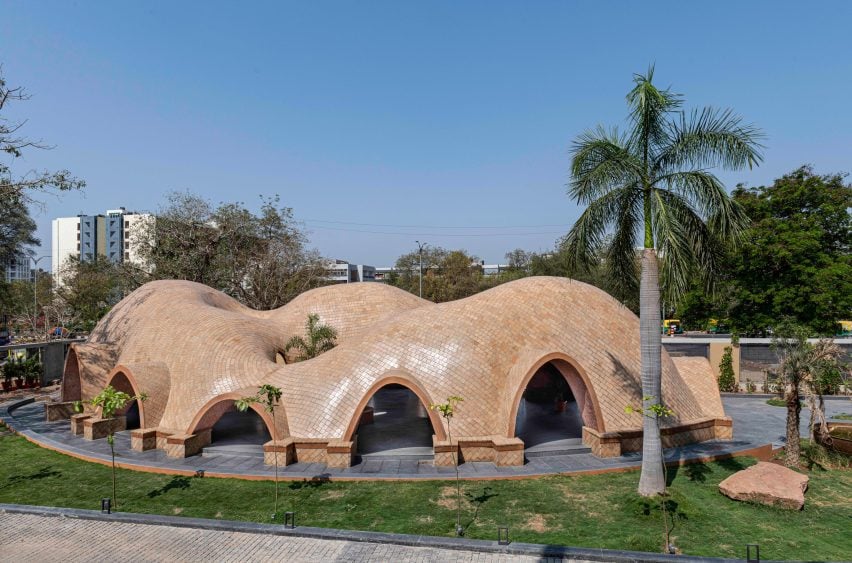
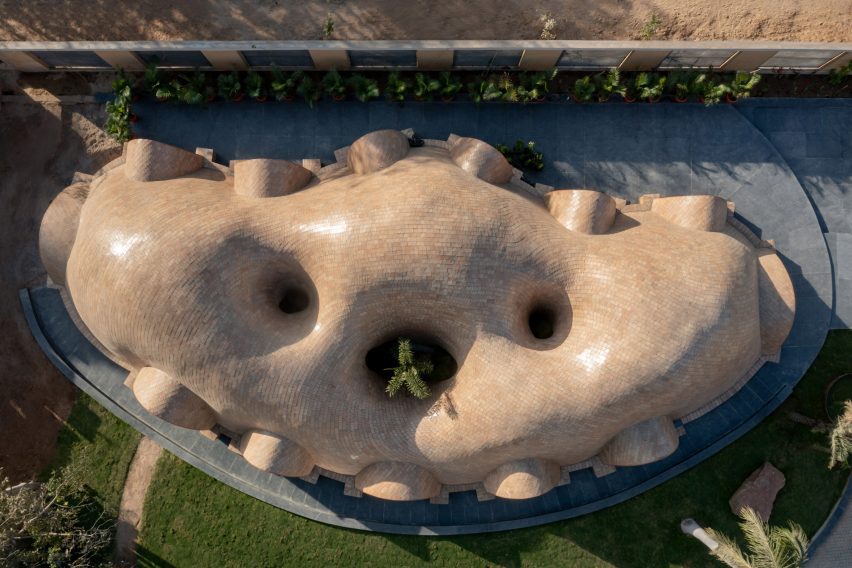
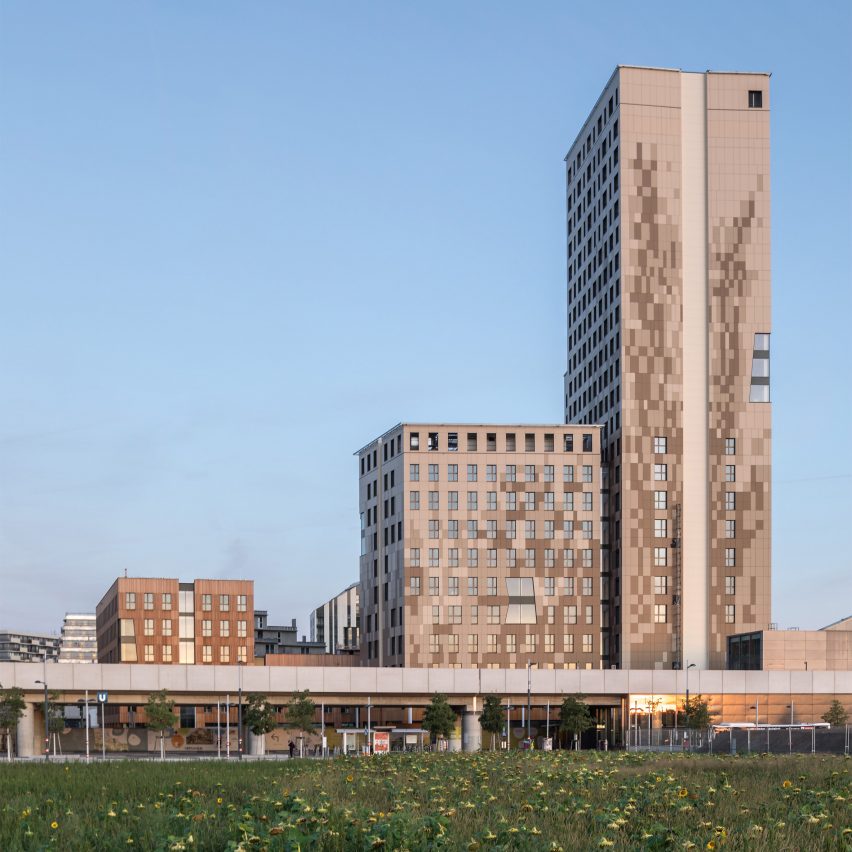
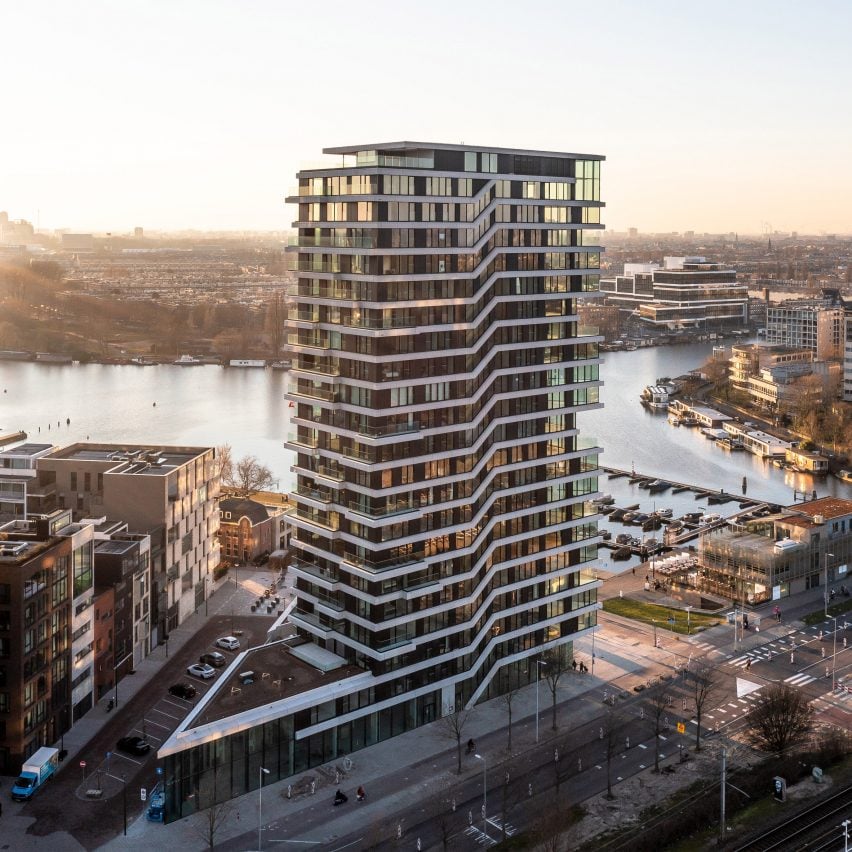
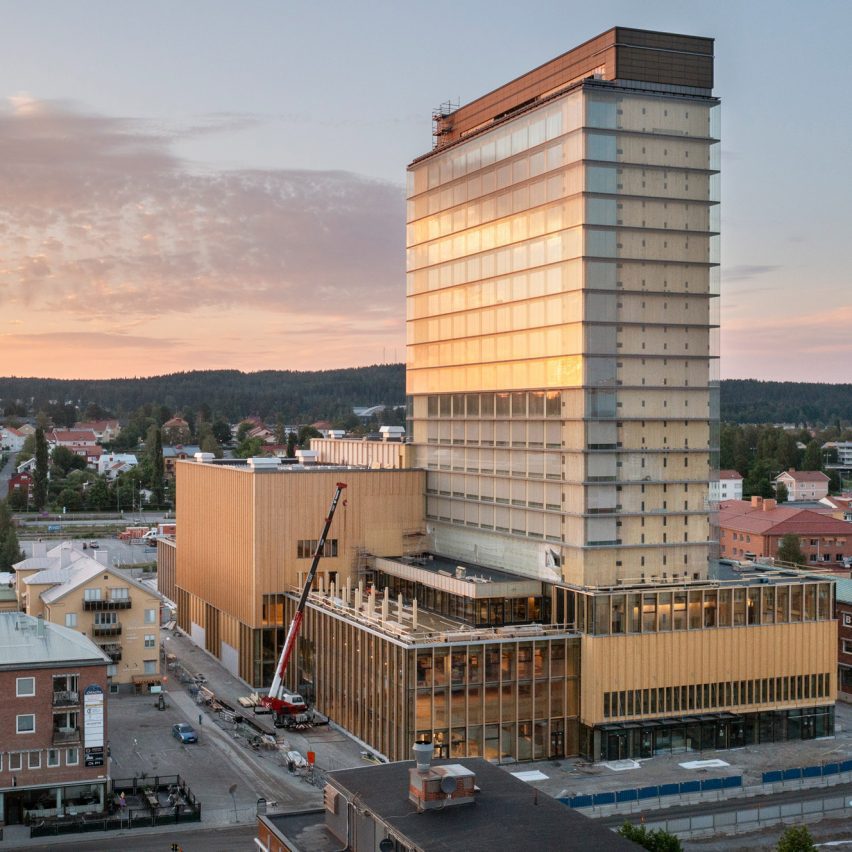
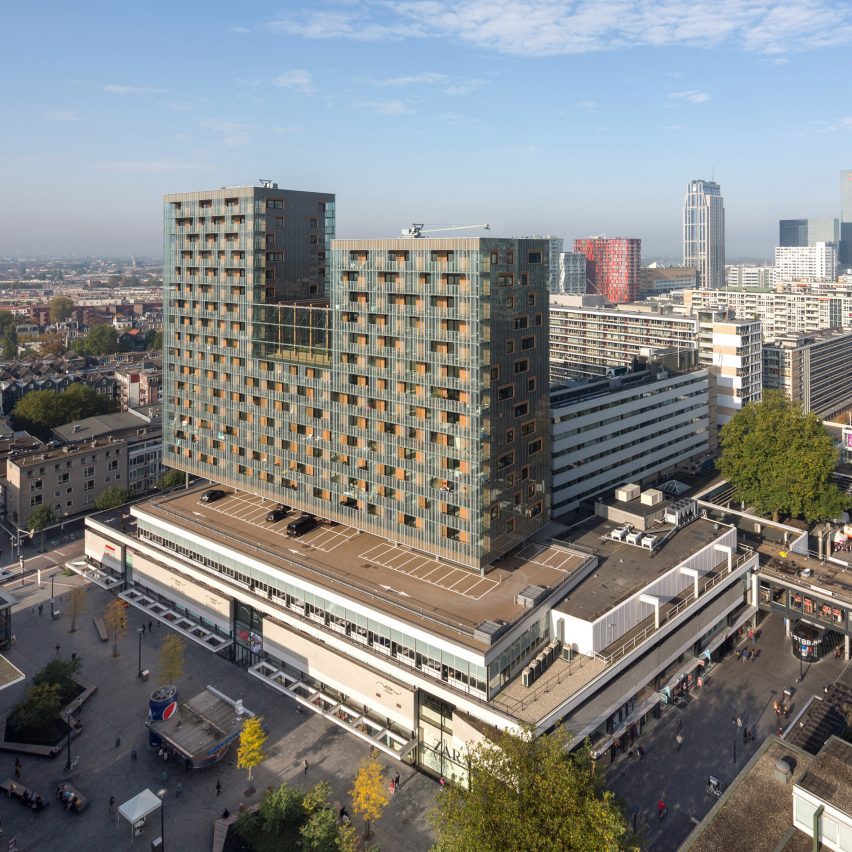
Architizer’s global architectural awards program, the 12th Annual A+Awards, is now accepting submissions, with a Main Entry Deadline of December 15th, 2023. As well as celebrating some of the most innovative, recently completed projects around the globe, the A+Awards also serve as an incredible indicator of which designers will be at the forefront of innovation in the coming year.
In recognition of this fact, Architizer is delighted to present the much-anticipated fifth edition of the coveted A+List, an annual rundown of every firm that scooped an A+Award and A+Firm Award in the previous season. The A+List forms a comprehensive guide to the world’s best architecture firms and is refreshed each year based on the results of the annual A+Awards program. You can see last season’s A+List here.
The A+List is arranged alphabetically, with more information available by clicking on the link to each firm’s profile. We’ve also curated a selection of featured firms, providing some extra background on their A+Award triumphs.
Get Your Firm On the Next A+List
If you missed entering last season’s program and would like to secure your position on the next A+List, we encourage you to enter your firm’s recent projects in the 12th Annual A+Awards. Every winner features in this definitive directory of high-quality firms, and will also see their work published in a stunning, hardbound compendium on the World’s Best Architecture, as well as gaining continual publicity through our year-round global celebration of design.
Start Submission
Without further ado, explore the work of each of these immensely talented firms below, and good luck with your submissions to this year’s program!
AD ARCHITECTURE
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Art
Adjaye Associates
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Multi Unit Housing – High Rise (16+ Floors)
Aidlin Darling Design
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Mixed Use (S <25,000 sq ft.)
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Private House (XL >6000 sq ft)
Alencar Arquitetura
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt – Multi-Unit Housing (S <10 Floors)
all(zone)
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Color
Altura Architects
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Private House (S 1000 – 2000 sq ft)
ANT ARCH
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +For Good

