Augmented Drawing: Redefining Sketching for the Digital Age
Calling all architects to join the conversation! Rate and review your favorite design softwares and hardwares on Architizer’s Tech Directory, a new library of tech tools for designers.
“Imagine if you could see your ideas materialize in a matter of seconds, onsite and without waiting for construction to be finalized to evaluate and experience your design.”
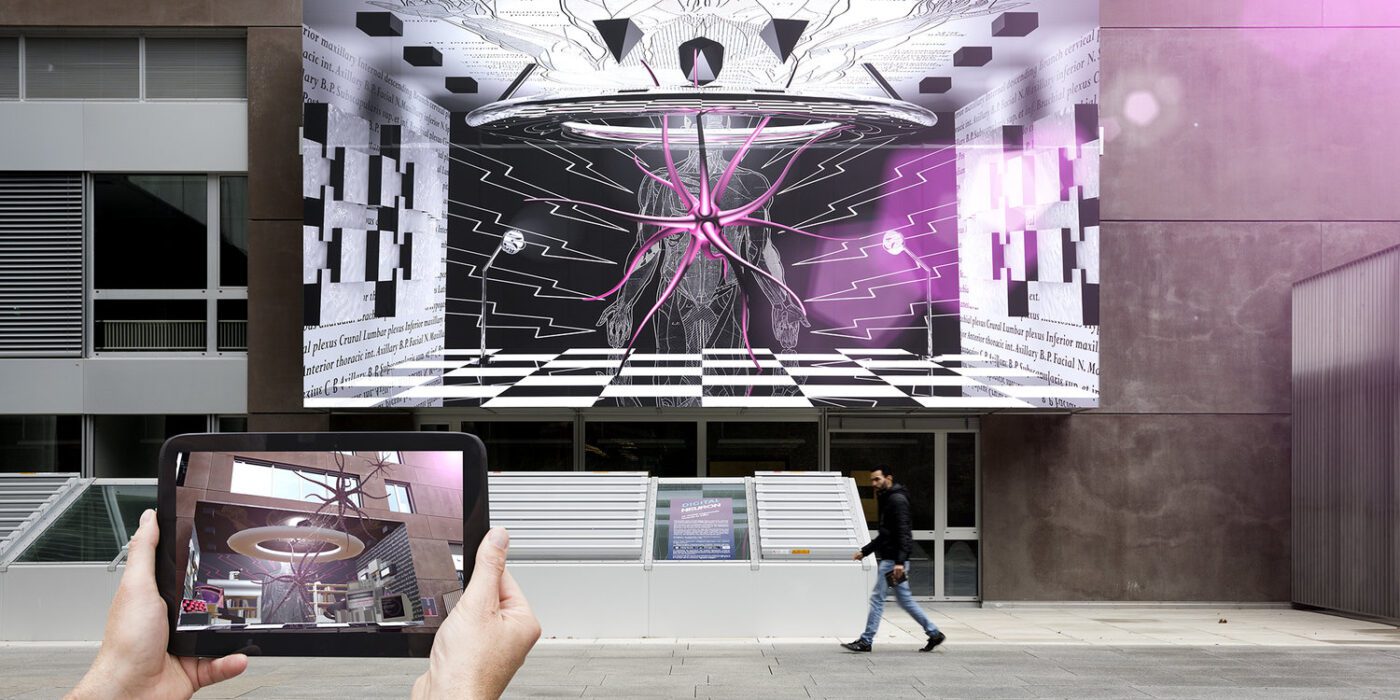
Augmented drawing involves overlaying digital content onto the physical world through the lens of augmented reality. This process smoothly integrates digital elements, such as 3D models, animations or interactive effects, into real-world environments. Unlike traditional drawing methods confined to paper or canvas, augmented drawing liberates architects and designers from spatial limitations, enabling them to interact with their creations dynamically.
One of its most exciting aspects of augmented drawing is its interactive nature. Unlike static sketches on paper, augmented drawings can come to life through animations, sound effects and interactive elements. Architects can create dynamic compositions that respond to user input or change over time, transforming passive viewers into active participants. This level of interactivity adds a new layer of engagement and immersion to the creative process, captivating audiences in ways that traditional sketches cannot. By overlaying digital models onto physical environments in real-time, architects can explore spatial relationships, evaluate design proposals and visualize concepts with unprecedented clarity.
