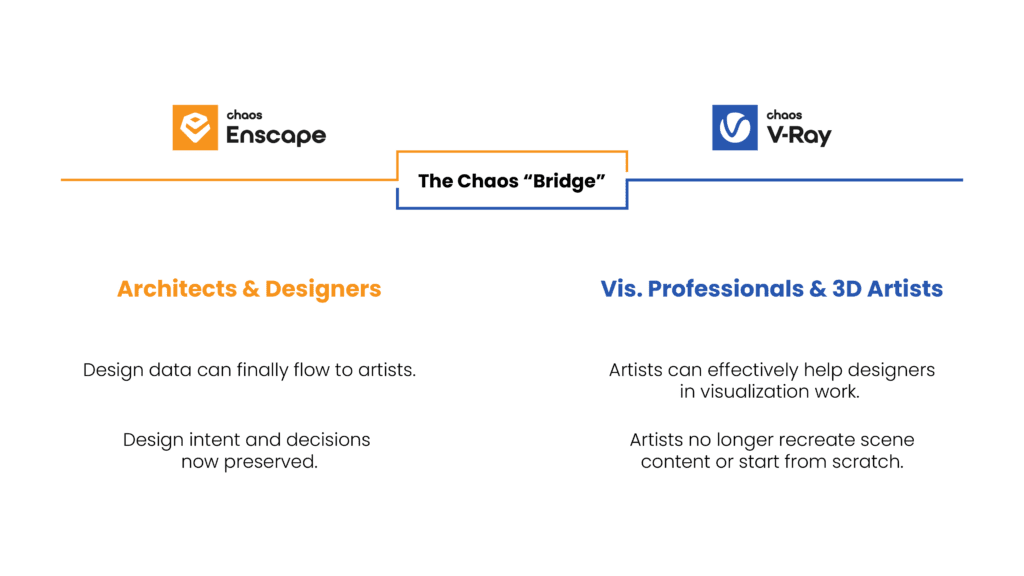
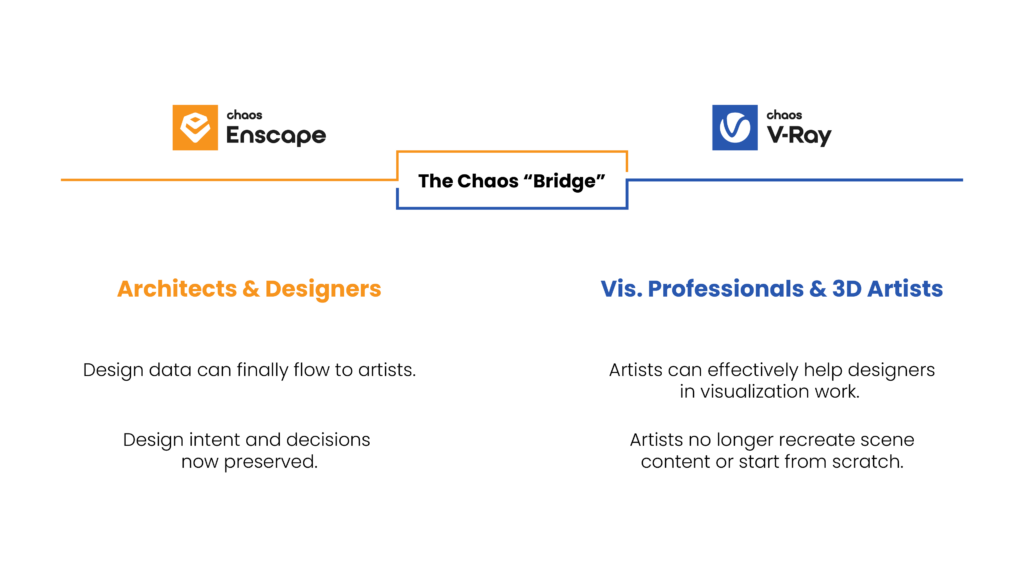 A new solution to this workflow problem has arrived in the form of the Bridge between Enscape and V-Ray.
A new solution to this workflow problem has arrived in the form of the Bridge between Enscape and V-Ray. 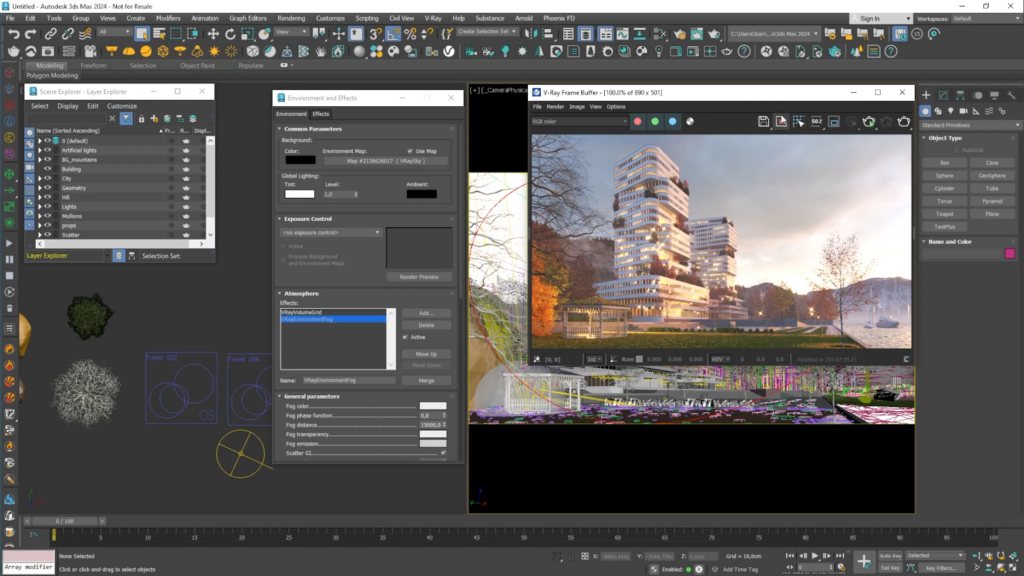 The best illustration of the Bridge’s benefits can be seen in V-Ray’s hyper-realistic lighting and material rendering capabilities. When opened in V-Ray, lights defined by designers in Enscape feature a far greater degree of control over intensity, color, and physical accuracy. Materials in V-Ray likewise exhibit more realistic interaction with light than they do in Enscape, enhancing the ability to depict translucency, subsurface scattering, tinted glass surfaces and mirror surfaces. In the hands of a professional visualization artist, these capabilities make the difference between a compelling rendering and a jaw-dropping, life-like image.
The best illustration of the Bridge’s benefits can be seen in V-Ray’s hyper-realistic lighting and material rendering capabilities. When opened in V-Ray, lights defined by designers in Enscape feature a far greater degree of control over intensity, color, and physical accuracy. Materials in V-Ray likewise exhibit more realistic interaction with light than they do in Enscape, enhancing the ability to depict translucency, subsurface scattering, tinted glass surfaces and mirror surfaces. In the hands of a professional visualization artist, these capabilities make the difference between a compelling rendering and a jaw-dropping, life-like image.
