Architectural Drawings: Seoulâs Cultural Projects in Plan and Section
Architects: Want to have your project featured? Showcase your work through Architizer and sign up for our inspirational newsletters.
Seoul blends the old with the new, tradition with innovation. The bustling capital of South Korea is a city where history and modern life are juxtaposed in the built environment itself. Showcasing a diverse range of architectural styles and projects, Seoul’s cultural landscape is home to inventive and inspiring buildings that are grounded in human experience.
Architectural plans and section drawings tell a story of Seoul through intricate details and comprehensive design strategies. Each of the following projects explores construction and process through built work. They reveal the ideas behind some of the city’s most notable projects. From grand museums to intimate galleries and sprawling complexes to innovative community spaces, Seoul’s architectural scene is as diverse as the city itself. Through a survey of section and plan drawings, we gain insight into the spatial organization, materiality and conceptual framework of these projects, uncovering the stories and inspirations that shape Seoul’s identity today.
National Assembly Communication Building
By HAEAHN Architecture and H-Architecture, Seoul, South Korea
Popular Choice Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Government & Civic Buildings
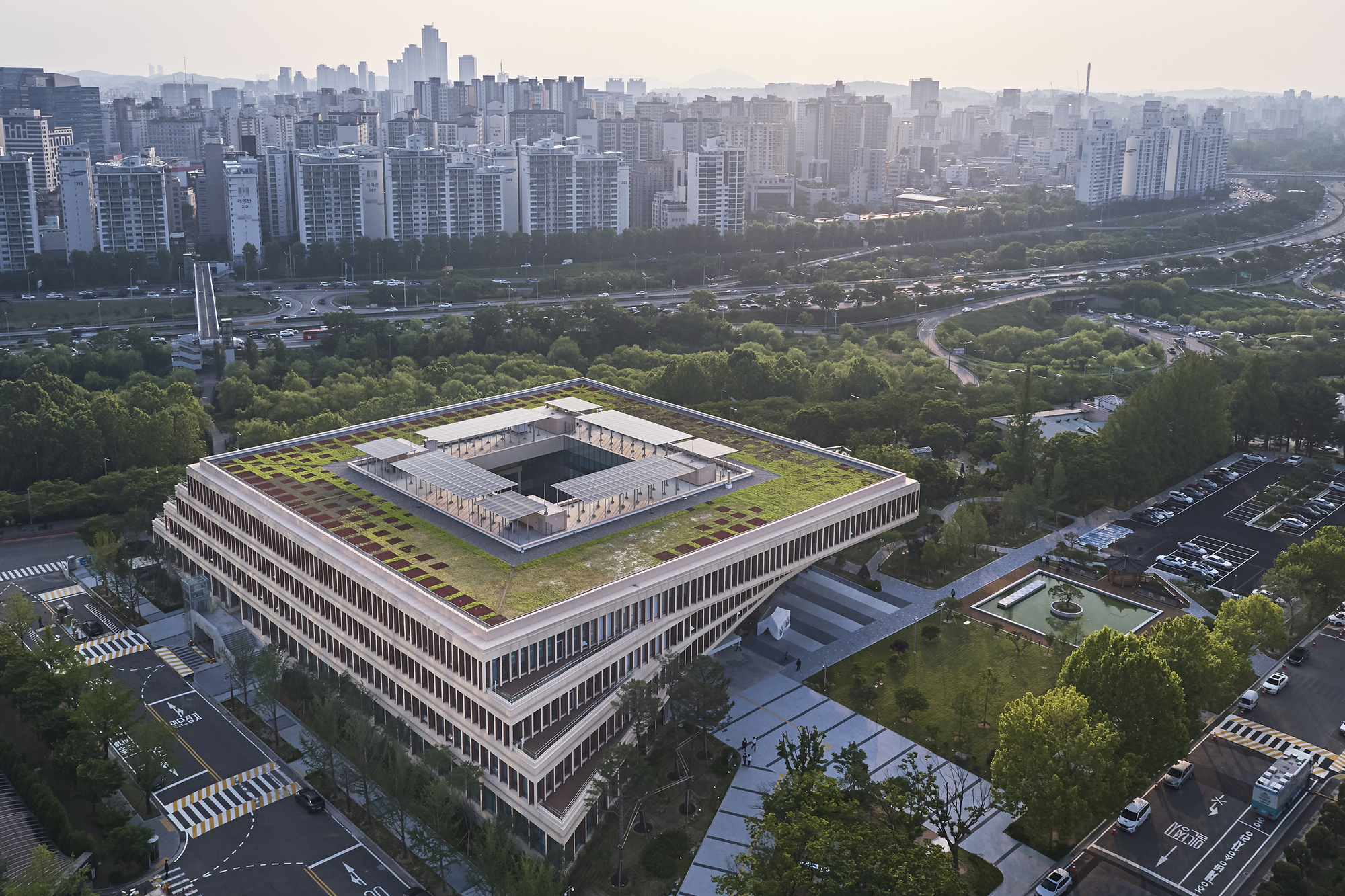
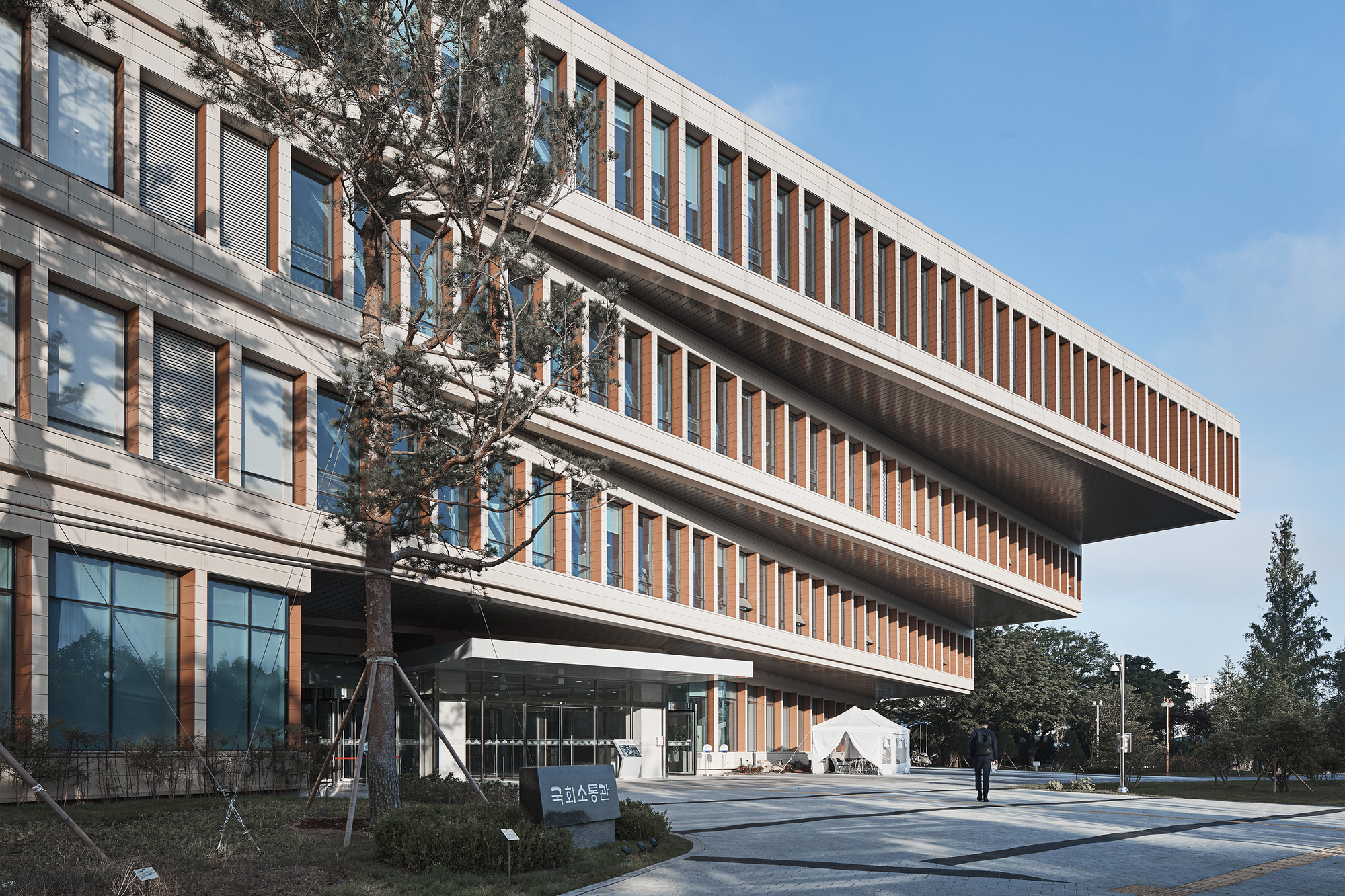
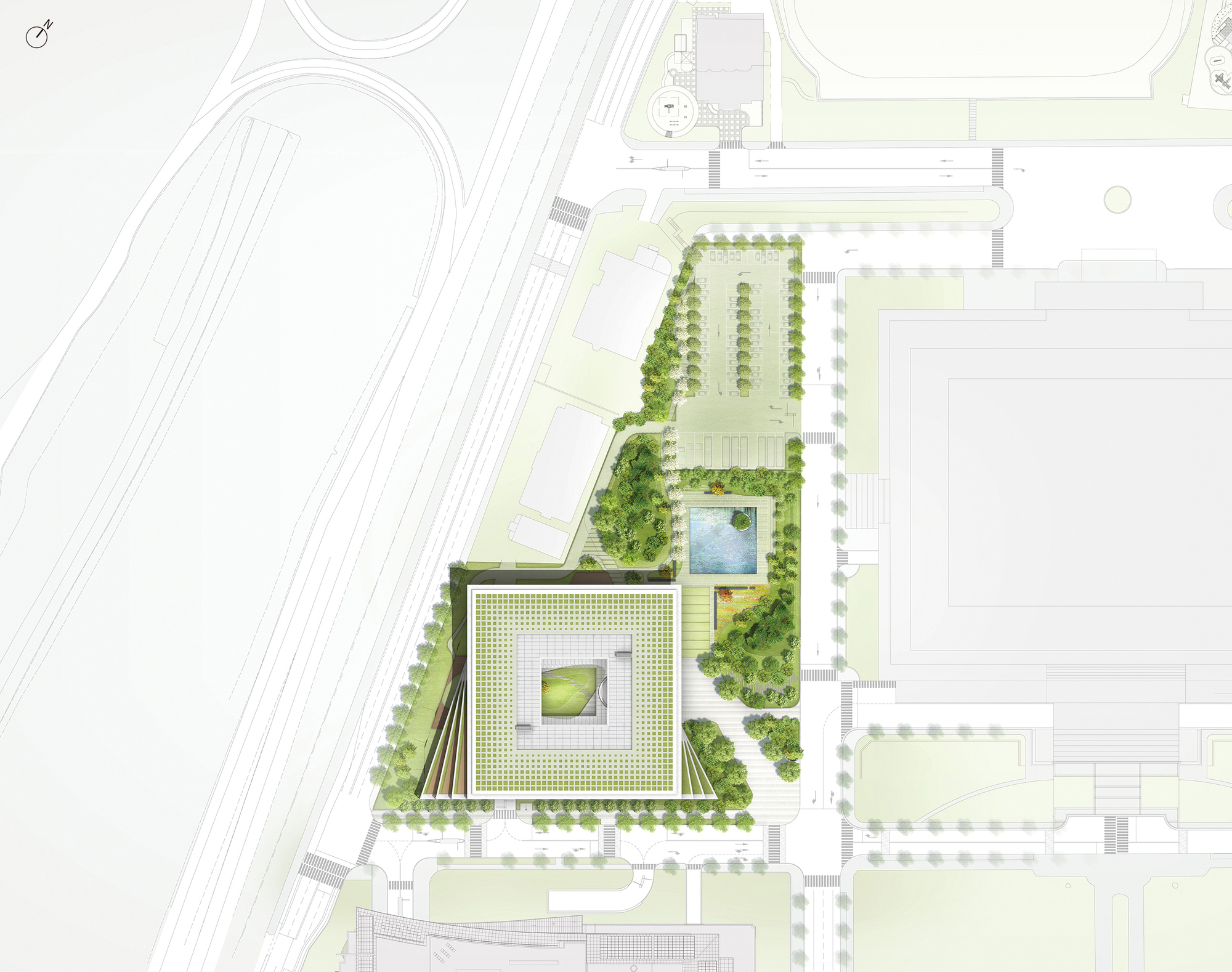
 The National Assembly Communication Building at the Republic of Korea Complex embodies the ideals of flexibility and openness. It integrates seamlessly with the existing monumental masterplan while catering to daily activities. The four-story structure is designed to blend into its surroundings, respecting the existing tree line and maintaining a height of 30 to 40 feet. The building’s layout is organized into horizontal zones to accommodate diverse users, ensuring privacy and efficiency.
The National Assembly Communication Building at the Republic of Korea Complex embodies the ideals of flexibility and openness. It integrates seamlessly with the existing monumental masterplan while catering to daily activities. The four-story structure is designed to blend into its surroundings, respecting the existing tree line and maintaining a height of 30 to 40 feet. The building’s layout is organized into horizontal zones to accommodate diverse users, ensuring privacy and efficiency.
Circulation and security are handled by four cores around a central courtyard. The modular structure system allows for future adaptations. The building symbolizes democratic values and houses various public, media, political, and administrative programs. Its design fosters communication and interaction, both inside and outside the building, as seen in plan. The design creates a vibrant and welcoming environment.
Saemoonan Church
By Lee Eunseok+KOMA, Seoul, South Korea
Jury Winner, 8th Annual A+Awards, Religious buildings & Memorials
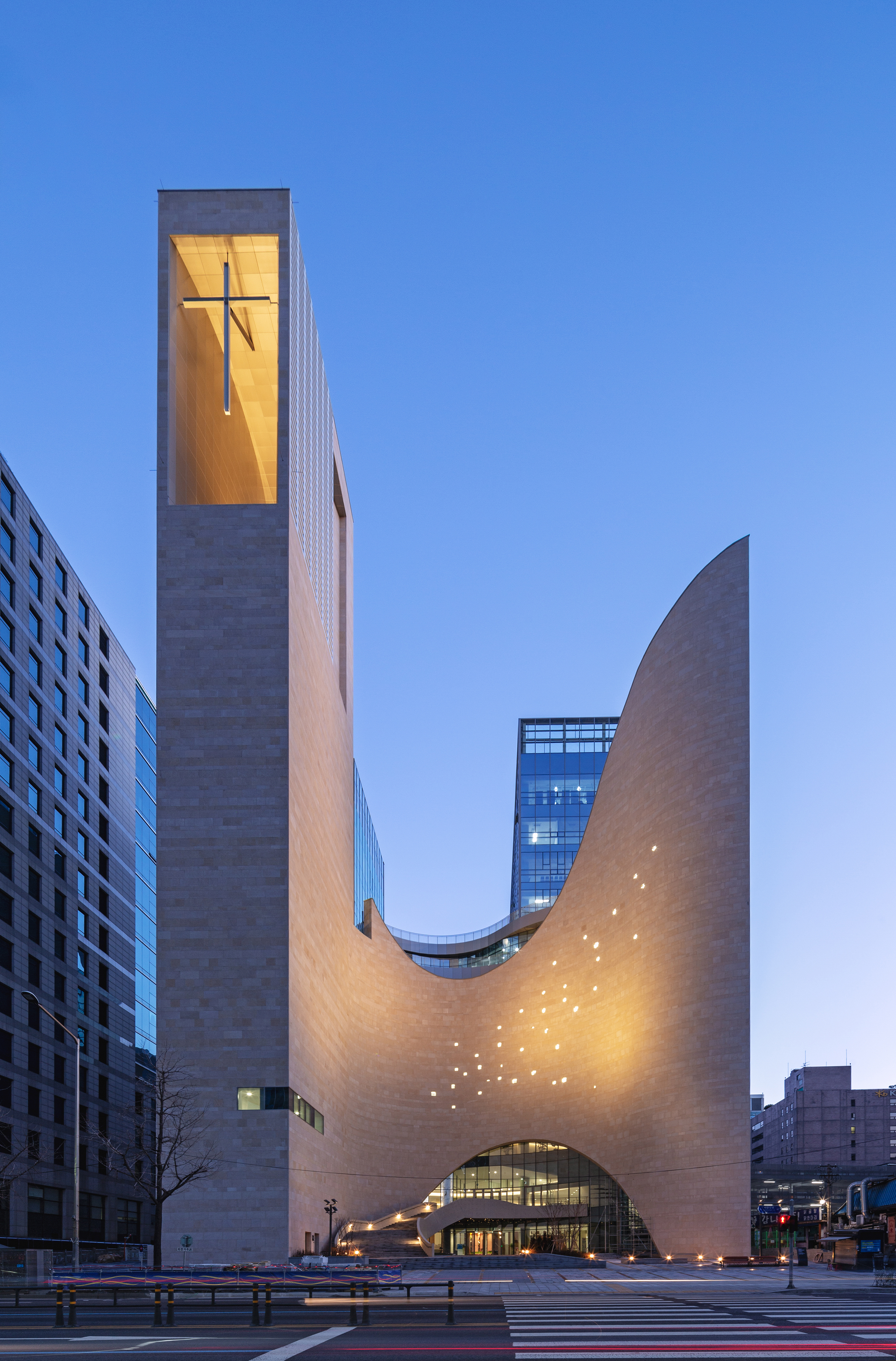
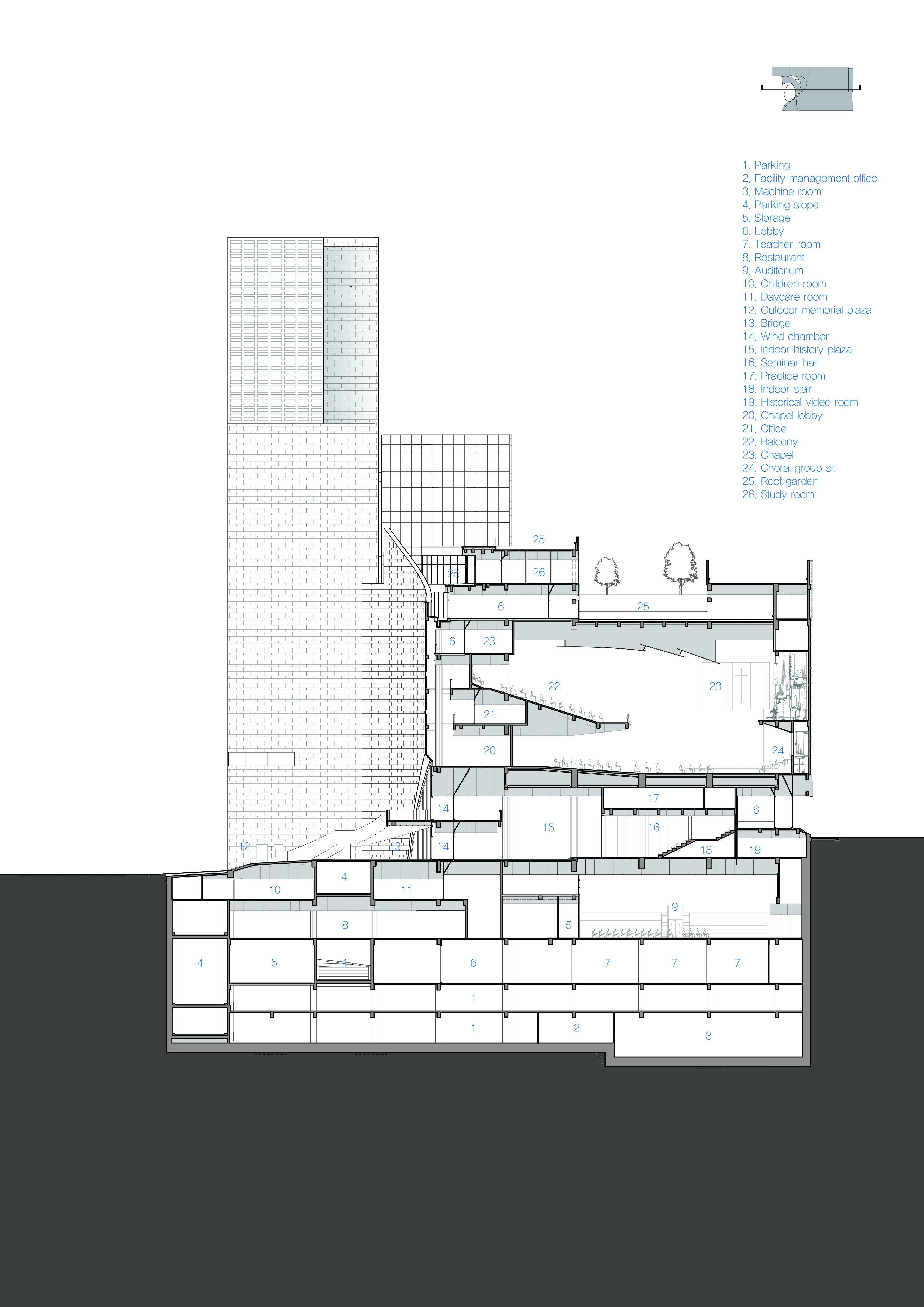
 Saemoonan Church, the first Korean Protestant church, celebrated its 132nd anniversary and opened a new church in Gwanghwamun Sinmunno. The design, resembling a mother’s embracing arms reaching toward the sky, breaks from traditional spire and Gothic architecture, a significant shift in modern church design. The new church focuses on four themes: historicity, symbolizing its role as the mother church of the Korean Protestant Church; spatiality, portraying Christ as light through an open door to heaven; a water space representing baptism’s meaning; and harmony. These themes were revised to incorporate God’s love and neighborly love into the design, emphasized through spatial symbolism and outward appearance.
Saemoonan Church, the first Korean Protestant church, celebrated its 132nd anniversary and opened a new church in Gwanghwamun Sinmunno. The design, resembling a mother’s embracing arms reaching toward the sky, breaks from traditional spire and Gothic architecture, a significant shift in modern church design. The new church focuses on four themes: historicity, symbolizing its role as the mother church of the Korean Protestant Church; spatiality, portraying Christ as light through an open door to heaven; a water space representing baptism’s meaning; and harmony. These themes were revised to incorporate God’s love and neighborly love into the design, emphasized through spatial symbolism and outward appearance.
The design emphasizes simplicity and abstraction, with the facade’s soft curve symbolizing love and mercy, and the fan-shaped chapel encouraging dynamic participation in worship. The architecture prioritizes public engagement, with the facade’s concave surface and courtyard of Saemoonan-ro serving as public spaces, welcoming citizens and fostering community interaction. The church also includes a small chapel made from its old bricks, serving as an open cultural space.