Admittedly, Augmenter Reality’s (AR) most groundbreaking quality is its ability to connect each specific architectural design with its site context. Consequently, augmented drawing offers architects a powerful toolkit for site analysis and contextual integration, enabling them to overlay digital models onto real-world environments to assess factors such as sunlight exposure, topography and surrounding architecture. By contextualizing designs within their physical surroundings, architects can ensure that their proposals harmonize with existing landscapes and urban contexts, enhancing the overall sustainability and livability of built environments.
Explore Architizer’s Tech Directory
Augmented drawings also facilitate collaboration among stakeholders throughout the design and construction phases. By creating shared virtual environments, architects, clients, engineers and contractors can collectively visualize and interact with design proposals, fostering consensus and alignment on project objectives. It also provides intuitive tools for marking, highlighting and annotating design elements within the augmented environment. This visual communication not only promotes clarity but also reduces the potential for misinterpretation, leading to more efficient decision-making and smoother project workflows during construction.
Still, apart from these more “obvious” applications of AR, there have been numerous innovative projects where augmented drawings are used to access environments and spaces, which so far have been out of reach. One example is CapitolaVR’s Rembrant Reality App in Mauritshuis museum, which allows visitors to literally enter Rembrandt van Rijn’s painting The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp.
The painting’s virtual environment was made through 3D scanning techniques and actors, who posed as the subjects of the painting, creating a portal to a past, fictional setting. This revolutionary merging of art and technology suggests countless possibilities for architects and uncovers ways of accessing, experiencing and even redesigning spaces that were not only physically but also conceptually perceived.