Longmenshan Town · Woyun Platform by Archermit, Peng Bai Lu, Peng Zhou Shi, Cheng Du Shi, China | Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Cultural & Expo Centers
Founded in 2015, this Chengdu-based firm has achieved a considerable amount before reaching its first decade milestone. Archermit’s core concept is to create new multidimensional spatial experiences. This is evident in the poetic environments they create, which break the mold of traditional architectural forms and massing; theirs is an exploration of the contemporary and locality of Chinese architecture. Across their work is an emphasis on reconfiguring the relationship between building users and the surrounding environment. While embracing modern technology, the firm celebrates unique local architectural expression.
Archi-Tectonics
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Innovation
ARCHITECTS 49
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best Large Firm (41+ employees)
Arsh 4D Studio
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt – Multi-Unit Housing (L >10 Floors)
ASAS arkitektur AS
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Multi Unit Housing – Low Rise (1 – 4 Floors)
ASPECT Studios
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best Landscape Design Firm
B² Architecture
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Commercial Interiors (<25,000 sq ft.)
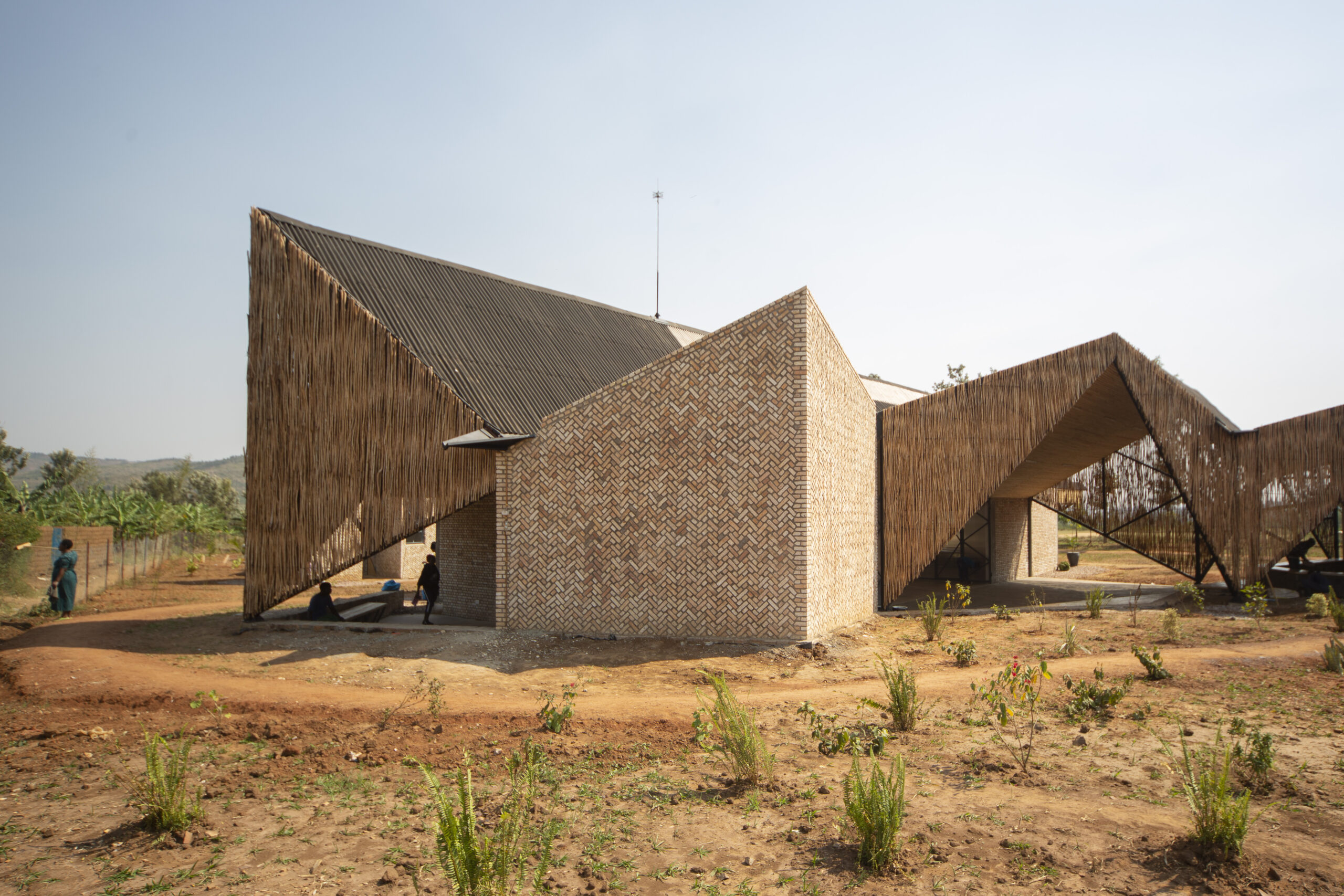

Komera Leadership Center by BE_Design, Rwanda | 11th Annual A+Awards: Jury Vote Winner in Architecture +For Good; Jury Vote & Popular Choice Winner in Architecture +Low Cost Design; Jury Vote Winner in Architecture +Community; Popular Vote Winner in Community Centers
After living in Rwanda for several years, Bruce Engel founded BE_DESIGN in 2016 upon his return to New York. The team comprises Alain Yves Twizeyimana, Emmanuel Havugimana, Aziz Farid Shyaka, and Marie Minerve Dukunde. Together, the five are creating progressive educational and community projects that serve rural and underprivileged areas in Rwanda, Tanzania, Kenya, and Ghana. The young firm is already garnering awards and recognition for their incredibly intricate fusion of local artistic traditions, talents and techniques with program brief and architectural form. Exemplified in the Komera Leadership Center, which swept at the 11th Annual A+Awards, this firm is one to keep a close eye on.
Beijing AN-Design Architects
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Residential Renovations & Additions
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Urban & Masterplan
Birdseye
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Gallery & Exhibition Spaces
Blue Temple
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best X-Small Firm (1 – 5 employees)
BRAG Arquitectos
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Multi Unit Housing – High Rise (16+ Floors)
Bureau Fraai
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Residential Interiors (>3000 sq ft)
CAA
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Sustainable Sports & Recreation Building
CAZA
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Religious Buildings & Memorials
Cumulus Studio
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Bars & Wineries
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Cultural & Expo Centers
D/DOCK
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Coworking Space
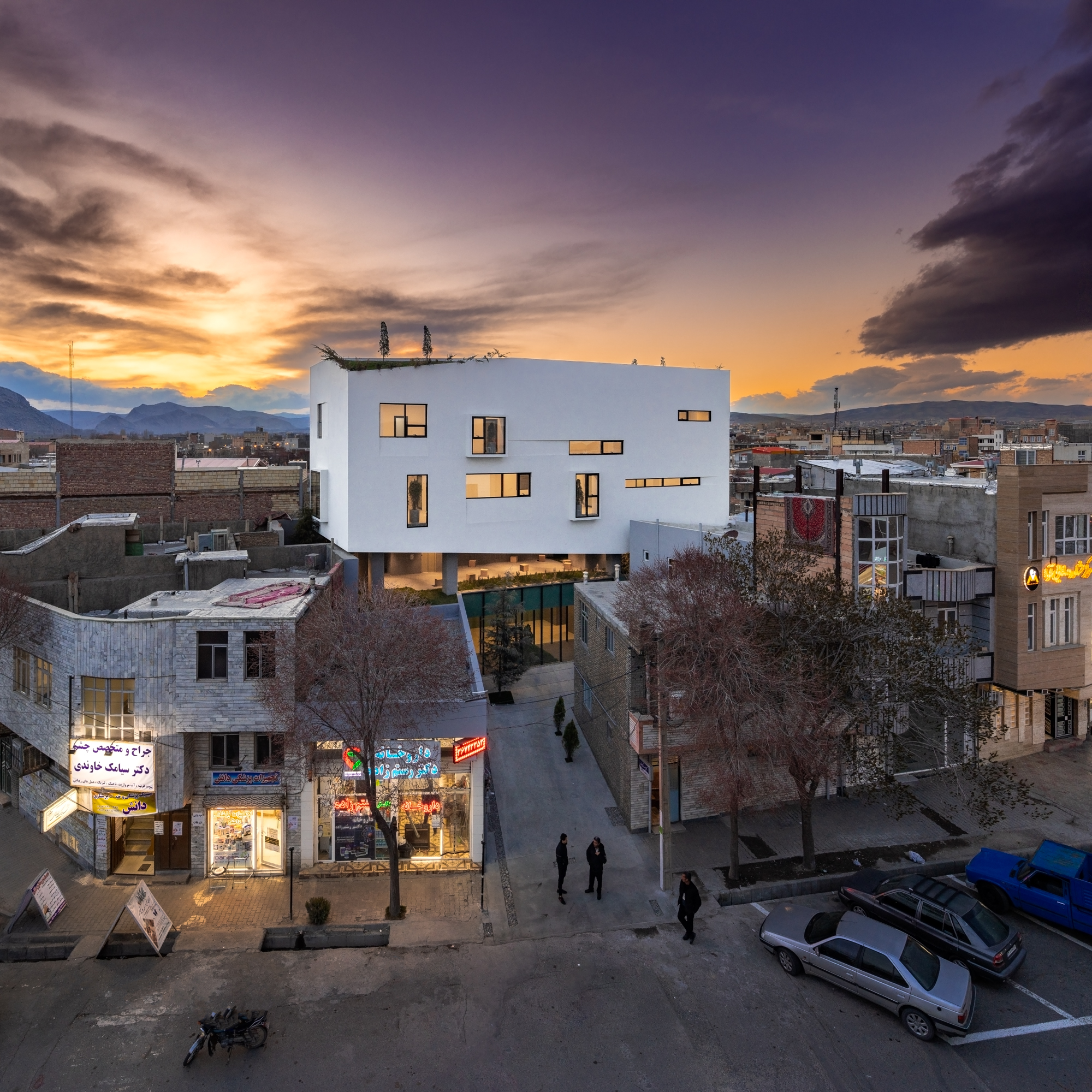

Kia Lab by Davood Boroojeni Office, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran | Popular Choice Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Hospitals & Healthcare Centers
Davood Boroojeni Office’s vast range of experience is evident in one look at the Tehran-based firm’s profile. With over 15 years of professional experience, their team has developed expertise in all areas of architectural production — from preliminary design ideas to schematic design and development, as well as producing submittal packages, visual presentations, construction documents, layouts and details through close dialogue with clients, producers and engineers. This multifaceted approach is evident in projects such as Kia Lab, which take a holistic view of the programmatic brief, embedding the building’s function with the broader urban and cultural environment.
Dedang Design
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Community Centers
Design Workshop
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best Landscape Design Firm
Dubuisson
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Gyms & Recreation Centers
DXA studio
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best Residential Firm
ECADI
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt Sports & Recreation
Edition Office
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Multi Unit Housing – Low Rise (1 – 4 Floors)
EHDD
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Sustainable Sports & Recreation Building
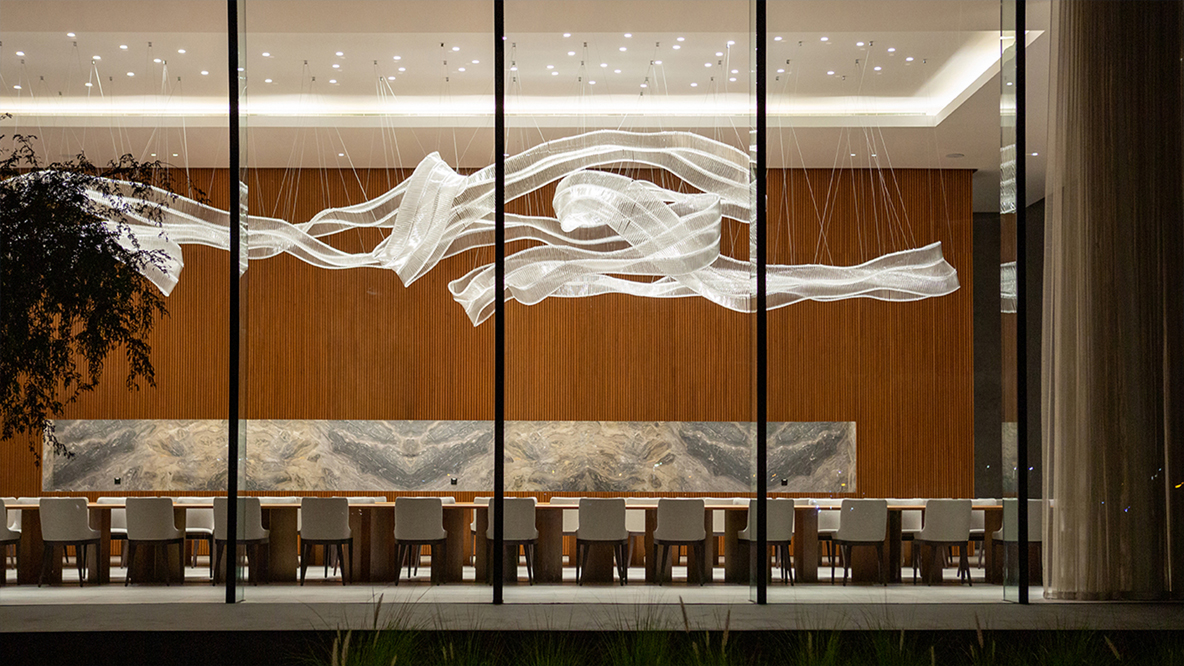