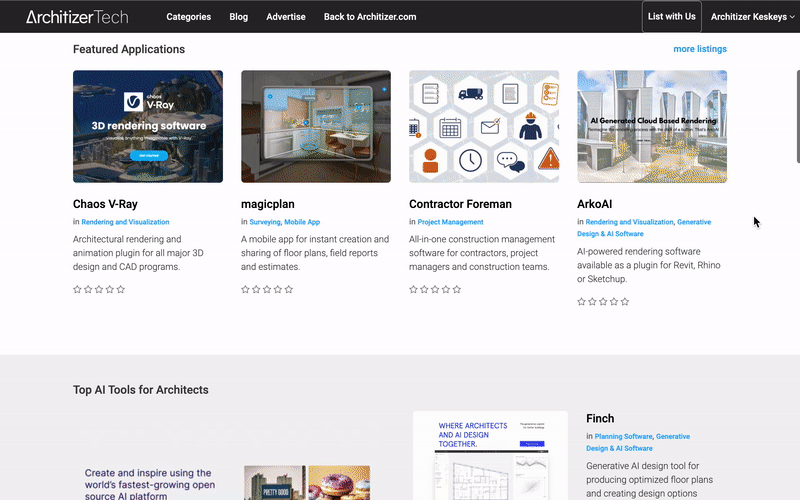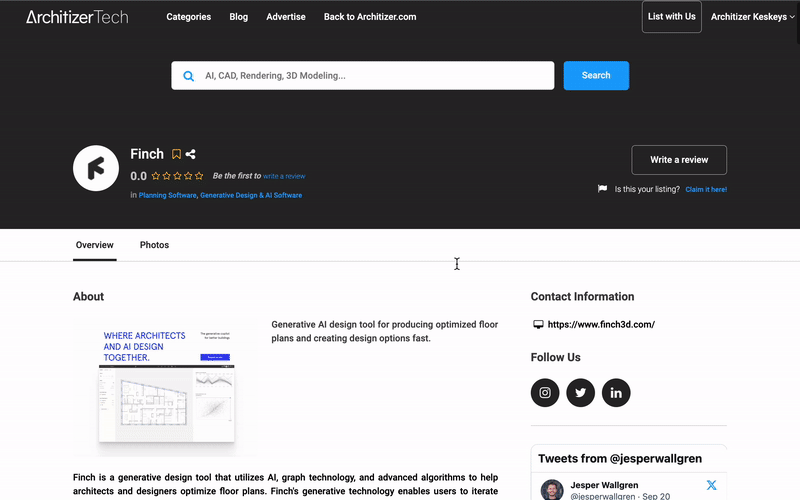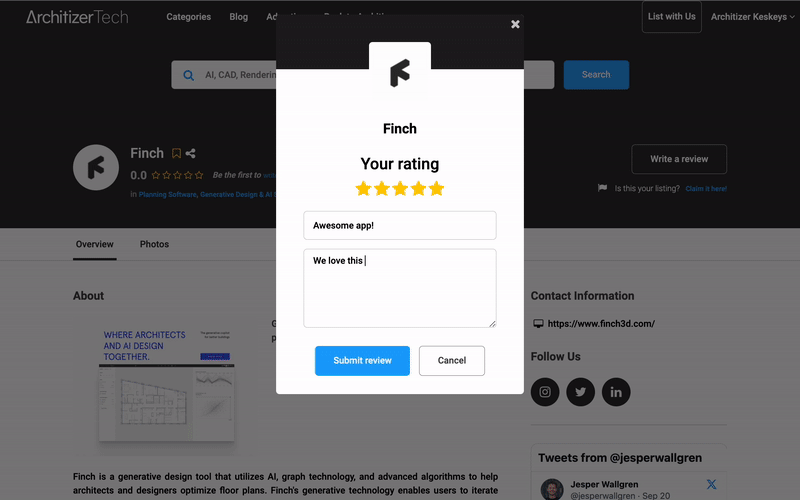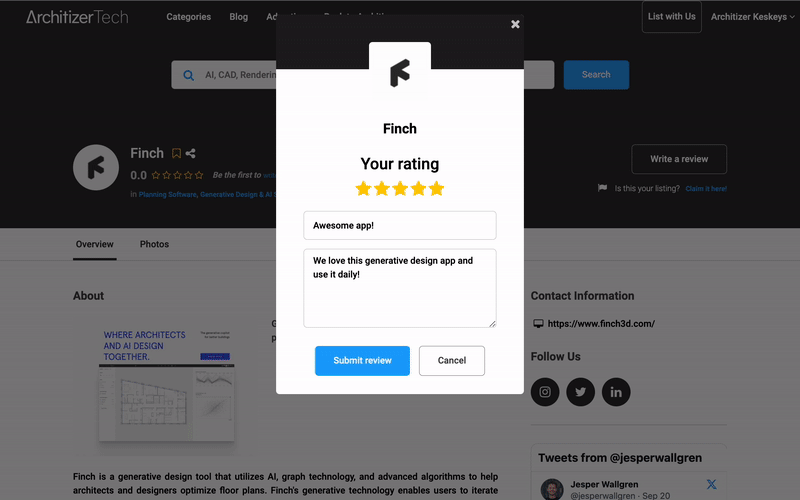 Incentivizing Your Participation
Incentivizing Your Participation Calling All Innovators in AEC Technology: Add Your App
Calling All Innovators in AEC Technology: Add Your App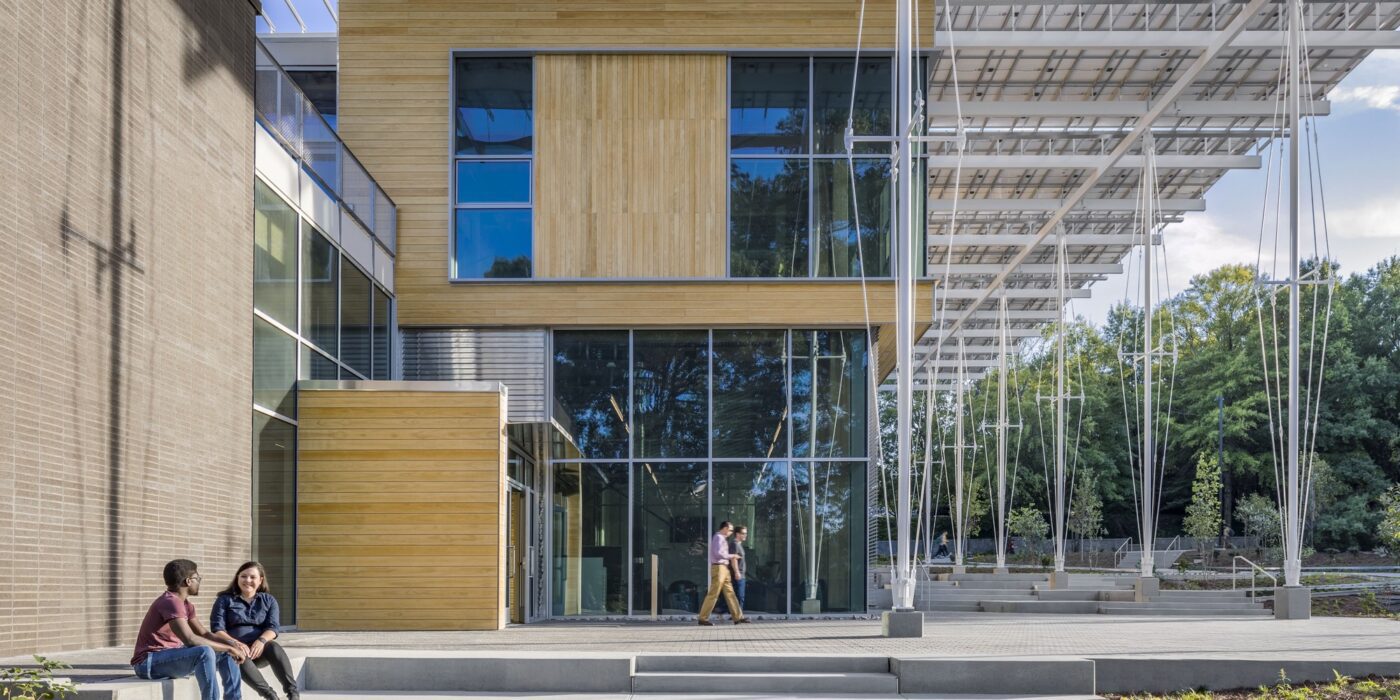
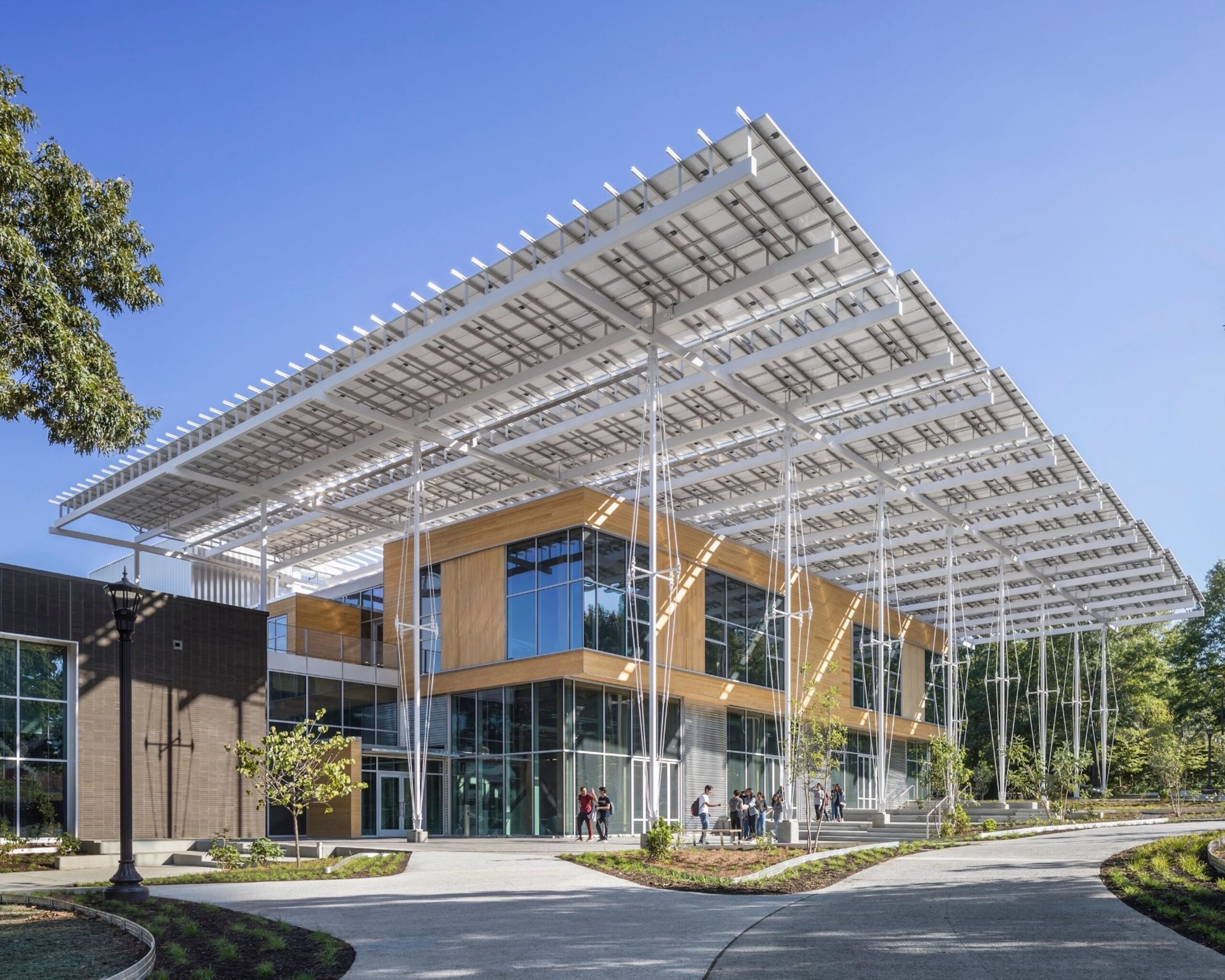