Several tools and platforms have emerged to facilitate augmented drawing experiences. Techniques for augmented drawing vary depending on the desired outcome and the chosen platform. Architects may begin by sketching outlines on paper before overlaying digital elements using AR-enabled devices. Alternatively, they can directly draw within AR environments, leveraging tools like gesture recognition and spatial tracking to refine their compositions with precision. The one thing that remains constant, however, is that augmented drawing not only expands the possibilities of artistic expression but also transforms the creative process itself.
By bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds, AR fosters a symbiotic relationship between the artist and their creation, blurring the lines between creator and spectator. It also democratizes creativity by lowering barriers to entry and fostering inclusivity. With accessible tools and intuitive interfaces, individuals from diverse backgrounds can engage in the artistic process, transcending traditional skill barriers to unleash their creative potential.
Since the beginning of the profession, sketching has been the most freeing tool for architectural drawing. It translates ideas, concepts and intentions to lines, textures and experiences, becoming the mediator between inception and reality. Ironically, augmented drawing blurs these boundaries even more. Its constant improvement on producing accurate spatial mappings and high-resolution augmented overlays leads to the creation of countless highly realistic augmented environments, which become backdrops for pioneering architectural designs, architectural conservation practices and real-time assembly processes.
Calling all architects to join the conversation! Rate and review your favorite design softwares and hardwares on Architizer’s Tech Directory, a new library of tech tools for designers.
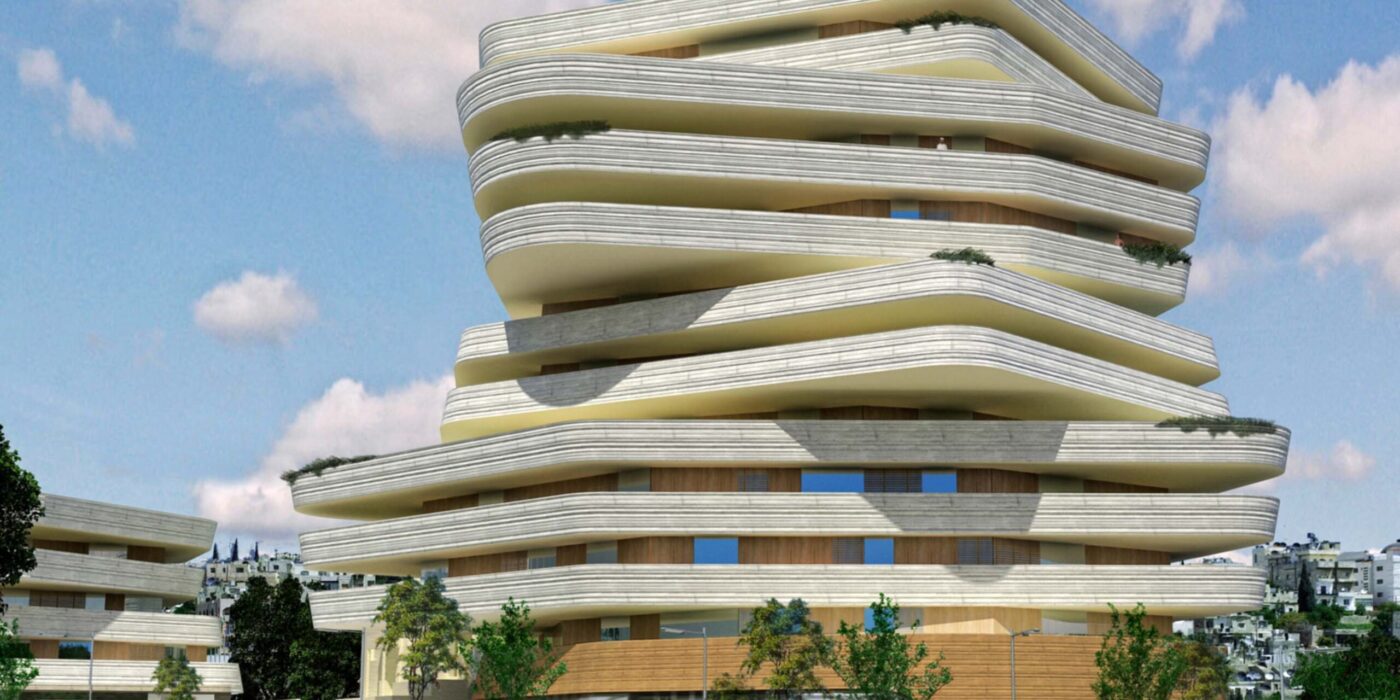
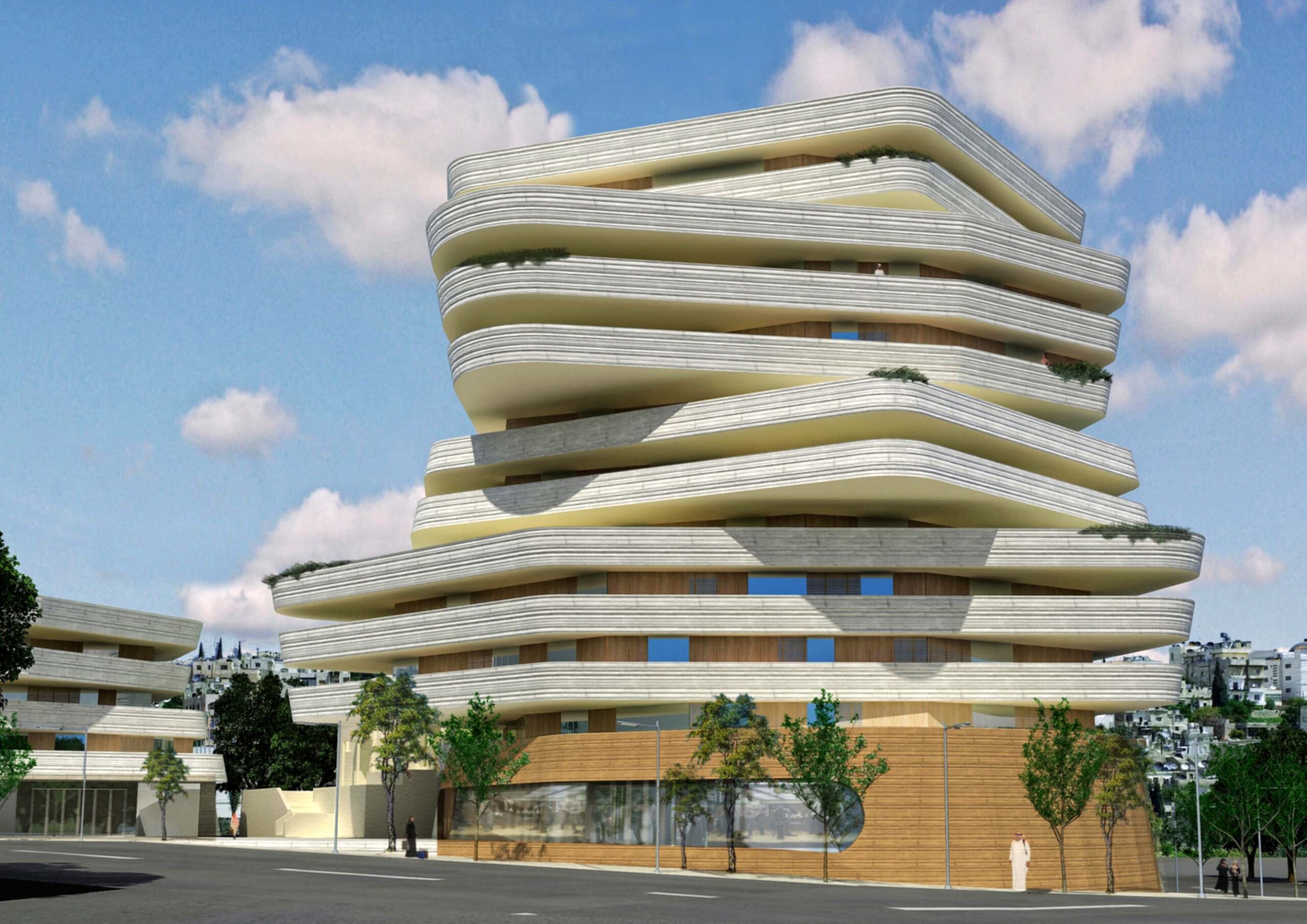
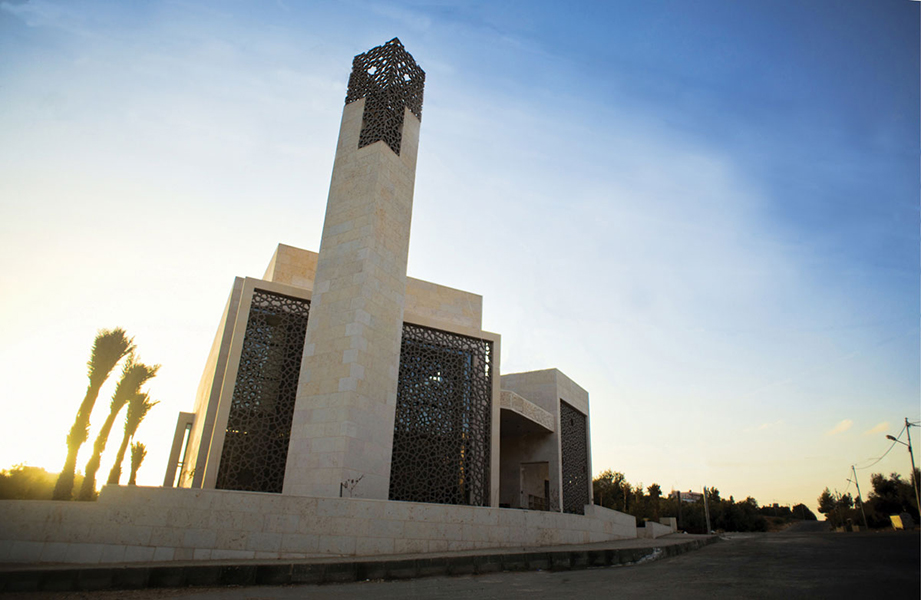
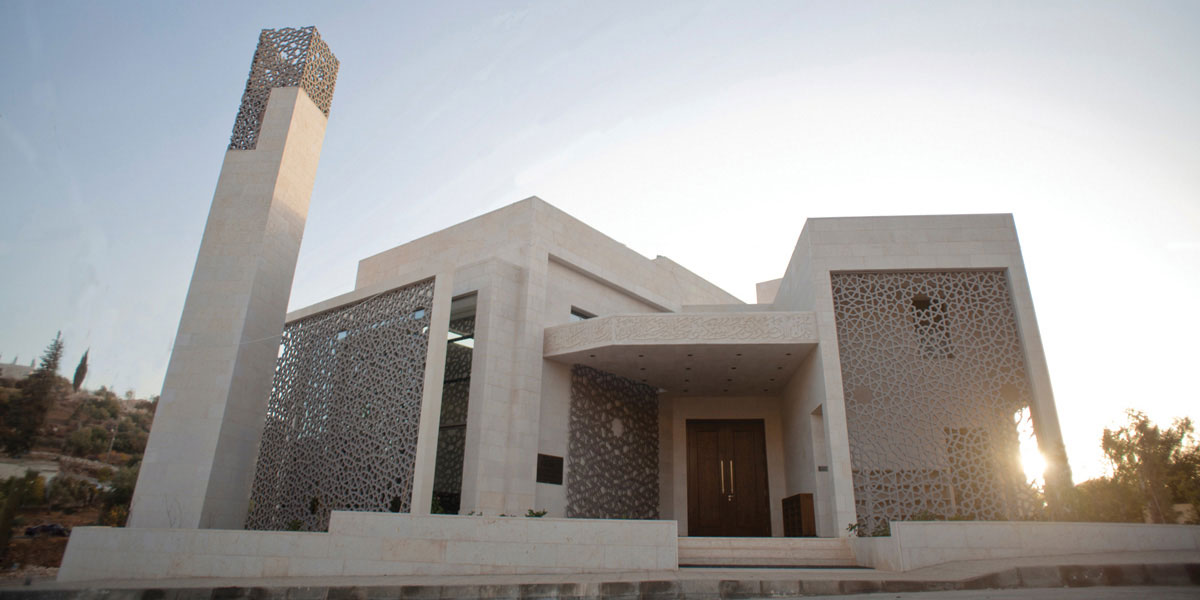










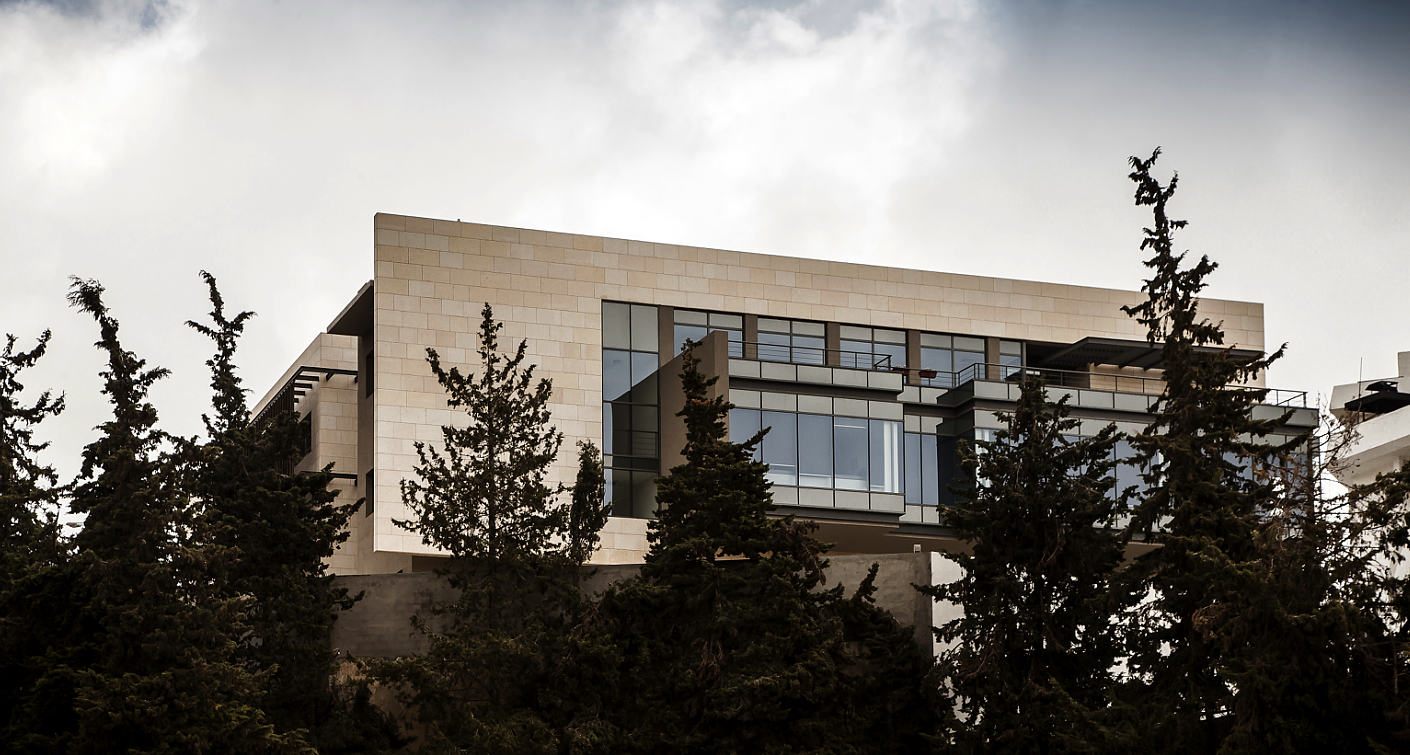
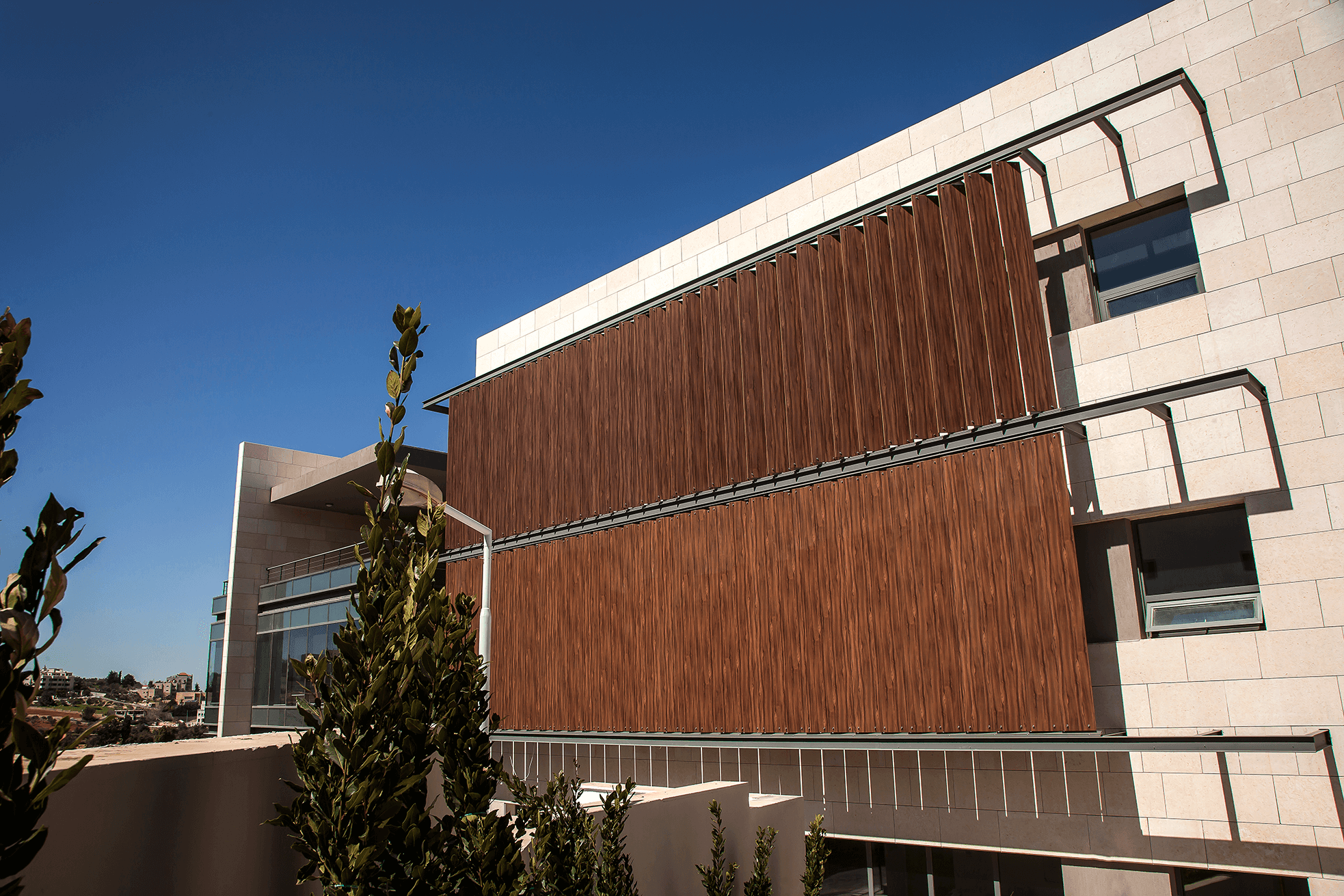
 How can the design of a mosque become more contemporary and reflective of its time? That was the question that guided the local designing team of Al Rawada Mosque in Amman, who worked together to create what they described as the first contemporary mosque in Amman.
How can the design of a mosque become more contemporary and reflective of its time? That was the question that guided the local designing team of Al Rawada Mosque in Amman, who worked together to create what they described as the first contemporary mosque in Amman.

 Through the design of this school, the designing team proved that less is more. Consisting of simple rectilinear forms, the design of the school depended on the use of strong horizontal and vertical lines that produced the building’s geometry and guided the process of designing the openings.
Through the design of this school, the designing team proved that less is more. Consisting of simple rectilinear forms, the design of the school depended on the use of strong horizontal and vertical lines that produced the building’s geometry and guided the process of designing the openings.