Ghaf Majlis by Etereo Design, Ajman, United Arab Emirates | 11th Annual A+Awards: Popular Vote Winner in Best Young Interior Design Firm; Popular Vote Winner in Mixed Use (S <25,000 sq ft.)
Etereo Design is both a singular studio with a unique output and a cosmopolitan firm of the 21st century, which is to say it draws strength from the intersection of cultures. As the firm puts it, “with an astute understanding of architecture, a vibrant and artistically abundant Italian heritage, dotted with influences from the Middle East and harmoniously brought together with passion, Etereo is born.” From this starting point, the firm creates breathtakingly elegant spaces that exude creative force and revel in an expert selection of materials and finishes, which are honored in the painstaking execution of their project’s finer details.
EYAC Arquitec
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Urban Transformation
Foster + Partners
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Stadium & Arena
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Sustainable Commercial Building
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Health
gad
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Spa & Wellness
Gensler
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt Masterplan
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Sustainable Commercial Building
GN Architects
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Small Projects
H Architecture
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Government & Civic Buildings
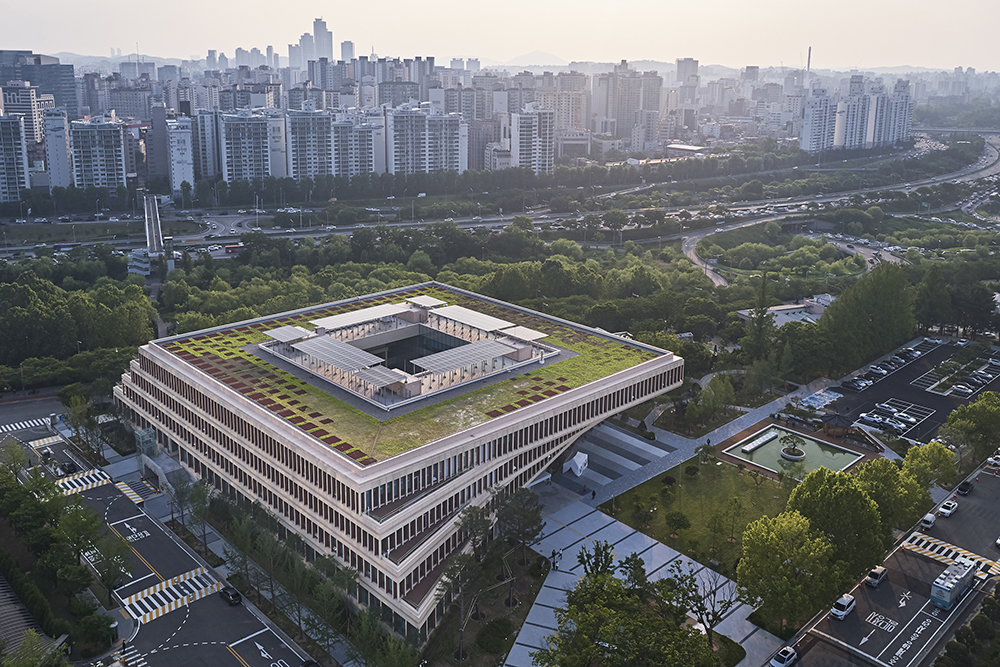

National Assembly Communication Building by HAEAHN Architecture and H-Architecture, Seoul, South Korea | Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Government & Civic Buildings
HAEAHN is the brainwork of over 1,300 employees, spread over offices across the world — from its headquarters in Seoul to new branches in Baghdad, Ho Chi Minh City, Riyadh and Savannah (Georgia) that came about through the firm’s alliance with H Architecture New York in 2011. This radical internationality translates to the broad expanse of the firm’s expertise: employees specialize in a range of fields, from architecture to environmental design to urban planning to interior design and more. Since it was founded in 1990, HAEAHN Architecture, has strove to design ambitious and impactful urban environmental projects, deeply rooted in a spirit of innovation.
HDR
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Health
Heatherwick Studio
Jury Vote & Popular Choice Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Shopping Center
HGA
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Higher Education & Research Facilities
HLW
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Adaptive Reuse
HOK
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Transportation Infrastructure
Hooba Design
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best Medium Firm (16 – 40 employees)
Inrestudio
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Brick
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Office – Low Rise (1 – 4 Floors)
JSPA Design
Jury Vote & Popular Choice Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Factories & Warehouses
K-Studio
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Stone
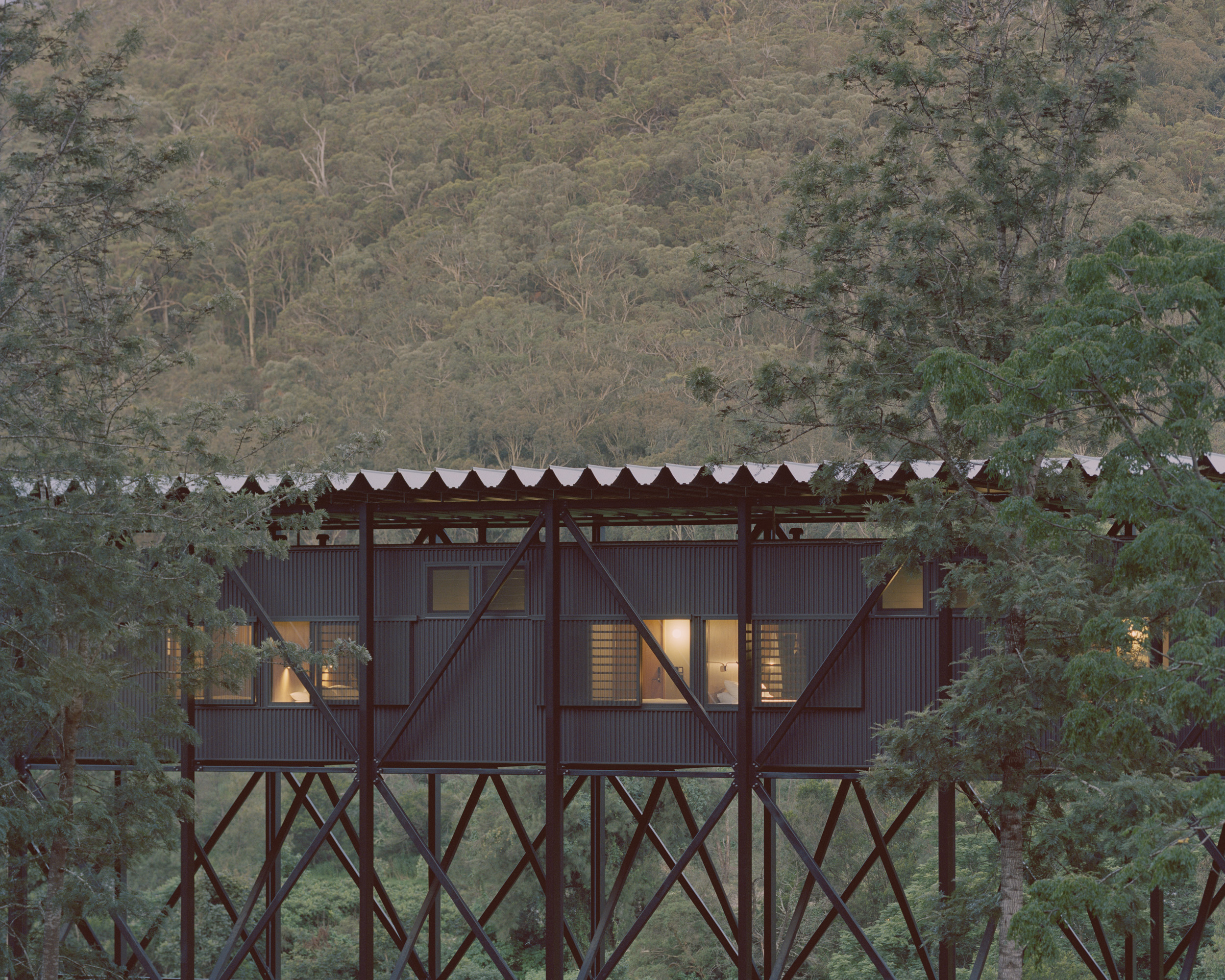

Bundanon Art Museum + Bridge by Kerstin Thompson Architects (KTA), Illaroo, Australia | 11th Annual A+Awards: Jury Vote Winner in Architecture +Environment; Jury Vote Winner in Sustainable Cultural/Institutional Building | Photo by Rory Gardiner
The output of Kerstin Thompson Architects (KTA) configures architecture as an inherently civic endeavor; to do so, each design has strong multidisciplinary foundations. Indeed, the team has forged strong relationships with engineers, emerging technology specialists and landscape and heritage consultants, and their expertise informs the approach to each project, injecting innovation and environmental sensitivity to the specificities of a given project whilst evolving the firm’s design approach for future commissions. The result is an oeuvre of sensitive, site-responsive architecture that synergize form and function with landscape, resulting in highly meaningful and resilient places.
Kosloff Architecture
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Libraries
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Learning
LAAB Architects
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Apartment
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Branding
Laguarda.Low Architects
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Office – High Rise (16+ Floors)
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Urban & Masterplan
Landao Design
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Landscape
Laney LA
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt – Private House (L >3000 sq ft)
Lazor/Office
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Wood
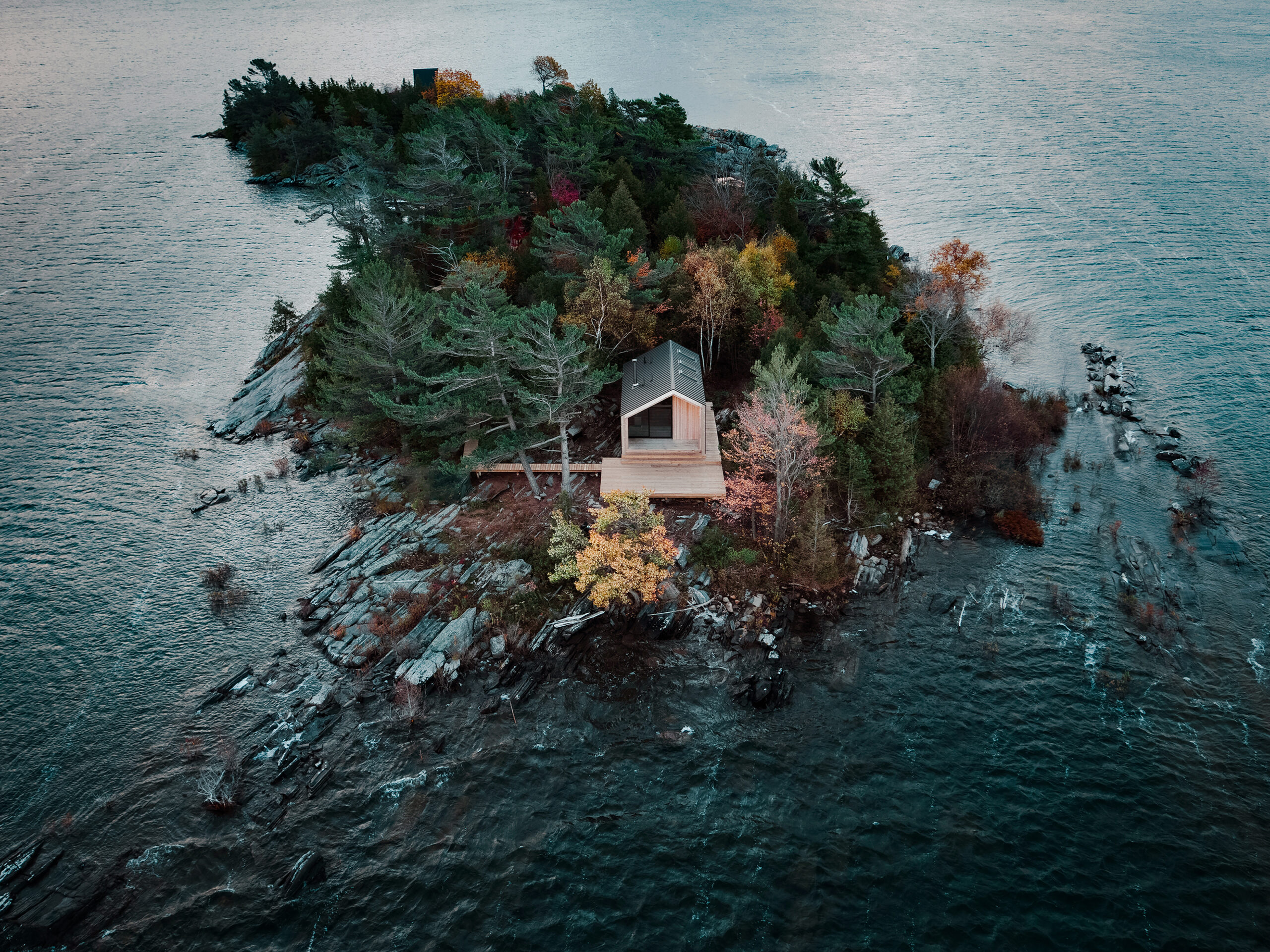