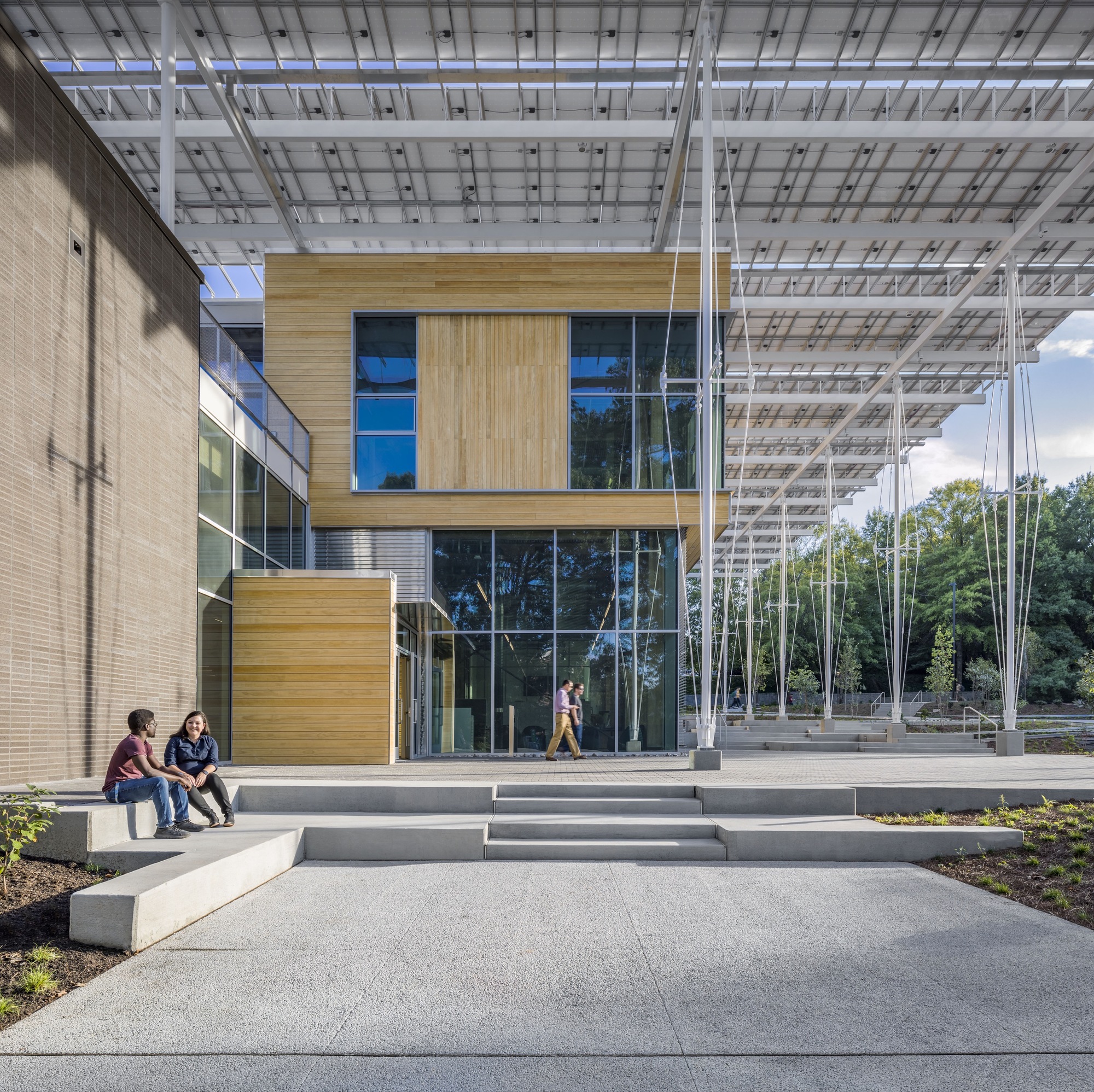 Located in the heart of Atlanta, The Kendeda Building was designed to make a statement. Created for the Georgia Institute of Technology, the building’s design also became an expression of its value system. These ideas are shown on display both inside and out, from the massing to material choices like mass timber. Working with Lord Aeck Sargent, a Katerra Company (LAS), the team at Miller Hull wanted to demonstrate that rigorous design and sustainability go hand-in-hand.