 The designing team of Farah General Hospital understood the healing powers of nature, and for those reasons, designed a hospital that was in conversation with its environment, utilizing green strategies that maximized patient comfort and care. The design of the building also made use of advanced medical technologies that helped serve the patients, while also allowing the building to enhance its environmental efficiency and performance.
The designing team of Farah General Hospital understood the healing powers of nature, and for those reasons, designed a hospital that was in conversation with its environment, utilizing green strategies that maximized patient comfort and care. The design of the building also made use of advanced medical technologies that helped serve the patients, while also allowing the building to enhance its environmental efficiency and performance.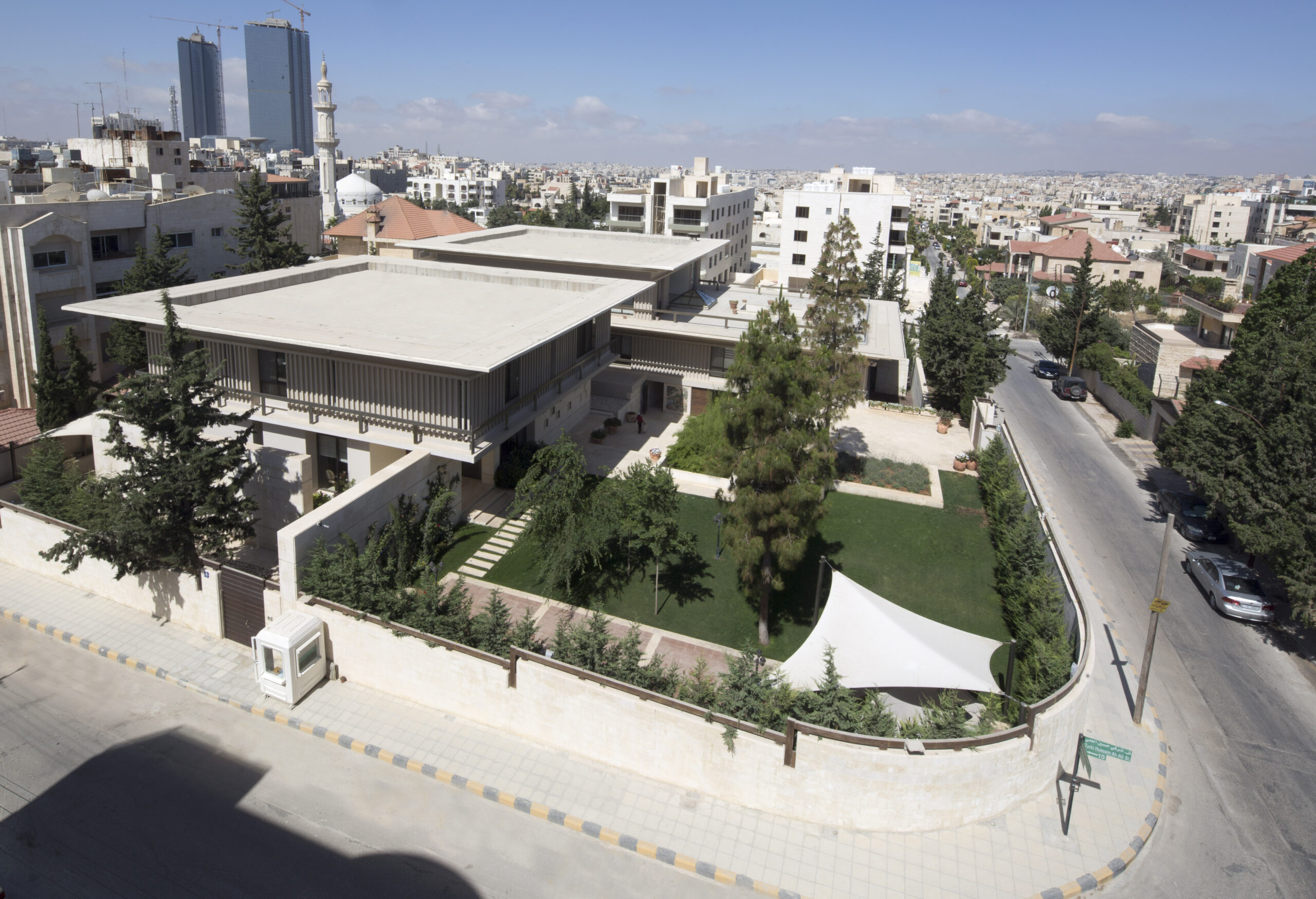
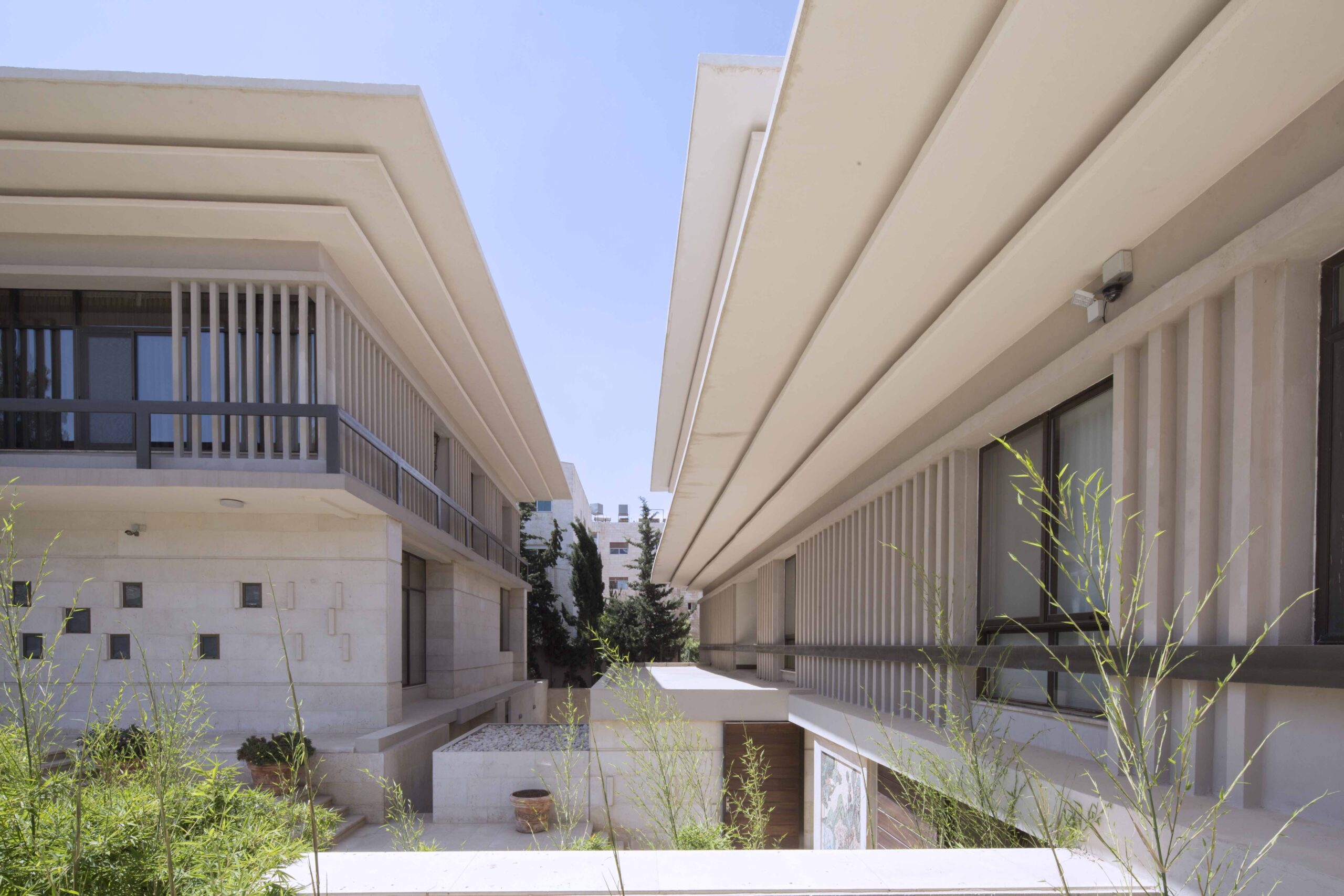 Within the walls of this complex sits the Visa Center for the Republic of China-Taiwan, the ambassador residence and a public garden. Through an intricate yet dynamic design, the local design office managed to organize the space in a manner that ensured the needed privacy for the embassy and ambassador residence, while also opening up the space for the public to enjoy the garden and access the visa center. The architecture of the buildings also aimed to celebrate the Taiwanese and Jordanian culture, and present a space that merged notions and values of both nations.
Within the walls of this complex sits the Visa Center for the Republic of China-Taiwan, the ambassador residence and a public garden. Through an intricate yet dynamic design, the local design office managed to organize the space in a manner that ensured the needed privacy for the embassy and ambassador residence, while also opening up the space for the public to enjoy the garden and access the visa center. The architecture of the buildings also aimed to celebrate the Taiwanese and Jordanian culture, and present a space that merged notions and values of both nations.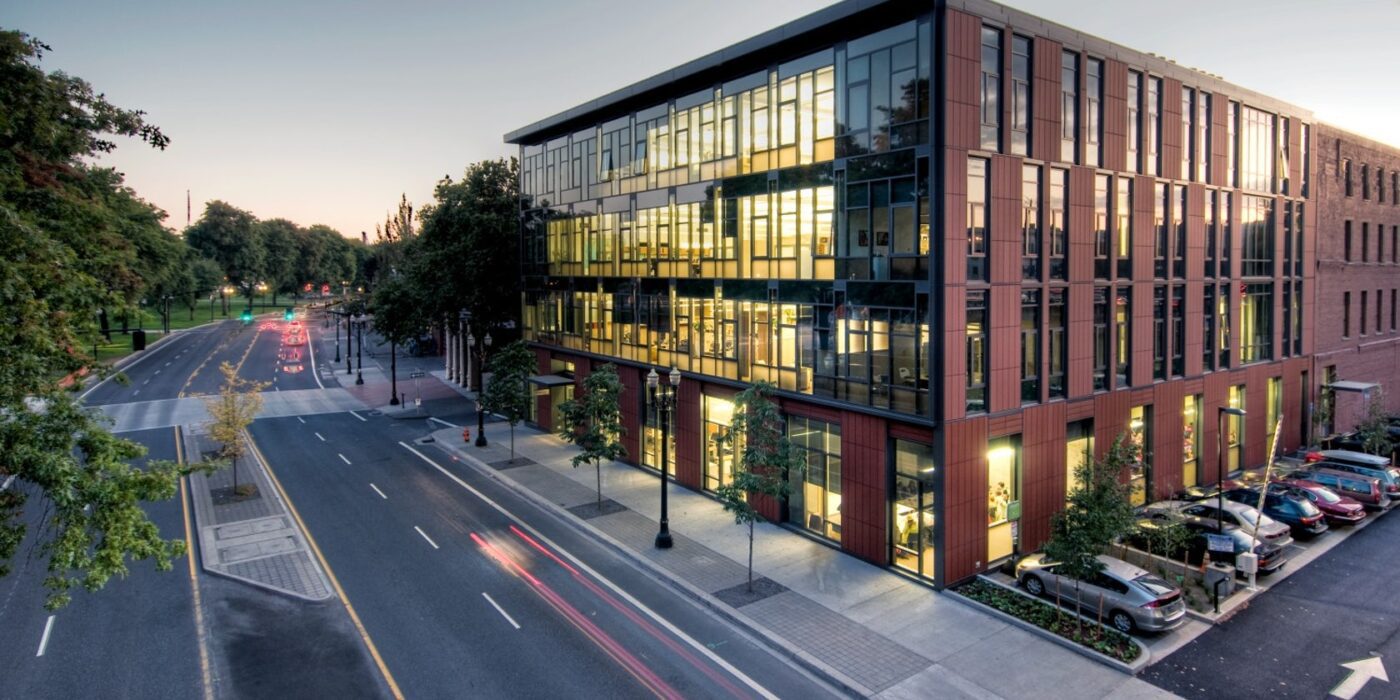