Backcountry Hut Company by Leckie Studio Architecture + Design | Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best Young Firm
The Vancouver-based inter-disciplinary design studio was founded on ambition, with the aim of “pushing the traditional boundaries of architectural practice as a catalyst for cultural change.” Designing across a variety of scales and media, the eighteen person team emphasizes highly collaborative approaches to project development. Impressively, their internal digital visualization lab creates an integrated workflow for testing and developing design ideas. Moreover, the team comprises a variety of specializations including interior design, prefabrication, mass-timber, industrial design, digital fabrication, graphic design and architectural visualization, allowing them to tackle projects of substantial size and complexity.
Leehong Kim Architects
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Transportation Infrastructure
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Glass
LUO studio
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Sustainable Interior Project
MAD Architects
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best Cultural Firm
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Concrete
MADO ARCHITECTS
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt Institutional
MARS Studio
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best Small Firm (6 – 15 employees)
McGregor Coxall
Jury Vote & Popular Choice Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Teamwork
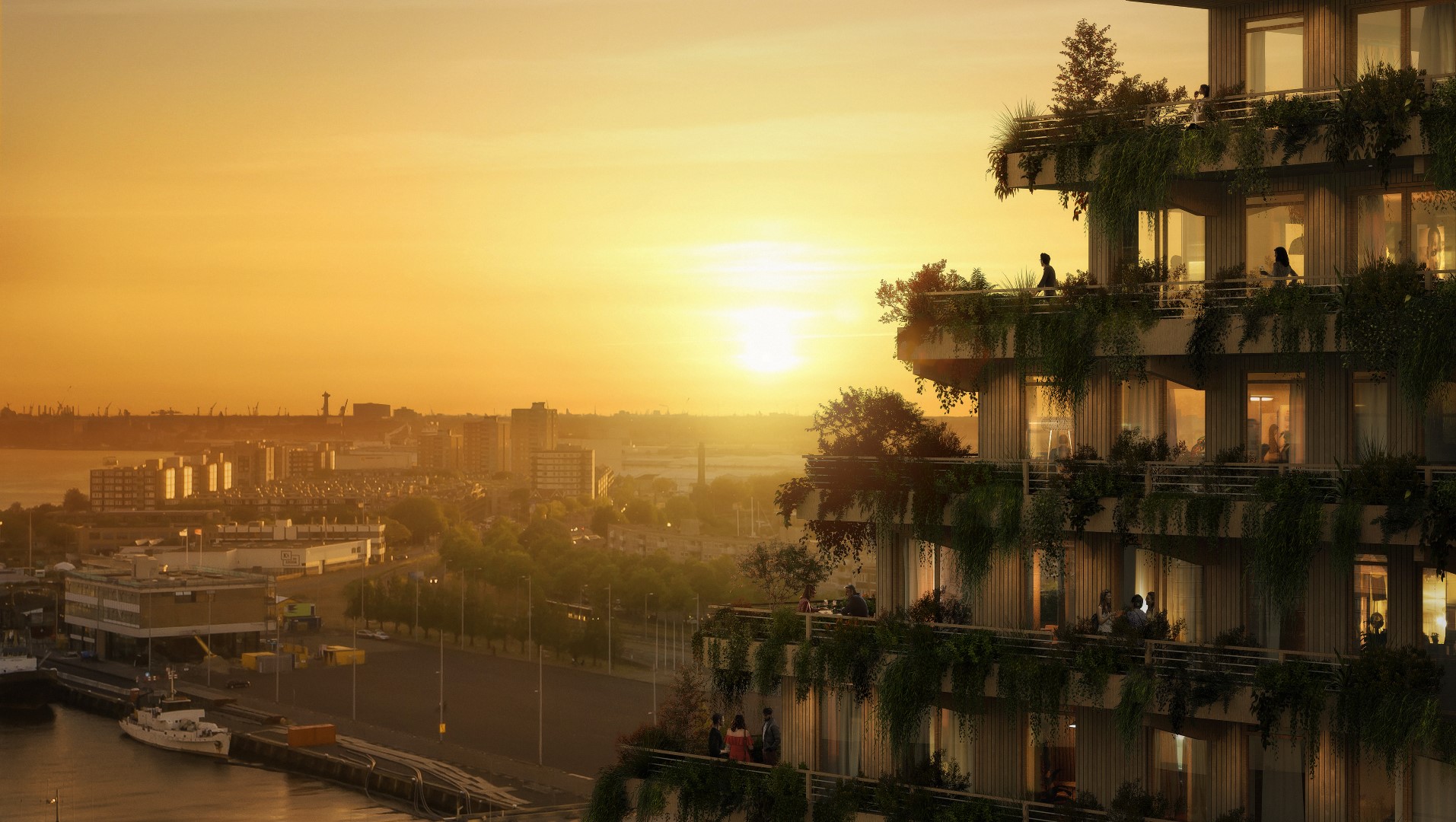

SAWA by Mei architects and planners, Rotterdam, Netherlands | Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt Sustainable Residential Project
The word “environment” carries many associations, and for Mei architects and planners, the term serves as an anchor for all projects: the history of the location, the current context and future living environment. The Rotterdam-based office is structured around the knowledge divisions of Building Transformation, New Construction and Urban Development. With a dash of courage, the resulting design champion innovative technical applications and user concepts aimed at social and ecological sustainability. With the design and development of SAWA, a fully wooden residential building in Rotterdam, Mei established themselves as pioneers in creating future-proof, nature-inclusive housing.
MESH Architectures
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Sustainable Multi-Unit Residential Building
Mix Architecture
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Sustainable Hospitality Building
modus studio
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Pavilions
Moneo Brock
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Community
Morphosis Architects
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Branding
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Museum
MQ Architecture
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best Small Firm (6 – 15 employees)
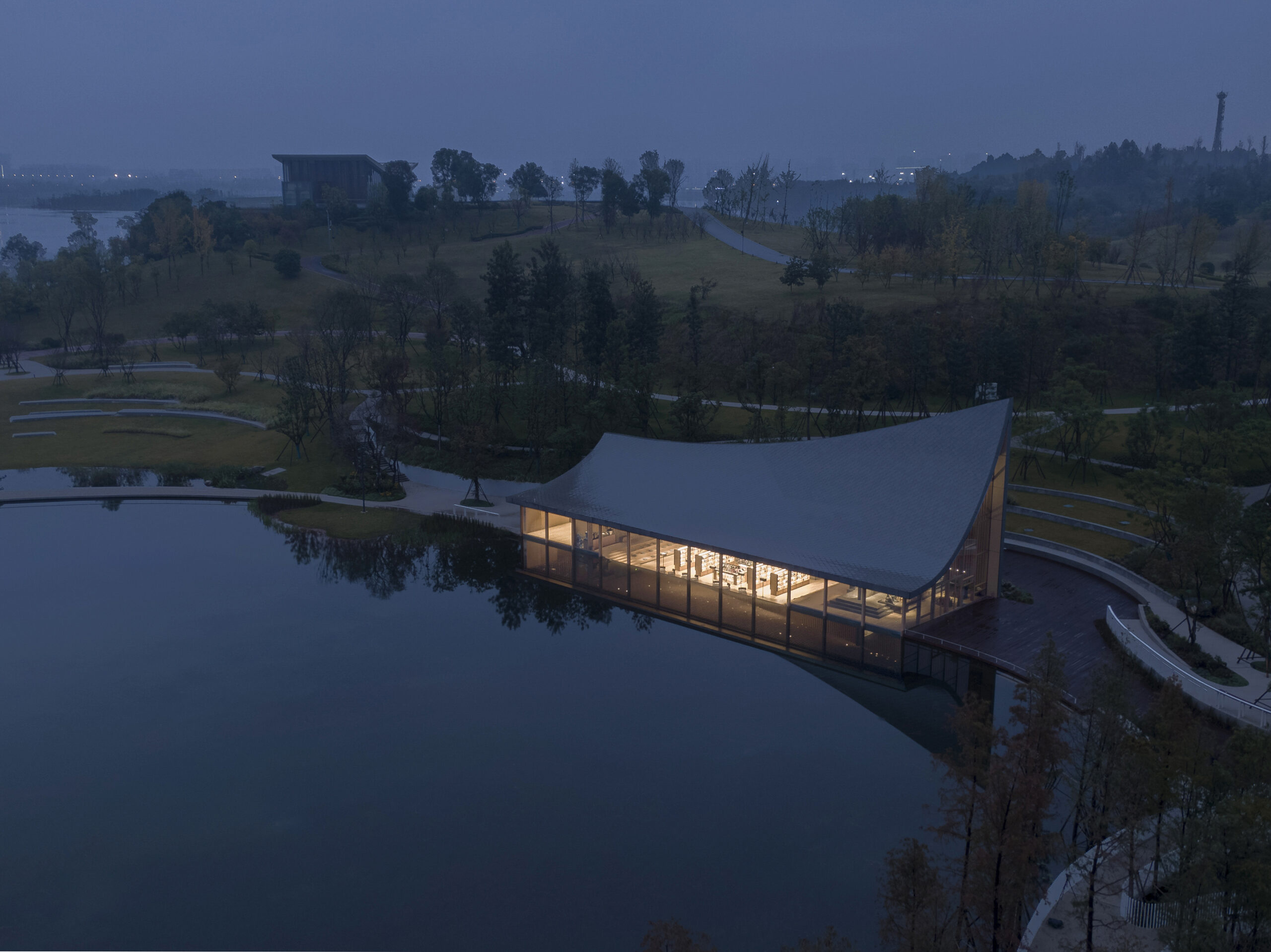