Located in the heart of Atlanta, The Kendeda Building was designed to make a statement. Created for the Georgia Institute of Technology, the building’s design also became an expression of its value system. These ideas are shown on display both inside and out, from the massing to material choices like mass timber. Working with Lord Aeck Sargent, a Katerra Company (LAS), the team at Miller Hull wanted to demonstrate that rigorous design and sustainability go hand-in-hand.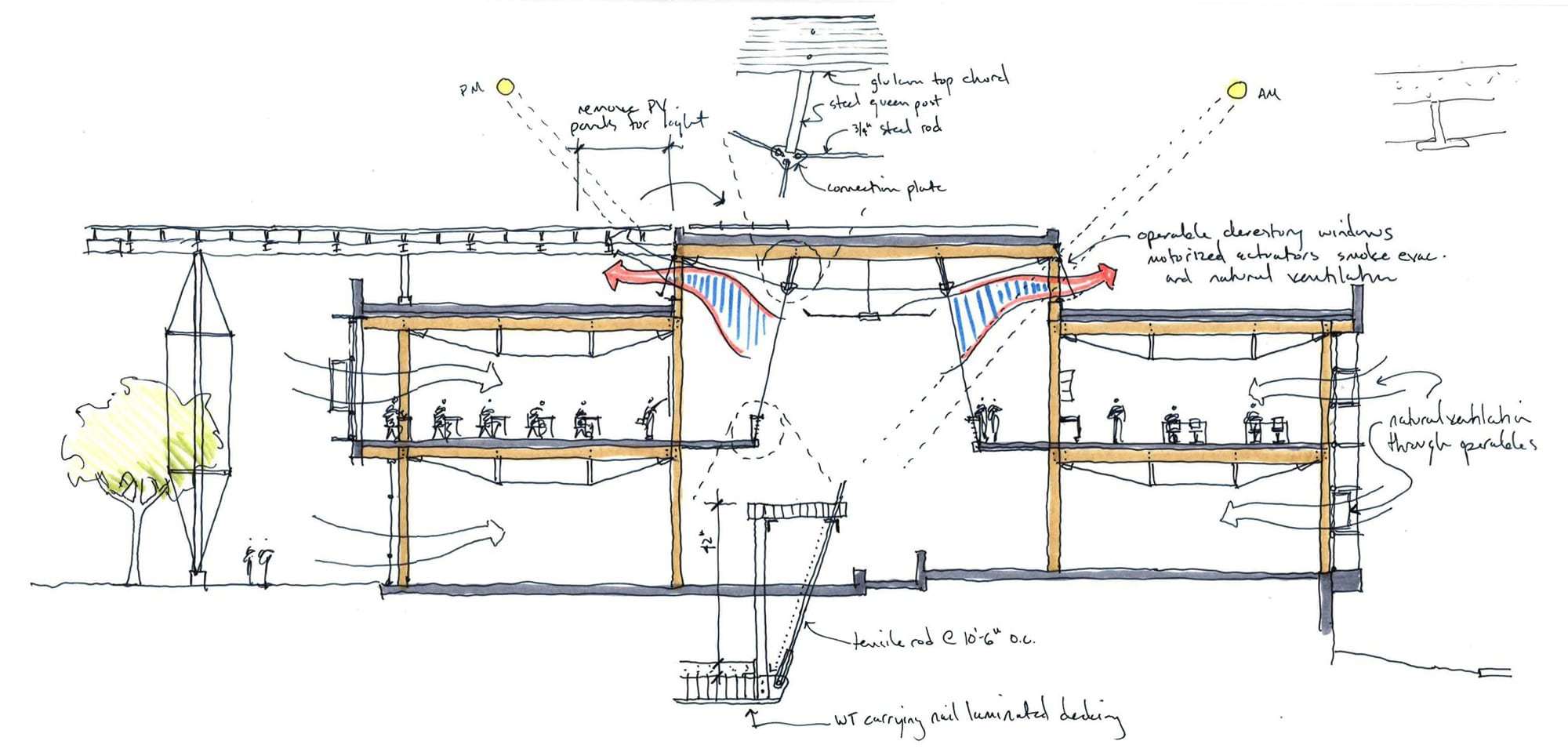 The concept of The Kendeda Building is inspired by the vernacular southern porch. Taking this element and expanding it from the residential to the civic scale, the team imagined a “regenerative porch” that could create a cool microclimate on the surrounding site. The resulting structure invites visitors inside to rest, learn and to look up as they learn about the space around them. Inside, the building continues the concept of learning by example through the design itself. As the team explained, gravity and lateral elements are left exposed creating a visual register of the structural forces at work.