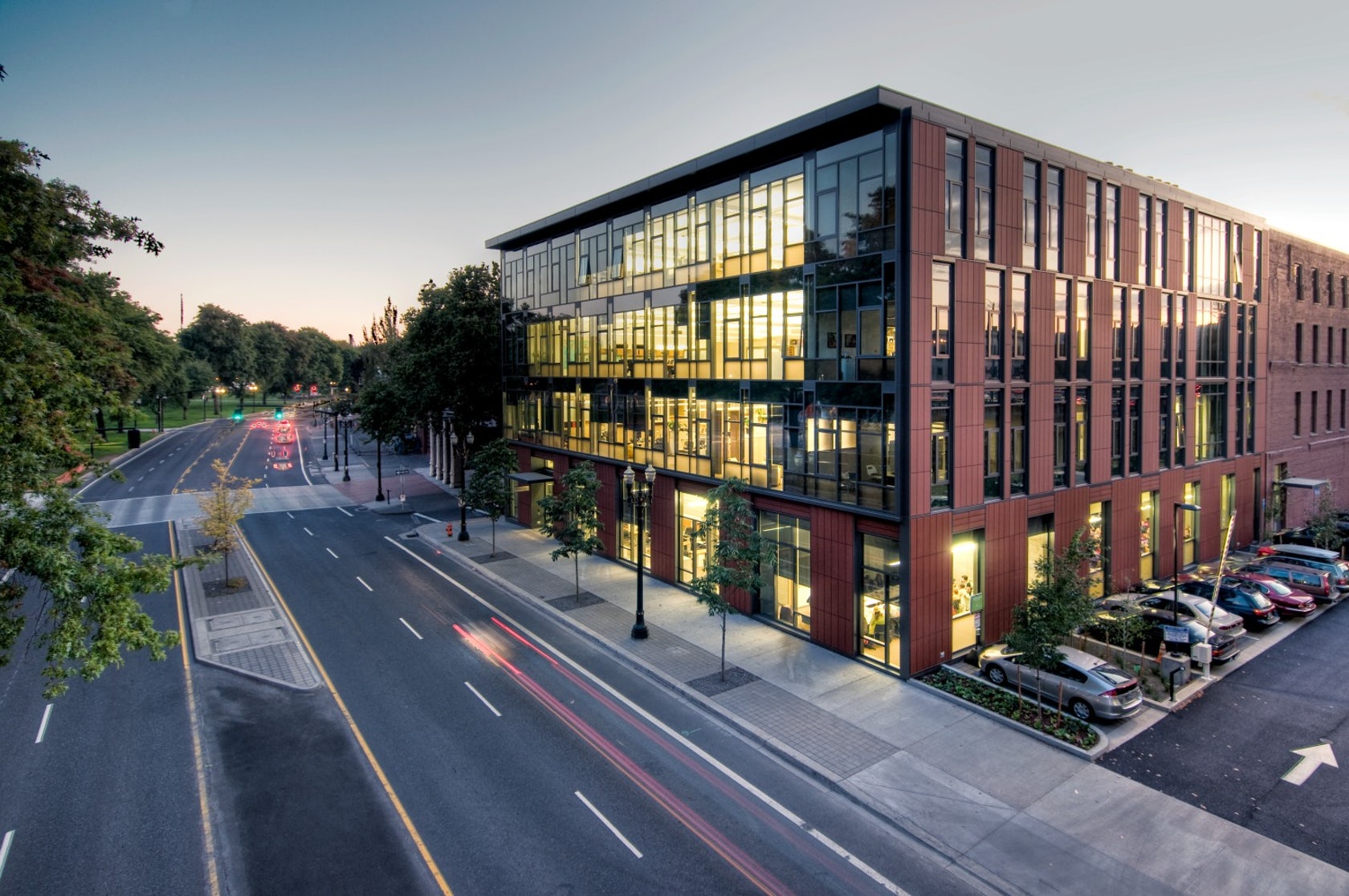
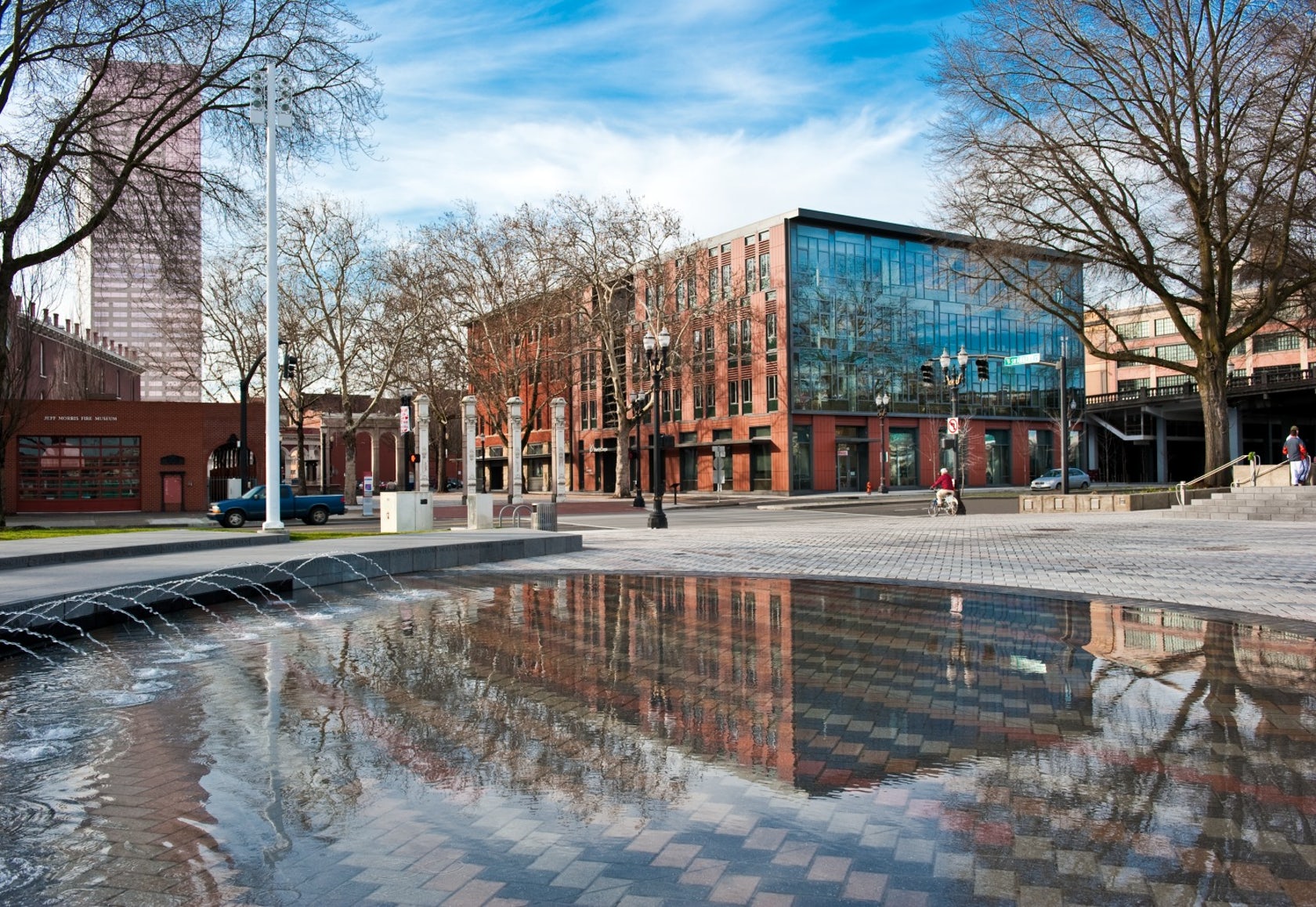
 Designed to teach and encourage visitors to engage with contemporary issues, the Mercy Corps building was built to exemplify a sustainable, community-focused approach. Doubling the size of the historic Portland Packer-Scott Building, the landmark project combined a green roof, with resource-friendly landscaping and a glass and terracotta envelope.
Designed to teach and encourage visitors to engage with contemporary issues, the Mercy Corps building was built to exemplify a sustainable, community-focused approach. Doubling the size of the historic Portland Packer-Scott Building, the landmark project combined a green roof, with resource-friendly landscaping and a glass and terracotta envelope.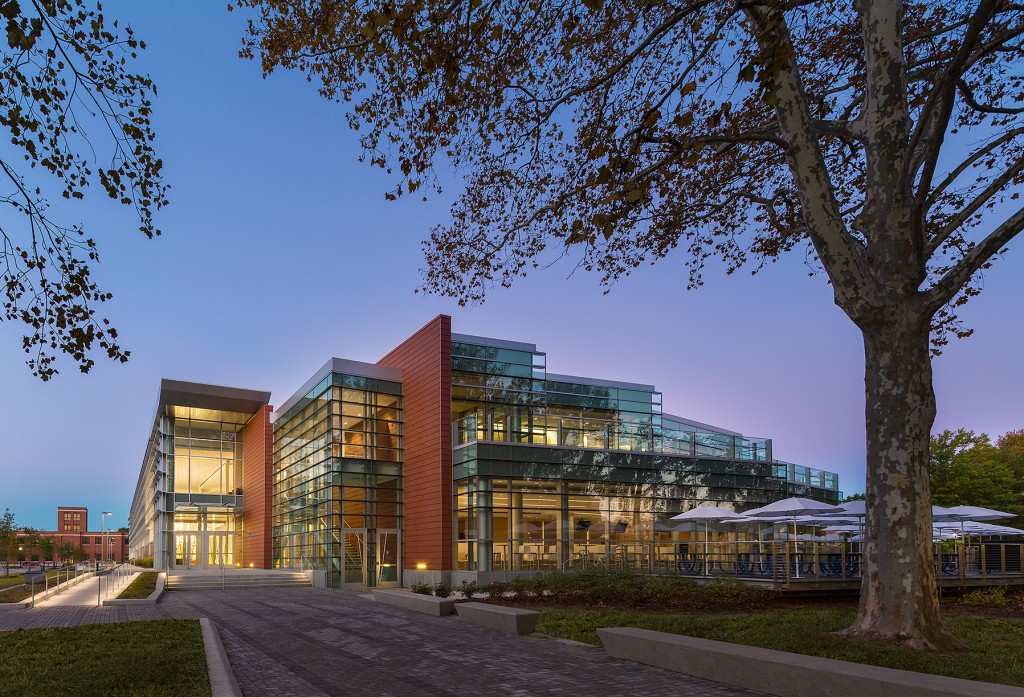
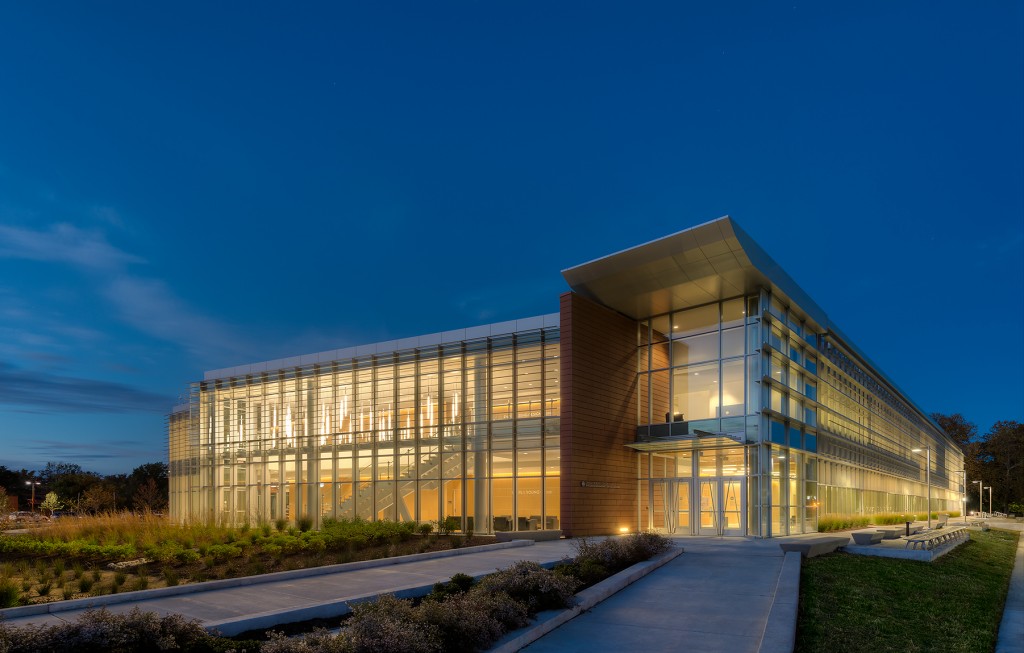
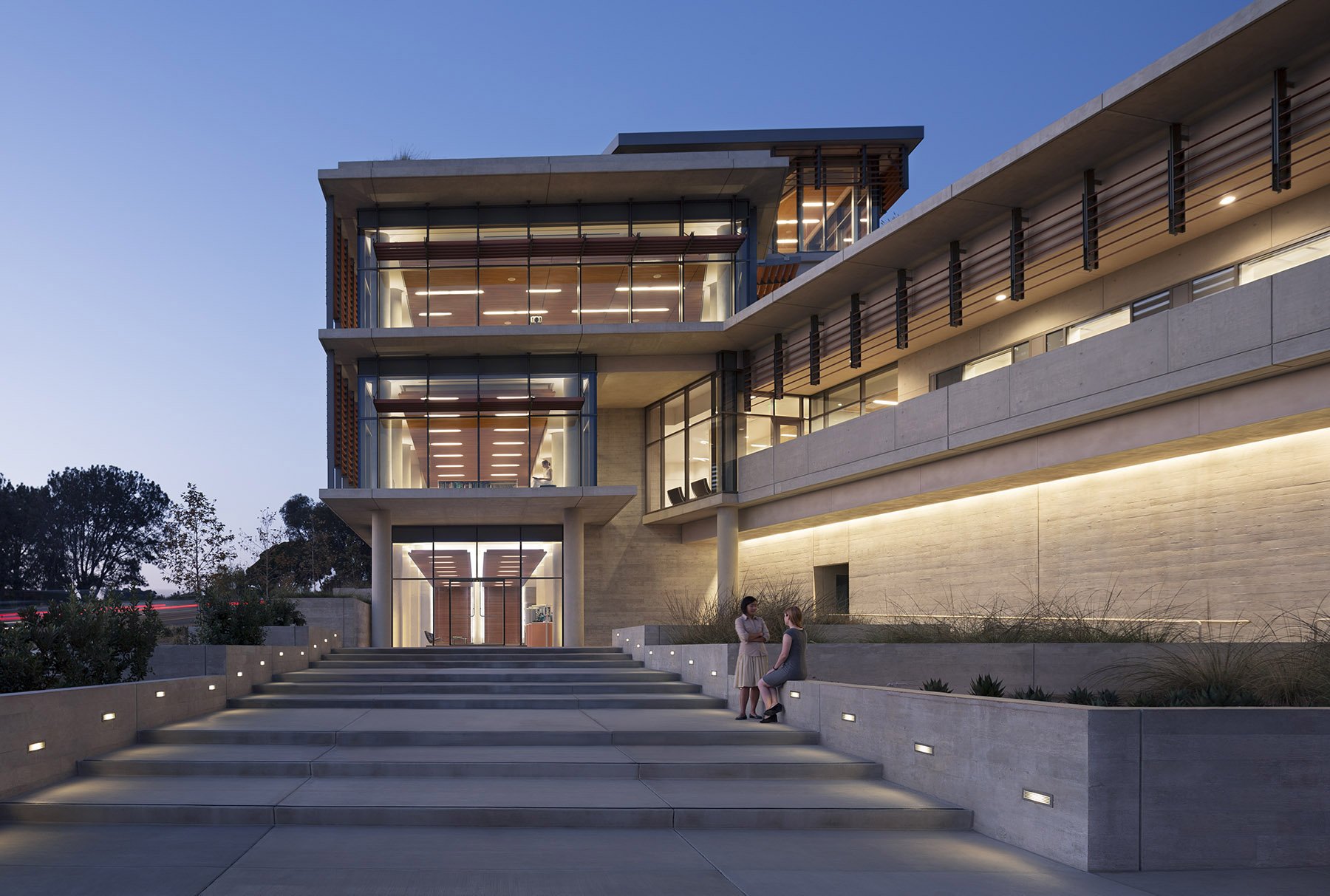
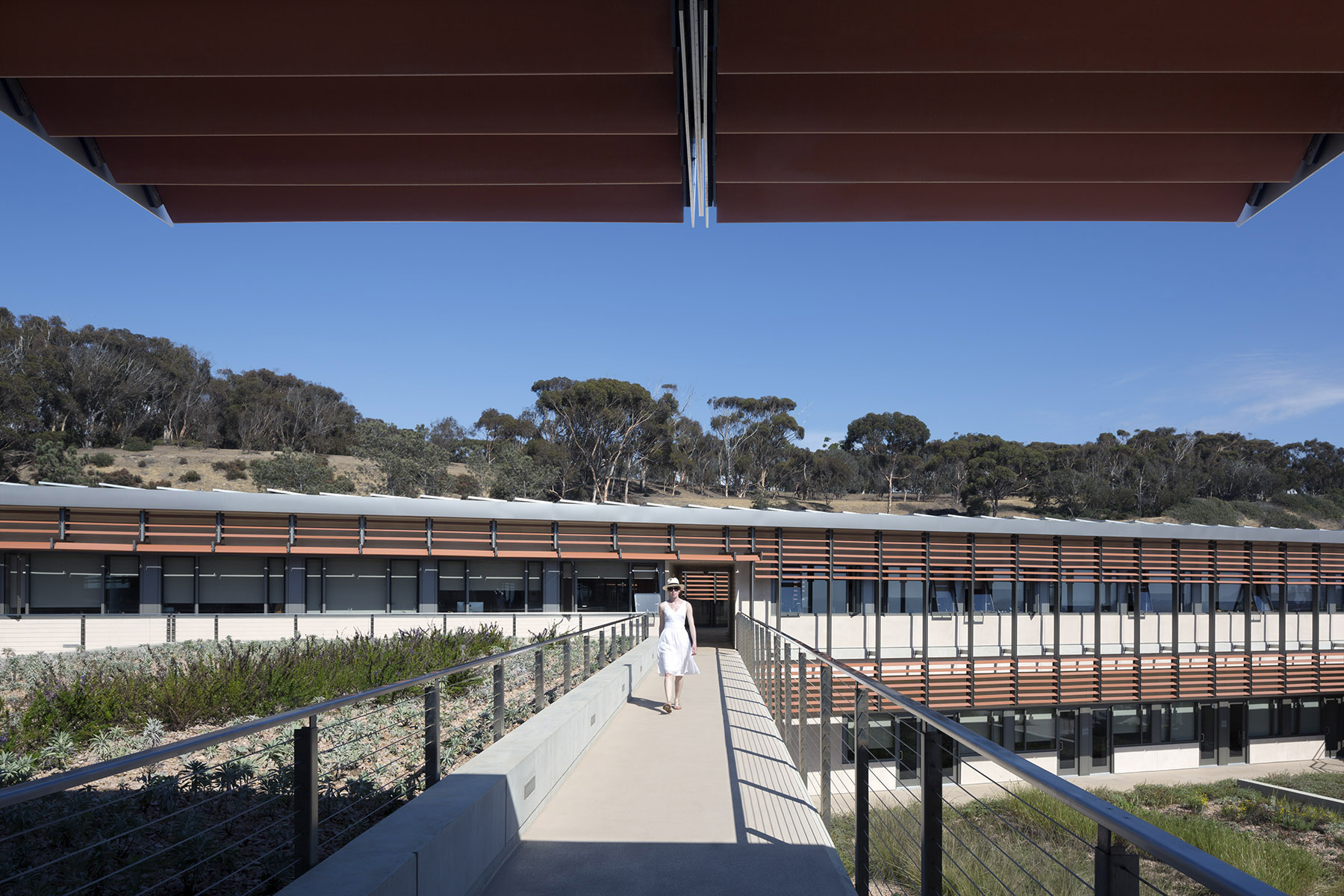

 For the design of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)’s Southwest Fisheries building, the team partnered with the University of California San Diego to design a facility that would pay homage to a world-class site and create a sustainable building for environmental stewards of the ocean.
For the design of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)’s Southwest Fisheries building, the team partnered with the University of California San Diego to design a facility that would pay homage to a world-class site and create a sustainable building for environmental stewards of the ocean.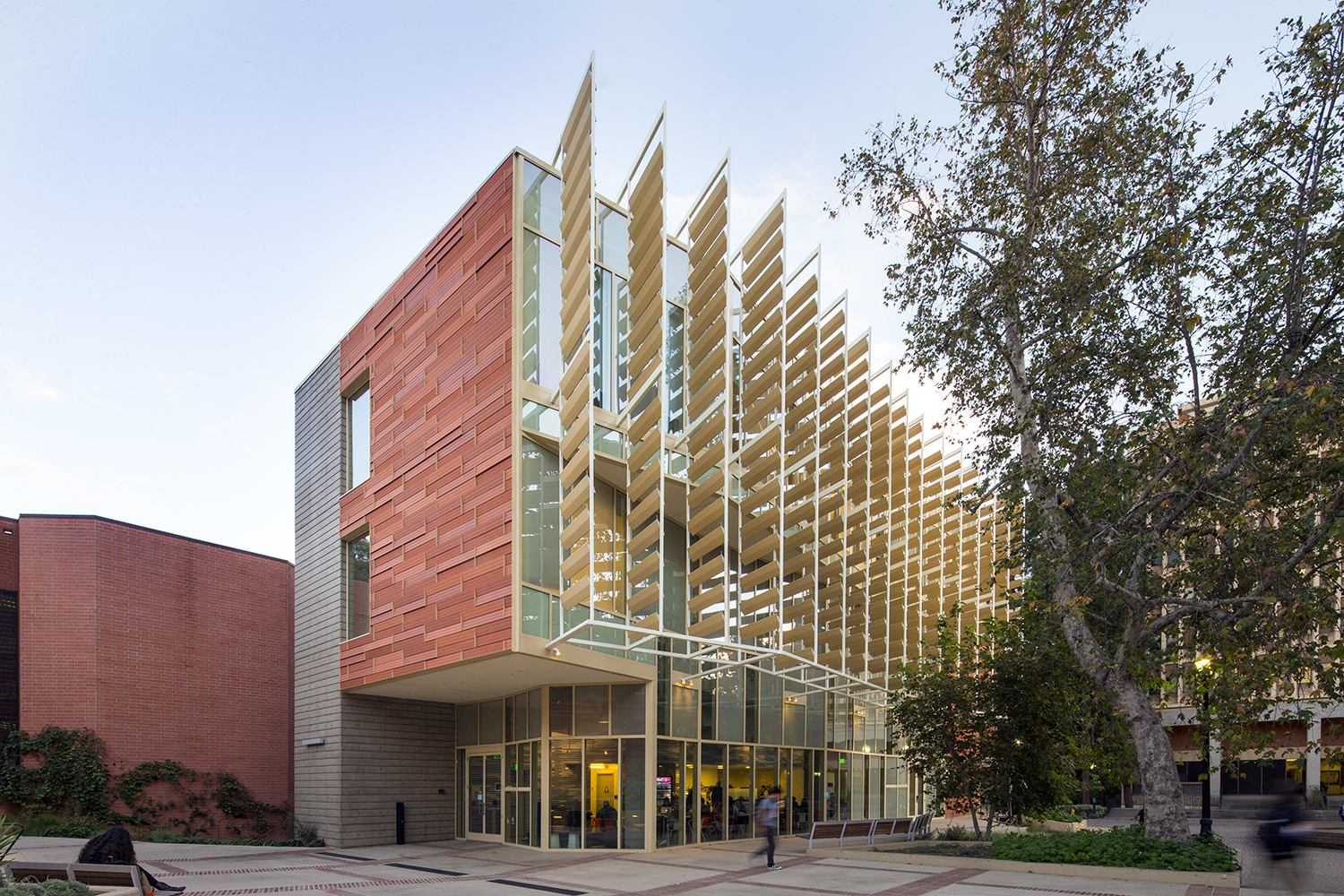