Nodeul Island
By mmkplus, Seoul, South Korea
Popular Choice Winner, 8th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Urban Transformation
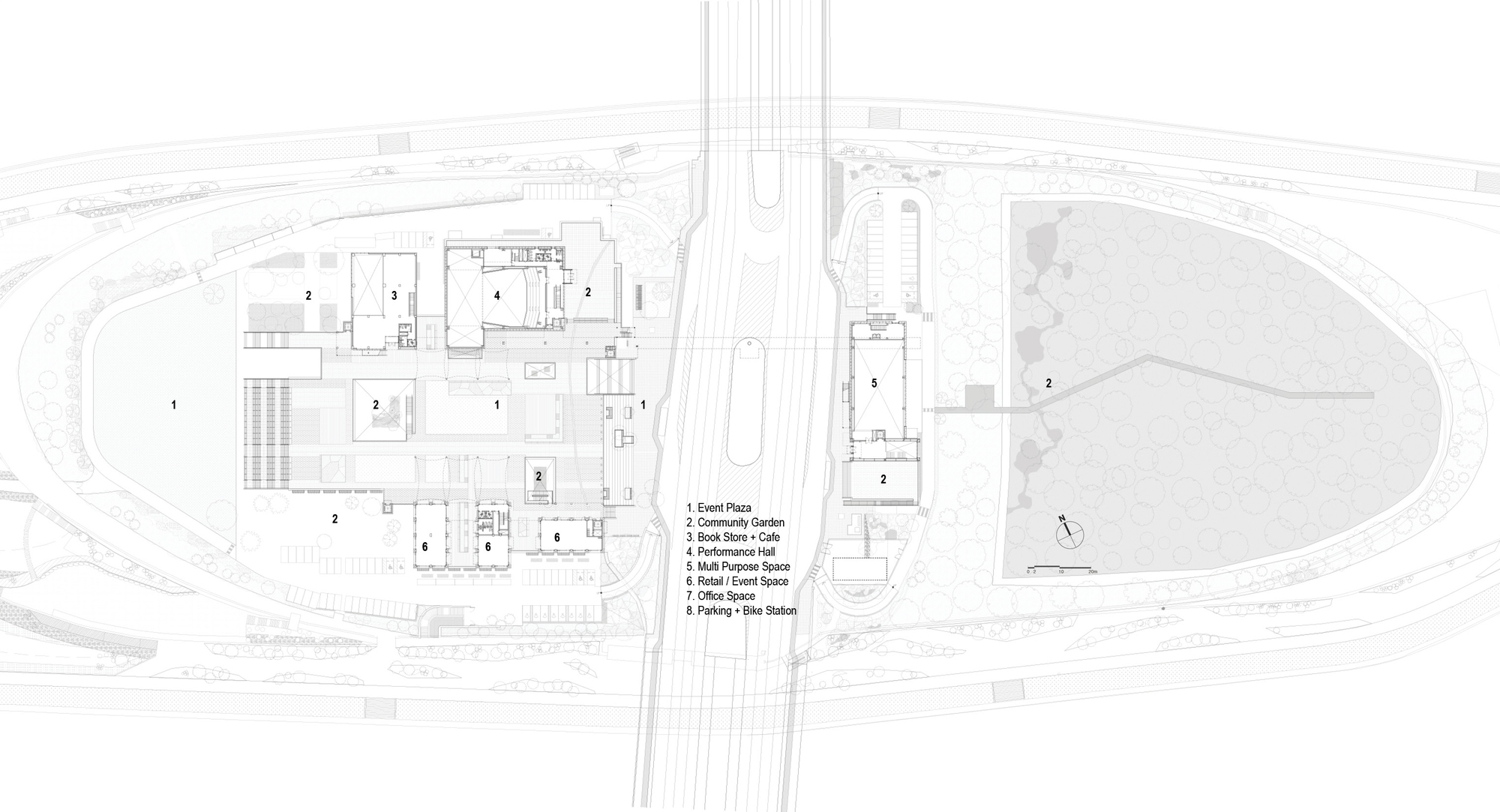
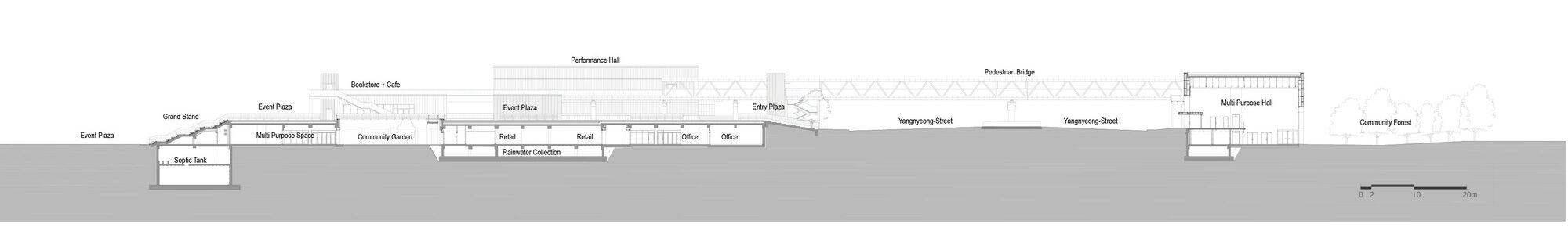
 Nodeul Island, an artificial island in Seoul’s Han River, was long neglected despite its natural beauty and central location. This project revitalizes the island, creating multi-level public spaces with cultural programs that honor its history. The redesigned island offers diverse activities and fosters a connection between visitors and the city’s landscape. The island features two main levels: the original ground level hosts cultural venues, while an upper platform provides public plazas and viewing decks.
Nodeul Island, an artificial island in Seoul’s Han River, was long neglected despite its natural beauty and central location. This project revitalizes the island, creating multi-level public spaces with cultural programs that honor its history. The redesigned island offers diverse activities and fosters a connection between visitors and the city’s landscape. The island features two main levels: the original ground level hosts cultural venues, while an upper platform provides public plazas and viewing decks.
A village-like setting houses offices, shops, galleries and performance halls, fostering a harmonious community. The island’s landscape encourages social interactions, offering a park-like experience. Restoration efforts include sustainable strategies and an eco-habitat for endangered species. A new public promenade, upgraded terraces and gardens enhance the island’s history. Nodeul Island is now a vibrant public park and cultural venue, inviting visitors to explore its historical significance and potential.
Seoul Square Ice Rink
By CoRe Architects, Seoul, South Korea
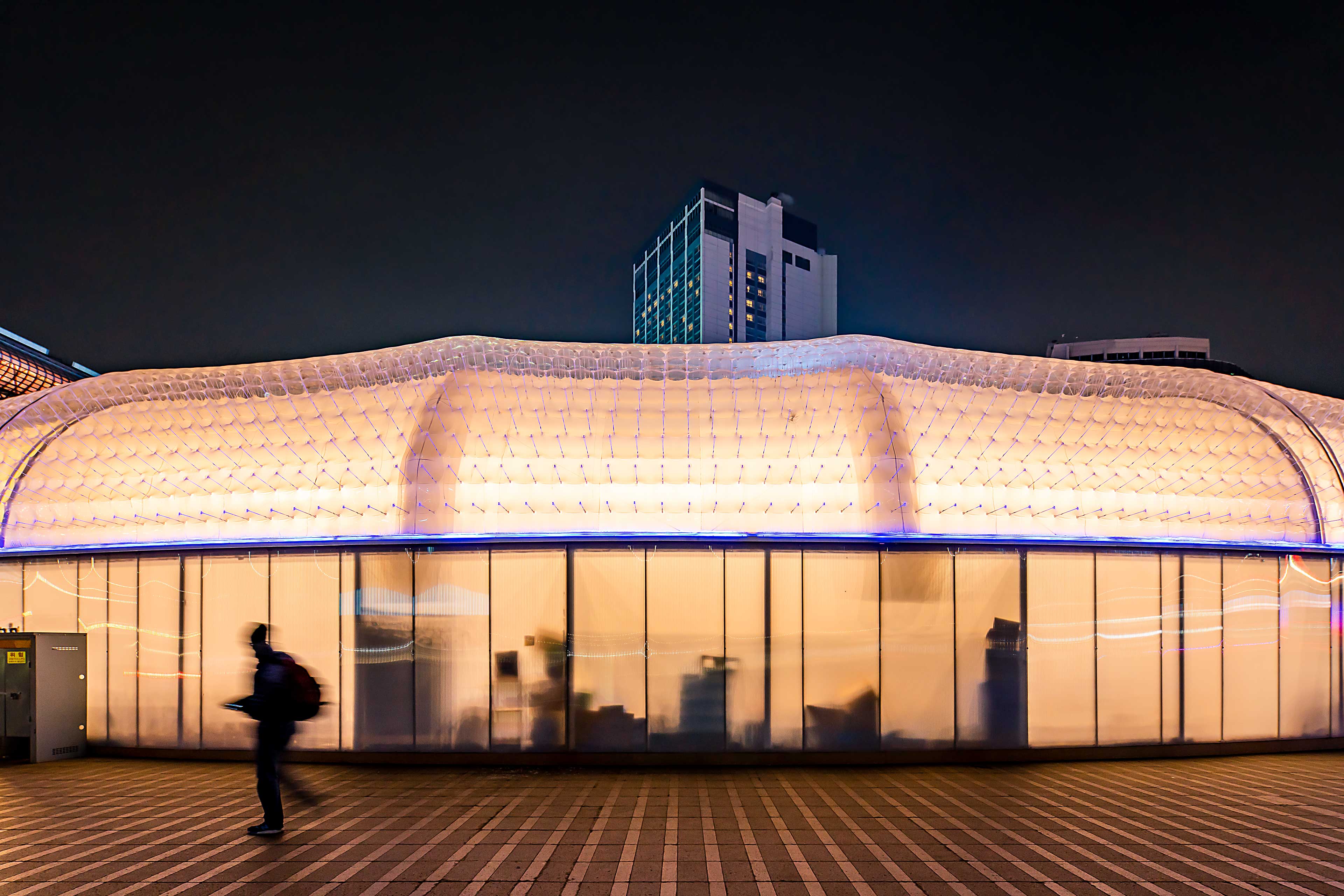
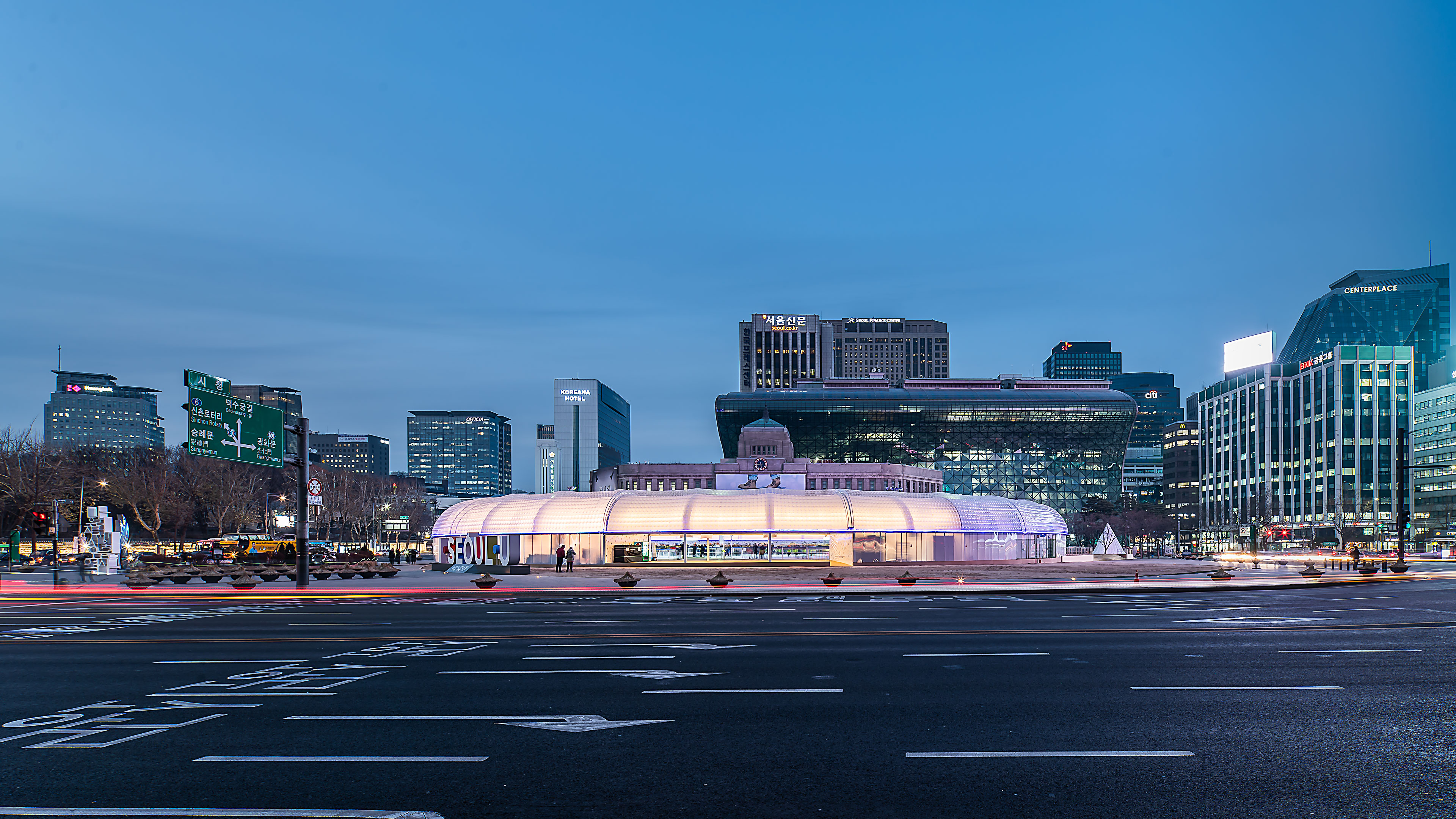
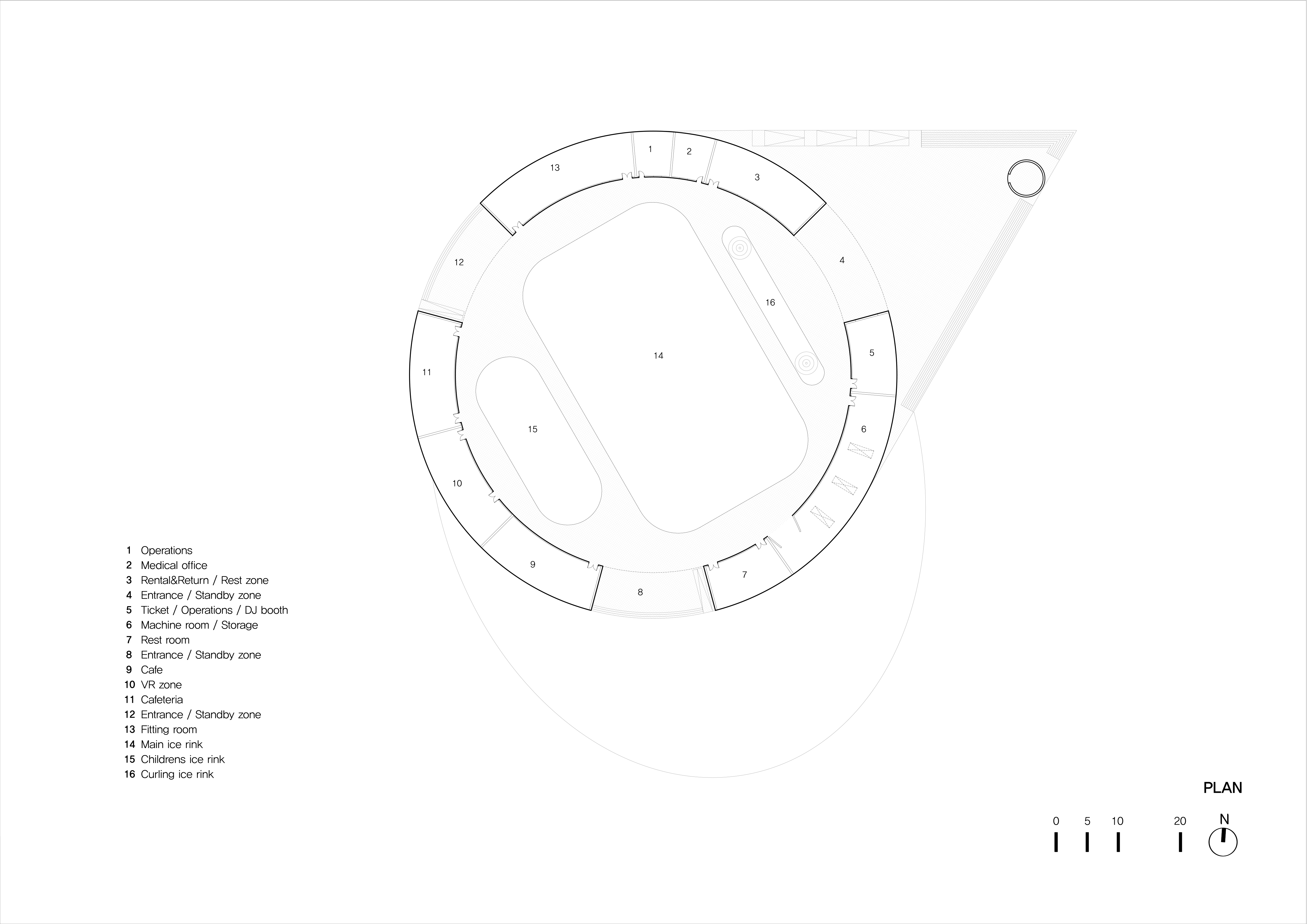
 Seoul Plaza transforms into a winter sports hub for citizens from Christmas through February, featuring skating and curling. The skating rink, redesigned and reopened in 2018 through a public competition, introduces a new, easily recyclable structural concept. Unlike previous years, that year’s rink boasted a “new structural alternative” that could be swiftly installed and recycled. Originally conceived as a light vinyl house, it evolved into a double air-dome system for easier reuse or recycling.
Seoul Plaza transforms into a winter sports hub for citizens from Christmas through February, featuring skating and curling. The skating rink, redesigned and reopened in 2018 through a public competition, introduces a new, easily recyclable structural concept. Unlike previous years, that year’s rink boasted a “new structural alternative” that could be swiftly installed and recycled. Originally conceived as a light vinyl house, it evolved into a double air-dome system for easier reuse or recycling.
The roof is a double air-membrane structure made of transparent laminated urethane and opaque flame-retarded urethane. The membranes, supported by about 40,000 ropes, allow natural light during the day and internal light at night, creating a unique façade. The skating rink’s design combined equilateral triangles and circles, with a triangular deck facilitating movement between the plaza and the Seoul Library. A circular auxiliary facility complements the modern reinterpretation, enhancing citizens’ spatial and temporal experiences.