The concept of The Kendeda Building is inspired by the vernacular southern porch. Taking this element and expanding it from the residential to the civic scale, the team imagined a “regenerative porch” that could create a cool microclimate on the surrounding site. The resulting structure invites visitors inside to rest, learn and to look up as they learn about the space around them. Inside, the building continues the concept of learning by example through the design itself. As the team explained, gravity and lateral elements are left exposed creating a visual register of the structural forces at work.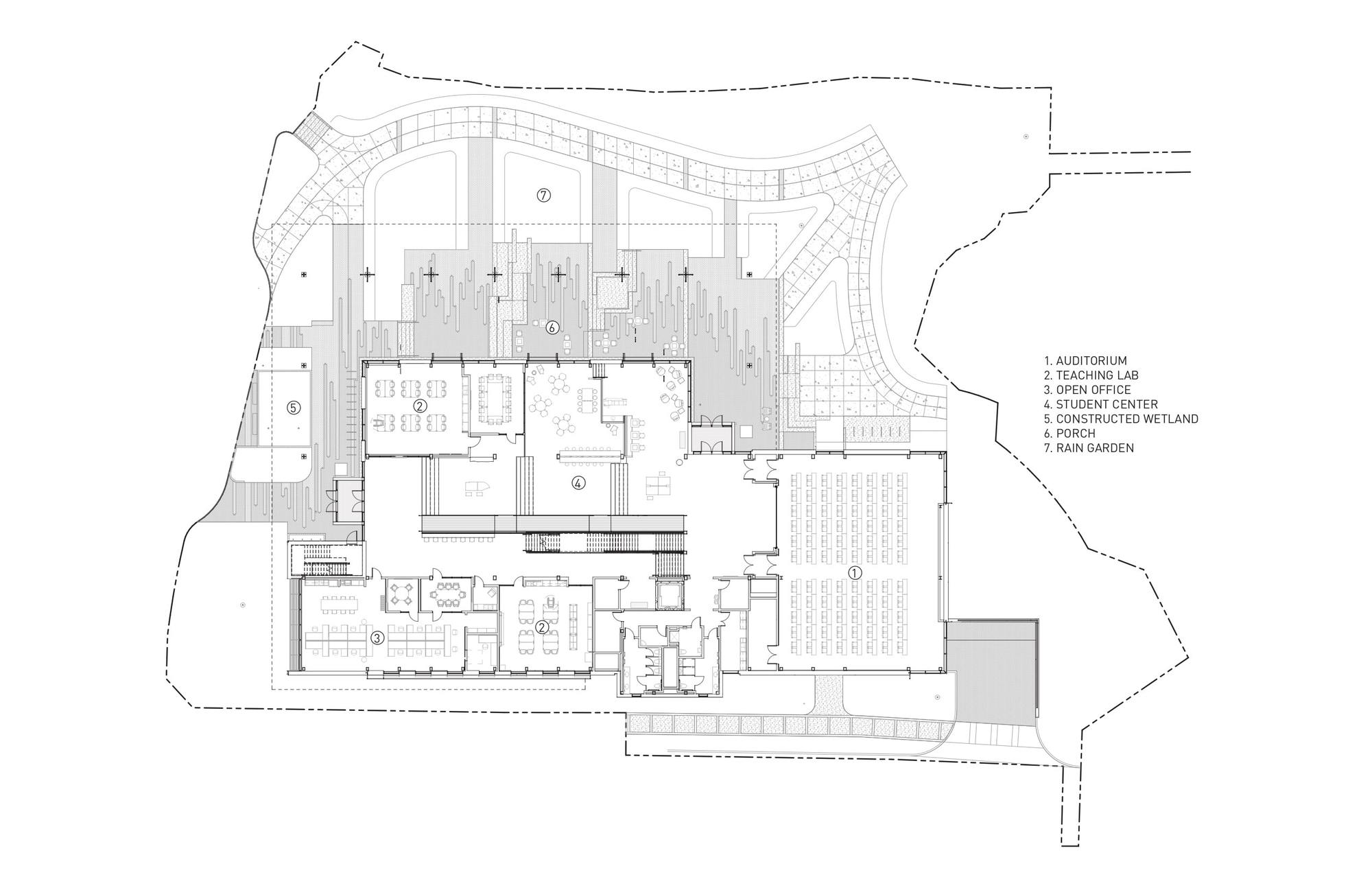
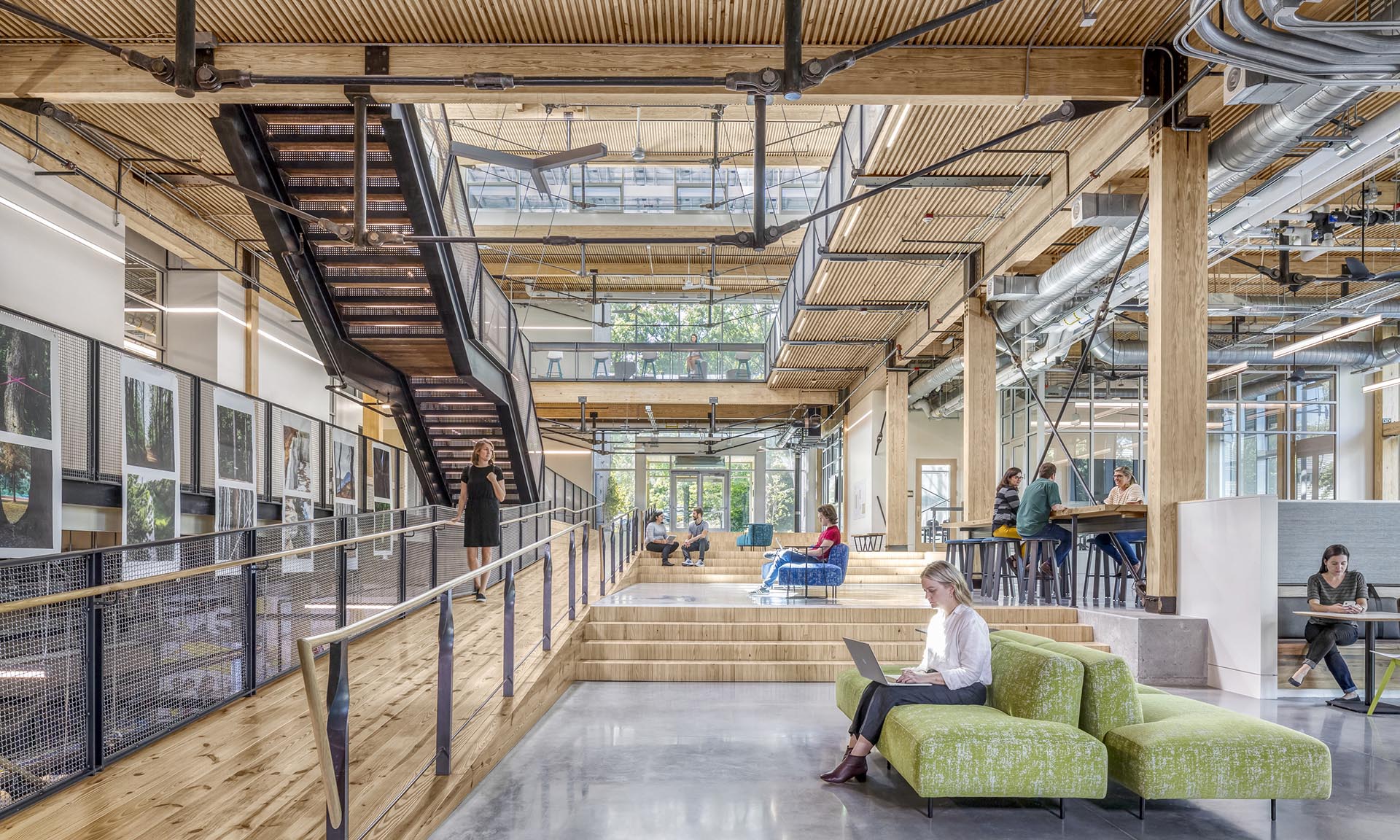 The Kendeda Building hosts a variety of learning spaces to welcome all students and disciplines from campus. Traditional classrooms as well as laboratory space and meeting rooms fill the building. Each space has generous daylighting, operable windows and is free of Red List chemicals. Indoor environmental quality was the primary driver in the design of these spaces to support learning. The Kendeda Building is Georgia Tech’s first timber building since its earliest load bearing masonry and timber structures from the 1880s. Climate smart mass timber was selected for its significantly smaller embodied carbon footprint, compared to concrete and steel systems.
