The world’s largest flow battery energy storage system

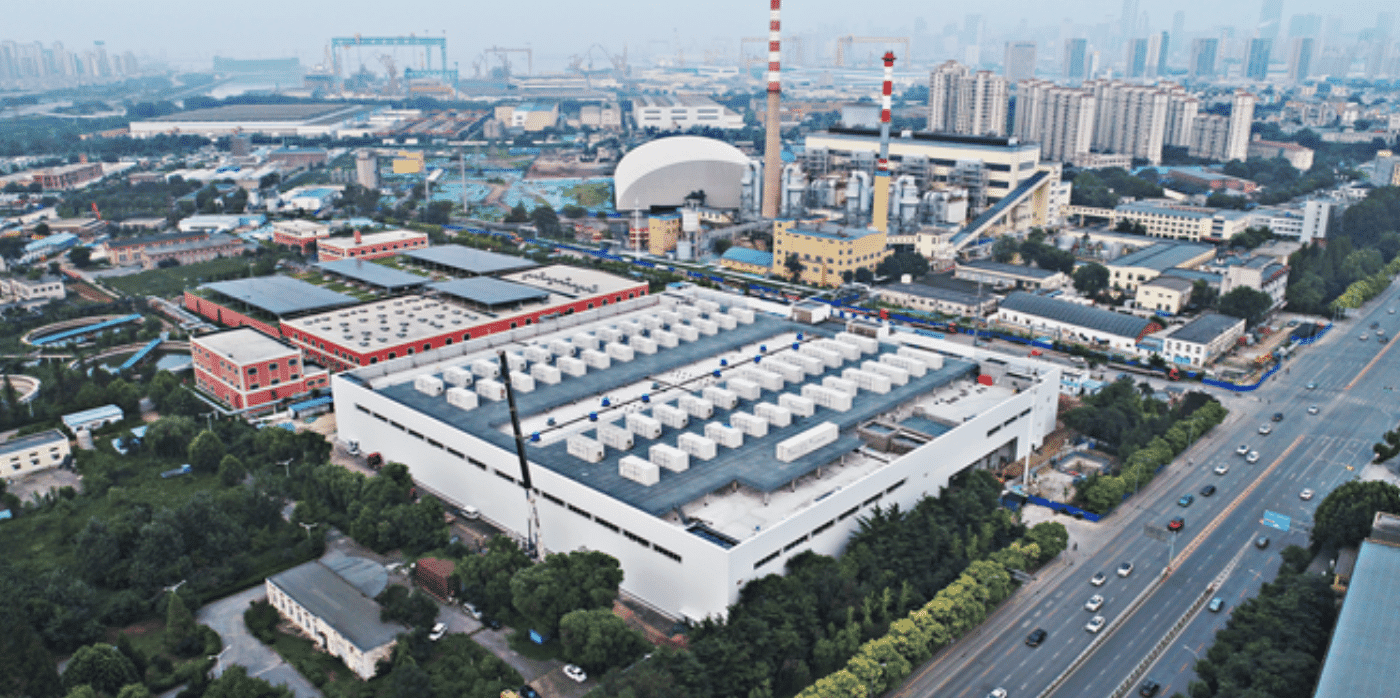
Spotted: As the world strives to achieve carbon neutrality, energy storage technology is becoming increasingly important. Renewable energy sources like wind and solar power are intermittent, meaning they’re not always available when needed. Energy storage can help to even out these fluctuations, making renewables a more reliable and consistent source of power. One of the largest energy storage projects in the world is currently being completed in Dalian, China.
The Dalian Flow Battery Energy Storage Peak-shaving Power Station will have a capacity of 100 megawatts/400 megawatt-hours, making it one of the largest storage facilities in terms of both power and capacity. The project is due to be completed in mid-October and will play an important role in helping China meet its climate goals.
The Dalian Power Station, which is based on vanadium flow battery technology developed by the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP), will serve as the city’s power bank while helping Dalian make use of renewable energy – such as wind and solar energy. The Power Station will convert electrical energy into battery-stored chemical energy and back into electrical energy, providing a reliable source of power for the city.
The power station plans to meet the daily electricity demand of about 200,000 residents. Looking ahead the aim is for these numbers to increase as the power station eventually produces 200 megawatts/800 megawatt-hours of electricity. The Power Station is an important step in Dalian’s transition to a clean energy future, and it is hoped that it will help to make the city a model for others in China and around the world.
The roll-out of renewables is gathering pace and with that roll-out comes innovation in energy storage. Springwise has recently spotted innovations such as a thermal energy storage system and a new system that stores energy in the form of heat and compressed air.
Written By: Katrina Lane