Kukje Gallery
By SO – IL, Seoul, South Korea
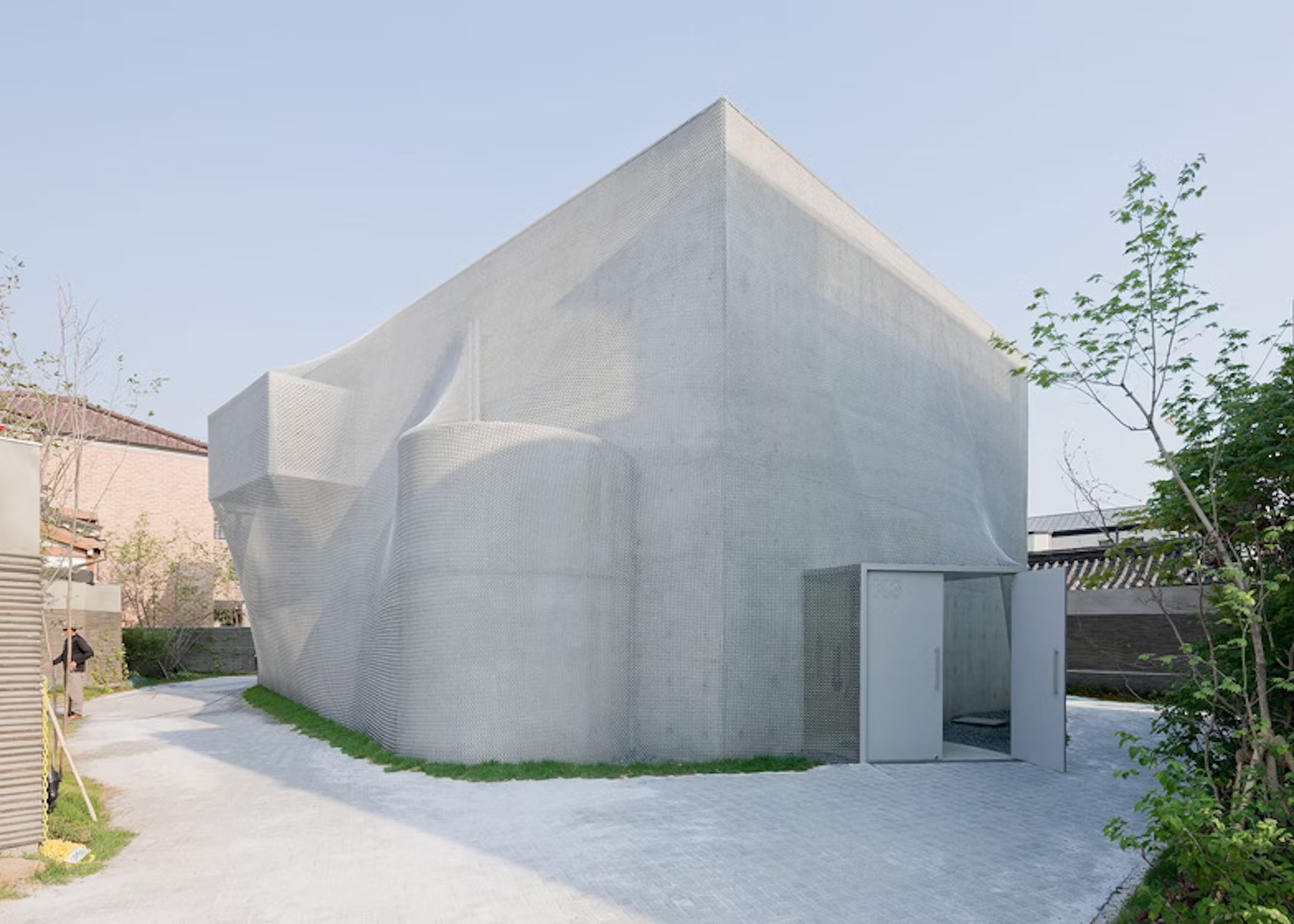
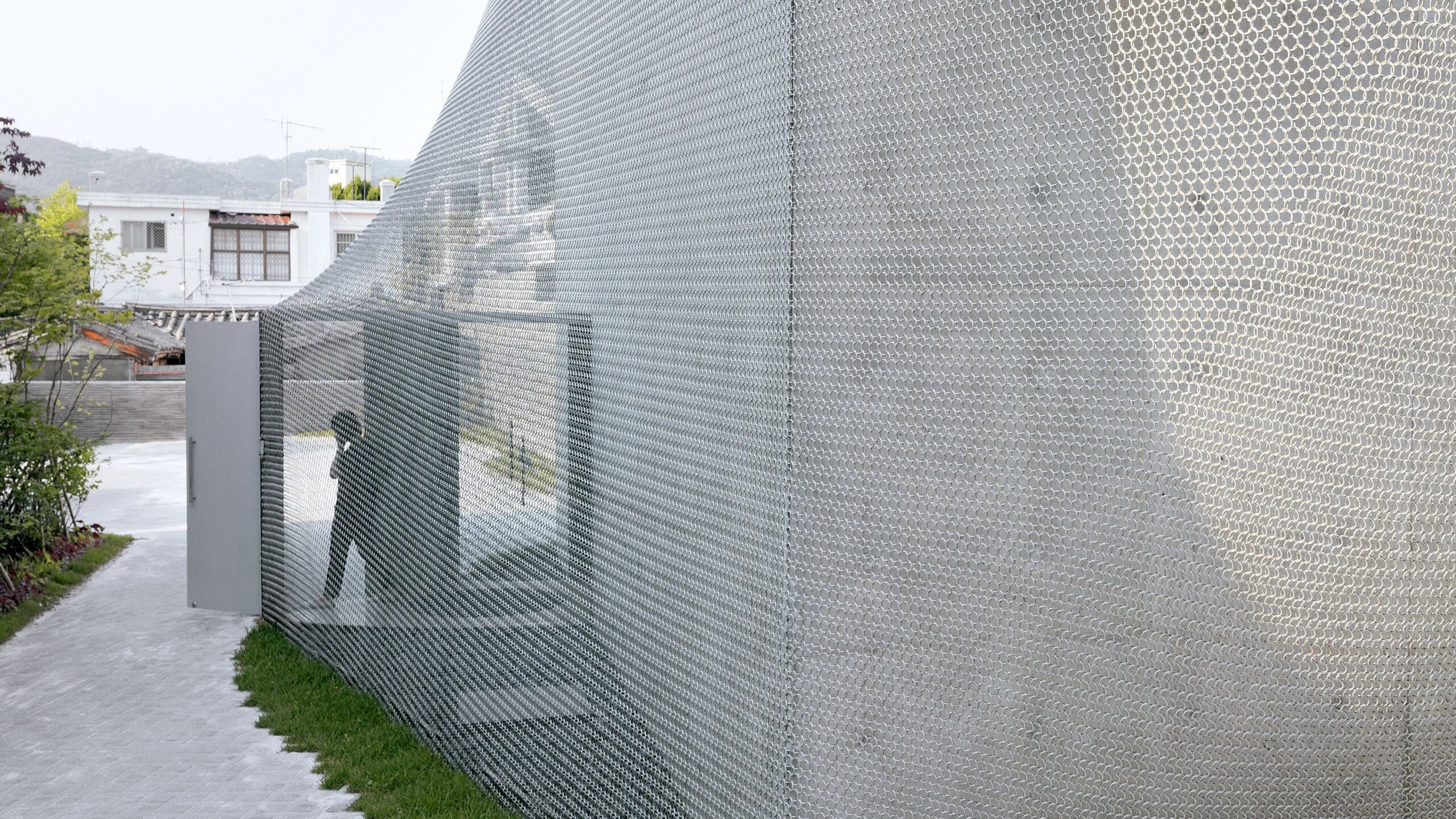
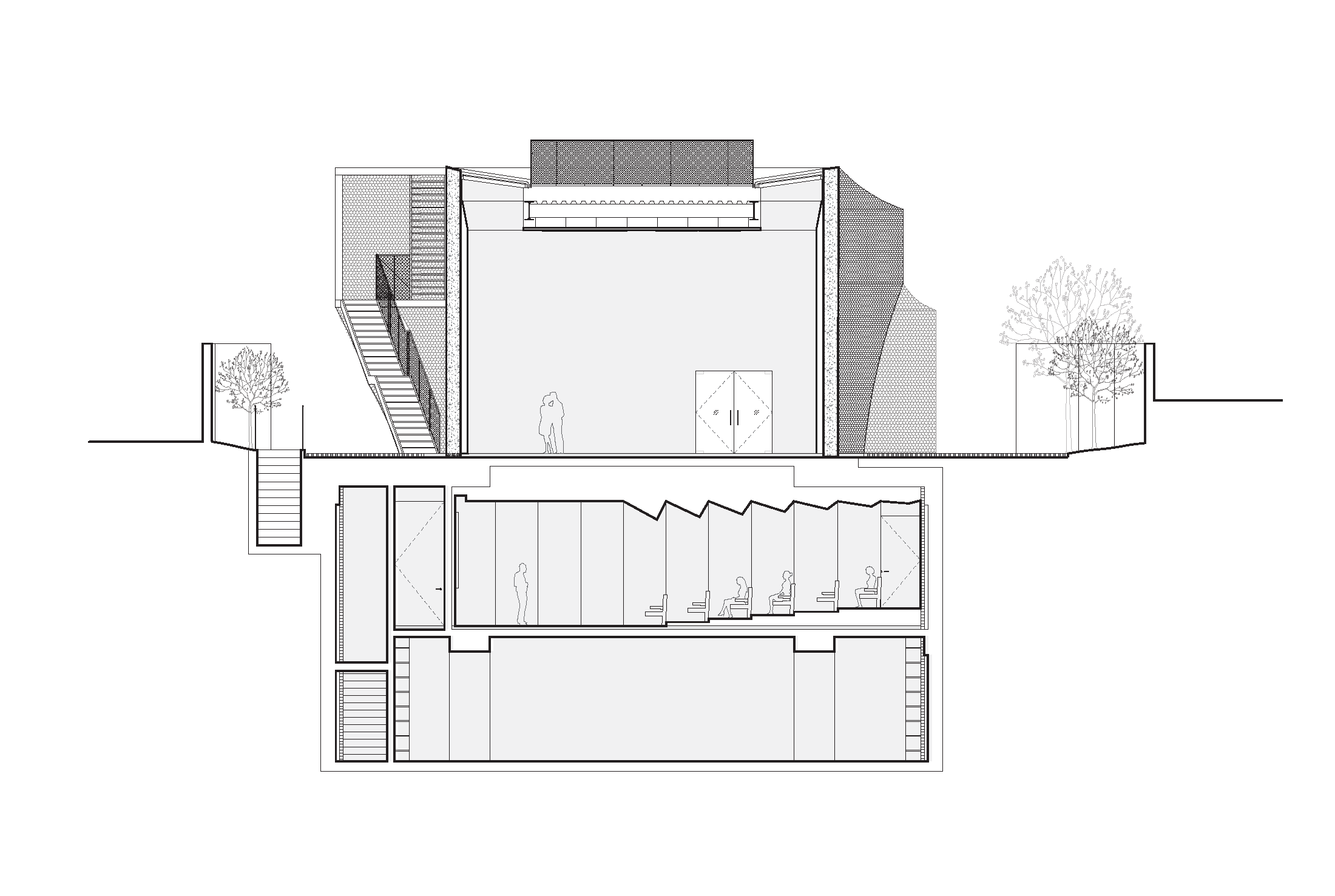
 The project aims to enhance Korea’s cultural presence globally while harmonizing with the historic surroundings of northern Seoul. The design blends modern aesthetics with traditional techniques, featuring a unique chainmail veil façade made of 510,000 metal rings. To integrate seamlessly into the historic urban fabric, the gallery’s circulation is pushed to the edges, and the entire structure is wrapped in the hand-fabricated veil. This approach, developed in collaboration with engineers at Front Inc., marries computational processes with traditional craftsmanship.
The project aims to enhance Korea’s cultural presence globally while harmonizing with the historic surroundings of northern Seoul. The design blends modern aesthetics with traditional techniques, featuring a unique chainmail veil façade made of 510,000 metal rings. To integrate seamlessly into the historic urban fabric, the gallery’s circulation is pushed to the edges, and the entire structure is wrapped in the hand-fabricated veil. This approach, developed in collaboration with engineers at Front Inc., marries computational processes with traditional craftsmanship.
The gallery’s design is sensitive to its context, with materials and patterns inspired by cobblestone streets and regional building styles. Located amidst traditional hannok homes, the gallery serves as a landmark in a cultural campus and aids in public wayfinding. The building’s form, reflecting the surrounding rooflines, creates a sense of lightness and blends with the environment. Despite its compact size, the gallery offers a versatile space for art exhibitions and events, including a 60-seat auditorium for lectures, films, and performances. Support spaces such as offices and storage are located underground, ensuring flexibility in gallery use.
Platform-L Contemporary Art Center
By JOHO Architecture, Seoul, South Korea
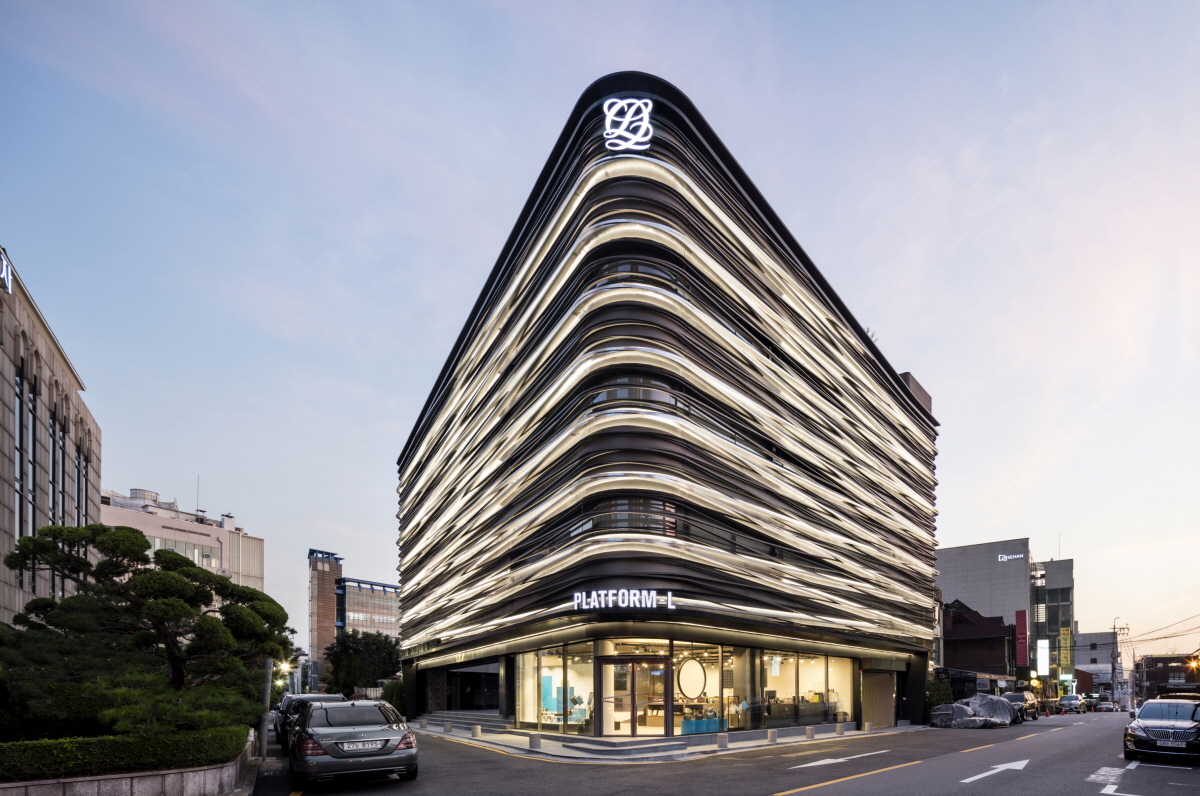
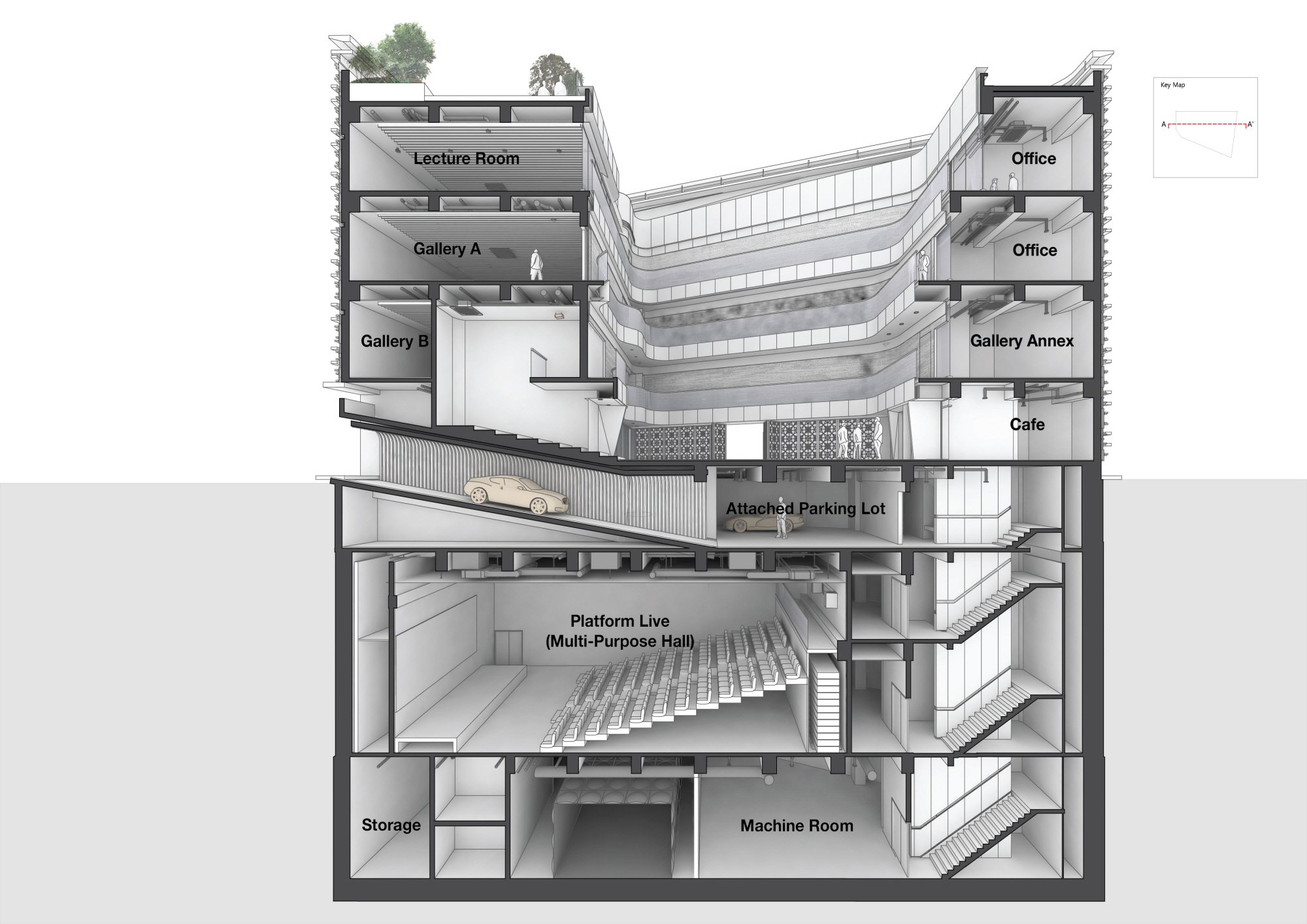
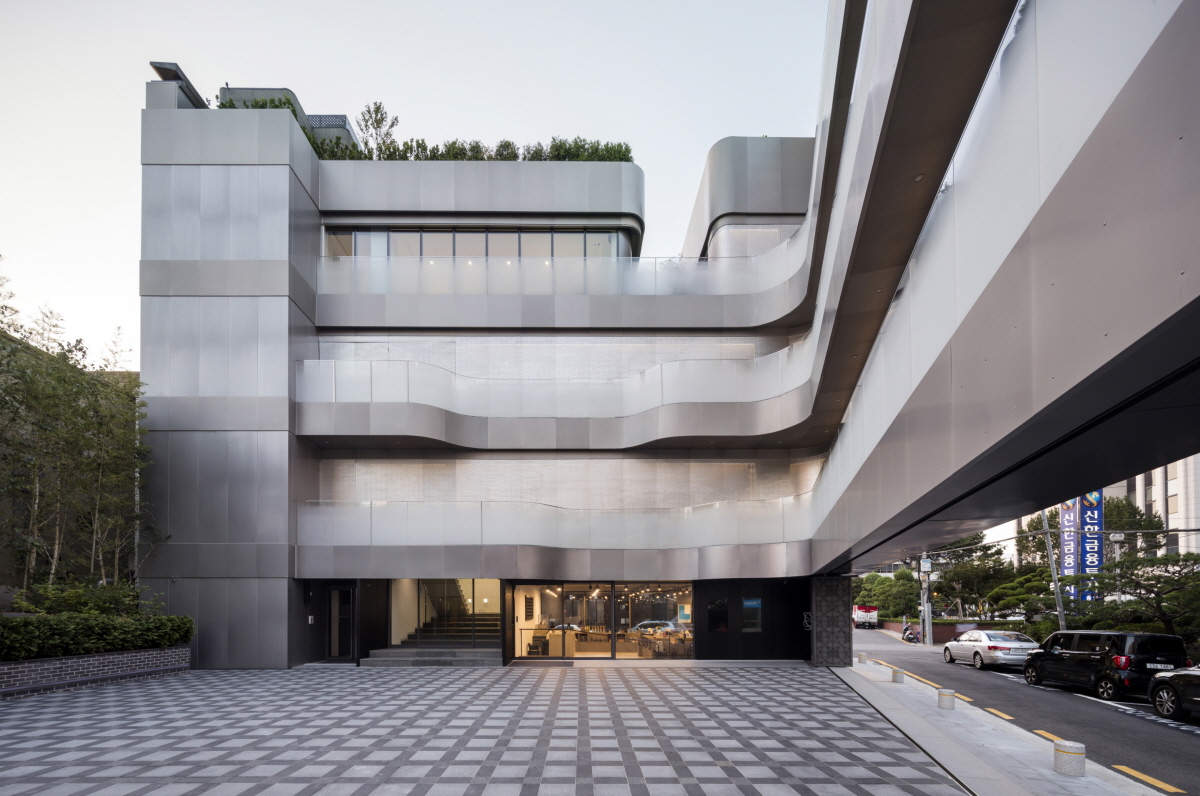

 Platform-L Contemporary Art Center is situated in Seoul’s Gangnam district, nestled in a residential area. The site’s unique irregular trapezoid shape, surrounded by streets on three sides, posed a distinctive design challenge. Adhering to architectural regulations limiting the building ratio to 60% of the total site area, Platform-L took a unique approach by placing parking underground, creating a voided space on grade.
Platform-L Contemporary Art Center is situated in Seoul’s Gangnam district, nestled in a residential area. The site’s unique irregular trapezoid shape, surrounded by streets on three sides, posed a distinctive design challenge. Adhering to architectural regulations limiting the building ratio to 60% of the total site area, Platform-L took a unique approach by placing parking underground, creating a voided space on grade.
The center’s design features two independent masses with a central courtyard facing west, maximizing space efficiency. The north mass houses the museum’s entrance, exhibition spaces, a VIP lounge, and a roof terrace offering cityscape views. On the south end, a café/restaurant and office spaces are located. The exterior facade design draws inspiration from Louis Quatorze fashion design company, the sponsor of Platform-L, reflecting Louis XIV’s basic geometries. This reinterpretation symbolizes the company’s commitment to fashion and culture, serving as a new emblem for its values.