The Kendeda Building hosts a variety of learning spaces to welcome all students and disciplines from campus. Traditional classrooms as well as laboratory space and meeting rooms fill the building. Each space has generous daylighting, operable windows and is free of Red List chemicals. Indoor environmental quality was the primary driver in the design of these spaces to support learning. The Kendeda Building is Georgia Tech’s first timber building since its earliest load bearing masonry and timber structures from the 1880s. Climate smart mass timber was selected for its significantly smaller embodied carbon footprint, compared to concrete and steel systems.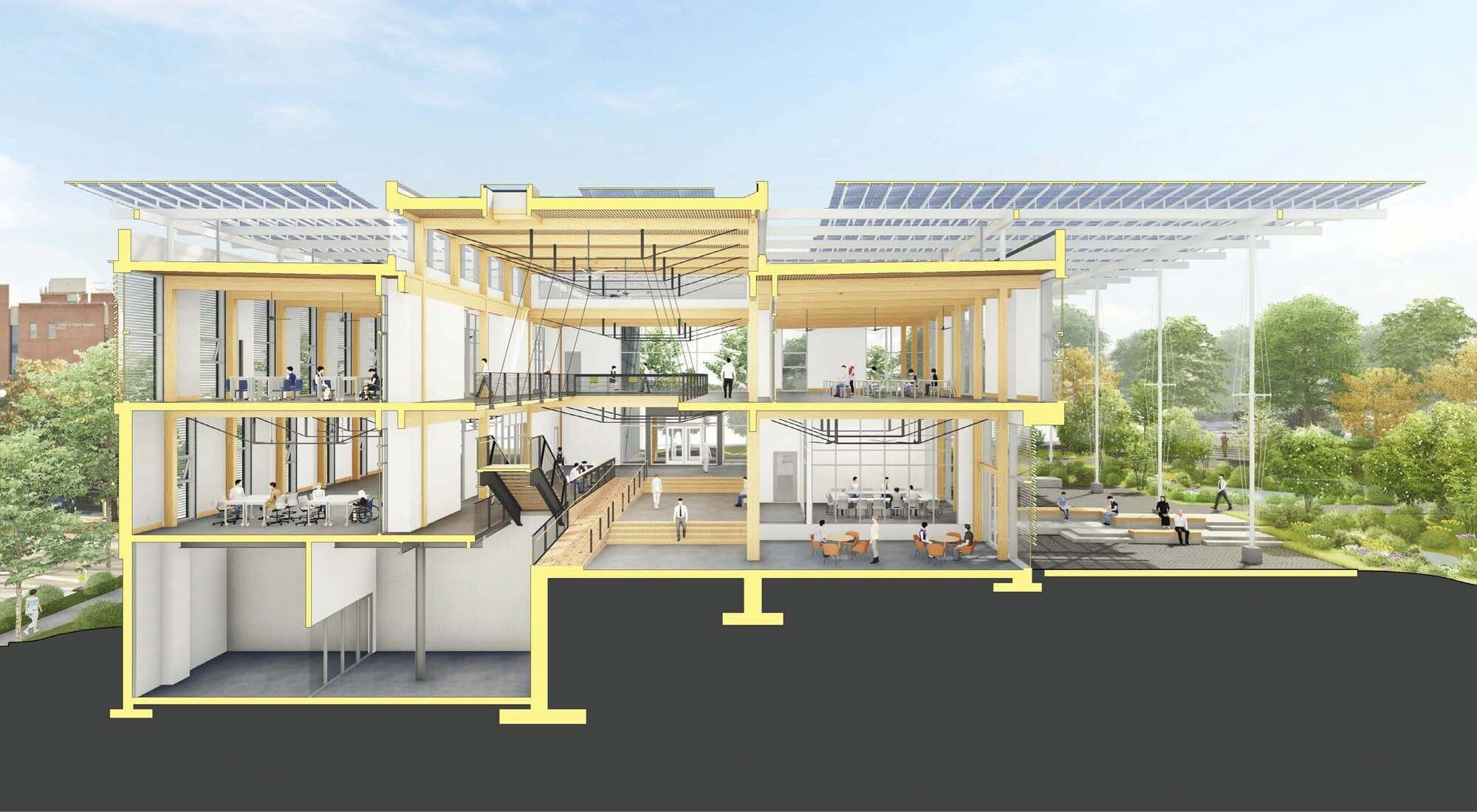
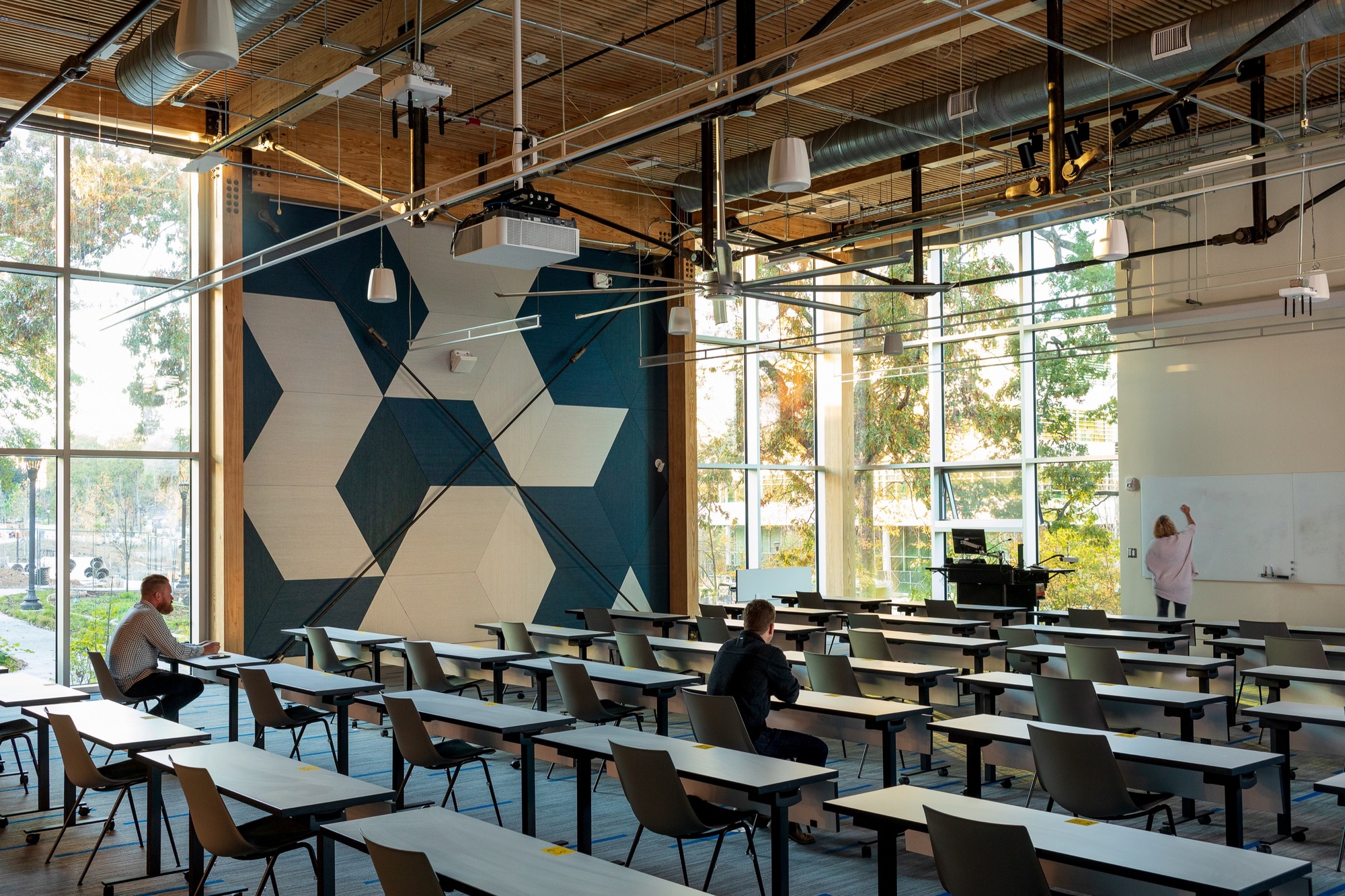 The design of the Kendeda Building demonstrates that ‘Living Buildings’ are possible in even the most demanding climates. The
The design of the Kendeda Building demonstrates that ‘Living Buildings’ are possible in even the most demanding climates. The 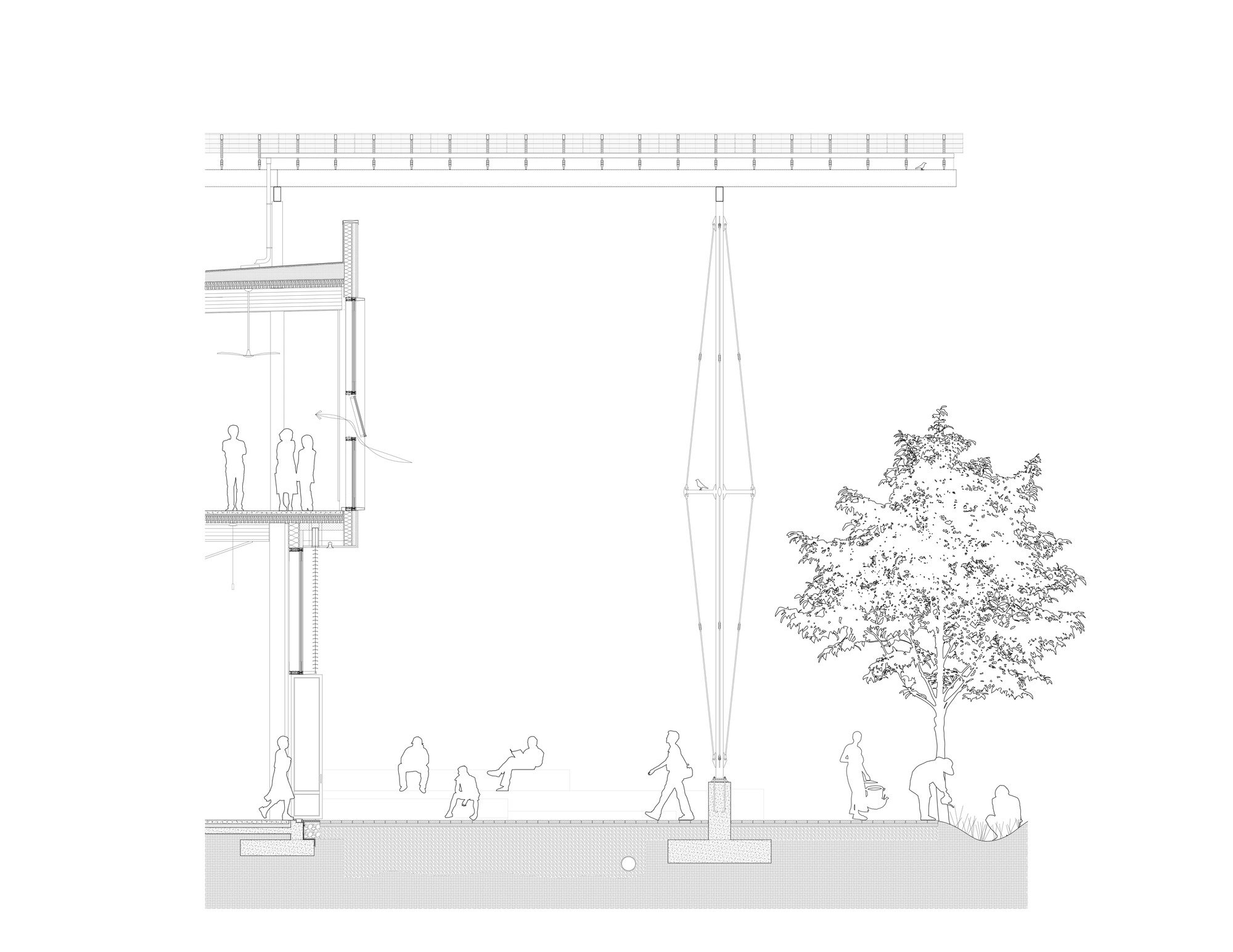 Yet, the project achieved full Living Building Certification in 2021 after proving its net positive energy and water performance during its year-long occupancy period. At the heart of this was the “Regenerative Porch” — a structural system and PV canopy that generates more than 100% of the building’s energy demand and captures enough rainwater to meet 100% of the water used in the building. At the same time, the design blurs interior and exterior conditions while providing weather-protected outdoor classroom space. As the first Living Building of its kind in the Southeast US, the project set a new standard for design.