Xinglong Lake CITIC Bookstore by MUDA-Architects, Chengdu, China | Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best Young Firm
MUDA-Architects are an exciting and daring young firm that has dominated the architectural landscape in recent years. The up-and-coming practice is keen to showcase its diverse talent on the global stage, and with a rapidly expanding portfolio of fascinating projects, the young team is already gaining recognition for its creativity and leadership. Initially founded in Boston, the US, in 2015 and currently based in Southwest China, MUDA-Architects occupies offices in Beijing and Chengdu. Their work in the public realm ranges from bookshops to hotels and is united by their dedication to finding the right solution without compromising aesthetics.
Multistudio
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Libraries
Multitude Of Sins
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Sustainable Interior Project
MVRDV
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Facades
NAPUR Architect
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Museum
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Facades
NEWSUBSTANCE
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Pop-Ups & Temporary
NICOLEHOLLIS
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Residential Interiors (<3000 sq ft)
NIKKEN SEKKEI LTD
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Transport Interiors
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Primary & High Schools
NOA
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Spa & Wellness
Noxon Giffen
Jury Vote & Popular Choice Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Teamwork
Office AIO
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best Interior Design Firm
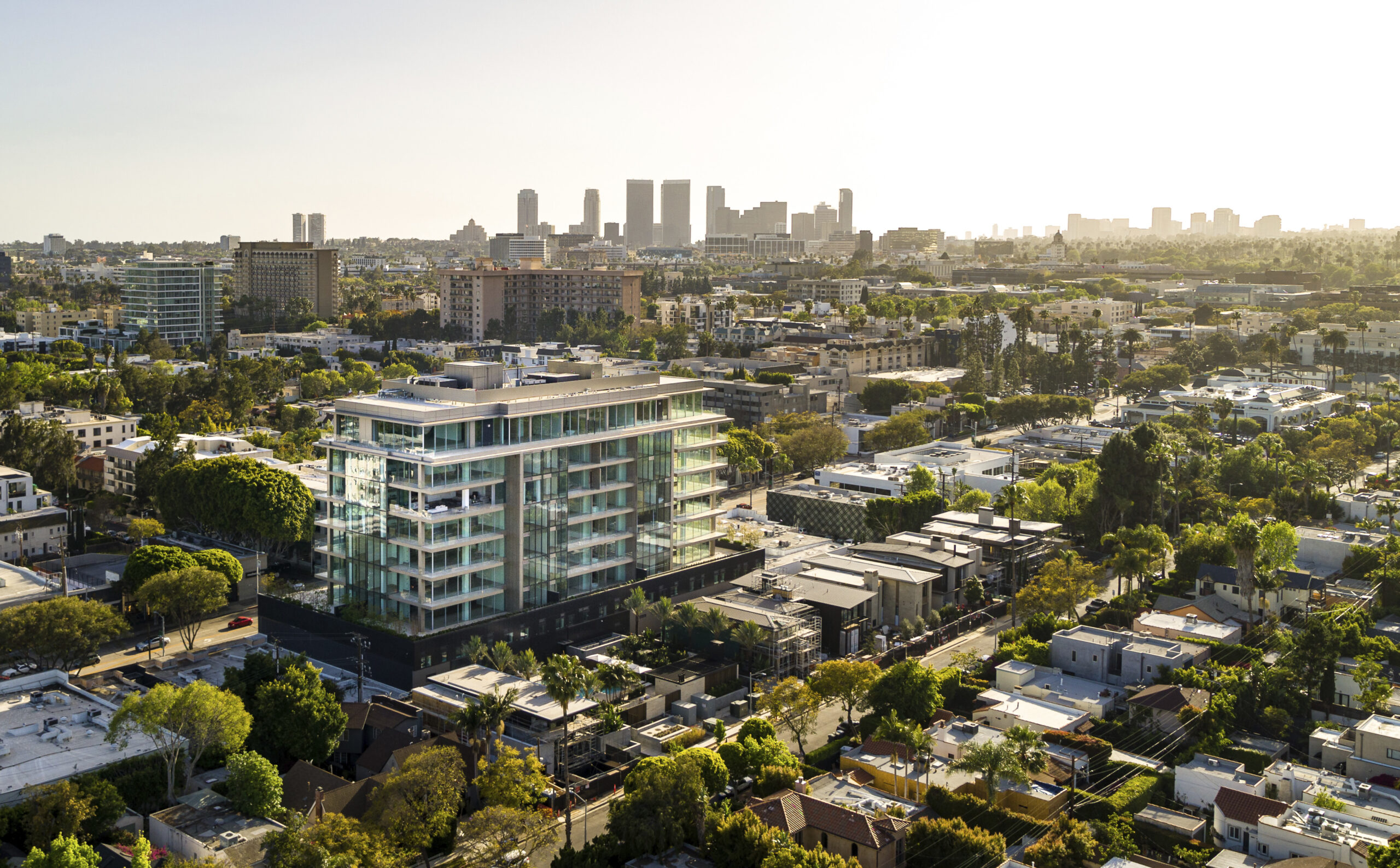

8899 Beverly Boulevard by Olson Kundig, West Hollywood, California | 11th Annual A+Awards: Jury Vote Winner in Best Large Firm (41+ employees); Jury Vote Winner in Gallery & Exhibition Spaces;
The portfolio of Olson Kundig is vast, varied and captivating. The Seattle-based firm’s completed works read as a long list of distinctive projects that span more than fifteen countries across five continents. Founded by Jim Olson in 1966, the studio began its life exploring the relationship between dwelling and landscape — a provenance that remains at the heart of the company’s ethos that has since evolved, morphing in productive new directions as applied to a range of typologies and across dense urban and expansive rural settings. Every finished project manifests a “macro to micro” level of attention, from the big ideas to the smallest details.
Omar Gandhi Architects
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Private House (M 2000 – 4000 sq ft)
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Restaurants (L >1000 sq ft)
Orange Architects
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Multi Unit Housing – Mid Rise (5 – 15 Floors)
PAN Cabins
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Metal
Park + Associates
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Apartment
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Restaurants (S <1000 sq ft)
Perkins&Will
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best Sustainable Firm
PPAG architects
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Restaurants (L >1000 sq ft)
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Sustainable Hospitality Building
Provencher_Roy
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Hospitals & Healthcare Centers
RAAD Studio
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Residential Interiors (<3000 sq ft)
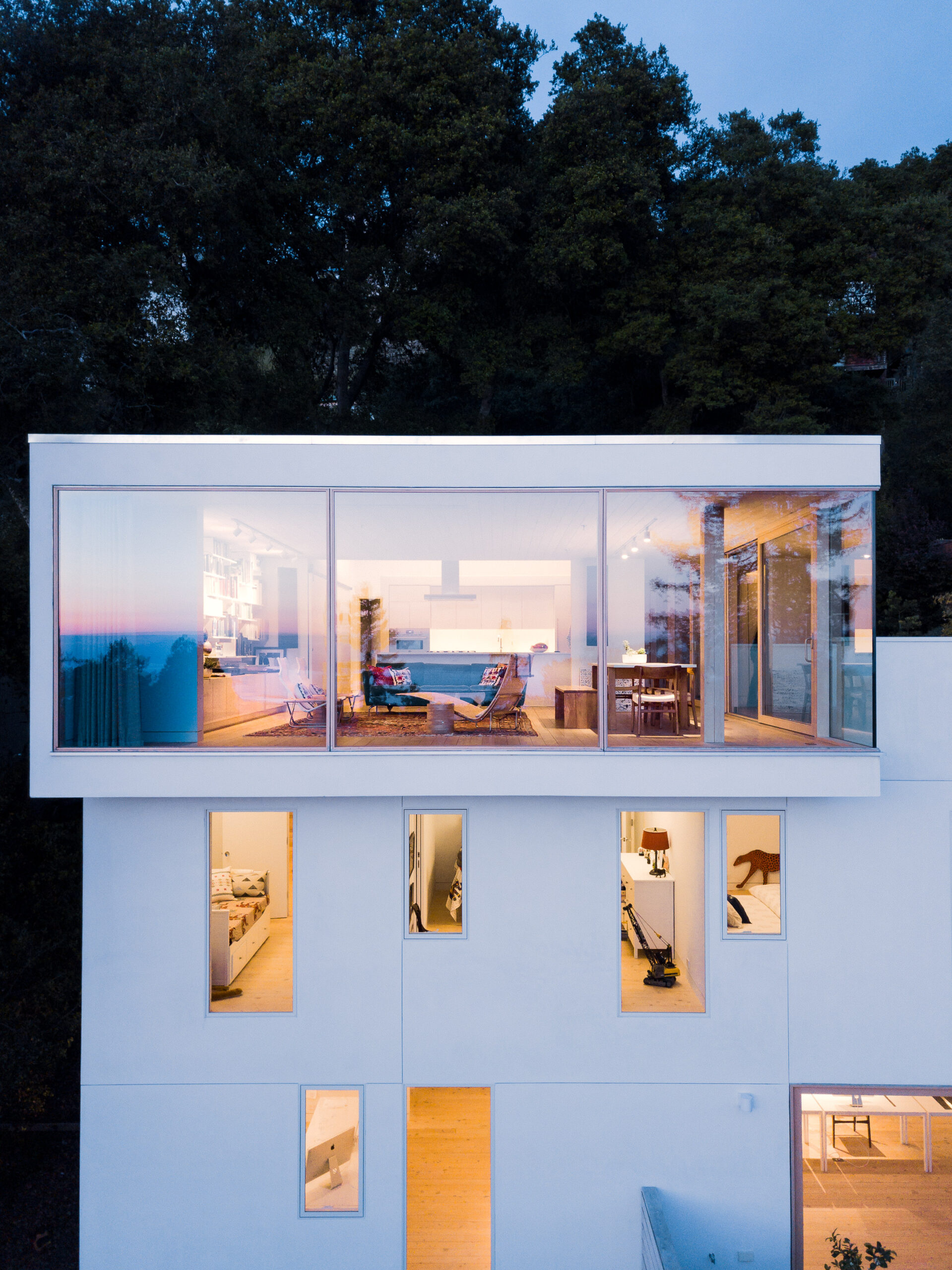