Roof Sentiment
By SoA(Society of Architecture), Seoul, South Korea
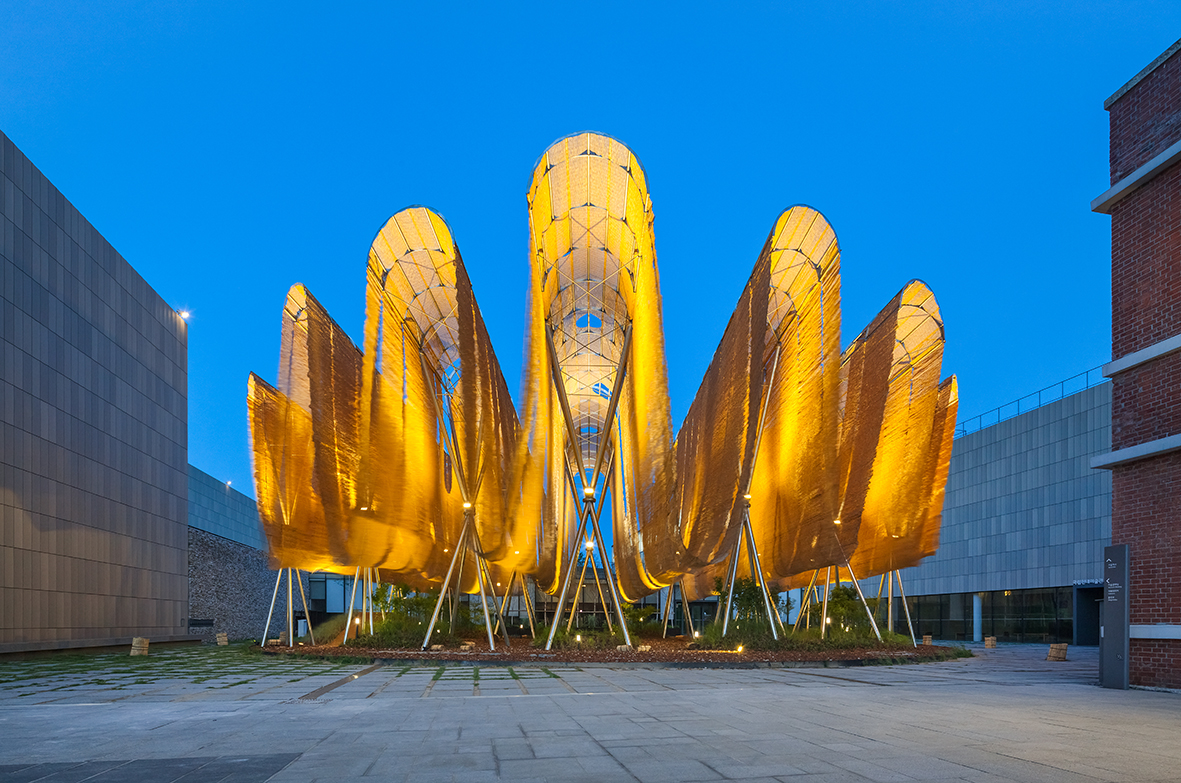
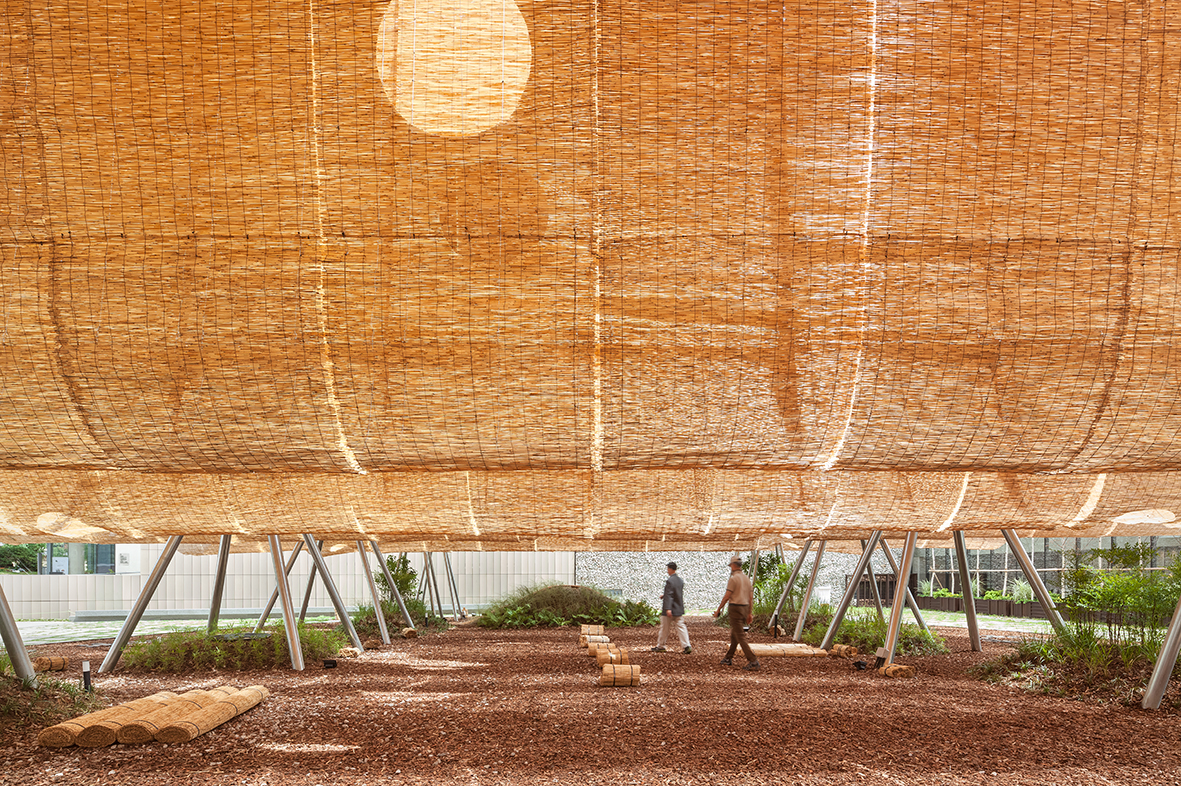
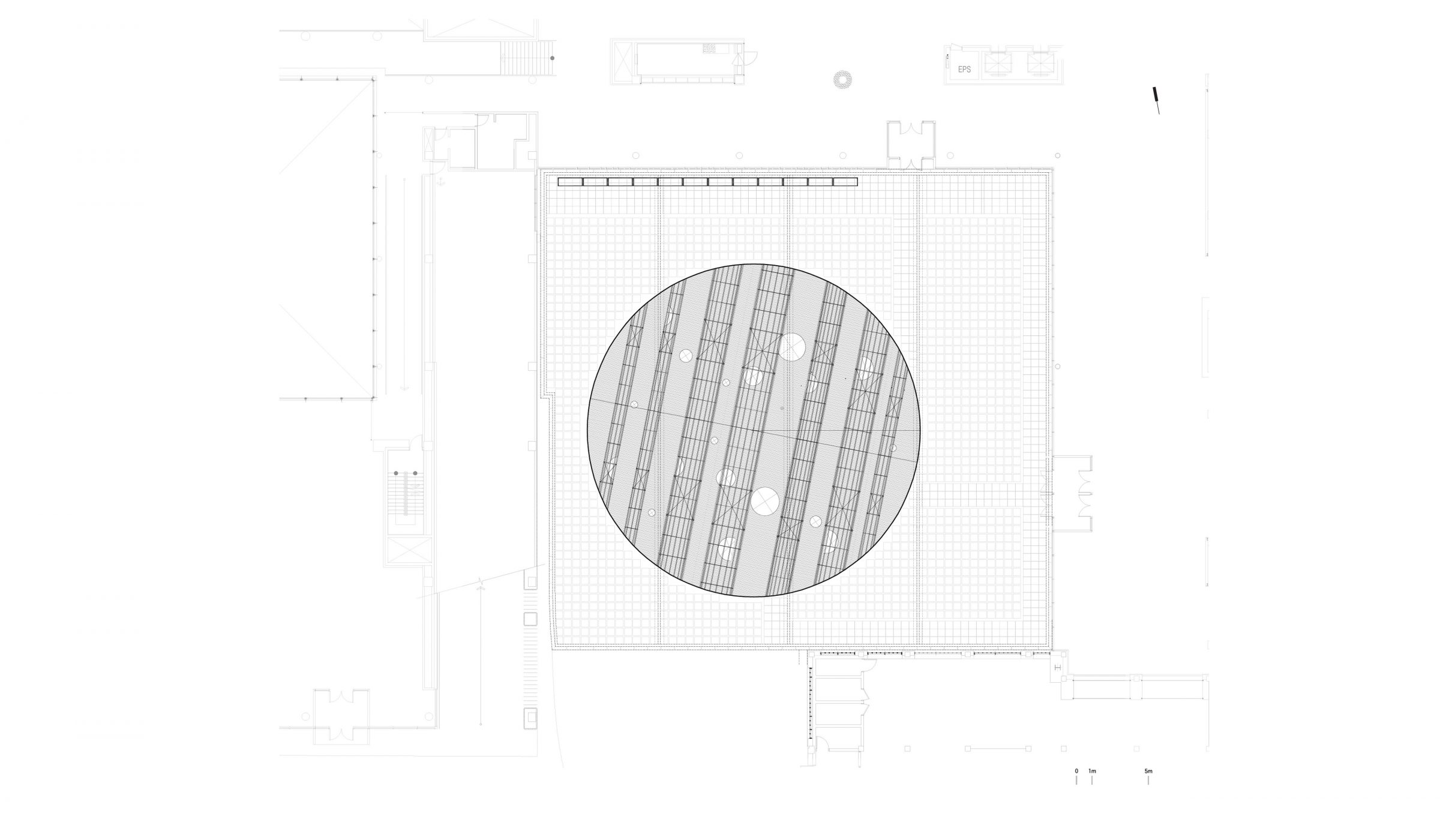
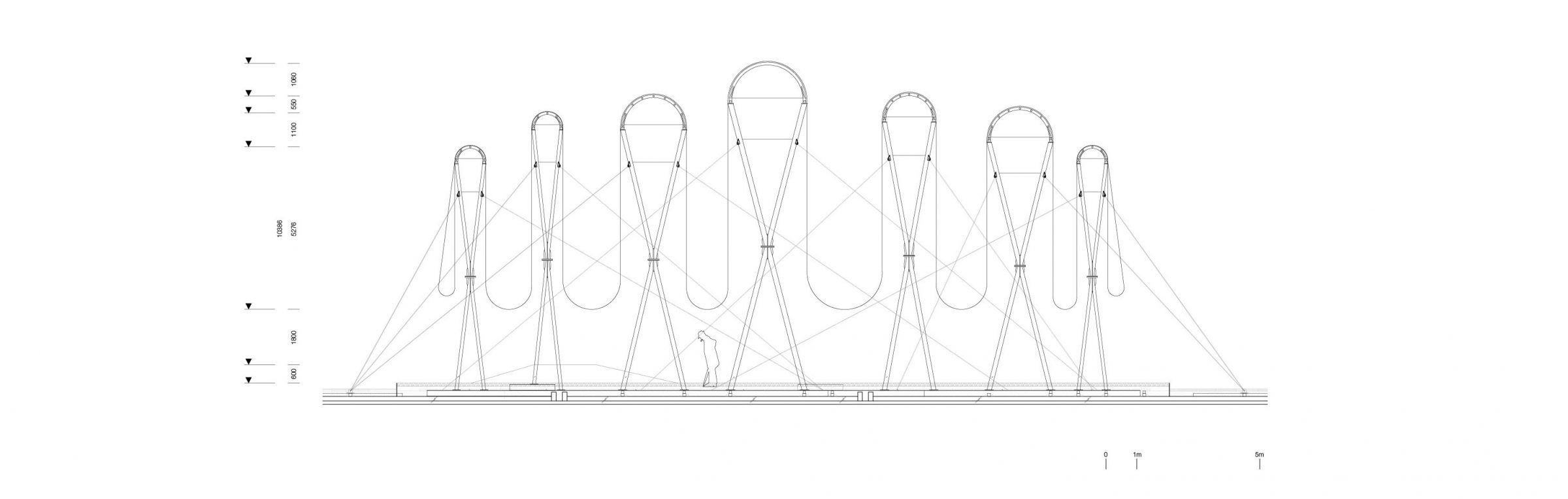
 The front yard of MMCA Seoul faces the Gyeongbokgung Palace, a strong site-specific context. This space, once part of the Jongchinbu (Office of the Royal Genealogy in the Lee dynasty), is now an open public area of MMCA Seoul and serves as a platform for Y.A.P in the summer. Traditional architecture in Gyeongbokgung Palace is characterized by its prominent roofs. Han-ok (traditional Korean style-house) roofs were large and heavy to support the wooden pillars, creating a high and deep space underneath.
The front yard of MMCA Seoul faces the Gyeongbokgung Palace, a strong site-specific context. This space, once part of the Jongchinbu (Office of the Royal Genealogy in the Lee dynasty), is now an open public area of MMCA Seoul and serves as a platform for Y.A.P in the summer. Traditional architecture in Gyeongbokgung Palace is characterized by its prominent roofs. Han-ok (traditional Korean style-house) roofs were large and heavy to support the wooden pillars, creating a high and deep space underneath.
The lines of these roofs framed the scenery with the mountains in the background, symbolizing a connection to the heavens and expressing political, sacral, and societal meanings. The ‘Roof sentiment’ project aims to rekindle people’s feelings and senses by creating a wrinkle roof using reed blinds. This roof sways in the breeze, offering glimpses of the scenery through its gaps. Unlike traditional roofs that cover the under space, the wrinkle roof uncovers people’s sentiments, serving as an agent to awaken people to the summers and the area’s unique atmosphere.
National Aviation Museum of Korea
By HAEAHN Architecture, Seoul, South Korea
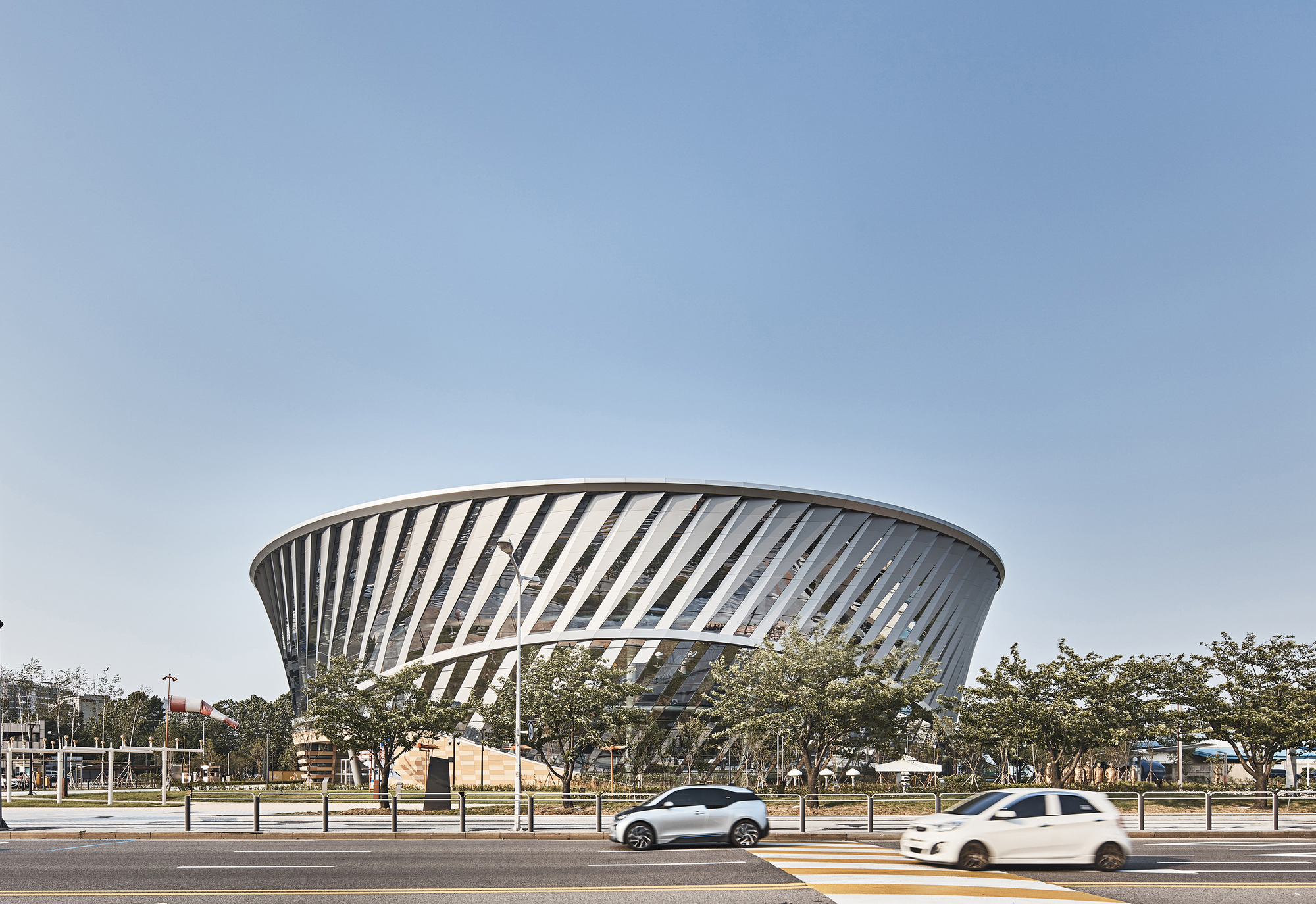
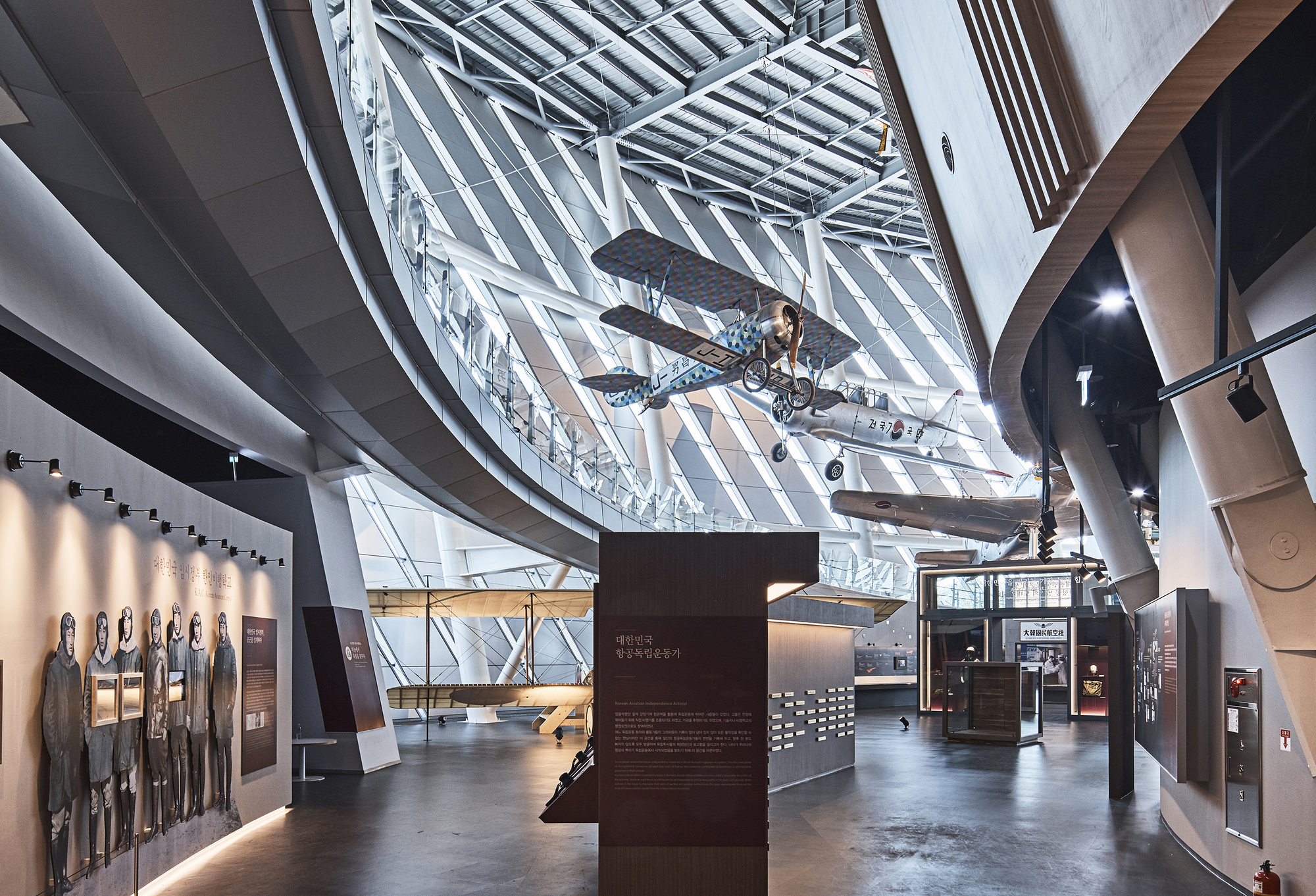
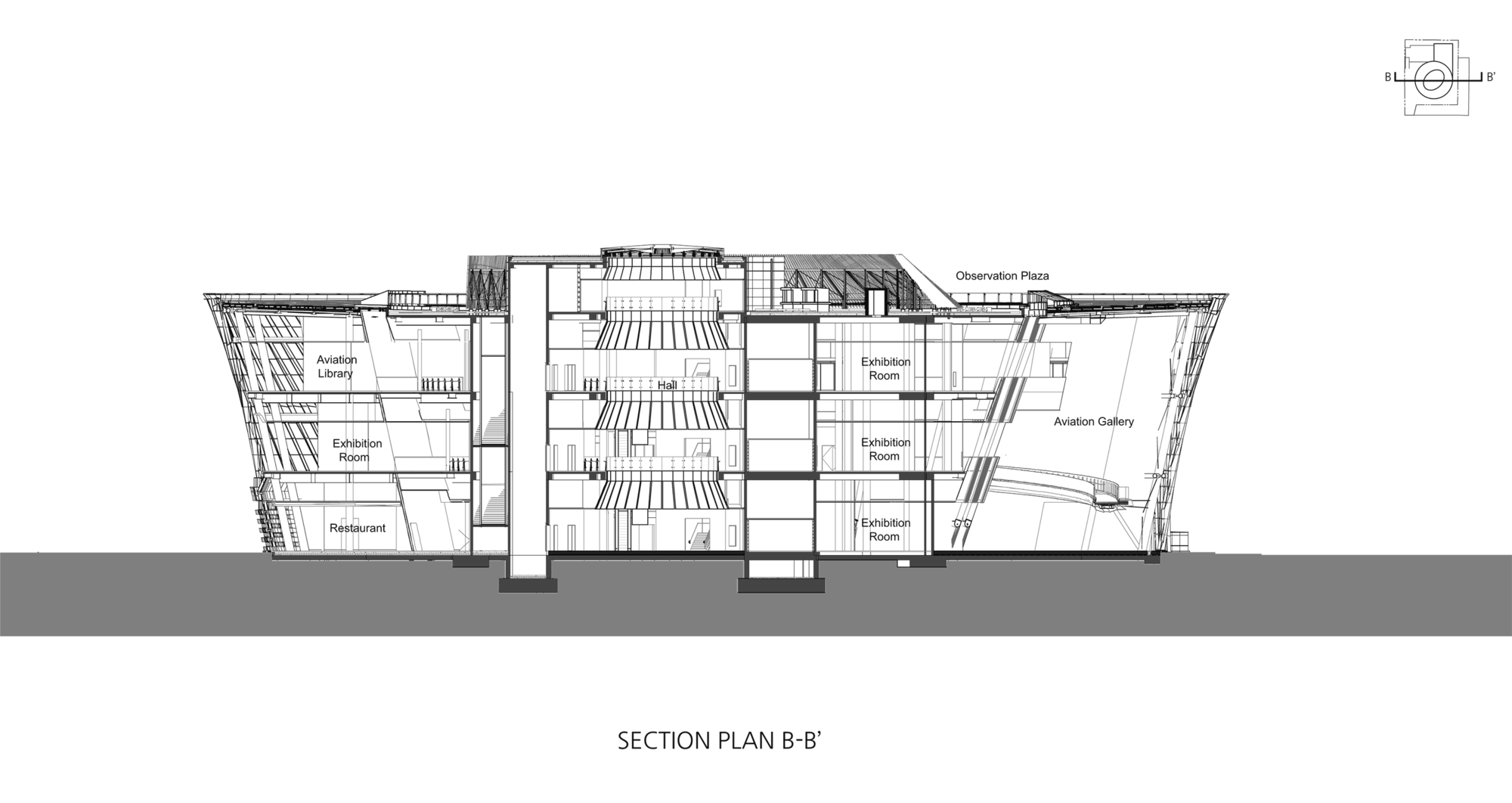
 The National Aviation Museum, located in Gimpo Airport, aimed to elevate the Korean aviation industry’s status through a multi-cultural space promoted by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport. The museum’s design reflects three core ideas: “Air Turbine,” inspired by airplane turbines, symbolizes the integration of mechanical aesthetics and science technology; “Air Show,” an aviation gallery, presents the history of Korean aviation in a dynamic, panoramic exhibition space; and “Air Walk,” a three-dimensional walkway, offers a dynamic experience amid the architectural structure’s shining lights.
The National Aviation Museum, located in Gimpo Airport, aimed to elevate the Korean aviation industry’s status through a multi-cultural space promoted by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport. The museum’s design reflects three core ideas: “Air Turbine,” inspired by airplane turbines, symbolizes the integration of mechanical aesthetics and science technology; “Air Show,” an aviation gallery, presents the history of Korean aviation in a dynamic, panoramic exhibition space; and “Air Walk,” a three-dimensional walkway, offers a dynamic experience amid the architectural structure’s shining lights.
The site’s layout is circular, including the southern beltway and the main entrance road, creating a central position between the airport and support complex. A three-floor void in the permanent exhibition space allows for integrated indoor-outdoor exhibitions through a transparent façade. The museum features two buildings: a circular exhibition hall designed for aviation displays and a rectangular management building optimized for various functions. The interior of the eco-friendly air turbine is a spiral exhibition space, guiding visitors through the planes on the ceiling and creating a dynamic experience.
Architects: Want to have your project featured? Showcase your work through Architizer and sign up for our inspirational newsletters.