Yet, the project achieved full Living Building Certification in 2021 after proving its net positive energy and water performance during its year-long occupancy period. At the heart of this was the “Regenerative Porch” — a structural system and PV canopy that generates more than 100% of the building’s energy demand and captures enough rainwater to meet 100% of the water used in the building. At the same time, the design blurs interior and exterior conditions while providing weather-protected outdoor classroom space. As the first Living Building of its kind in the Southeast US, the project set a new standard for design.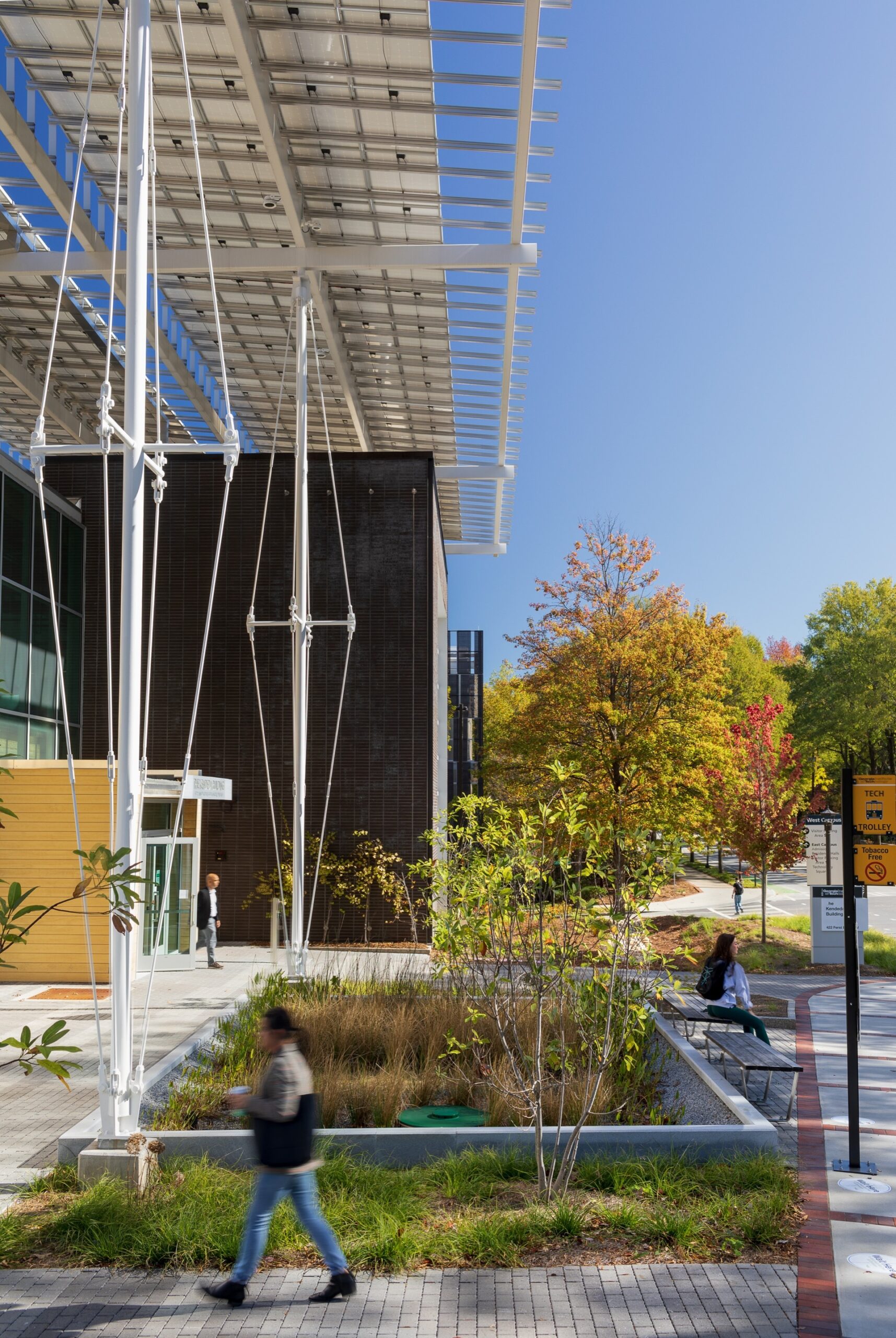
 The Kendeda Fund provided ongoing funding to support programs in the building that engage local Atlanta communities beyond the university. The atrium, lecture hall, roof garden, and multipurpose room were all designed to be made available for community events. As the team outlined, Georgia Tech’s mission is to maximize the impact of the building by exposing as many students as possible to the project. After learning in a building expressing such a strong position on resiliency and sustainability, the hope is that they will take those values with them into the future.