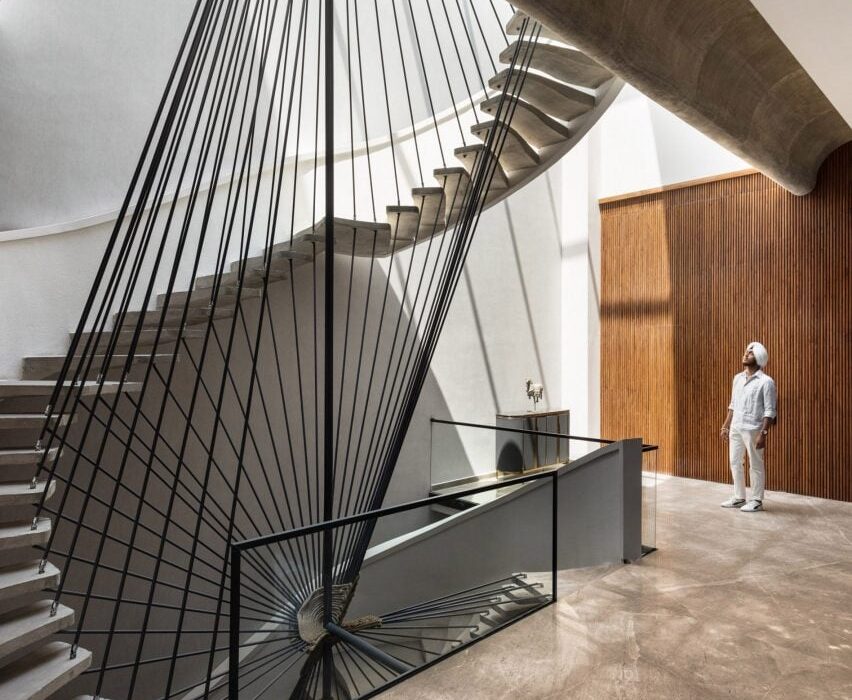
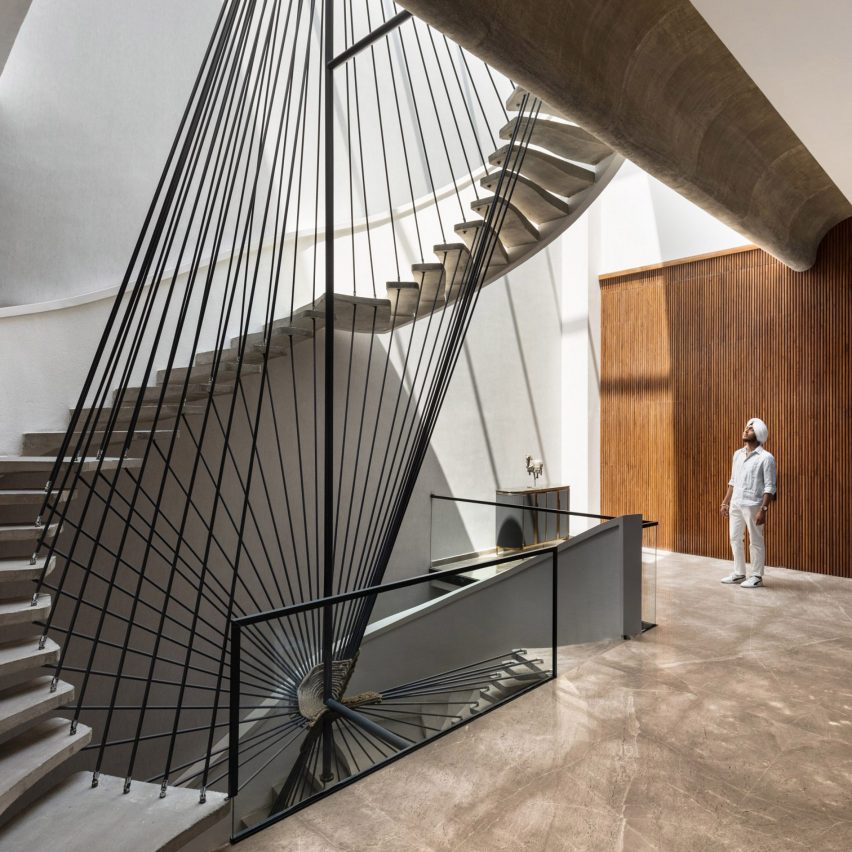
House of Light by Rangr Studio, Berkeley, CA, United States | Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best X-Small Firm (1 – 5 employees) | Photo by Joe Fletcher Photography
Since 2004, Rangr Studio has deployed the principles of ancient design with contemporary materials and methods to find poetic and harmonious solutions to a wide variety of design challenges. Rather than imposing a structure on an environment, the studio creates essential architectural forms in harmony with the surrounding landscape — whether rural or urban in setting. Founder Jasmit Singh Rangr grew up on the coasts of India, and in the UK, was educated at Yale, and is currently bi-coastal between California and New York. His life experience and training inform Rangr Studio’s philosophy — an approach that is deeply sensitive to the interaction between climate, landscape, culture, and architecture.
RAU
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt Sustainable Residential Project
RIOS
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Workspace
RVAD STUDIO
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Models & Rendering
Sasaki
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Sustainable Landscape/Planning Project
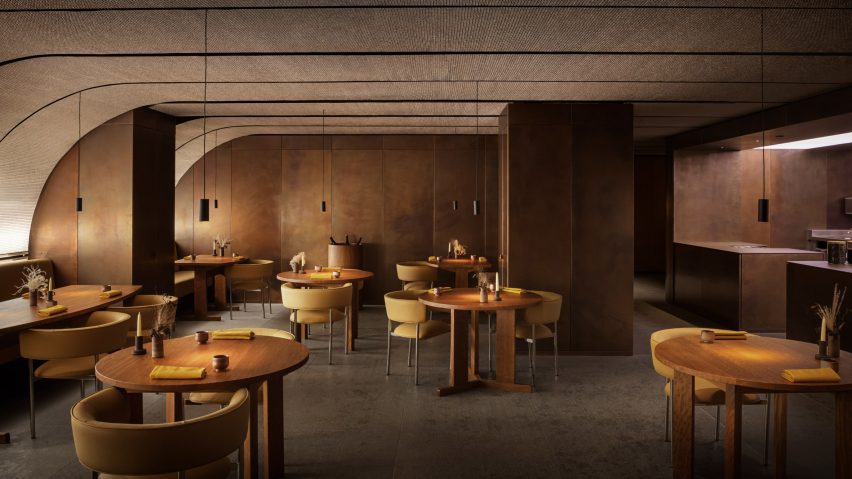
Featured Firm: SAVA
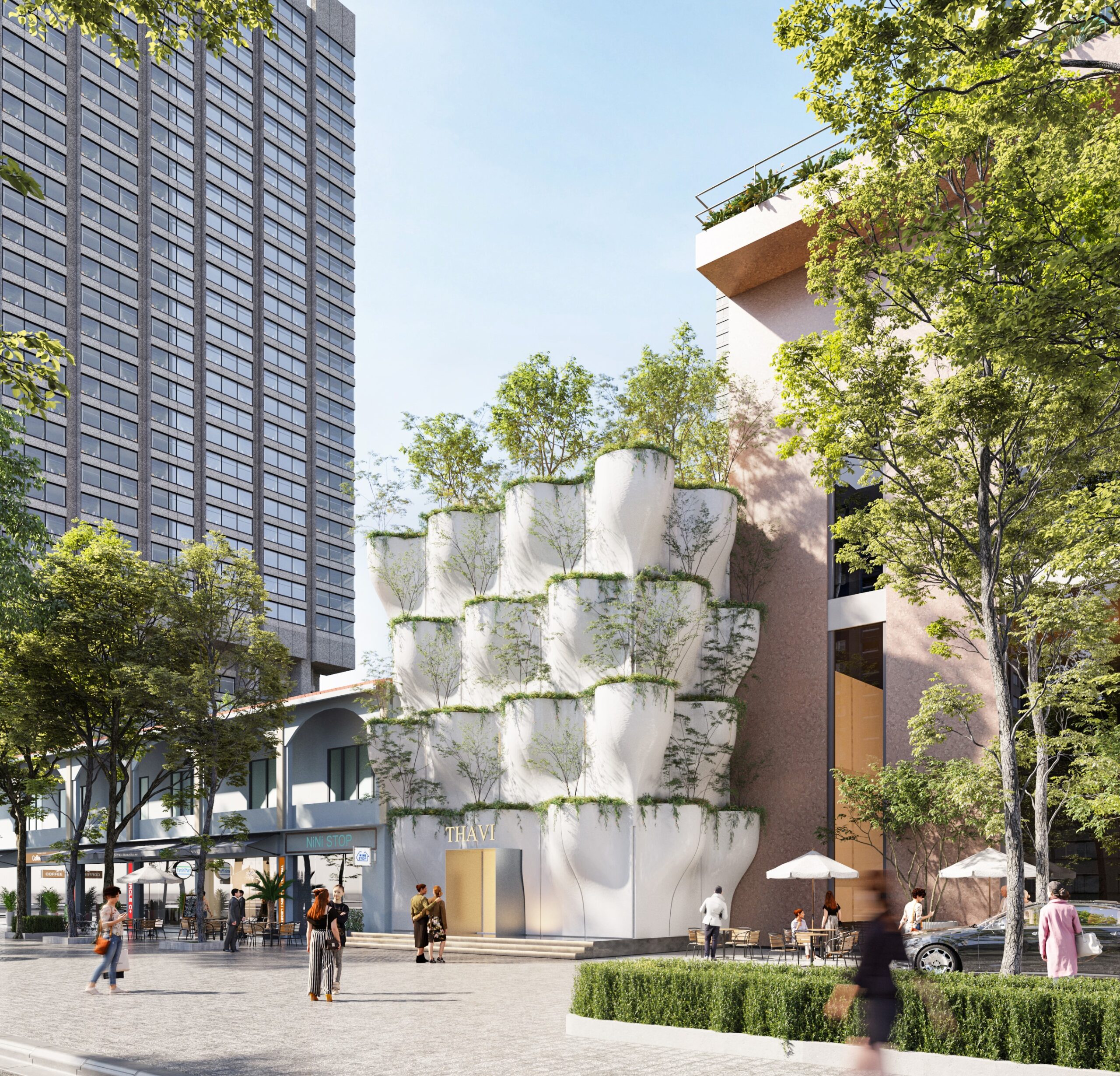

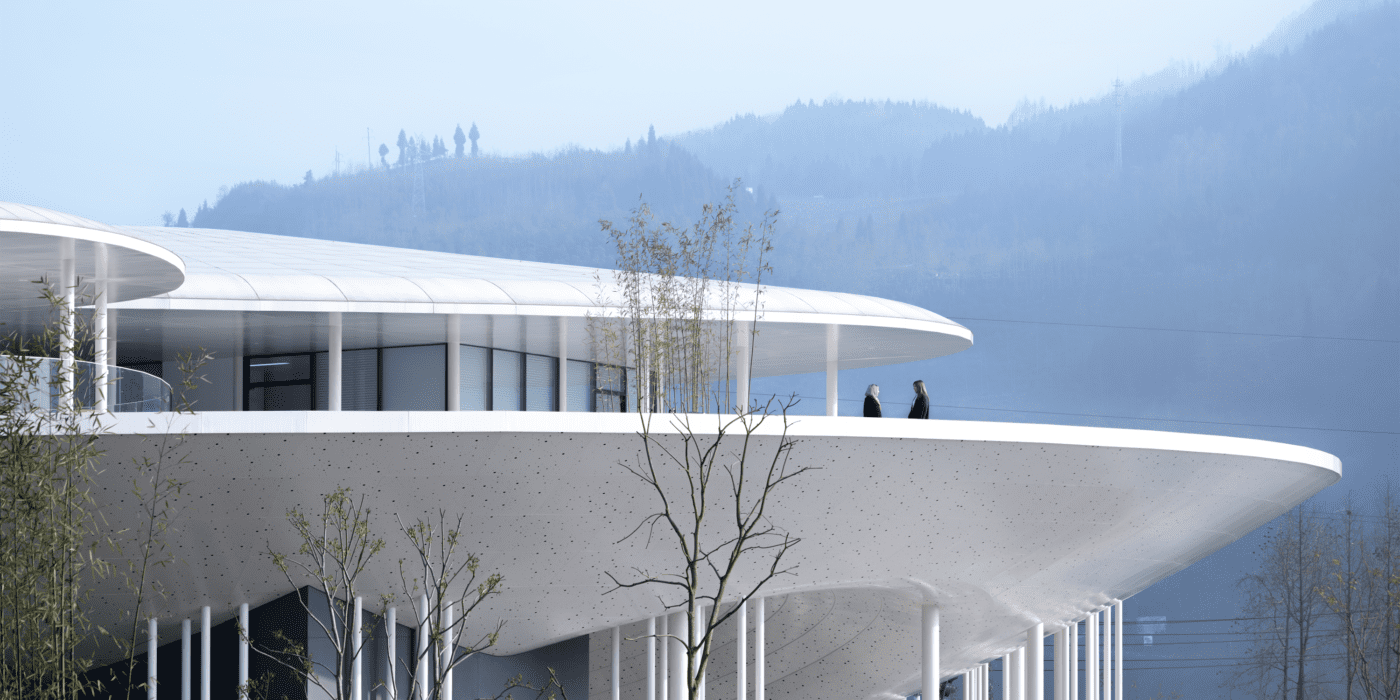
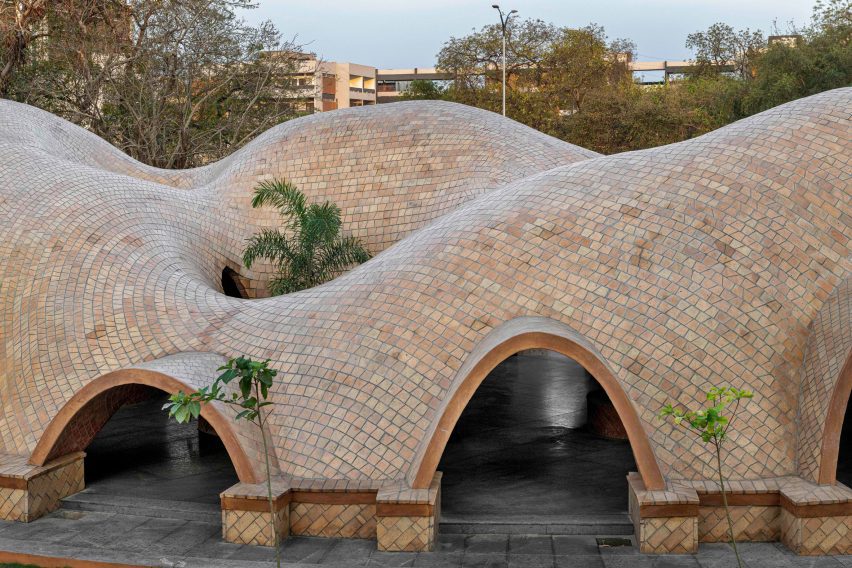
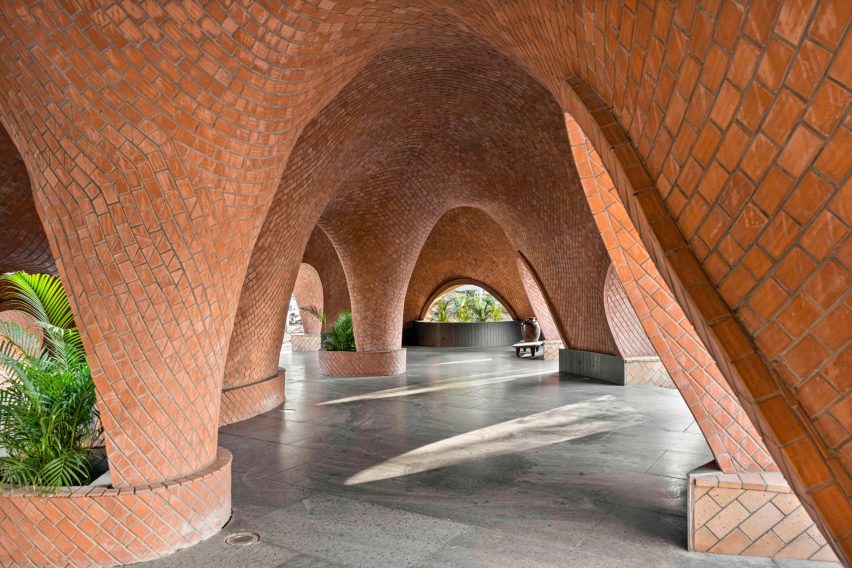
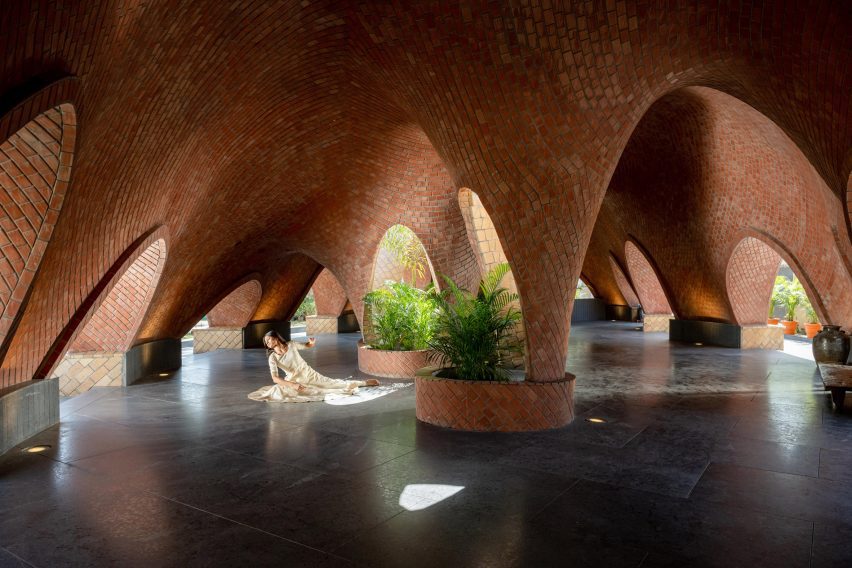
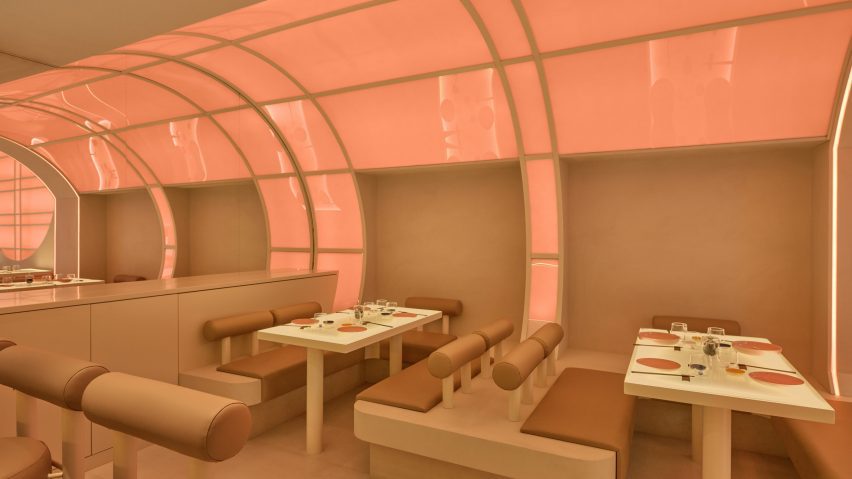
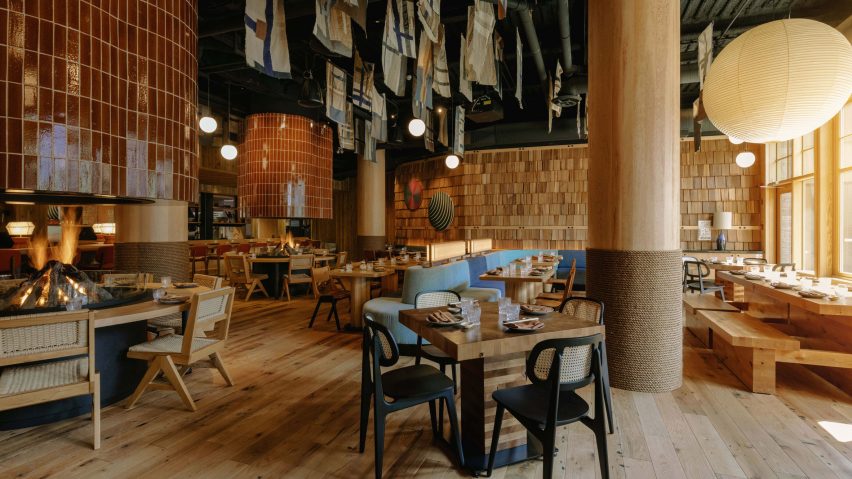
Thavi Cosmetics Showroom by SAVA, Vinh, Vietnam | Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt Commercial (Also pictured in top image).
With headquarters in Borneo, Malaysia and Danang, Vietnam, SAVA draws inspiration from mountains and coastlines. Committed to designing spaces for people from every walk of life, the firm consciously designs to harness locally-sourced materials and building techniques with the aim of bringing people closer to nature — especially those in an urban environment. Indeed, the firm draws on its past experience in masterplanning, housing and bamboo architecture in Asia and Europe to produce architecture that goes beyond aesthetics — even if the result is a visually playful array of perforated geometries with openings that create new relationships to the surrounding environment.
Shape Architecture
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt Sustainable Non-Residential Project
Shejin Space Design
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Commercial Interiors (<25,000 sq ft.)
SkB Architects
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Commercial Interiors (>25,000 sq ft.)
Sordo Madaleno
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Restaurants (S <1000 sq ft)
SPARK
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Retail
Featured Firm: STARH
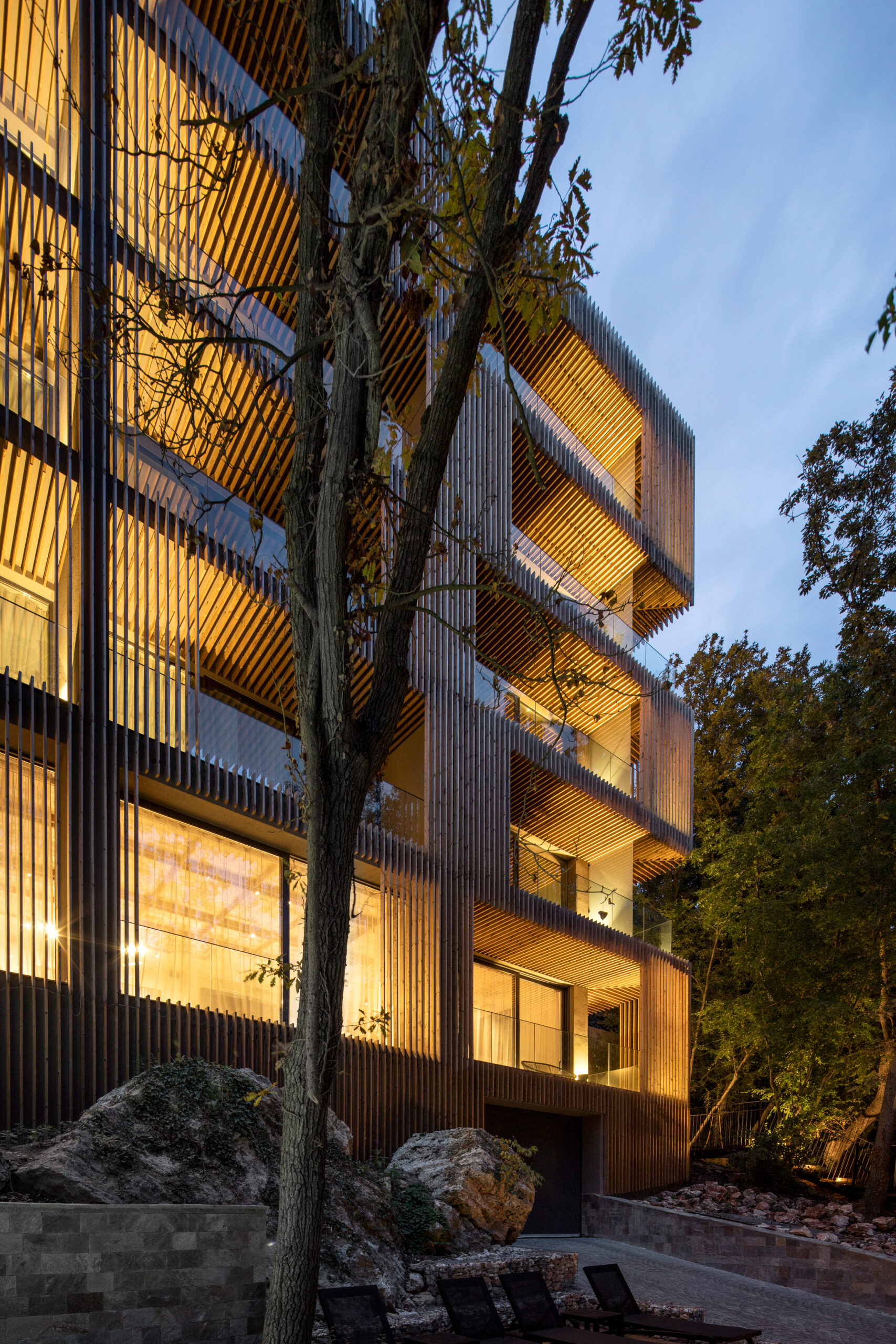