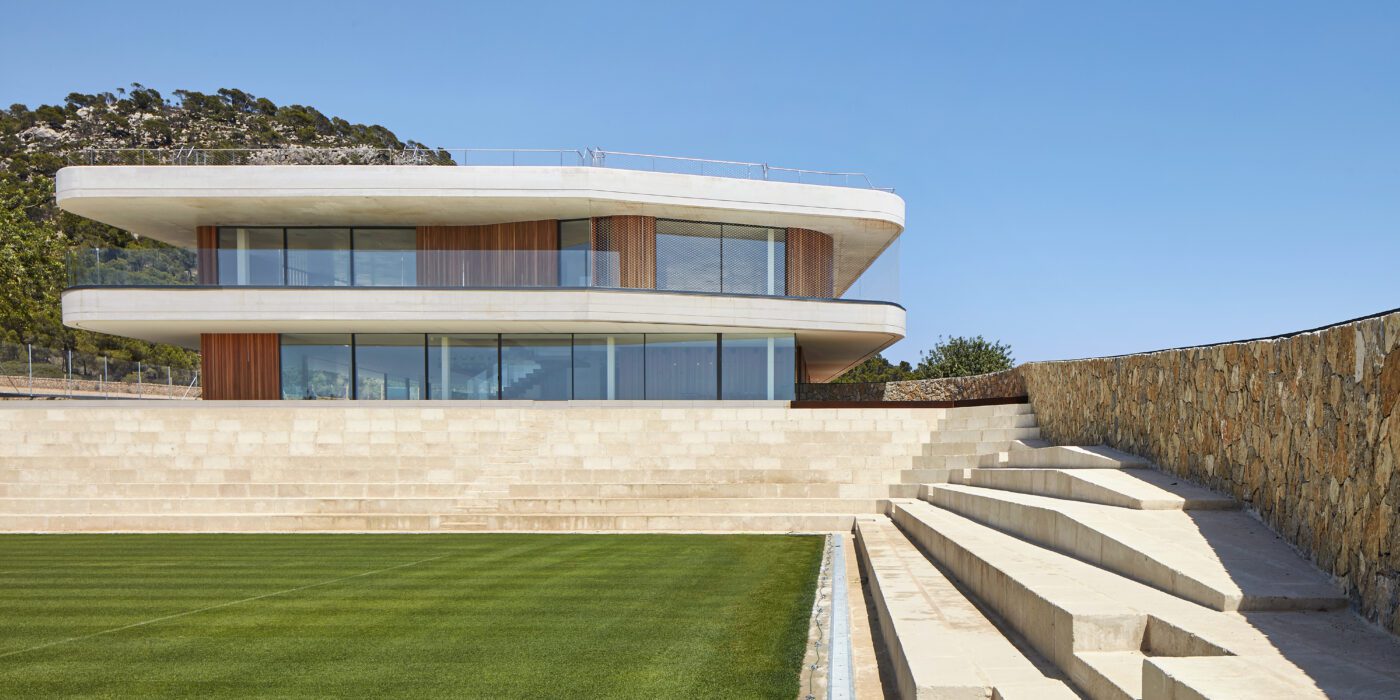
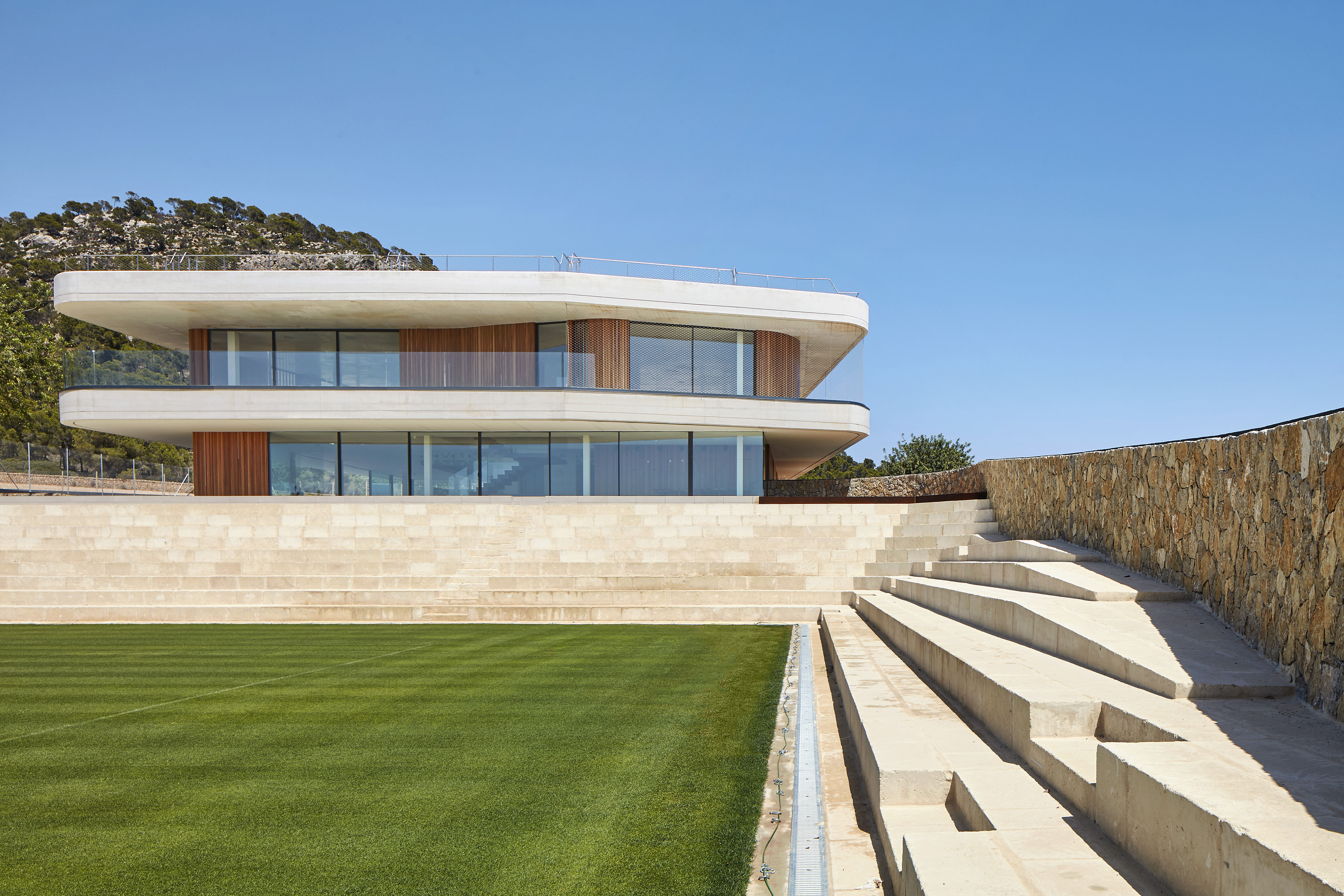
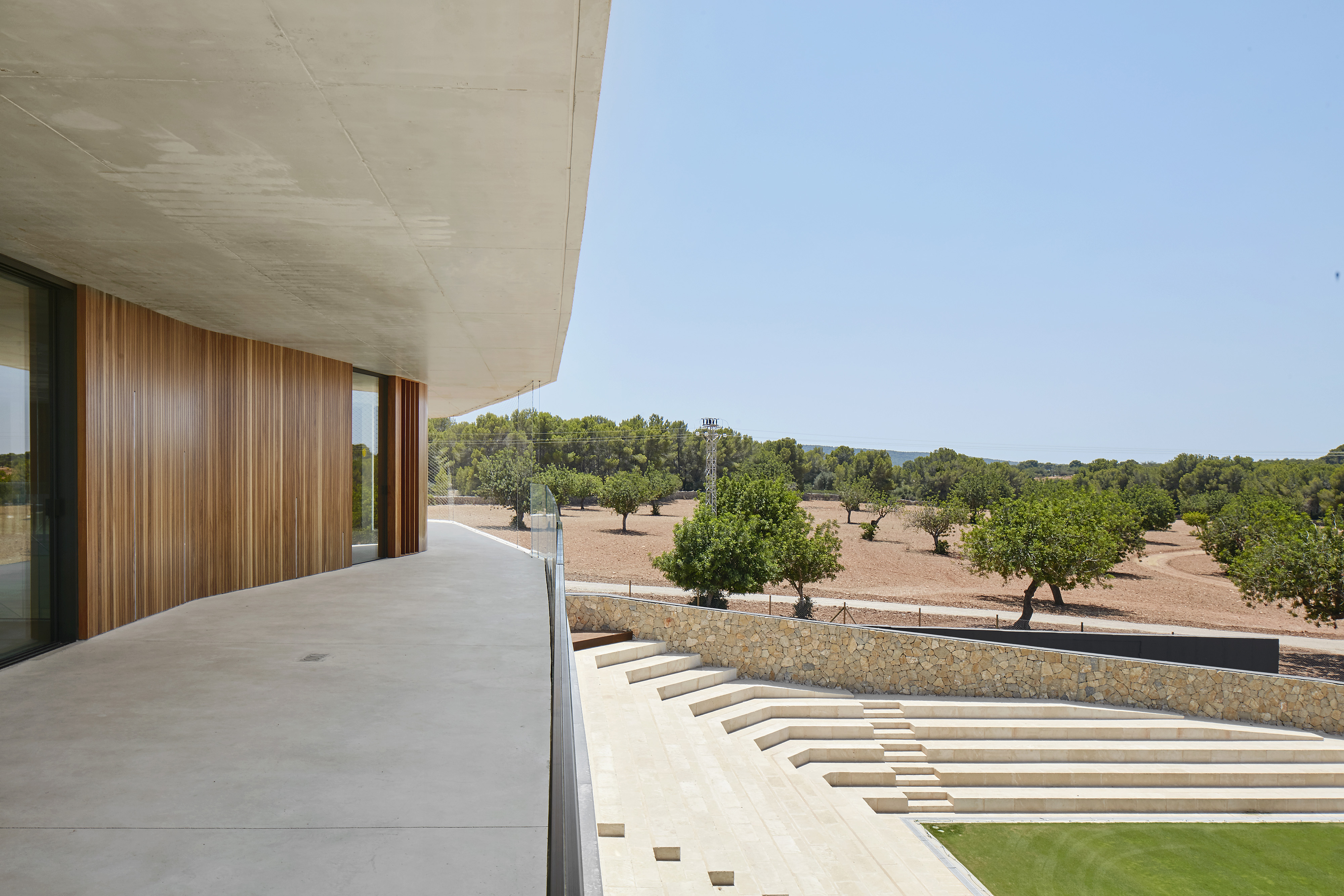





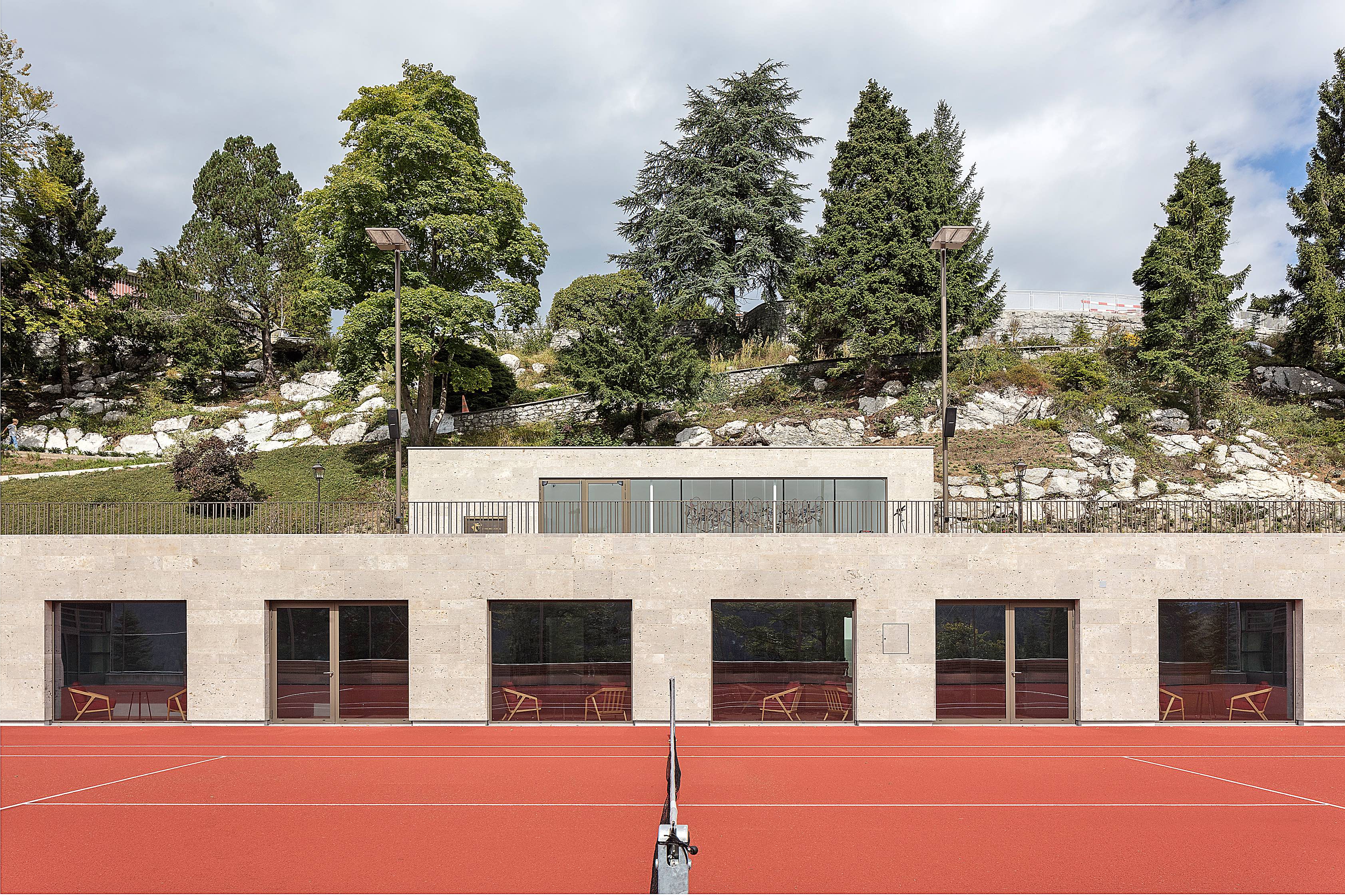
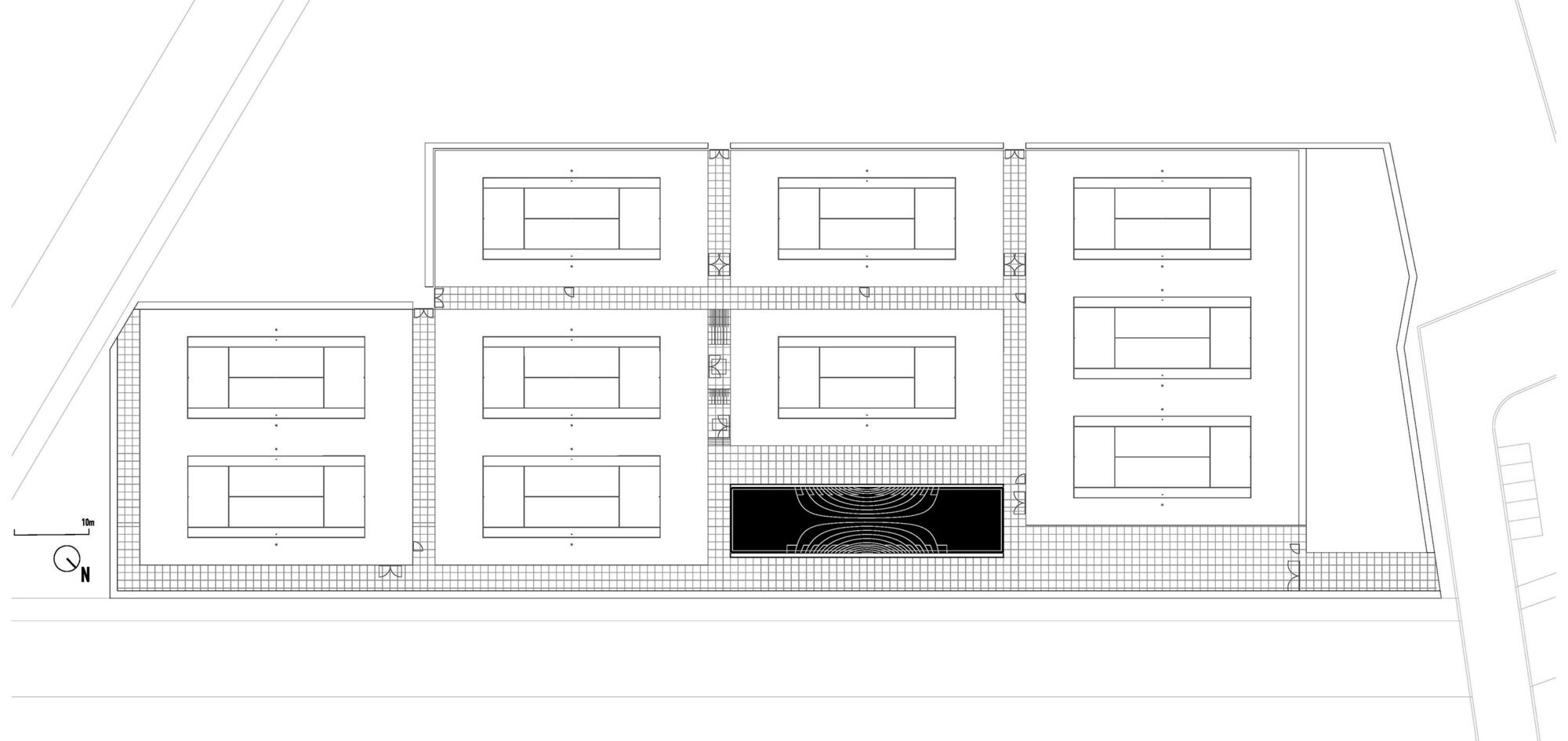
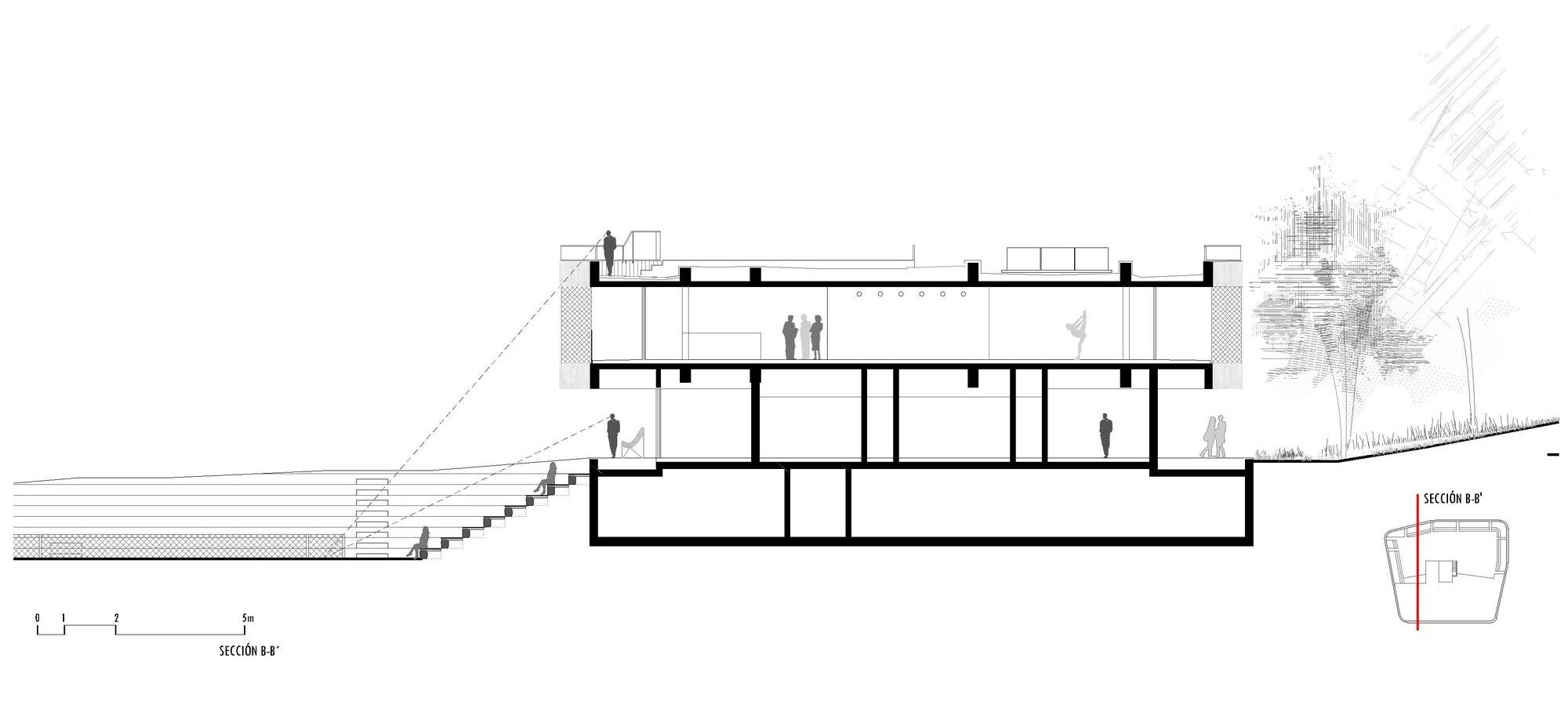 This elegant tennis facility is defined by white concrete and cantilevered slabs in Spain. The complex includes a total of seventeen courts of all surfaces, from grass to clay. The topography of the land called for a terracing strategy in order to place the different courts at different levels following the slope of the hill. As a result, the team set out to design the building as a continuation of that terracing: as seen in section, multiple floating terraces overlook the tennis compound. The Centre Court is the heart of the project. A series of terraces are carved in the hill create a natural stone stadium to seat up to 1500 spectators.