The Kendeda Fund provided ongoing funding to support programs in the building that engage local Atlanta communities beyond the university. The atrium, lecture hall, roof garden, and multipurpose room were all designed to be made available for community events. As the team outlined, Georgia Tech’s mission is to maximize the impact of the building by exposing as many students as possible to the project. After learning in a building expressing such a strong position on resiliency and sustainability, the hope is that they will take those values with them into the future.
 To this end, we are thrilled to announce the launch of Architizer’s Tech Directory, a database of tech tools that benefit all those involved in architecture, from concept to construction.
To this end, we are thrilled to announce the launch of Architizer’s Tech Directory, a database of tech tools that benefit all those involved in architecture, from concept to construction.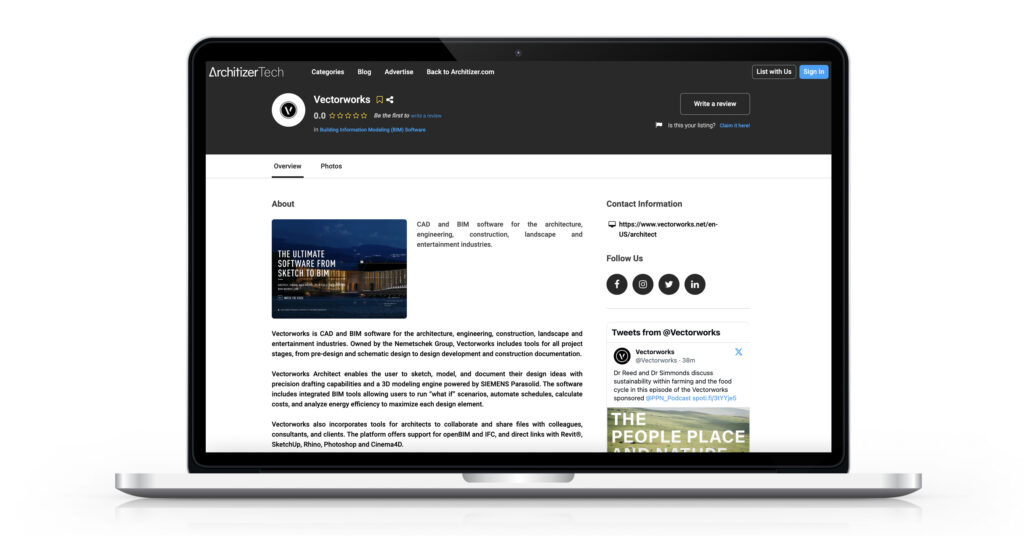
 We hope you enjoy exploring the Tech Directory and find it useful when doing your research into the latest architectural technology. As noted, this is just the beginning: We plan to develop this platform into a comprehensive directory that will benefit everyone in the construction industry.
We hope you enjoy exploring the Tech Directory and find it useful when doing your research into the latest architectural technology. As noted, this is just the beginning: We plan to develop this platform into a comprehensive directory that will benefit everyone in the construction industry.
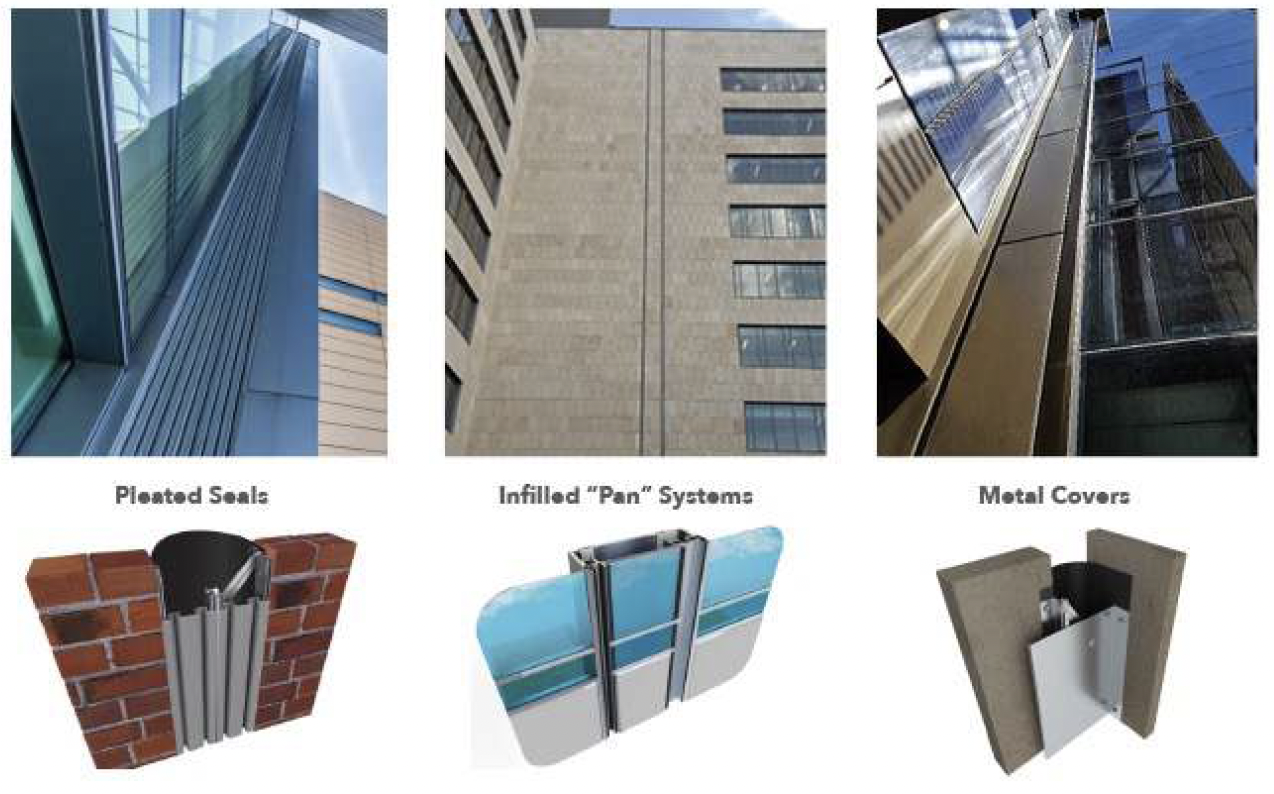



 In the webinar, Ryan thoroughly explored the ins and outs of wall protection — from materials and installations to key decision-making processes, highlighting the main challenges architects often face.
In the webinar, Ryan thoroughly explored the ins and outs of wall protection — from materials and installations to key decision-making processes, highlighting the main challenges architects often face. The presentation offers deep insights, real-world examples and straightforward guidance, making it a must-watch for every architect and builder. Dive in to strengthen your designs and focus on lasting interiors.
The presentation offers deep insights, real-world examples and straightforward guidance, making it a must-watch for every architect and builder. Dive in to strengthen your designs and focus on lasting interiors.