Umani Hotel by STARH, Varna, Bulgaria | Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Environment | Photo by Dian Stanchev
STARH is an architecture studio with a mission to overcome stereotypes in the architectural environment. The Bulgarian studio has established a name for itself by creating high-quality designs, from both a functional and material standpoint, with a high level of attention to detail and longevity. Through this approach, the firm achieves innovative design solutions with a distinctive signature. STARH’s portfolio covers projects of different scales and complexity that are united by bold and rhythmic geometries resulting forceful formal statements.
STL Architects
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt Institutional
Studio FEI
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt Cultural
Studio Gang
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt – Multi-Unit Housing (L >10 Floors)
studio mk27
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Private House (L 4000 – 6000 sq ft)
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Art
StudioPOD
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Sustainable Transportation Project
Superbloom
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt Sustainable Non-Residential Project
Superkül
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Educational Interiors
SWA GROUP
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Public Parks & Green Spaces
temporary work
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Models & Rendering
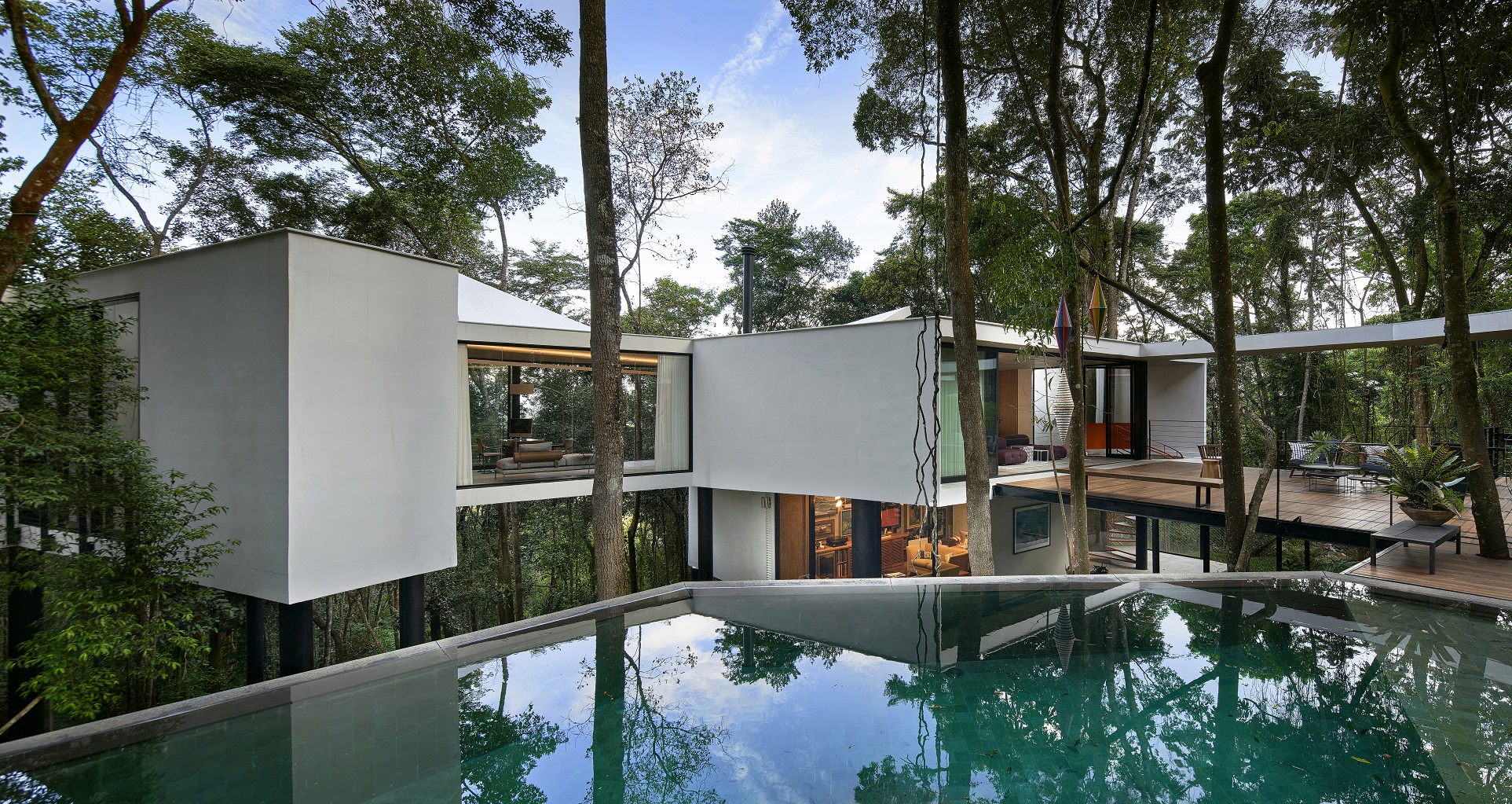