This elegant tennis facility is defined by white concrete and cantilevered slabs in Spain. The complex includes a total of seventeen courts of all surfaces, from grass to clay. The topography of the land called for a terracing strategy in order to place the different courts at different levels following the slope of the hill. As a result, the team set out to design the building as a continuation of that terracing: as seen in section, multiple floating terraces overlook the tennis compound. The Centre Court is the heart of the project. A series of terraces are carved in the hill create a natural stone stadium to seat up to 1500 spectators.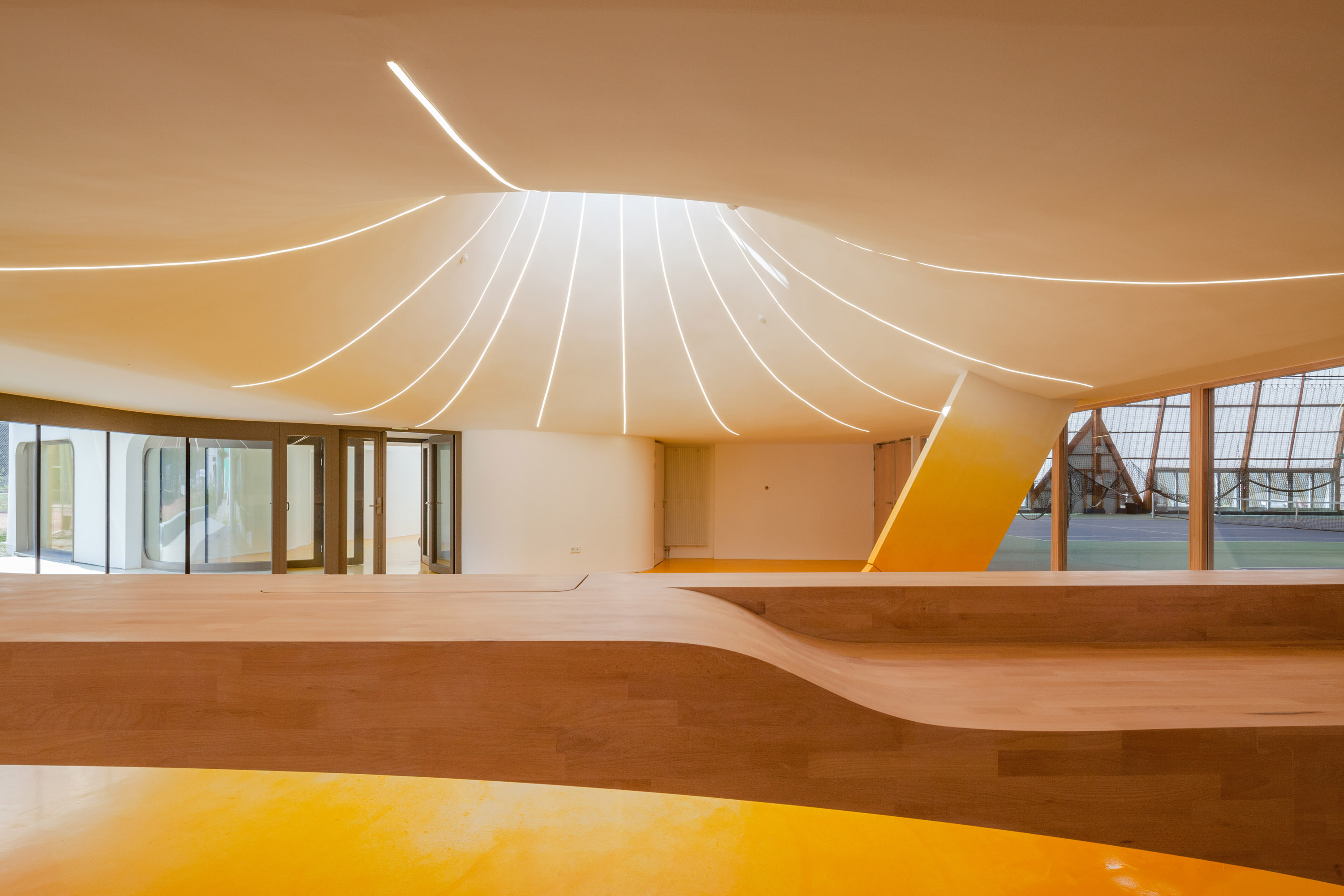
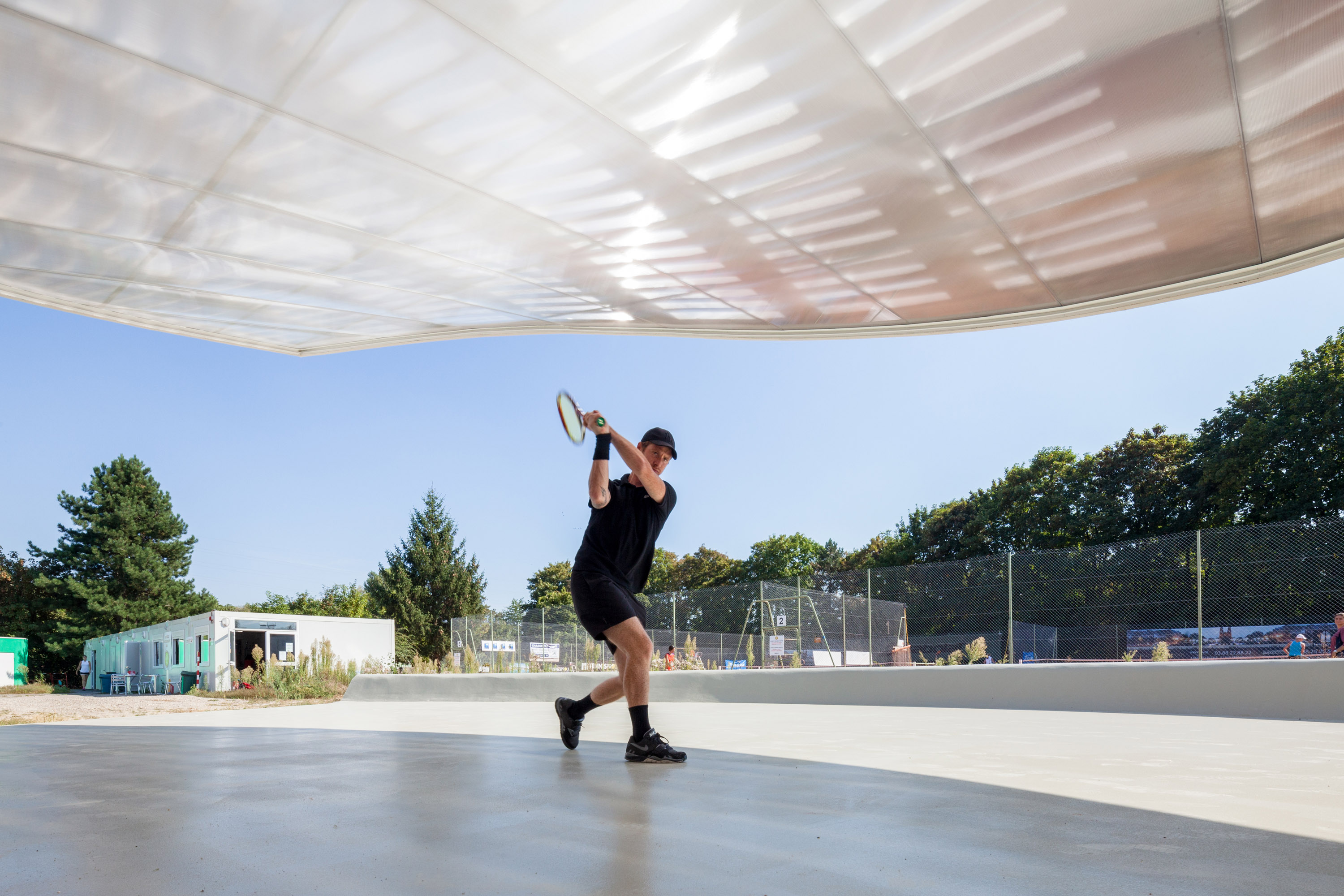
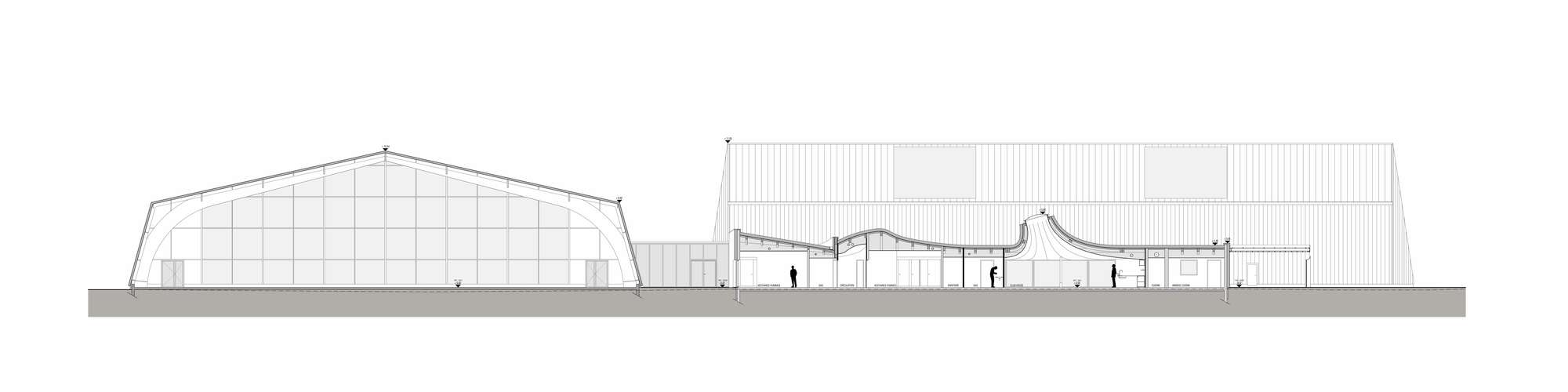
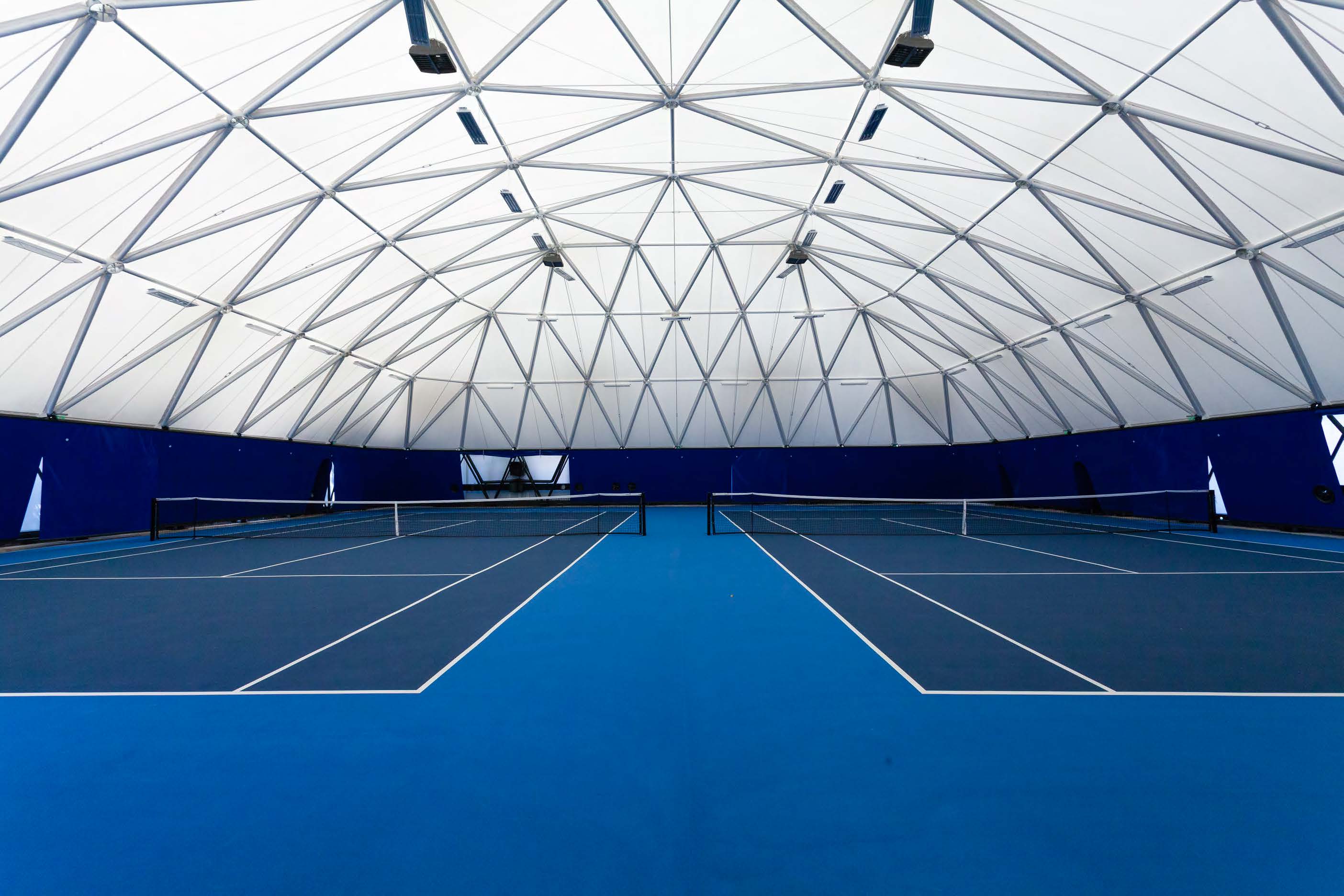
 In Strasbourg, the idea was to create a new tennis hall building for three covered tennis courts and and a new club house. The design is directly inspired by people and how they flow in and through the building. Inside, sky domes and a special color treatment on the floor was chosen to increase day light. Areas where natural light falls were treated with a beige resin, while the room borders and corners are treated with a deep orange resin. The soaring roof forms and domes are readily seen in section, and how the building compares in scale to adjacent structures.
In Strasbourg, the idea was to create a new tennis hall building for three covered tennis courts and and a new club house. The design is directly inspired by people and how they flow in and through the building. Inside, sky domes and a special color treatment on the floor was chosen to increase day light. Areas where natural light falls were treated with a beige resin, while the room borders and corners are treated with a deep orange resin. The soaring roof forms and domes are readily seen in section, and how the building compares in scale to adjacent structures.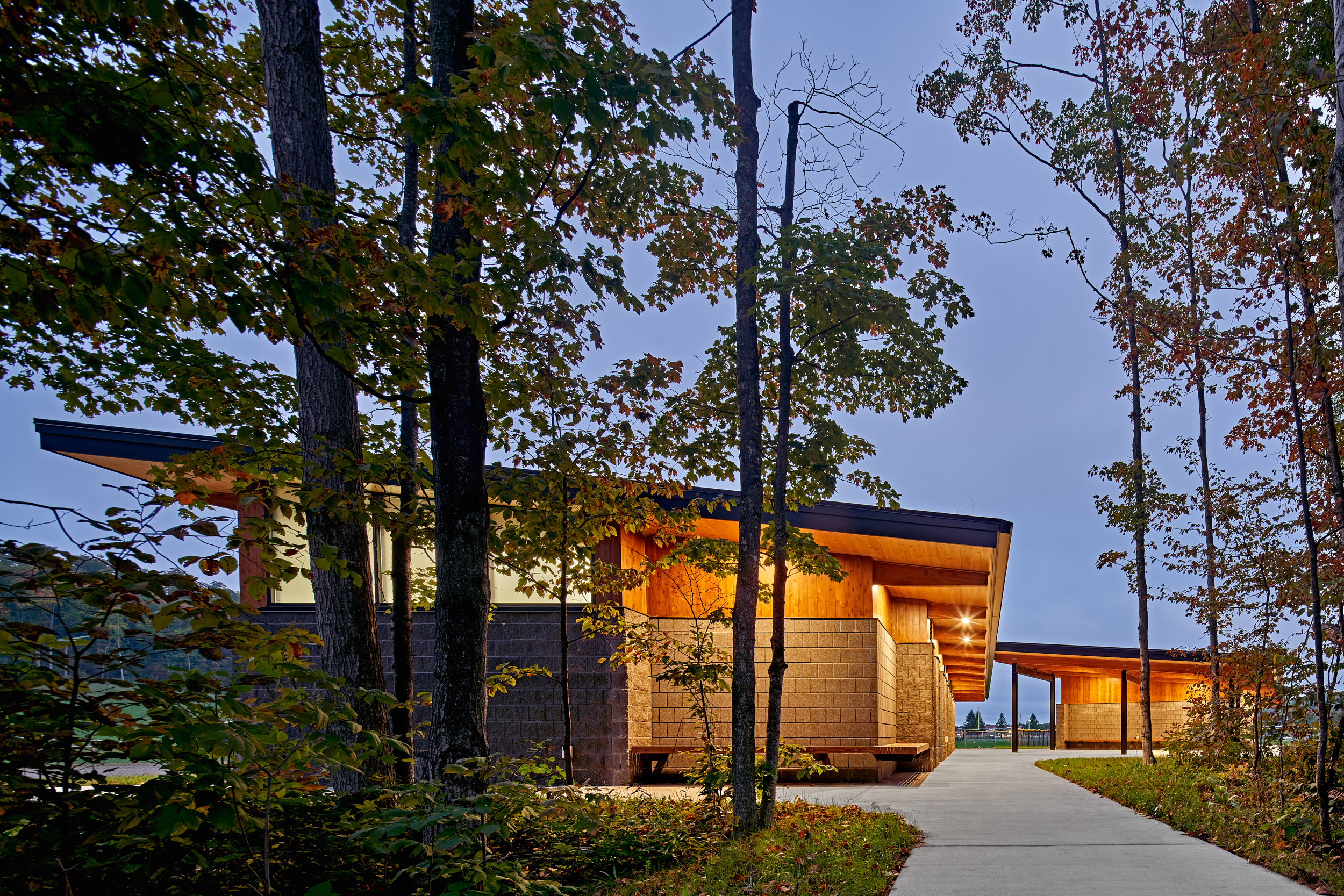
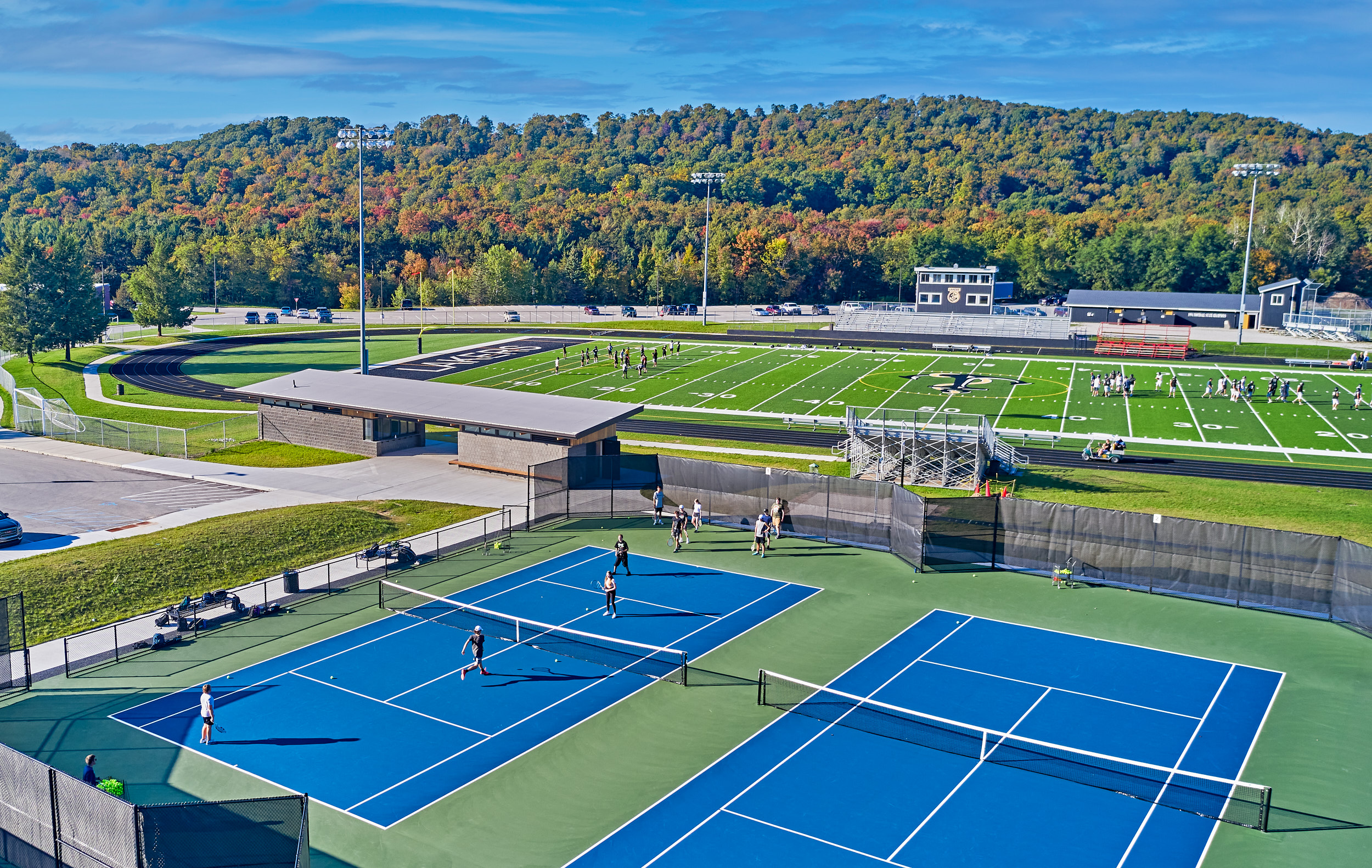

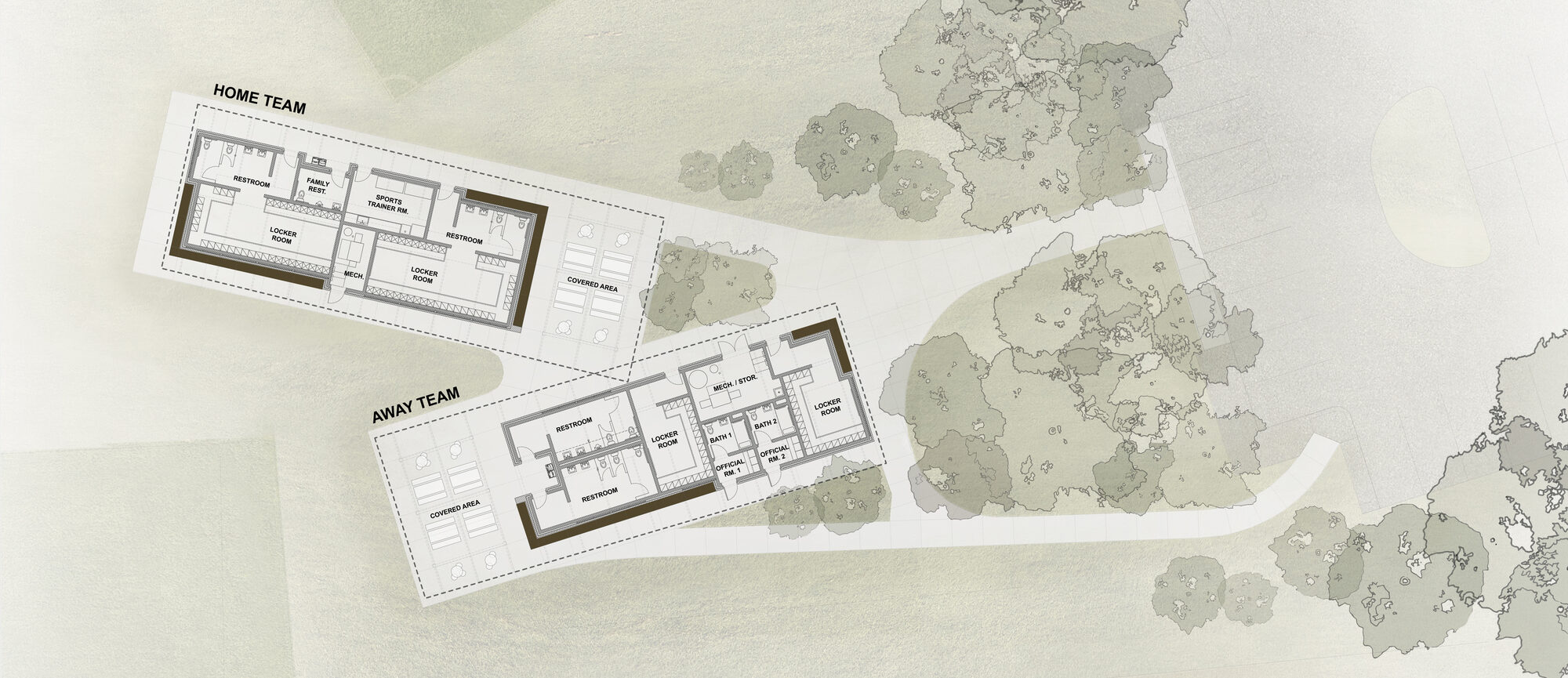 The Glen Lake Community Schools project was made with three components: a new bus garage; new team rooms for home team and visitor teams for soccer and softball; and a new tennis complex with a gateway building. The floor plan drawing for the team rooms showcases how the pavilion structures were organized and designed, emphasizing connection to the outdoors and with a series of welcoming overhangs. By opening to natural light, using natural materials like glulam beams, and the use of insulated roof panels, the team wanted to highlight the uniqueness of the Glen Lake community and its commitment to the natural environment and energy efficiency.