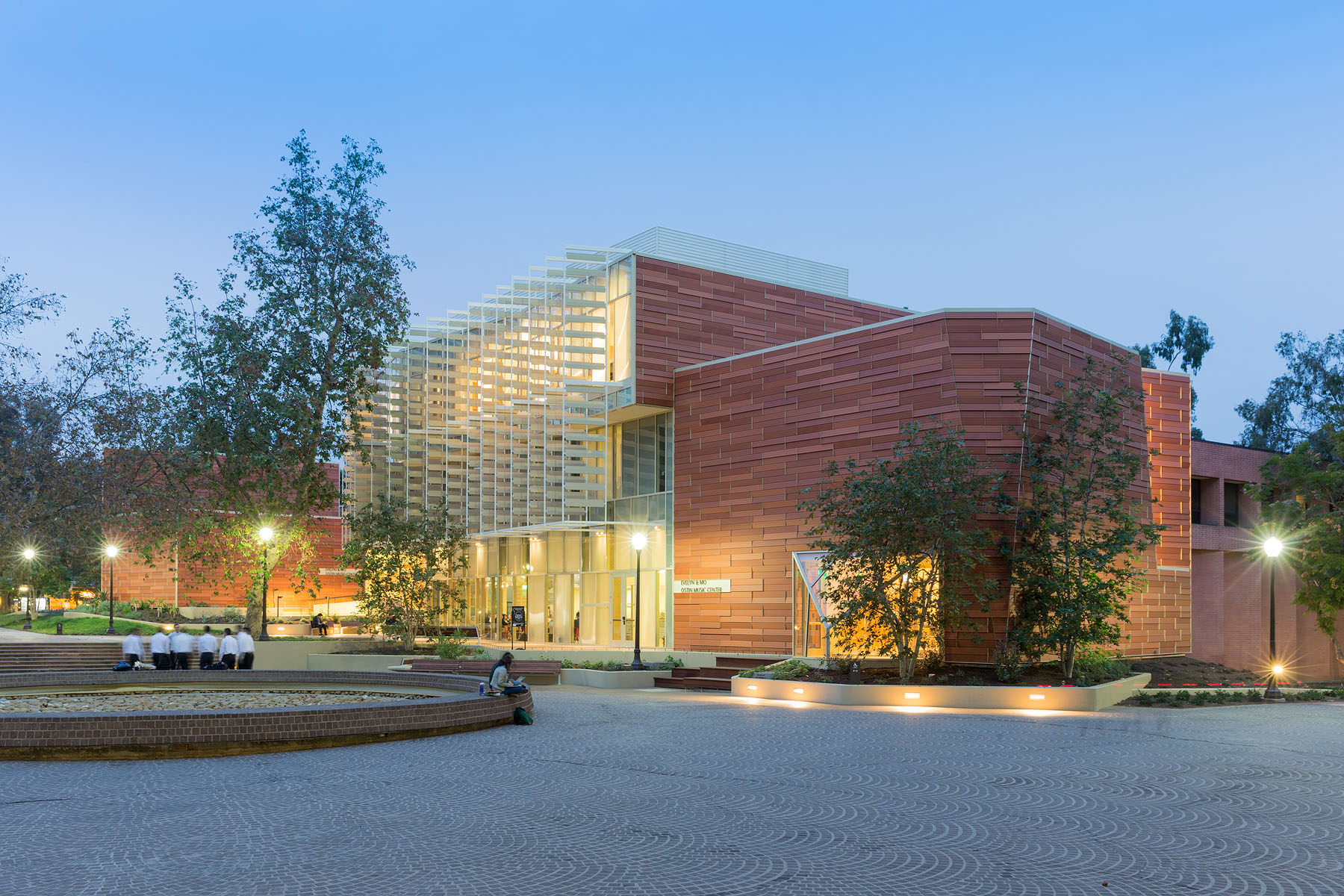 For this music center in Los Angeles ,the project includes a high-tech recording studio, spaces for rehearsal and teaching, a café and social space for students, and an Internet-based music production center. Music industry executive and philanthropist Morris “Mo” Ostin donated $10 million to UCLA for the music facility, now known as the Evelyn and Mo Ostin Music Center. Adjacent to the Schoenberg Music Building and the Inverted Fountain, the new structures provide faculty and students access to the latest advances in music technology, research and technology.
For this music center in Los Angeles ,the project includes a high-tech recording studio, spaces for rehearsal and teaching, a café and social space for students, and an Internet-based music production center. Music industry executive and philanthropist Morris “Mo” Ostin donated $10 million to UCLA for the music facility, now known as the Evelyn and Mo Ostin Music Center. Adjacent to the Schoenberg Music Building and the Inverted Fountain, the new structures provide faculty and students access to the latest advances in music technology, research and technology.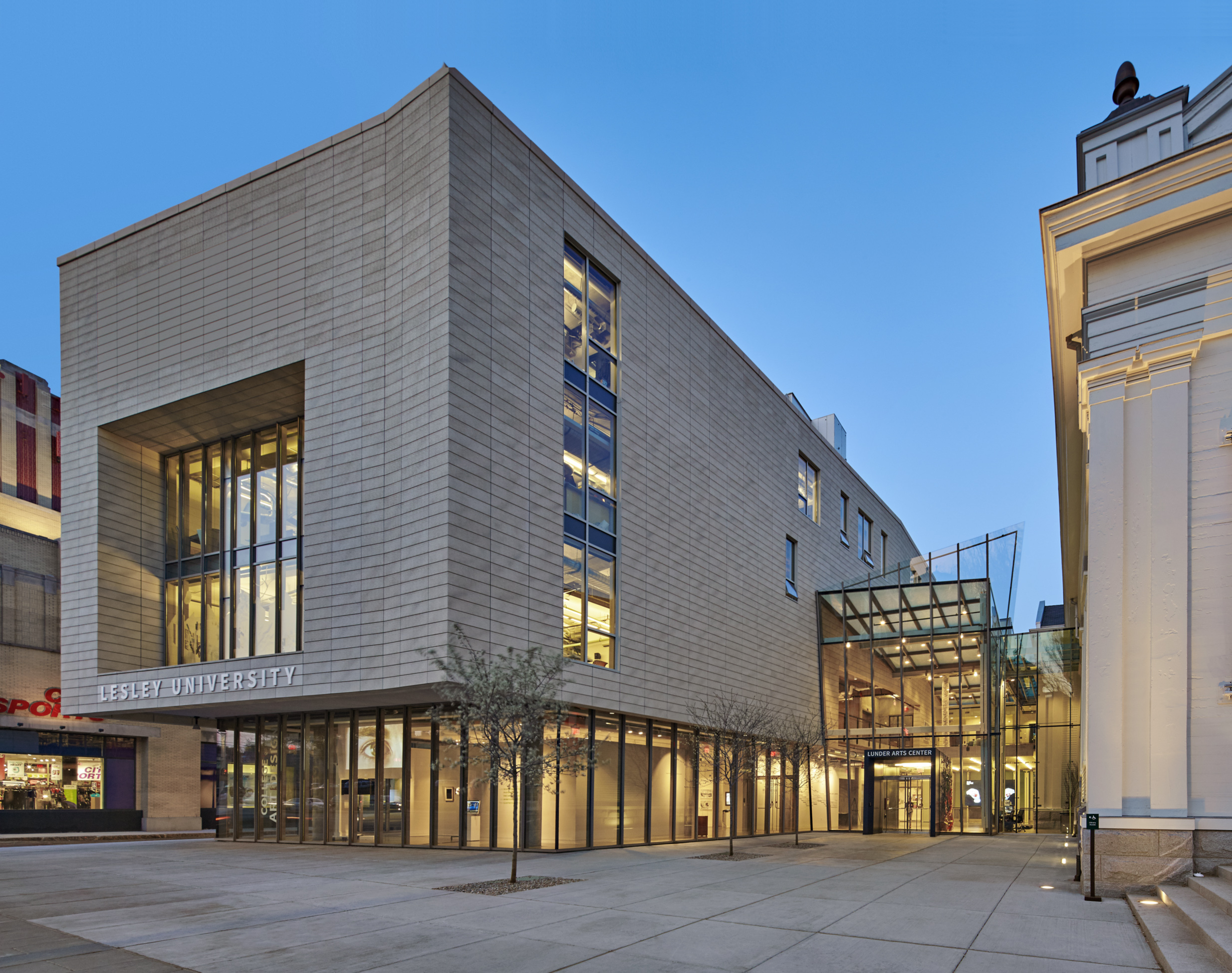
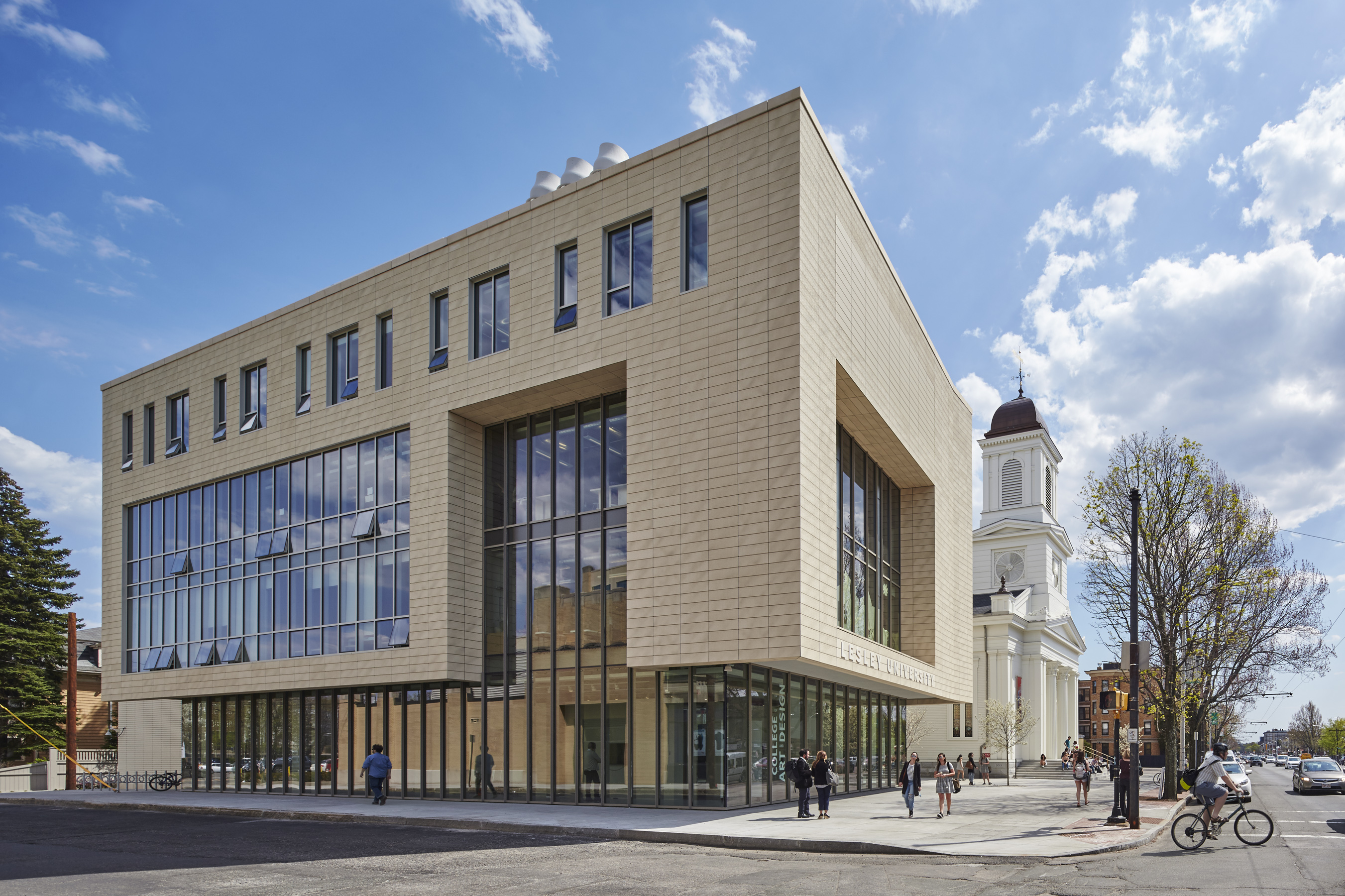 The Lunder Arts Center at Lesley was designed to be the new heart of the College of Art and Design. A center for art teaching and making, the campus is a crossroads for academic, artistic, and neighborhood communities. The terra-cotta and glass design foregrounds the site’s important historic church, initiating a dialog between 19th century religious and 21st century educational icons. An art gallery in the new glass building and a library in the historic church anchor the building at both ends; both are open to the public.