Açucena House by Tetro Arquitectura, Nova Lima, Brazil | Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Private House (M 2000 – 4000 sq ft)
Flowing roofs that soar over meandering structures are some of the hallmarks in the remarkable portfolio of this Brazilian firm. Based in Belo Horizonte, the office grounds its work in the careful study of the premises and conditions of the site. This approach is evident in the resulting structures, each highly unique and unrepeatable. In the words of the firm, “fundamentals such as integration with nature, use of natural materials and exploration of architectural voids are characteristics that permeate every project, from urban scale to furniture design.” This is true across typologies, from museums and venues to commercial, residential and industrial buildings.
TM Light
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Light
tono
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Sustainable Private House
Turner Arquitectos
Jury Vote & Popular Choice Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Mixed Use (L >25,000 sq ft.)
UNStudio
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Sustainable Cultural/Institutional Building
West of West
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt – Multi-Unit Housing (S <10 Floors)
WOJR
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt – Private House (S <3000 sq ft)
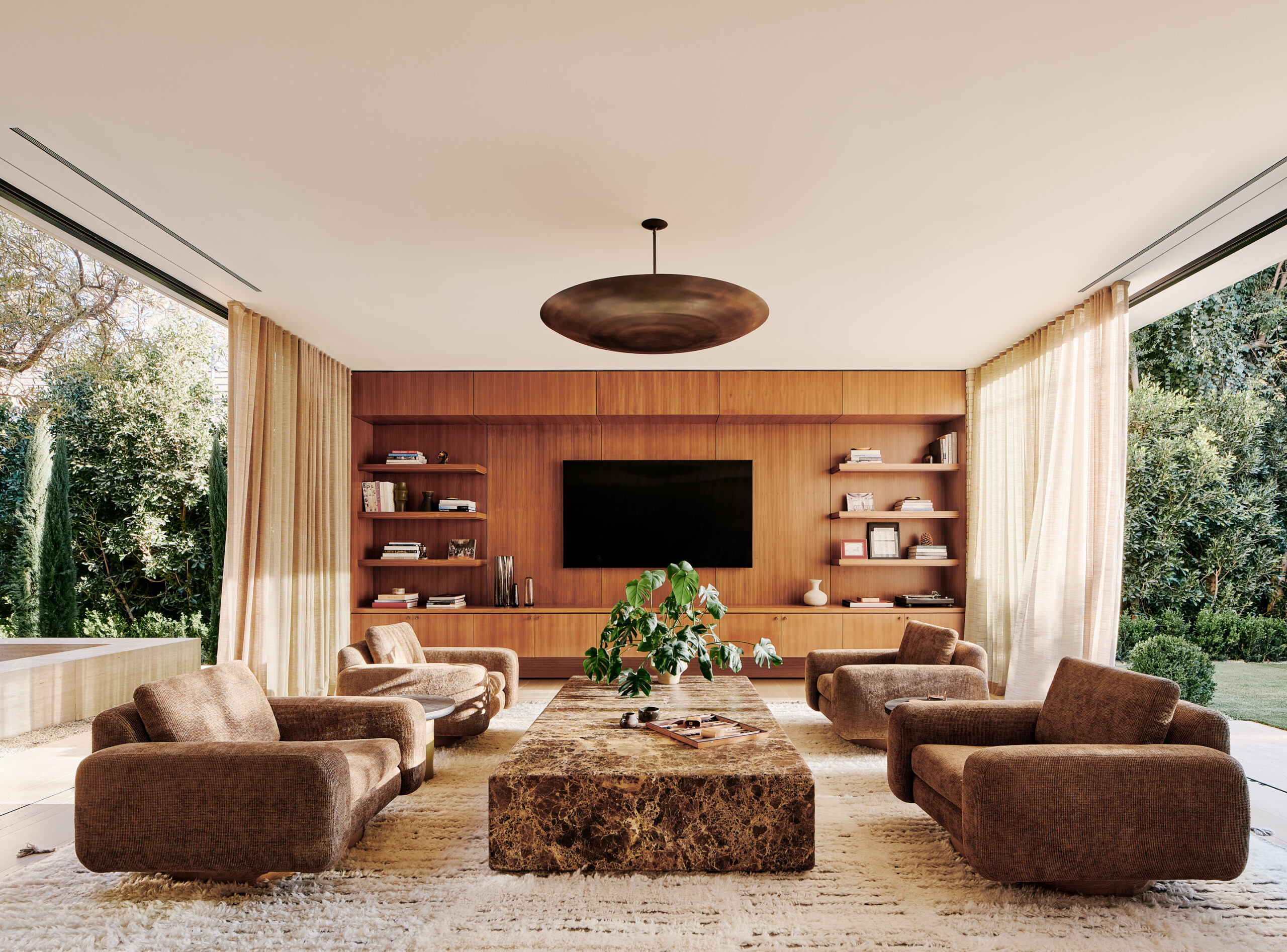

Twentieth by WOODS + DANGARAN, Santa Monica, California | Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Best Medium Firm (16 – 40 employees)
Woods + Dangaran’s portfolio boasts an array of warm, elegant residences that exude a timeless California cool and hinge on opening interiors to the outer world. However, going beyond buildings, this Los Angeles-based firm designs at every scale, and their work even includes custom furnishings. The team prides itself on building collaborative relationships — whether with clients throughout the design process or tradespeople for working out uncompromising in craftsmanship.
XISUI Design
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Joy
XMArchitect
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Metaverse
ZGF Architects
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Higher Education & Research Facilities
ZZYY Studio
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt Commercial
Jury Vote & Popular Choice Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Unbuilt Transportation
Great architecture comes to fruition through the work of talented teams and collaborators. There are numerous A+Award-winning companies that fall outside of the traditional architectural role, but that deserve recognition for their contributions. They include:
BR+A, L.F. Driscoll and Balfour Beatty (PennFIRST IPD Team)
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Health
Chongqing Qimo Architectural Design Consulting
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Hotels & Resorts
Deed Studio (photography)
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Photography & Video
feinknopf (photography)
Jury Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Architecture +Photography & Video
Shanghai Rail Transit Line 18 Development
Popular Vote Winner, 11th Annual A+Awards, Transport Interiors
You can check out previous editions of the A+List here: First Edition, Second Edition, Third Edition, Fourth Edition
To secure your position on next year’s A+List, make sure to enter the 12th Annual A+Awards before the Main Entry Deadline on December 15th:
Enter the 12th Annual A+Awards













































 To this end, we are thrilled to announce the launch of Architizer’s Tech Directory, a database of tech tools that benefit all those involved in architecture, from concept to construction.
To this end, we are thrilled to announce the launch of Architizer’s Tech Directory, a database of tech tools that benefit all those involved in architecture, from concept to construction.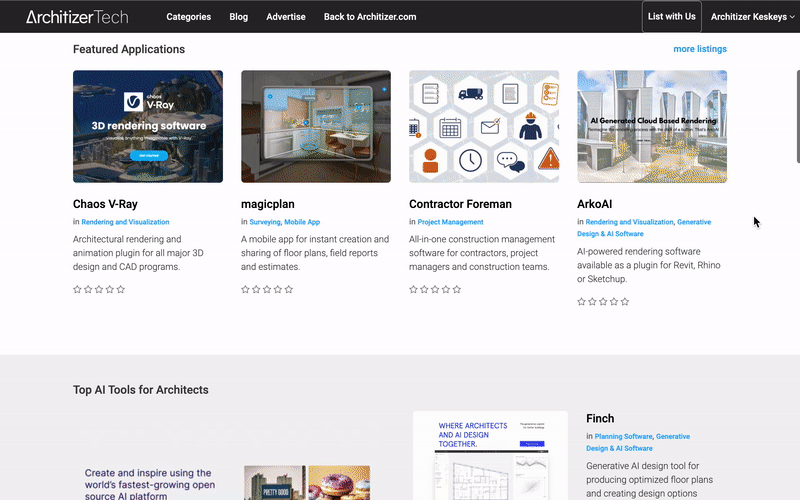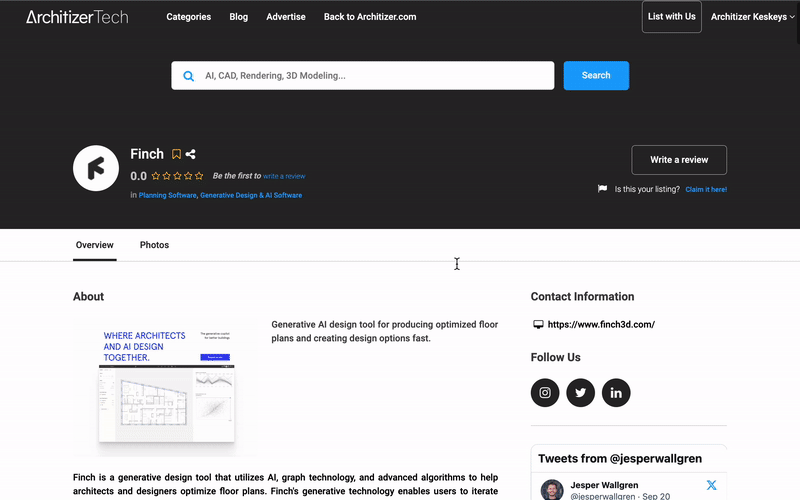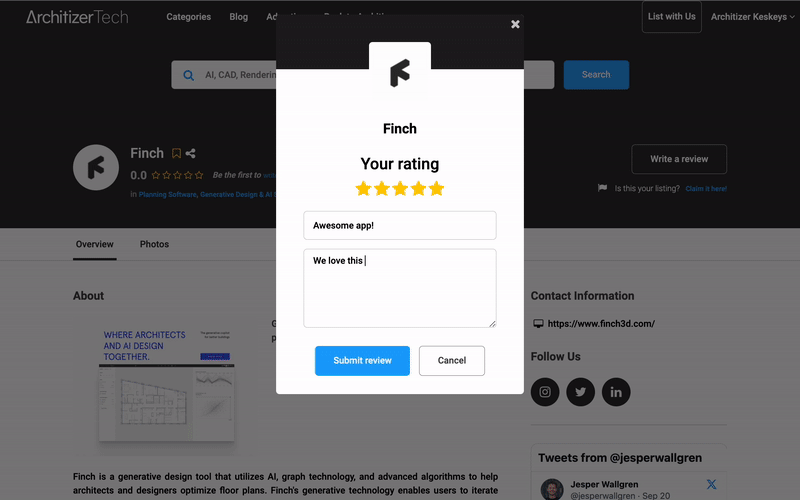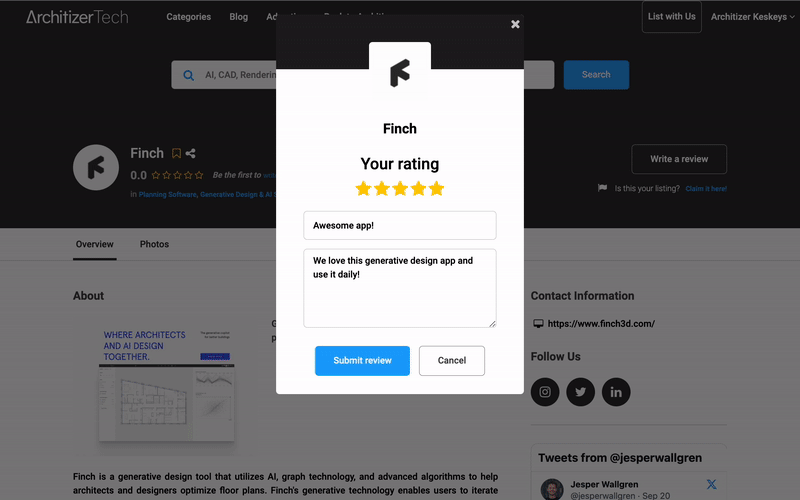
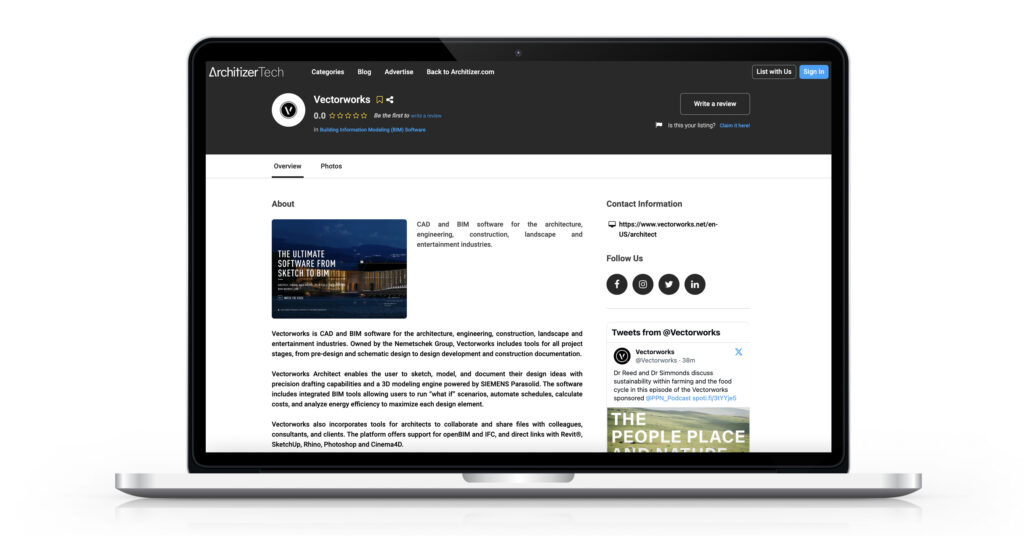
 We hope you enjoy exploring the Tech Directory and find it useful when doing your research into the latest architectural technology. As noted, this is just the beginning: We plan to develop this platform into a comprehensive directory that will benefit everyone in the construction industry.
We hope you enjoy exploring the Tech Directory and find it useful when doing your research into the latest architectural technology. As noted, this is just the beginning: We plan to develop this platform into a comprehensive directory that will benefit everyone in the construction industry.