The Glen Lake Community Schools project was made with three components: a new bus garage; new team rooms for home team and visitor teams for soccer and softball; and a new tennis complex with a gateway building. The floor plan drawing for the team rooms showcases how the pavilion structures were organized and designed, emphasizing connection to the outdoors and with a series of welcoming overhangs. By opening to natural light, using natural materials like glulam beams, and the use of insulated roof panels, the team wanted to highlight the uniqueness of the Glen Lake community and its commitment to the natural environment and energy efficiency.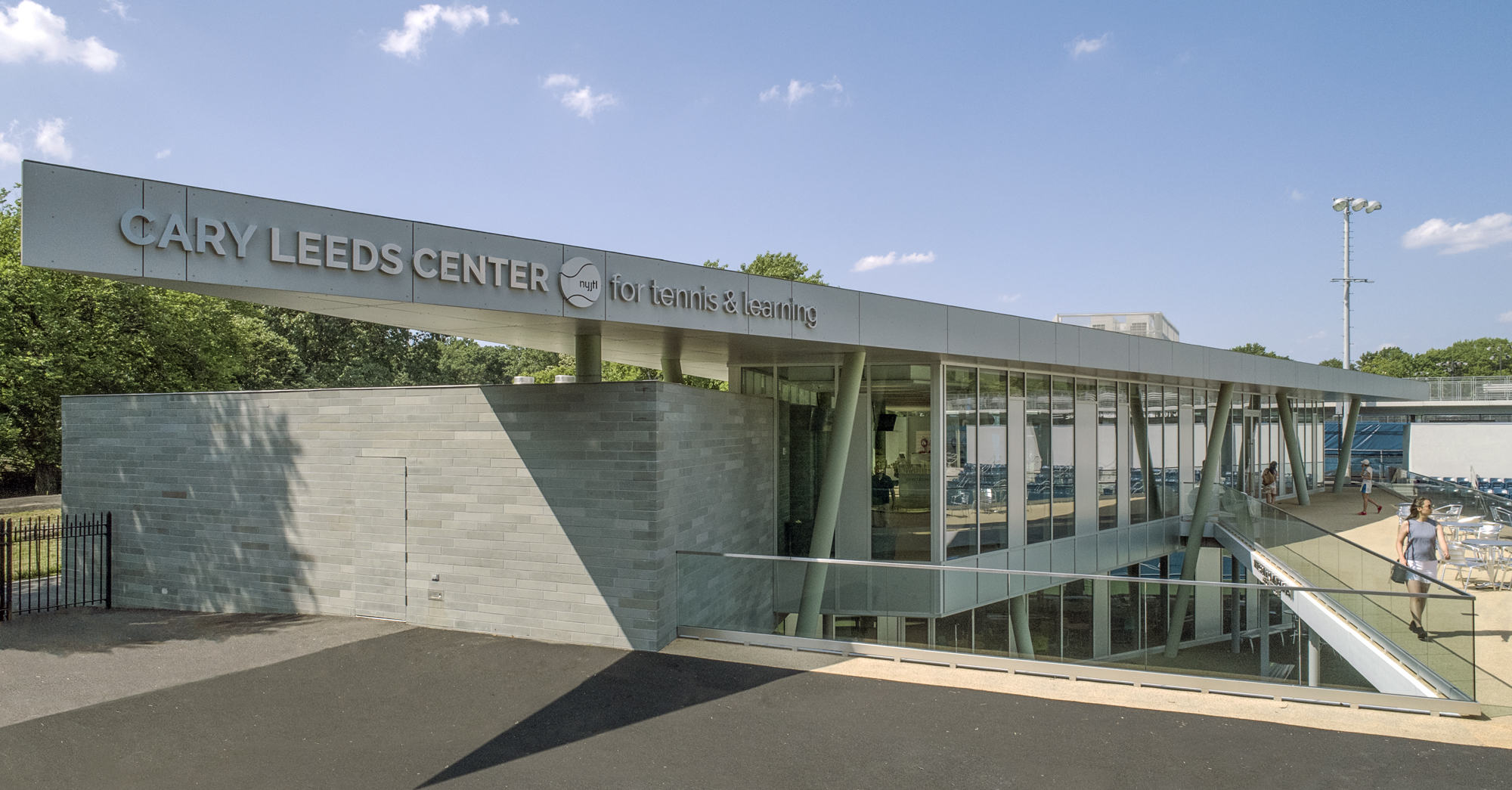
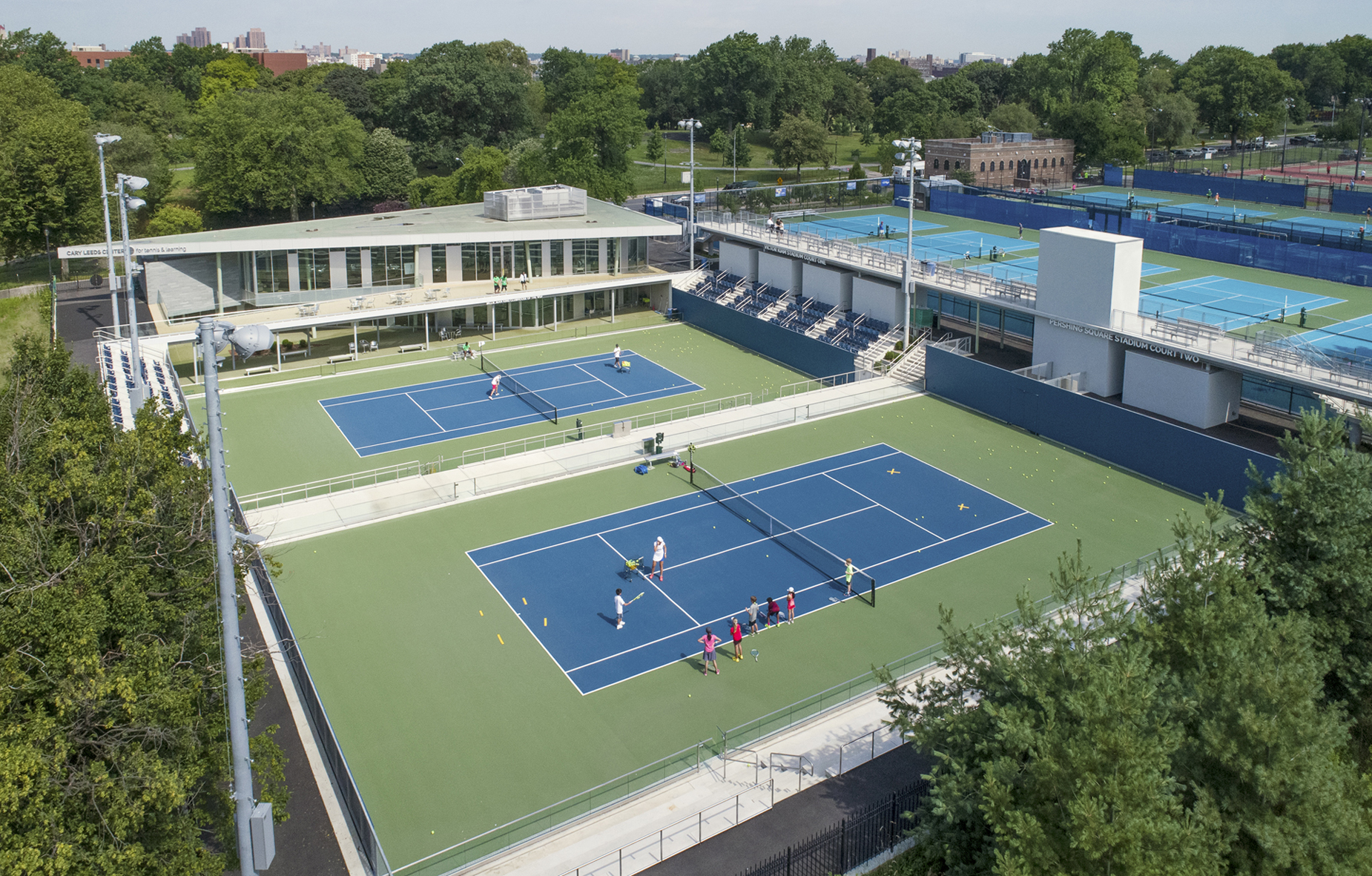

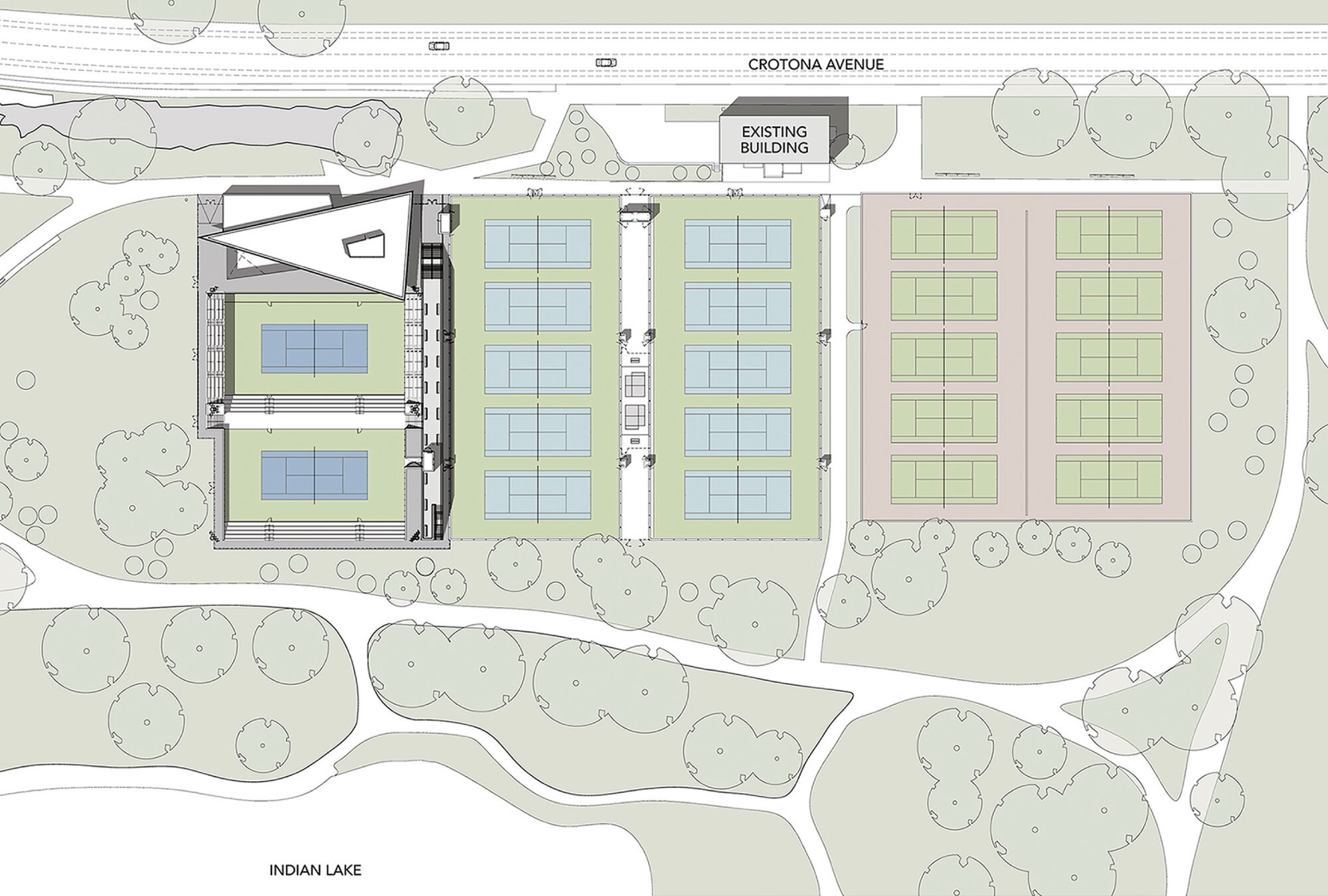 GLUCK+ designed the Cary Leeds Center for Tennis & Learning as a multi-use facility. The complex is where underserved youth in New York City can receive free tennis lessons and academic help. As the flagship site for New York Junior Tennis & Learning, the center was made to host local, national and international tournaments. Sited in the natural parkland of Crotona Park, the project included a clubhouse, public tennis courts, and sunken exhibition courts. The building and stadium courts were partially buried as a strategy to minimize the impact of a large structure in the park and also to take advantage of geothermal heating and cooling.
GLUCK+ designed the Cary Leeds Center for Tennis & Learning as a multi-use facility. The complex is where underserved youth in New York City can receive free tennis lessons and academic help. As the flagship site for New York Junior Tennis & Learning, the center was made to host local, national and international tournaments. Sited in the natural parkland of Crotona Park, the project included a clubhouse, public tennis courts, and sunken exhibition courts. The building and stadium courts were partially buried as a strategy to minimize the impact of a large structure in the park and also to take advantage of geothermal heating and cooling.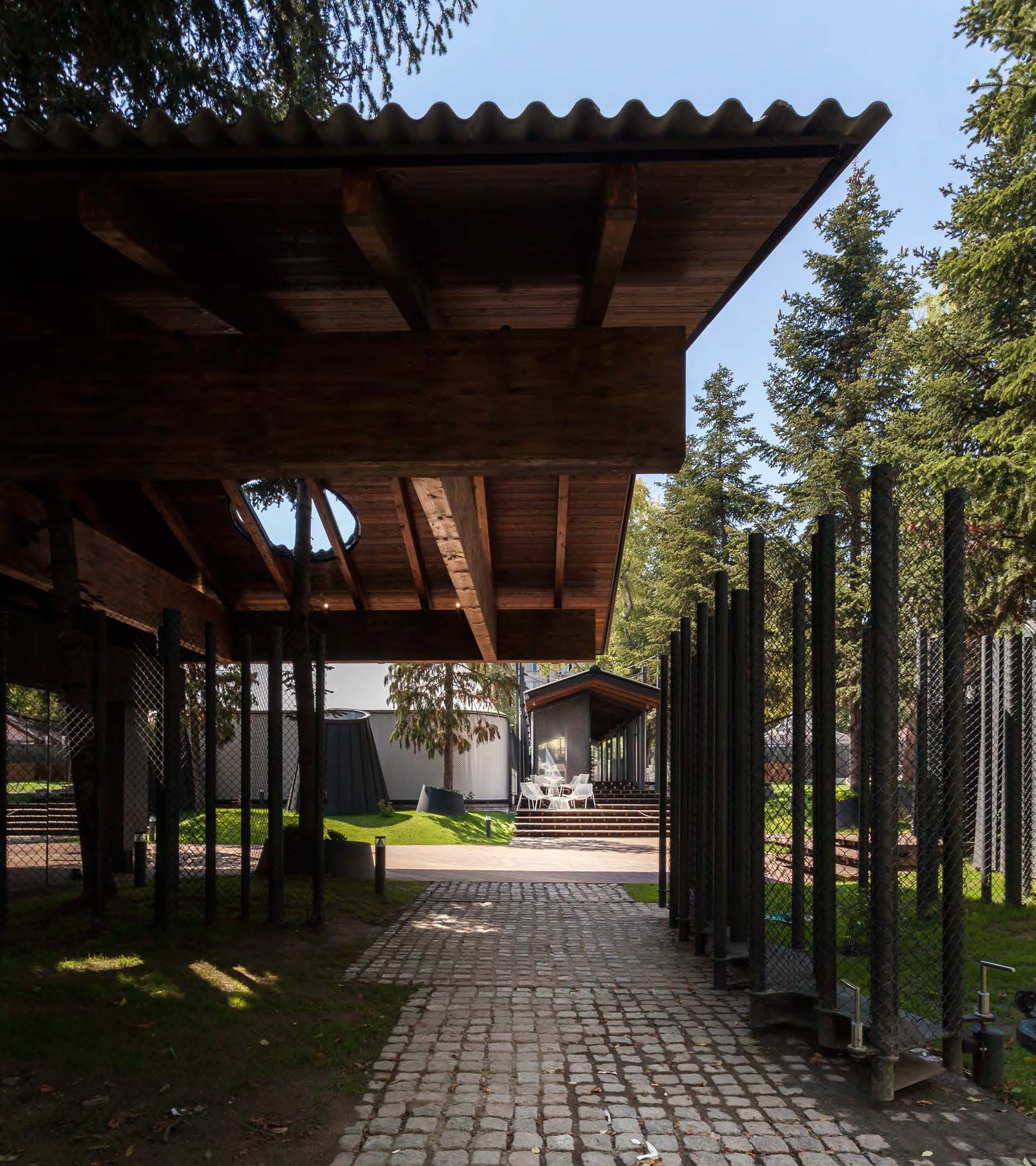
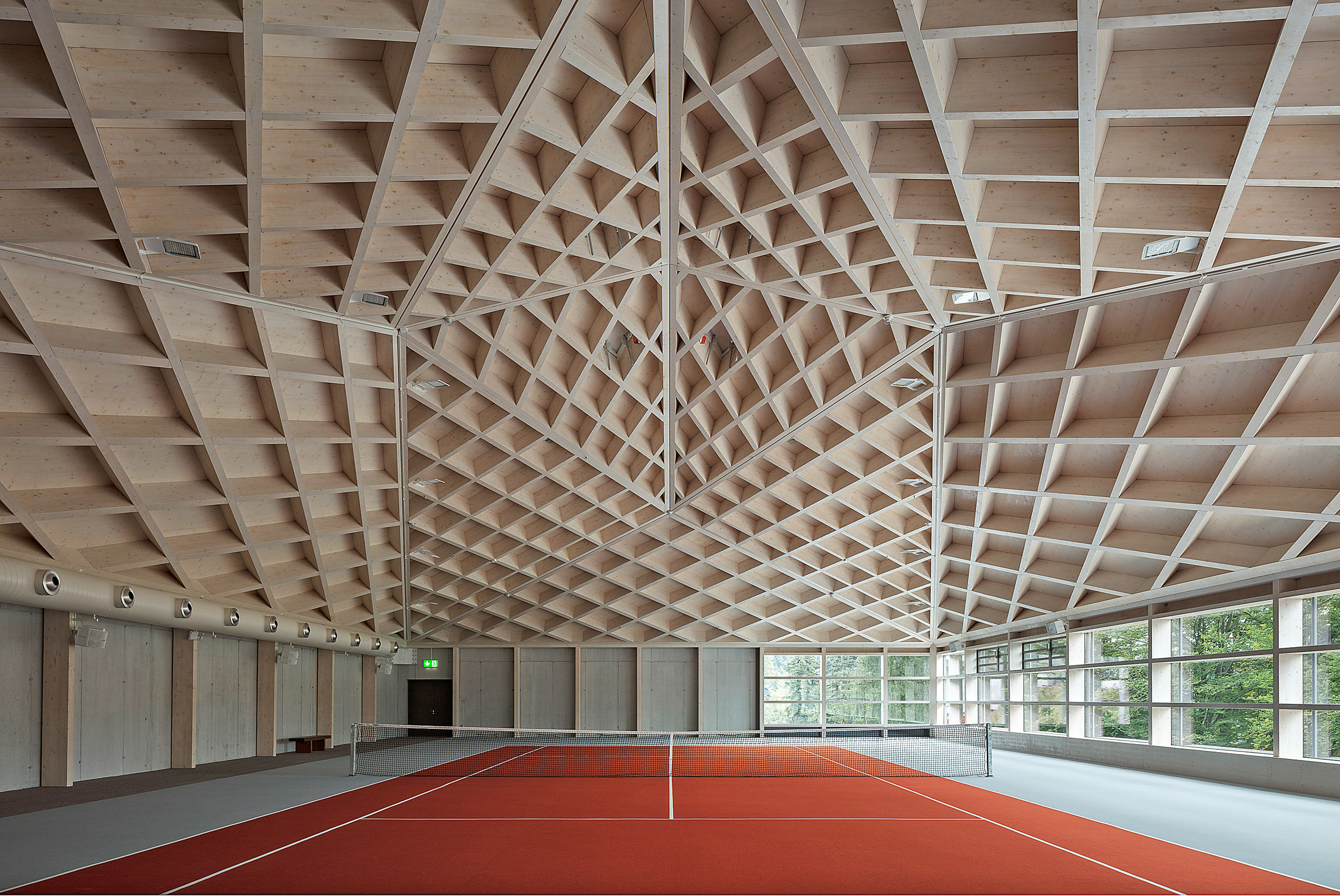

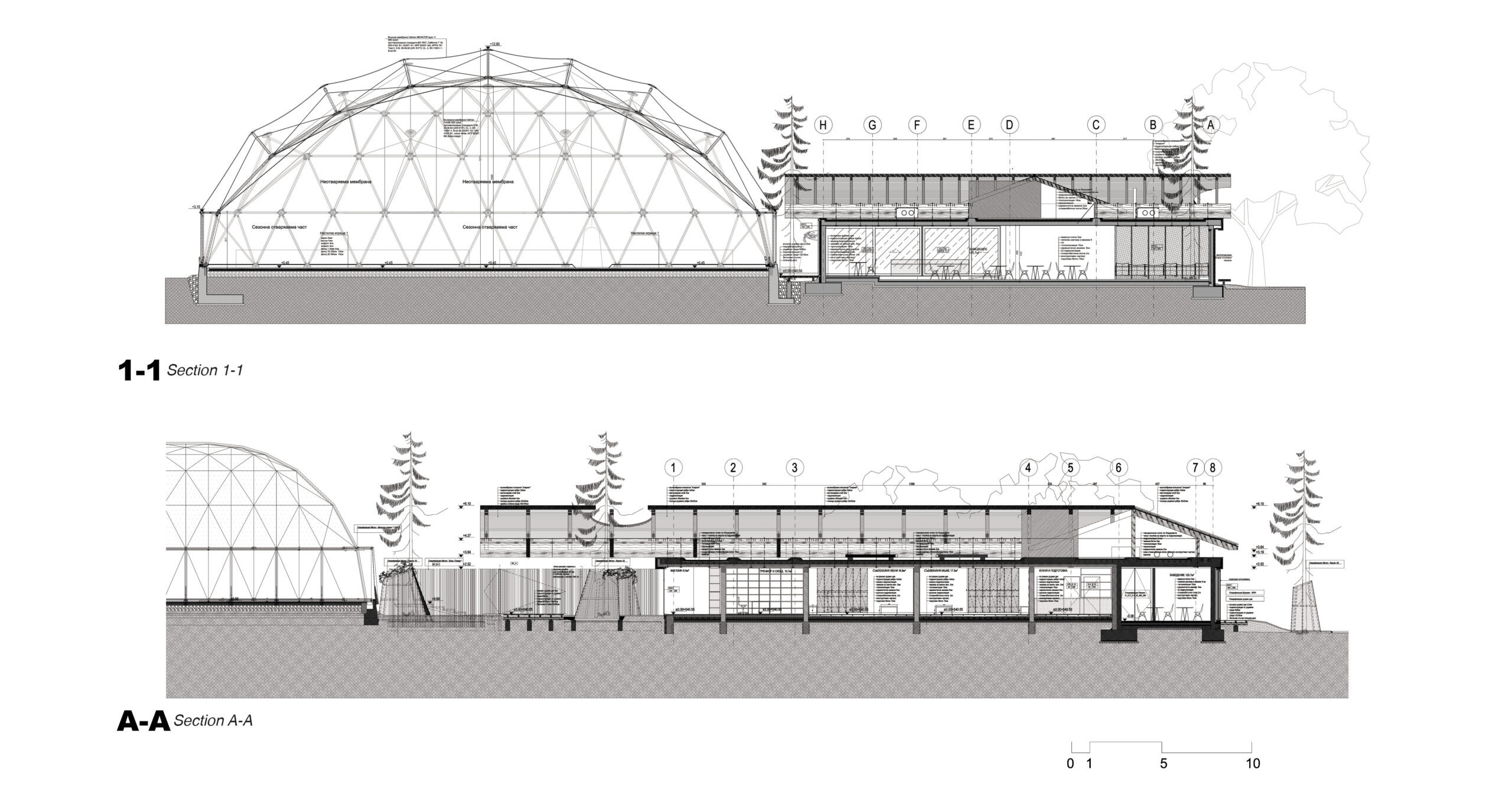


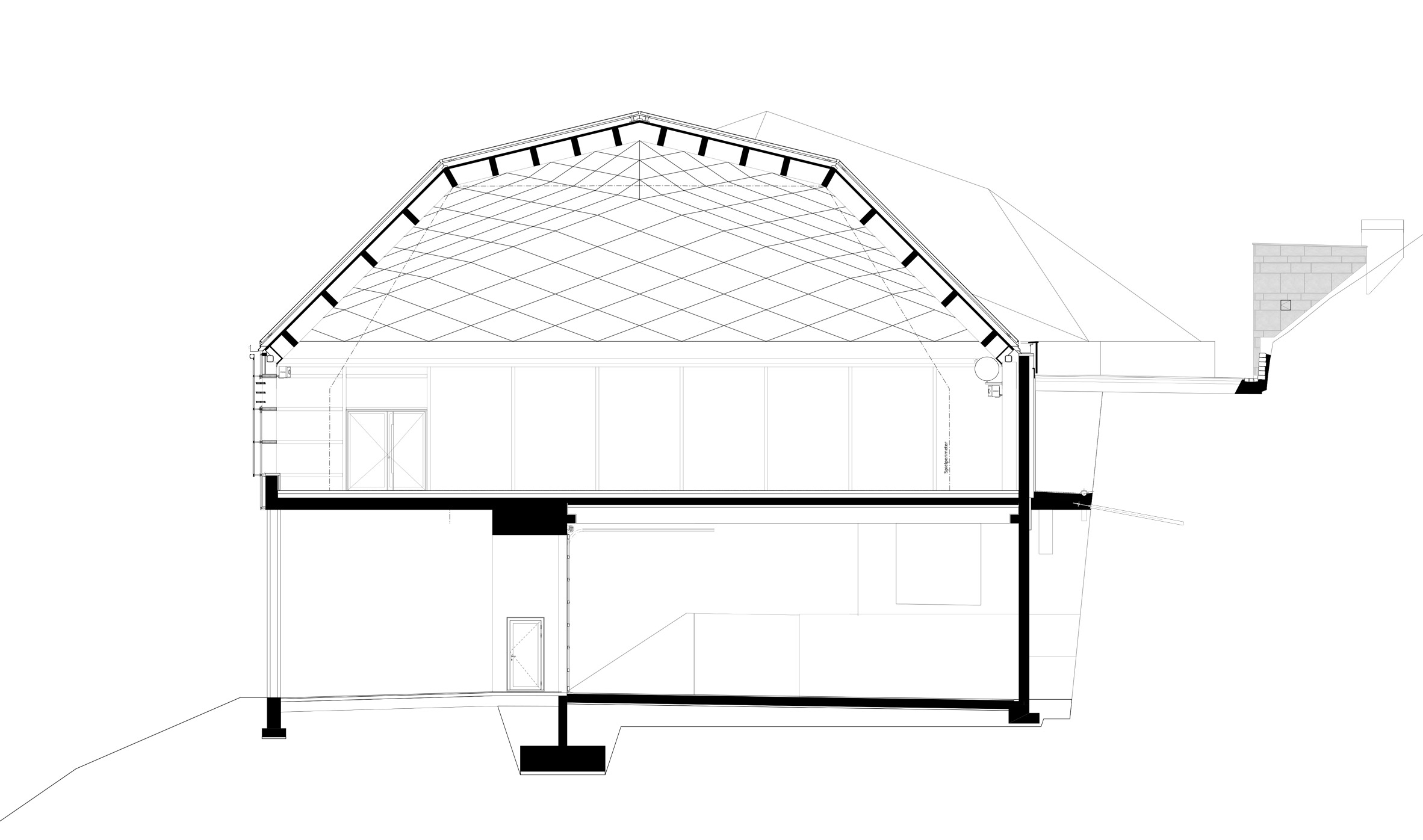 This temple to tennis was built in Switzerland. As seen in the drawings, the
This temple to tennis was built in Switzerland. As seen in the drawings, the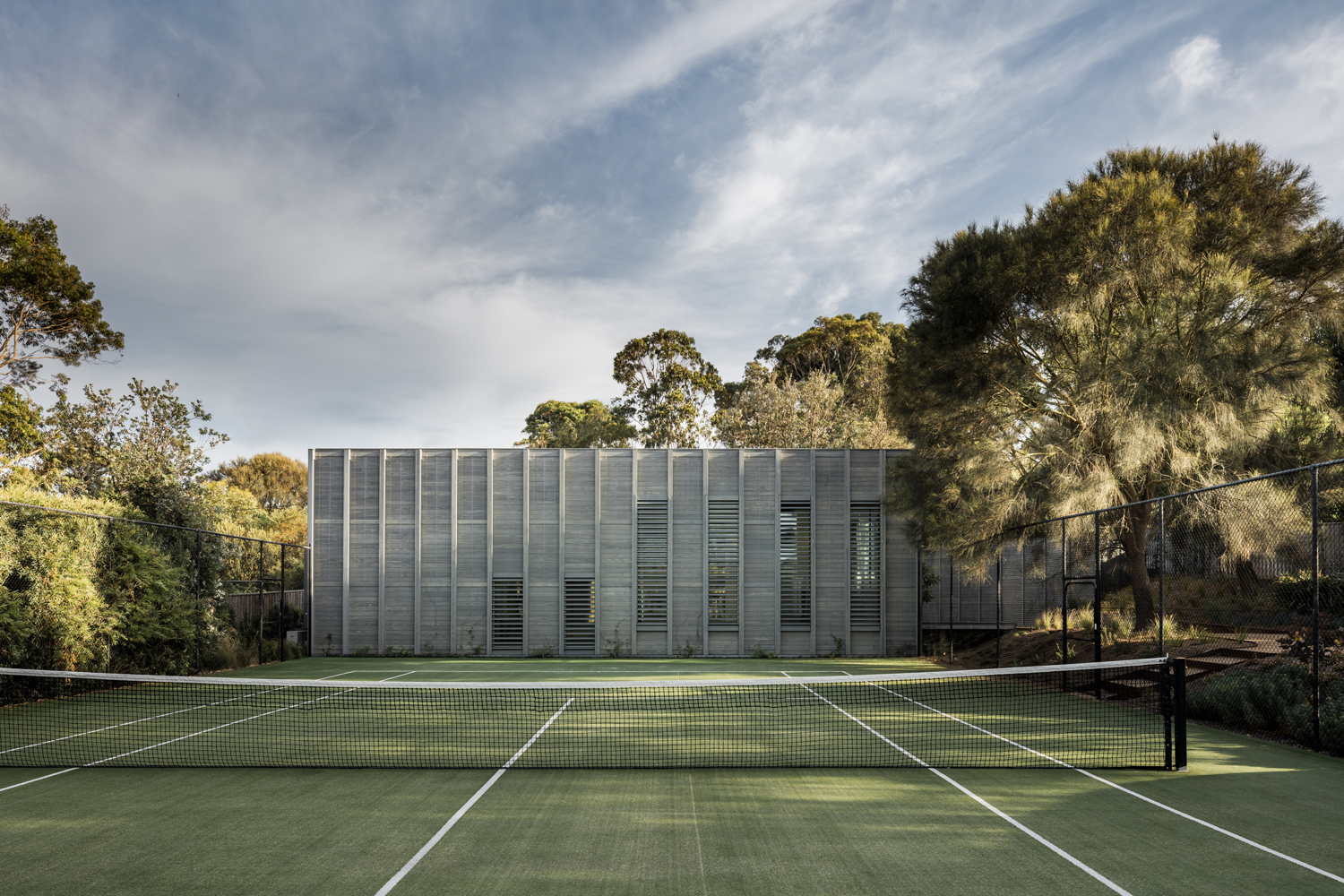 
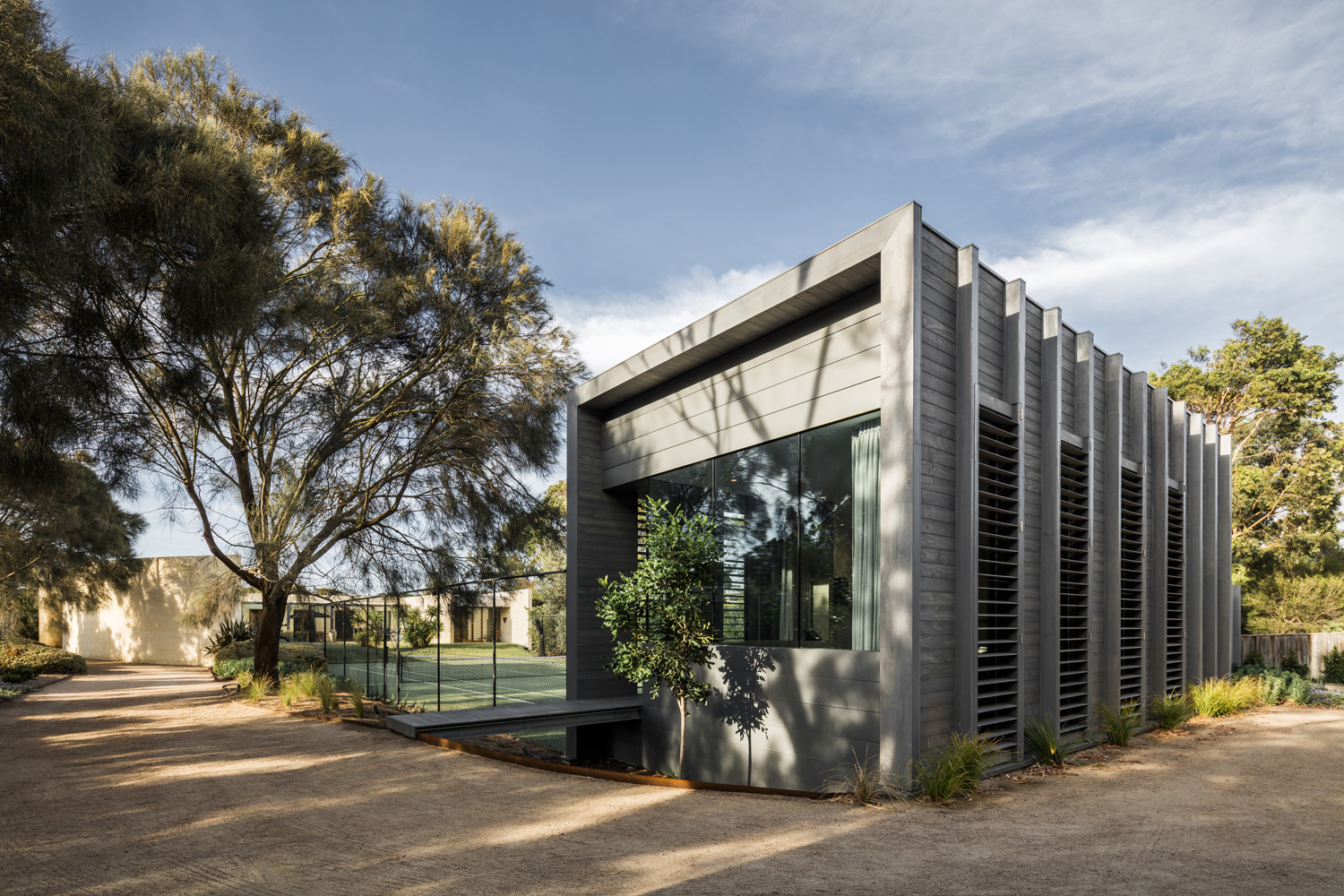