The Lunder Arts Center at Lesley was designed to be the new heart of the College of Art and Design. A center for art teaching and making, the campus is a crossroads for academic, artistic, and neighborhood communities. The terra-cotta and glass design foregrounds the site’s important historic church, initiating a dialog between 19th century religious and 21st century educational icons. An art gallery in the new glass building and a library in the historic church anchor the building at both ends; both are open to the public.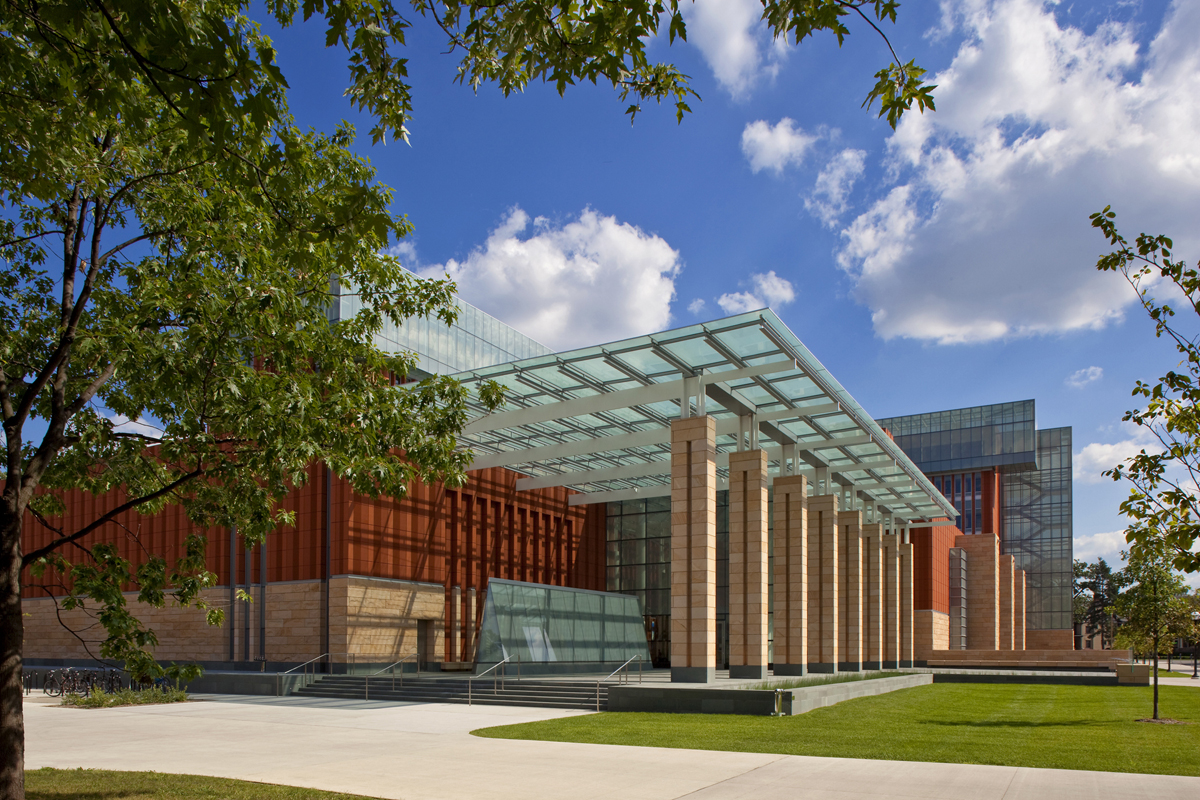
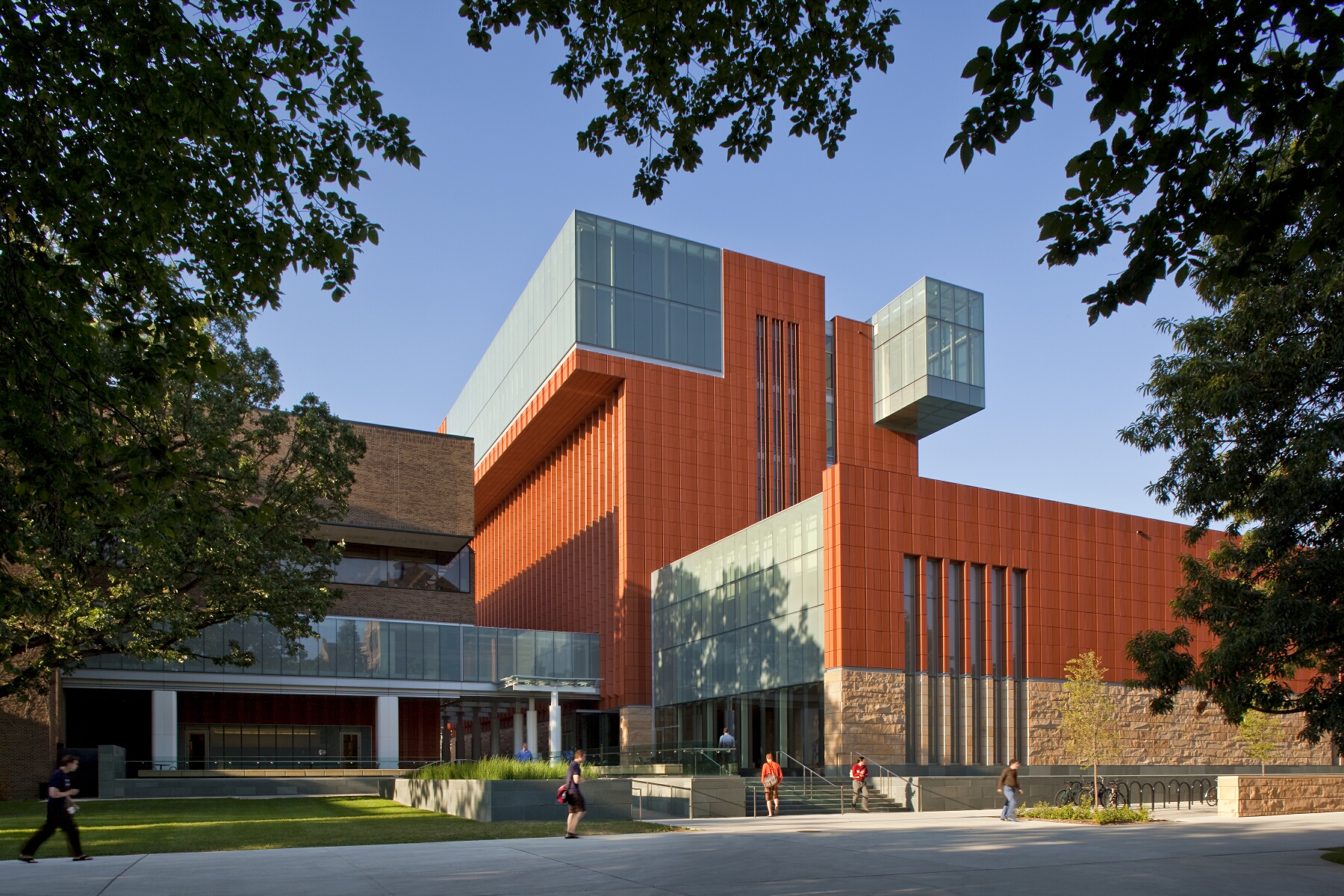 Key to the success of the design of the new Stephen M. Ross School building was relating the typical tiered classroom to group study spaces. To do so, the design team developed a model for early site planning studies to address the pedagogical needs of the school, which focused on assessing the capacity of existing buildings to accommodate new teaching spaces. Equally important was a sense of local identity, both for the building on the university campus and for distinct groups within the school.
Key to the success of the design of the new Stephen M. Ross School building was relating the typical tiered classroom to group study spaces. To do so, the design team developed a model for early site planning studies to address the pedagogical needs of the school, which focused on assessing the capacity of existing buildings to accommodate new teaching spaces. Equally important was a sense of local identity, both for the building on the university campus and for distinct groups within the school.