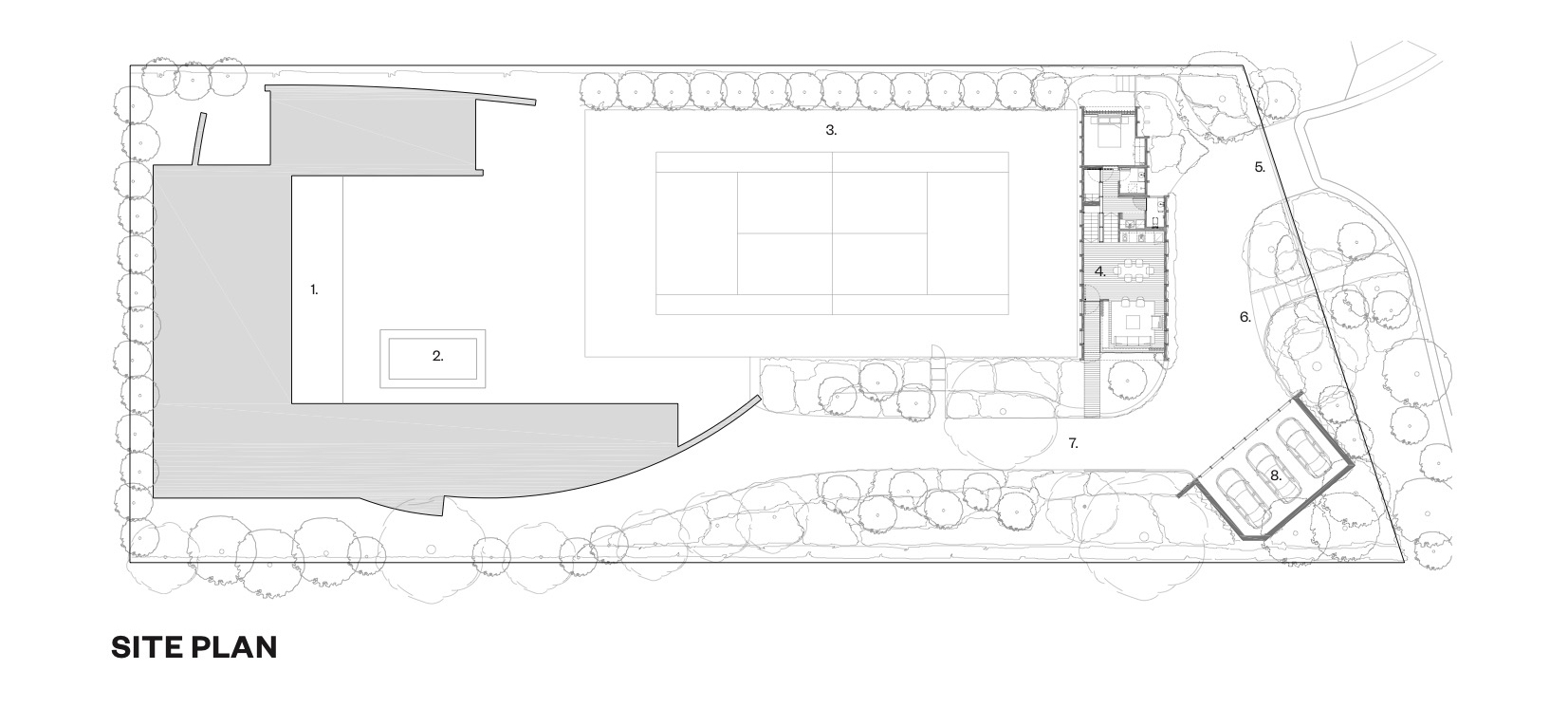 Adjacent to the court, this guest house is located within the grounds of an existing family beach house in a secluded coastal setting. The client required a guest house that would embrace the native landscape while establishing its own identity distinct from the existing house. The team’s design concept was to create a building as a landscape element that forms a backdrop to the existing tennis court and is nestled within the surrounding vegetation. A rectilinear timber pavilion was built with weathered grey cladding and climbers growing up over the walls to give the appearance of a simple timber fence within the landscape.
Adjacent to the court, this guest house is located within the grounds of an existing family beach house in a secluded coastal setting. The client required a guest house that would embrace the native landscape while establishing its own identity distinct from the existing house. The team’s design concept was to create a building as a landscape element that forms a backdrop to the existing tennis court and is nestled within the surrounding vegetation. A rectilinear timber pavilion was built with weathered grey cladding and climbers growing up over the walls to give the appearance of a simple timber fence within the landscape.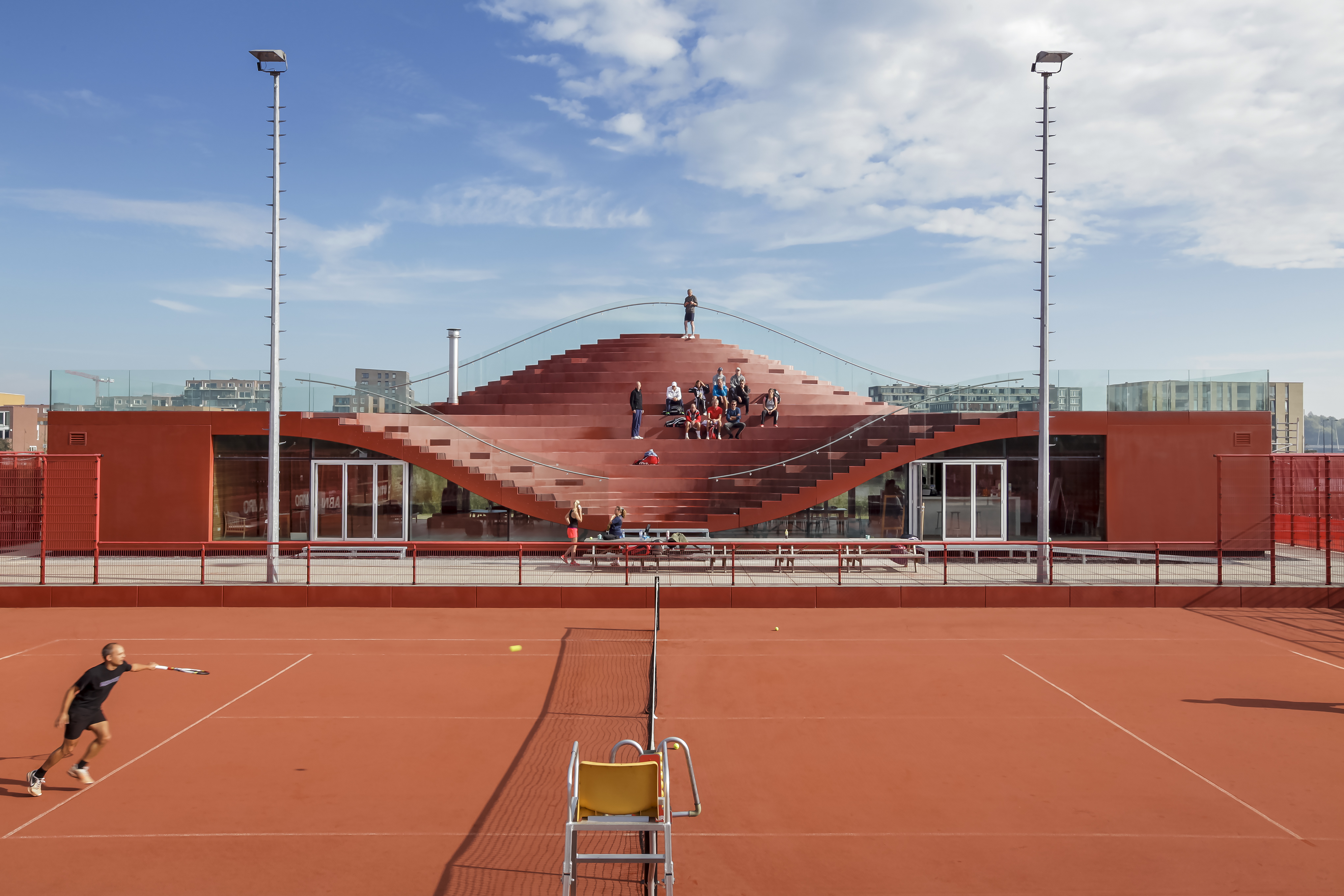

 MVRDV’s famous Couch project was built in IJburg, a new district to the east of Amsterdam. The newly formed IJburg Tennis Club included ten clay courts and a tennis school. The clubhouse was made to be the heart of the center, providing both a viewing platform and a club overlooking the water. The challenge was to create a building that worked as a central gathering area, a living room for IJburg. The result is a clubhouse with a roof dipping down towards the south and raised towards the north, creating an informal tribune for the club. Inside, the construction is clad with FSC-certified wood, with the outside fully sealed with an EPDM polymer hotspray in the same color and texture as the clay tennis courts.
MVRDV’s famous Couch project was built in IJburg, a new district to the east of Amsterdam. The newly formed IJburg Tennis Club included ten clay courts and a tennis school. The clubhouse was made to be the heart of the center, providing both a viewing platform and a club overlooking the water. The challenge was to create a building that worked as a central gathering area, a living room for IJburg. The result is a clubhouse with a roof dipping down towards the south and raised towards the north, creating an informal tribune for the club. Inside, the construction is clad with FSC-certified wood, with the outside fully sealed with an EPDM polymer hotspray in the same color and texture as the clay tennis courts.